Membrane Interaction of Ibuprofen with Cholesterol-Containing Lipid Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Large Unilamellar Vesicles
2.3. NMR Sample Preparation
2.4. Solid-State NMR Measurements
2.5. Measurement of Dithionite Permeation
2.6. Measurement of Ascorbate Permeation
2.7. Measurement of 6-Carboxyfluorescein Leakage
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, D.B. The effects of drugs on membrane fluidity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1984, 24, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Leite, C.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Interaction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with membranes: In vitro assessment and relevance for their biological actions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsop, R.J.; Armstrong, C.L.; Maqbool, A.; Toppozini, L.; Dies, H.; Rheinstadter, M.C. Cholesterol expels ibuprofen from the hydrophobic membrane core and stabilizes lamellar phases in lipid membranes containing ibuprofen. Soft. Matter 2015, 11, 4756–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaede, H.C.; Gawrisch, K. Multi-dimensional pulsed field gradient magic angle spinning NMR experiments on membranes. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2004, 42, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajeh, A.; Modarress, H. The influence of cholesterol on interactions and dynamics of ibuprofen in a lipid bilayer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, C.B.; Horton, R.A.; Harris, J.M. Detection of drug-membrane interactions in individual phospholipid vesicles by confocal Raman microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4918–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggara, M.B.; Mihailescu, M.; Krishnamoorti, R. Structural association of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with lipid membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19669–19676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberger, L.M.; Zhou, Y.; Jayaraman, V.; Doyen, J.R.; O’Neil, R.G.; Dial, E.J.; Volk, D.E.; Gorenstein, D.G.; Boggara, M.B.; Krishnamoorti, R. Insight into NSAID-induced membrane alterations, pathogenesis and therapeutics: Characterization of interaction of NSAIDs with phosphatidylcholine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Sendecki, A.M.; Pullanchery, S.; Huang, D.; Yang, T.; Cremer, P.S. Multistep Interactions between Ibuprofen and Lipid Membranes. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10782–10792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique-Moreno, M.; Heinbockel, L.; Suwalsky, M.; Garidel, P.; Brandenburg, K. Biophysical study of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) ibuprofen, naproxen and diclofenac with phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloncyova, M.; Berka, K.; Otyepka, M. Molecular insight into affinities of drugs and their metabolites to lipid bilayers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berka, K.; Hendrychova, T.; Anzenbacher, P.; Otyepka, M. Membrane position of ibuprofen agrees with suggested access path entrance to cytochrome P450 2C9 active site. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 11248–11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheidt, H.A.; Pampel, A.; Nissler, L.; Gebhardt, R.; Huster, D. Investigation of the membrane localization and distribution of flavonoids by high-resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1663, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheidt, H.A.; Huster, D. The interaction of small molecules with phospholipid membranes studied by 1H NOESY NMR under magic-angle spinning. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boggara, M.B.; Krishnamoorti, R. Small-angle neutron scattering studies of phospholipid-NSAID adducts. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5734–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, E. A study on the interaction between ibuprofen and bilyaer lipid membrane. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5754–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaksch, S.; Lipfert, F.; Koutsioubas, A.; Mattauch, S.; Holderer, O.; Ivanova, O.; Frielinghaus, H.; Hertrich, S.; Fischer, S.F.; Nickel, B. Influence of ibuprofen on phospholipid membranes. Phys. Rev. E. Stat. Nonlin. Soft. Matter Phys. 2015, 91, 022716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fellmann, P.; Zachowski, A.; Devaux, P.F. Synthesis and use of spin-labeled lipids for studies of the transmembrane movement of phospholipids. In Methods in Molecular Biology. Biomembrane Protocols: II. Architecture and Function; Graham, J.M., Higgins, J.A., Eds.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, L.D.; Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 858, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.H.; Jefferey, K.R.; Bloom, M.; Valic, M.I.; Higgs, T.P. Quadrupolar Echo Deuteron Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in ordered Hydrocarbon Chains. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1976, 42, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternin, E.; Bloom, M.; MacKay, A.L. De-Paking of NMR-Spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 1983, 55, 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Lafleur, M.; Fine, B.; Sternin, E.; Cullis, P.R.; Bloom, M. Smoothed orientational order profile of lipid bilayers by 2H-nuclear magnetic resonance. Biophys. J. 1989, 56, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volke, F.; Pampel, A. Membrane hydration and structure on a subnanometer scale as seen by high resolution solid state nuclear magnetic resonance: POPC and POPC/C12EO4 model membranes. Biophys. J. 1995, 68, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntyre, J.C.; Sleight, R.G. Fluorescence assay for phospholipid membrane asymmetry. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 11819–11827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomorski, T.; Herrmann, A.; Zachowski, A.; Devaux, P.F.; Muller, P. Rapid determination of the transbilayer distribution of NBD-phospholipids in erythrocyte membranes with dithionite. Mol. Membr. Biol. 1994, 11, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheidt, H.A.; Haralampiev, I.; Theisgen, S.; Schirbel, A.; Sbiera, S.; Huster, D.; Kroiss, M.; Muller, P. The adrenal specific toxicant mitotane directly interacts with lipid membranes and alters membrane properties depending on lipid composition. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 428, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralampiev, I.; Scheidt, H.A.; Abel, T.; Luckner, M.; Herrmann, A.; Huster, D.; Muller, P. The interaction of sorafenib and regorafenib with membranes is modulated by their lipid composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 2871–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greube, A.; Muller, K.; Topfer-Petersen, E.; Herrmann, A.; Muller, P. Influence of the bovine seminal plasma protein PDC-109 on the physical state of membranes. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 8326–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerklotz, H.; Tsamaloukas, A. Gradual change or phase transition: Characterizing fluid lipid-cholesterol membranes on the basis of thermal volume changes. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Scheidt, H.A.; Kaur, N.; Kaur, A.; Kang, T.S.; Huster, D.; Mithu, V.S. Amphiphilic Ionic Liquid-Induced Membrane Permeabilization: Binding Is Not Enough. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 6763–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, P.G.; Seelig, J. Electric Charge effects on Phospholipid Headgroups. Phosphatidcholine in Mixtures with Cationic and Anionic Amphiphiles. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 7720–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrache, H.I.; Dodd, S.W.; Brown, M.F. Area per lipid and acyl length distributions in fluid phosphatidylcholines determined by 2H-NMR spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 3172–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jablonowska, E.; Bilewicz, R. Interactions of ibuprofen with Langmuir monolayers of membrane lipids. Thin Solid Films 2006, 515, 3962–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrache, H.I.; Tu, K.; Nagle, J.F. Analysis of simulated NMR order parameters for lipid bilayer structure determination. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsop, R.J.; Toppozini, L.; Marquardt, D.; Kucerka, N.; Harroun, T.A.; Rheinstadter, M.C. Aspirin inhibits formation of cholesterol rafts in fluid lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manrique-Moreno, M.; Londoño-Londoño, J.; Jemioła-Rzemińska, M.; Strzałka, K.; Villena, F.; Avello, M.; Suwalsky, M. Structural effects of the Solanum steroids solasodine, diosgenin and solanine on human erythrocytes and molecular models of eukaryotic membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castano, S.; Desbat, B.; Dufourcq, J. Ideally amphipathic beta-sheeted peptides at interfaces: Structure, orientation, affinities for lipids and hemolytic activity of (KL)(m)K peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1463, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SDBSWeb. National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. Available online: https://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Stamm, H.; Jäckel, H. Relative