Abstract
Prostaglandin (PG) A2, one of cyclopentenone PGs, is known to induce activation of apoptosis in various cancer cells. Although PGA2 has been reported to cause activation of apoptosis by altering the expression of apoptosis-related genes, the role of p53, one of the most critical pro-apoptotic genes, on PGA2-induced apoptosis has not been clarified yet. To address this issue, we compared the apoptosis in HCT116 p53 null cells (HCT116 p53-/-) to that in HCT116 cells containing the wild type p53 gene. Cell death induced by PGA2 was associated with phosphorylation of histone H2A variant H2AX (H2AX), activation of caspase-3 and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 in HCT116 cells. Induction of apoptosis in PGA2-treated cells was almost completely prevented by pretreatment with a pan-caspase inhibitor, z-VAD-Fmk, or an inhibitor of protein synthesis, cycloheximide. While PGA2 induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells, phosphorylation of p53 and transcriptional induction of p53-target genes such as p21WAF1, PUMA, BAX, NOXA, and DR5 occurred. Besides, pretreatment of pifithrin-α (PFT-α), a chemical inhibitor of p53’s transcriptional activity, interfered with the induction of apoptosis in PGA2-treated HCT116 cells. Pretreatment of NU7441, a small molecule inhibitor of DNA-activated protein kinase (DNA-PK) suppressed PGA2-induced phosphorylation of p53 and apoptosis as well. Moreover, among target genes of p53, knockdown of DR5 expression by RNA interference, suppressed PGA2-induced apoptosis. In the meanwhile, in HCT116 p53-/- cells, PGA2 induced apoptosis in delayed time points and with less potency. Delayed apoptosis by PGA2 in HCT116 p53-/- cells was also associated with phosphorylation of H2AX but was not inhibited by either PFT-α or NU7441. Collectively, these results suggest the following. PGA2 may induce p53-dependent apoptosis in which DNA-PK activates p53, and DR5, a transcriptional target of p53, plays a pivotal role in HCT116 cells. In contrast to apoptosis in HCT116 cells, PGA2 may induce apoptosis in a fashion of less potency, which is independent of p53 and DNA-PK in HCT116 p53-/- cells
1. Introduction
Tumor suppressor gene, p53, which is one of the most crucial tumor suppressor genes, exerts its anti-cancer effect by activating cell death, including apoptosis and autophagic cell death, as well as cell cycle arrest in cancer cells [1]. Apoptosis induced by p53 is carried out by apoptosis-relating proteins whose expression is modulated by p53. Besides, p53 can induce apoptosis by directly stimulating cytochrome c release from mitochondria through its mitochondrial translocation [2,3,4]. The intracellular level of p53 protein is negatively regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). In the basal state, p53 is ubiquitinylated by MDM2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, and then degraded in the 26S proteasome, thereby keeping the level of p53 protein at the minimum. On the other hand, genotoxic stresses such as gamma-irradiation, ultraviolet (UV) light, and oxidative stress, increase the level of p53 protein via protein kinase cascade phosphorylating p53. Since phosphorylated p53 does not bind to MDM2, p53 escapes from UPS, resulting in the upregulation of p53 protein [5,6]. Increased p53, in turn, stimulates the transcription of numerous genes, including PUMA, NOXA, and BAX which can trigger apoptosis as well as p21WAF1, an inhibitor of CDK4/6, and CDK2, which blocks the cell cycle progression in late G1 phase. The p53 gene is mutated in over 50% of all human cancers, and the introduction of intact p53 in cancer cells containing mutant p53 induces growth suppression and apoptosis. Therefore, p53 is considered as the most critical transcription factor that induces apoptosis in cancer cells, which is reflected by the fact that most anti-cancer therapeutics, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy, induce apoptosis by activating p53 [1,7].
Prostaglandin (PG) A2, one of cyclopentenone PGs (cyPGs), is produced from PGE2 by non-enzymatic dehydration. In contrast to PGE2, which acts through its cognate receptor in the cytoplasmic membrane [8,9], PGA2 directly transports to the nucleus, where it induces de novo synthesis of proteins on which the biological functions of PGA2 are dependent [8]. Many research groups have reported that PGA2 affects various biological processes such as differentiation of leukemic cells, cell cycle progression and induction of apoptosis in various cancer cell lines, including hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, cervical cancer, and leukemia [10,11,12,13]. Treatment of PGA2 activates apoptosis both in caspase-dependent and -independent manners by modulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins. For example, PGA2 induces the expression of BAX in MCF-7 cells [14] and SOX-4 and c-MYC in Hep3B cells, and these proteins were critical in inducing apoptosis [15,16].
However, the role of p53 in the PGA2-induced apoptosis in cancer cells has not been elucidated yet. In hepatoma cells, PGA2 increased p53 protein during the induction of apoptosis and 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 (15d-PGJ2) activated p53 via ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) activation, suggesting that PGA2-induced apoptosis may be mediated by p53 [15,17]. On the contrary to these reports, it has been reported that PGA2 and 15d-PGJ2 inhibit the transcriptional activity of p53 through their direct binding to p53 resulting in conformational changes of p53 [18,19].
