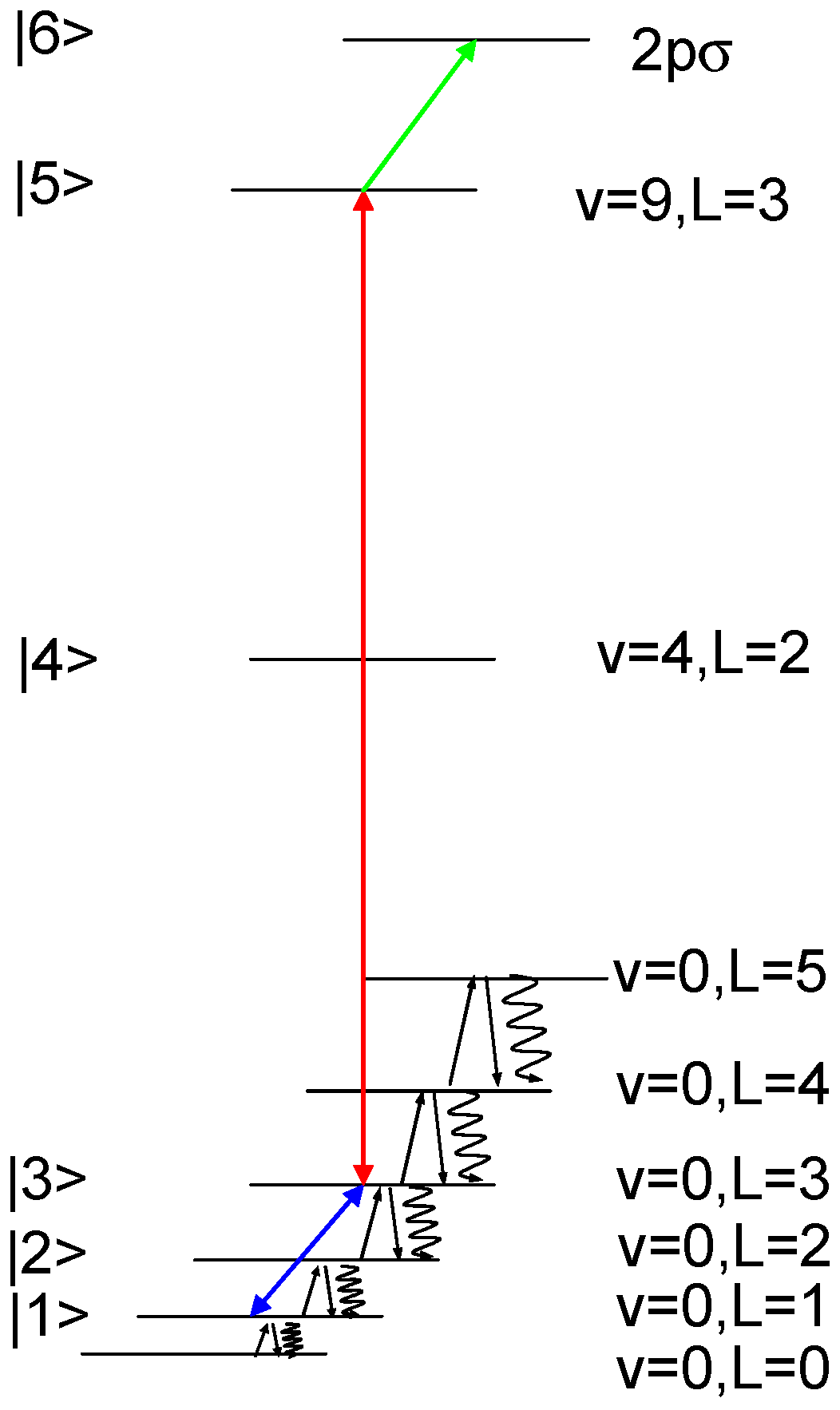1. Introduction
Precision measurements with atoms and molecules improved our understanding of the structure of matter and of its interaction with light. Predictions of the quantum electrodynamics (QED) were compared with accurate experimental data to test the validity of the theory and to extract the values of fundamental constants [
1]. Precision spectroscopy of atomic hydrogen and deuterium is used to extract the Rydberg constant, the proton radius, and the deuteron radius. Significant discrepancies were noticed between the proton radius and the deuteron radius determined from regular (electronic) hydrogen and deuterium and from exotic (muonic) hydrogen and deuterium, respectively [
2]. This problem, called “the proton radius puzzle”, motivated several works [
3]. The agreement between independent determinations of physical constants may check the validity of theoretical and experimental results. Moreover, space-time variations of fundamental constants are allowed in theories beyond the Standard Model (see [
4] for a review). Constraints on possible variation of the proton-to-electron mass ratio were derived from astrophysical spectra or laboratory studies (see for example [
5]).
