Improving Protein Subcellular Location Classification by Incorporating Three-Dimensional Structure Information
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Protein Structural Features
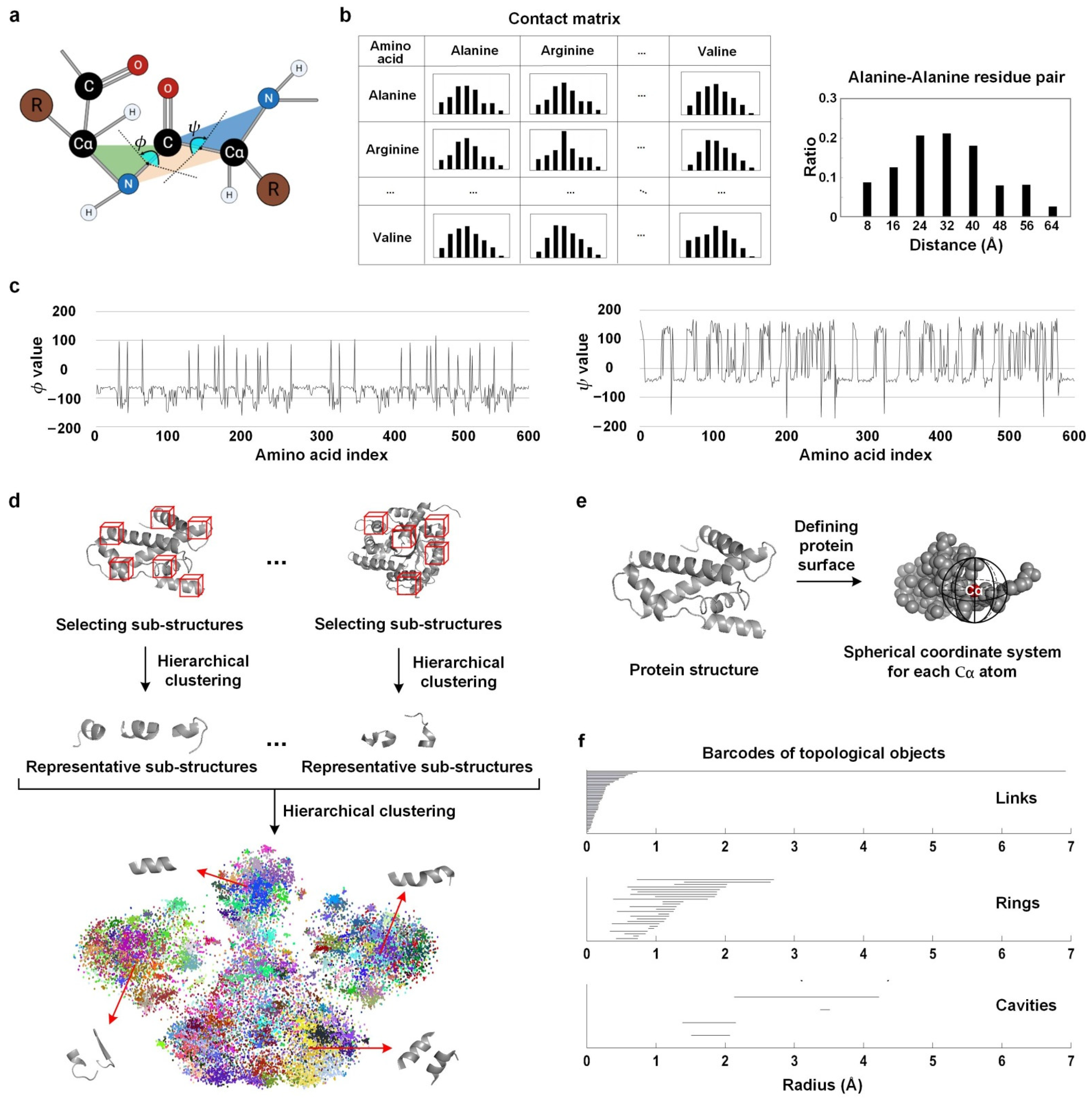
2.2.1. Physical Features
Contact Matrix
Dihedral Angle Features
Sub-Structure Frequency
2.2.2. Chemical Features
2.2.3. Topological Features
Gauss Integrals
Persistent Homology
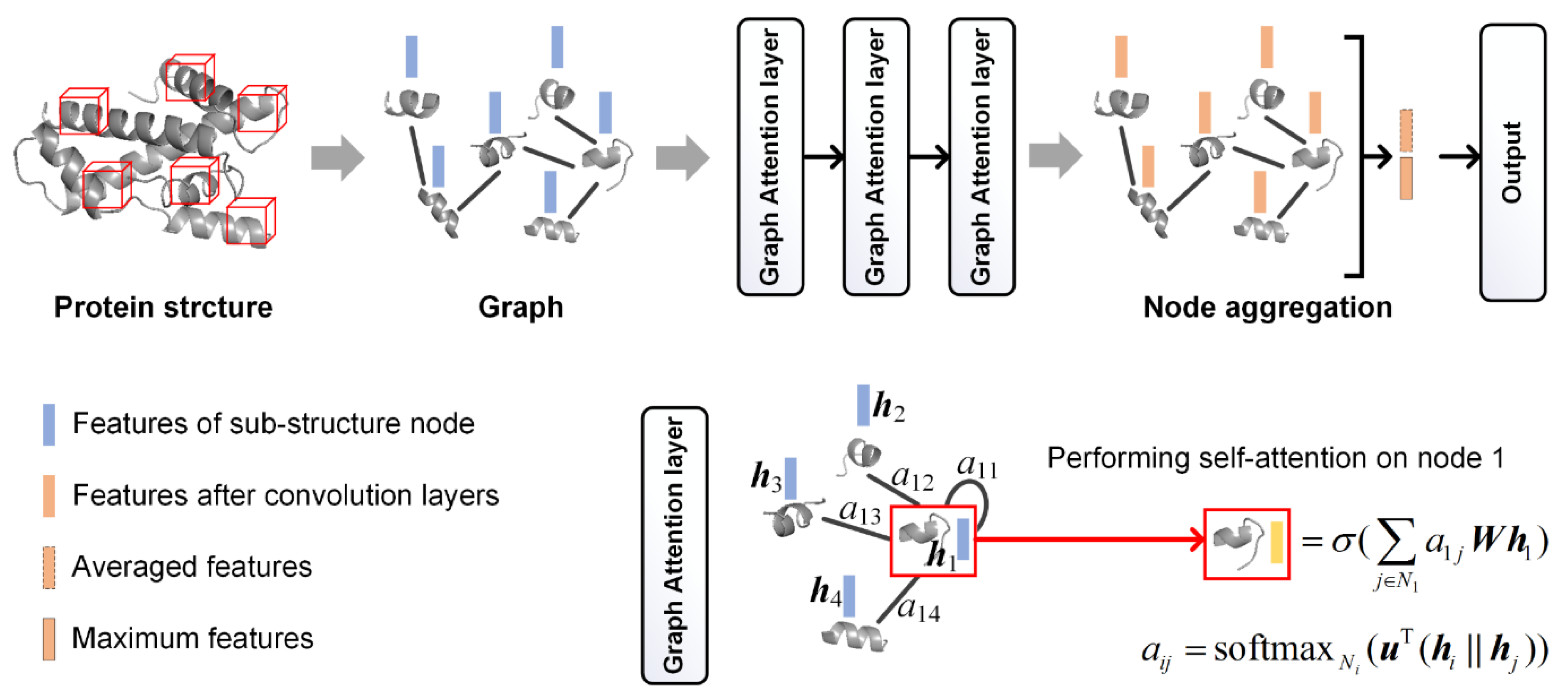
2.2.4. Deep Learning Features
CNN Features
GCN Features
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Classification Results of Single Descriptors
3.2. Results of Fusing Different Descriptors
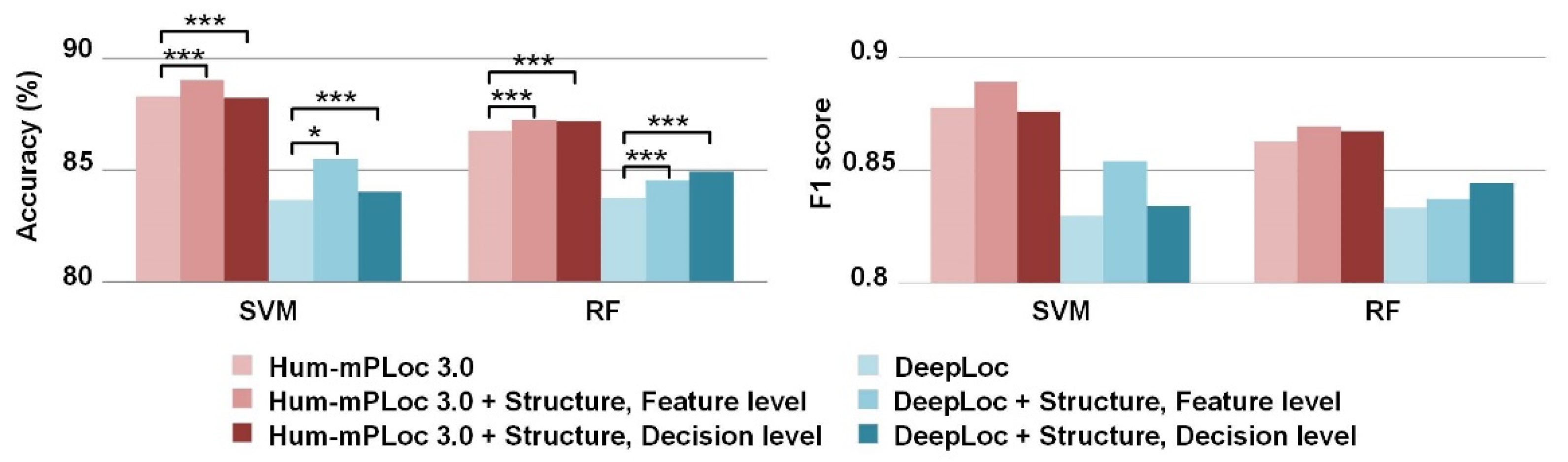
3.3. Improvements by the Incorporation of Sequence Features
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thul, P.J.; Åkesson, L.; Wiking, M.; Mahdessian, D.; Geladaki, A.; Ait Blal, H.; Alm, T.; Asplund, A.; Björk, L.; Breckels, L.M.; et al. A subcellular map of the human proteome. Science 2017, 356, eaal3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbo, H.; Sato, M.; Okoshi, A.; Fukuchi, S. Functional Segments on Intrinsically Disordered Regions in Disease-Related Proteins. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Dhanda, S.K. Bird Eye View of Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction. Life 2020, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Shen, H.-B. Hum-mPLoc 3.0: Prediction enhancement of human protein subcellular localization through modeling the hidden correlations of gene ontology and functional domain features. Bioinformatics 2016, 33, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savojardo, C.; Martelli, P.L.; Fariselli, P.; Casadio, R. SChloro: Directing Viridiplantae proteins to six chloroplastic sub-compartments. Bioinformatics 2016, 33, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteros, J.J.A.; Sønderby, C.K.; Sønderby, S.K.; Nielsen, H.; Winther, O. DeepLoc: Prediction of protein subcellular localization using deep learning. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, R.; Varadwaj, P.K. HumDLoc: Human Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction Using Deep Neural Network. Curr. Genom. 2020, 21, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.D.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, V.; Ferone, A.; Petrosino, A.; Di Baja, G.S. A Supervised Approach to 3D Structural Classification of Proteins. In International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhifli, W.; Diallo, A.B. ProtNN: Fast and accurate protein 3D-structure classification in structural and topological space. BioData Min. 2016, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northey, T.C.; Barešić, A.; Martin, A.C.R. IntPred: A structure-based predictor of protein–protein interaction sites. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Choi, I.S. Three-dimensionally embedded graph convolutional network (3dgcn) for molecule interpretation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.09794. [Google Scholar]