Recently, we have reported that PGA2 hinders cell cycle progression by activating the transcription of GADD45a and HO-1, which was initiated by oxidative stress [20]. Furthermore, we observed that inhibition of p53’s transcriptional activity prevented the expression of HO-1, and PGA2 treatment in cancer cells led to phosphorylation of p53, via activation of DNA-PK [21]. These findings strongly suggest the possibility that PGA2 may induce apoptosis via activation of p53. To address this issue, we analyzed whether PGA2 induces the activation of p53 during the induction of apoptosis by comparing the level of apoptosis between HCT116 cells containing the wild-typep53 gene and HCT116 p53 null isogenic (HCT116 p53 -/-) cells. Besides, the molecular mechanism involved in PGA2-induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells was investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Prostaglandin A2 was obtained from Biomol International Inc. (Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA). Pifithrin-α (PFT-α), cycloheximide (CHX) and z-VAD-Fmk were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Inc. (St. Louis, MO, USA). NU7441 was from Tocris Bioscience (Bristol, UK). All reagents used in this study were of molecular biology, or cell culture tested grade.
2.2. Cell Culture
Human colorectal HCT116 cells obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) (Manassas, VA, USA) were maintained in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA), 100 units/mL penicillin (Hyclone) and glutamate (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) at 37 °C under 5% CO2. The subculture of cells or replacement of media was done every three days.
2.3. Cell Death Assay
Cell death induced by PGA2 was assessed by annexin V assay. After PGA2 treatment, cells were stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled annexin V to measure the translocation of phosphatidylserine from inner leaflets to outer leaflets in the cytoplasmic membranes and propidium iodide to detect necrotic nuclei using Annexin V apoptosis assay kit (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). Then, fluorescence of stained cells was measured on FACSCanto II (BD Biosciences) and analyzed using BD FACSDiva program.
2.4. Immunoblot Analysis
For the detection of changes in the expression of proteins in PGA2-treated cells, cells were lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer containing cocktails of protease inhibitors (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) and phosphatase inhibitors (FIVEphoton Biochemicals, San Diego, CA). All antibodies were commercially available as follows. Rabbit anti-p53, anti-phospho-p53 (Ser-15), DR5 (death receptor 5), and anti-active caspase-3 were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Boston, MA, USA). Rabbit cleaved PARP1 (c-PARP1) and chicken anti-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) antibodies were obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, UK) and Merck Millipore Korea (Seoul, Korea), respectively. Peroxidase-conjugated antibodies (HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit or -mouse IgG) were from Sigma-Aldrich Inc., and KPL (Gaithersburg, MD, USA, HRP-conjugated anti-chicken IgG).
2.5. Quantitative Real Time Polymerase-Chain Reaction
For the analysis of the mRNA level of target genes of p53 in PGA2-treated cells, quantitative real time polymerase-chain reaction (qPCR) was performed as follows. First-strand cDNA was synthesized from total RNA using PrimeScriptTM RT reagent Kit (Takara Korea Biomedical Inc., Seoul, Korea). First-strand cDNA was then amplified by specific primers against target genes of p53 using SYBR FAST qPCR Kit (KAPAbiosystems, Woburn, MA, USA) on ABI 7300 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA). GAPDH mRNA level normalized each mRNA level of p53-target genes in the same sample and their relative changes among samples were calculated by the ΔΔCt method [22].
2.6. Transfection of Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
For the knockdown of DR5 expression, siRNA against DR5 was transfected into HCT116 cells using LipofectamineTM RNAiMAX Transfection reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The final concentration of DR5 siRNA was 1 nM, and the volume of transfection reagent was 3 µL.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All data in this study are expressed as the means standard error of the mean, which were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical analysis was performed using a paired Student’s t-test. P-values of data were indicated in each figure.
3. Results
3.1. PGA2 Induces Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in HCT116 Cells But Not in HCT116 p53-/- Cells
First, we attempted to observe the difference in the level of apoptosis between HCT116 cells and HCT116 p53-/- cells treated with PGA2. As shown in Figure 1A,B, and Figure S1A–C, annexin V-positive HCT116 cells were increased according to concentrations and incubation times of PGA2, but in HCT116 p53-/- cells treated with PGA2, annexin V-positive cells were hardly increased. To be consistent with the result of annexin V assay, PGA2 induced cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) and caspase-3 only in HCT116 cells (Figure 1C). Moreover, when HCT116 cells were pretreated by z-VAD-Fmk, a pan-caspase inhibitor, PGA2-induced apoptosis was almost wholly prevented (Figure 1D,E). Collectively, these data suggested that PGA2 induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in a p53-dependent manner in HCT116 cells.

Figure 1.
