Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Metabolic Diseases and Underlying Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. NAFLD, Diabetes and Obesity
3. Benefit of Bariatric Surgery
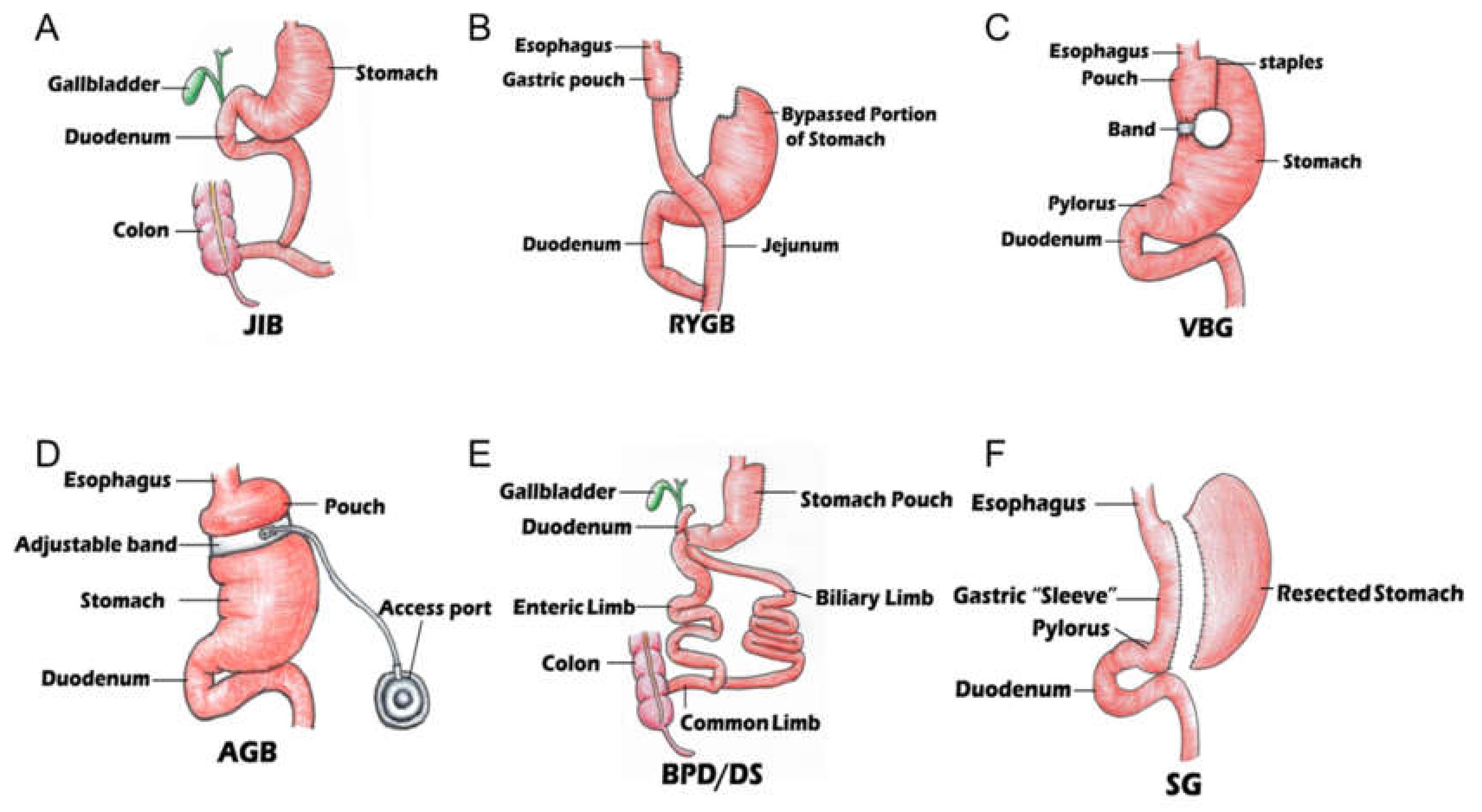
Types of Bariatric Surgery
4. Consequences of Bariatric Surgery
4.1. Eating Habits
4.2. Weight Loss
4.3. Effect on Diabetes
4.4. Effect on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases
4.5. Effects on NAFLD
5. Endocrine Function after Bariatric Surgery
5.1. GLP-1
5.2. FGF19 and FGF21
5.3. Pancreatic Peptide YY
6. Other Effects of Bariatric Surgery
6.1. Gut Microbiota
6.2. Bile Acids
7. Complications of Bariatric Surgery
7.1. Osteoporosis
7.2. Diarrhea
7.3. Iron Deficiency and Anemia
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanyal, A.J.; Brunt, E.M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Kowdley, K.V.; Chalasani, N.; LaVine, J.E.; Ratziu, V.; McCullough, A. Endpoints and clinical trial design for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Makhlouf, H.R. Histology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Adults and Children. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, J.M.; Diehl, A.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An underrecognized cause of cryptogenic cirrhosis. JAMA 2003, 289, 3000–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, J.; Choi, S.S.; Diehl, A.M. Mechanisms of Disease Progression in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2008, 28, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Devaki, P.; Ha, N.B.; Jun, D.W.; Te, H.S.; Cheung, R.C.; Nguyen, M.H. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk factors for advanced fibrosis and mortality in the United States. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adipose tissue, obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Minerva Endocrinol. 2017, 42, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Castiglione, A.; Crocè, L.S.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellentani, S. Incidence and natural course of fatty liver in the general population: The Dionysos study. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhala, N.; Jouness, R.; Bugianesi, E. Epidemiology and Natural History of Patients with NAFLD. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5169–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazel, Y.; Koenig, A.; Sayiner, M.; Goodman, Z.D.; Younossi, Z.M. Epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.-G.; Kim, S.-U.; Wong, V.W.-S. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.C.; Malik, V.; Jia, W.; Kadowaki, T.; Yajnik, C.S.; Yoon, K.H.; Hu, F.B. Diabetes in Asia: Epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 2009, 301, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakizaki, S.; Takizawa, D.; Yamazaki, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Sato, K.; Takagi, H.; Mori, M.; Kasama, K. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Japanese patients with severe obesity who received laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (LRYGB) in comparison to non-Japanese patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deurenberg, P.; Deurenberg-Yap, M.; Guricci, S. Asians are different from Caucasians and from each other in their body mass index/body fat per cent relationship. Obes. Rev. 2002, 3, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misra, A.; Bhardwaj, S. Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome in Developing Countries: Focus on South Asians. In The Importance of Nutrition as an Integral Part of Disease Management; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 78, pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Celio, A.C.; Pories, W.J. A History of Bariatric Surgery: The Maturation of a Medical Discipline. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 96, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, H. The Evolution of Metabolic/Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, S.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Wolski, K.; Watanabe, R.M.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Abood, B.; Pothier, C.E.; Brethauer, S.; Nissen, S.; Gupta, M.; et al. Metabolic Effects of Bariatric Surgery in Patients with Moderate Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: Analysis of a randomized control trial comparing surgery with intensive medical treatment. