Immune Regulation, but Not Antibacterial Activity, Is a Crucial Function of Hepcidins in Resistance against Pathogenic Bacteria in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linn.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
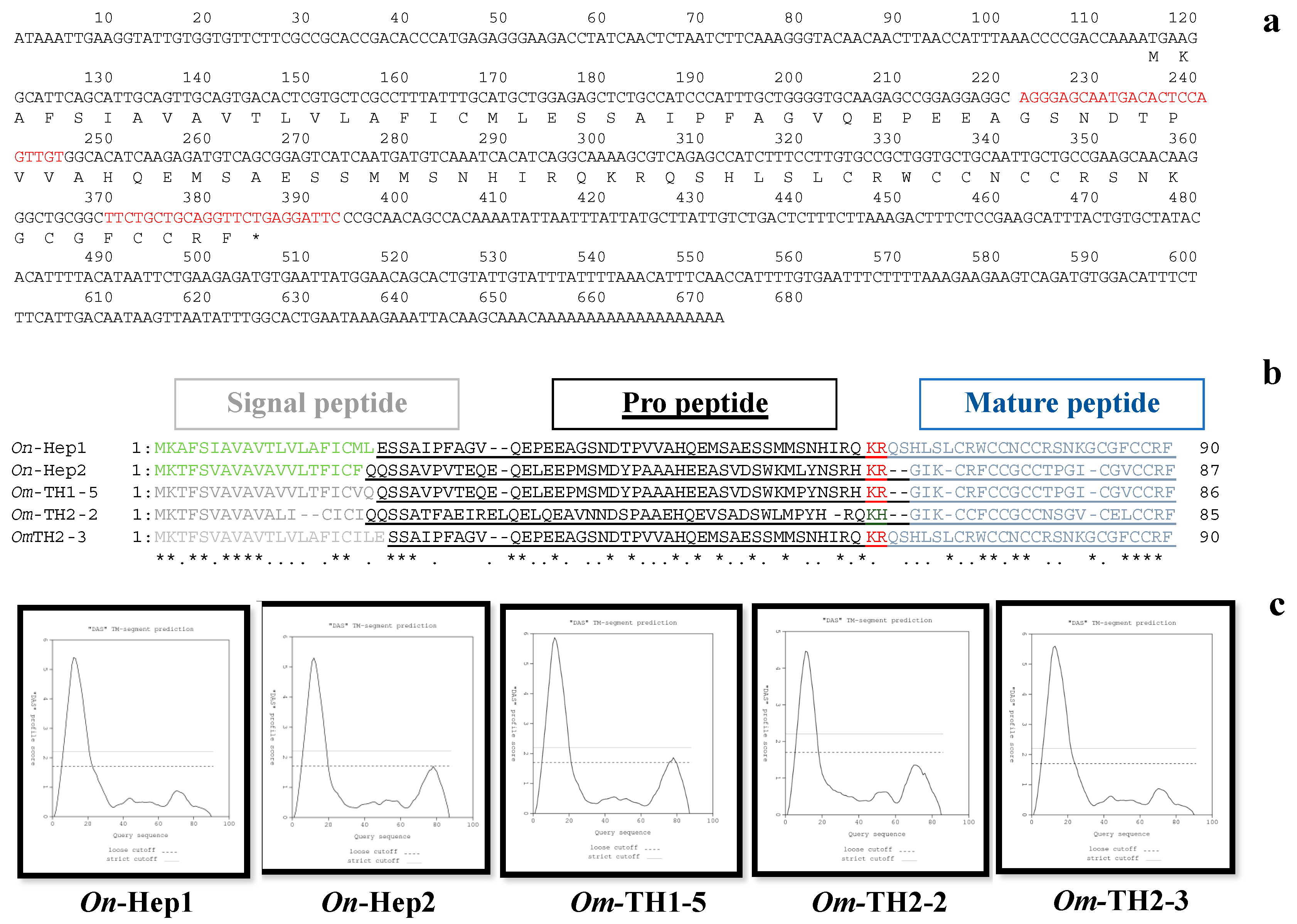
2.1. Characterization of the Full-Length cDNA Encoding On-Hep1
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of On-Hep1 and Various Hepcidin Genes of Other Vertebrates
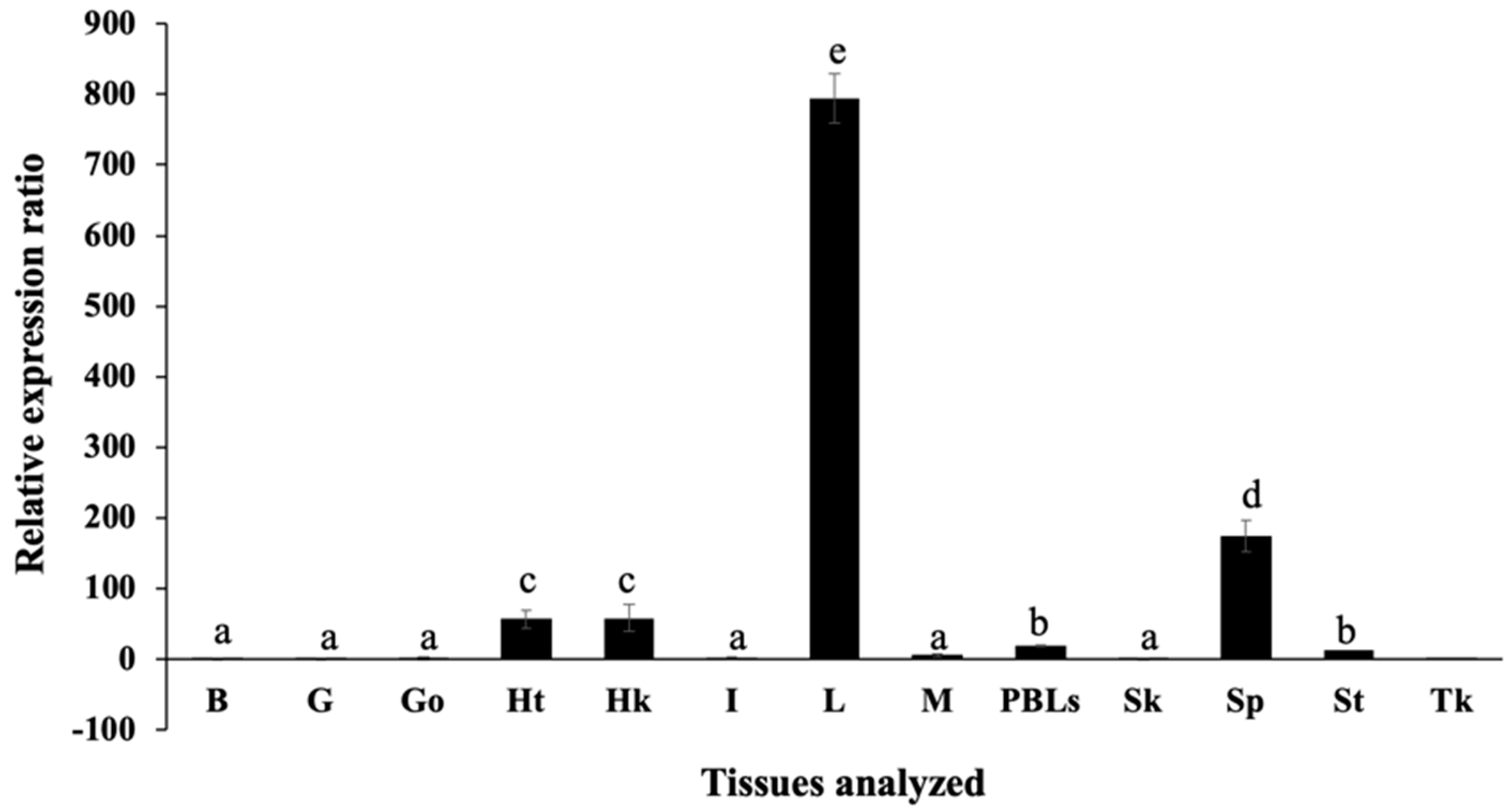
2.3. Expression Analysis of On-Hep1 Transcripts in Various Tissues of Normal Nile Tilapia Using Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.3.1. Experimental Animals
2.3.2. Total RNA Isolation and First-Strand cDNA Synthesis
2.3.3. qRT-PCR Analysis
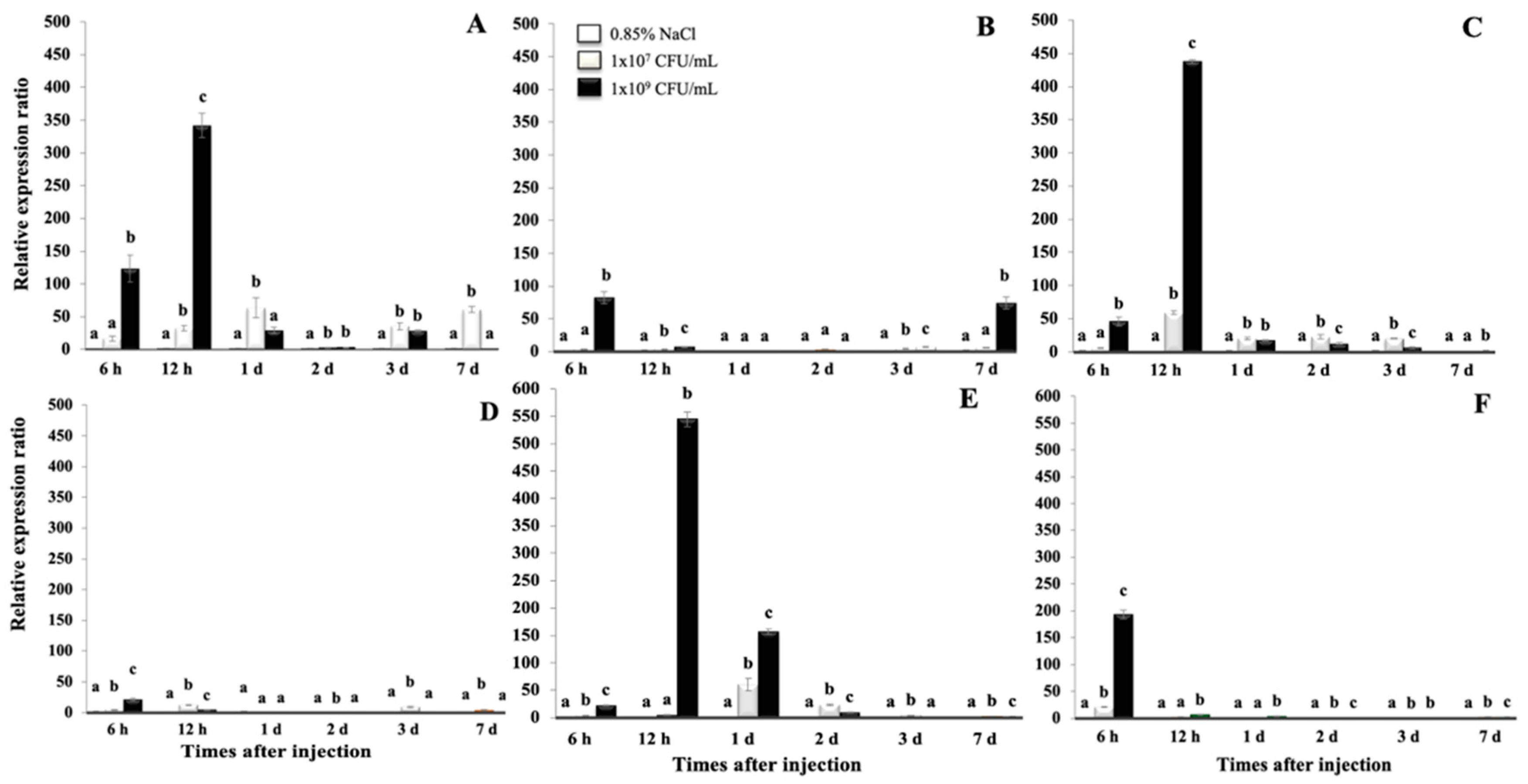
2.4. Transcriptional Response Analysis of On-Hep1 in Liver, Spleen and Head Kidney under Flavobacterium columnare and Streptococcus Agalactiae Infection
2.4.1. Bacterial Strains and Preparation
2.4.2. Experimental Animals and Design
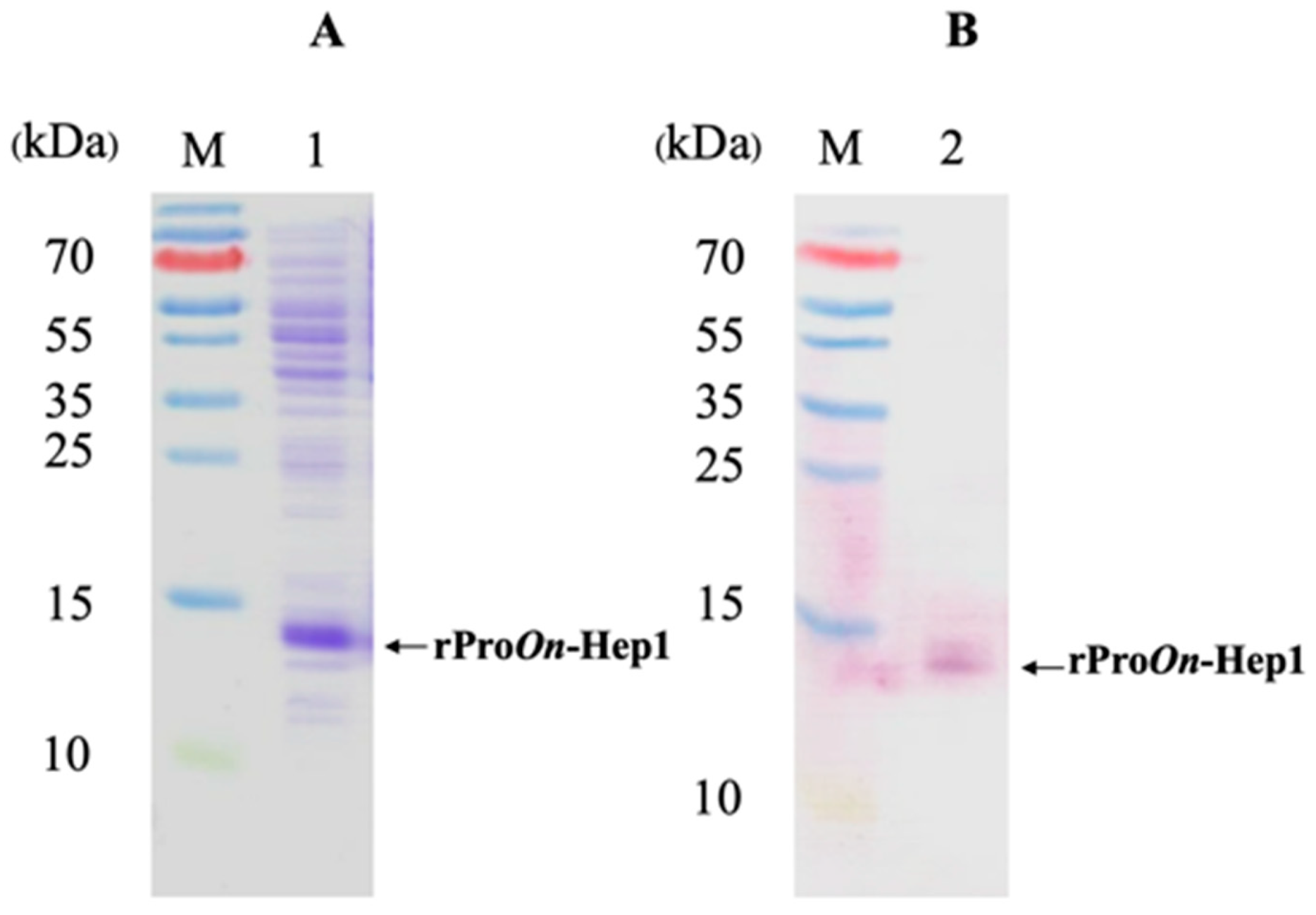
2.5. Overexpression, Production and Purification of Recombinant On-Hep1 Propeptide (rProOn-Hep1)
2.5.1. Construction of Recombinant rProOn-Hep1 DNA
2.5.2. Overexpression of rProOn-Hep1 Using a Bacterial System
2.5.3. rProOn-Hep1 Purification
2.5.4. Western Blot Analysis
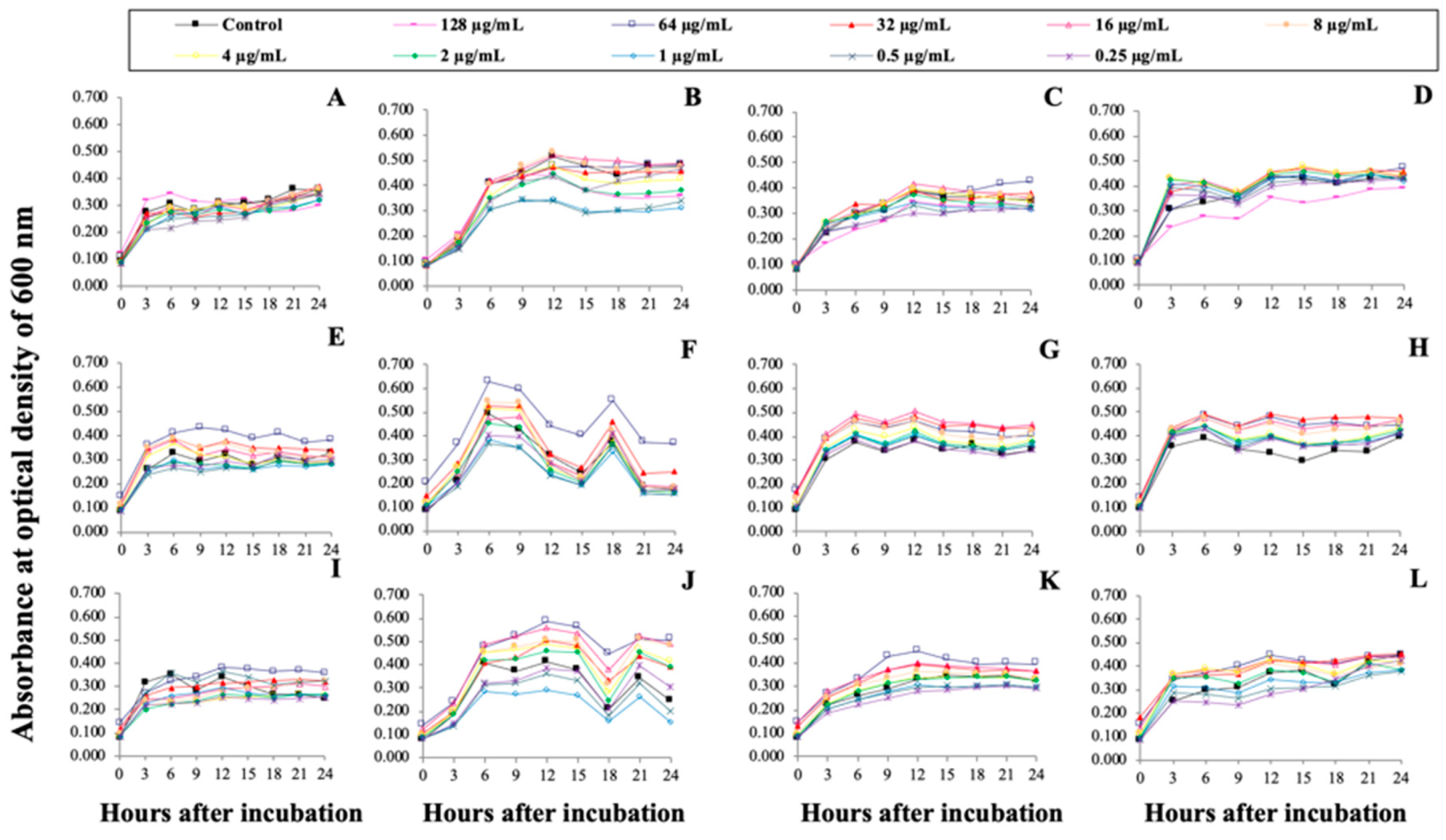
2.6. Antimicrobial Activities of rProOn-Hep1, sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 (In Vitro)
2.7. Effects of rProOn-Hep1, sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 on Phagocytosis of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) (In Vitro)
2.7.1. Experimental Animal and Isolation of PBMCs
2.7.2. Phagocytic Activity Analysis
2.8. Pathogenic Bacterial Binding Activity of sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 (In Vitro)
2.8.1. Preparation of Pathogenic Bacteria
2.8.2. Cell Binding Analysis
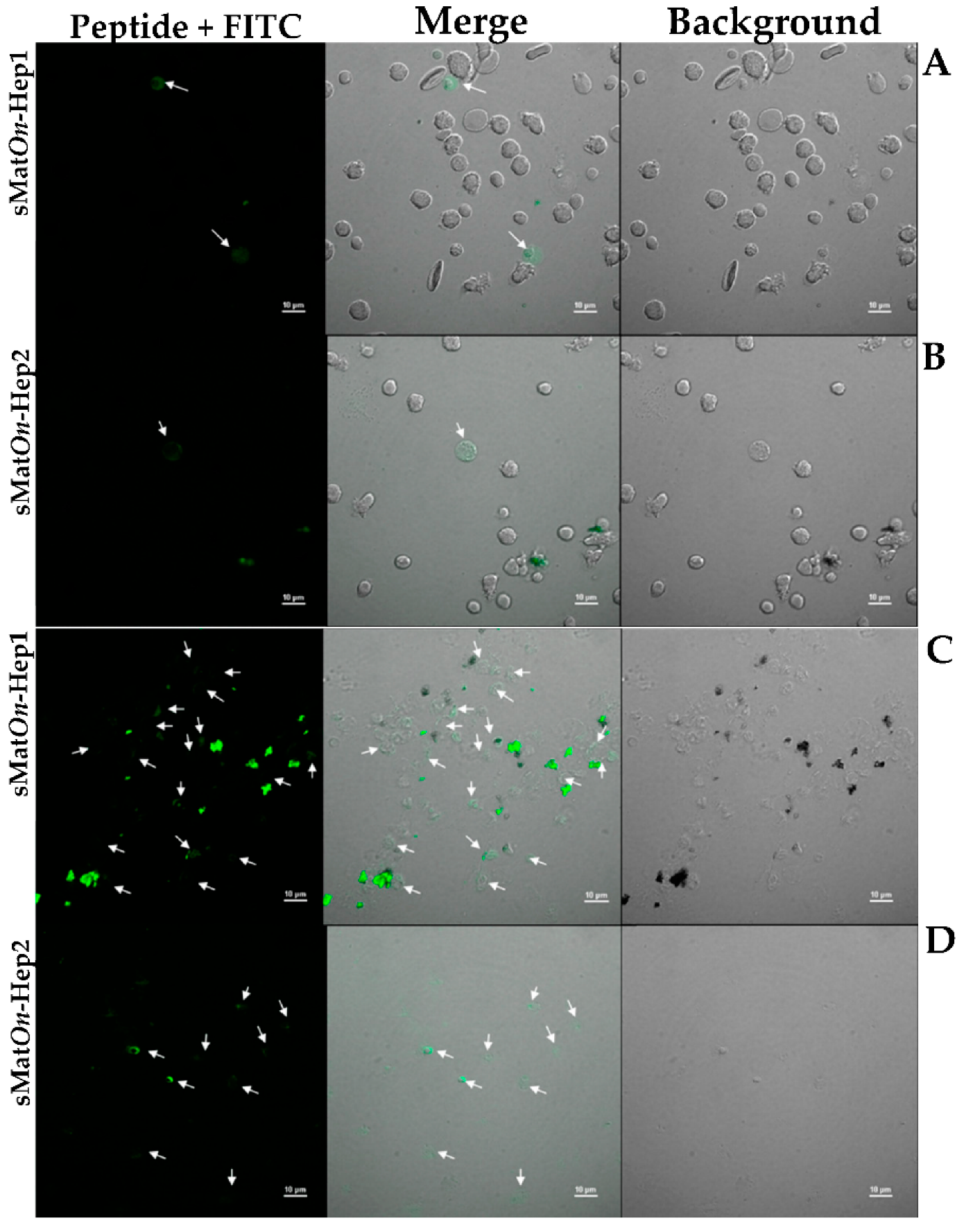
2.9. Localization of sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 on Leukocytes from PBMCs and Head Kidney of Nile Tilapia (In Vitro)
2.9.1. Preparation of Blood Leukocytes
2.9.2. Localization Assay
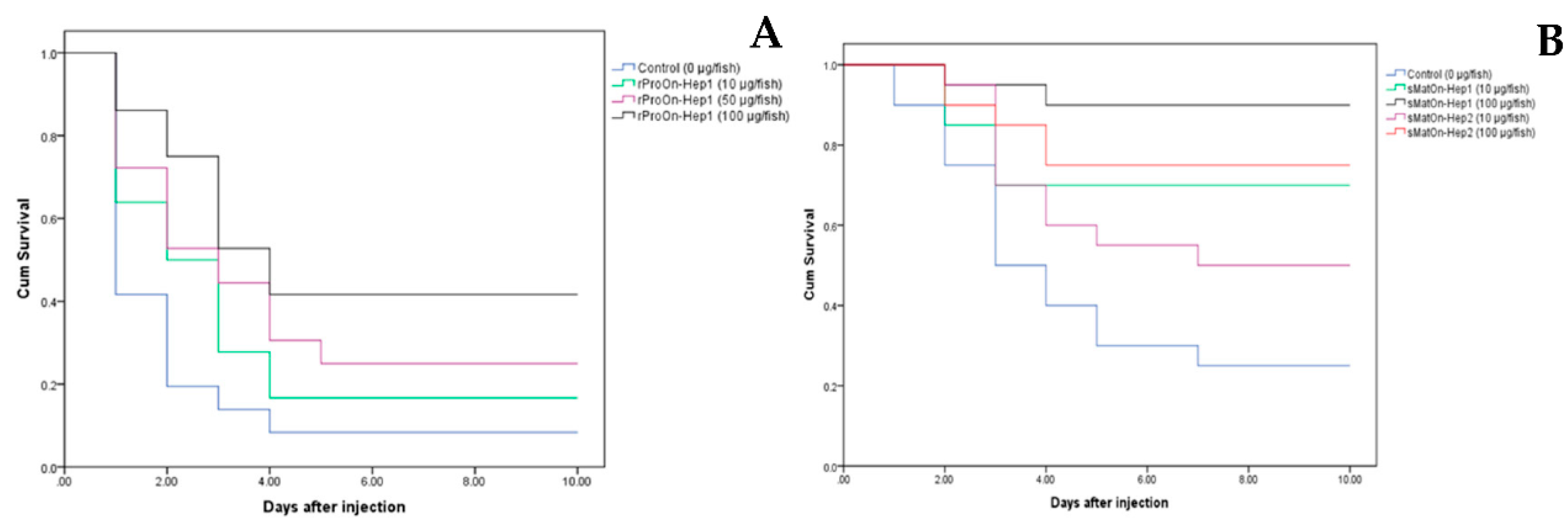
2.10. Effects of rProOn-Hep1 on Resistance to Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile Tilapia (In Vivo)
2.10.1. Experimental Animals
2.10.2. Preparation of Streptococcus agalactiae and rProOn-Hep1
2.10.3. Bacterial Challenge
2.11. Effects of sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 on Resistance against Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile Tilapia (In Vivo)
2.11.1. Experimental Animals