The hydrogen molecular ions are the simplest molecules. They have an important role in molecular quantum mechanics [
6]. High-resolution infrared spectroscopy associated with accurate ab-initio calculations open the way to applications for the determination of fundamental constants and for testing QED [
7]. QED calculations of the energy levels of the hydrogen molecular ions were performed including corrections up to the mα
8 order [
8,
9,
10,
11] and reduced the relative uncertainty for fundamental vibrational transitions to 7.6 × 10
−12. Accurate experimental results were obtained using hydrogen molecular ions stored in radiofrequency (r.f.) traps and sympathetically cooled by laser-cooled Be
+ ions. In addition, it is possible to efficiently prepare HD
+ ions in the fundamental rotational level [
12,
13]. Weak rovibrational overtone transitions are allowed by electrical-quadrupole coupling for H
2+ ions and by electrical-dipole coupling for HD
+ ions. The natural linewidths of the rovibrational transitions are at the 10 Hz level for HD
+ and the 10
−7 Hz level for H
2+ [
14]. The systematic frequency shifts were accurately calculated for hydrogen molecular ions [
15,
16]. The experimental accuracy with a dipole-allowed rovibrational overtone transition of HD
+ was 1.1 × 10
−9 [
17]. The agreement with theoretical results at 1.1 × 10
−9 allowed a test of QED, provided a determination of the proton-to-electron mass ratio, as suggested by [
18], and constrained the effect of “fifth forces” [
19]. The experimental uncertainty of HD
+ ion lines was limited by Doppler broadening. Doppler-free two-photon spectroscopy of a rovibrational overtone transition of HD
+ was proposed to improve the uncertainty beyond the 1 × 10
−12 level [
20]. In this approach, efficient two-photon excitation in HD
+ is provided by driving a pair of dipole-allowed E1-E1 rovibrational transitions with lasers tuned close to resonance with an intermediate energy level. The trapped HD
+ ions are in the Lamb-Dicke regime, as their oscillatory motion in the trap is confined over a distance smaller than the effective laser wavelength, that allows to probe the two-photon transition virtually without Doppler and recoil effects. The advantage of the two-photon spectroscopy approach is to suppress the first-order Doppler effect even without strong spatial confinement. The observation of an electric-quadrupole allowed E2 transition for homonuclear diatomic ions, demonstrated with N
2+ [
21], may be an alternative to increase the accuracy with Doppler-free spectroscopy in the Lamb-Dicke regime.
This contribution proposes to determine the Rydberg constant, the nuclear-to-electron mass ratios, and the nuclear radii using Doppler-free spectroscopy of hydrogen molecular ions. A THz/infrared double resonance two-photon spectroscopy study on trapped HD
+ ions may allow joint measurements of E1-E1 rotational transitions in the vibrational ground state and of E1-E1 rovibrational transitions with different sensitivities on fundamental constants. The rotational levels in the vibrational ground state have long (1 s level) radiative lifetimes, compared to 10 ms level lifetimes of excited rovibrational levels, that may lead to an improvement of the resolution beyond the 10
−12 level. Efficient detection of molecular transitions may be provided by state-selective resonance-enhanced multiphoton dissociation (REMPD) [
20]. The double resonance spectroscopy scheme, proposed here, based on (v,L) = (0,1)→(0,3) and (v,L) = (0,3)→(9,3) two-photon transitions, may provide complementary experimental data to previous microwave/infrared double resonance studies on HD
+ ion beams [
6]. This article addresses the hyperfine structure of the rovibrational energy levels to calculate two-photon transition rates and lightshifts with the two-photon tensor operator formalism [
22]. The lineshapes obtained in the double resonance two-photon spectroscopy scheme are determined using a rate equation model that describes the interaction with the blackbody radiation (BBR). The frequency stability, the Zeeman shift, and the lightshift are evaluated for a molecular clock based on HD
+ two-photon rotational lines. Finally, the determination of fundamental constants is discussed.
3. Two-Photon Spectroscopy Scheme
The two-photon rovibrational transition (v,L) = (0,3)→(9,3) of HD
+ may be addressed by Doppler-free laser spectroscopy at 1.44 µm and detected by REMPD using a 532 nm laser [
20]. The experiment proposed in this contribution is to probe also a two-photon rotational transition in the vibrational ground state, that is here (v,L) = (0,1)→(0,3). Doppler-free rotational spectroscopy may be performed with two counterpropagating THz-waves tuned around the rotational transition. That induces a change of the population in the rotational levels that can be detected on the REMPD signal. In addition, there is the effect of the blackbody radiation that recycles continuously the HD
+ ions between the rotational levels of the vibrational ground state. The closed set of energy levels coupled by the two-photon spectroscopy scheme is shown in
Figure 2. The rovibrational levels have small radiative decay widths, for example Γ
3/(2π) = 0.037 Hz and Γ
5/(2π) = 13.1 Hz [
28].