- Torng, W.; Altman, R.B. 3D deep convolutional neural networks for amino acid environment similarity analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharaki, E.I. Prediction of protein function using a deep convolutional neural network ensemble. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2017, 3, e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Lang, B.; Huang, L. DGCNN: Disordered graph convolutional neural network based on the Gaussian mixture model. Neurocomputing 2018, 321, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanaei, A.; Anandanadarajah, N.; Maida, A.; Loganantharaj, R. A Deep Learning Model for Predicting Tumor Suppressor Genes and Oncogenes from PDB Structure. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Kansas City, MO, USA, 13–16 November 2017; p. 177378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorijević, V.; Renfrew, P.D.; Kosciolek, T.; Leman, J.K.; Berenberg, D.; Vatanen, T.; Chandler, C.; Taylor, B.C.; Fisk, I.M.; Vlamakis, H.; et al. Structure-based protein function prediction using graph convolutional networks. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.; O’Donoghue, S.; Rost, B. Adaptation of protein surfaces to subcellular location. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 276, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Taneja, T.K.; Hagen, B.M.; Kim, B.-Y.; Ortega, B.; Lederer, W.J.; Welling, P.A. Golgi Export of the Kir2.1 Channel Is Driven by a Trafficking Signal Located within Its Tertiary Structure. Cell 2011, 145, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ortega, B.; Kim, B.; Welling, P.A. A Common Signal Patch Drives AP-1 Protein-dependent Golgi Export of Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 14963–14972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R. LOC3D: Annotate sub-cellular localization for protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, B.L. Protein subcellular multi-localization prediction using a min-max modular support vector machine. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2010, 20, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.Y.; Lo, A.; Chiu, H.S.; Sung, T.Y.; Hsu, W.L. Protein subcellular localization prediction based on compartment-specific biological features. In Proceedings of the Computational Systems Bioinformatics Conference (CSB), Stanford, CA, USA, 14–18 August 2006; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.-L.; Liu, Y.-L.; Zuo, Y.-C.; Mei, H.-X.; Rang, Y.; Hou, B.-Y.; Zhao, Y. acACS: Improving the Prediction Accuracy of Protein Subcellular Locations and Protein Classification by Incorporating the Average Chemical Shifts Composition. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 864135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Dunbrack, R.L. PISCES: A protein sequence culling server. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1589–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Zhou, H.; Murphy, R.F.; Shen, H.B. Consistency and variation of protein subcellular location annotations. Proteins 2021, 89, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, E.; Lieberherr, D.; Tognolli, M.; Schneider, M.; Bansal, P.; Bridge, A.; Poux, S.; Bougueleret, L.; Xenarios, I. UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, the manually annotated section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase: How to use the entry view. In Plant Bioinformatics; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1374, pp. 23–54. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jennrich, R.I. Stepwise Discriminant Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 77–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kountouris, P.; Hirst, J.D. Prediction of backbone dihedral angles and protein secondary structure using support vector machines. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.G.; Kwon, J.; Kim, S.H. Local feature frequency profile: A method to measure structural similarity in proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3797–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolau, D.V.; Paszek, E.; Fulga, F.; Nicolau, D.V. Mapping hydrophobicity on the protein molecular surface at atom-level resolution. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhead, D.R.; Slidel, T.W.F.; Flores, T.P.J.; Thornton, J.M. Protein structural topology: Automated analysis and diagrammatic representation. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogen, P.; Fain, B. Automatic classification of protein structure by using Gauss integrals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomsma, W.; Frellsen, J.; Harder, T.; Bottaro, S.; Johansson, K.E.; Tian, P.; Stovgaard, K.; Andreetta, C.; Olsson, S.; Valentin, J.B.; et al. PHAISTOS: A framework for Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation and inference of protein structure. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, Z.; Wei, G.W. TopologyNet: Topology based deep convolutional and multi-task neural networks for biomolecular property predictions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, N.; Porter, M.A.; Tillmann, U.; Grindrod, P.; Harrington, H.A. A roadmap for the computation of persistent homology. EPJ Data Sci. 2017, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S.; Anishchenko, I.; Dagar, A.; Baker, D.; Talukdar, P. ProteinGCN: Protein model quality assessment using Graph Convolutional Networks. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Liò, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph Attention Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, M.; Chen, L.; Du, Y.; Tianyi Zhou, J.; Zhang, C. Deep reinforcement learning with stacked hierarchical attention for text-based games. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; Volume 33, pp. 16495–16507. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Shen, W.; Yang, Y.; Quan, X.; Wang, R. Relational Graph Attention Network for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.12362. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D. Human cell structure-driven model construction for predicting protein subcellular location from biological images. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Yang, F.; Shen, H.B. Incorporating organelle correlations into semi-supervised learning for protein subcellular localization prediction. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Adler, J.; Wu, Z.; Green, T.; Zielinski, M.; Žídek, A.; Bridgland, A.; Cowie, A.; Meyer, C.; Laydon, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction for the human proteome. Nature 2021, 596, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Subcellular Location | Number of Proteins |
|---|---|
| Nucleoplasm | 385 |
| Plasma membrane | 281 |
| Cytosol | 275 |
| Mitochondria | 111 |
| Total | 1052 |
| Feature Category | Descriptor | Brief Description | Feature Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical features | Contact matrix | Statistics of distances between amino acid pairs | 1680 |
| Dihedral angle features | Frequency domain and wavelet transform features extracted from dihedral angle curves along protein chain | 30 | |
| Sub-structure frequency | Frequencies of small sub-structures of one protein in clusters | 184 | |
| Chemical features | Chemical features | Composition and chemical properties of surface amino acids | 42 |
| Topological features | Gauss integrals | Type and number of crossings in planar projections of protein curve | 31 |
| Persistent homology | Features extracted from persistent barcodes of topological objects in protein structure | 34 | |
| Deep learning features | Convolutional neural network features | Features learned by a convolutional neural network with contact distances and dihedral angles as input | 1000 |
| Graph convolutional neural network features | Features learned by a graph convolutional network with attention layers | 84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Zhai, Y.-J.; Xue, Z.-Z.; Xu, Y.-Y. Improving Protein Subcellular Location Classification by Incorporating Three-Dimensional Structure Information. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111607
Wang G, Zhai Y-J, Xue Z-Z, Xu Y-Y. Improving Protein Subcellular Location Classification by Incorporating Three-Dimensional Structure Information. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(11):1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111607
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ge, Yu-Jia Zhai, Zhen-Zhen Xue, and Ying-Ying Xu. 2021. "Improving Protein Subcellular Location Classification by Incorporating Three-Dimensional Structure Information" Biomolecules 11, no. 11: 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111607
APA StyleWang, G., Zhai, Y.-J., Xue, Z.-Z., & Xu, Y.-Y. (2021). Improving Protein Subcellular Location Classification by Incorporating Three-Dimensional Structure Information. Biomolecules, 11(11), 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111607