Comparison of PGA2-induced apoptosis between HCT116 cells (p53 +/+) and HCT116 p53 null cells (p53 -/-). (A) Cells were seeded at a density of 4 x 105 cells/well and treated with indicated concentrations of PGA2 the next day. After 12 h post-treatment, cells were stained with annexin V and propidium iodide, which were subjected to flow cytometric analysis. The result is representative of three independent experiments. (B) The result of three independent annexin V assay performed in (A) was presented as mean standard error of the mean (SEM). (C) Whole cell lysates (WCL) of two cell lines treated the same as described in (A) were subjected to immunoblot analysis against cleaved PARP1 (c-PARP1), cleaved caspase-3 (c-Caspase-3), and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) which was used as an internal reference protein for normalization. (D) HCT116 cells were pretreated with z-VAD-Fmk for 1 h and treated with PGA2 (15 µg/mL) for another 12 h. Cells were then subjected to annexin V assay. The result is representative of three independent experiments. (E) The result of three independent annexin V assay performed in (D) was presented as mean SEM.
3.2. PGA2 Activates p53 via DNA-PK during the Induction of Apoptosis in HCT116 cells
Then, we analyzed whether and how p53 was activated in HCT116 cells during the PGA2-induced apoptosis. Whereas HCT116 p53-/- cells showed no expression of p53, p53 was phosphorylated at Ser-15 and at Ser-46 by PGA2 treatment in HCT116 cells, and the extent of p53 phosphorylation was increased in parallel with concentrations of PGA2 (Figure 2A, Supplementary S2). Notably, the protein level of p53 was also increased in the same pattern with that of p53 phosphorylation, implying that phosphorylation of p53 protein may result in its stabilization.
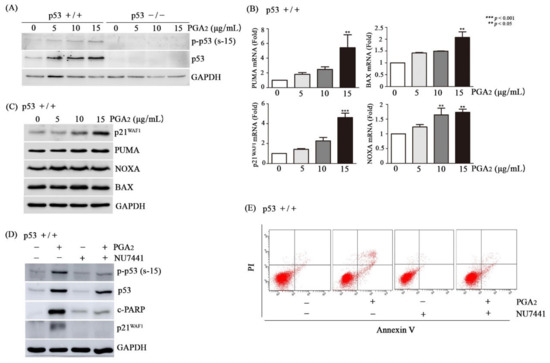
Figure 2.
Activation of p53 by DNA-PK in PGA2-treated HCT116 cells. (A) HCT116 cells (p53 +/+) and HCT116 p53 null cells (p53 -/-) were treated with indicated concentrations of PGA2. After 12 h, WCLs were subjected to immunoblot analysis against phospho-p53 [Ser-15, p-p53 (s-15)], p53, and GAPDH as an internal reference protein. (B) Total cellular RNA of HCT116 cells treated with indicated concentrations of PGA2 for 12 h were subjected to qPCR against indicated genes using GADPH as an internal reference gene for normalization. (C) HCT116 cells treated the same as described in (B) were subjected to immunoblot analysis against indicated proteins using GADPH as an internal reference protein. (D) HCT116 cells were treated with vehicle or NU7441, an inhibitor of DNA-PK, for 1 h and were incubated in the absence or presence of PGA2 (15 µg/mL) for another 18 h. Cells were then subjected to immunoblot analysis against phospho-p53 (Ser-15), p53, p21WAF1, cleaved PARP1 (c-PARP1), and cleaved caspase-3 (c-Caspase-3) using GAPDH as an internal reference protein. (E) HCT116 cells treated the same as described in (D) were subjected to annexin V assay. The result is representative of three independent experiments.
Transcripts of p53’s target genes such as PUMA, BAX, p21WAF1, and NOXA were augmented by PGA2 treatment in HCT116 cells but not in HCT116 p53-/- cells, suggesting that PGA2 should increase transcriptional activity of p53 by phosphorylating it (Figure 2B, Figure S3A). Messenger RNAs of p21WAF1 and NOXA showed an increasing tendency in PGA2–treated HCT116 p53 -/- cells, implying p53-independent gene expression by PGA2. However, pifithrin (PFT)-α, a chemical inhibitor of p53’s transcriptional activity, prevented the increase of p21WAF1 and NOXA mRNAs in HCT116 cells, but not in HCT116 p53 -/- cells (Figure S3B). It was reported that PGA2 can increase the level of p21WAF1 mRNA via HuR-mediated stabilization of p21WAF1 mRNA in the absence of p53 [23]. In addition, it was shown that transcription factors such as SP1, p73, ATF3 and ATF4 can activate transcription of NOXA without involvement of p53 [24,25]. So, it can be speculated that PGA2 activates p53-dependent transcription in HCT116 cells, and PGA2 also increases of p21WAF1 and NOXA mRNAs in HCT116 p53-/- cells through mRNA stabilization and activation of various transcription factors. The increase of p21WAF1, PUMA, and NOXA expression was also observed at the level of protein (Figure 2C, Figure S4). While multiple protein kinases including HIPK-2, p38MAPK, PKC-δ, and DYRK2 phosphorylate p53 at Ser-46, enzymes involved in DNA damage response such as DNA-PK, ATM, and ATR, phosphorylate p53 at Ser-15 [26,27]. Since phosphorylation of p53 Ser-46 is very subtle and PGA2 was reported to activate DNA-PK [21], DNA-PK was suspected to be a principal enzyme to phosphorylate p53 Ser-15 and induce apoptosis. And as expected, NU7441, an inhibitor of DNA-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) prevented PGA2-induced phosphorylation of p53 and increase of p21WAF1 protein (Figure 2D), demonstrating a causative role of DNA-PK in activation of p53. To be consistent with its effect on PGA2-induced transcriptional activity of p53, NU7441 suppressed PGA2-induced apoptotic findings such as cleavage of PARP1 and increase of annexin V-positive cells as well (Figure 2D,E). NU7441 showed no effect on survival of HCT116 p53-/- cells (Figure S5). Accordingly, these data suggested that PGA2 may activate p53 via inducing DNA-PKcs activity, which plays a critical role in PGA2-induced apoptosis.