The parameters used for modelisation are taken from the experimental setups with HD
+ ions (see for example [
17]). A number of ~100 HD
+ ions in linear r.f.-traps are cooled sympathetically at ~10 mK with Be
+ ions which are laser-cooled at 313 nm. The two-species solidify in a Coulomb crystal. Secular motion of HD
+ ions in the trap may be excited and the fluorescence at 313 nm from the laser-cooled Be
+ ions can be used to monitor the number of trapped HD
+ ions. The spectroscopy scheme uses conjointly 1.44 µm, 532 nm, and 313 nm lasers and the THz-wave. The trap displays ~100 s storage time that allows a typical interrogation time of the HD
+ ions of 10 s. The number of HD
+ ions lost by REMPD is measured by exciting the secular motion and monitoring the fluorescence signal.
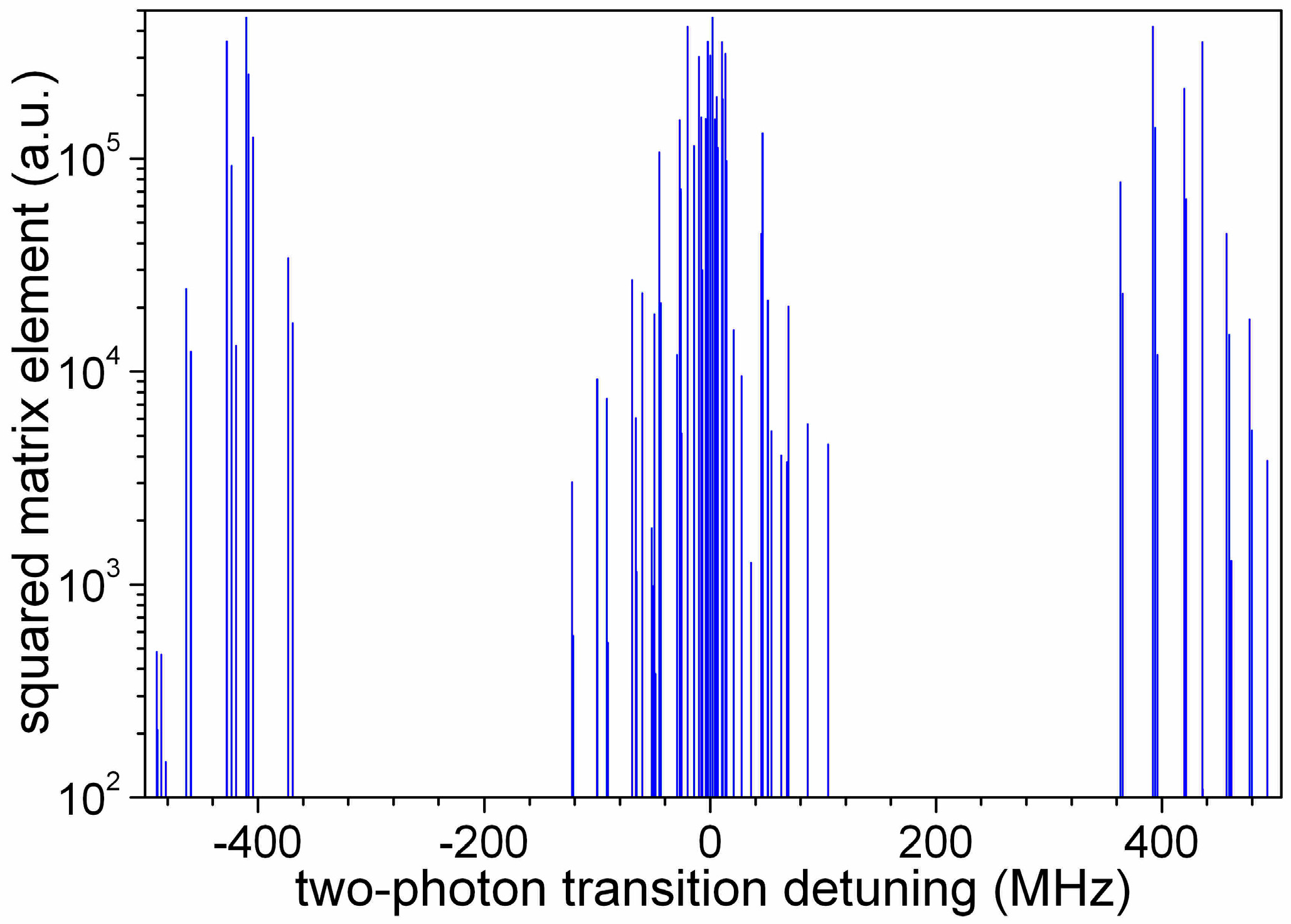
The linewidths of the laser sources and of the THz-waves are assumed negligible in this modelisation. The hyperfine structure of the levels is neglected in this section. The transition rate for the two-photon rovibrational transition (at the angular frequency ω
v) that is taken here at Γ
2ph,v = 10 s
−1 may be easily reached with a laser intensity by 5 mW/mm
2 [
20]. The hyperfine-free rotational transition (at the angular frequency ω
r) has a two-photon operator squared matrix element of ~10
5 a.u. [
29]. That allows to reach a transition rate estimated at Γ
2ph,r = 2 × 10
3 s
−1 for a THz-wave intensity of 1 mW/mm
2. The 532 nm laser drives dissociation at a rate assumed here at Γ
diss = 200 s
−1 reached with a laser intensity by 56 mW/mm
2 [
20].