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castagneto-Gissey, L.; Mingrone, G. Insulin sensitivity and secretion modifications after bariatric surgery. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2012, 35, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassailly, G.; Caiazzo, R.; Buob, D.; Pigeyre, M.; Verkindt, H.; Labreuche, J.; Raverdy, V.; Leteurtre, E.; Dharancy, S.; Louvet, A.; et al. Bariatric Surgery Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Morbidly Obese Patients. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 379–388, quiz e315–e376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumithran, P.; Prendergast, L.A.; Delbridge, E.; Purcell, K.; Shulkes, A.; Kriketos, A.; Proietto, J. Long-Term Persistence of Hormonal Adaptations to Weight Loss. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fried, M.; Yumuk, V.; Oppert, J.M.; Scopinaro, N.; Torres, A.; Weiner, R.; Yashkov, Y.; Frühbeck, G. Interdisciplinary European Guidelines on Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, X.; Yin, L. Circadian Rhythms in Liver Physiology and Liver Diseases. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 917–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Covas, M.I.; Ibarrola-Jurado, N.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; et al. Prevention of diabetes with Mediterranean diets: A subgroup analysis of a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magkos, F.; Fraterrigo, G.; Yoshino, J.; Luecking, C.; Kirbach, K.; Kelly, S.C.; De Las Fuentes, L.; He, S.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Effects of Moderate and Subsequent Progressive Weight Loss on Metabolic Function and Adipose Tissue Biology in Humans with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannah, W.N., Jr.; Harrison, S.A. Lifestyle and Dietary Interventions in the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, E.; Reeds, D.N.; Finck, B.N.; Mayurranjan, M.S.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S. Dietary Fat and Carbohydrates Differentially Alter Insulin Sensitivity during Caloric Restriction. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stefater, M.A.; Inge, T.H. Bariatric Surgery for Adolescents with Type 2 Diabetes: An Emerging Therapeutic Strategy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, P.R.; Hanipah, Z.N.; Rubino, F. Metabolic surgery for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus: Now supported by the world’s leading diabetes organizations. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84 (Suppl. 1), S47–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankir, M.K.; Rullmann, M.; Seyfried, F.; Preusser, S.; Poppitz, S.; Heba, S.; Gousias, K.; Hoyer, J.; Schütz, T.; Dietrich, A.; et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery progressively alters radiologic measures of hypothalamic inflammation in obese patients. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e131329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerit, Z. Bariatric surgery, diabetes mellitus, and epicardial adipose tissue. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugale, S.; Agarwal, D.; Satwalekar, V.; Rao, N.; Ugale, A. Bariatric surgery as an option for diabetes mellitus prevention and treatment in obese persons. Minerva Endocrinol. 2016, 41, 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald, H.; Buchwald, J.N. Metabolic (Bariatric and Nonbariatric) Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes: A Personal Perspective Review. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Argyropoulos, G. Bariatric Surgery: Prevalence, Predictors, and Mechanisms of Diabetes Remission. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2015, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquati, A.; Shantavasinkul, P.C.; Omotosho, P.; Corsino, L.; Spagnoli, A. Perioperative changes in prouroguanylin hormone response in severely obese subjects after bariatric surgery. Surgery 2019, 166, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangalakis, L.L.; Tabone, L.; Spagnoli, A.; Muehlbauer, M.; Omotosho, P.; Torquati, A. Effects of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Osteoclast Activity and Bone Density in Morbidly Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Obes. Surg. 2019, 30, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Pérez, F.; Casajoana, A.; Gómez-Vaquero, C.; Virgili, N.; López-Urdiales, R.; Hernández-Montoliu, L.; Pujol-Gebelli, J.; Osorio, J.; Alves, C.; Perez-Maraver, M.; et al. Changes in Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes after Different Bariatric Surgery Procedures and the Role of Gastrointestinal Hormones. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallafré, V.C.; Llauradó, G.; Keiran, N.; Benaiges, E.; Astiarraga, B.; Martínez, L.; Pellitero, S.; González-Clemente, J.M.; Rodríguez, A.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; et al. Preoperative Circulating Succinate Levels as a Biomarker for Diabetes Remission after Bariatric Surgery. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samczuk, P.; Hady, H.R.; Adamska-Patruno, E.; Citko, A.; Dadan, J.; Barbas, C.; Kretowski, A.; Ciborowski, M. In-and-out Molecular Changes Linked to the Type 2 Diabetes Remission after Bariatric Surgery: An Influence of Gut Microbes on Mitochondria Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, D.P.; Johnson, E.; Haneuse, S.; Arterburn, D.; Coleman, K.J.; O’Connor, P.; O’Brien, R.; Bogart, A.; Theis, M.K.; Anau, J.; et al. Association between Bariatric Surgery and Macrovascular Disease Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Severe Obesity. JAMA 2018, 320, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doumouras, A.G.; Wong, J.A.; Paterson, J.M.; Lee, Y.; Sivapathasundaram, B.; Tarride, J.E.; Thabane, L.; Hong, D.; Yusuf, S.; Anvari, M. Bariatric Surgery and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study. Circulation 2021, 143, 1468–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech-Ximenos, B.; Cuba, V.; Daunis-I-Estadella, P.; Thió-Henestrosa, S.; Jaldo, F.; Biarnes, C.; Molina, X.; Xifra, G.; Ricart, W.; Bardera, A.; et al. Bariatric Surgery-Induced Changes in Intima-Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Class 3 Obesity: A 3-Year Follow-Up Study. Obesity 2020, 28, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminian, A.; AlEassa, E.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Tu, C.; Khorgami, Z.; Schauer, P.R.; Brethauer, S.A.; Daigle, C.R. Bariatric surgery is associated with a lower rate of death after myocardial infarction and stroke: A nationwide study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- English, W.J.; Williams, D.B. Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery: An Effective Treatment Option for Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, L.M.; Pereira, A.Z.; Carneiro, G.; Arasaki, C.H.; Zanella, M.T. Postprandial Adiponectin Levels Are Associated with Improvements in Postprandial Triglycerides after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2013, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osto, E.; Doytcheva, P.; Corteville, C.; Bueter, M.; Dörig, C.; Stivala, S.; Buhmann, H.; Colin, S.; Rohrer, L.; Hasballa, R.; et al. Rapid and Body Weight-Independent Improvement of Endothelial and High-Density Lipoprotein Function after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. Circulation 2015, 131, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, H.; Poitou, C.; Habich, C.; Bouillot, J.-L.; Eckel, J.; Clément, K. Heat Shock Protein 60 in Obesity: Effect of Bariatric Surgery and its Relation to Inflammation and Cardiovascular Risk. Obesity 2017, 25, 2108–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaiges, D.; Climent, E.; Goday, A.; Roux, J.A.F.-L.; Pedro-Botet, J. Bariatric surgery and hypertension: Implications and perspectives after the GATEWAY randomized trial. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 9, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, G.S.; Småstuen, M.C.; Sandbu, R.; Nordstrand, N.; Hofsø, D.; Lindberg, M.; Hertel, J.K.; Hjelmesæth, J. Association of Bariatric Surgery vs Medical Obesity Treatment with Long-term Medical Complications and Obesity-Related Comorbidities. JAMA 2018, 319, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diemieszczyk, I.; Woźniewska, P.; Gołaszewski, P.; Drygalski, K.; Nadolny, K.; Ładny, J.R.; Hady, H.R. Does weight loss after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy contribute to reduction in blood pressure? Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, S.G.; Velcu, L.M.; Rabinovitz, M.; Demetris, A.J.; Krasinskas, A.M.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; Eid, G.M.; Ramanathan, R.; Taylor, D.S.; Schauer, P.R. Surgically-Induced Weight Loss Significantly Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Metabolic Syndrome. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottin, C.C.; Moretto, M.; Padoin, A.; Kupski, C.; Swarowsky, A.M.; Glock, L.; Duval, V.; da Silva, V.D. Histological Behavior of Hepatic Steatosis in Morbidly Obese Patients after Weight Loss Induced by Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2005, 15, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto, M.; Kupski, C.; Da Silva, V.D.; Padoin, A.; Mottin, C.C. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Liver Fibrosis. Obes. Surg. 2011, 22, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcz, W.K.; Krawczykowski, D.; Kuesters, S.; Marjanovic, G.; Kulemann, B.; Grobe, H.; Karcz-Socha, I.; Hopt, U.T.; Bukhari, W.; Grueneberger, J.M. Influence of Sleeve Gastrectomy on NASH and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 765473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blauw, L.L.; Li, Z.; Rensen, S.S.; Greve, J.W.M.; Verhoeven, A.; Derks, R.J.; Giera, M.; Wang, Y.; Rensen, P.C. Metabolic liver inflammation in obesity does not robustly decrease hepatic and circulating CETP. Atherosclerosis 2018, 275, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Leonetti, F.; Capoccia, D.; Di Cristofano, C.; Silecchia, G.; Orho-Melander, M.; Melander, O.; Cavallo, M.G. Increased Plasma Proneurotensin Levels Identify NAFLD in Adults with and without Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livadariu, R.; Timofte, D.; Trifan, A.; Danila, R.; Ionescu, L.; Sîngeap, A.; Ciobanu, D. Vitamin D Deficiency, a Noninvasive Marker of Steatohepatitis in Patients with Obesity and Biopsy Proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Acta Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammah, A.A. Endocrine and metabolic complications after bariatric surgery. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, R.E.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Asarian, L.; Horowitz, M.; Beglinger, C.; Geary, N. Ghrelin CCK, GLP-1, and PYY(3–36): Secretory Controls and Physiological Roles in Eating and Glycemia in Health, Obesity, and after RYGB. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 411–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, C. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Thyroid Function in Obese Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 3292–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliaki, C.; Liatis, S.; Le Roux, C.W.; Kokkinos, A. The role of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes: Current challenges and perspectives. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2017, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holst, J.J. The Physiology of Glucagon-like Peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, N.B.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Dirksen, C.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Naver, L.P.S.; Hvolris, L.; Clausen, T.R.; Wulff, B.S.; Worm, D.; Hansen, D.L.; et al. Acute and long-term effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on glucose metabolism in subjects with Type 2 diabetes and normal glucose tolerance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E122–E131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, A.; Casamitjana, R.; Viaplana-Masclans, J.; Lacy, A.; Vidal, J. GLP-1 Action and Glucose Tolerance in Subjects with Remission of Type 2 Diabetes after Gastric Bypass Surgery. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, A.; Mari, A.; Casamitjana, R.; Lacy, A.; Ferrannini, E.; Vidal, J. GLP-1 and Glucose Tolerance after Sleeve Gastrectomy in Morbidly Obese Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3372–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersen, A.; Lund, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. Glucagon-like peptide 1 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutch, C.R.; Sandoval, D. The Role of GLP-1 in the Metabolic Success of Bariatric Surgery. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 4139–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webb, D.-L.; Abrahamsson, N.; Sundbom, M.; Hellström, P.M. Bariatric surgery—Time to replace with GLP-1? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouyal, C.; Andreelli, F. Increasing GLP-1 Circulating Levels by Bariatric Surgery or by GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Therapy: Why Are the Clinical Consequences so Different? J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 5908656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, E.P.; Polanco, G.; Yaqub, A.; Salehi, M. Altered glucose metabolism after bariatric surgery: What’s GLP-1 got to do with it? Metabolism 2018, 83, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, S.; Pucci, A.; Batterham, R.L. GLP-1: A Mediator of the Beneficial Metabolic Effects of Bariatric Surgery? Physiology 2015, 30, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Arciniegas, A.; Falckenheiner-Soria, J.; Reyes, J.B.