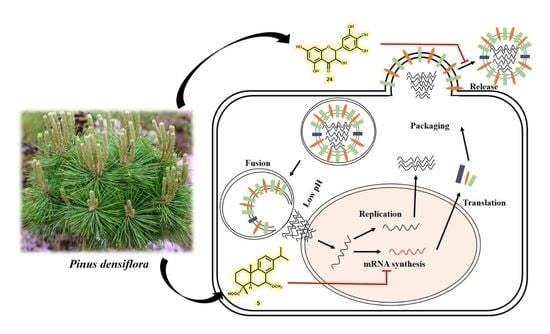
Antiviral Activities of Compounds Isolated from Pinus densiflora (Pine Tree) against the Influenza A Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Extraction and Isolation
2.4. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of 2
2.5. Preparation of 2,9-Di-(S)-MTPA Ester (2b) and 2,9-Di-(R)-MTPA Ester (2c) from 2a
2.6. Sugar Analysis of Compounds 1 and 2
2.7. Cell Culture and Virus Stock
2.8. Cytopathic Effect (CPE) Inhibition Assay
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.10. Western Blotting Analysis
2.11. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.12. Flow Cytometric Analysis of the Cell Cycle
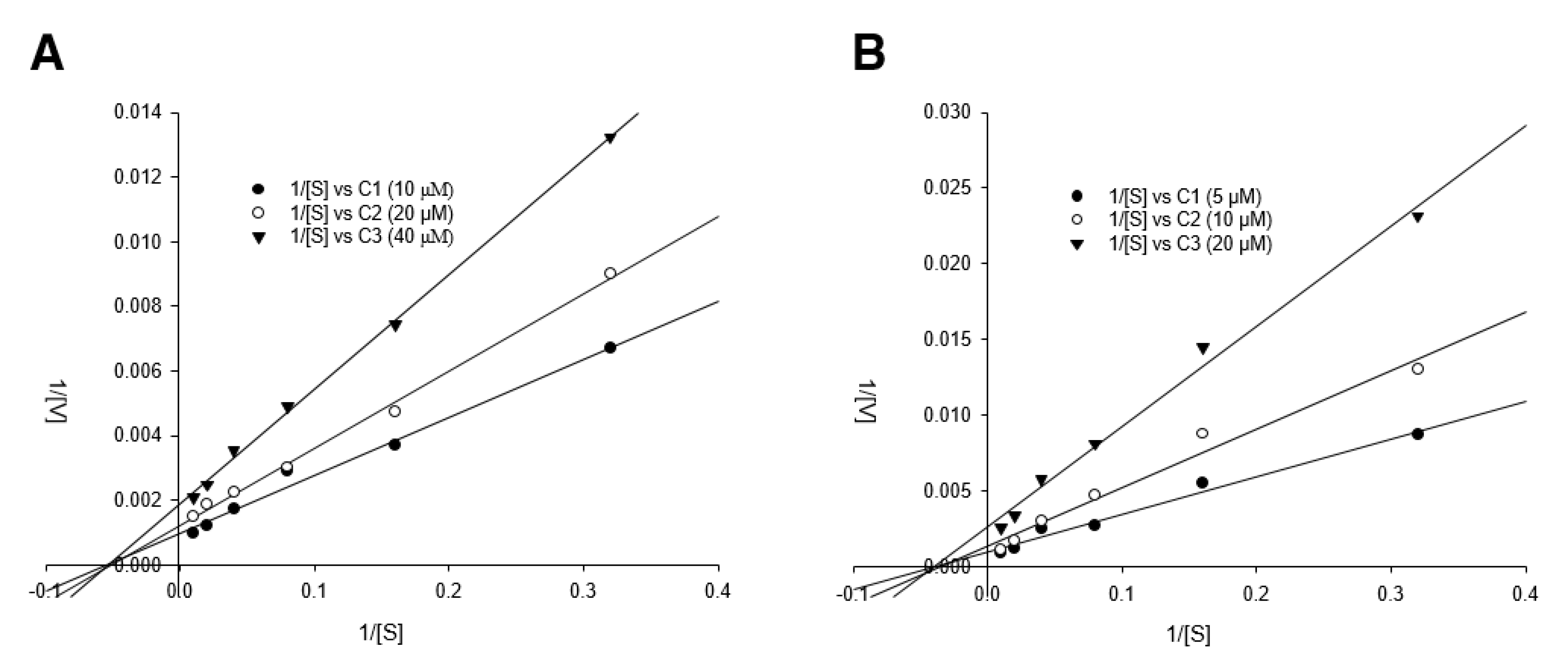
2.13. Neuraminidase Inhibition and Kinetic Assays
2.14. Cell Protection Assay for H1N1 Infection via Coincubation
2.15. Virus Particles Assay for H1N1 Infection via Coincubation
2.16. Nitric Oxide (NO) Production Assay
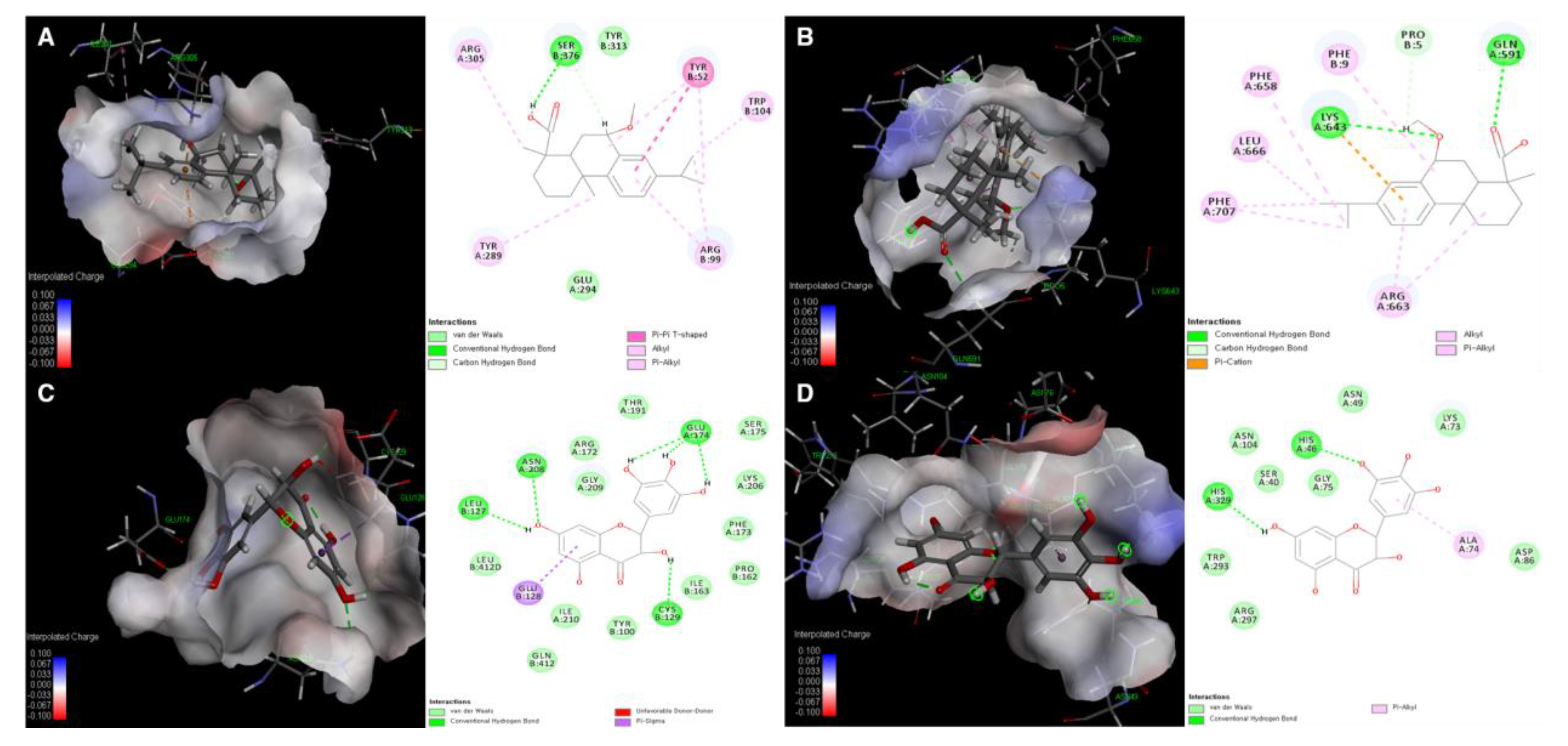
2.17. Simulation of Binding Affinity via Molecular Docking
2.18. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
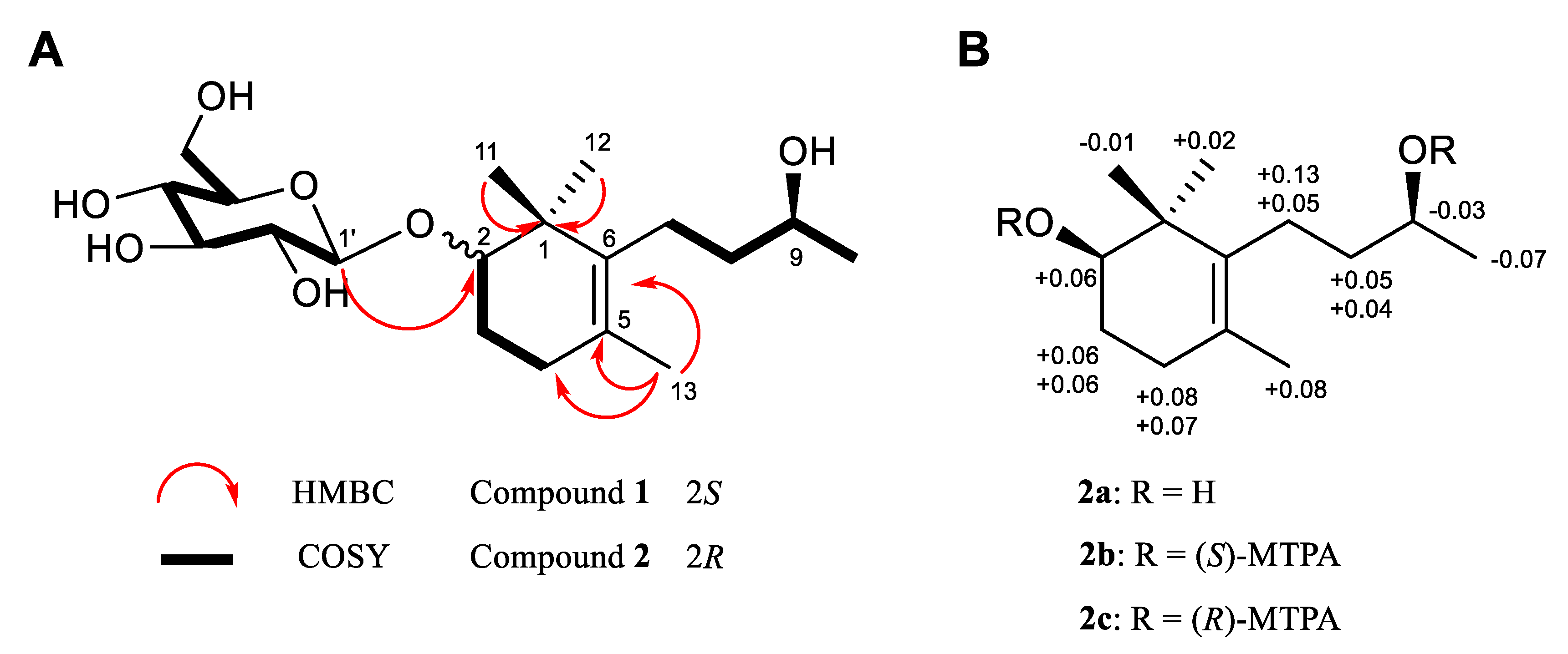
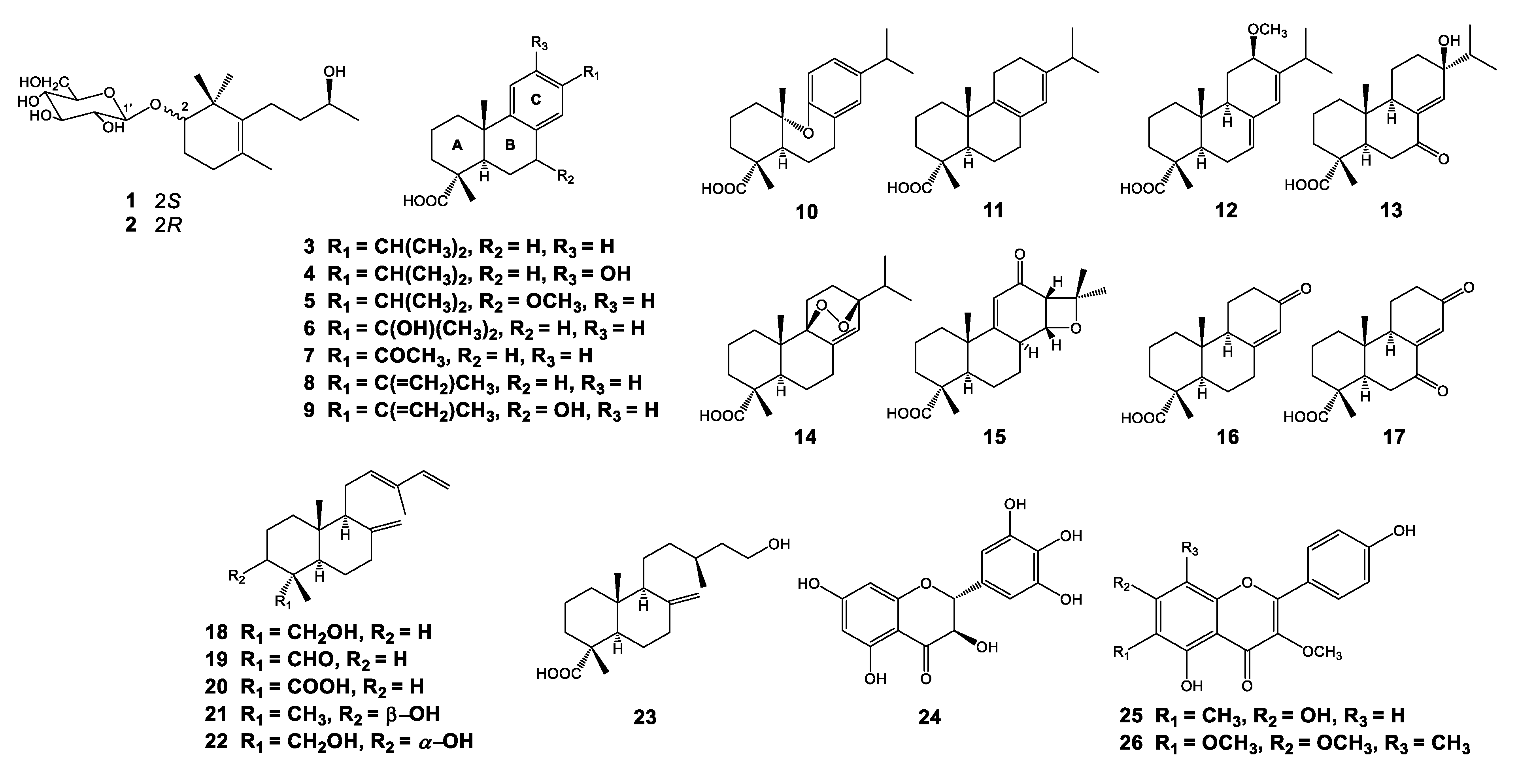
3.1. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Compounds Isolated from P. densiflora
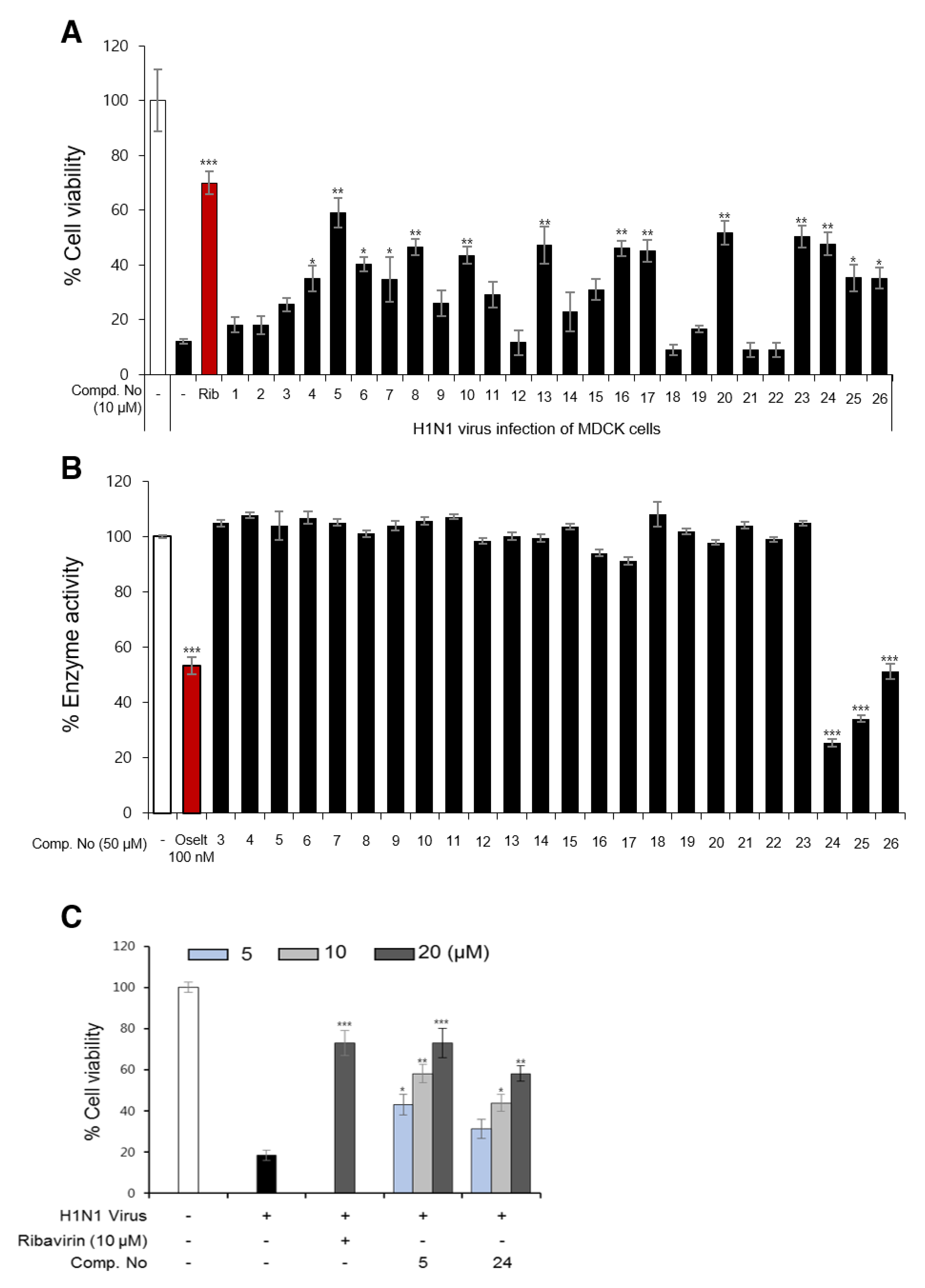
3.2. Influenza Viral Inhibition and Structure-Activity Relationships (SARs) of Isolated Compounds from P. densiflora
3.3. The Effects of Diterpenoids on mRNA and Protein Expression during H1N1 Replication
3.4. Detailed Neuraminidase Inhibition Assay of Compound 24 against Various Subtypes of Influenza A Virus
3.5. Molecular Docking Simulation of Compounds 5 and 24 with Expected Target Proteins
3.6. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Isolated Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paget, J.; Spreeuwenberg, P.; Charu, V.; Taylor, R.J.; Iuliano, A.D.; Bresee, J.; Simonsen, L.; Viboud, C. Global mortality associated with seasonal influenza epidemic: New burden estimates and predictors from the GLaMOR project. J. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 020421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoor, S.; Maqbool, I. Swine flu a seasonal pandemic, symptoms, diagnostics and prevention. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 30, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyeki, T.M.; Peiris, M. Novel avian influenza A virus infections of humans. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2019, 33, 907–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shie, J.-J.; Fang, J.-M. Development of effective anti-influenza drugs: Congeners and conjugates—A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 84, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Both, G.W.; Sleigh, M.J.; Cox, N.J.; Kendal, A.P. Antigenic drift in influenza virus H3 hemagglutinin from 1968 to 1980: Multiple evolutionary pathways and sequential amino acid changes at key antigenic sites. J. Virol. 