2.11.2. Preparation of S. agalactiae Solution and sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 Peptide
2.11.3. Bacterial Challenge
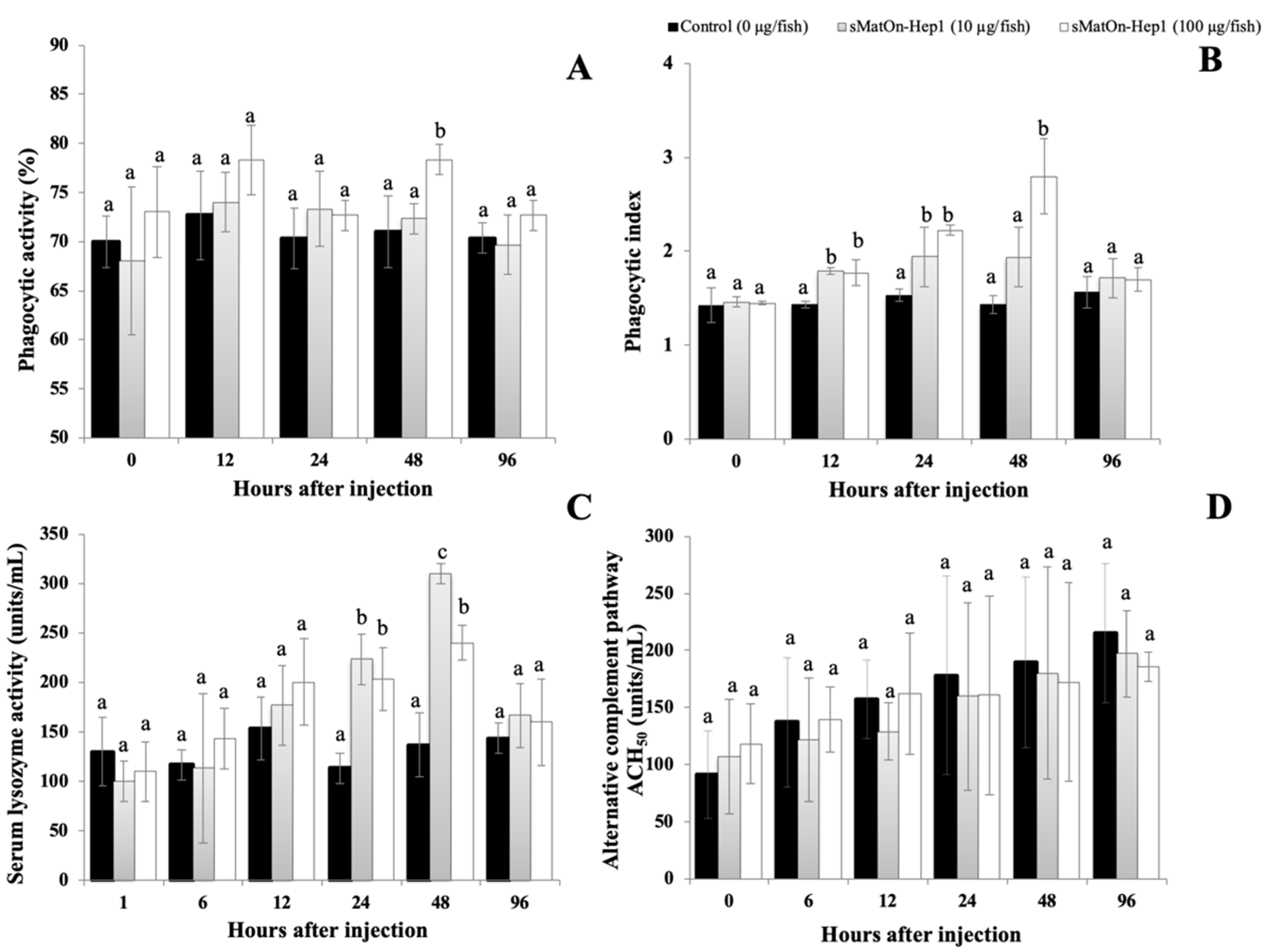
2.12. Effects of the sMatOn-Hep1 Peptide on Immune Responses and Iron, Zinc and Copper Concentrations in Nile Tilapia
2.12.1. Preparation of sMatOn-Hep1 Peptide
2.12.2. Experimental Animals and Experimental Design
2.12.3. Innate Immune Parameter Analysis
Phagocytic Activity
Lysozyme Activity
Alternative Complement Activity (ACH50)
Concentrations of Iron, Zinc and Copper in the Liver, Blood Corpuscles and Serum
2.13. Effects of sMatOn-Hep1 on the Regulation of Immune-Related Genes Using qRT-PCR and Bacterial Resistance
2.13.1. Challenge Analysis
Preparation of Virulent S. agalactiae
Challenge Procedure
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Full-Length cDNA of On-Hep1
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Hepcidin Genes in Vertebrates
3.3. Distribution of On-Hep1 Transcripts in Various Tissues of Healthy Nile Tilapia
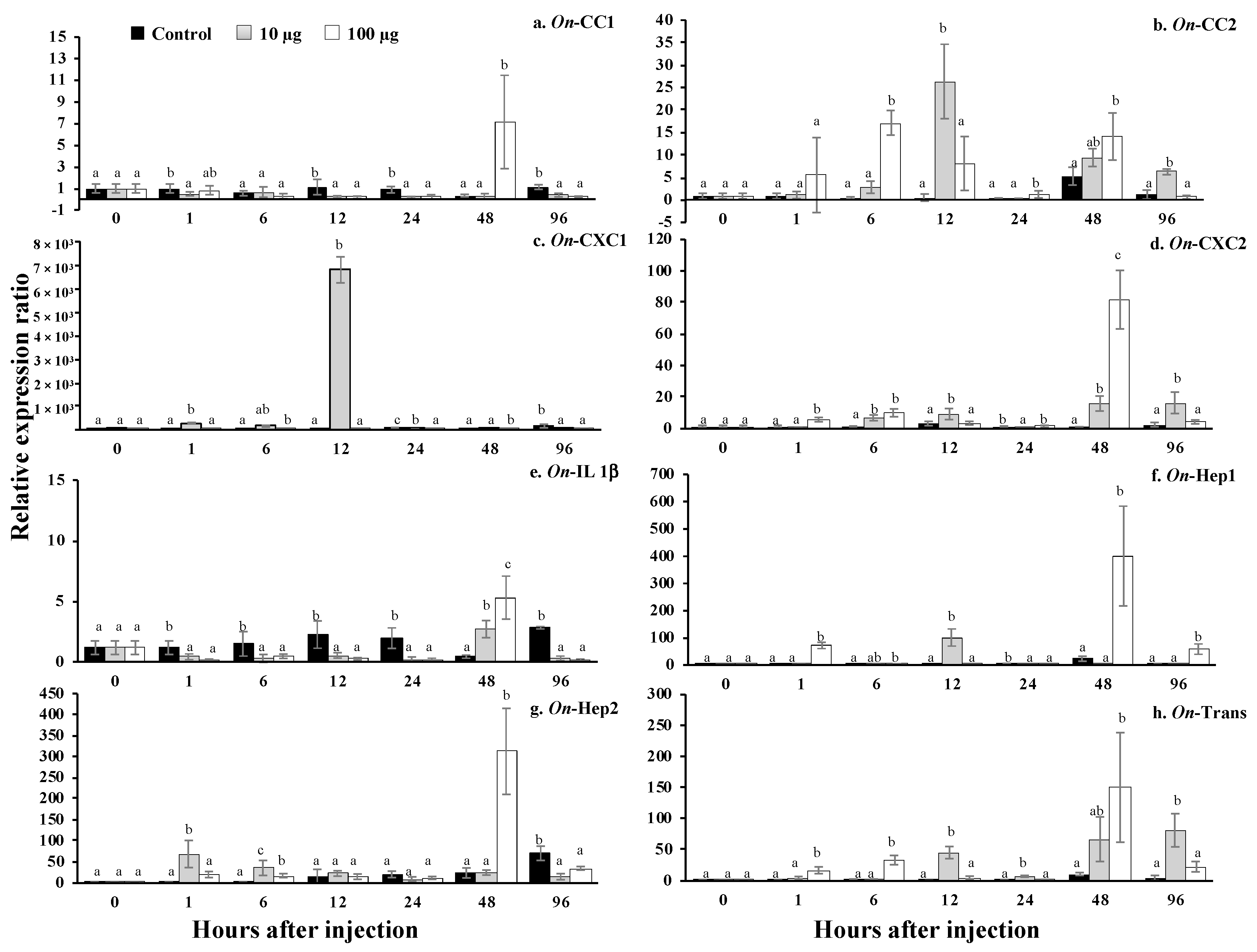
3.4. Analysis of Transcriptional Response of On-Hep1 in Liver, Spleen and Head Kidney under S. agalactiae and F. columnare Infection
3.5. Characterization of rProOn-Hep1
3.6. Functional Analyses of rProOn-Hep1, sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 in Controlling Pathogenic Bacteria
3.7. Effects of rProOn-Hep1, sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 on Phagocytic Activity (In Vitro)
3.8. sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 Binding of Bacterial Cells
3.9. Localization of sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 in PBMCs and Leukocytes from Head Kidney
3.10. Efficacy of rProOn-Hep1 on S. agalactiae Resistance in Nile Tilapia
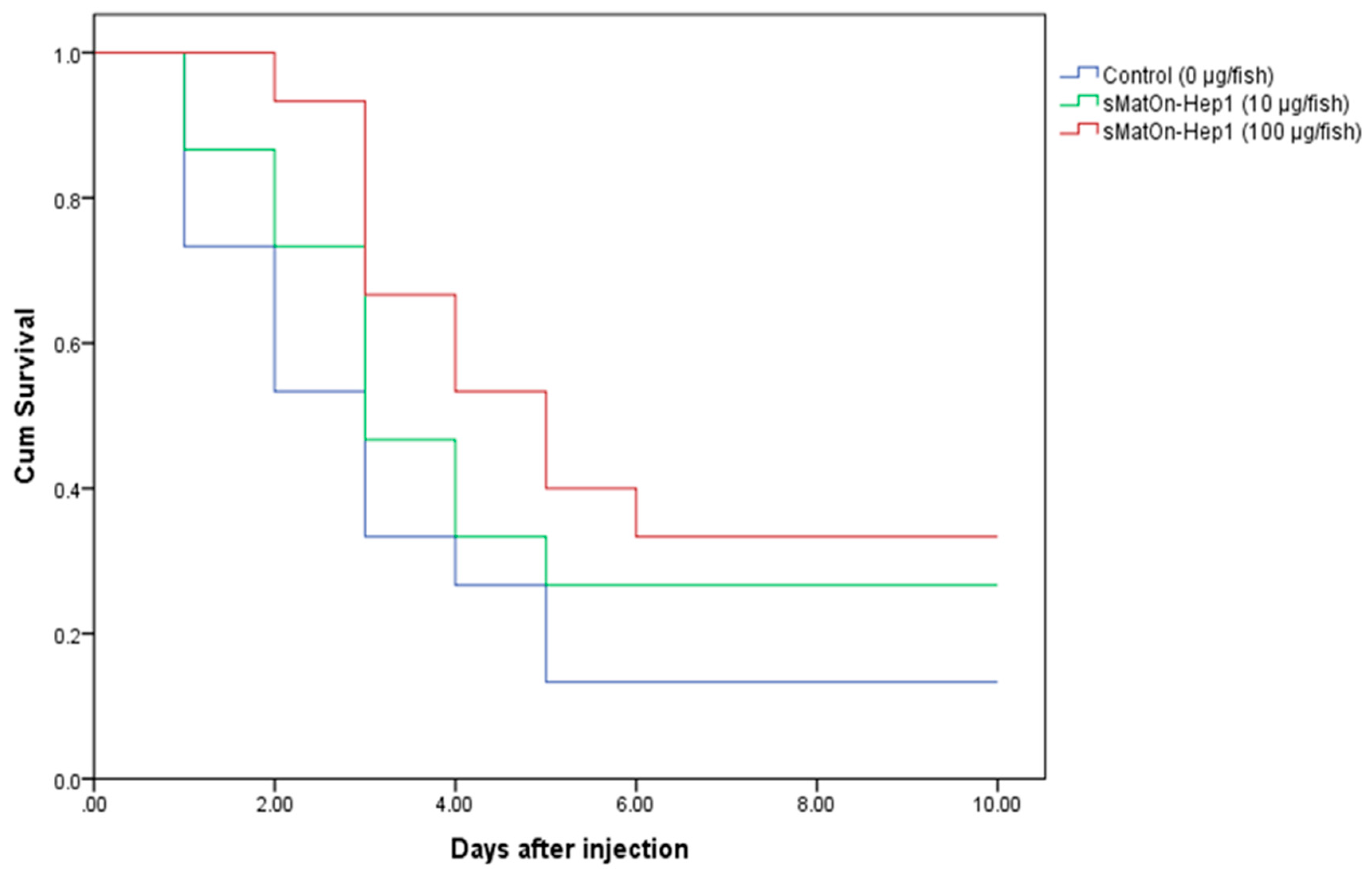
3.11. Efficacy of sMatOn-Hep1 and sMatOn-Hep2 on S. agalactiae Resistance in Nile Tilapia
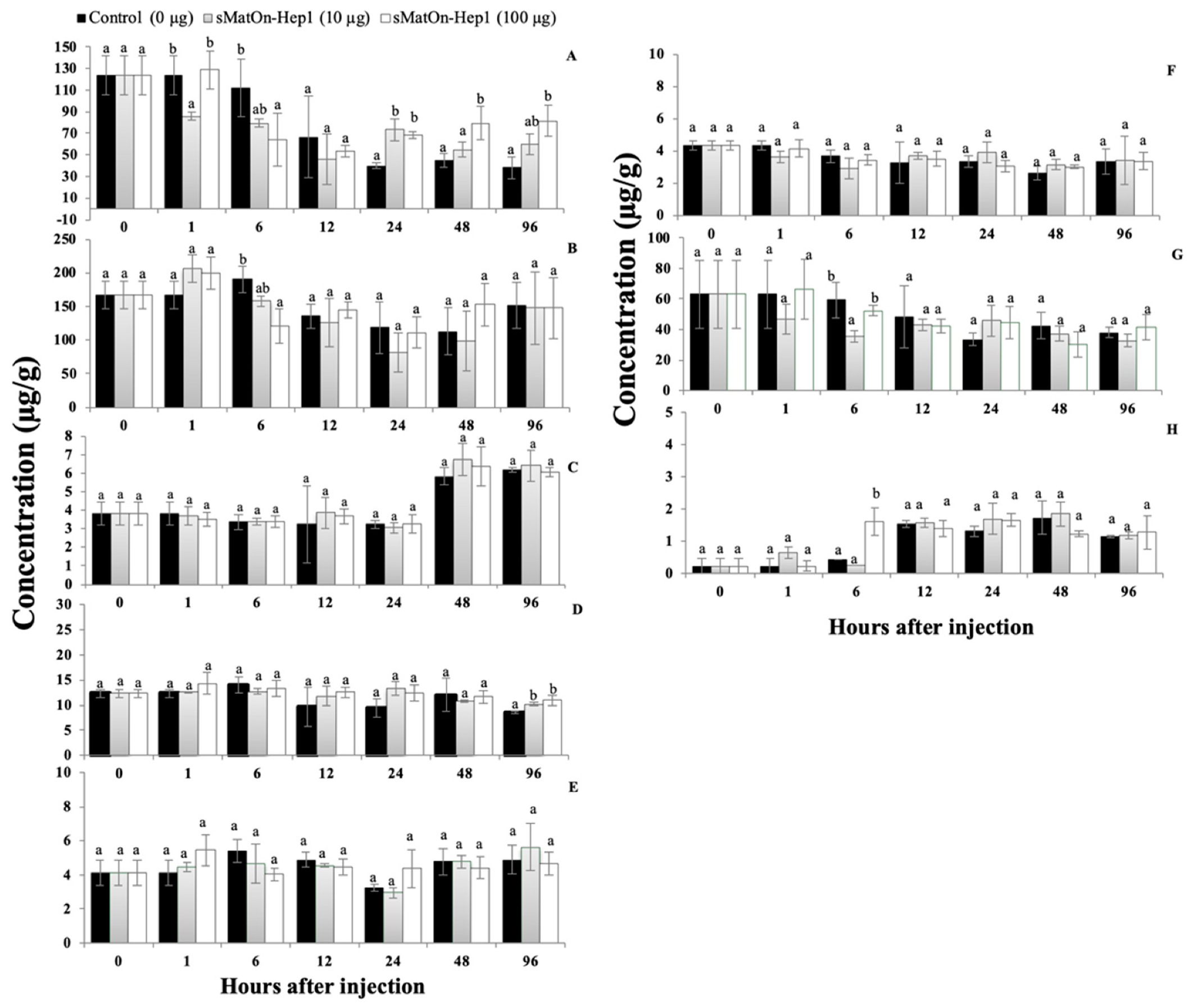
3.12. Effects of the sMatOn-Hep1 Peptide on Immune Responses and Heavy Metal Concentrations
3.12.1. Phagocytic Activity
3.12.2. Lysozyme Activity
3.12.3. Alternative Complement Activity (ACH50)
3.12.4. Concentrations of Iron, Zinc and Copper in the Liver, Blood Corpuscles and Serum
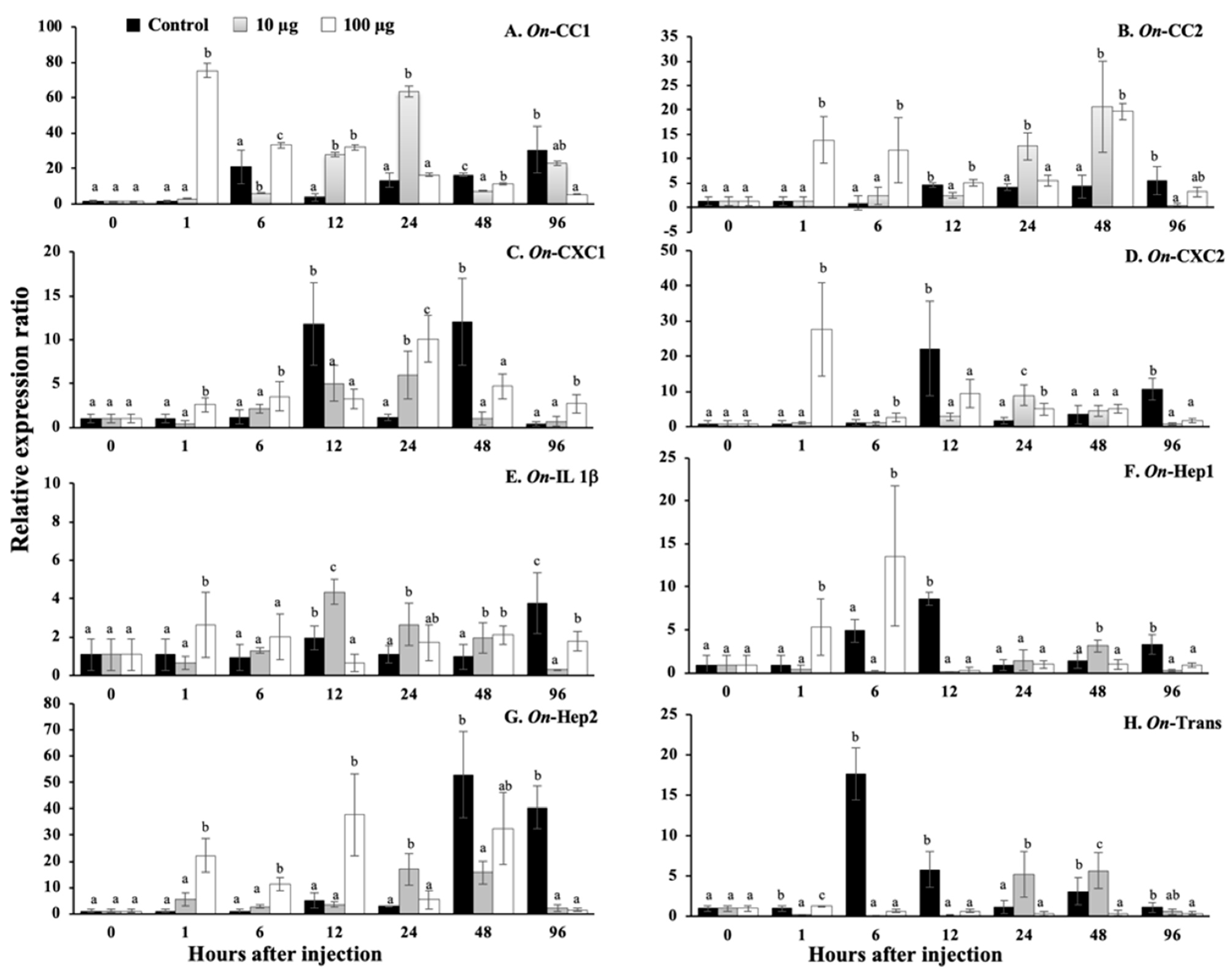
3.13. Regulation Analysis of Immune-Related Genes in Nile Tilapia, Stimulated by sMatOn-Hep1 Protein