-D.L.; Camacho-Ramírez, A.; Mayo-Ossorio, M.D.L.A.; Pacheco-García, J.M.; Pérez-Arana, G.M.; Prada-Oliveira, J.A. The main participation of the enterohormone GLP-1 after bariatric surgery. Minerva Chir. 2019, 74, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretault, M.; Laroche, S.; Lacorte, J.-M.; Barsamian, C.; Polak, M.; Raffin-Sanson, M.-L.; Touraine, P.; Bouillot, J.-L.; Czernichow, S.; Carette, C. Postprandial GLP-1 Secretion after Bariatric Surgery in Three Cases of Severe Obesity Related to Craniopharyngiomas. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharakan, G.; Behary, P.; Albrechtsen, N.W.; Chahal, H.; Kenkre, J.; Miras, A.; Ahmed, A.R.; Holst, J.J.; Bloom, S.R.; Tan, T. Roles of increased glycaemic variability, GLP-1 and glucagon in hypoglycaemia after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Hull, D.; Guo, K.; Barton, D.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Gathercole, L.; Nasiri, M.; Yu, J.; Gough, S.C.; Newsome, P.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 decreases lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bozadjieva, N.; Heppner, K.M.; Seeley, R.J. Targeting FXR and FGF19 to Treat Metabolic Diseases—Lessons Learned from Bariatric Surgery. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, L.-A.L.S.; Smith, G.; Mittendorfer, B.; Eagon, J.C.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery Has Unique Effects on Postprandial FGF21 but Not FGF19 Secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 3858–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez de la Escalera, L.; Kyrou, I.; Vrbikova, J.; Hainer, V.; Sramkova, P.; Fried, M.; Piya, M.K.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, G.; McTernan, P.G. Impact of gut hormone FGF-19 on type-2 diabetes and mitochondrial recovery in a prospective study of obese diabetic women undergoing bariatric surgery. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Gallego-Escuredo, J.M.; Catalan, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Domingo, P.; Moncada, R.; Valentí, V.; Salvador, J.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F.; et al. FGF19 and FGF21 serum concentrations in human obesity and type 2 diabetes behave differently after diet- or surgically-induced weight loss. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paoli, A.M.; Zhou, M.; Kaplan, D.D.; Hunt, S.C.; Adams, T.D.; Learned, R.M.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. FGF19 Analog as a Surgical Factor Mimetic That Contributes to Metabolic Effects beyond Glucose Homeostasis. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandhu, D.S.; Baichoo, E.; Roberts, L.R. Fibroblast growth factor signaling in liver carcinogenesis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, S. Keratinocyte Growth Factor: A Unique Player in Epithelial Repair Processes. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1998, 9, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, R.; Lu, J.; Dokpuang, D.; Booth, M.; Plank, L.D.; Murphy, R. Increased Bile Acids and FGF19 after Sleeve Gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Correlate with Improvement in Type 2 Diabetes in a Randomized Trial. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2672–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, N. Hormone-like (endocrine) Fgfs: Their evolutionary history and roles in development, metabolism, and disease. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 2010, 342, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, F.M.; Estall, J.; Adams, A.C.; Antonellis, P.J.; Bina, H.A.; Flier, J.S.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Maratos-Flier, E. Integrated Regulation of Hepatic Metabolism by Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) in Vivo. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2996–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Nakatake, Y.; Konishi, M.; Itoh, N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gene Struct. Expr. 2000, 1492, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Barroso, E.; Palomer, X.; Dai, J.; Rada, P.; Quesada-López, T.