Interaction of HD
+ ions with the blackbody radiation is described by rate equations driven by Einstein coefficients for the spontaneous emission
from an upper state i = (v,L) to a lower state f = (v
′,L
′), respectively, for the stimulated absorption
and for stimulated emission
that are expressed as:
The angular frequency of the transition is ω
fi. The line strength factor S(i;f) is expressed with the matrix elements of the dipole operator between the rovibrational wavefunctions, and its value is given on the last line in function of the reduced matrix elements of the dipole operator µ
vL,v′L′. The ions are distributed initially among the (v = 0,L = 0,…, 5) levels. These levels are coupled with BBR-driven transitions. Upon application of THz-waves and infrared and visible lasers, time dependences of the populations in the rovibrational levels
v,L(t) and in the dissociated state
2pσ(t) can be calculated with a set of rate equations using the two-photon transition rates at resonance Γ
2ph,r,v and the two-photon transition detunings δω
r,v = ω
r,v−ω
13,35/2:
The BBR spectral energy for a temperature T at an angular frequency ω is denoted WT(ω). Optical pumping is considered fast enough to neglect the spontaneous emission from excited vibrational levels.
Equation (21) is numerically integrated by assuming Σ
v,Lv,L(t) +
2pσ(t) = 1 and an initial distribution of populations
v,L(t = 0) given by a thermal distribution with a temperature for the BBR of 300 K. The temporal dependences of the populations are shown in
Figure 3. The populations in the (v,J) = (0,1) and (0,3) levels equalize at the 1/Γ
2ph,r timescale and decline further at the 1/Γ
2ph,v timescale. The HD
+ ions in the other (v = 0,J) levels are dissociated at slower timescales determined by the rates of BBR-driven transitions. The (v = 0,J = 0) level acts as a dark state, and its population is slowly modified by interaction with the BBR. The result is an increase of its relative proportion (shown on the right-axis).
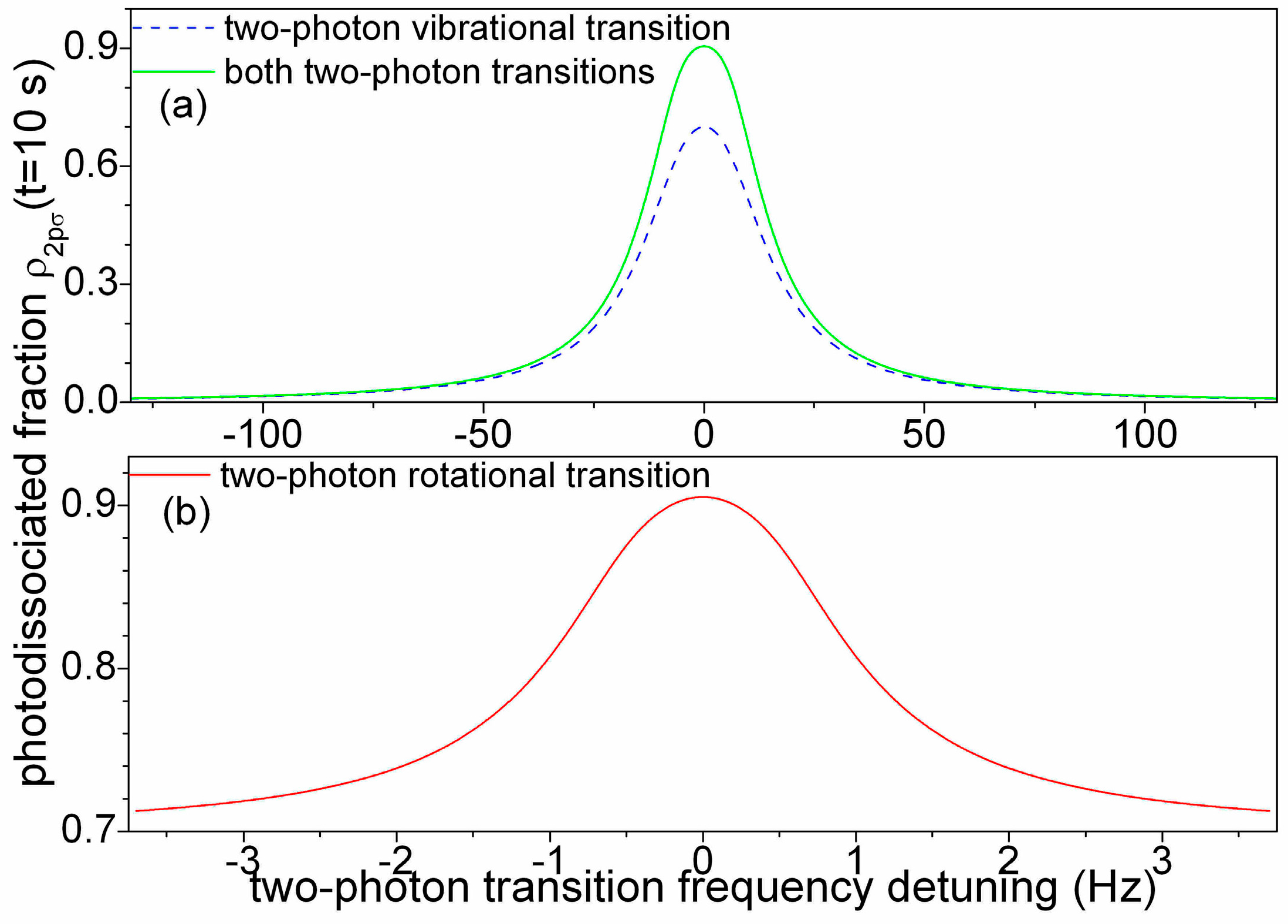
Figure 4a displays the spectral profile of the photodissociated fraction in function of the two-photon rovibrational detuning δω
v/(2π) with or without coupling on the two-photon rotational resonance.