1983, 48, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styk, B.; Russ, G.; Pola’kova, K. Antigenic glycopolypeptides HA1 and HA2 of influenza virus hemagglutinin. III. Reactivity with human convalescent sera. Acta Virol. 1979, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gocník, M.; Fislová, T.; Mucha, V.; Sládková, T.; Russ, G.; Kostolanský, F.; Varečková, E. Antibodies induced by the HA2 glycopolypeptide of influenza virus haemagglutinin improve recovery from influenza A virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Luo, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, F.; Xie, X.; Chen, D.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Ye, C.; Lu, S.; et al. Potent influenza A virus entry inhibitors targeting a conserved region of hemagglutinin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 144, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.-Z.; Jiang, L.-Z.; Song, G.-P.; Wang, S.; Xiong, P.; Ke, C.-W. Study on the antiviral activities and hemagglutinin-based molecular mechanism of novel chlorogenin 3-O-β-chacotrioside derivatives against H5N1 subtype viruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosono, S.; Kasai, A.; Komaba, S.; Matsubara, T.; Sato, T.; Takahashi, D.; Toshima, K. Novel hemagglutinin-binding sulfated oligofucosides and their effect on influenza virus infection. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, R.U.; Wilson, I.A. Structural basis of influenza virus fusion inhibition by the antiviral drug Arbidol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leneva, I.A.; Falynskova, I.N.; Makhmudova, N.R.; Poromov, A.A.; Yatsyshina, S.B.; Maleev, V.V. Umifenovir susceptibility monitoring and characterization of influenza viruses isolated during ARBITR clinical study. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S. Treating influenza infection, from now and into the future. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barik, S. New treatments for influenza. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C. Antiviral therapy for the next influenza pandemic. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-Y.; Jang, M.-K.; Lee, D.-G.; Yu, K.-H.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.G.; Yoo, B.H.; Lee, S.-H. Comparison of methods for proanthocyanidin extraction from pine (Pinus densiflora) needles and biological activities of the extracts. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2020, 4, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J. Dongeubogam; Dongeuhak Institute, Ryo-gang Pub. Co.: Seoul, Korea, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Compendium of Materia Medica (Bencao Gangmu); Huaxia Press: Beijing, China, 2012; (1593 republished in 2012). [Google Scholar]
- The Korean Herbal Pharmacopoeia; Food and Drug Administration: Seoul, Korea, 2020.
