Abstract
High quality nuclear data lie at the heart of accurately modelling stellar systems and terrestrial nuclear reactors. However, some key reaction cross sections have large uncertainties, which limit such models in predicting isotopic abundances and other aspects of stellar evolution, along with key operational parameters for nuclear reactors. Reactions involving neutrons are particularly difficult to measure experimentally in laboratories, not least due to the unique challenges involved when detecting neutrons. We present a new approach to measuring nuclear reactions involving neutrons by exploiting the Thick-Target Inverse Kinematics (TTIK) approach. For such measurements, a new detector called ATTIKUS (A Thick-Target Inverse Kinematics detector by Universities in Sheffield) is under construction. Here we present designs and Geant4 Monte-Carlo simulations of the detector. The simulations indicate that a neutron position reconstruction resolution of 10 cm is obtainable and demonstrate how this device could be applied to the 13C(α,n) reaction, which is considered to be the main neutron source for the s-process in low-mass Asymptotic Giant Branch stars. In the TTIK method, the emission position of the neutron (the nuclear interaction position in a gaseous target) is directly linked to the centre-of-mass energy of the reaction. Therefore, a position resolution will translate into an energy resolution, depending on the beam-target combination. The inverse reaction, 16O(n,α), causes a large uncertainty in calculating the effective neutron multiplication factor, Keff in nuclear reactors, so improvements are required here.
PACS:
26.00.00; 29.40.Mc; 28.20.-v
1. Introduction
Nuclear reactions are responsible for nucleosynthesis; the formation of elements in the universe [1]. Big-Bang nucleosynthesis at the beginning of the universe mainly produced isotopes of hydrogen, helium, and lithium. To give rise to the full abundance of nuclei seen in nature, this primordial nucleosynthesis is followed by the formation of stars where elements up to iron are produced. Even heavier elements are then synthesised by various processes, such as neutrino-induced reactions [2], neutron capture [3], and explosive events in supernovae [4]. Astrophysical scenarios and stellar models are widely discussed in existing literature [5,6].
Our understanding of stellar evolution is limited, in part, by the accuracy of nuclear data libraries, which detail the cross sections of known nuclear reactions, and form a key input to stellar evolution models [7]. Some key reaction cross sections have very large uncertainties, particularly at low energies where the cross sections are small. The reaction rate during measurements is low, meaning that data are scarce, subject to large statistical uncertainties and more susceptible to the influences of backgrounds.
Further, as we continue to exploit nuclear reactions as an energy source here on Earth, welcoming in next generation fission reactors, and looking forward to the possibility of fusion energy, the importance of high quality nuclear data is quickly becoming apparent [8,9]. A well-established knowledge of nuclear reactions including reaction cross sections, fission and decay properties is critical for the design and operation of new reactors and nonproliferation.
The fact that many key reactions in astrophysics and for nuclear power generation involve neutrons presents extra hurdles when measuring these reactions in laboratories. Production of mono-energetic neutron beams is notoriously difficult [10] and detection of neutrons as reaction products presents its own challenges. Neutron detection is an indirect process whereby neutrons react with the nuclei in certain materials to instigate the release of one or more charged particles. These charged particles produce signals that can then be processed by a detection system. Therefore, neutron detection requires conversion materials as active elements of the detection system. Traditionally, the most commonly used is helium-3. In these systems, a neutron will interact with a helium-3 nucleus (helion) to produce a triton and a proton.
Due to a global helium shortage, and the soaring costs of helium-3, neutron detection is now a rapidly evolving field, where novel detection technologies are being explored [11]. A hugely promising avenue is that of novel organic and inorganic scintillating materials. These materials are sensitive to both neutrons and gamma-rays, but the the two may be separated using pulse shape discrimination (PSD) techniques [12]. These devices have the advantage of being able to measure a mixed radiation field, offer energy sensitivity, and, in their liquid form, have a lower cost than helium-3. However, they have typically suffer from higher backgrounds than traditional counters and the liquid scintillators are highly toxic, limiting their transportability and safety. Solid plastic scintillators with PSD capabilities are also available [13], which are safer to use but come at a premium cost, making them impractical for large-area devices.