Figure 4b displays the spectral profile of the photodissociated fraction at two-photon rovibrational resonance in function of the two-photon rotational detuning δω
r/(2π). The two-photon rovibrational spectra are sensibly broader than the two-photon rotational spectrum. The rotational lineshape is well adjusted by a Lorentzian with 2.09 Hz full width at half maximum (FWHM) linewidth. The two-photon rotational line with an amplitude of 0.17 is superposed on a flat baseline with an offset of 0.6 that corresponds to the on-resonance two-photon rovibrational signal. The fractional resolution of 6 × 10
−13 reached with the two-photon rotational transition improves by two orders of magnitude the resolution of the two-photon rovibrational spectroscopy scheme [
20].
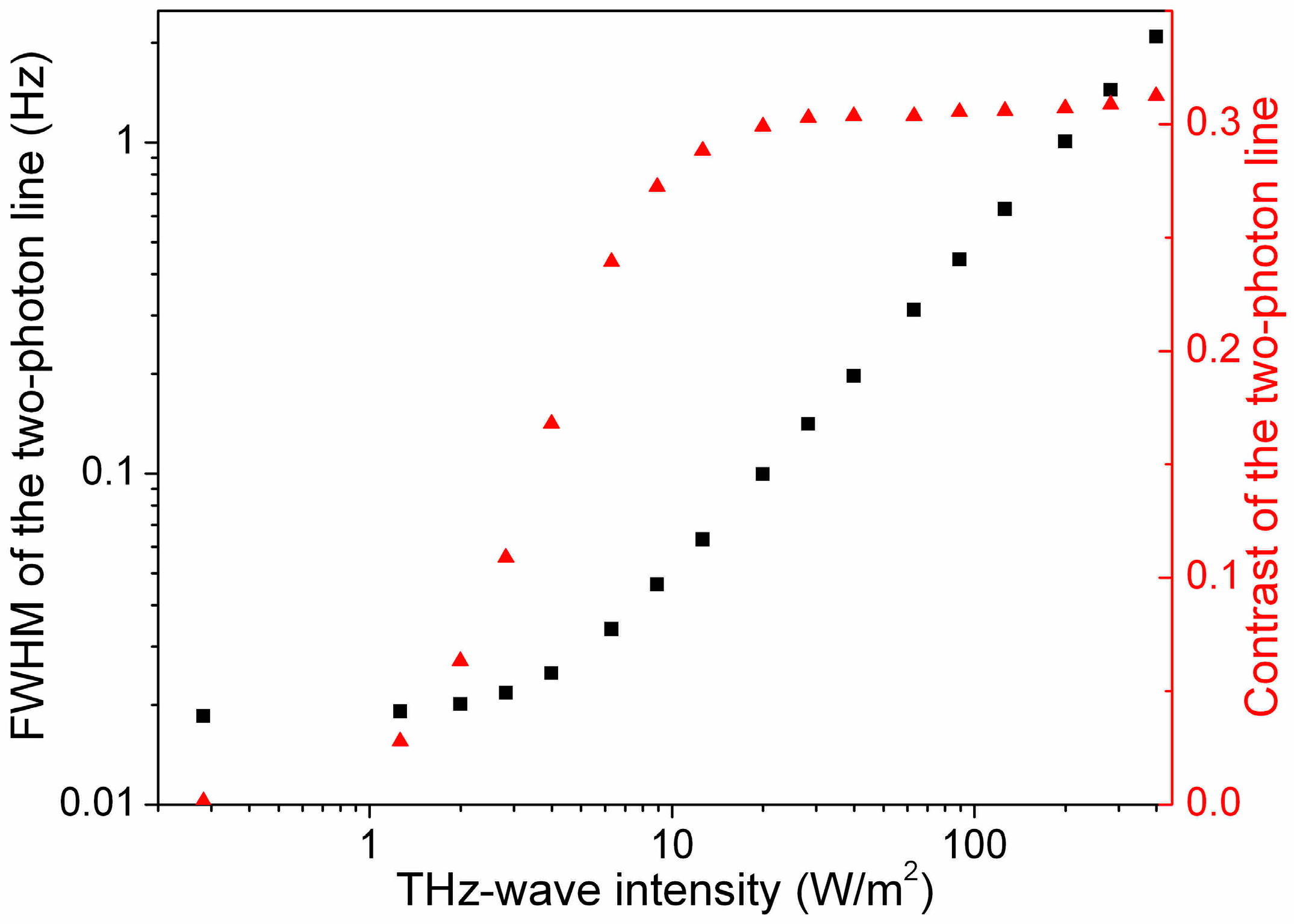
The linewidth of the two-photon rotational line is determined by power broadening.
