Confocal Endomicroscopy of Neuromuscular Junctions Stained with Physiologically Inert Protein Fragments of Tetanus Toxin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics, Animals and Tissues
2.2. Human Tissue: Ethics and Sampling
2.3. GFP-TetC Constructs
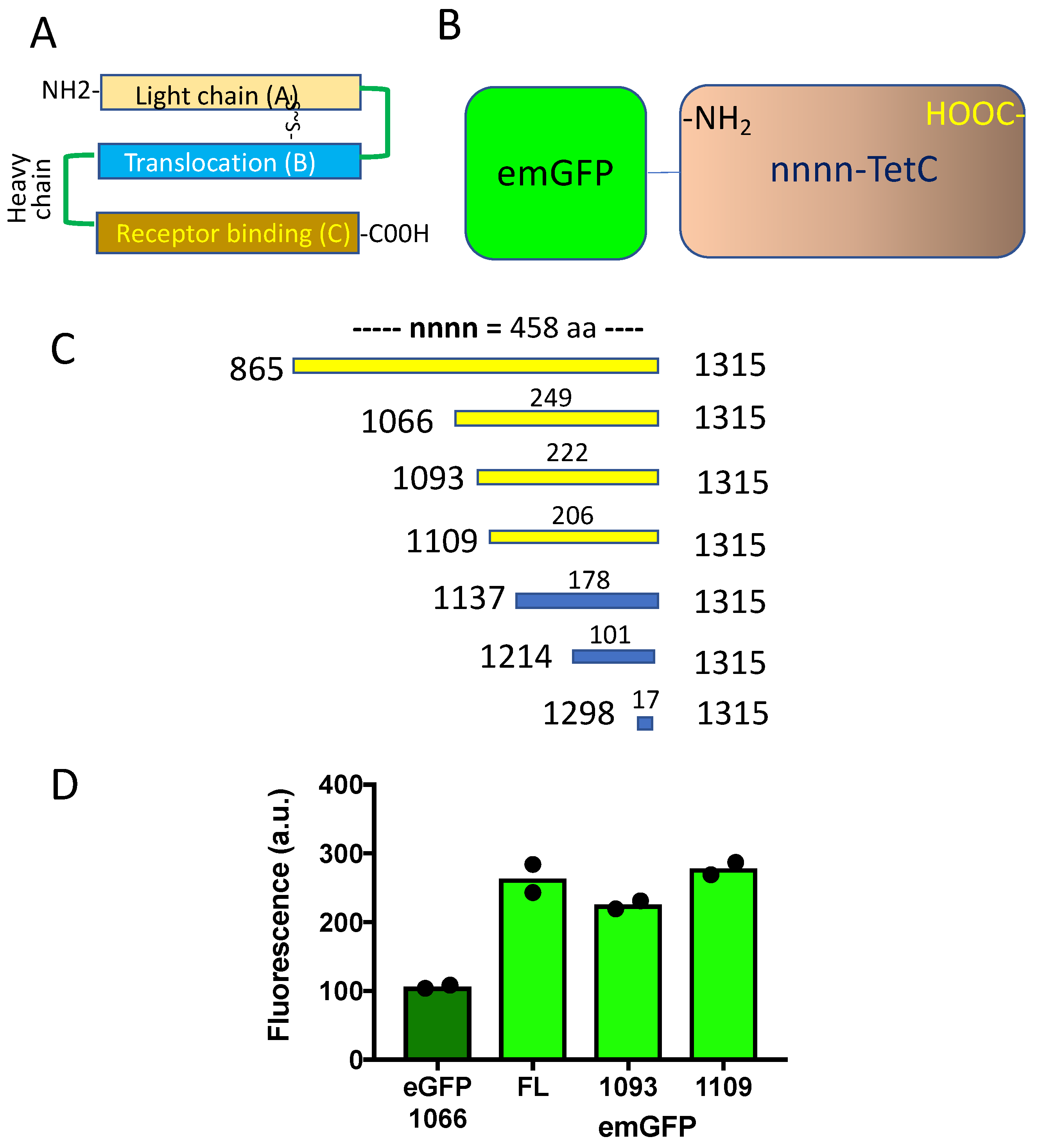
2.4. Truncated TetC Constructs
2.5. DNA Extraction from Bacteria
2.6. Bacterial Expression and Protein Purification
2.7. Fluorescence Measurements of TetC Conjugates
2.8. Alexa488 Labeling of TetC Constructs
2.9. TetC Staining and LSCM Imaging
2.10. Tension Measurements and Electrophysiology
2.11. Confocal Endomicroscopic (CEM) Imaging
2.12. Statistics and Graphics
3. Results
3.1. GFP-TetC Constructs Selectively Stain Motor Nerve Terminals
3.2. Truncated emGFP-TetC Constructs Also Stain Nerve Terminals
3.3. emGFP-TetC Constructs Stain Neonatal Motor Nerve Terminals
3.4. emGFP-TetC Constructs Also Stained Other Cell Types
3.5. emGFP-TetC Constructs Do Not Impair Neuromuscular Transmission or Function
3.6. CEM Visualises Adult Nerve Terminals Stained with emGFP-TetC Constructs
3.7. Dual-Waveband CEM Resolves NMJ Pathology in Real Time
4. Discussion
4.1. Binding of GFP-TetC Derivatives
4.2. Limitations of CEM and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krarup, C. Lower motor neuron involvement examined by quantitative electromyography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, C.R.; Fawcett, P.R.W.; Walls, T.J.; Lyons, P.R.; Bailey, S.; Beeson, D.; Young, C.; Gardner-Medwin, D. Pre- and post-synaptic abnormalities associated with impaired neuromuscular transmission in a group of patients with ‘limb-girdle myasthenia’. Brain 2006, 129, 2061–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, A.G. Genetic basis and phenotypic features of congenital myasthenic syndromes. Frontal Lobes 2018, 148, 565–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, N.G.; Huynh, W.; Vucic, S.; Talbot, K.; Kiernan, M.C. Motor neuron disease: Current management and future prospects. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Chalabi, A.; Hardiman, O.; Kiernan, M.C.; Chiò, A.; Rix-Brooks, B.; Berg, L.H.V.D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Moving towards a new classification system. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, T.M.; Alix, J.J.P.; Fingret, J.; Esmail, T.; Hoggard, N.; Baster, K.; McDermott, C.; Wilkinson, I.D.; Shaw, P. Longitudinal multi-modal muscle-based biomarker assessment in motor neuron disease. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, L.; Olivari, D.; Nardo, G.; Trolese, M.C.; Bendotti, C.; Piccirillo, R.; Bonetto, V. Micro-computed tomography for non-invasive evaluation of muscle atrophy in mouse models of disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.G.; Porcari, P.; Braz, L.; Williams, T.L.; Schofield, I.S.; Blamire, A.M. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of human motor unit fasciculation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkbeck, M.G.; Heskamp, L.; Schofield, I.S.; Blamire, A.M.; Whittaker, R.G. Non-invasive imaging of single human motor units. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, L.R.; Culver, D.G.; Tennant, P.; Davis, A.A.; Wang, M.; Castellano-Sanchez, A.; Khan, J.; Polak, M.A.; Glass, J.D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a distal axonopathy: Evidence in mice and man. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 185, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, A.M.; Sanes, J.R.; Lichtman, J.W. A compensatory subpopulation of motor neurons in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 490, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillingwater, T.H.; Thomson, D.; Mack, T.G.A.; Soffin, E.M.; Mattison, R.J.; Coleman, M.P.; Ribchester, R.R. Age-Dependent Synapse Withdrawal at Axotomised Neuromuscular Junctions in Wld s Mutant and Ube4b/Nmnat Transgenic Mice. J. Physiol. 