3.3. PGA2-Induced Apoptosis Was Dependent on the Transcriptional Activity of p53
Activation of p53 induces apoptosis in a manner of both dependent on and independent of its transcriptional activity in which these two pathways are not mutually exclusive [1,28]. Then, we attempted to determine whether the effect of p53 was exerted via transcriptional regulation of apoptotic genes or via its effect on the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in PGA2-induced apoptosis. As shown in Figure 3A,B, and Figure S1D, PGA2-induced apoptosis was gradually decreased according to concentrations of PFT-α. Consistently with these findings, cleavage of PARP1 and caspase-3 was reduced, but phosphorylation of p53 was marginally affected, indicating that the caspase activation cascade was downstream of p53 activation (Figure 3C). Considering that pretreatment of PFT-α reduced expression of PGA2-induced p21WAF1, the inhibitory effect of PFT-α on PGA2-induced apoptosis must be due to its inhibitory effect against the transcriptional activity of p53 (Figure 3C). Besides, p53 did not move to mitochondria and, instead, was accumulated in cytosol (Figure S6A). Furthermore, phosphorylated p53, which has transcriptional activity, was increased in the nuclear fraction (Figure S6B). Therefore, these results suggested that PGA2-induced apoptosis may be dependent on the transcriptional activity of p53 but not mitochondrial p53.
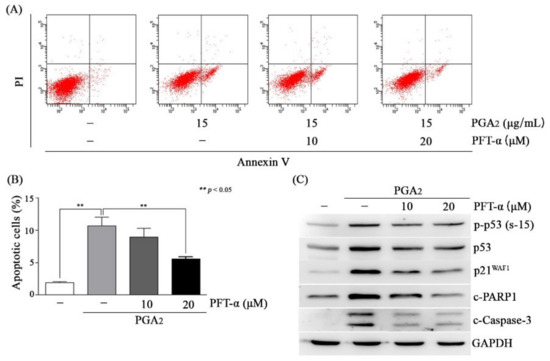
Figure 3.
The effect of pifithrin-α (PFT-α) on PGA2-induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells. (A,B) HCT116 cells treated with indicated concentrations of PFT-α for 1 h were incubated in the absence or presence of PGA2 (15 µg/mL) for another 18 h. Cells were then subjected to annexin V assay. The representative images and statistical analysis of three independent experiments were shown in (A) and (B), respectively. The result of three independent annexin V assay was presented as mean SEM. (C) Whole cell lysates (WCLs) were prepared and subjected to immunoblot analysis against indicated proteins using GAPDH as an internal reference protein.
3.4. PGA2-Induced Apoptosis Is Dependent on de novo Protein Synthesis of p53 Target Genes
Then, we speculated that proteins of p53 target genes might play a critical role in PGA2-induced apoptosis. To prove this speculation, we analyzed the effect of cycloheximide (CHX), an inhibitor of translation, on PGA2-induced apoptosis. Pretreatment of CHX prevented the induction of apoptosis by PGA2 (Figure S7A,B), and cleavage of both PARP1 and caspase-3 as well without an effect on phosphorylation of p53 (Figure S7C), implying the critical role of de novo proteins synthesized by p53 in this apoptosis model. Although PUMA and NOXA proteins were synthesized by p53, knockdown of PUMA and NOXA using siRNAs did not suppress PGA2-induced apoptosis (Figure S8). Not only pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins but also death receptor (DR) proteins such as DR4 (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10a, TNFRSF10A), DR5 (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10b, TNFRSF10B), and FAS (Fas cell surface death receptor) are involved in the induction of p53-induced apoptosis [29,30]. Among death receptors, DR5 but neither DR4 nor FAS was significantly increased at the level of protein by PGA2, which was accompanied by phosphorylation of p53, an increase of p21WAF1 protein, and cleavage of both PARP1 and caspase-3 (Figure 4A). In the reporter-luciferase gene assay, the promoter activity of DR5 gene was upregulated by PGA2 treatment in HCT116 cells but not in HCT116 p53-/- cells, which was suppressed by pretreatment with PFT-α, indicating an increase of DR5 expression at the level of transcription by PGA2-induced transcriptional activity of p53 (Figure 4E).