The following paper details the design and simulation of a new neutron detector array, called ATTIKUS (A Thick-Target Inverse Kinematics detector by Universities in Sheffield), that will permit reactions in nuclear astrophysics to be measured in Thick-Target Inverse Kinematics (TTIK) [14]. In contrast to typical nuclear data measurements, where a light ion beam impinges onto a solid target made from heavier nuclei, the TTIK method involves directing a heavy ion beam onto a light gaseous target. As it passes through the gas, the beam loses energy, meaning that nuclear reactions can be measured over a range of centre-of-mass energies, while using just a single incident beam energy. The position that the nuclear reaction happens in the chamber uniquely defines the centre-of-mass energy of the reaction, hence a position-sensitive detector is required. The ATTIKUS detector design utilises a novel neutron/gamma discrimination method, without recourse to using expensive PSD scintillators, and allows neutron detection position sensitivity, with a resolution of 10 cm. The design of the detector permits the measurement of neutrons over a range of energies. However, higher energy neutrons will be measured with lower efficiency, and lower energy neutrons with a poorer position resolution. These properties are discussed later in the paper.
This paper will begin by describing the TTIK method, and why it is useful for nuclear cross section measurements for astrophysics. The application of the ATTIKUS detector to this technique will then be covered. Monte-Carlo simulations of the detector will then be detailed. These provide useful information on the optimisation of detector geometry in order to maximise the efficiency and resolution for position-sensitive neutron detection, while maintaining low cost. This is crucial information for construction of the detector.
As a test case for the detector, its simulated performance in measuring the 13C(α,n) reaction will be explored. This is a particularly important reaction in nuclear astrophysics, as it is one of the main neutron sources for the astrophysical s-process in Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) stars [15], and is also important for the weak s-process in Massive stars (≥10) [16,17]. To model the nucleosynthesis during the former process, the reaction cross section needs to be reliably measured in the 150–230 keV energy window (Gamow peak). A well-constrained 13C(α,n) cross section is also important in nuclear data for terrestrial nuclear reactors, given that the reverse reaction, 16O(n,α), is crucial in understanding neutron multiplication and helium production in nuclear reactors. Oxygen is a major component in various nuclear reactors, either in UO2 or PuO2 fuels or in an H2O moderator. It has previously been determined that the current uncertainty in the 16O(n,α) reaction leads to a 100 pcm (0.1%) uncertainty in the reactivity and a 5–10% uncertainty in helium production [18].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Thick-Target Inverse Kinematics
In a typical experiment measuring the 13C(α,n) reaction, mono-energetic beams of alpha particles are directed onto a 13C target and the cross section is measured by counting the neutrons emitted by the target. This is a slow process; a typical experiment [19] measured a 0.5 MeV region of the cross section over 20 separate beam energies, requiring 19 beam energy changes, which is inefficient and takes a long time.
The ATTIKUS detector will measure the same reaction in Thick Target Inverse Kinematics (TTIK), by firing a heavy 13C beam onto a metre-long gaseous 4He target. By tuning the beam energy and the gas pressure, the beam and target nuclei can trace out a customisable range of centre-of-mass energies during the passage through the gas. This means that cross section can be determined over a range of centre-of-mass energies at a single beam energy setting. By measuring the position that the neutrons exit the detector, the energy of the reaction on an event-by event basis can be uniquely determined. This technique should permit more rapid and high-statistics measurements due to not needing frequent beam energy changes, which can be time consuming. The gas also provides a large effective target thickness, boosting the reaction rate.
Although the TTIK method for this reaction was entirely novel at the time of commencement of the project, there has since been an experiment recently published [20], which measured the 13C(α,n) using TTIK at a 180° centre-of-mass angle only. Their result showed very poor agreement with previous measurements/global R matrix parameters and further highlights the large uncertainties mentioned earlier. Our planned experiment is most sensitive to centre-of-mass angles from 100–130° so will provide a novel insight to the cross section particularly at these angles. An extension to the project to measure 180° centre-of-mass angle with an additional detector could be implemented to verify the conclusions of [20].
2.2. ATTIKUS Overview
We have designed a large-area, low-cost, position-sensitive neutron detector that can be used in an inverse kinematics set-up. In principle, such a detector could consist of a large volume of plastic or liquid scintillator, with neutron/gamma discrimination capabilities, as was achieved previously [21]. However, given the size of the detector required to efficiently stop the neutrons, such exotic scintillator materials are prohibitively expensive. Therefore, a novel and inexpensive detector construction has been proposed to achieve neutron/gamma discrimination for large-area detectors. A rendering of an optimised ATTIKUS detector module is shown in Figure 1. It consists of layers of neutron-sensitive material, moderator and light guides.
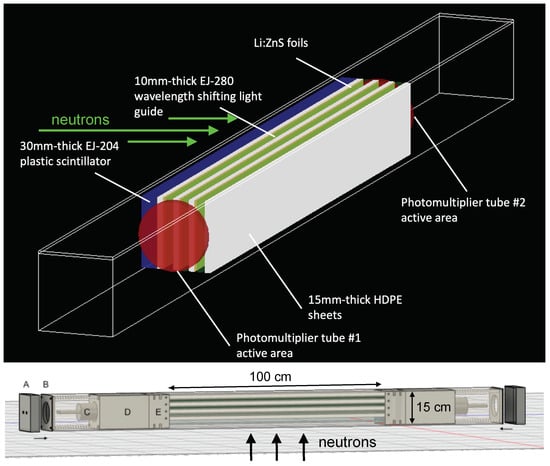
Figure 1.