2002, 543, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribchester, R.R.; Thomson, D.; Wood, N.I.; Hinks, T.; Gillingwater, T.; Wishart, T.; Court, F.; Morton, A.J. Progressive abnormalities in skeletal muscle and neuromuscular junctions of transgenic mice expressing the Huntington’s disease mutation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 3092–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Court, F.A.; Brophy, P.J.; Ribchester, R.R. Remodeling of motor nerve terminals in demyelinating axons of periaxin-null mice. Glia 2008, 56, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, F.E.; Romero, R.; Williams, D.; Gillingwater, T.; Hilton, H.; Dick, J.; Riddoch-Contreras, J.; Wong, F.; Ireson, L.; Powles-Glover, N.; et al. Upregulation of PKD1L2 provokes a complex neuromuscular disease in the mouse. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 3553–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilley, J.; Ribchester, R.R.; Coleman, M.P. Sarm1 Deletion, but Not Wld S, Confers Lifelong Rescue in a Mouse Model of Severe Axonopathy. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megia-Fernandez, A.; Marshall, A.; Akram, A.R.; Mills, B.; Chankeshwara, S.V.; Scholefield, E.; Miele, A.; McGorum, B.C.; Michaels, C.; Knighton, N.; et al. Optical Detection of Distal Lung Enzyme Activity in Human Inflammatory Lung Disease. BME Front. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, X.; McCormick, D.T.; Wong, K.; Wong, S.T. Multimodal nonlinear endo-microscopy probe design for high resolution, label-free intraoperative imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 2283–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benias, P.C.; Wells, R.G.; Sackey-Aboagye, B.; Klavan, H.; Reidy, J.; Buonocore, D.; Miranda, M.; Kornacki, S.; Wayne, M.; Carr-Locke, D.L.; et al. Structure and Distribution of an Unrecognized Interstitium in Human Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4947–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.; Fan, L.; Wells, S.; Hartley, R.; MacKenzie, F.E.; Oyebode, O.; Brown, R.; Thomson, D.; Coleman, M.P.; Blanco, G.; et al. Axonal and neuromuscular synaptic phenotypes in WldS, SOD1G93A and ostes mutant mice identified by fiber-optic confocal microendoscopy. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2009, 42, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Dissanayake, K.N.; Skehel, P.A.; Ribchester, R.R. Endomicroscopy and electromyography of neuromuscular junctions in situ. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 867–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrassi, L.; Purves, D.; Lichtman, J.W. Fluorescent probes that stain living nerve terminals. J. Neurosci. 1987, 7, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balice-Gordon, R.J.; Lichtman, J.W. In vivo visualization of the growth of pre- and postsynaptic elements of neuromuscular junctions in the mouse. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Chang, L.-H.; Pires-Alves, M.; Thyagarajan, B.; Bloom, J.E.; Gu, Z.; Aberle, K.K.; Teymorian, S.A.; Bannai, Y.; Johnson, S.C.; et al. Recombinant botulinum neurotoxin A heavy chain-based delivery vehicles for neuronal cell targeting. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2010, 24, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, V.B.; Ovsepian, S.V.; Raghunath, A.; Huo, Q.; Lawrence, G.W.; Smith, L.; O Dolly, J.; O’Leary, V. Innocuous full-length botulinum neurotoxin targets and promotes the expression of lentiviral vectors in central and autonomic neurons. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, A.C.; Oliván, S.; Manzano, R.; Zaragoza, P.; Aguilera, J.; Osta, R. Fragment C of Tetanus Toxin: New Insights into Its Neuronal Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6883–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surana, S.; Tosolini, A.P.; Meyer, I.F.; Fellows, A.D.; Novoselov, S.; Schiavo, G. The travel diaries of tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2018, 147, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, S.; Colasante, C.; Saint Cloment, C.; Barbier, J.; Curie, T.; Girard, E.; Molgó, J.; Brûlet, P. Internalization of a GFP-tetanus toxin C-terminal fragment fusion protein at mature mouse neuromuscular junctions. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 30, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnert, S.; Schiavo, G. Tetanus Toxin Is Transported in a Novel Neuronal Compartment Characterized by a Specialized pH Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42336–42344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, J.; Loftus, A. Characterization of the receptor-binding domain of tetanus toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11188–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubitt, A.B.; Woollenweber, L.A.; Heim, R. Chapter 2: Understanding Structure—Function Relationships in the Aequorea victoria Green Fluorescent Protein. Methods Cell Biol. 1998, 58, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helting, T.B.; Zwisler, O.; Wiegandt, H. Structure of tetanus toxin. II. Toxin binding to ganglioside. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helting, T.B.; Zwisler, O. Structure of tetanus toxin. I. Breakdown of the toxin molecule and discrimination between polypeptide fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercsenyi, K.; Schmieg, N.; Bryson, J.B.; Wallace, M.; Caccin, P.; Golding, M.; Zanotti, G.; Greensmith, L.; Nischt, R.; Schiavo, G. Nidogens are therapeutic targets for the prevention of tetanus. Science 2014, 346, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.A.; Harrison, C.; Eaton, S.L.; Hurtado, M.L.; Graham, L.C.; Alkhammash, L.; Oladiran, O.A.; Gale, A.; Lamont, D.J.; Simpson, H.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Anatomy of the Human Neuromuscular Junction. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 2348–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, J.; Chow-Worn, O.; Spaven, L.; Silman, N.J.; Hallis, B.; Shone, C.C. Tyrosine-1290 of tetanus neurotoxin plays a key role in its binding to gangliosides and functional binding to neurones. FEBS Lett. 2001, 493, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Fotinou, C.; Black, I.; Fairweather, N.F.; Charles, I.G.; Watts, C.; Hewitt, E.; Isaacs, N.W. The structures of the H(C) fragment of tetanus toxin with carbohydrate subunit complexes provide insight into ganglioside binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8889–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekoff, A.; Betz, W.J. Physiological properties of dissociated muscle fibres obtained from innervated and denervated adult rat muscle. J. Physiol. 1977, 271, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.; Hynes-Allen, A.; Swan, A.; Dissanayake, K.; Gillingwater, T.; Ribchester, R. Activity-dependent degeneration of axotomized neuromuscular synapses in WldS mice. Neuroscience 2015, 290, 300–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.C.; Jansen, J.K.; Van Essen, D. Polyneuronal innervation of skeletal muscle in new-born rats and its elimination during maturation. J. Physiol. 1976, 261, 387–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribchester, R.R.; Teriakidis, A. Neuromuscular Junction: Synapse Elimination. Ref. Modul. Neurosci. Biobehav. Psychol. 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, C.R. Postnatal maturation of nerve-muscle junctions in hindlimb muscles of the mouse. Dev. Biol. 1982, 94, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mense, S. Functional Anatomy of Muscle: Muscle, Nociceptors and Afferent Fibers. In Muscle Pain: Understanding the Mechanisms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 17–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolf, R.; Khan, M.M.; Witzemann, V. Motor Endplate—Anatomical, Functional, and Molecular Concepts in the Historical Perspective. Cells 2019, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, A.; Kaske, A.; Mense, S. Inflammation-induced increase in the density of neuropeptide-immunoreactive nerve endings in rat skeletal muscle. Exp. Brain Res. 1998, 121, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Court, F.A.; Gillingwater, T.; Melrose, S.; Sherman, D.L.; Greenshields, K.N.; Morton, A.J.; Harris, J.B.; Willison, H.J.; Ribchester, R.R. Identity, developmental restriction and reactivity of extralaminar cells capping mammalian neuromuscular junctions. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3901–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, C.R.; Lyons, P.R.; Walls, T.J.; Fawcett, P.R.; Young, C. Structure and function of neuromuscular junctions in the vastus lateralis of man. A motor point biopsy study of two groups of patients. Brain 1992, 115, 451–478. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, C.R. The Structure of Human Neuromuscular Junctions: Some Unanswered Molecular Questions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, T.G.A.; Reiner, M.; Beirowski, B.; Mi, W.; Emanuelli, M.; Wagner, D.; Thomson, D.; Gillingwater, T.; Court, F.; Conforti, L.; et al. Wallerian degeneration of injured axons and synapses is delayed by a Ube4b/Nmnat chimeric gene. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyebode, O.; Hartley, R.; Singhota, J.; Thomson, D.; Ribchester, R. Differential protection of neuromuscular sensory and motor axons and their endings in WldS mutant mice. Neuroscience 2012, 200, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldink, J.; Bär, P.; Joosten, E.; Otten, M.; Wokke, J.; Berg, L.V.D. Sexual differences in onset of disease and response to exercise in a transgenic model of ALS. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2003, 13, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, R.J.; Bennett, E.J.; Kennerley, A.J.; Sharp, P.; Sunyach, C.; Kasher, P.; Berwick, J.; Pettmann, B.; Battaglia, G.; Azzouz, M.; et al. Optimised and Rapid Pre-clinical Screening in the SOD1G93A Transgenic Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, E.; Martineau, É.; Robitaille, R. Opposite Synaptic Alterations at the Neuromuscular Junction in an ALS Mouse Model: When Motor Units Matter. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 8901–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, É.; Di Polo, A.; Velde, C.V.; Robitaille, R. Dynamic neuromuscular remodeling precedes motor-unit loss in a mouse model of ALS. eLife 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.B.; Ribchester, R.R. Neuromuscular transmission is adequate in identified abnormal dystrophic muscle fibres. Nat. Cell Biol. 1978, 271, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.B.; Ribchester, R.R. The relationship between end-plate size and transmitter release in normal and dystrophic muscles of the mouse. J. Physiol. 1979, 296, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribchester, R.R.; Mao, F.; Betz, W.J. Optical measurements of activity-dependent membrane recycling in motor nerve terminals of mammalian skeletal muscle. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 1994, 255, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, E.M.; Barry, J.A.; Ribchester, R.R. Co-regulation of synaptic efficacy at stable polyneuronally innervated neuromuscular junctions in reinnervated rat muscle. J. Physiol. 1999, 521, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, J.; Ribchester, R.R. Persistent polyneuronal innervation in partially denervated rat muscle after reinnervation and recovery from prolonged nerve conduction block. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6327–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Costanzo, E.M.; Barry, J.A.; Ribchester, R.R. Competition at silent synapses in reinnervated skeletal muscle. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribchester, R.R.; Tsao, J.W.; Barry, J.A.; Asgari-Jirhandeh, N.; Perry, V.H.; Brown, M.C. Persistence of Neuromuscular Junctions after Axotomy in Mice with Slow Wallerian Degeneration (C57BL/Wlds). Eur. J. Neurosci. 1995, 7, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, W.J.; Mao, F.; Bewick, G.S. Activity-dependent fluorescent staining and destaining of living vertebrate motor nerve terminals. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, W.J.; Bewick, G. Optical monitoring of transmitter release and synaptic vesicle recycling at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 1993, 460, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fu, Z.; Kim, J.