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Cedó, L.; Zali, M.R.; Molaei, M.; et al. Hepatic regulation of VLDL receptor by PPARbeta/delta and FGF21 modulates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Metab. 2018, 8, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crujeiras, A.B.; Gomez-Arbelaez, D.; Zulet, M.; Carreira, M.C.; Sajoux, I.; de Luis, D.; Castro, A.; Baltar, J.; Baamonde, I.; Sueiro, A.; et al. Plasma FGF21 levels in obese patients undergoing energy-restricted diets or bariatric surgery: A marker of metabolic stress? Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.; Khan, F.H.; Kohli, R. Impact of Fibroblast Growth Factors 19 and 21 in Bariatric Metabolism. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batterham, R.L.; Cowley, M.A.; Small, C.J.; Herzog, H.; Cohen, M.A.; Dakin, C.L.; Wren, A.M.; Brynes, A.E.; Low, M.J.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Gut hormone PYY3-36 physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature 2002, 418, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.; Cohen, M.A.; Ellis, S.M.; Le Roux, C.; Withers, D.; Frost, G.S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Inhibition of Food Intake in Obese Subjects by Peptide YY3–36. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandarana, K.; Gelegen, C.; Karra, E.; Choudhury, A.I.; Drew, M.E.; Fauveau, V.; Viollet, B.; Andreelli, F.; Withers, D.J.; Batterham, R.L. Diet and gastrointestinal bypass-induced weight loss: The roles of ghrelin and peptide YY. Diabetes 2011, 60, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magouliotis, D.E.; Tasiopoulou, V.S.; Sioka, E.; Chatedaki, C.; Zacharoulis, D. Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Metabolic and Gut Microbiota Profile: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullman, E.L.; Kelly, K.R.; Haus, J.; Fealy, C.E.; Scelsi, A.R.; Pagadala, M.R.; Flask, C.A.; McCullough, A.J.; Kirwan, J.P. Short-term aerobic exercise training improves gut peptide regulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 120, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guida, C.; Stephen, S.; Guitton, R.; Ramracheya, R.D. The Role of PYY in Pancreatic Islet Physiology and Surgical Control of Diabetes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, C.; Stephen, S.; Watson, M.; Dempster, N.; Larraufie, P.; Marjot, T.; Cargill, T.; Rickers, L.; Pavlides, M.; Tomlinson, J.; et al. PYY plays a key role in the resolution of diabetes following bariatric surgery in humans. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Gao, Z.; Williams, D.B.; Wang, C.; Lee, S.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, P. Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy on fasting gastrointestinal and pancreatic peptide hormones: A prospective nonrandomized trial. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2018, 14, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, M.; Baldi, S.; Mari, A.; Colligiani, D.; Guarino, D.; Camastra, S.; Barsotti, E.; Berta, R.; Moriconi, D.; Bellini, R.; et al. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy: Mechanisms of Diabetes Remission and Role of Gut Hormones. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4391–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boursier, J.; Diehl, A.M. Implication of Gut Microbiota in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota determines development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut 2013, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graessler, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, J.; Licinio, J.; Wong, M.L.; Xu, A.; Chavakis, T.; Bornstein, A.B.; Ehrhart-Bornstein, M.; et al. Metagenomic sequencing of the human gut microbiome before and after bariatric surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: Correlation with inflammatory and metabolic parameters. Pharm. J. 2013, 13, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.-P.; Liu, C.-Q.; Qi, L.; Sheng, Y.; Zou, D.-J. Modulation of the gut microbiome: A systematic review of the effect of bariatric surgery. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damms-Machado, A.; Mitra, S.; Schollenberger, A.E.; Kramer, K.M.; Meile, T.; Königsrainer, A.; Huson, D.H.; Bischoff, S.C. Effects of Surgical and Dietary Weight Loss Therapy for Obesity on Gut Microbiota Composition and Nutrient Absorption. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 806248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleja, A.; Kashani, A.; Allin, K.H.; Nielsen, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Brach, T.; Liang, S.; Feng, Q.; Jørgensen, N.B.; et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery of morbidly obese patients induces swift and persistent changes of the individual gut microbiota. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanmiguel, C.P.; Jacobs, J.; Gupta, A.; Ju, T.; Stains, J.; Coveleskie, K.; Lagishetty, V.; Balioukova, A.; Chen, Y.; Dutson, E.; et al. Surgically Induced Changes in Gut Microbiome and Hedonic Eating As Related to Weight Loss: Preliminary Findings in Obese Women Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Tolone, S.; Gravina, A.G.; Patrone, V.; Romano, M.; Tuccillo, C.; Mozzillo, A.L.; Amoroso, V.; Misso, G.; et al. Gastrointestinal Hormones, Intestinal Microbiota and Metabolic Homeostasis in Obese Patients: Effect of Bariatric Surgery. in vivo 2016, 30, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Tremaroli, V.; Karlsson, F.; Werling, M.; Ståhlman, M.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Olbers, T.; Fändriks, L.; Le Roux, C.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Vertical Banded Gastroplasty Induce Long-Term Changes on the Human Gut Microbiome Contributing to Fat Mass Regulation. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaska, L.; Sledzinski, T.; Chomiczewska, A.; Dettlaff-Pokora, A.; Swierczynski, J. Improved glucose metabolism following bariatric surgery is associated with increased circulating bile acid concentrations and remodeling of the gut microbiome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8698–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anhê, F.F.; Varin, T.V.; Schertzer, J.D.; Marette, A. The Gut Microbiota as a Mediator of Metabolic Benefits after Bariatric Surgery. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnouti, Y. Bile Acid Sulfation: A Pathway of Bile Acid Elimination and Detoxification. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Karpen, S.J.; Dawson, P.A.; Arrese, M.; Trauner, M. Bile acids and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. Hepatology 2017, 65, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, M.D.; Lee, Y.-H.; Guo, G.L. The role of bile acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 56, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albaugh, V.; Banan, B.; Antoun, J.; Xiong, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ping, J.; Alikhan, M.; Clements, B.A.; Abumrad, N.N.; Flynn, C.R. Role of Bile Acids and GLP-1 in Mediating the Metabolic Improvements of Bariatric Surgery. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1041–1051.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, M.; Faria, G.; Preto, J.; Costa-Maia, J. Gallstones and Bariatric Surgery: To Treat or Not to Treat? World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 2904–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östlund, M.P.; Wenger, U.; Mattsson, F.; Ebrahim, F.; Botha, A.; Lagergren, J. Population-based study of the need for cholecystectomy after obesity surgery. BJS 2012, 99, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, E.; Marsk, R.; Rasmussen, F.; Freedman, J. Incidence of postoperative gallstone disease after antiobesity surgery: Population-based study from Sweden. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2010, 6, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, U.; Benthin, L.; Granström, L.; Groen, A.K.; Sahlin, S.; Einarsson, C. Changes in gallbladder bile composition and crystal detection time in morbidly obese subjects after bariatric surgery. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melmer, A.; Sturm, W.; Kuhnert, B.; Engl-Prosch, J.; Ress, C.; Tschoner, A.; Laimer, M.; Laimer, E.; Biebl, M.; Pratschke, J.; et al. Incidence of Gallstone Formation and Cholecystectomy 10 Years after Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-H.; Tsai, M.-S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-M.; Cheng, C.-F.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Yin, W.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Bariatric Surgery Did Not Increase the Risk of Gallstone Disease in Obese Patients: A Comprehensive Cohort Study. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakhtoura, M.T.; Nakhoul, N.N.; Shawwa, K.; Mantzoros, C.; Fuleihan, G.A.E.H. Hypovitaminosis D in bariatric surgery: A systematic review of observational studies. Metabolism 2016, 65, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakhtoura, M.; Rahme, M.; Fuleihan, G.E.