- Kim, Y.S.; Shin, D.H. Volatile components and antibacterial effects of pine needle (Pinus densiflora S. and Z.) extracts. Food Microbiol. 2005, 22, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.S.; Kim, J.-M.; Choi, E.H.; Chang, N. Neuroprotective effects of several Korean medicinal plants traditionally used for stroke remedy. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Paudyal, D.P.; Hwang, I.; Tripathi, G.R.; Yang, Y.; Cheong, H. Production of fermented needle extracts from red pine and their functional characterization. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2008, 13, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, C.S.; Moon, S.C.; Lee, M.S. Antioxidant, antimutagenic, and antitumor effects of pine needles (Pinus densiflora). Nutr. Cancer 2006, 56, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuthnot, P. Antiviral Drugs: Aspects of Clinical Use and Recent Advances; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; p. 180. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Cho, B.J.; Ko, M.S.; Jung, J.M.; Kim, H.R.; Song, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Sim, S.S.; Kim, C.J. Anti-oxidant and anti-aging activities of essential oils of Pinus densiflora needles and twigs. Yakhak Hoeji 2010, 54, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, M.J.; Jung, H.A.; Kang, S.S.; Hwang, G.S.; Choi, J.S. A new abietic acid-type diterpene glucoside from the needles of Pinus densiflora. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Lee, H.J.; Min, H.Y.; Park, E.J.; Lee, K.M.; Ahn, Y.H.; Cho, Y.J.; Pyee, J.H. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of pinosylvin, a constituent of pine. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, M.Z.; Jeon, Y.-M.; Moon, S.-S. Labdane-type diterpenes active against acne from pine cones (Pinus densiflora). Planta Med. 2008, 74, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yu, B.; Hu, J.; Wu, T.; Hui, H. Three new homoisoflavanone glycosides from the bulbs of Ornithogalum caudatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoye, T.R.; Jeffrey, C.S.; Shao, F. Mosher ester analysis for the determination of absolute configuration of stereogenic (chiral) carbinol carbons. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nakashima, T.; Ueda, T.; Tomii, K.; Kouno, I. Facile discrimination of aldose enantiomers by reversed-phase HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.K.Q.; Dao, T.T.; Nguyen, N.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Cho, T.O.; On, W.K. Antiviral phenolics from the leaves of Cleistocalyx operculatus. Fitoterapia 2016, 110, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Ha, T.K.Q.; Oh, W.K.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.-C. Antiviral indolosesquiterpenoid xiamycins C-E from a halophilic actinomycete. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.M.; Doan, T.P.; Ha, T.K.Q.