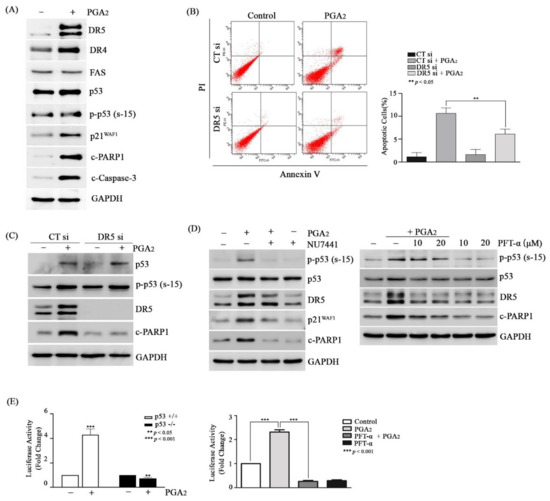
Figure 4.
The effect of DR5 on PGA2-induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells. (A) HCT116 cells were treated with PGA2 (15 µg/mL). After 18 h, WCLs were subjected to immunoblot analysis against indicated proteins using GAPDH as an internal reference protein. (B) HCT116 cells were transfected with scrambled RNA or siRNA targeting DR5 for 24 h and incubated in the presence of vehicle or PGA2 (15 µg/ml) for an additional 18 h. Cells were harvested and subjected to annexin V assay. The representative images (left) and statistical analysis (right) of three independent experiments were shown, respectively. The result of three independent annexin V assay was presented as mean SEM. (C) WCLs of HCT116 cells treated the same as described in (B) were subjected to immunoblot analysis against indicated proteins using GAPDH as an internal reference protein. (D) HCT116 cells treated with Nu-7441 (left) or PFT-α (right) for 1 h were incubated in the presence of vehicle or PGA2 (15 µg/ml) for another 18 h. WCLs were subjected to immunoblot analysis against indicated proteins using GADPH as an internal reference protein. (E) (left) After DR5 promoter-luciferase construct (pGL3-DR5) was transfected into HCT116 cells and HCT116 p53-/- cells along with renilla luciferase for 24 h, HCT116 cells were treated with vehicle or PGA2 (15 µg/mL). (right) After DR5 promoter-luciferase construct (pGL3-DR5) was transfected into HCT116 cells along with renilla luciferase for 24 h, HCT116 cells were treated with vehicle or PFT-α (20 µM) for 1 h and were incubated in the absence or presence of PGA2 (15 µg/mL). At 18 h post-treatment of PGA2, firefly luciferase activity of DR5 promoter was measured by Dual luciferase assay method using renilla luciferase activity as the normalizer.
Supporting the result of reporter gene assay, expression of DR5 mRNA was increased by PGA2 treatment, and this increase was alleviated by PFT-α pretreatment (Figure S9). Notably, knockdown of DR5 expression using siRNA suppressed both an increase of annexin V-positive cells (Figure 4B) and cleavage of PARP1 (Figure 4C) in PGA2-treated cells. Moreover, both NU7441 and PFT-α, which suppressed PGA2-induced apoptosis, prevented the expression of DR5 as well as cleavage of PARP1 (Figure 4D). Collectively, these data suggested that DR5 upregulated by p53 plays a pivotal role in PGA2-induced apoptosis.
4. Discussion
The results of this study can be, collectively, summarized that PGA2 induces the activation of p53 in HCT116 cells via DNA-PK, and p53, in turn, upregulates the expression of DR5 at the level of transcription, which finally leads to caspase-dependent apoptosis.
In this study, how PGA2 increases the activity of DNA-PKcs was not clarified. The activation of DNA-PKcs occurs through multiple pathways [31]. DNA-PKcs is primarily activated in response to the damaged DNA via interaction with Ku70 and Ku80 proteins, which are recruited to the end of broken DNA. DNA-PKcs is also activated through protein kinases such as AKT and casein kinase II even in the absence of DNA damage. In the previous report, PGA2-induced DNA-PKcs activity was owing to reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced DNA damage [21]. However, 15d-PGJ2, another cyclopentenone PG, induced activation of ATM, a protein kinase responsible for breakage of double stranded DNA, by direct interaction with ATM at cysteine residues, resulting in activation of ATM [32]. So, it may be possible that PGA2 induces activation of DNA-PKcs through damaging DNA via ROS accumulation and physical interaction with DNA-PKcs as well. To identify the involvement of DNA damage in PGA2-induced apoptosis, phosphorylation of histone H2A variant H2AX at Ser-139 (γ-H2AX), which is a sensitive marker of DNA damage [33], was detected by immunoblot analysis. As shown in Figure S10A, PGA2 treatment increased γ-H2AX remarkably, indicating that DNA damage occurred in PGA2-treated cells. Besides, pretreatment of PFT-α did not affect the level of γ-H2AX, while it reduced the level of cleaved PARP1 (Figure S10A, Figure 4D). Moreover, PGA2 treatment increased γ-H2AX in HCT116 p53-/- cells as well, which was not suppressed by either PFT-α or NU7441 (Figure S10B). Therefore, it can be speculated that activation of DNA-PK may be due to damaged DNA, and both DNA damage and hence activation of DNA-PK occur upstream of p53 activation and induction of apoptosis.