-H. Vitamin D Metabolism in Bariatric Surgery. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 947–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzorno, L. Bariatric Surgery: Bad to the Bone, Part 2. Integr. Med. 2016, 15, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Petereit, R.; Jonaitis, L.; Kupčinskas, L.; Maleckas, A. Gastrointestinal symptoms and eating behavior among morbidly obese patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Medicina 2014, 50, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, S.; Kelly, S.B.; Seymour, K.; Woodcock, S.; Werner, A.-D.; Mathers, J.C. The Effects of Bariatric Procedures on Bowel Habit. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2348–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sileri, P.; Franceschilli, L.; Cadeddu, F.; De Luca, E.; D’Ugo, S.; Tognoni, V.; Camperchioli, I.; Benavoli, D.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Gaspari, A.L.; et al. Prevalence of Defaecatory Disorders in Morbidly Obese Patients before and after Bariatric Surgery. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2012, 16, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RobersonJon, E.N.; Gould, J.C.; Wald, A. Urinary and Fecal Incontinence after Bariatric Surgery. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nett, P.C.; Borbély, Y.M.; Kröll, D. Micronutrient Supplementation after Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch in the Long Term. Obes Surg 2016, 26, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borbély, Y.; Osterwalder, A.; Kröll, D.; Nett, P.C.; Inglin, R. Diarrhea after bariatric procedures: Diagnosis and therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4689–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesquiere, I.; Lannoo, M.; Augustijns, P.; Matthys, C.; Van der Schueren, B.; Foulon, V. Iron Deficiency after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: Insufficient Iron Absorption from Oral Iron Supplements. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steenackers, N.; Van der Schueren, B.; Mertens, A.; Lannoo, M.; Grauwet, T.; Augustijns, P.; Matthys, C. Iron deficiency after bariatric surgery: What is the real problem? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brolin, R. Malabsorptive Gastric Bypass in Patients with Superobesity. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2002, 6, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanbhai, M.; Dubb, S.; Patel, K.; Ahmed, A.; Richards, T. The prevalence of iron deficiency anaemia in patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, L.; Schiavo, L.; Sebastianelli, L.; Fabre, R.; Pradier, C.; Iannelli, A. Anemia and Bariatric Surgery: Results of a National French Survey on Administrative Data of 306,298 Consecutive Patients between 2008 and 2016. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| JIB | RYGB | VBG | AGB | BPD&DS | SG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | 1953 | 1977 | 1982 | 1986 | 1998 | 2005 |
| Gastric Body | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Bypass | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Biliopancreatic diversion | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Bowel anastomosis | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Weight loss(36M) | - | 90 Lbs/41 kg | 71 Lbs/32 kg | - | 117 Lbs/53 kg | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Y.; Lee, H.; Kaura, S.; Yip, J.; Sun, H.; Guan, L.; Han, W.; Ding, Y. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Metabolic Diseases and Underlying Mechanisms. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111582
Ji Y, Lee H, Kaura S, Yip J, Sun H, Guan L, Han W, Ding Y. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Metabolic Diseases and Underlying Mechanisms. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(11):1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111582
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Yu, Hangil Lee, Shawn Kaura, James Yip, Hao Sun, Longfei Guan, Wei Han, and Yuchuan Ding. 2021. "Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Metabolic Diseases and Underlying Mechanisms" Biomolecules 11, no. 11: 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111582
APA StyleJi, Y., Lee, H., Kaura, S., Yip, J., Sun, H., Guan, L., Han, W., & Ding, Y. (2021). Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Metabolic Diseases and Underlying Mechanisms. Biomolecules, 11(11), 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111582