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, B.W.; Pham, H.T.T.; Cho, T.O.; Oh, W.K. Dereplication by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectroscopy (qTOF-MS) and antiviral activities of phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, D.; Kusagaya, Y.; Endo, N.; Sometani, A.; Takeo, S.; Suzuki, T.; Arima, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Suzuki, Y. Thujaplicin-copper chelates inhibit replication of human influenza viruses. Antivir. Res. 1998, 39, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.-T.; Tung, B.-T.; Nguyen, P.-H.; Thuong, P.-T.; Yoo, S.-S.; Kim, E.-H.; Kim, S.-K.; Oh, W.-K. C-methylated flavonoids from Cleistocalyx operculatus and their inhibitory effects on novel influenza A (H1N1) neuraminidase. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theisen, L.L.; Muller, C.P. EPs® 7630 (Umckaloabo®), an extract from Pelargonium sidoides roots, exerts anti-influenza virus activity in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2012, 94, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecil, C.E.; Davis, J.M.; Cech, N.B.; Laster, S.M. Inhibition of H1N1 influenza A virus growth and induction of inflammatory mediators by the isoquinoline alkaloid berberine and extracts of goldenseal (Hydrastis canadensis). Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.M.; Espey, M.G.; Wink, D.A. A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide 2001, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeghoobi, M.; Frimayanti, N.; Chee, C.F.; Ikram, K.K.; Najjar, B.O.; Zain, S.M.; Abdullah, Z.; Wahab, H.A.; Rahman, N.A. QSAR, in silico docking and in vitro evaluation of chalcone derivatives as potential inhibitors for H1N1 virus neuraminidase. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrits, S.W.; Cianci, C.; Kim, S.; Pearce, B.C.; Deminie, C.; Discotto, L.; McAuliffe, B.; Minassian, B.F.; Shi, S.; Zhu, S.; et al. Inhibition of influenza virus replication via small molecules that induce the formation of higher-order nucleoprotein oligomers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15366–15371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayashi, E.; Yoshida, H.; Kawai, F.; Shibayama, N.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagata, K.; Tame, J.R.H.; Park, S.-Y. The structural basis for an essential subunit interaction in influenza virus RNA polymerase. Nature 2008, 454, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavricka, C.J.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Qi, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Gao, F.; Liu, J.; Feng, E.; He, J.; et al. Structural and functional analysis of laninamivir and its octanoate prodrug reveals group specific mechanisms for influenza NA inhibition. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.J.; Haire, L.F.; Lin, Y.P.; Liu, J.; Russell, R.J.; Walker, P.A.; Skehel, J.J.; Martin, S.R.; Hay, A.J.; Gamblin, S.J. Crystal structures of oseltamivir-resistant influenza virus neuraminidase mutants. Nature 2008, 453, 1258–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, H.; Tamaki, A. Platanionosides D-J: Megastigmane glycosides from the Leaves of Alangium platanifolium (SIEB. Et ZUCC.) HARMS var. platanifolium. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P. NMR spectroscopy in the structural elucidation of oligosaccharides and glycosides. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 3307–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, R.; Suzuo, M.; Asakawa, J.; Tanaka, O. Carbon-13 chemical shifts of isoprenoid-β-D-glucopyranosides and -β-D-mannopyranosides. Stereochemical influences of aglycones alcohols. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 2, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, J.M.M.D.; Gordaliza, M.; Salinero, M.A.; San Feliciano, A. 13C NMR data for abieta-8,11,13-triene diterpenoids. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1994, 32, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinouchi, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Matsunaga, S.; Tanaka, R. Potential antitumor-promoting diterpenoids from the stem bark of Picea glehni. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, Y.-L.; Li, S.-M.; Yang, X.-W.; Xia, J.-H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.-D. Systematic phytochemical investigation of Abies spectabilis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1646–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, H.T.A.; Miyase, T.; Lenguyen, M.P.; Smal, M.A. Further acidic constituents and neutral components of Pinus massoniana Resin. Tetrahedron 1973, 49, 7903–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-W.; Li, S.-M.; Feng, L.; Shen, Y.-H.; Tian, J.-M.; Liu, X.-H.; Zeng, H.-W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.-D. Abiesanordines A-N: Fourteen new norditerpenes from Abies georgei. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 4354–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Ohtsu, H.; Matsunaga, S. Abietane diterpene acids and other constituents from the leaves of Larix kaempferi. Phytochemistry 1997, 46, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, P.; Legault, J.; Lavoie, S.; Grenon, C.; Pichette, A. Diterpenoids from the buds of Pinus banksiana Lamb. Molecules 2012, 17, 9716–9727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, H.; Tanaka, R.; Matsunaga, S.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H. Anti-tumor-promoting rearranged abietane diterpenes from the leaves of Larix kaempferi. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 664–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landucci, L.L.; Zinkel, D.F. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of the abietadienoic resin acids. Holzforschung 1991, 45, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Gong, Q.-F.; Yang, J.-Q.; Zeng, G.-Z.; Tan, N.-H. Antioxidant constituents from Pinus massoniana. Plant Divers. Resour. 