3.14. Challenge Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tveteras, R.; Nystoyl, R.; Jory, D.E. Global Finfish Production Review and Forecast: Nearly Doubled in a Decade. Global Aquaculture Advocate. 2018. Available online: https://www.aquaculturealliance.org/advocate/global-finfish-production-review-forecast-nearly-doubled-decade/ (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Kayansamruaj, P.; Pirarat, N.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I.; Rodkhum, C. Genomic comparison between pathogenic Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from Nile tilapia in Thailand and fish-derived ST7 strains. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 36, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.E. Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophides, G.K.; Vlachou, D.; Kafatos, F.C. Comparative and functional genomics of the innate immune system in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, C.A.; Guzmán, F.; Cárdenas, C.; Marshall, S.H.; Mercado, L. Antimicrobial activity of trout hepcidin. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shike, H.; Lauth, X.; Westerman, M.E.; Ostland, V.E.; Carlberg, J.M.; Van Olst, J.C.; Shimizu, C.; Bulet, P.; Burns, J.C. Bass hepcidin is a novel antimicrobial peptide induced by bacterial challenge. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2232–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.E.; Gallant, J.W.; Liebscher, R.S.; Dacanay, A.; Tsoi, S.C. Identification and expression analysis of hepcidin-like antimicrobial peptides in bony fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shike, H.; Shimizu, C.; Lauth, X.; Burns, J.C. Organization and expression analysis of the zebrafish hepcidin gene, an antimicrobial peptide gene conserved among vertebrates. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, G.X. Hepcidin protects against iron overload-induced inhibition of bone formation in zebrafish. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Peatman, E.; Li, P.; He, C.; Liu, Z. Catfish hepcidin gene is expressed in a wide range of tissues and exhibits tissue-specific upregulation after bacterial infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Kuo, C.M. Three different hepcidins from tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus: Analysis of their expressions and biological functions. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.C.; Pan, C.Y.; Chen, J.Y. Tilapia hepcidin (TH) 2-3 as a transgene in transgenic fish enhances resistance to Vibrio vulnificus infection and causes variations in immune-related genes after infection by different bacterial species. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Cai, J.J.; Liu, H.P.; Fan, D.Q.; Peng, H.; Wang, K.J. Recombinant medaka (Oryzias melastigmus) pro-hepcidin: Multifunctional characterization. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol Biol. 2012, 161, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.G.; Liu, S.S.