Upper panel: A single detector module rendered in Geant4, with individual components labelled. White sheets: HDPE. Green: wavelength shifting light guides. Yellow: Li:ZnS foil. Blue: EJ-204 plastic scintillator. Red: Photomultiplier tube face. Lower panel: The CAD rendering of a single detector module.
The blue face is a plastic scintillator, EJ-204, which is sensitive to both neutrons and γ-rays. However, upon interacting in the plastic, the scattered fast neutron will then be moderated by the white HDPE sheets and when sufficiently slow, will be captured on a Li:ZnS foil, emitting scintillation light, which is then transmitted to the WLS light guides. The light from both the wavelength shifters (WLS) and plastic scintillators attenuates as it reaches two photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) at either end of the detector length. This means that the position of the detection can be determined by the relative pulse heights measured at each end. Relative timing information can also be used to determine the hit position, however, improved digitisers with sufficiently higher sample rates are required for that to be feasible. The active length of the detector is one metre. The power of this technique is that fast neutron/γ discrimination is obtained without recourse to scintillator materials with intrinsic neutron/γ discrimination properties, which would be prohibitively expensive for a detector of this size. It is achieved by triggering on a delayed pulse from the moderated neutron. Measurements of astrophysical nuclear reactions, such as 13C(α,n) are typically sensitive to the effects of backgrounds given that during experiments, very low count rates are expected. As such, influences from common environmental gamma-rays, such as the 1461 keV from potassium-40 become important. The construction of ATTIKUS will lower the influence of background gamma rays, using the coincidence trigger, which will only apply to neutrons. The overall experimental set-up will include four identical ATTIKUS detector modules surrounding a target chamber containing low-pressure helium gas, as shown in Figure 2. The heavy ion beam will be oriented to travel along the length of the detector modules.
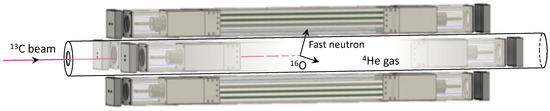
Figure 2.
The arrangement of four ATTIKUS detector modules around the gas target vessel and ion beam. The set-up is shown specifically for measuring the 13C(α,n) cross section. As the 13C ion beam passes through the 4He gas, it loses energy. The interaction point (emission position of the neutron) dictates the centre-of-mass energy of the nuclear reaction. The centre-of-mass energy resolution of the detector is therefore limited by the position reconstruction position of the neutron.
The remainder of this paper details the Monte-Carlo optimisation that has been performed in order to best inform the components that should be used to construct the detector. The efficiency of the device was optimised by varying the dimensions of certain components and the achievable position resolution was quantified.
2.3. Monte-Carlo Simulations
The Monte Carlo simulations were performed using the CRESTA framework [22], previously developed by J. P. Stowell in 2018. The program, CRESTA, is a front end package designed to interface with the Geant4 framework, and allows the user to quickly generate different detector geometries through modification of a series of input files, without needing to recompile the program. It is therefore ideal for rapid optimisation studies. The back-end of CRESTA, Geant4 [23], is a toolkit for the simulation of the passage of particles through matter. Built-in Geant4 libraries cover phenomena useful to this project, such as: standard EM processes, low energy EM processes, hadronic processes, photon/lepton-hadron processes and optical photon processes. In all cases, the simulations were carried out with the Shielding physics list in Geant 4.10.7, with extensions for Cherenkov and scintillation photon transport.
2.3.1. Efficiency Studies
The detector efficiency (number of detected neutrons/number of incident neutrons) has been optimised for a flat distribution of neutron energies between 2 and 4 MeV. The layered nature of the detector construction means that quick changes to the geometry can be made if necessary, when working with a different neutron energy spectrum. Monte Carlo studies have indicated, as expected, that higher energy neutrons will require larger amounts of moderator and so, the relative sizes of each detector layer will need to be changed. The sandwich-like detector construction permits this very easily.
These initial, basic simulations work on truth-level Monte-Carlo. The chosen energy distribution of neutrons is directed into the detector perpendicularly as shown in Figure 3. This figure shows the paths of neutrons entering the detector and their paths inside the detector. Some scatter inside the detector and escape, some (not shown) pass directly through the detector without interacting, and others do interact and are captured inside the detector. Two classes of events were considered. Firstly, those that moderate and stop somewhere in the detector. Secondly, coincidence events that interact in the plastic scintillator (blue) then later go on to be captured in another detector layer (necessary for neutron/gamma discrimination).