2013, 35, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsu, H.; Tanaka, R.; In, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H. New abietane diterpenoids from the cones of Larix kaempferi. Can. J. Chem. 2000, 78, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, A.F.; Sanchez, J.F.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.J.R.; Dorado, M.M.; Haidour, A. Endoperoxide diterpenoids and other constituents from Abies marocana. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Cai, X.-H.; Tan, Q.-G.; Luo, X.-D. Abietane diterpenoids and a lignin from Pinus yunnanensis. Z. Naturforsch. 2010, 2010, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, J.; Noda, N.; Ida, Y.; Komori, T.; Kawasaki, T. Studies on the constituents of the crude drug “Fritillariae Bulbus.” IV. On the diterpenoid constituents of the crude drug “Fritillariae Bulbus”. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1982, 30, 3922–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, J.; Yatagai, M.; Ohira, T. Abietane-type and labdane-type diterpenoids from the cones of Chamaecyparis obtuse. J. Wood. Sci. 2002, 48, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, M.-L.; Chen, R.-Y.; Yu, D.-Q. Two new bislabdane-type diterpenoids and three new diterpenoids from the roots of Cunninghamia lanceolata. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, F.; Czerson, H. Neue labdan- und pimaren-derivate aus Palafoxia rosea. Phytochemistry 1979, 18, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, F.; Adler, A.; King, R.M.; Robinson, H. Ent-labdanes from Mikania alvimii. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeon, Y.Y.; Lee, H.J. A composition comprising the extract of pine tree leaf or the compounds isolated therefrom for the prevention and treatment of cancer disease by inhibiting HPV virus and the uses thereby. U.S. Patent Application No. 14/366,093, 5 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-S.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Wang, B.; Li, L.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Chemical constituents from Ampelopsis grossedentata. J. Chin. Pharm. 2006, 15, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, R.; Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Zeng, H.; Li, B.; Yuan, H.; He, Y.; Shan, L.; Zhang, W. 6-C-methyl flavonoids isolated from Pinus densata inhibit the proliferation and promote the apoptosis of the HL-60 human promyelocytic leukaemia cell line. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Zaid, M.; Dumas, M.; Chauret, D.; Watson, A.; Thompson, D. C-methyl flavonols from the fungus Colletotrichum dematium f.sp. epilobii. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, S.; Gan, M.; Zi, J.; Song, W.; Fan, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Abietane and C20-norabietane diterpenes from the stem bark of Fraxinus sieboldiana and their biological activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, A.; Kim, S.Y.; Kobayakawa, N.; Tanaka, N.; Kashiwada, Y. Miltiorins A-D, diterpenes from radix Salviae miltiorrhizae. Fitoterapia 2015, 102, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-C.