Tuning the Nonlinear Optical Properties of Quantum Dot by Noise-Anharmonicity Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
3. Results and Discussion
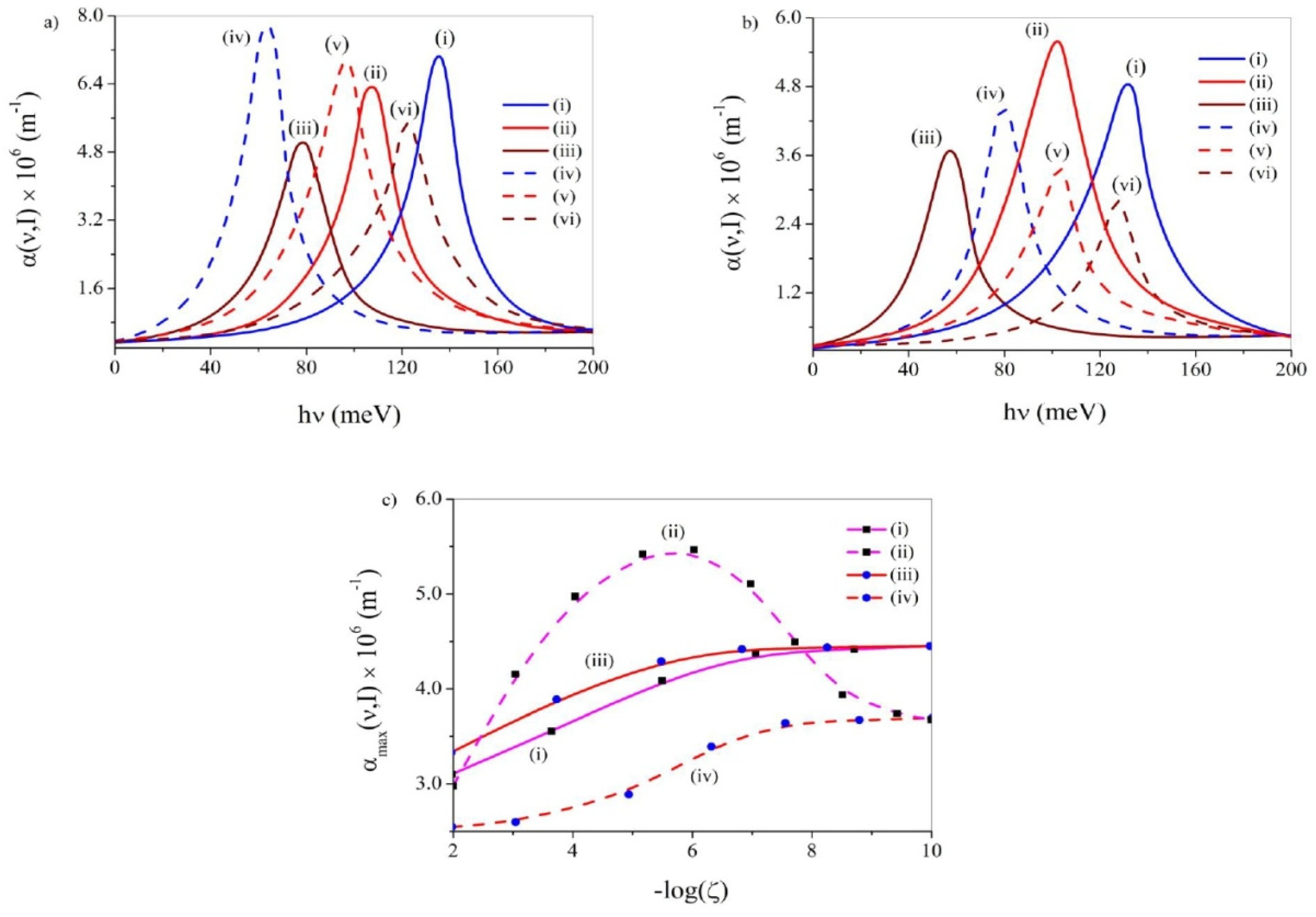
3.1. Total Optical Absorption Coeffcient (TOAC)
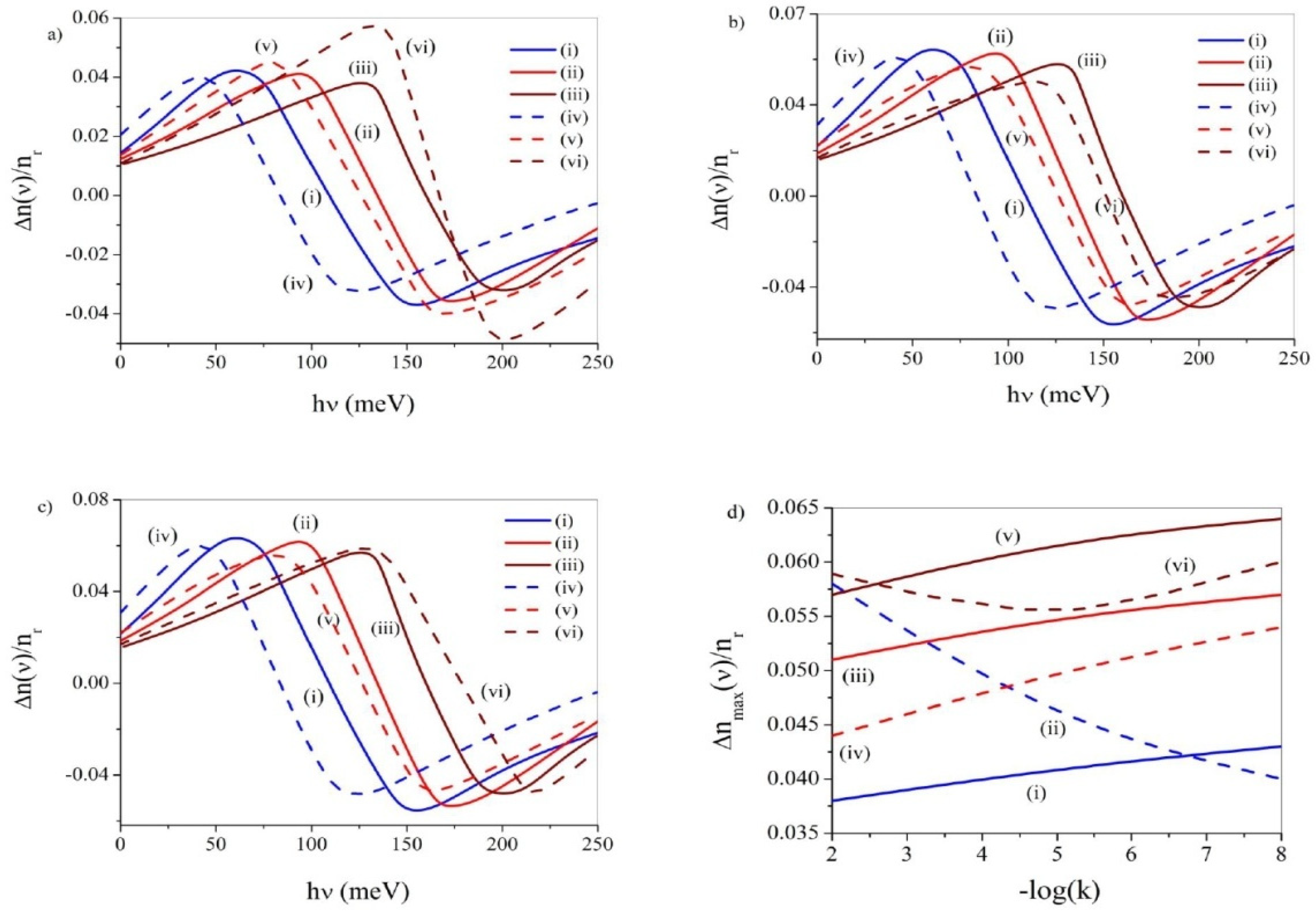
3.2. Total Optical Refractive Index Change (TORIC)
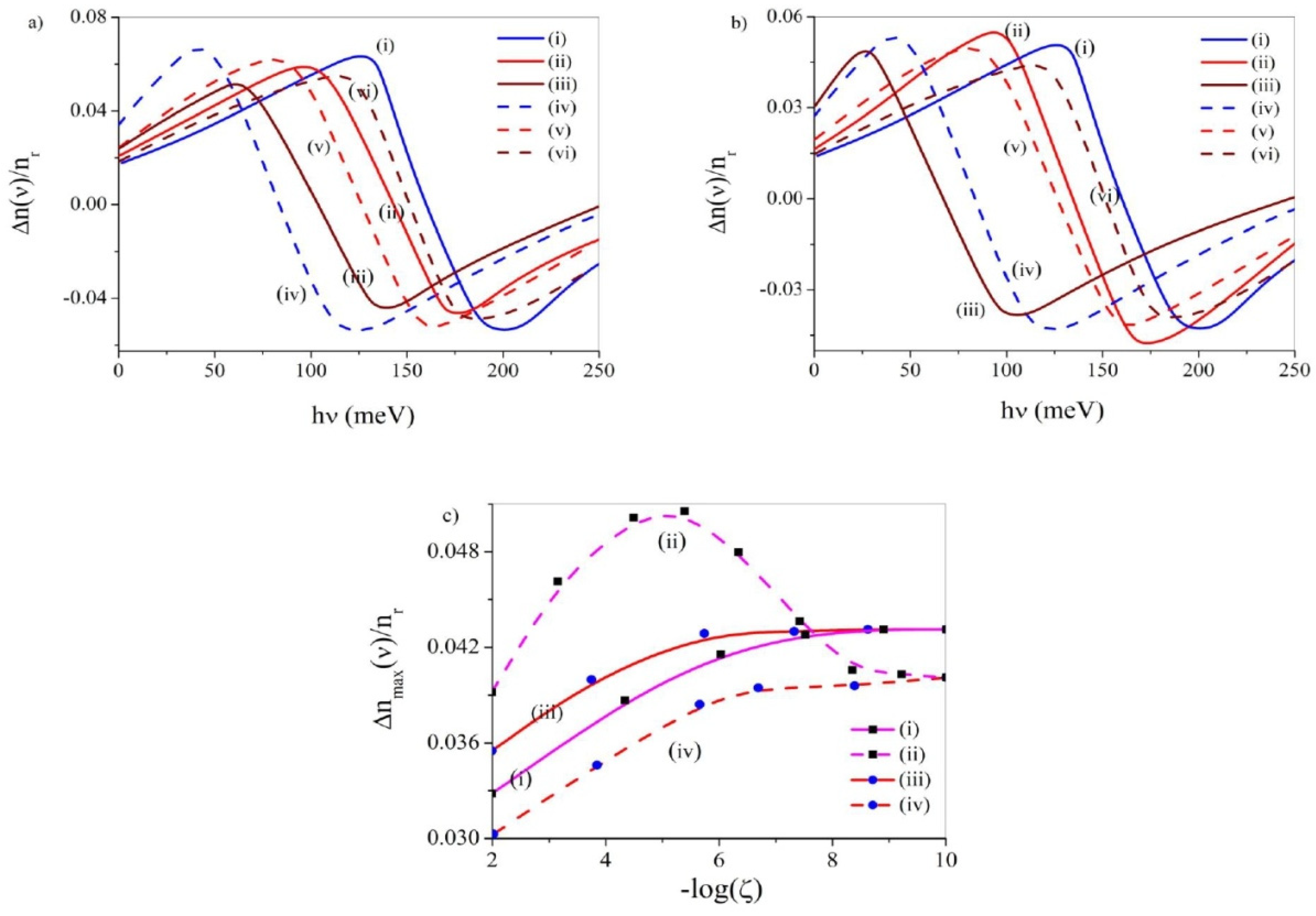
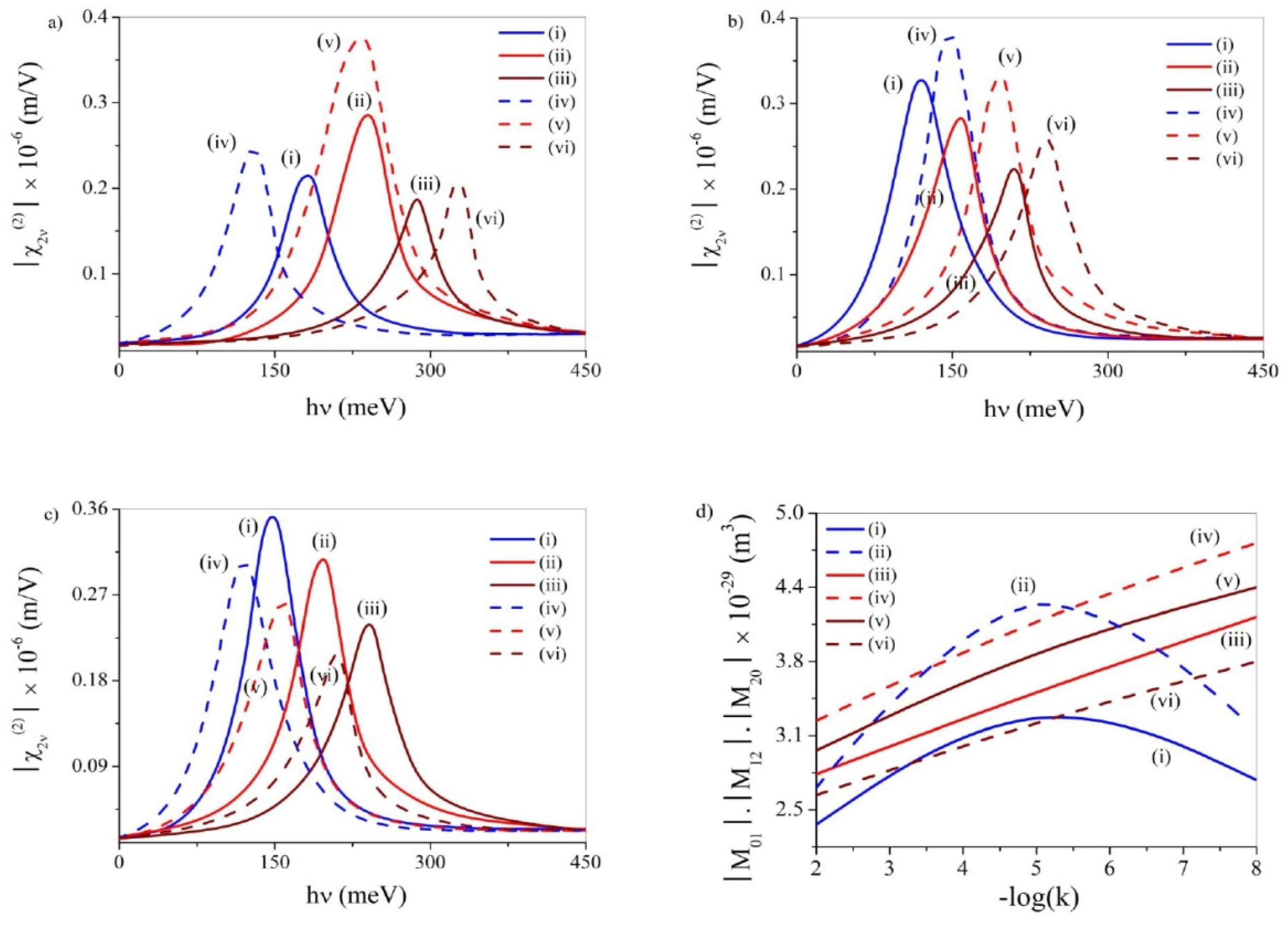
3.3. Nonlinear Optical Rectification (NOR)
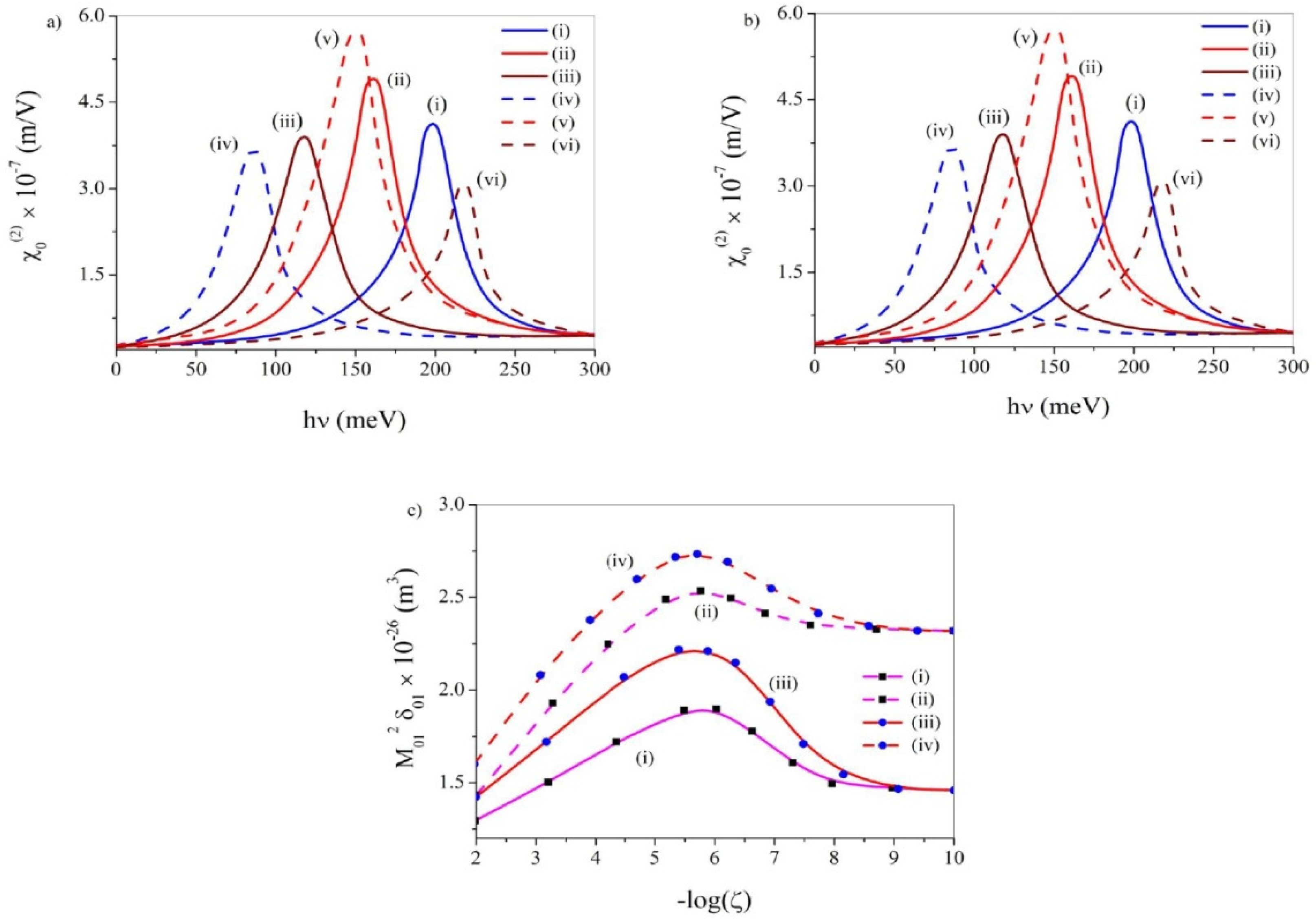
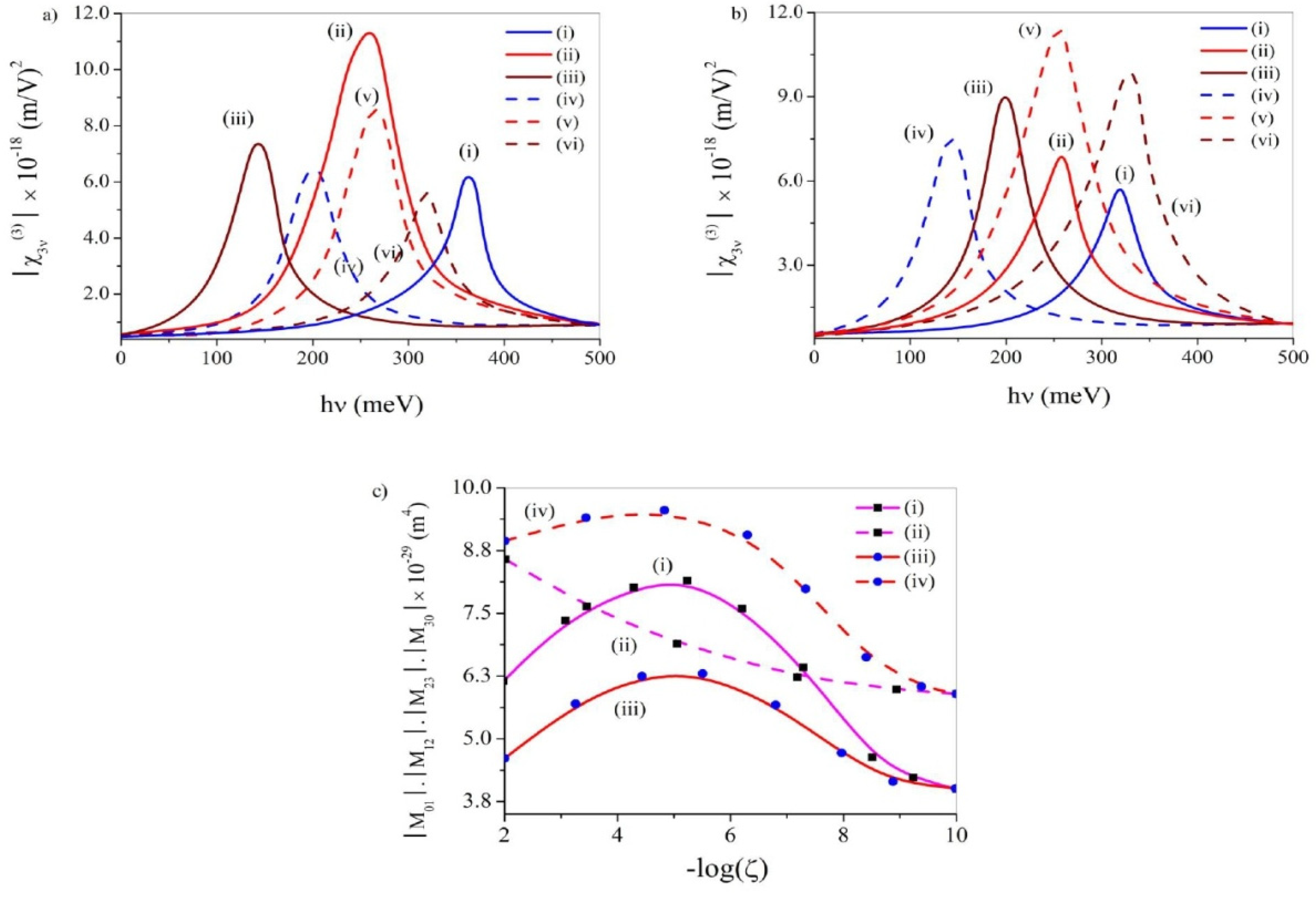
3.4. Second Harmonic Generation (SHG)
3.5. Third Harmonic Generation (THG)
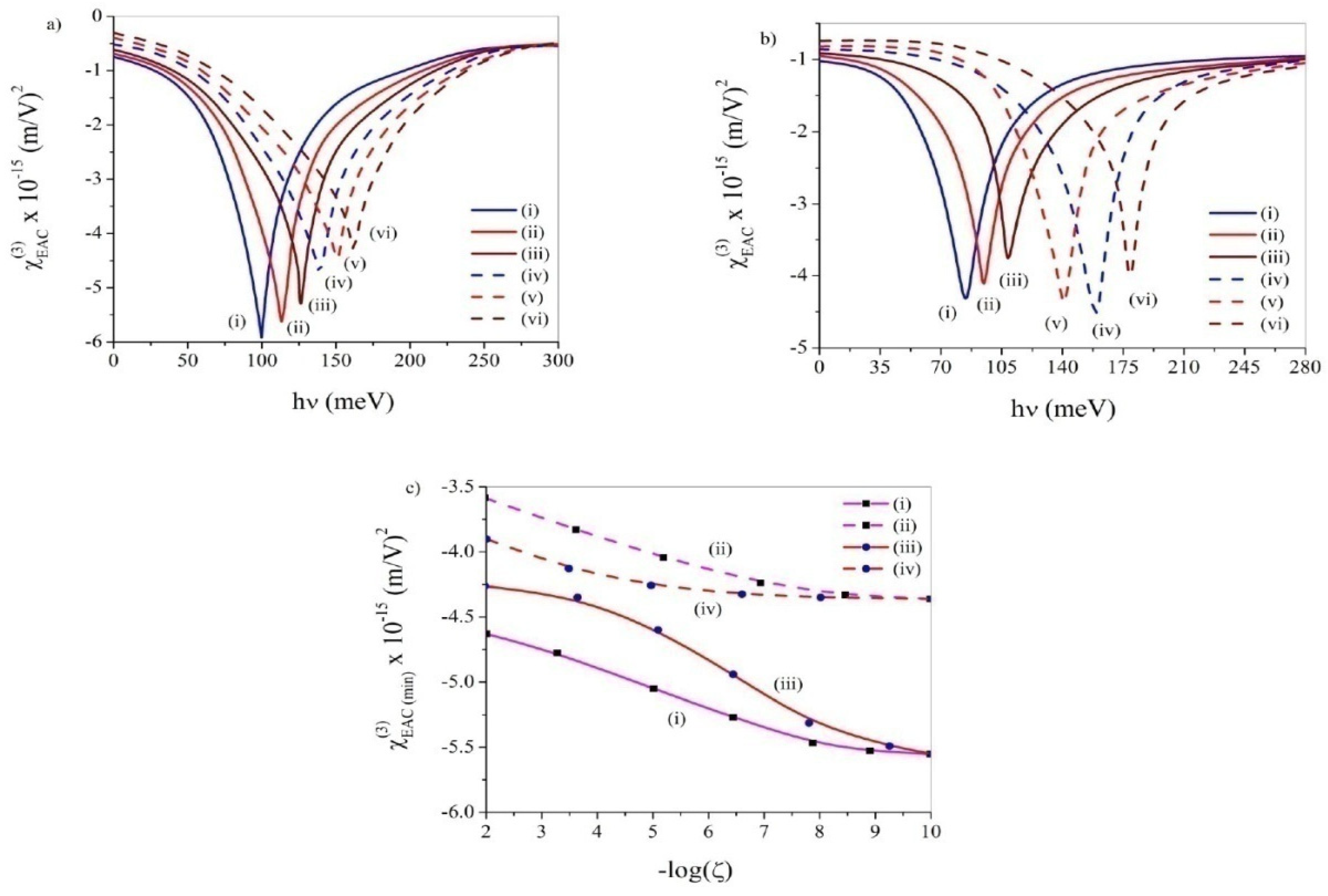
3.6. Electro-Absorption Coeffcient (EAC)
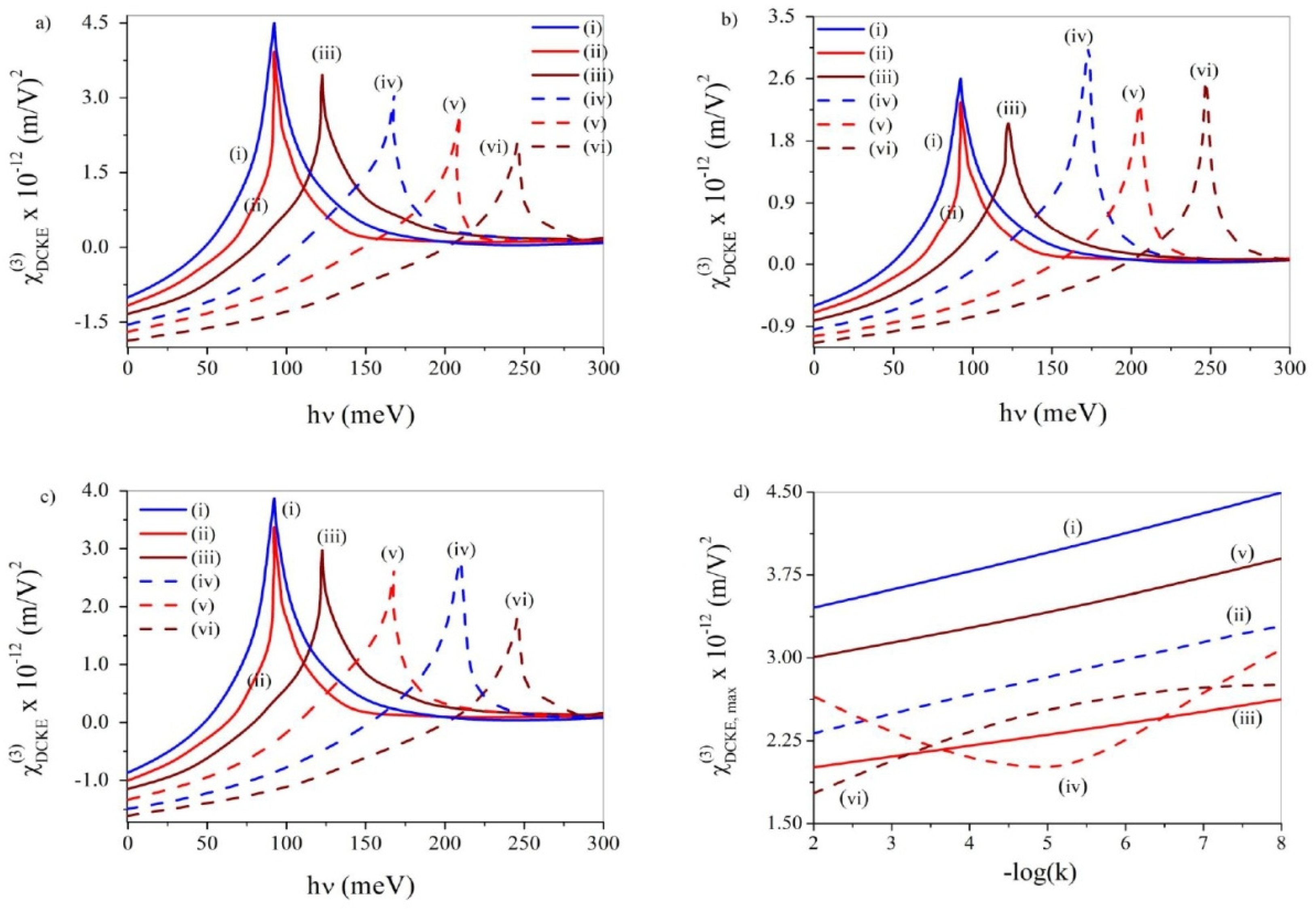
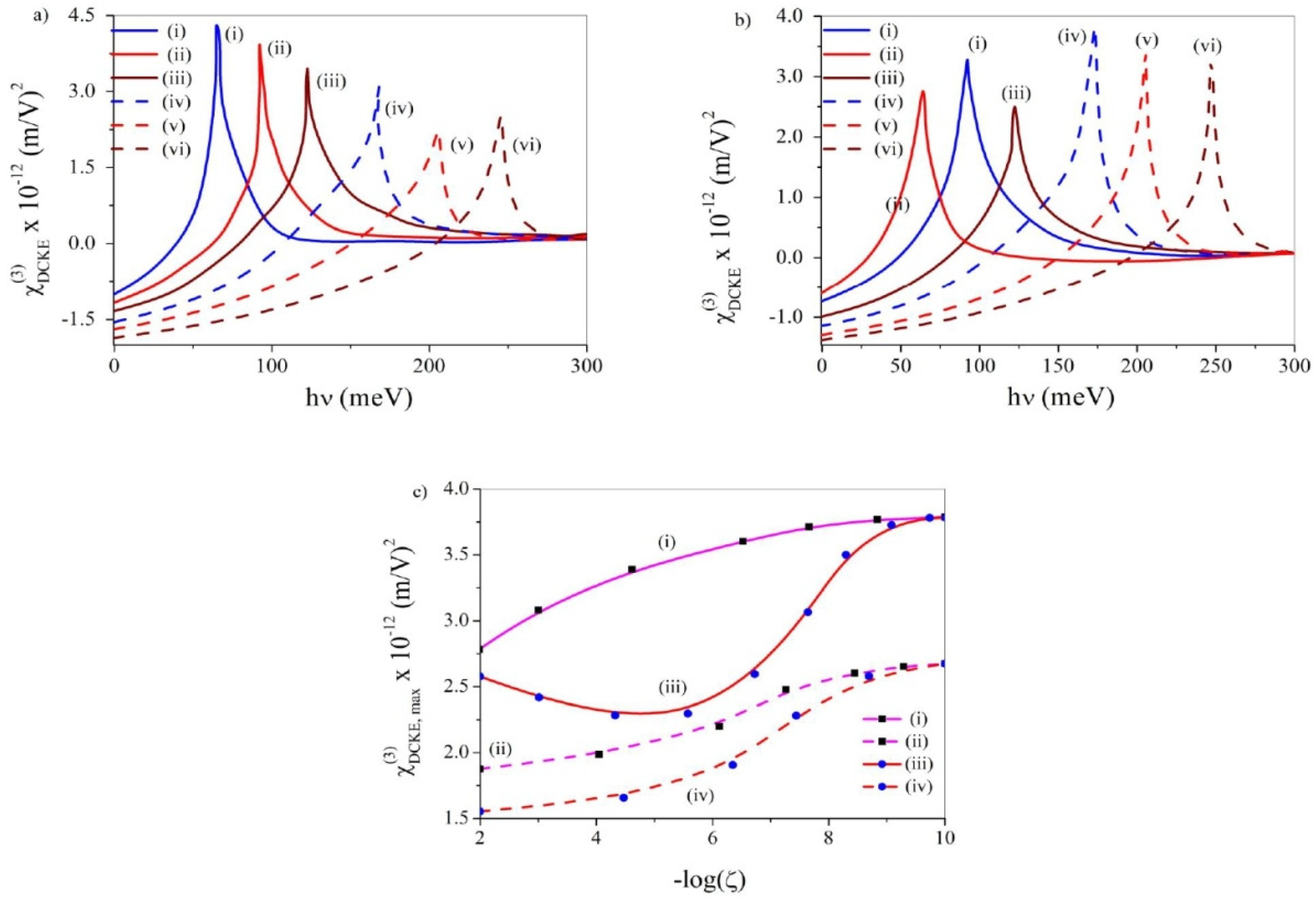
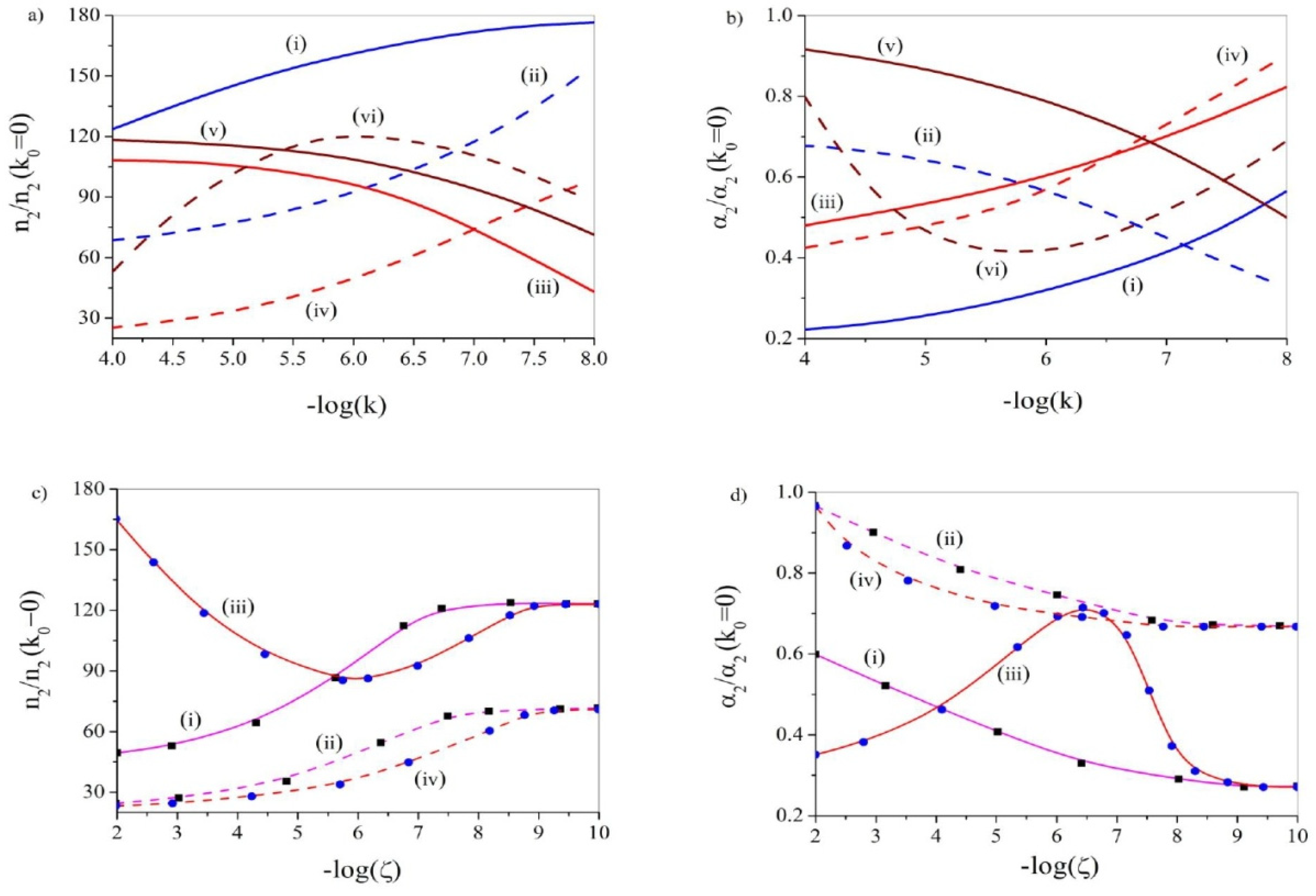
3.7. DC-Kerr Effect (DCKE)
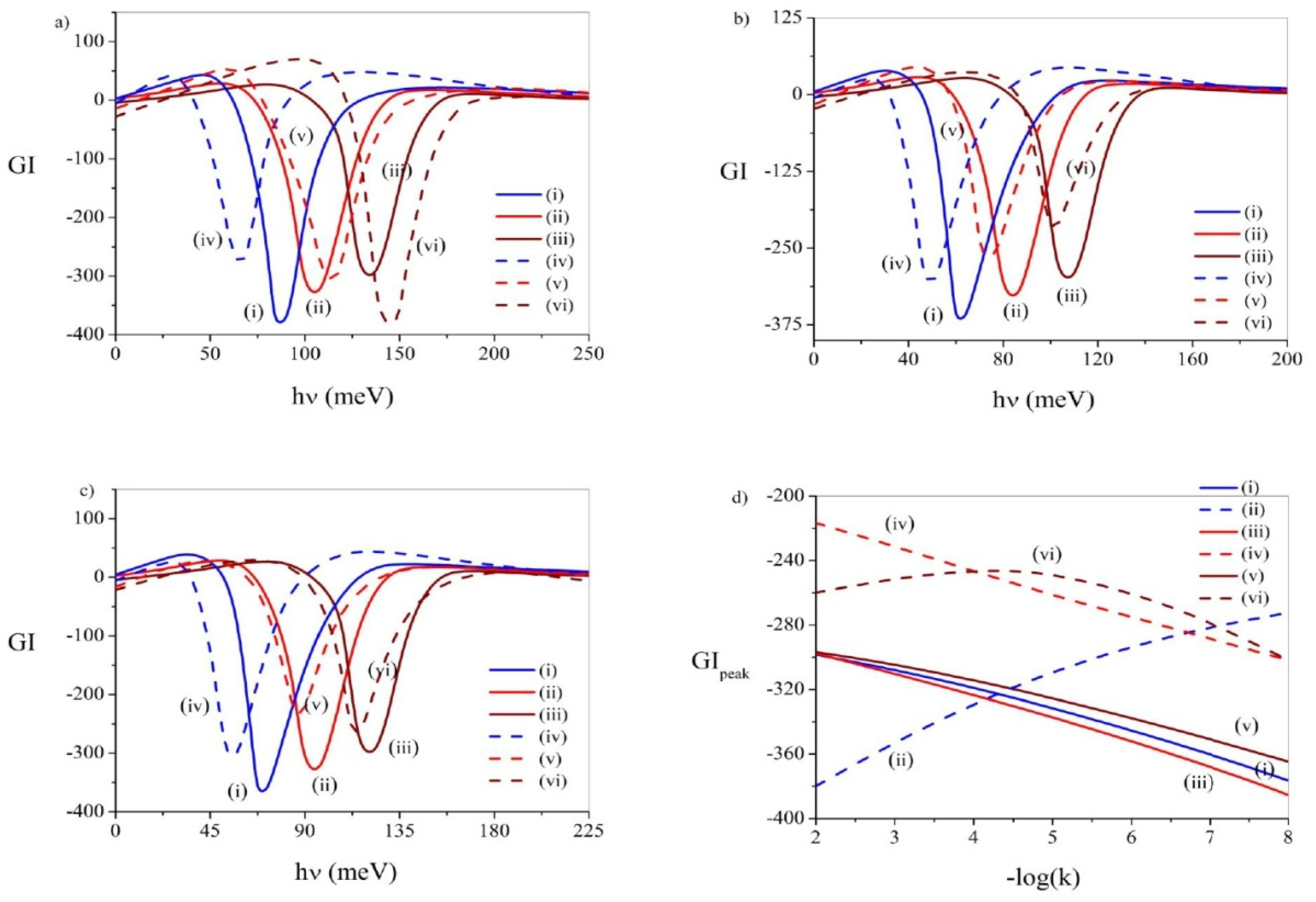
3.8. Group Index (GI)
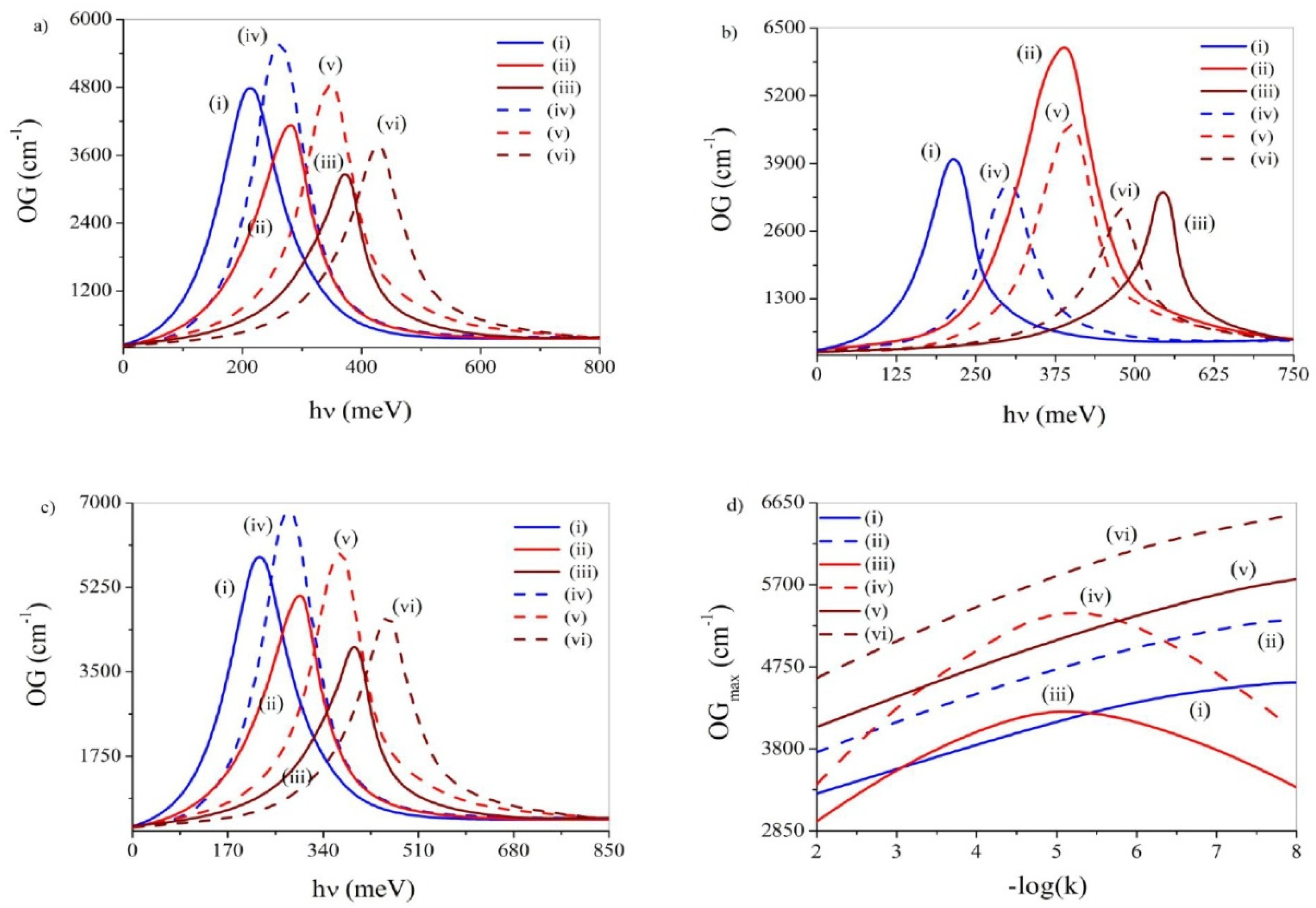
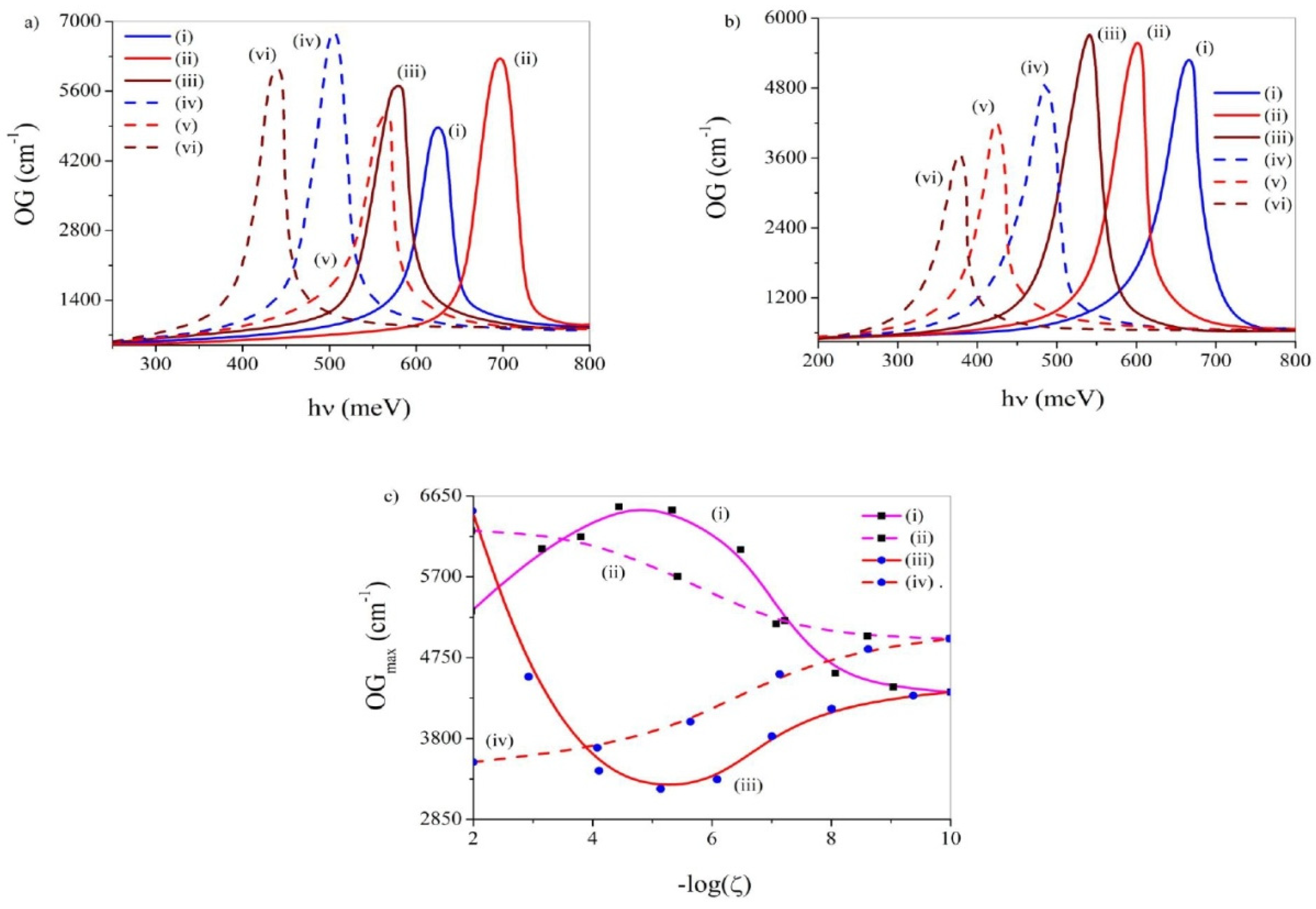
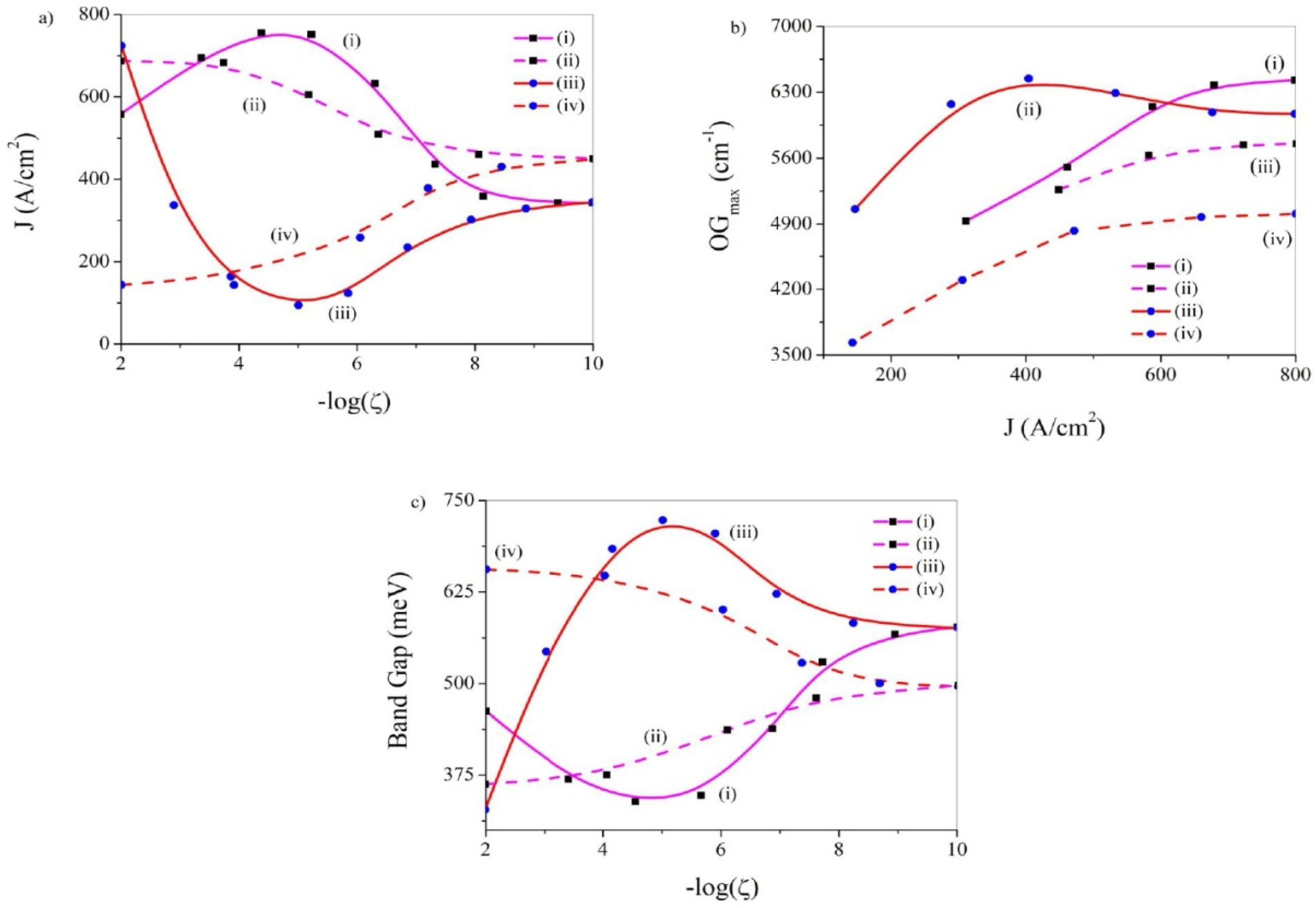
3.9. Optical Gain (OG)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khordad, R.; Bahramiyan, H. Impurity position effect on optical properties of various quantum Dots. Phys. E 2015, 66, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, G.; Vahdani, M.R.K.; Vaseghi, B. Nonlinear optical properties of a hydrogenic impurity in an ellipsoidal finite potential quantum dot. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapoglu, E.; Duque, C.A.; Mora-Ramos, M.E.; Restrepo, R.L.; Ungan, F.; Yesilgul, U.; Sari, H.; Sökmen, I. Combined effects of intense laser field, electric and magnetic fields on the nonlinear optical properties of the step-like quantum well. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 154, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimyfard, A.; Barseghyan, M.G.; Kirakosyan, A.A. Simultaneous effects of pressure and magnetic field on intersubband optical transitions in Pöschl-Teller quantum well. Phys. E 2009, 41, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khordad, R.; Bahramiyan, H. Optical properties of a GaAscone-like quantum dot: Second and third-harmonic generation. Opt. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, H.; Ungan, F.; Sakiroglu, S.; Yesilgul, U.; Sökmen, I. Impurity-related optical response in cylindrical quantum dots with a δ-doped axial potential under an intense laser field. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kria, M.; El-Yadri, M.; Aghoutane, N.; Pérez, L.M.; Laroze, D.; Feddi, E. Forecasting and analysis of nonlinear optical responses by tuning the thickness of a doped hollow cylindrical quantum dot. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 66, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitman, D.; Bollweg, K.; Gudmundsson, V.; Kurth, T.; Riege, S.P. Far-infrared spectroscopy of quantum wires and dots, breaking Kohn’s theorem. Phys. E 1997, 1, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, S.; Roy, D.; Ghosh, M. Influence of noise-anharmonicity interplay on a few physical properties of quantum dots. Phys. Status Solidi B 2022, 259, 2100497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Arif, S.; Ghosh, M. Modulation of electrical and optical properties of quantum dot by noise-anharmonicity interplay. Braz. J. Phys. 2022, 52, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, I.; Atav, Ü.; Şafak, H.; Tomak, M. Linear and nonlinear intersubband optical absorptions in an asymmetric rectangular quantum well. Eur. Phys. J. B 2007, 55, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ҫakir, B.; Yakar, Y.; Özmen, A.; Sezer, M.Ö.; Şahin, M. Linear and nonlinear optical absorption coeffcients and binding energy of a spherical quantum dot. Superlattices Microstruc. 2010, 47, 556–566. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, G.; Vaseghi, B.; Taghizadeh, F.; Vahdani, M.R.K.; Karimi, M.J. Intersubband optical absorption coeffcient changes and refractive index changes in a two-dimensional quantum pseudodot system. Superlattices Microstruc. 2010, 48, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Şahin, M. Third-order nonlinear absorption spectra of an impurity in a spherical quantum dot with different confining potential. Phys. Status Solidi B 2010, 247, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakar, Y.; Ҫakir, B. Calculation of linear and nonlinear optical absorption coeffcients of a spherical quantum dot with parabolic potential. Opt. Commun. 