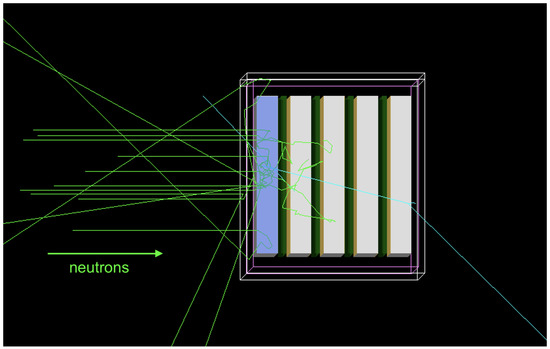
Figure 3.
Neutron tracks entering and moderating inside the detector volume. Two classes of events were considered. Firstly, those that moderate and stop somewhere in the detector. Secondly, coincidence events that interact in the plastic scintillator (blue) then later go on to be captured in another detector layer. Neutrons were simulated from a flat distribution between 2–4 MeV.
The efficiency is largely determined by the ratio of thicknesses of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and wavelength shifters (WLS) inside the detector volume. The EJ-280 WLS, produced by Eljen, is manufactured in fixed thicknesses and for the optimisation purposes, 10 mm- and 20 mm-thick pieces were considered. The efficiency was then recorded as a function of HDPE thickness. The HDPE moderator is significantly cheaper than the WLS, so cost is also something that should be factored into the discussion. Figure 4 shows the total efficiency for neutron capture inside the detector as a function of HPDE thickness for WLS of 10 mm and 20 mm.
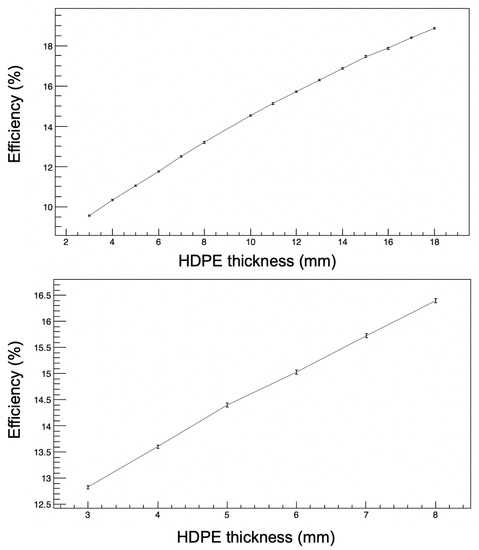
Figure 4.
Efficiency for neutron capture inside the detector as a function of HPDE thickness, for WLS thicknesses of: upper panel, 10 mm and lower panel, 20 mm. Neutrons were simulated from a flat distribution between 2–4 MeV.
However, the important quantity is the coincidence efficiency for events that interact in the plastic scintillator then later go on to be captured in another detector layer, permitting neutron/gamma discrimination. As expected, the absolute efficiency for this process is significantly lower than for simple neutron capture. Figure 5 shows the coincidence efficiency as a function of HDPE thickness. The efficiency for interaction in the plastic scintillator layer was seen to increase linearly with the thickness of this layer and a 30 mm-thick piece was chosen due to cost constraints. This coincidence efficiency does not account for the dead-time (up to 1000 μs) that will be introduced when measuring neutrons in practice. Given that a plastic scintillator pulse is followed by the capture pulse from the Li:ZnS, during this time window, the detector should not be sensitive to additional neutron interactions. This count-rate-dependent effect will lower the coincidence efficiency. This effect will be count rate dependent, and will be further explored once the detector is constructed.
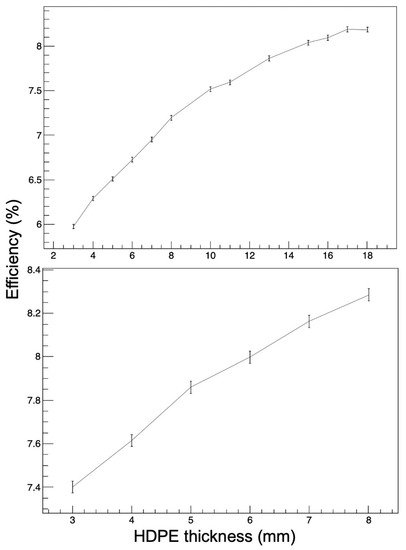
Figure 5.
