Modification of Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase with Nitric Oxide: Role in Signal Transduction and Development of Apoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
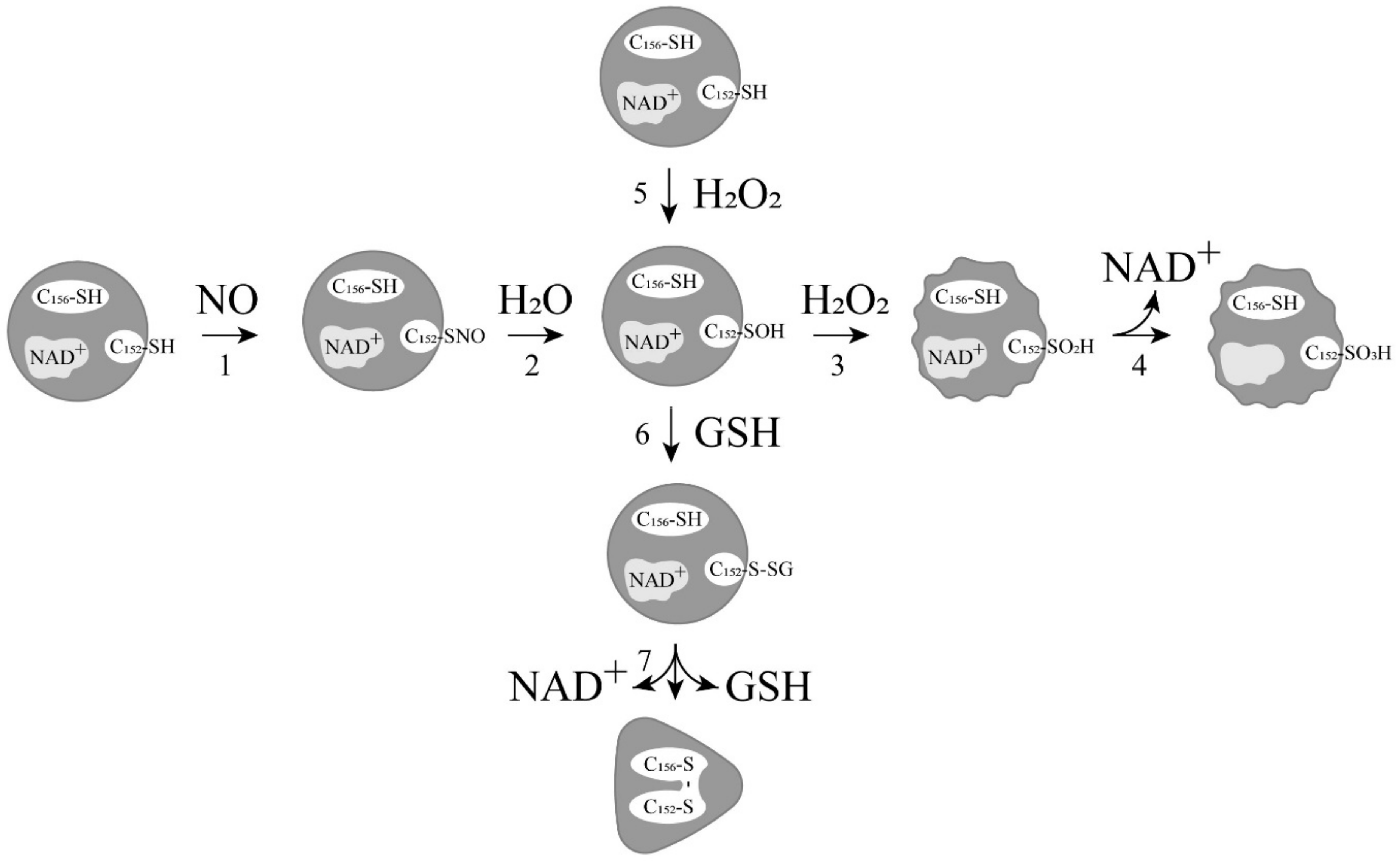
2. Relationship between ADP-Ribosylation of GAPDH and Its Modification with Nitric Oxide
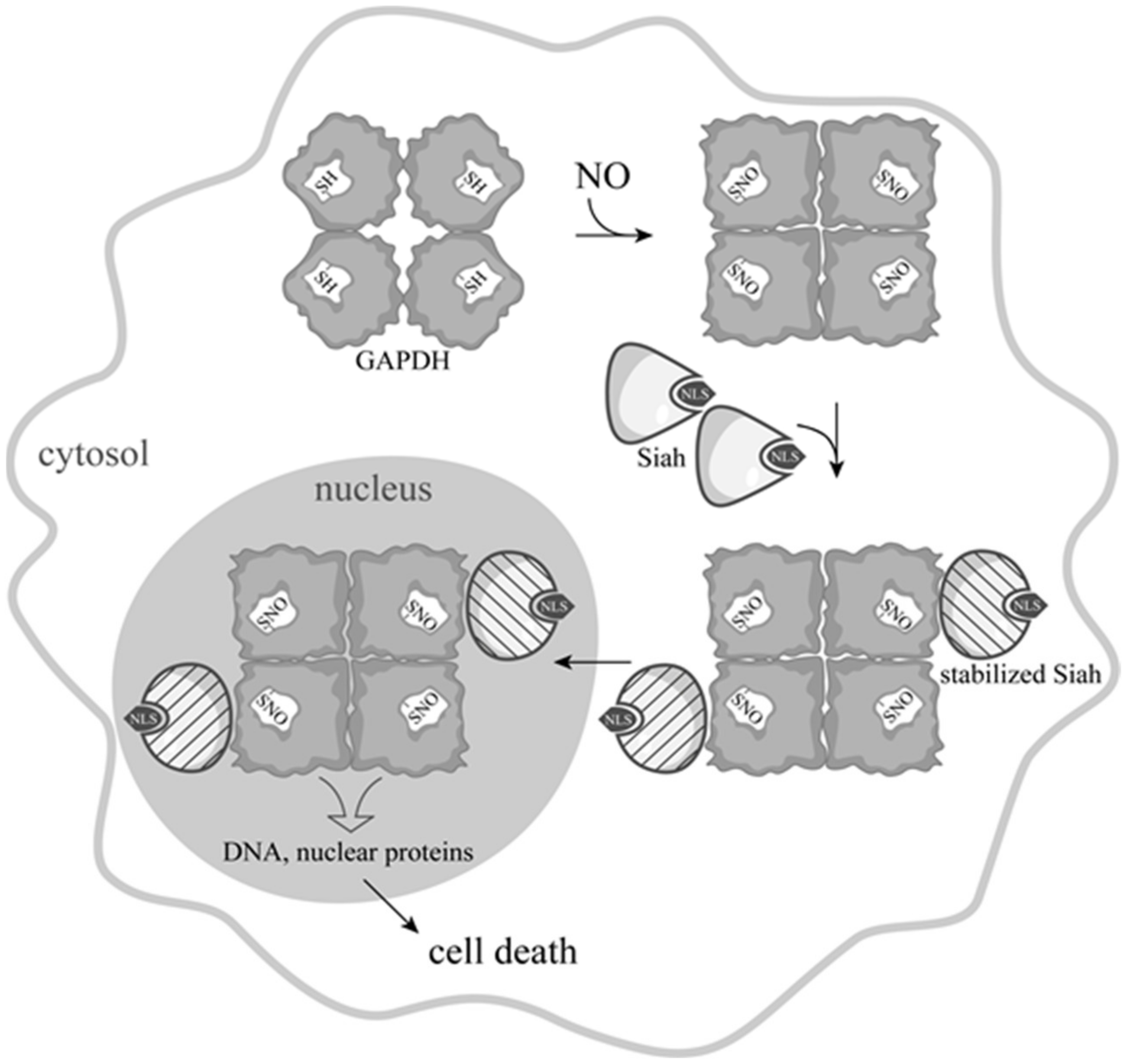
3. Development of Ideas about the Induction of Apoptosis with the Participation of GAPDH
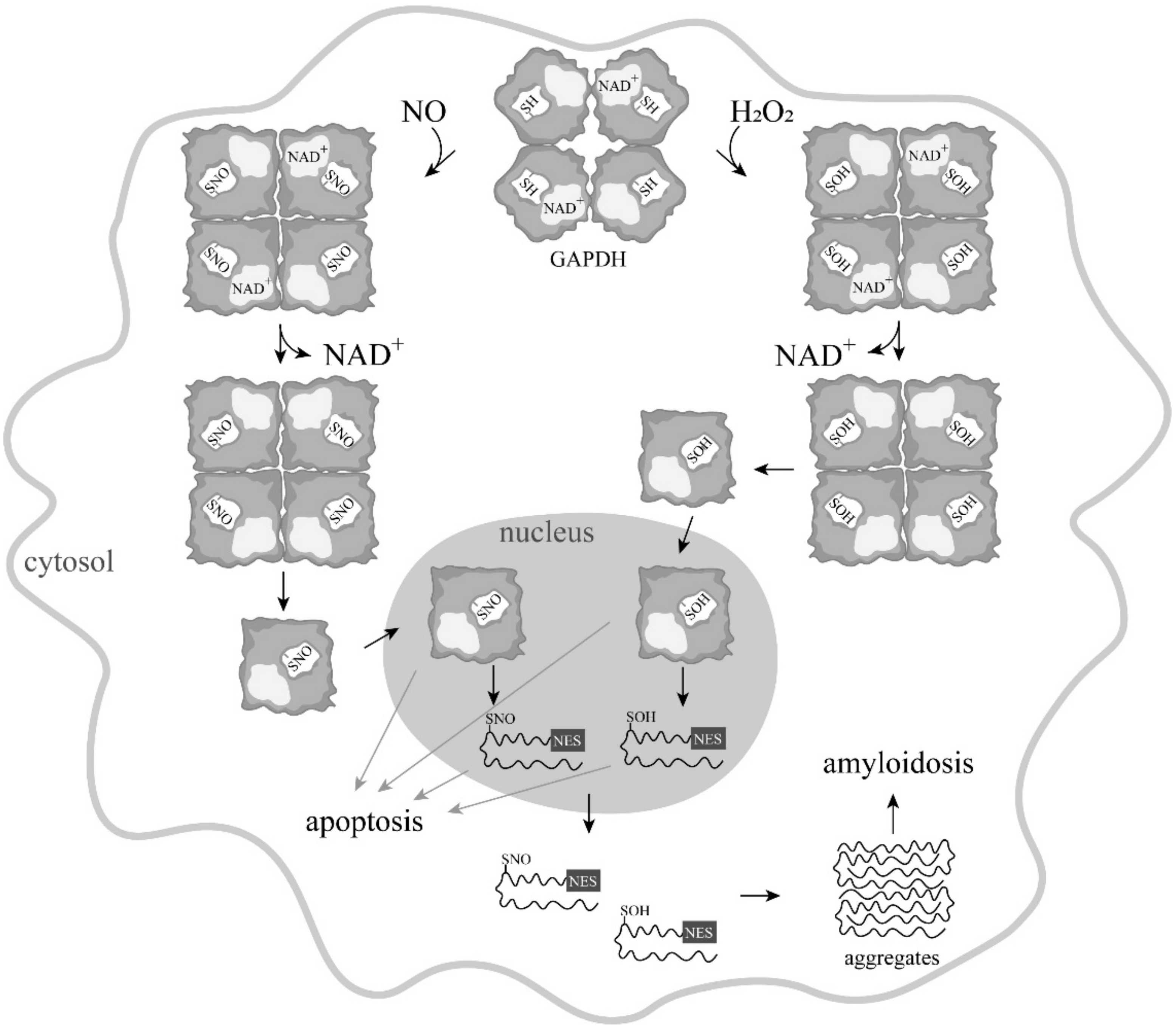
4. Induction of Apoptosis by Oxidation and Other Modifications of the Catalytic Cysteines of GAPDH
5. Is GAPDH-SNO an Obligatory Participant in NO-Induced Apoptosis?
6. Conclusions
- -
- To isolate, or obtain from isolated proteins, complexes of S-nitrosylated GAPDH with partner proteins, and prove that the tetrameric GAPDH molecule is capable of forming such complexes;
- -
- To reveal the presence of tetrameric GAPDH molecules in the nucleus;
- -
- To study the possibility of the formation of complexes between S-nitrosylated, oxidized, and S-glutathionylated GAPDH with the partner proteins;
- -
- To prove or disprove the possibility of participation of the oxidized or S-glutathionylated GAPDH in the induction of apoptosis.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hess, D.T.; Matsumoto, A.; Kim, S.O.; Marshall, H.E.; Stamler, J.S. Protein S-nitrosylation: Purview and parameters. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.W.; Hess, D.T.; Stamler, J.S. Protein S-nitrosylation in health and disease: A current perspective. Trends Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tossounian, M.A.; Zhang, B.; Gout, I. The writers, readers, and erasers in redox regulation of GAPDH. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muronetz, V.I.; Melnikova, A.K.; Saso, L.; Schmalhausen, E.V. Influence of Oxidative Stress on Catalytic and Non-glycolytic Functions of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2040–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ruiz, A.; Araújo, I.M.; Izquierdo-Álvarez, A.; Hernansanz-Agustín, P.; Lamas, S.; Serrador, J.M. Specificity in S-nitrosylation: A short-range mechanism for NO signaling? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1220–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaffrey, S.R.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Ferris, C.D.; Tempst, P.; Snyder, S.H. Protein S-nitrosylation: A physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gow, A.J.; Chen, Q.; Hess, D.T.; Day, B.J.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Stamler, J.S. Basal and Stimulated Protein S-Nitrosylation in Multiple Cell Types and Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9637–9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gekeler, V.; Weger, S.; Probst, H. Mdr1P-glycoprotein gene segments analyzed from various human leukemic cell lines exhibiting different multidrug resistance profiles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 169, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, X.; Xue, H.; Lang, Y. The Relationship Between Protein S-Nitrosylation and Human Diseases: A Review. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 2815–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghetti, E.; Gasperini, L.; Virgilio, T.; Moda, F.; Tagliavini, F.; Benetti, F.; Legname, G. Prions Strongly Reduce NMDA Receptor S-Nitrosylation Levels at Pre-symptomatic and Terminal Stages of Prion Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 6035–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, S.; Khan, R.; Oellerich, M.; Ahmed, N.; Asif, A.R. Differential S-nitrosylation of proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 2014, 256, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Oh, C.; Zhang, X.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Lipton, S.A. Protein Transnitrosylation Signaling Networks Contribute to Inflammaging and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 531–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.; Saha, P.; Sen, N. Nitrosylation of GAPDH augments pathological tau acetylation upon exposure to amyloid-β. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizza, S.; Cardaci, S.; Montagna, C.; Di Giacomo, G.; De Zio, D.; Bordi, M.; Maiani, E.; Campello, S.; Borreca, A.; Puca, A.A.; et al. S-nitrosylation drives cell senescence and aging in mammals by controlling mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3388–E3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, K.K.K.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Nitric oxide, S-nitrosylation and neurodegeneration. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2005, 51, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, X.; Huang, Y.; Qian, S. Protein Tyrosine Nitration in Lung Cancer: Current Research Status and Future Perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3435–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Maarschalkerweerd, A.; Pedersen, M.N.; Peterson, H.; Nilsson, M.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Skamris, T.; Rand, K.; Vetri, V.; Langkilde, A.E.; Vestergaard, B. Formation of covalent di-tyrosine dimers in recombinant α-synuclein. Intrinsically Disord. Proteins 2015, 3, e1071302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, N.W. GAPDH: Biological Properties and Diversity; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 985. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.I.; Waters, M. Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. In The Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Oxidation-Reduction Part C; Boyer, P.D., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1976; Volume XIII, pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sirover, M.A. On the functional diversity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Biochemical mechanisms and regulatory control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011, 1810, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirover, M.A. Moonlighting glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Posttranslational modification, protein and nucleic acid interactions in normal cells and in human pathology. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 55, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirover, M.A. The role of posttranslational modification in moonlighting glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase structure and function. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakschik, S.B.; Needleman, P. Sulfhydryl reactivity of organic nitrates: Biochemical basis for inhibition of glyceraldehyde-P dehydrogenase and monoamine oxidase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1973, 53, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, W.S.; Connors, M.J. The activation and inactivation of the acyl phosphatase activity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1970, 136, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.-S.; Benitez, L.V.; McConachie, W.A.; Allison, W.S. The conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehyrogenase to an acylphosphatase by trinitroglycerin and inactivation of this activity by azide and ascorbate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Enzymol. 1975, 384, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kots, A.Y.; Skurat, A.V.; Sergienko, E.A.; Bulargina, T.V.; Severin, E.S. Nitroprusside stimulates the cysteine-specific mono(ADP-ribosylation) of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from human erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1992, 300, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimmeler, S.; Lottspeich, F.; Brüne, B. Nitric oxide causes ADP-ribosylation and inhibition of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 16771–16774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Snyder, S.H. Nitric oxide stimulates auto-ADP-ribosylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9382–9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hara, M.R.; Snyder, S.H. Nitric Oxide–GAPDH–Siah: A Novel Cell Death Cascade. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2006, 26, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Snyder, S.H. Purification of a nitric oxide-stimulated ADP-ribosylated protein using biotinylated. beta.-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2228–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kots, A.Y.; Sergienko, E.A.; Bulargina, T.V.; Severin, E.S. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate activates auto-ADP-ribosylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1993, 324, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, L.J.; Moss, J. Stimulation by nitric oxide of an NAD linkage to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6238–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlile, G.W.; Chalmers-Redman, R.M.; Tatton, N.A.; Borden, K.E.; Tatton, W.G. Reduced apoptosis after nerve growth factor and serum withdrawal: Conversion of tetrameric glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase to a dimer. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 57, 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, V.M.; Krynetski, E.Y.; Krynetskaia, N.F.; Grieger, D.; Mukatira, S.T.; Murti, K.G.; Slaughter, C.A.; Park, H.-W.; Evans, W.E. A Novel CRM1-mediated Nuclear Export Signal Governs Nuclear Accumulation of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase following Genotoxic Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5984–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dastoor, Z.; Dreyer, J.L. Potential role of nuclear translocation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in apoptosis and oxidative stress. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arutyunova, E.I.; Domnina, L.V.; Chudinova, A.A.; Makshakova, O.N.; Arutyunov, D.Y.; Muronetz, V.I. Localization of non-native D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in growing and apoptotic HeLa cells. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatton, W.; Chalmers-Redman, R.; Tatton, N. Neuroprotection by deprenyl and other propargylamines: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase rather than monoamine oxidase B. J. Neural Transm. 2003, 110, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorieva, J.A.; Dainiak, M.B.; Katrukha, A.G.; Muronetz, V.I. Antibodies to the Nonnative Forms of d-Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase: Identification, Purification, and Influence on the Renaturation of the Enzyme. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 369, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunova, E.I.; Danshina, P.V.; Domnina, L.V.; Pleten, A.P.; Muronetz, V.I. Oxidation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase enhances its binding to nucleic acids. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 307, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhar, M.; Stamler, J.S. A central role for S-nitrosylation in apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Poon, H.F.; Cai, J.; Pierce, W.M.; Merchant, M.; Klein, J.B.; Markesbery, W.R.; Butterfield, D.A. Identification of nitrated proteins in Alzheimer’s disease brain using a redox proteomics approach. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 22, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.; Heales, S. Nitric oxide and neurological disorders. Mol. Aspects Med. 2005, 26, 67–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borutaite, V.; Brown, G.C. Nitric oxide induces apoptosis via hydrogen peroxide, but necrosis via energy and thiol depletion. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüne, B.; Lapetina, E.G. Protein thiol modification of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a target for nitric oxide signaling. Genet. Eng. 1995, 17, 149–164. [Google Scholar]