-J.P.; Barbieri, J.T.; Baldwin, M.R. Gangliosides as High Affinity Receptors for Tetanus Neurotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26569–26577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, S.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Kumaran, D.; Swaminathan, S. Common binding site for disialyllactose and tri-peptide in C-fragment of tetanus neurotoxin. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 61, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, R.E.; Specht, C.; Collins, B.E.; Woods, A.S.; Cotter, R.J.; Schnaar, R. Identification of a Ganglioside Recognition Domain of Tetanus Toxin Using a Novel Ganglioside Photoaffinity Ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30380–30386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffield, M.A.; Rizzoli, S.O.; Betz, W.J. Mobility of Synaptic Vesicles in Different Pools in Resting and Stimulated Frog Motor Nerve Terminals. Neuron 2006, 51, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.; Reich, C.D.; Dissanayake, K.N.; Kristmundsdottir, F.; Findlater, G.S.; Ribchester, R.R.; Simmen, M.W.; Gillingwater, T.H. NMJ-morph reveals principal components of synaptic morphology influencing structure–function relationships at the neuromuscular junction. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 160240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciriza, J.; Moreno-Igoa, M.; Calvo, A.; Yague, G.; Palacio, J.; Mena, F.J.M.; Muñoz, M.J.; Zaragoza, P.; Brûlet, P.; Osta, R. A genetic fusion GDNF-C fragment of tetanus toxin prolongs survival in a symptomatic mouse ALS model. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2008, 26, 459–465. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Igoa, M.; Calvo, A.C.; Ciriza, J.; Muñoz, M.J.; Zaragoza, P.; Osta, R. Non-viral gene delivery of the GDNF, either alone or fused to the C-fragment of tetanus toxin protein, prolongs survival in a mouse ALS model. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2012, 30, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toivonen, J.M.; Oliván, S.; Osta, R. Tetanus Toxin C-Fragment: The Courier and the Cure? Toxins 2010, 2, 2622–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.A.; Kim, E.; Duffy, A.; Adalbert, R.; Phillips, B.U.; Peters, O.M.; Stephenson, J.; Yang, S.; Massenzio, F.; Lin, Z.; et al. TDP-43 gains function due to perturbed autoregulation in a Tardbp knock-in mouse model of ALS-FTD. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roesl, C.; Evans, E.R.; Dissanayake, K.N.; Boczonadi, V.; Jones, R.A.; Jordan, G.R.; Ledahawsky, L.; Allen, G.C.C.; Scott, M.; Thomson, A.; et al. Confocal Endomicroscopy of Neuromuscular Junctions Stained with Physiologically Inert Protein Fragments of Tetanus Toxin. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101499
Roesl C, Evans ER, Dissanayake KN, Boczonadi V, Jones RA, Jordan GR, Ledahawsky L, Allen GCC, Scott M, Thomson A, et al. Confocal Endomicroscopy of Neuromuscular Junctions Stained with Physiologically Inert Protein Fragments of Tetanus Toxin. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(10):1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101499
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoesl, Cornelia, Elizabeth R. Evans, Kosala N. Dissanayake, Veronika Boczonadi, Ross A. Jones, Graeme R. Jordan, Leire Ledahawsky, Guy C. C. Allen, Molly Scott, Alanna Thomson, and et al. 2021. "Confocal Endomicroscopy of Neuromuscular Junctions Stained with Physiologically Inert Protein Fragments of Tetanus Toxin" Biomolecules 11, no. 10: 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101499
APA StyleRoesl, C., Evans, E. R., Dissanayake, K. N., Boczonadi, V., Jones, R. A., Jordan, G. R., Ledahawsky, L., Allen, G. C. C., Scott, M., Thomson, A., Wishart, T. M., Hughes, D. I., Mead, R. J., Shone, C. C., Slater, C. R., Gillingwater, T. H., Skehel, P. A., & Ribchester, R. R. (2021). Confocal Endomicroscopy of Neuromuscular Junctions Stained with Physiologically Inert Protein Fragments of Tetanus Toxin. Biomolecules, 11(10), 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101499