Many target genes of p53 are involved in apoptosis [29,30,31,34]. As shown in Figure S11, mRNA levels of p53 target genes that were reported to induce apoptosis including FAS and FAS ligand (Fas-L) in PGA2-treated cells were not significantly increased by PGA2 treatment. So, it seems that in HCT116 cells, PGA2-activated p53 induces expression of limited numbers of pro-apoptotic genes such as BAX, PUMA, NOXA, and DR5. Therefore, DNA-PK-p53-DR5 pathway might be a sole apoptosis-activating mechanism for PGA2-induced apoptosis in HCT116, although transcriptional target genes of p53 involved in apoptosis were not investigated at the level of transcriptome in this study, and thus the possibility of involvement of (a) novel gene(s) still remains. It is not clarified in this study how DNA-PK/p53 activation leads to specific transcriptional induction of DR5. Based on the report of Woo et al, it can be speculated that DNA-PK activation is necessary but not sufficient for p53-mediated DR5 transcription [35]. When HCT116 cells were treated with nutlin-3, an inhibitor of MDM2, which does not activate DNA-PK, p53 target genes were induced (Figure S12) and moreover, transcription of DR5 was turned out to increase through stabilized p53 [36]. Thus, DNA-PK activity seems to be necessary for stabilization of p53 but not binding of p53 protein to p53 response element in promoter region of target genes.
Active p53 protein can affect both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis by upregulating the expression of several genes of each pathway or physical interaction with mitochondria [28]. Although it is not clear if p53 affect the intrinsic apoptosis or the extrinsic apoptosis at this point in PGA2-induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells, considering no attenuating effect of siRNAs against PUMA and NOXA on PGA2-induced apoptosis (Figure S8) and no release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into cytosol (Figure S13) leads to the speculation that PGA2-induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells may occur through the extrinsic apoptotic pathway which is activated by upregulated DR5.
Several reports have demonstrated that PGA2 inhibits the growth and induce cell death in cancer cells [8,37]. Although the growth inhibitory pathway and apoptotic pathway induced by PGA2 are all dependent on de novo protein synthesis, their relationship is not clearly established. In this study, PGA2 induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells containing wild-type p53 gene to a much higher extent than that in HCT116 p53-/- cells. However, surprisingly, PGA2 inhibited the growth of both HCT116 cells and HCT116 p53-/- cells to similar extent in a dose-dependent manner by CCK-8 assay which detects live cells (Figure S14). In cell cycle distribution analysis, PGA2 induced G2M arrest in both cell lines, but accumulated sub-G1 apoptotic cells, only in HCT116 cells (Figure S15). Therefore, the growth inhibitory effect of PGA2 may be exerted through both p53-dependent and –independent manners in HCT116 cells, although PGA2-induced apoptosis was dependent on p53 in HCT116 cells. Based on the result that PGA2 induced G2M arrest at higher level in HCT116 p53 -/- cells than in HCT116 cell, it can be assumed that PGA2 might activate stronger cell cycle arrest in HCT116 p53 -/- cells than that in HCT116 cells or PGA2 might activate p53-independent growth inhibitory mechanism in HCT116 p53 -/- cells, finally resulting in similar CCK-8 results.
Besides, PGA2 has also been reported to induce apoptosis in HL-60 cells and Hep3B cells whose p53 is deleted or mutated [11,15]. So, the dependency of PGA2-induced apoptosis on p53 may not be applied for all cell types. In HL-60 cells, PGA2 induced intrinsic apoptosis by direct interaction with mitochondria without the involvement of de novo protein synthesis. In Hep3B cells, PGA2 induced apoptosis via up-regulation of SOX-4, suggesting that PGA2 can induce apoptosis via multiple pathways according to cellular contexts. Interestingly, PGA2 induced apoptosis in HepG2 and Hep3B cells in a caspase-independent manner. Therefore, these reports suggested that PGA2 induces apoptosis via the combinatorial pathways composed of caspase and new protein synthesis. The involvement of caspase activity may be determined by the proteins induced by PGA2.
Since cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) which synthesizes PGE2 is highly expressed in many types of cancer, PGE2 is elevated in cancer tissues. PGE2 secreted from cancer tissues increases cancer cell survival, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis, playing a promoting role in carcinogenesis and immunosuppression in microenvironment around cancers [38,39]. Thus, COX-2/PGE2 axis has been proposed as a therapeutic target in cancer treatment [40]. In the meanwhile, PGA2 which is produced from PGE2 by non-enzymatic dehydration, shows opposite effects to those of PGE2 against cancers, proposing PGA2 as a therapeutic molecule for cancer treatment [41]. So, it can be speculated that the relative amount between PGE2 and PGA2 in tumor microenvironment may contribute to the determination of the efficacy of both anti-cancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy, the effect of which is dependent on p53 activity. Therefore, the genetic information of cancer tissues should be integrated with profiles of inflammatory cytokines, including PGE2 and PGA2 in tumor microenvironment to maximize the effects of anti-cancer therapeutics in the future.