2010, 283, 1795–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ҫakir, B.; Yakar, Y.; Özmen, A. Refractive index changes and absorption coeffcients in a spherical quantum dot with parabolic potential. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, R.; Xie, W. Optical absorption of a hydrogenic impurity in a disc-shaped quantum dot. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghramyan, H.M.; Barseghyan, M.G.; Kirakosyan, A.A.; Restrepo, R.L. Linear and nonlinear optical absorption coeffcients in GaAs/Ga1-xAlxAsconcentric double quantum rings: Effects of hydrostatic pressure and aluminium concentration. J. Lumin. 2013, 134, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, H.E.; Jorio, A.; Zorkani, I. Linear and nonlinear intra-conduction band optical absorption in (In,Ga)N/GaNspherical QD under hydrostatic pressure. Opt. Commun. 2014, 331, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Xie, W.; Hassanabadi, H. Linear and nonlinear optical absorption coeffcients and refractive index changes in a two-electron quantum dot. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 063108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskoutas, S.; Garoufalis, C.S.; Terzis, A.F. Linear and nonlinear optical absorption coeffcients in inverse parabolic quantum wells under static external electric field. Eur. Phys. J. B 2011, 84, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şakiroğlu, S.; Ungan, F.; Yesilgul, U.; Mora-Ramos, M.E.; Duque, C.A.; Kasapoglu, E.; Sari, H.; Sökmen, I. Nonlinear optical rectification and the second and third harmonic generation in Pöschl-Teller quantum well under the intense laser field. Phys. Lett. A 2012, 376, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanabadi, H.; Liu, G.; Lu, L. Nonlinear optical rectification and the second-harmonic generation in semi-parabolic and semi-inverse quantum wells. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskoutas, S.; Paspalakis, E.; Terzis, A.F. Effects of excitons in nonlinear optical rectification in semiparabolic quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 153306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, İ.; Şafak, H.; Tomak, M. Nonlinear optical rectification in asymmetrical semiparabolic quantum wells. Solid State Commun. 