Coincidence efficiency for simple neutron capture inside the detector as a function of HPDE thickness. Upper panel: WLS thickness 10 mm and EJ-204 thickness of 30 mm. Lower panel: WLS thickness 20 mm and EJ-204 thickness of 20 mm. Neutrons were simulated from a flat distribution between 2–4 MeV.
The parameters that were chosen are: HDPE thickness 15 mm, WLS thickness 10 mm and EJ-204 plastic scintillator thickness 30 mm. Although the efficiency for 20 mm-thick WLS was slightly higher by 0.2%, it corresponded to a significant cost increase of 15%.
These simulations optimise the efficiency for detection of 2–4 MeV neutrons, as expected for measuring the astrophysical reaction of interest. However, a future study to assess the efficiency as a function of neutron energy is planned. It is important to quantify this to apply ATTIKUS to measuring neutrons from other nuclear reactions. The coincidence efficiency will fall with increasing neutron energy, given that higher energy neutrons are less likely to fully moderate in the limited available layers of HDPE before escaping, and thus are less likely to satisfy the coincidence trigger conditions.
2.3.2. Basic Position Resolution Studies
The neutron track in Figure 3 indicates that the neutrons can undertake significant “walk” inside the detector before being captured. This worsens the resolution with which the position of incidence can be determined, which is crucial for determining the centre-of-mass energy of the reaction being measured in TTIK. To explore the extent of this effect, a uniform flux of 2–4 MeV neutrons was simulated to enter perpendicularly into the efficiency-optimised detector, along its whole 1-metre length, and the eventual capture position of the neutron was compared with its incidence position along the beam direction. The difference between these two quantities is plotted as a histogram in Figure 6.
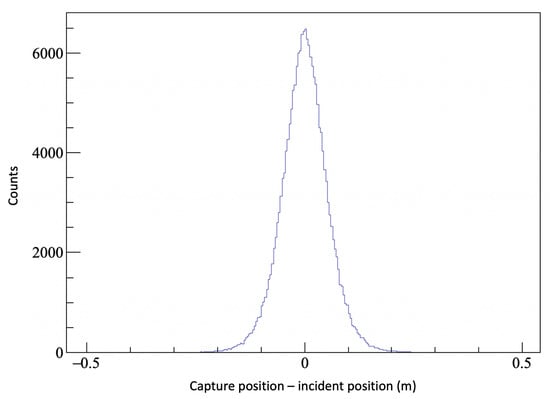
Figure 6.
The difference between the incidence and capture position of the simulated 2–4 MeV neutrons.
The distribution has a FWHM of around 15 cm. This spatial resolution translates into an energy resolution, because, as mentioned in Section 2.1, the heavy ion beam loses energy as it traverses the gas, and the emission position of the neutron uniquely determines the centre-of-mass energy of the reaction. Since this resolution is derived from the true capture position of the neutron, this is limited by the chosen thicknesses of HDPE layers. No amount of improvements to scintillator light collection or readout electronics could significantly improve on this. This resolution was found to be fairly insensitive to the HDPE and WLS thicknesses optimised in the previous section.
The incidence position of the neutron is better obtained from the interaction position in the fast neutron layer of the detector. The plastic scintillator is the first layer of the detector that a neutron strikes and therefore it makes sense that the interaction point in this layer is much closer to the initial point of incidence. The difference between the incidence and plastic scintillator interaction position of the incident neutrons is shown in Figure 7.
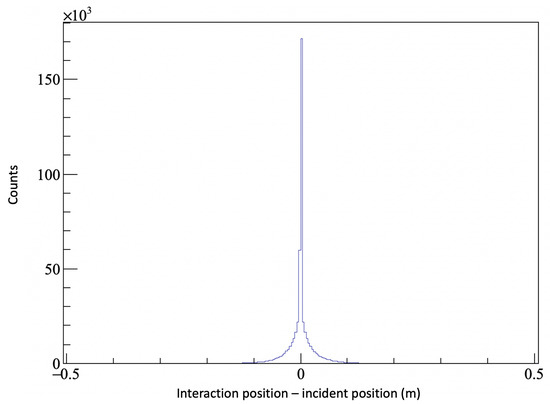
Figure 7.
The difference between the incidence and hit position of the incident 2–4 MeV neutrons in the plastic scintillator layer. Neutrons were simulated from a flat distribution between 2–4 MeV.
It can also be noted that for neutrons incident perpendicularly on the detector, that the fast neutron interaction point in the plastic scintillator and the point of capture of the moderated neutron are correlated. Figure 8 shows a histogram of the difference between these two interaction positions, as measured along the length of the detector. This correlation could, in principle, be used to coarsely determine the angle of neutrons as they enter the detector.