Figure 5 displays the dependence of the broadening in function of the THz-wave power (left-axis). The calculated linewidth decreases linearly with the THz-wave power before stabilizing at a level determined by the natural linewidth of the transition. The dependence of the contrast of the two-photon rotational line is shown on the right-axis. The offset remains stable when the THz-wave power varies. A lower THz-wave power may be used to increase the resolution of the two-photon line at the expense of the reduction of its contrast.
This two-photon spectroscopy scheme may be extended to other vibrational energy levels. Some two-photon rovibrational transitions have been identified between v = 0 and v
′ = 2 and between v = 0 and v
′ = 4 for L, L
′ ≤ 5, respectively [
30]. The HD
+ ions in the v = 2 level require excitation to another vibrational level before dissociation. The HD
+ ions in the v = 4 level can be efficiently dissociated with a 266 nm laser.
4. Perspectives in Stability and Accuracy from Two-Photon Rotational Transitions
The stability of a molecular clock based on the transitions of HD
+ constrains the integration time required to determine the fundamental constants at a given level of statistical uncertainty. When the quantum projection noise dominates among other sources of noise, the stability is given by [
31]:
The quality factor of the two-photon transition Q = ω
2ph/Δω
HWHM is expressed in terms of the half-linewidth determined ultimately by the natural lifetimes of the molecular levels. The cycle time T
c is associated to a single measurement with N
ion ions at two-photon resonance and successive measurements are averaged during an interrogation time τ > T
c. The two-photon transitions between the rotational levels with L < 5 in the vibrational ground state are more interesting because they display lifetimes which are ~10
2–10
3 greater than those of the two-photon rovibrational transitions to v > 4 levels [
28]. Using the two-photon transition rate lineshape and supposing that the same number of ions are detected during the same measurement times, it appears that a molecular clock based on the fundamental two-photon rotational transition (v,L) = (0,0)→(0,2) may improve the stability by an order of magnitude compared to the stability reached by using the two-photon rovibrational transition (v,L) = (0,3)→(9,3) [
20]. For example, using a cycle time of T
c = 2 s, the stability of a single-ion HD
+ clock based on the rotational transition (v,L) = (0,1)→(0,3) is estimated at σ
y(τ) = 1.4 × 10
−15τ
−1/2, which is comparable with the stability of the optical atomic clocks based on trapped ions [
31].
The higher resolution allowed by two-photon rotational spectroscopy opens the way to address individual Zeeman components of hyperfine structure energy levels. For the levels in the vibrational ground state with the same (F,S,J), the increase of L is associated generally to a decrease of Zeeman shift coefficients [
25]. For metrological applications, it is interesting to select transitions with minimal Zeeman shifts as was suggested in [
25,
32]:
- -
Transitions ππ between Jz = 0→J′z = 0 states that have only quadratic Zeeman shift.
- -
Transitions σ±σ± between “stretched states”, that are pure eigenvectors of the angular momentum coupling with maximum total angular momentum and projection on the quantisation axis |v,L,F = 1,S = 2,J = L + 2,Jz = ±(L + 2)>, for which the Zeeman shifts depend linearly with the magnetic field, have the same magnitude but opposite values.
Zeeman shift coefficients are calculated for hyperfine components of rotational transitions using the polynomial expansion of the Zeeman shift of the energy levels from [
25]. Transitions with small Zeeman shifts are shown in
Table 3. The transition (v = 0,L = 1,F = 0,S = 1,J = 1,J
z = 0)→(v’ = 0,L’ = 3,F’ = 0,S’ = 1,J’ = 3,J’
z = 0) benefits from a strong cancellation of the quadratic Zeeman shifts of the upper and lower levels. Assuming conservatively that the uncertainty is given by the Zeeman shift, estimated at 71.2 mHz for a value of the magnetic field of B = 0.02 G, the accuracy is 2.2 × 10
−14. The Zeeman shift coefficients for two-photon rotational transitions between stretched states increase with L. The transition (v = 0,L = 0,F = 1,S = 2,J = 2,J
z = 2)→(v’ = 0,L’ = 2,F’ = 1,S’ = 2,J’ = 4,J’
z = 4) benefits from the compensation between the linear Zeeman coefficients in the upper and lower levels. The Zeeman shift, estimated at −11.12 Hz for a value of the magnetic field of B = 0.02 G, leads to an accuracy of 5.6 × 10
−12.