2005, 135, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, G.; Vaseghi, B.; Khordad, R.; Kenary, H.A. Optical rectification coeffcient of a twodimensional quantum pseudodot system. Phys. E 2011, 43, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskoutas, S.; Paspalakis, E.; Terzis, A.F. Electronic structure and nonlinear optical rectification in a quantum dot: Effects of impurities and external electric field. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 395024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrsia, R.B.; Choubani, M.; Bouzaїene, L.; Maaref, H. Nonlinear optical rectification in a vertically coupled lens-shaped InAs/GaAsquantum dots with wetting layers under hydrostatic pressure and temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 671, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-B.; Zhu, S.-N.; Guo, K.-X. Excitonic effects on the nonlinear optical rectification in one-dimensional quantum dots. Phys. Lett. A 2005, 335, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, H.; Tomak, M. Nonlinear optical properties of a Pöschl-Teller quantum well. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W. Nonlinear optical rectification of a hydrogenic impurity in a disc-like quantum dot. Physical B 2009, 404, 4142–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, H.-J. Electric field effect on the second-order nonlinear optical properties of parabolic and semiparabolic quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 235315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, İ.; Atav, Ü.; Şafak, H. Comment on “Electric field effect on the second-order nonlinear optical properties of parabolic and semiparabolic quantum wells”. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 207301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, S.; Boucaud, P.; Brunhes, T.; Glotin, F.; Prazeres, R.; Ortega, J.M.; Gérard, J.M. Second-harmonic generation resonant with s-p transition in InAs/GaAsself-assembled quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 113312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedrakian, D.M.; Khachatrian, A.Z.; Andresyan, G.M.; Badalyan, V.D. The second harmonic generation in the symmetric well containing a rectangular barrier. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2004, 36, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Guo, K.-X.; Zhang, C.-J.; Zheng, Y.-B. The second harmonic generation in parabolic quantum dots in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. Phys. Lett. A 2007, 367, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, S.; Boucaud, P.; Glotín, F.; Prazeres, R.; Ortega, J.-M.; Lemaître, A.; Gérard, J.-M.; Thierry-Mieg, V. Third-harmonic generation in InAs/GaAsself-assembled quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 9830–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, H.-J. Bound states and third-harmonic generation in a semi-parabolic quantum well with an applied electric field. Phys. E 2004, 22, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Third-harmonic generation in cylindrical parabolic quantum wires with an applied electric field. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 155329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Guo, K.-X.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Li, N.; Peng, C. Third-harmonic generation in cylindrical quantum dots in a static magnetic field. Solid State Commun. 2011, 151, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, H.; Tomak, M. Third-harmonic generation in a quantum well with adjustable asymmetry under an electric field. Phys. Stats. Solidi B 2006, 243, 4057–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Guo, K.-X.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Li, N.; Peng, C. Studies on the third-harmonic generations in cylindrical quantum dots with an applied electric field. Superlattices Microstruc. 2010, 48, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, J.E.Q.; Lyra, M.L.; Lima, R.P.A. Crossover from strong to weak exciton confinement and third-harmonic generation on one-dimensional quantum dots. Photonics Nanostruc. 