ring-curruent effects based on a new model for aromatic-solvent-induced shifts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6544–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiullina, L.F.; Scheidt, H.A.; Huster, D.; Aganov, A.; Klochkov, V. Interaction of statins with phospholipid bilayers studied by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huster, D.; Arnold, K.; Gawrisch, K. Investigation of Lipid Organization in Biological Membranes by Two-Dimensional Nuclear Overhauser Enhancement Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidt, H.A.; Badeau, R.M.; Huster, D. Investigating the membrane orientation and transversal distribution of 17beta-estradiol in lipid membranes by solid-state NMR. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2010, 163, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siarheyeva, A.; Lopez, J.J.; Glaubitz, C. Localization of multidrug transporter substrates within model membranes. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 6203–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.H.; Ladokhin, A.S.; Jayasinghe, S.; Hristova, K. How Membranes Shape Protein Structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32395–32398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alsop, R.J.; Barrett, M.A.; Zheng, S.; Dies, H.; Rheinstadter, M.C. Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) increases the solubility of cholesterol when incorporated in lipid membranes. Soft. Matter 2014, 10, 4275–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
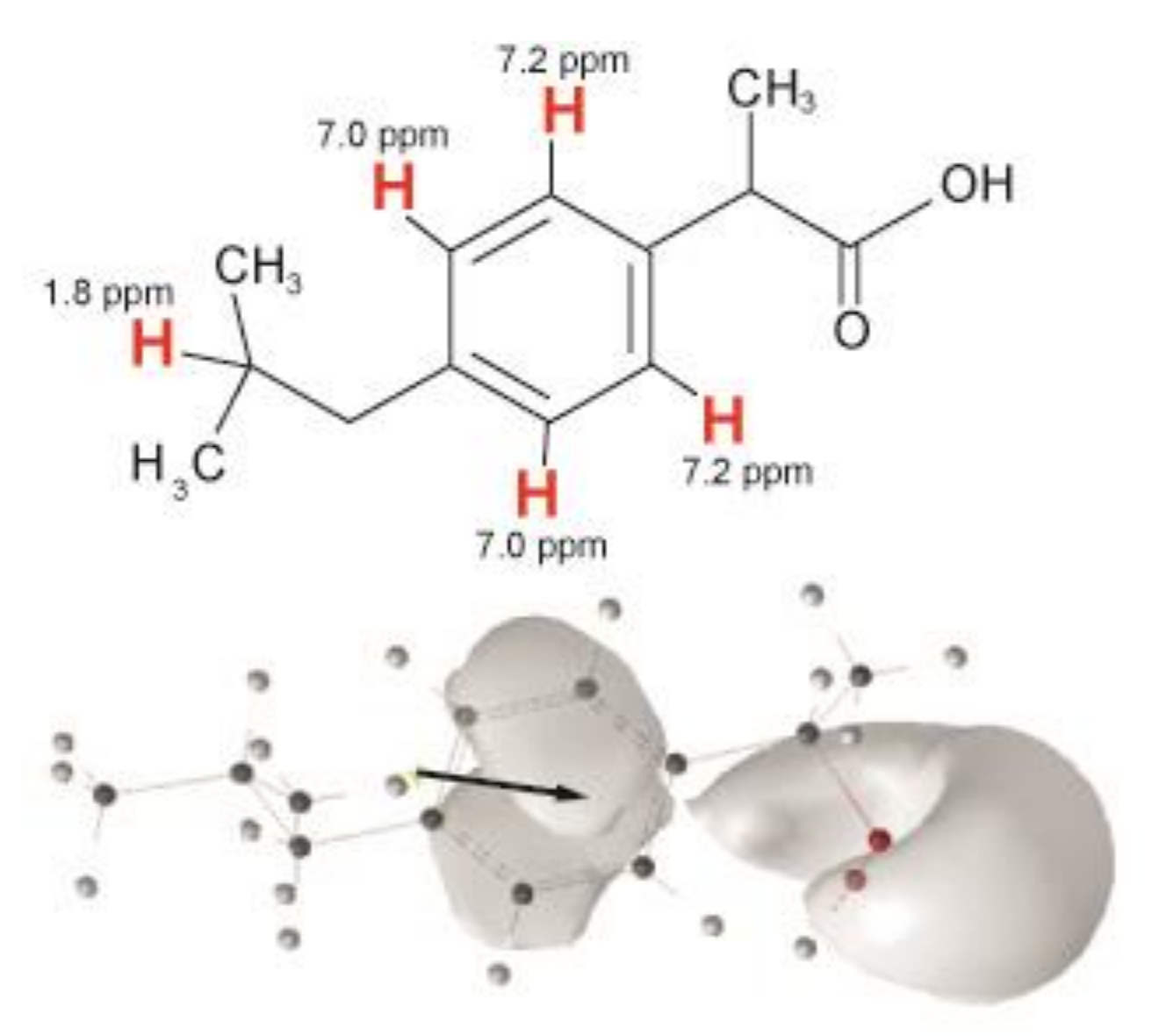
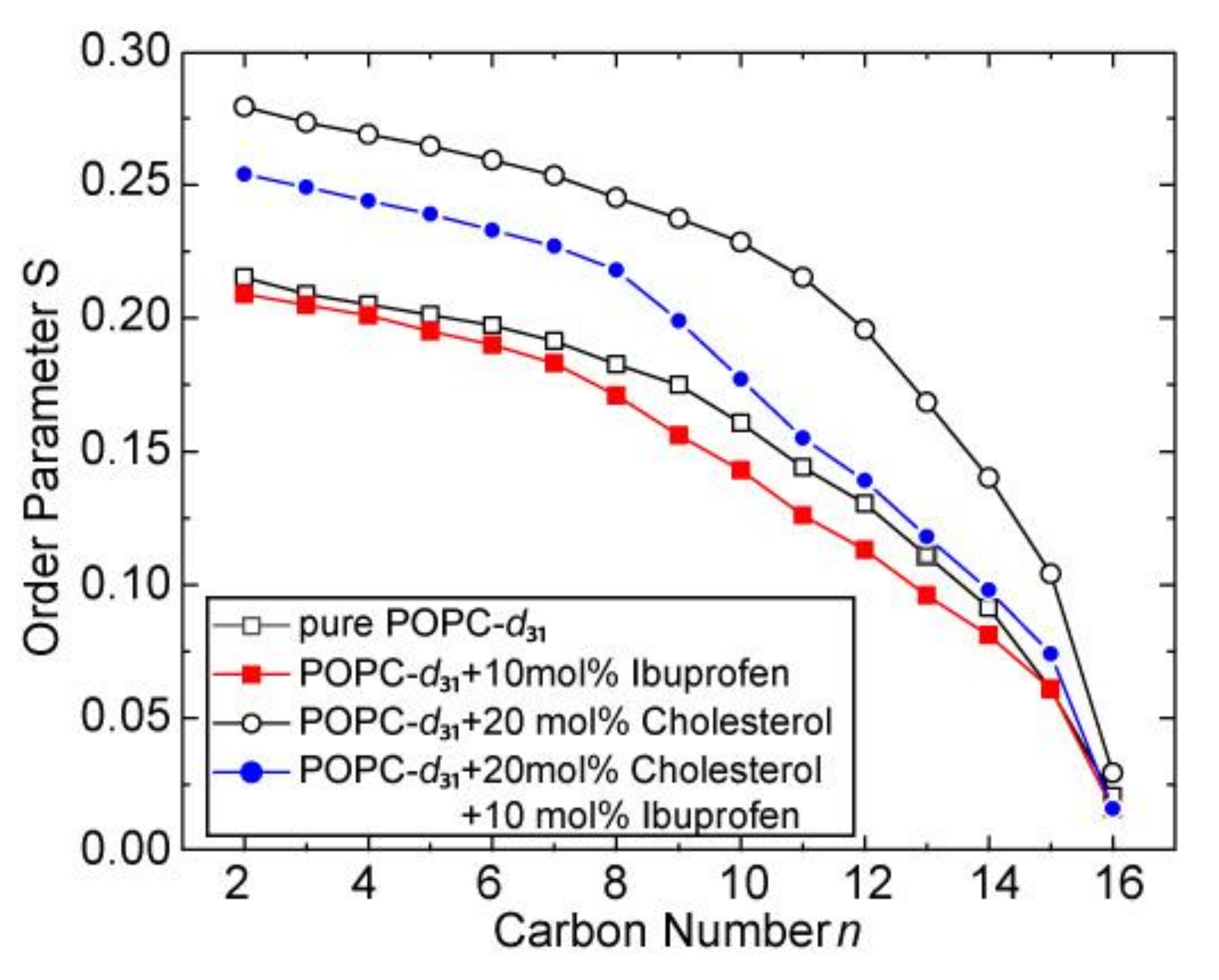

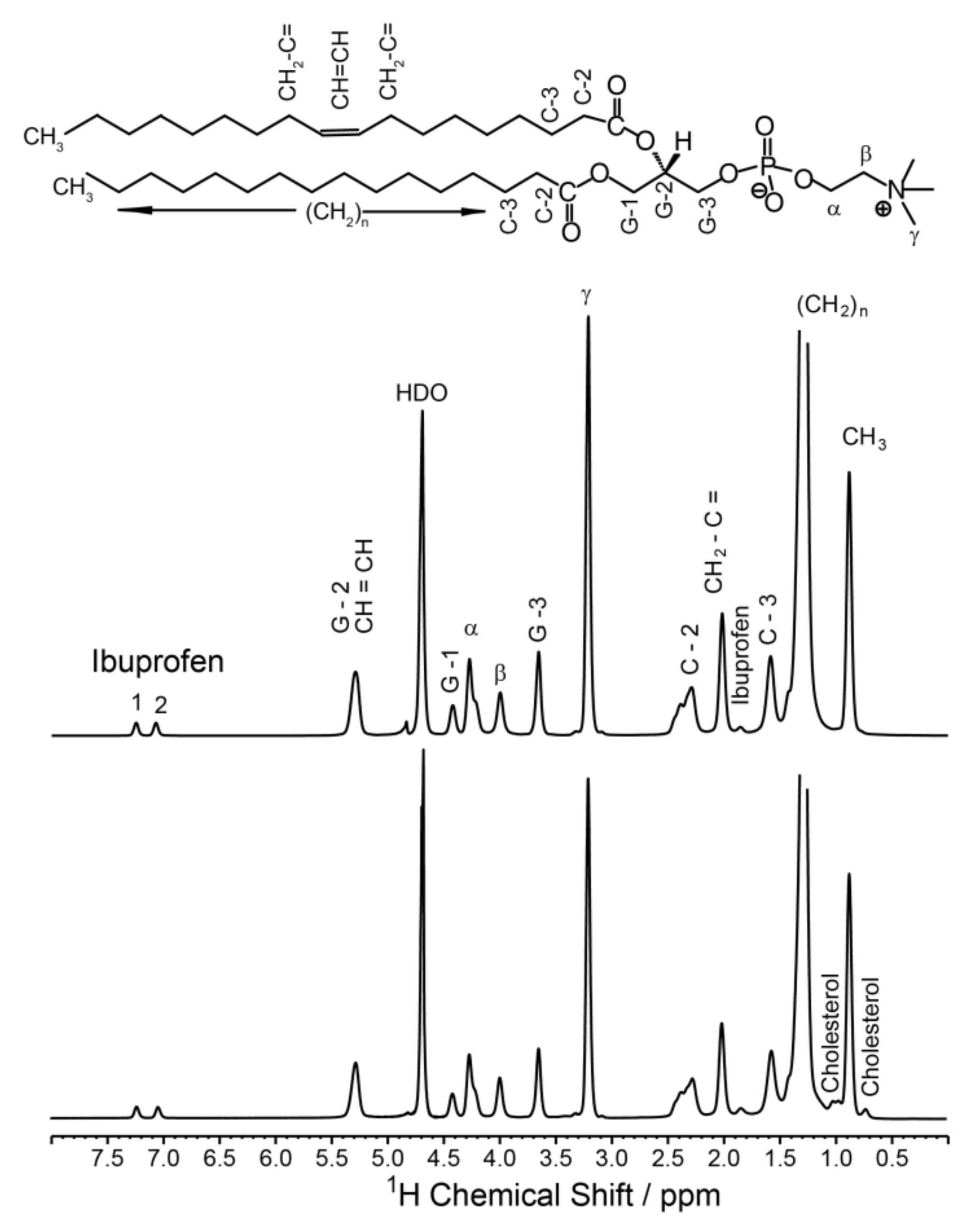
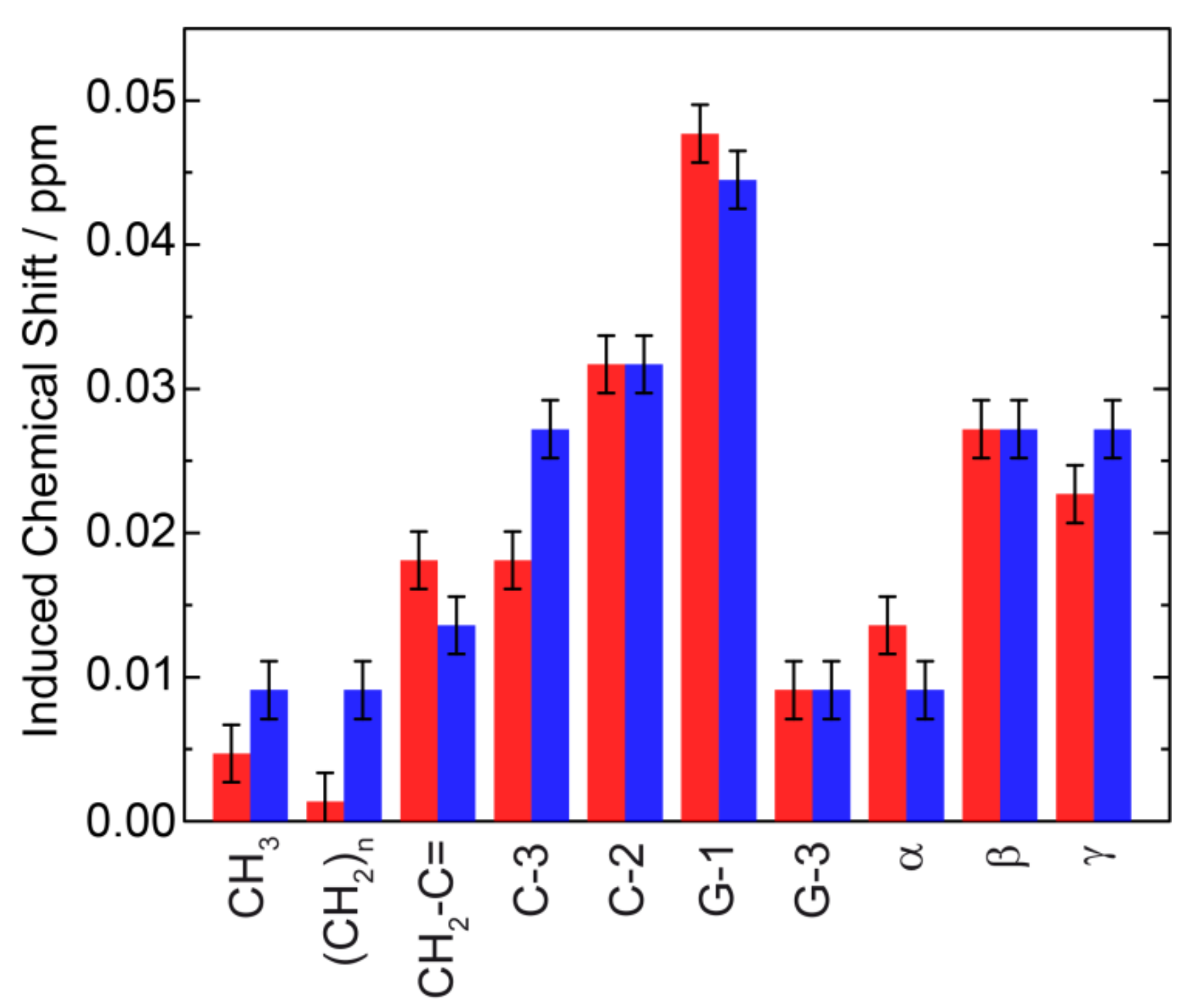
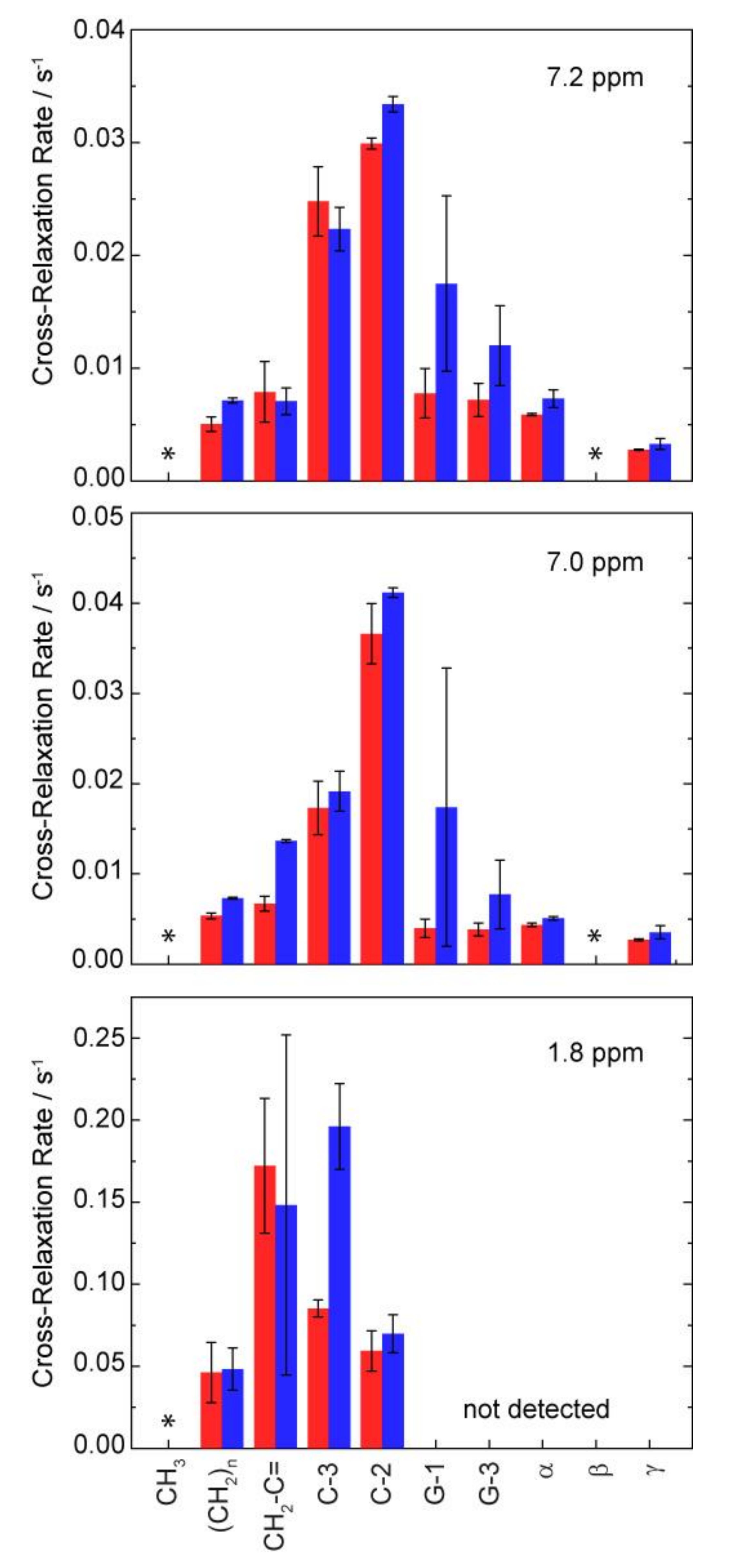
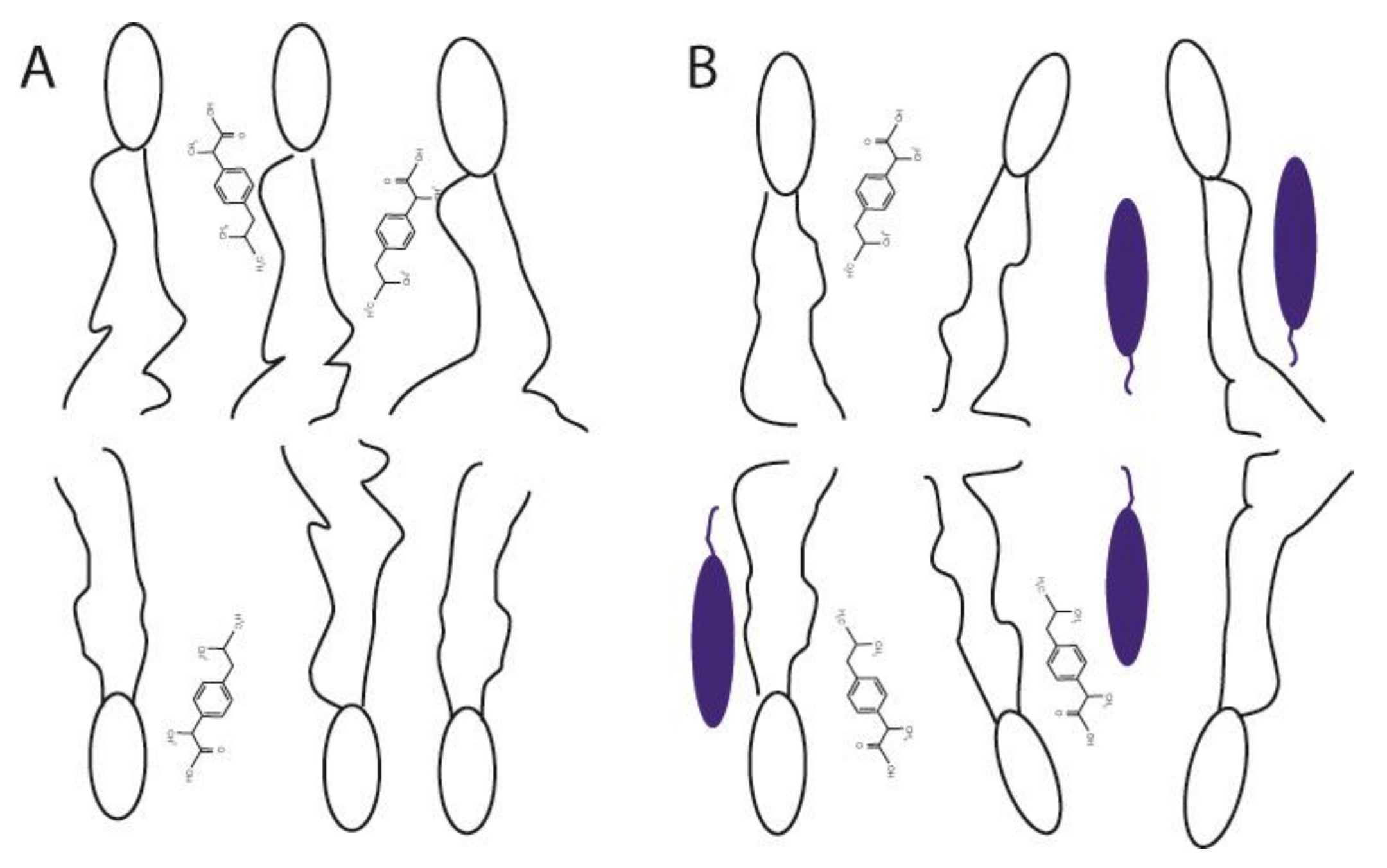
| Sample | 31P CSA Δσ/ppm | Lc*/Å |
|---|---|---|
| POPC-d31 | 45.5 | 11.7 |
| 10 mol% Ibuprofen/POPC-d31 | 40.2 | 11.1 |
| 20 mol% Ibuprofen/POPC-d31 | 40.2 | 11.2 |
| 30 mol% Ibuprofen/POPC-d31 | 38.0 | 10.4 |
| 20 mol% cholesterol/POPC-d31 | 44.0 | 13.2 |
| 10 mol% Ibuprofen/20 mol% cholesterol/POPC-d31 | 40.2 | 12.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kremkow, J.; Luck, M.; Huster, D.; Müller, P.; Scheidt, H.A. Membrane Interaction of Ibuprofen with Cholesterol-Containing Lipid Membranes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101384
Kremkow J, Luck M, Huster D, Müller P, Scheidt HA. Membrane Interaction of Ibuprofen with Cholesterol-Containing Lipid Membranes. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(10):1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101384
Chicago/Turabian StyleKremkow, Jan, Meike Luck, Daniel Huster, Peter Müller, and Holger A. Scheidt. 2020. "Membrane Interaction of Ibuprofen with Cholesterol-Containing Lipid Membranes" Biomolecules 10, no. 10: 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101384
APA StyleKremkow, J., Luck, M., Huster, D., Müller, P., & Scheidt, H. A. (2020). Membrane Interaction of Ibuprofen with Cholesterol-Containing Lipid Membranes. Biomolecules, 10(10), 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101384