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Yang, T.; Jiang, M.-Y.; Liu, D.; Li, H.-M.; Li, R.-T. Six new ent-abietane-type diterpenoids from the stem bark of Euphorbia neriifolia. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 34, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.-L.; Wang, H.-D.; Lee, S.M.; Wang, Y.-T.; Du, G.-H. Structure-activity relationship of flavonoids as influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitors and their in vitro anti-viral activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 7141–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscona, A. Neuraminidase inhibitors of influenza. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Chang, C.; Li, L.; Klenk, C.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Xia, N.; Shu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gabriel, G.; et al. Sumoylation of influenza A virus nucleoprotein is essential for intracellular trafficking and virus growth. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9379–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.-L.; Wu, C.-Y.; Su, W.-C.; Jeng, K.-S.; Lai, M.M.C. Ubiquitination and deubiquitination of NP protein regulates influenza A virus RNA replication. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3879–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianci, C.; Gerritz, S.W.; Deminie, C.; Krystal, M. Influenza nucleoprotein: Promising target for antiviral chemotherapy. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2012, 23, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, D.; Revol, R.; Östbye, H.; Wang, H.; Daniels, R. Influenza A virus cell entry, replication, virion assembly and movement. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilligay, D.; Tarendeau, F.; Resa-Infante, T.; Coloma, R.; Crepin, T.; Sehr, P.; Lewis, J.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Ortin, J.; Hart, D.J.; et al. The structural basis for cap binding by influenza virus polymerase subunit PB2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.; Bouvier, D.; Crépin, T.; McCarthy, A.A.; Hart, D.J.; Baudin, F.; Cusack, S.; Ruigrok, R.W. The cap-snatching endonuclease of influenza virus polymerase resides in the PA subunit. Nature 2009, 458, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, S.; Becker, C.; Ridge, K.M.; Budinger, G.R. Influenza virus-induced lung injury: Pathogenesis and implications for treatment. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julkunen, I.; Melén, K.; Nyqvist, M.; Pirhonen, J.; Sareneva, T.; Matikainen, S. Inflammatory responses in influenza a virus infection. Vaccine 2000, 19, S32–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, J.S.M.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Yen, H.-L. Host response to Influenza virus: Protection versus immunopathology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | 1a | 2a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 1 | 41.5 | 40.6 | ||