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, N.; Chen, S.L. Iron-metabolic function and potential antibacterial role of hepcidin and its correlated genes (ferroportin 1 and transferrin receptor) in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, L.P.; Li, M.F.; Sun, L. Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) hepcidin-1 and hepcidin-2 possess antimicrobial activity and promote resistance against bacterial and viral infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 38, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.S.; Xu, C. Molecular cloning and antibacterial activity of hepcidin from Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Electron J. Biotechin. 2015, 18, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. Two hepcidins from spotted scat (Scatophagus argus) possess antibacterial and antiviral functions in vitro. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 50, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Chai, Y.; Zhai, T.; Zhu, Q. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of the hepcidin gene from roughskin sculpin (Trachidermus fasciatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Huo, J.; Guan, Y.; Fan, D.; Xiao, X.; Wei, J.; Li, Q.; Mu, P.; Ao, J.; Chen, X. An improved genome assembly for Larimichthys crocea reveals hepcidin gene expansion with diversified regulation and function. Commun. Biol. 2018, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Obiefuna, V.; Hodgkinson, J.W.; McAllister, M.; Belosevic, M. Teleost antimicrobial peptide hepcidin contributes to host defense of goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) against Trypanosoma carassii. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 94, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Secombes, C.J. Analysis of events occurring within teleost macrophages during the respiratory burst. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1988, 89, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-(ΔΔCT) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakharuthai, C.; Areechon, N.; Srisapoome, P. Molecular characterization, functional analysis, and defense mechanisms of two CC chemokines in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in response to severely pathogenic bacteria. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 59, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetru, C.; Bulet, P. Strategies for the isolation and characterization of antimicrobial peptides of invertebrates. Methods Mol. Biol. 1997, 78, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sardar, M.R.; Thompson, K.D.; Penman, D.J.; McAndrew, B.J. Immune responses of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linn.) clones: I. Non–specific responses. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuno, J.; Esteban, M.A.; Meseguer, J. Effects of short-term crowding stress on the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) innate immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2001, 11, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.S.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Marranca, J.M. Identification of centrarchid hepcidins and evidence that 17 beta-estradiol disrupts constitutive expression of hepcidin-1 and inducible expression of hepcidin-2 in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Nie, L.; Zhu, G.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J.Z. Advances in research of fish immune relevant genes: A comparative overview of innate and adaptive immunity in teleosts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.G.; Wei, J.G.; Xu, D.; Cui, H.C.; Yan, Y.; Ou-Yang, Z.L.; Huang, X.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Qin, Q.W. Molecular cloning and characterization of two novel hepcidins from orange spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Gu, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xu, G. Identification and expression of the hepcidin gene from brown trout (Salmo trutta) and functional analysis of its synthetic peptide. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.N.; Vazquez-Dorado, S.; Neves, J.V.; Wilson, J.M. Dual function of fish hepcidin: Response to experimental iron overload and bacterial infection in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solstad, T.; Larsen, A.N.; Seppola, M.; Jorgensen, T. Identification, cloning and expression analysis of a hepcidin cDNA of the Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, K.J.; Chen, J.H.; Qu, H.D.; Li, S.J. Genomic organization and tissue-specific expression analysis of hepcidin-like genes from black porgy (Acanthopagrus schlegelii B). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decostere, A. Flavobacterium columnare infections in fish: The agent and its adhesion to the gill tissue. Verh. K. Acad. Geneeskd. Belg. 2002, 64, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, J.V.; Caldas, C.; Vieira, I.; Ramos, M.F.; Rodrigues, P.N.S. Multiple hepcidins in a teleost fish, Dicentrarchus labrax: Different hepcidins for different roles. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 2696–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, I.; Hwang, J.Y.; Ono, Y.; Kurobe, T.; Ohira, T.; Nozaki, R.; Aoki, T. Two different types of hepcidins from the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 5257–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.O.; Park, E.M.; Nam, B.H.; Kong, H.J.