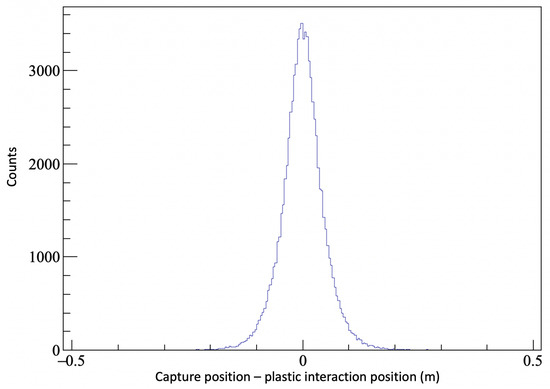
Figure 8.
The difference between the capture position of the moderated neutrons and the hit position of the incident neutrons in the plastic scintillator layer. Neutrons were simulated from a flat distribution between 2–4 MeV.
2.3.3. Optical Simulation
The work detailed so far has concerned truth-level Monte-Carlo, where we have insight into the exact interaction positions of the particles in the detector. However, if we wish to fully simulate the detector and a realistic response to neutron interactions, optical photon processes need to be included. In the detector, the photons generated due to the interaction of charged particles propagate to the photomultiplier tubes, which gives rise to the detector response.
In Geant4/CRESTA, optical and scintillation properties of materials can be included in the simulation. This allows scintillation photons to be generated due to the interaction of charged particles in scintillating media. Relevant parameters for the simulation include: scintillation efficiency (photons per 1 MeV electron); emission spectrum; light attenuation length; rise time and decay time; refractive index; reflectivity and absorption properties at all material boundaries. For the light detecting medium (PMT), the spectral response function is required. The absorption and emission spectra of the EJ-204 (plastic scintillator) and EJ-280 (WLS), along with the sensitivity of the Hamamatsu R1250 PMT is shown in Figure 9.
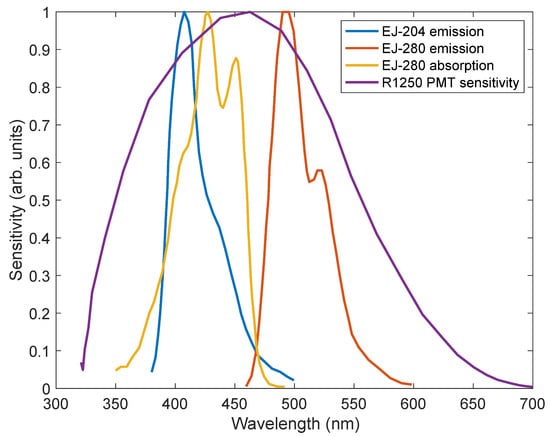
Figure 9.
Absorption and emission spectra of detector components along with the PMT sensitivity.
Once this has been included, the paths of individual photons can be tracked through the detector towards the PMTs. Graphical visualisation of this process is difficult because it is computationally intensive due to the number of optical photons. Nonetheless, the optical simulation of a single coincidence neutron detection is shown in Figure 10.
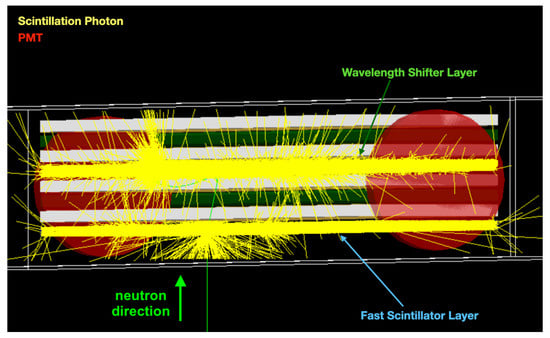
Figure 10.
The full simulation of a coincidence neutron interaction in the detector. The incident 3 MeV neutron path is shown in green. The initial scatter in fast scintillation layer and resulting capture after moderating give rise to optical photons in the plastic scintillator and one of the WLS light guides. The optical photons are shown in yellow.
Simulations showing rejected events, which do not meet the coincidence trigger, are shown in Figure 11. Here the neutron either interacts in the plastic scintillator or is captured after it is moderated, but not both.
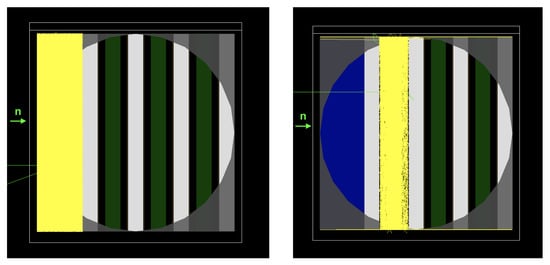
Figure 11.
