A Simple and Direct Assay for Monitoring Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Product-Specificity by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Standards
2.2. FASN Activity Assay
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Mass Spectrometric Analysis
2.5. Lipid Identification and Quantification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Specific Detection of 13C-Labeled NEFA Produced In Vitro by FASN
3.2. Optimized Workflow for MS-Based Analysis of FASN Activity
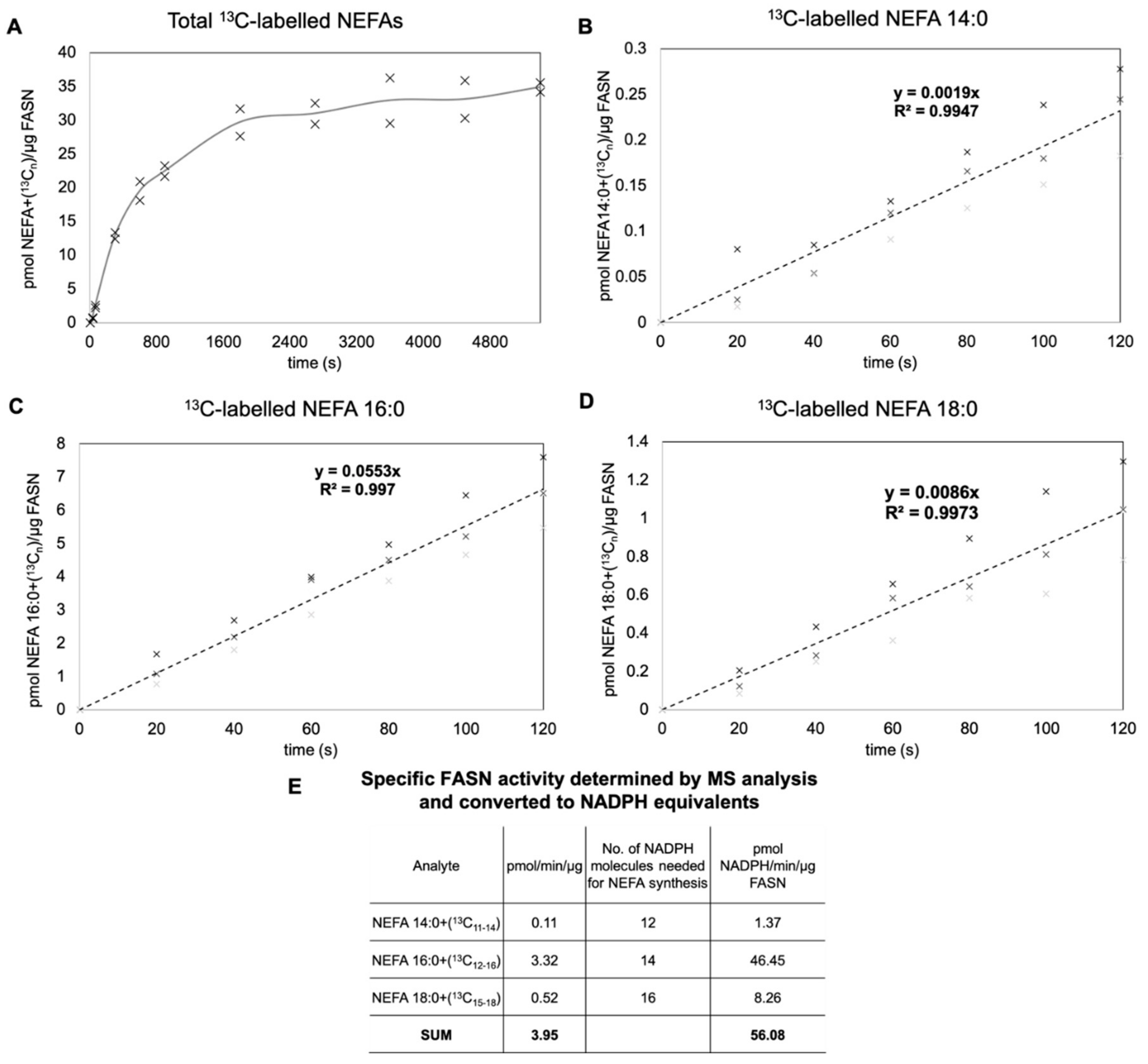
3.3. Determination of Specific FASN Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, S.; Witkowski, A.; Joshi, A.K. Structural and functional organization of the animal fatty acid synthase. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, T.; Leibundgut, M.; Boehringer, D.; Ban, N. Structure and function of eukaryotic fatty acid synthases. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2010, 43, 373–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, E.; Hofmann, J. Microbial type I fatty acid synthases (FAS): Major players in a network of cellular FAS systems. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2004, 68, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhajda, F.P. Fatty-acid synthase and human cancer: New perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition 2000, 16, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.A.; Lupu, R. Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrig, F.; Schulze, A. The multifaceted roles of fatty acid synthesis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.S.; Bae, G.D.; Baek, D.J.; Park, E.Y.; Jun, H.S. Fatty Acid-Induced Lipotoxicity in Pancreatic Beta-Cells During Development of Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, G.; Shulman, G.I. Free fatty acids in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Defining their role in the development of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Ussher, J.R.; Folmes, C.D.; Jaswal, J.S.; Stanley, W.C. Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 207–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillmore, N.; Mori, J.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation alterations in heart failure, ischaemic heart disease and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Garcia, J.; Goldenthal, M.J. Fatty acid metabolism in cardiac failure: Biochemical, genetic and cellular analysis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 54, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Zhou, Y.J.; Huang, M.; Liu, Q.; Pereira, R.; David, F.; Nielsen, J. Reprogramming Yeast Metabolism from Alcoholic Fermentation to Lipogenesis. Cell 2018, 174, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, E.J.; Kang, Y.; Bokinsky, G.; Hu, Z.; Schirmer, A.; McClure, A.; Del Cardayre, S.B.; Keasling, J.D. Microbial production of fatty-acid-derived fuels and chemicals from plant biomass. Nature 2010, 463, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runguphan, W.; Keasling, J.D. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of fatty acid-derived biofuels and chemicals. Metab. Eng. 2014, 21, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, T.; Leibundgut, M.; Ban, N. The crystal structure of a mammalian fatty acid synthase. Science 2008, 321, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenni, S.; Leibundgut, M.; Maier, T.; Ban, N. Architecture of a fungal fatty acid synthase at 5 A resolution. Science 2006, 311, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomakin, I.B.; Xiong, Y.; Steitz, T.A. The crystal structure of yeast fatty acid synthase, a cellular machine with eight active sites working together. Cell 2007, 129, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husen, P.; Tarasov, K.; Katafiasz, M.; Sokol, E.; Vogt, J.; Baumgart, J.; Nitsch, R.; Ekroos, K.; Ejsing, C.S. Analysis of lipid experiments (ALEX): A software framework for analysis of high-resolution shotgun lipidomics data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynen, F. Yeast fatty acid synthase. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969; Volume 14, pp. 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Roncari, D.A. Fatty acid synthase from human liver. Methods Enzymol. 1981, 71, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.R.; Glickman, J.F. Characterization of fatty acid synthase activity using scintillation proximity. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2003, 1, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, N.W.; Hill, A.D.; Kariv, I. A simplified scintillation proximity assay for fatty acid synthase activity: Development and comparison with other FAS activity assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 2009, 14, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, M.C.; Karl Maluf, N.; Wellberg, E.A.; Johnson, C.A.; Murphy, R.C.; Anderson, S.M. Mammalian fatty acid synthase activity from crude tissue lysates tracing ¹³C-labeled substrates using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 428, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Otsuka, H.; Seyama, Y. Assay of fatty acid synthetase by mass fragmentography using [13C]malonyl-CoA. J. Biochem. 1985, 97, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyama, Y.; Kawaguchi, A.; Okuda, S.; Yamakawa, T. New assay method for fatty acid synthetase with mass fragmentography. J. Biochem. 1978, 84, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego, S.F.; Hermansson, M.; Liebisch, G.; Hodson, L.; Ejsing, C.S. Total Fatty Acid Analysis of Human Blood Samples in One Minute by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules 2018, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G.; Cohen, P. Purification and physicochemical properties of fatty acid synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland. Eur. J. Biochem. 1978, 92, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.R.; Paine, M.R.L.; Eijkel, G.B.; Pauling, J.K.; Husen, P.; Jervelund, M.W.; Hermansson, M.; Ejsing, C.S.; Heeren, R.M.A. Automated, parallel mass spectrometry imaging and structural identification of lipids. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L. Biochemistry, 5th ed.; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmeyer, H.U. New values for the molar extinction coefficients of NADH and NADPH for the use in routine laboratories (author’s transl). Z. Klin. Chem. Klin. Biochem. 1975, 13, 507–508. [Google Scholar]
- Horecker, B.L.; Kornberg, A. The extinction coefficients of the reduced band of pyridine nucleotides. J. Biol. Chem. 1948, 175, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Flavin, R.; Peluso, S.; Nguyen, P.L.; Loda, M. Fatty acid synthase as a potential therapeutic target in cancer. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fafian-Labora, J.; Carpintero-Fernandez, P.; Jordan, S.J.D.; Shikh-Bahaei, T.; Abdullah, S.M.; Mahenthiran, M.; Rodriguez-Navarro, J.A.; Niklison-Chirou, M.V.; O’Loghlen, A. FASN activity is important for the initial stages of the induction of senescence. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.R.; Wallace, M.; Divakaruni, A.S.; Phillips, S.A.; Murphy, A.N.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Metallo, C.M. Branched-chain amino acid catabolism fuels adipocyte differentiation and lipogenesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.; Green, C.R.; Roberts, L.S.; Lee, Y.M.; McCarville, J.L.; Sanchez-Gurmaches, J.; Meurs, N.; Gengatharan, J.M.; Hover, J.D.; Phillips, S.A.; et al. Enzyme promiscuity drives branched-chain fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissues. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Topolska, M.; Martínez-Montañés, F.; Ejsing, C.S. A Simple and Direct Assay for Monitoring Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Product-Specificity by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010118
Topolska M, Martínez-Montañés F, Ejsing CS. A Simple and Direct Assay for Monitoring Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Product-Specificity by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(1):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010118
Chicago/Turabian StyleTopolska, Magdalena, Fernando Martínez-Montañés, and Christer S. Ejsing. 2020. "A Simple and Direct Assay for Monitoring Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Product-Specificity by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Biomolecules 10, no. 1: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010118
APA StyleTopolska, M., Martínez-Montañés, F., & Ejsing, C. S. (2020). A Simple and Direct Assay for Monitoring Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Product-Specificity by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules, 10(1), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010118