5. Conclusions
Treatment of PGA2 induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in HCT116 cells containing wild type p53 gene, but not in HCT116 p53-/- cells which are deficient in functional p53. Activation of p53 by PGA2 in HCT116 cells was dependent on the activity of DNA-PKcs. Among transcriptional target genes of p53, DR5 was responsible for the induction of apoptosis in PGA2-treated cells. PGA2 increases the expression of DR5 at the level of transcription via p53 activity. Therefore, PGA2 induces p53-dependent apoptosis by activating DNA-PKcs-p53-DR5 pathway in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/10/3/492/s1, Figure S1: Induction of apoptosis by PGA2 in HCT116 cells. Figure S2: Phosphorylation of p53 at Ser-46 by PGA2. Figure S3: Measurement of p53 target genes. Figure S4: Densitometric analysis of p53 target genes. Figure S5: The effect of NU7441 on survival of HCT116 p53-/- cells. Figure S6: The subcellular localization of p53 expression in PGA2-treated cells. Figure S7: The effect of CHX on the PGA2-induced apoptosis in HCT116 cells. Figure S8: The effect of knockdown of PUMA and NOXA expression on PGA2-induced apoptosis. Figure S9: The effect of PFT-α on the PGA2-induced increase of DR5 mRNA. Figure S10: Phosphorylation of histone H2AX by PGA2. Figure S11: Measurement of pro-apoptotic p53 target genes in PGA2-treated cells. Figure S12: Induction of p53 target genes by nutlin-3. Figure S13: Analysis of cytochrome c release in PGA2-treated cells. Figure S14: The effect of PGA2 on the growth of HCT116 cells and HCT116 p53-/- cells. Figure S15: The effect of PGA2 on the distribution of cell cycle of HCT116 cells and HCT116 p53-/- cells.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-B.L., S.-Y.L., and H.-S.K.; methodology, S.-B.L., S.-Y.L., and H.-S.K.; data acquisition, S.-B.L., and S.L.; formal analysis, S.-B.L., S.L., J.-Y.P., S.-Y.L., and H.-S.K.; investigation, S.-B.L., S.-Y.L., and H.-S.K.; data curation, S.-B.L., S.-Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-B.L., S.-Y.L., and H.-S.K.; writing—review and editing, S.-Y.L., and H.-S.K.; supervision, H.-S.K.; project administration, S.-Y.L., and H.-S.K.,; funding acquisition, S.-Y.L., and H.-S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded (NRF-2016R1A6A3A01010433 to S.-Y.L., NRF-2016R1D1A1B03934999 and 2019R1A5A2027588 to H.-S.K).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Taeg Kyu Kwon (Department of Immunology, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Republic of Korea) for providing DR5 promoter-reporter gene construct.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding this study and publication.
References
- Aubrey, B.J.; Kelly, G.L.; Janic, A.; Herold, M.J.; Strasser, A. How does p53 induce apoptosis and how does this relate to p53-mediated tumour suppression? Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchenko, N.D.; Moll, U.M. Mitochondrial death functions of p53. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 1, e955995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, U.M.; Zaika, A. Nuclear and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways of p53. FEBS Lett. 2001, 493, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Erster, S.; Zaika, A.; Petrenko, O.; Chittenden, T.; Pancoska, P.; Moll, U.M. p53 has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, F.; Wahl, G.M. Regulating the p53 pathway: In vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, U.M.; Petrenko, O. The MDM2-p53 Interaction. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the p53 network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubich, A.I.; Sholukh, M.V. Biochemistry of prostaglandins A. Biochemistry 2006, 71, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Q. Prostaglandin EP2 receptor: Novel therapeutic target for human cancers (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, A.M.; Panzer, A.; Bianchi, P.C.; Lottering, M.L. The effects of prostaglandin A2 on cell growth, cell cycle status and apoptosis induction in HeLa and MCF-7 cells. Cancer Lett. 2003, 191, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Rhim, H.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, I.K. Induction of apoptosis dependent on caspase activities and growth arrest in HL-60 cells by PGA2. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002, 70, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Shim, J.C.; Choi, J.Y.; Rhim, H.; Kim, I.K. Prostaglandin A2 induces caspase-independent apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Korean J. Hepatol. 2005, 11, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.K.; Lee, J.H.; Sohn, H.W.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.H. Prostaglandin A2 and delta 12-prostaglandin J2 induce apoptosis in L1210 cells. FEBS Lett. 1993, 321, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, A.; Bianchi, P.; Maritz, C.; Joubert, F. Influence of prostaglandin A2 on Bax, Bcl-2 and PCNA expression in MCF-7 cells. Biomed. Res. 2006, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahn, S.G.; Jeong, S.Y.; Rhim, H.; Kim, I.K. The role of c-Myc and heat shock protein 70 in human hepatocarcinoma Hep3B cells during apoptosis induced by prostaglandin A2/Delta12-prostaglandin J2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1448, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.G.; Kim, H.S.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, B.E.; Rhim, H.; Shim, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, I.K. Sox-4 is a positive regulator of Hep3B and HepG2 cells’ apoptosis induced by prostaglandin (PG)A(2) and delta(12)-PGJ(2). Exp. Mol. Med. 2002, 34, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, I.K. Induction of p53 and apoptosis by delta 12-PGJ2 in human hepatocarcinoma SK-HEP-1 cells. FEBS Lett. 1995, 368, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, P.J.; Edes, K.; Fitzpatrick, F.A. Inactivation of wild-type p53 tumor suppressor by electrophilic prostaglandins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9215–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullally, J.E.; Moos, P.J.; Edes, K.; Fitzpatrick, F.A. Cyclopentenone prostaglandins of the J series inhibit the ubiquitin isopeptidase activity of the proteasome pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30366–30373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, Y.