2013, 11, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, E.C.; Cristea, M.; Radu, A. magnetic field effect on third-harmonic generation in quantum well wires with triangular cross-section. Phys. E 2014, 57, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirak, M.; Altinok, Y. The electric field effects on the third-harmonic generation in spherical quantum dots with parabolic confinement. Eur. Phys. J. B 2012, 85, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhi, M. Electric field effect on the quadratic electro optic effects and electro absorption process in GaN/AlGaNspherical quantum dot. Optik 2016, 127, 3379–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, A.; Moghadam, F.R. Quadratic electro-optic effect and electro-absorption process in CdSe-ZnS-CdSestructure. Physical E 2012, 44, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, M.; Radu, A.; Niculescu, E.C. Electric field effect on the third-order nonlinear optical susceptibility in inverted core-shell nanodots with dielectric confinement. J. Lumin. 2013, 143, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiong, G. Quadratic electro-optic effects and electro-absorption process in InGaN/GaNcylinder quantum dots. Microelectron. J. 2006, 37, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhi, M.; Vahedi, A.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Joo, S.W. Investigation of quadratic electro-optic effects and electro-absorption process in GaN/AlGaNspherical quantum dot. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Xiong, G.; Feng, X.; Chen, Z. Characteristics of quadratic electro-optic effects and electro-absorption process in CdSeparabolic quantum dots. Microelectron. J. 2007, 38, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadpour, S.H.; Sahrai, M.; Sadighi-Bonabi, R.; Soltani, A.; Mahrami, H. Enhancement of Kerr nonlinearity at long wavelength in a quantum dot nanostructure. Phys. E 2011, 43, 1759–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadpour, S.H.; Hamedi, H.R.; Eslami-Majd, A.; Sahrai, M. Enhanced Kerr nonlinearity in a tunnel-coupled quantum well. Phys. E 2011, 44, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nashy, B.; Amin, S.M.M.; Al-Khursan, A.H. Kerr effect in quantum dot structure. Optik 2014, 125, 4873–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- delCoso, R.; Solis, J. Relation between nonlinear refractive index and third-order susceptibility in absorbing media. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2004, 21, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Chuang, S.L. Room-temperature slow light with semiconductor quantum-dot devices. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Chuang, S.L.; Ku, P.C.; Chang-Hasnain, C.J. Slow light using semiconductor quantum dots. J. Phys. Condens. Matters 2004, 16, S3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Hasnain, C.J.; Chuang, S.L. Slow and fast light in semiconductor quantum-well and quantum-dot devices. J. Light. Technol. 2006, 24, 4642–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, L.; Filipović, N.; Pavlović, V. Effect of magnetic field on absorption coeffcients, refractive index changes and group index of spherical quantum dot with hydrogenic impurity. Opt. Mater. 2019, 91, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flayyih, A.H.; Al-Khursan, A.H. Integral gain in quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. Superlattices Microstruc. 2013, 62, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owji, E.; Keshavarz, A.; Mokhtari, H. The effects of temperature, hydrostatic pressure and size on optical gain for GaAsspherical quantum dot laser with hydrogen impurity. Superlattices Microstruc. 2016, 98, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanamoorthy, S.N.; Peter, A.J.; Lee, C.W. Optical peak gain in PbSe/CdSecore-shell quantum dot in the presence of magnetic field for mid-infrared laser applications. Chem. Phys. 2017, 483–484, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owji, E.; Keshavarz, A.; Mokhtari, H. The effects of geometrical size, external electric fields and impurity on the optical gain of a quantum dot laser with a semi-parabolic spherical well potential. Phys. B 2017, 508, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, W.J.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.W. Electronic structure and optical gain of InAsPN/GaP(N) quantum dots. Superlattices Microstruc. 