A cancellation procedure was proposed for the linear Zeeman shift with pairs of transitions J
z→J
z and −J
z→−J
z [
16] or for the Zeeman shift with pairs of transitions between stretched states J
z = ±(L + 2)→J’
z = ±(L
′ + 2) [
16,
25]. The idea was to calculate the mean frequency of such a pair of Zeeman-shifted hyperfine components. Consider here that each linecenter is determined within 1% of an experimental linewidth that is taken at 1 Hz. The uncertainty of the determination of the average frequency is 0.01 ×
Hz, that may be improved by a factor of 10 by doing the linear regression of the dependence of the frequency splitting on the magnetic field. The estimated accuracy is 4.3 × 10
−16 for hyperfine components of the (v,L) = (0,1)→(0,3) two-photon rotational transition.
The dynamic polarisabilities for the selected hyperfine levels coupled by two-photon rotational transitions are determined with Equations (17)–(19) and displayed in
Table 3. The polarisabilities in the upper and lower levels are efficiently compensated for many hyperfine components of J
z = 0→J
′z = 0 transitions. The lightshifts are estimated for a THz-wave intensity of 1 mW/mm
2. The accuracies are ≤ 2 × 10
−13 and a value of 4 × 10
−15 is reached for the (v = 0,L = 1,F = 0,S = 1,J = 2,J
z = 0)→(v’ = 0,L’ = 3,F’ = 0,S’ = 1,J’ = 4,J’
z = 0) transition.
A method for the reduction of the lightshift, suggested in [
20], exploits two lasers with suitable power to probe the two-photon transition in the Lamb-Dicke regime. Alternatively, the interaction with sequences of suitably tailored laser pulses may provide a dramatic reduction of the lightshifts, as was suggested in a generalisation of the Ramsey spectroscopy method [
33]. A hyper-Ramsey scheme was successfully implemented on the octupole clock transition of a single trapped
171Yb
+ ion leading to the reduction of the lightshift by orders of magnitude below to the 10
−16 level [
34]. An approach was recently proposed for Doppler-free optical stimulated Raman transitions [
35].
5. Determination of Fundamental Constants
The comparison of experimental frequencies of HD
+ ions transitions with accurate theoretical predictions is used here to determine independent values for fundamental constants. This section follows the approach of CODATA least-squares adjustment [
36] that has been exploited with hydrogen molecular ion rovibrational transitions [
37].
The energy levels of HD
+ ions may be calculated in the frameworks of QED and quantum chromodynamics (QCD) as a series expansion:
in function of the Rydberg constant R
∞, the proton-to-electron mass ratio µ
pe = M
p/m
e, the deuteron-to-proton mass ratio µ
dp = M
d/M
p, the fine-structure constant α, the proton radius r
p, the deuteron radius r
d, and the Bohr radius a
0 = α/4πR
∞. The first term E
nr is the non-relativistic energy given by the Schrödinger equation. The next term is a series expansion of corrections to the energy levels in terms of α (QED corrections), Z
p,dα (relativistic corrections), and m
e/M
p,d (recoil corrections). The last term is a correction from QCD associated to the finite-size of the proton and the deuteron. Corrections of orders up to m
eα
8 to HD
+ energy levels were calculated in [
8,
9,
10,
11,
38,
39].
The sensitivity coefficient of a transition to a constant c is expressed as:
Here, f
0 is the HD
+ ion transition frequency calculated with the set of the recommended values of fundamental constants {c
0} given by CODATA 2014 [
1]. Sensitivity coefficients for selected two-photon HD
+ ion transitions are calculated and presented in
Table 4. The contribution from the non-relativistic energy is accounted for with the values of
∂E/
∂ln(µ
pe,dp) calculated in [
23]. The recoil corrections bring a negligible fractional contribution to the sensitivity coefficients to the nuclear-to-electron mass ratios. Sensitivity to α is not addressed here and the sensitivity coefficients to R
∞ may be taken as 1 for simplicity. The rotational transitions have sensitivity coefficients to the relevant constants by a factor of two higher than the corresponding sensitivity coefficients of the vibrational transitions.