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, S.J. Identification and molecular characterization of two hepcidin genes from black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 315, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, P.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. A novel hepcidin-like in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) highly expressed after pathogen challenge but not after iron overload. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.J.; Cai, J.J.; Cai, L.; Qu, H.D.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M. Cloning and expression of a hepcidin gene from a marine fish (Pseudosciaena crocea) and the antimicrobial activity of its synthetic peptide. Peptides 2009, 30, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, A.C.; Trewin, B.; Snape, N.; Kvennefors, E.C.; Baiano, J.C. Two hepcidin-like antimicrobial peptides in Barramundi Lates calcarifer exhibit differing tissue tropism and are induced in response to lipopolysaccharide. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.K.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, D.S. Molecular characterization of hepcidin gene from mud loach (Misgurnus mizolepis; Cypriniformes). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Rivera, S.; Gabayan, V.; Keller, C.; Taudorf, S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Ganz, T. IL-6 mediates hypoferremia of inflammation by inducing the synthesis of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.; Jung, C.-L.; Gabayan, V.; Deng, J.C.; Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E.; Bulut, Y. Hepcidin induction by pathogens and pathogen-derived molecules is strongly dependent on interleukin-6. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.; Peng, H.; Gelbart, T.; Beutler, E. The IL-6-and lipopolysaccharide-induced transcription of hepcidin in HFE-, transferrin receptor 2-, and β2-microglobulin-deficient hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9263–9265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, R.; Quinn, F.; Giri, P.K. Role of the hepcidin-ferroportin axis in pathogen-mediated intracellular iron sequestration in human phagocytic cells. Blood Adv. 2018, 22, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Huang, T.; Gu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, B. Characterization, expression, and functional analysis of the hepcidin gene from Brachymystax lenok. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 89, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, F.B.; Florence, W.C.; Satoskar, A.R.