2011, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, W.J.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.W.; Li, S.S.; Xia, J.B. Electronic structure and optical gain saturation of InAs1-xNx/GaAsquantum dots. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 123705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladysiewicz, M.; Kudrawiec, R.; Wartak, M.S. Theoretical studies of optical gain tuning by hydrostatic pressure in GaInNAs/GaAsquantum wells. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 033515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, I.; Samajdar, D.P.; Peter, A.J. Theoretical studies on band structure and optical gain of GaInAsN/GaAs/GaAscylindrical quantum dot. Superlattices Microstruc. 2018, 119, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, I.; Samajdar, D.P.; Das, T.D. Calculation of band structure and optical gain of type-II GaSbBi/GaAsquantum wells using 14-band k.pHamiltonian. Superlattices Microstruc. 2017, 109, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mageshwari, P.U.; Peter, A.J.; Lee, C.W. Magnetic field induced optical gain in a dilute nitride quaternary semiconductor quantum dot. Opt. Mater. 2016, 60, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, D.; Arif, S.M.; Datta, S.; Ghosh, M. Tuning the Nonlinear Optical Properties of Quantum Dot by Noise-Anharmonicity Interaction. Atoms 2022, 10, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms10040122
Roy D, Arif SM, Datta S, Ghosh M. Tuning the Nonlinear Optical Properties of Quantum Dot by Noise-Anharmonicity Interaction. Atoms. 2022; 10(4):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms10040122
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Debi, Sk. Md. Arif, Swarnab Datta, and Manas Ghosh. 2022. "Tuning the Nonlinear Optical Properties of Quantum Dot by Noise-Anharmonicity Interaction" Atoms 10, no. 4: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms10040122
APA StyleRoy, D., Arif, S. M., Datta, S., & Ghosh, M. (2022). Tuning the Nonlinear Optical Properties of Quantum Dot by Noise-Anharmonicity Interaction. Atoms, 10(4), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms10040122