Left panel: the optical photons generated by an initial neutron scatter in fast scintillation layer. Right panel: the optical photons generated by neutron capture after being moderated. The 3 MeV neutron path is shown in green and the optical photons in yellow.
Once this is done, the number of photons arriving at each of the PMTs as a function of time can be examined as is shown in Figure 12. This figure shows the pulses generated by a neutron entering the detector off-centre. This is signified by the offset in pulse heights. An off-centre interaction means that the optical photons entering one of the PMTs must travel further than the other. During this propagation, the light intensity attenuates in line with the optical properties of the materials, giving a mis-match in the pulse heights, which can be used to obtain the interaction position.
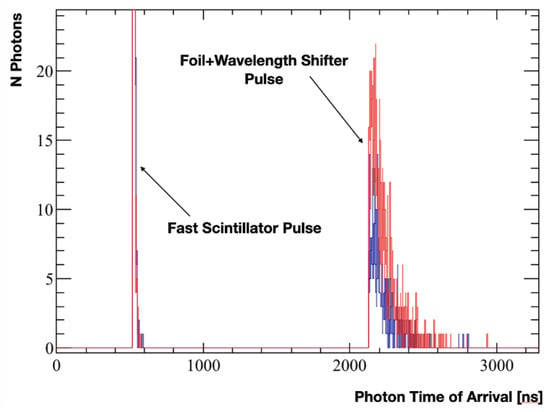
Figure 12.
Pulses calculated based on the number of photons entering the PMTs as a function of time for a 3 MeV incident neutron. The pulses from each PMT are shown in blue and red, respectively.
More realistic timing pulses were then generated by taking into account the properties of the PMT as introduced in reference [24]. The single photoelectron waveform model is used 1000 times for each photon to build up an accurate waveform. The code has been modified to match the Hamamatsu R1250 rise time, however there is still some uncertainty in the total magnitude of the pulse. It is not possible to fully model the gain and saturation until the specific PMTs are obtained and pulse height spectra are measured. The sample time is 2 ns, to match the 500 MHz CAEN digitiser that will be used as the data acquisition system for the detector, when built. The pulses may be seen in Figure 13.
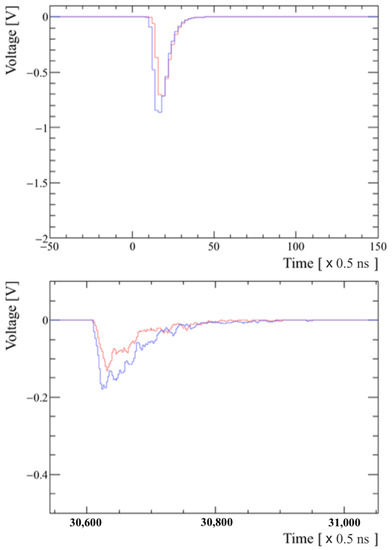
Figure 13.
Realistic timing pulses taking into account the PMT and digitiser properties, for a 3 MeV neutron. Upper panel: fast scintillator pulses. Lower panel: delayed capture pulses. Time on the horizontal axis is 2 ns per sample. The light and dark pulses are those recorded by the PMTs at each end of the detector, respectively.
2.3.4. Detailed Position Resolution Studies
With access to the scintillation pulses reaching each of the PMTs, as shown in Figure 12, realistic position resolution studies can be made. All events where neutrons scatter in the plastic scintillator layer and are captured after moderation are considered. There are two trigger windows. To constitute a “trigger” at least 10 photons are required in the first 1000 ns after the first photon arrives, and then another 10 photons in the 10,000–100,000 ns window. This trigger is not optimised at this stage; it is based on what seems reasonable to trigger on with the digitiser whilst still reliably discriminating the fast scintillator pulse from the delayed ZnS pulse.
The ZnS pulse produces a long pulse train, which is not captured by the simulation, so in reality, we will need a clear region where the fast scintillator pulses drop out (around 500 ns), before the neutron is captured in the ZnS layer, to clearly identify two separate events. Further trigger optimisation will be made in response to experimental tests of an operational detector module.
The position resolution of the detector was obtained by examining the pulse height asymmetry of the fast neutron pulses, due to interactions in the plastic scintillator layer, because, as previously discussed, the interaction position in the plastic scintillator is close to the incident neutron position. The pulse height asymmetry, A is calculated as
where and are the integrals of the fast neutron pulses measured at each end of the detector. The pulse height asymmetry, and incidence position are plotted together as a 2D heat map in Figure 14, which demonstrates a clear correlation.