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Zwilling, B.S.; Lafuse, W.P. Expression and localization of hepcidin in macrophages: A role in host defense against tuberculosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasulu, B.; Syvitski, R.; Seo, J.K.; Mattatall, N.R.; Knickle, L.C.; Douglas, S.E. Expression, purification and structural characterization of recombinant hepcidin, an anti-microbial peptide identified in Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 61, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Tuttle, M.S.; Powelson, J.; Vaughn, M.B.; Donovan, A.; Ward, D.M.; Ganz, T.; Kaplan, J. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its Internalization. Science 2004, 17, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, N.; Chen, D.D.; Nie, P.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, Y.A. B cell functions can be modulated by antimicrobial peptides in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: Novel insights into the innate nature of B cells in Fish. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherayil, B.J. The role of iron in the immune response to bacterial infection. Immunol. Res. 2011, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.N.; Rajanbabu, V.; Pan, C.Y.; Chan, Y.L.; Hui, C.F.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, C.J. Modulation of the immune-related gene responses to protect mice against Japanese encephalitis virus using the antimicrobial peptide, Tilapia hepcidin 1-5. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6804–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.Y.; Peng, K.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, J.Y. Transgenic expression of Tilapia hepcidin1-5 and shrimp chelonianin in zebrafish and their resistance to bacterial pathogens. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Rajanbabu, V.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, J.Y. Insights into the antibacterial and immunomodulatory functions of Tilapia hepcidin (Th)2-3 against Vibrio vulnificus infection in mice. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Sarath Babu, V.; Lin, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, G. Hepcidin protects grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) against Flavobacterium columnare infection via regulating iron distribution and immune gene expression. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 75, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, K.; Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T.; Mehrad, B. Hepcidin and host defense against infectious diseases. PLoS Pathog. 