-J.; Ko, K.-W.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, B.-C.; Kim, H.-S. PGA2-induced HO-1 attenuates G2M arrest by modulating GADD45α expression. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2016, 11, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, S.-S.; Park, J.-Y.; Choe, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-S. PGA2 induces the expression of HO-1 by activating p53 in HCT116 cells. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Fan, J.; Lal, A.; Yang, D.; Cheng, H.; Gorospe, M. Prostaglandin A2-mediated stabilization of p21 mRNA through an ERK-dependent pathway requiring the RNA-binding protein HuR. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 49298–49306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, L.; Bretones, G.; Rosa-Garrido, M.; Garrido-Martin, E.M.; Hernandez, T.; Fraile, S.; Botella, L.; de Alava, E.; Vidal, A.; Garcia del Muro, X.; et al. Transcription factors Sp1 and p73 control the expression of the proapoptotic protein NOXA in the response of testicular embryonal carcinoma cells to cisplatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26495–26505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Vu, T.T.; Cook, W.; Naseri, M.; Zhan, K.; Nakajima, W.; Harada, H. p53-independent Noxa induction by cisplatin is regulated by ATF3/ATF4 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazi, G.; Cecchinelli, B.; Bruno, T.; Manni, I.; Higashimoto, Y.; Saito, S.; Gostissa, M.; Coen, S.; Marchetti, A.; Del Sal, G.; et al. Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 phosphorylates p53 at Ser 46 and mediates apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogosawa, S.; Yoshida, K. Tumor suppressive role for kinases phosphorylating p53 in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3376–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Yoshida, K. Mechanical insights into the regulation of programmed cell death by p53 via mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Res. 2019, 1866, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.S.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Death and decoy receptors and p53-mediated apoptosis. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, K.M.; Bozza, W.P.; Alterovitz, W.L.; Zhang, B. Transcriptomic profiling reveals p53 as a key regulator of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, J.F.; Knudsen, K.E. Beyond DNA repair: DNA-PK function in cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ono, H.; Mihara, K.; Tauchi, H.; Komatsu, K.; Shibata, T.; Shimizu, H.; Uchida, K.; Yamamoto, K. ATM activation by a sulfhydryl-reactive inflammatory cyclopentenone prostaglandin. Genes Cells 2006, 11, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Zhang, Y.; Redon, C.E.; Reinhold, W.C.; Chen, A.P.; Fogli, L.K.; Holbeck, S.L.; Parchment, R.E.; Hollingshead, M.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; et al. Phosphorylated fraction of H2AX as a measurement for DNA damage in cancer cells and potential applications of a novel assay. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melino, G.; Vaux, D. p53 and Cell Death. In Cell Death; Wolyniec, K., Haupt, S., Haupt, Y., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 230–240. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, R.A.; McLure, K.G.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; Rancourt, D.E.; Lee, P.W. DNA-dependent protein kinase acts upstream of p53 in response to DNA damage. Nature 1998, 394, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, T.; Kondo, T.; Kanamori, M.; Tabuchi, Y.; Ogawa, R.; Zhao, Q.L.; Ahmed, K.; Yasuda, T.; Seki, S.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Nutlin-3 enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis through up-regulation of death receptor 5 (DR5) in human sarcoma HOS cells and human colon cancer HCT116 cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 287, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, J.; Alamo, I., Jr.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Genotoxic stress confers preferential and coordinate messenger RNA stability on the five gadd genes. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 5656–5662. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.B.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.S.; Park, I.; Kim, T.; Yang, S.Y.; Cho, C.J.; Hwang, D.; Jung, J.H.; Markowitz, S.D.; et al. Prostaglandin E2 Activates YAP and a Positive-Signaling Loop to Promote Colon Regeneration After Colitis but Also Carcinogenesis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prima, V.; Kaliberova, L.N.; Kaliberov, S.; Curiel, D.T.; Kusmartsev, S. COX2/mPGES1/PGE2 pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in tumor-associated macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.F.; Liu, T.Q.; Zhi, X.T.; Zou, J.; Zhong, J.T.; Li, T.; Mo, X.L.; Zhou, W.; Guo, W.W.; Liu, X.; et al. COX-2/PGE2 Axis Regulates HIF2alpha Activity to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Hypoxic Response and Reduce the Sensitivity of Sorafenib Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3204–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, S.H. The chemistry, biology and pharmacology of the cyclopentenone prostaglandins. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020, 148, 106408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).