| 2 | 3.43 dd (3.0, 11.0) | 87.9 | 3.62 dd (3.0, 10.2) | 83.0 |
| 3 | 2.04 m | 27.1 | 1.86 m | 23.9 |
| 1.79 m | 1.74 m | |||
| 4 | 2.05 m | 31.7 | 2.11 td (4.8, 16.8) | 31.3 |
| 2.02 m | ||||
| 5 | 127.3 | 127.1 | ||
| 6 | 137.3 | 137.5 | ||
| 7 | 2.15 dt (4.5, 13.0) | 26.0 | 2.21 dt (4.8, 12.0) | 26.1 |
| 2.00 m | 1.98 m | |||
| 8 | 1.51 m | 40.7 | 1.53 m | 40.8 |
| 9 | 3.72 m | 69.2 | 3.73 m | 69.2 |
| 10 | 1.18 d (6.0) | 23.3 | 1.19 d (6.6) | 23.3 |
| 11 | 1.15 s | 22.5 | 1.14 s | 22.7 |
| 12 | 1.05 s | 26.4 | 1.04 s | 26.7 |
| 13 | 1.61 s | 19.7 | 1.64 s | 19.7 |
| Glu1 | 4.35 d (8.0) | 106.6 | 4.36 d (7.8) | 101.8 |
| Glu2 | 3.22 t (8.0) | 75.7 | 3.22 dd (7.8, 9.0) | 75.1 |
| Glu3 | 3.36 m | 78.3 | 3.39 t (9.0) | 78.3 |
| Glu4 | 3.28 m | 71.7 | 3.31 t (9.0) | 71.9 |
| Glu5 | 3.26 m | 77.7 | 3.26 m | 77.8 |
| Glu6 | 3.86 dd (2.0, 11.5) | 62.8 | 3.88 dd (1.8, 11.4) | 63.0 |
| 3.68 dd (5.5, 11.5) | 3.69 dd (6.0, 11.4) | |||
| Comp. Name | H1N1 | H9N2 | H1N1 (wt) | H274Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO | 100 ± 2.69 | 100 ± 0.62 | 100 ± 1.04 | 100 ± 6.51 |
| Oseltamivir (100 nM) | 49.90 ± 3.74 | 10.79 ± 0.18 | 38.57 ± 4.32 | 91.10 ± 4.07 |
| Comp. 24 (5 μM) | 75.93 ± 1.17 | 64.19 ± 1.92 | 87.33 ± 1.67 | 76.73 ± 1.59 |
| Comp. 24 (10 μM) | 62.55 ± 0.94 | 49.79 ± 1.74 | 76.23 ± 2.67 | 72.38 ± 6.96 |
| Comp. 24 (20 μM) | 48.40 ± 1.35 | 35.34 ± 0.97 | 58.76 ± 1.85 | 57.22 ± 1.11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, T.K.Q.; Lee, B.W.; Nguyen, N.H.; Cho, H.M.; Venkatesan, T.; Doan, T.P.; Kim, E.; Oh, W.K. Antiviral Activities of Compounds Isolated from Pinus densiflora (Pine Tree) against the Influenza A Virus. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050711
Ha TKQ, Lee BW, Nguyen NH, Cho HM, Venkatesan T, Doan TP, Kim E, Oh WK. Antiviral Activities of Compounds Isolated from Pinus densiflora (Pine Tree) against the Influenza A Virus. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(5):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050711
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Thi Kim Quy, Ba Wool Lee, Ngoc Hieu Nguyen, Hyo Moon Cho, Thamizhiniyan Venkatesan, Thi Phuong Doan, Eunhee Kim, and Won Keun Oh. 2020. "Antiviral Activities of Compounds Isolated from Pinus densiflora (Pine Tree) against the Influenza A Virus" Biomolecules 10, no. 5: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050711
APA StyleHa, T. K. Q., Lee, B. W., Nguyen, N. H., Cho, H. M., Venkatesan, T., Doan, T. P., Kim, E., & Oh, W. K. (2020). Antiviral Activities of Compounds Isolated from Pinus densiflora (Pine Tree) against the Influenza A Virus. Biomolecules, 10(5), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050711