2015, e1004998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcheron, G.; Dozois, C.M. Interplay between iron homeostasis and virulence: Fur and ryhb as major regulators of bacterial pathogenicity. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Sun, X. Iron acquisition and regulation systems in Streptococcus species. Metallomics 2014, 6, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, B.A.; Sutcliffe, I.C.; Harrington, D.J. Expression of the MtsA lipoprotein of Streptococcus agalactiae A909 is regulated by manganese and iron. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2009, 95, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, A.E.; Eddowes, L.A.; Gileadi, U.; Cole, S.; Spottiswoode, N.; Selvakumar, T.A.; Ho, L.P.; Townsend, A.R.M.; Drakesmith, H. Hepcidin regulation by innate immune and infectious stimuli. Blood 2011, 118, 4129–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.F.; Liu, Z.F.; Lin, A.F.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J.Z. Coordination of bactericidal and iron regulatory functions of hepcidin in innate antimicrobial immunity in a zebrafish model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Iron homeostasis in host defence and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phan-Aram, P.; Mahasri, G.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Amparyup, P.; Srisapoome, P. Immune Regulation, but Not Antibacterial Activity, Is a Crucial Function of Hepcidins in Resistance against Pathogenic Bacteria in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linn.). Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081132
Phan-Aram P, Mahasri G, Kayansamruaj P, Amparyup P, Srisapoome P. Immune Regulation, but Not Antibacterial Activity, Is a Crucial Function of Hepcidins in Resistance against Pathogenic Bacteria in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linn.). Biomolecules. 2020; 10(8):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081132
Chicago/Turabian StylePhan-Aram, Pagaporn, Gunanti Mahasri, Pattanapon Kayansamruaj, Piti Amparyup, and Prapansak Srisapoome. 2020. "Immune Regulation, but Not Antibacterial Activity, Is a Crucial Function of Hepcidins in Resistance against Pathogenic Bacteria in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linn.)" Biomolecules 10, no. 8: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081132
APA StylePhan-Aram, P., Mahasri, G., Kayansamruaj, P., Amparyup, P., & Srisapoome, P. (2020). Immune Regulation, but Not Antibacterial Activity, Is a Crucial Function of Hepcidins in Resistance against Pathogenic Bacteria in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linn.). Biomolecules, 10(8), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081132