Fundamental constants are extracted with an uncertainty that depends on the accuracy of the experimental frequencies and the accuracy of the predictions. The experimental accuracy for all two-photon rovibrational transitions is assumed here to be 10
−12 as in [
20]. The estimation is based on linewidths ~500 Hz, determined by the spectral purity of the laser and power broadening and by the signal-to-noise ratio of an rovibrational signal of an experiment [
17]. The estimated uncertainty is, therefore, one tenth of the linewidth. It is assumed here that all two-photon rotational transitions may be observed with the same noise and with linewidths ~1 Hz determined by power broadening. Each two-photon rotational transition requires an extremely narrow THz source and provides a signal smaller than the signal from the corresponding two-photon rovibrational transition. The uncertainty for all two-photon rotational transitions is conservatively estimated here at one half of the linewidth and the accuracy is assumed at 5 × 10
−13. The uncertainties of the experimental frequencies due to various systematic effects are supposed to be below the estimated experimental accuracies. Calculations with corrections to order m
eα
7 predicted HD
+ ion frequencies with an accuracy estimated at 3–4 × 10
−11 [
10]. The inclusion of other corrections may improve the value of the theoretical uncertainty [
37] that is assumed here at 3 × 10
−12 for all transitions. In the least squares method, the dependence of the transition frequencies on the adjusted constants is linearized using a Taylor expansion around the starting values of the constants. The dependence is expressed with the matrix relation Y = AX, where Y = {y
1,y
2,…,y
N1}, with y
i = (f
i− f
i,0)/f
i,0, and X = {x
1,x
2,…,x
N2}, with x
j = (c
j− c
j,0)/c
j,0, are columns with N
1,2 elements respectively. The sensitivity matrix A is a N
1 × N
2 matrix with elements a
ij = d(lnf
0,i)/d(lnc
0,j). The covariance matrix of the solution X is expressed in terms of the covariance matrix of the input data V and the sensitivity matrix as:
The uncertainty of the input data is taken as the root-mean-square sum of the experimental and theoretical uncertainties. The covariances of the input data are given by the covariances of the predictions, by assuming that experimental frequencies are not correlated. Non-zero covariance arises from the uncalculated terms in the energy levels that are expressed as a particular constant multiplied by the common factor arising, for example, from the overlapping of the electron wavefunction with the extended nuclear charge distribution. A value of 1 for all correlation coefficients is taken here.
It is interesting to estimate the contributions to the theoretical uncertainty arising from the uncertainty of each fundamental constant. Using CODATA 2014 values and uncertainties of fundamental constants [
1], the uncertainty propagation law yields for the transition (v,L) = (0,1)→(0,3) of HD
+ the following values: [Δy(R
∞),Δy(μ
pe),Δy(μ
dp),Δy(r
p),Δy(r
d)] = [0.59,9.4,3.1,0.74,0.76] × 10
−11 (correlations between fundamental constants are not taken in account in this estimation). CODATA value of the proton-to-electron mass ratio is the main source of uncertainty. Discrepancies were noticed between CODATA values of r
p and r
d and the values inferred from muonic hydrogen [
40] and from muonic deuterium [
41]. The main disagreement concerns r
p, and it may be judicious here to account for it by using an increased uncertainty Δx(r
p) = 3.9 × 10
−2 that is equal to the difference between the r
p values from the CODATA 2014 adjustment and the muonic hydrogen spectroscopy. The uncertainties for R
∞ and r
d have to be increased in proportion because of high correlation coefficients r(R
∞,r
p) = 0.9891 and r(r
p,r
d) = 0.9994, respectively [
42]. The uncertainties for the rotational transition are now: [Δy(R
∞),Δy(μ
pe),Δy(μ
dp),Δy(r
p),Δy(r
d)] = [3.3,9.4,3.1,4.1,4.2] × 10
−11. The proton-to-electron mass ratio remains the main source of uncertainty, and the other constants bring contributions that are two or three times less.
Different combinations of transitions of H
2+ and HD
+ are tested in the least squares method and the uncertainties of the determination of fundamental constants are calculated. The results are displayed in
Table 5. The values of five constants (R
∞, μ
pe, μ
dp, r
p, r
d) may be derived independently of previous results from an adjustment of eight transitions (line B in
Table 5). The accuracy of the proton-to-electron mass ratio is improved by one order of magnitude compared to the CODATA 2014 value, and the accuracy of the deuteron-to-proton mass ratio is improved by nearly a factor of 20. The accuracies of R
∞, r
p, and r
d are comparable with the relevant values given by CODATA 2014. This adjustment may add clues to the proton radius puzzle, as the uncertainties for r
p and r
d are smaller than the corresponding discrepancies [
2]. If the proton radius puzzle is solved and r
p, r
d can be precisely determined by atomic spectroscopy of muonic hydrogen and muonic deuterium, respectively, three constants (R
∞, μ
pe, μ
dp) can be determined using an adjustment of four transitions (line C in
Table 5). The accuracies are improved by factors of (1.8, 25, 11) compared to the relevant CODATA 2014 values. Finally, if R
∞, r
p, and r
d may be determined accurately by atomic spectroscopy, one could address again the starting point of hydrogen molecular ions spectroscopy that is accurate nuclear-to-electron mass ratio determination. Using an adjustment of three transitions (line D in
Table 5), the proton-to-electron mass ratio and the deuteron-to-proton mass ratio may be determined with accuracies improved by factors of 26 and 12 compared to the relevant values given by CODATA 2014. Note that using in addition a two-photon rotational transition in the adjustment improves the accuracy by more than a factor of 1.5 compared to the result from [
37] with solely rovibrational data. Moreover, accurate values of the mass ratios µ
rp and µ
dp may be associated with the new value of the electron mass [
43], determined with an accuracy of 3 × 10
−11 from a measurement of the g-factor, to improve the determination of the proton and the deuteron relative masses.