- Brune, B.; Mohr, S. Protein Thiol Modification of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase and Caspase-3 by Nitric Oxide. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2001, 2, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, F.; Rossi, R.; Di Simplicio, P.; Floridi, A.; Canestrari, F. Protein Thiols and Glutathione Influence the Nitric Oxide-Dependent Regulation of the Red Blood Cell Metabolism. Nitric Oxide 2002, 6, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borderie, D. Nitric Oxide Modifies Glycolytic Pathways in Cultures Human Synoviocytes. Cell Biol. Int. 2000, 24, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Rovidati, S.; Ghibelli, L.; Canestrari, F. S-Nitrosylation of Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Decreases the Enzyme Affinity to the Erythrocyte Membrane. Nitric Oxide 1998, 2, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, M.R.; Cascio, M.B.; Sawa, A. GAPDH as a sensor of NO stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2006, 1762, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hara, M.R.; Snyder, S.H. Cell signaling and neuronal death. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, M.R.; Thomas, B.; Cascio, M.B.; Bae, B.-I.; Hester, L.D.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Sawa, A.; Snyder, S.H. Neuroprotection by pharmacologic blockade of the GAPDH death cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3887–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hara, M.R.; Agrawal, N.; Kim, S.F.; Cascio, M.B.; Fujimuro, M.; Ozeki, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Cheah, J.H.; Tankou, S.K.; Hester, L.D.; et al. S-nitrosylated GAPDH initiates apoptotic cell death by nuclear translocation following Siah1 binding. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, N.; Hara, M.R.; Kornberg, M.D.; Cascio, M.B.; Bae, B.-I.; Shahani, N.; Thomas, B.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L.; Snyder, S.H.; et al. Nitric oxide-induced nuclear GAPDH activates p300/CBP and mediates apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sen, N.; Hara, M.R.; Ahmad, A.S.; Cascio, M.B.; Kamiya, A.; Ehmsen, J.T.; Aggrawal, N.; Hester, L.; Doré, S.; Snyder, S.H.; et al. GOSPEL: A Neuroprotective Protein that Binds to GAPDH upon S-Nitrosylation. Neuron 2009, 63, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González, M.C.; Romero, J.M.; Ingaramo, M.C.; Muñoz Sosa, C.J.; Curtino, J.A.; Carrizo, M.E. Enhancement by GOSPEL protein of GAPDH aggregation induced by nitric oxide donor and its inhibition by NAD +. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2210–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, M.D.; Sen, N.; Hara, M.R.; Juluri, K.R.; Nguyen, J.V.K.; Snowman, A.M.; Law, L.; Hester, L.D.; Snyder, S.H. GAPDH mediates nitrosylation of nuclear proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, H.; Kubo, T.; Ihara, H.; Hikida, T.; Danjo, T.; Nakatsuji, M.; Shahani, N.; Itakura, M.; Ono, Y.; Azuma, Y.-T.; et al. Nuclear-translocated Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase Promotes Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase-1 Activation during Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress in Stroke. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14493–14503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naletova, I.; Schmalhausen, E.; Kharitonov, A.; Katrukha, A.; Saso, L.; Caprioli, A.; Muronetz, V. Non-native glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase can be an intrinsic component of amyloid structures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008, 1784, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muronetz, V.I.; Barinova, K.V.; Stroylova, Y.Y.; Semenyuk, P.I.; Schmalhausen, E.V. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Aggregation mechanisms and impact on amyloid neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 100, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, H.; Amano, W.; Fujita, A.; Fukuhara, A.; Azuma, Y.-T.; Hata, F.; Inui, T.; Takeuchi, T. The Active Site Cysteine of the Proapoptotic Protein Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase Is Essential in Oxidative Stress-induced Aggregation and Cell Death. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26562–26574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, H.; Amano, W.; Kubo, T.; Fukuhara, A.; Ihara, H.; Azuma, Y.-T.; Tajima, H.; Inui, T.; Sawa, A.; Takeuchi, T. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase aggregate formation participates in oxidative stress-induced cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 34331–34341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itakura, M.; Nakajima, H.; Semi, Y.; Higashida, S.; Azuma, Y.-T.; Takeuchi, T. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase aggregation inhibitor peptide: A potential therapeutic strategy against oxidative stress-induced cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazarev, V.F.; Nikotina, A.D.; Semenyuk, P.I.; Evstafyeva, D.B.; Mikhaylova, E.R.; Muronetz, V.I.; Shevtsov, M.A.; Tolkacheva, A.V.; Dobrodumov, A.V.; Shavarda, A.L.; et al. Small molecules preventing GAPDH aggregation are therapeutically applicable in cell and rat models of oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 92, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarev, V.F.; Tsolaki, M.; Mikhaylova, E.R.; Benken, K.A.; Shevtsov, M.A.; Nikotina, A.D.; Lechpammer, M.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Makarov, A.A.; Moskalev, A.A.; et al. Extracellular GAPDH Promotes Alzheimer Disease Progression by Enhancing Amyloid-β Aggregation and Cytotoxicity. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, J.L.; Sirover, M.A. Alteration of intracellular structure and function of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: A common phenotype of neurodegenerative disorders? Neurotoxicology 2002, 23, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, K.; Khomyakova, E.; Semenyuk, P.; Schmalhausen, E.; Muronetz, V. Binding of alpha-synuclein to partially oxidized glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase induces subsequent inactivation of the enzyme. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 642, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albina, J.E.; Mastrofrancesco, B.; Reichner, J.S. Acyl phosphatase activity of NO-inhibited glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH): A potential mechanism for uncoupling glycolysis from ATP generation in NO-producing cells. Biochem J. 1999, 341, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalhausen, E.V.; Medvedeva, M.V.; Serebryakova, M.V.; Chagovets, V.V.; Muronetz, V.I. Products of S-nitrosylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Relation between S-nitrosylation and oxidation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2021, 1866, 130032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, K.V.; Serebryakova, M.V.; Muronetz, V.I.; Schmalhausen, E.V. S-glutathionylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase induces formation of C150-C154 intrasubunit disulfide bond in the active site of the enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 3167–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barinova, K.V.; Serebryakova, M.V.; Eldarov, M.A.; Kulikova, A.A.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Muronetz, V.I.; Schmalhausen, E.V. S-glutathionylation of human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and possible role of Cys152-Cys156 disulfide bridge in the active site of the protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppe-Koistinen, I.; Moldeus, P.; Bergman, T.; Cotgreave, I.A. S-Thiolation of human endothelial cell glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase after hydrogen peroxide treatment. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 221, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, S.H.M.; Shao, D.; Tsukahara, Y.; Pimentel, D.R.; Weisbrod, R.M.; Hamburg, N.M.; McComb, M.E.; Matsui, R.; Bachschmid, M.M. Oxidized GAPDH transfers S-glutathionylation to a nuclear protein Sirtuin-1 leading to apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 174, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muronetz, V.I.; Medvedeva, M.V.; Sevostyanova, I.A.; Schmalhausen, E.V. Modification of Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase with Nitric Oxide: Role in Signal Transduction and Development of Apoptosis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111656
Muronetz VI, Medvedeva MV, Sevostyanova IA, Schmalhausen EV. Modification of Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase with Nitric Oxide: Role in Signal Transduction and Development of Apoptosis. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(11):1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111656
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuronetz, Vladimir I., Maria V. Medvedeva, Irina A. Sevostyanova, and Elena V. Schmalhausen. 2021. "Modification of Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase with Nitric Oxide: Role in Signal Transduction and Development of Apoptosis" Biomolecules 11, no. 11: 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111656
APA StyleMuronetz, V. I., Medvedeva, M. V., Sevostyanova, I. A., & Schmalhausen, E. V. (2021). Modification of Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase with Nitric Oxide: Role in Signal Transduction and Development of Apoptosis. Biomolecules, 11(11), 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111656