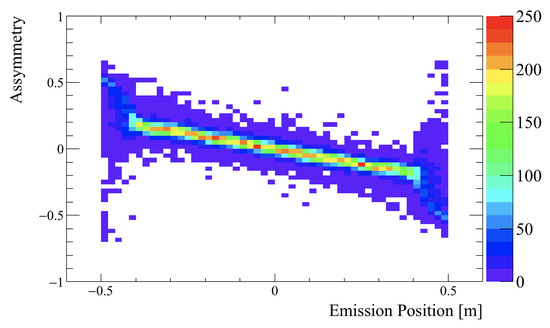
Figure 14.
Pulse height asymmetry as a function of known incident neutron position, for the fast neutron scattering pulses. Neutrons were simulated from a flat distribution between 2–4 MeV.
One dimensional slices of Figure 14 are shown in Figure 15 and Gaussian fits to these distributions demonstrate a typical position resolution of σ = 10 cm for the 2–4 MeV neutrons. This is close to the design goal. It is expected that the position reconstruction resolution will vary with incident neutron energy. One of the limiting factors in position resolution is the integral of the pulses measured in the PMTs at each end of the detector, which is dictated by photon counting statistics. Higher energy neutrons will result in larger signals in the plastic scintillator, resulting in more scintillation photons, meaning that the fractional uncertainty on the interaction position will reduce approximately as . This characteristic will be explored in future work.
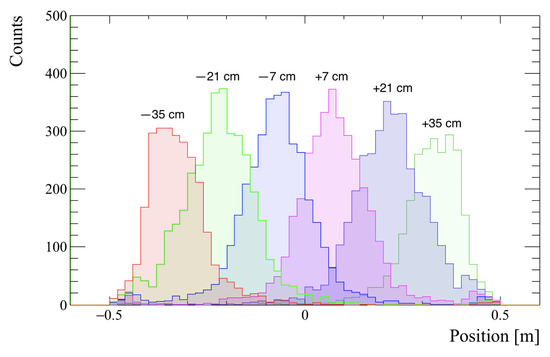
Figure 15.
One-dimensional slices to demonstrate the position resolution obtainable from the fast neutron pulses. The different colours indicate different slice positions along the detector length. Neutrons were simulated from a flat distribution between 2–4 MeV.
The range in pulse height asymmetry is limited here because of the relatively long attenuation length of the plastic scintillator. This could be improved by introducing losses at the surfaces of the plastic scintillator, either by sanding/dulling the surface or painting it matte black. This would lead to an improvement in the position resolution but an overall decrease in photon collection efficiency, leading to lower amplitude pulses. This is still being investigated.
Another way to improve the position resolution would be to work with the relative arrival times of the pulses, rather than the pulse heights. Given that the light entering each PMT travels different distances, there is an asymmetry seen in the arrival times of each pulse. This can be seen in Figure 13, where the blue pulse, corresponding to the closest PMT to the interaction point, has an earlier time of arrival and a larger pulse height. This method of position reconstruction has previously been used by the PROSPECT collaboration [21] who actually obtained a similar position resolution of 20 cm in a 117 cm-long liquid scintillator cell, although this value is limited due to the digitiser sampling time specification.
Digital electronics do exist that will sample at a high enough rate for this timing technique to be effectively applied to ATTIKUS. The company CAEN have produced a 742 model digitiser with a 5 GHz sampling rate. Given the refractive index of the EJ-204 = 1.58, each 0.2 ns time bin corresponds to a light propagation distance of around 4 cm, which dictates the position resolution obtainable. For the 742 digitiser, the analog inputs are continuously sampled by the 1024 capacitive cells in a DRS4 chip at the 5 GHz frequency. Once the trigger condition is met, the capacitors are released, and data are converted by a 12-bit ADC at a lower frequency and stored into a digital memory buffer. However, because the sampling and the analog-to-digital conversion are not simultaneous, a dead-time of >110 μs is introduced, during which the board cannot accept other triggers. So although this technique would work well for low rate experiments such as PROSPECT, for our purposes, it may introduce too much dead time.
Finally, it may be possible to determine the centre-of-mass energy of the reaction directly from the measured neutron energy. For most coincidence events, the neutron only scatters once within the plastic scintillator layer, meaning that the recoiling proton that gives rise to the scintillation light only carries away a fraction of the neutron energy. In future Monte-Carlo studies, we plan to determine if there is indeed a correlation between the incident neutron energy and the fast scintillator pulse.
2.3.5. Simulations under Beam Conditions
To understand the performance of the detector under realistic experimental conditions, further Monte-Carlo simulations were performed to properly simulate a 13C beam passing through the helium gas and losing energy. The 13C(α,n) reaction was simulated based on a custom cross section and neutrons were emitted from the reaction with an isotropic angular distribution. These generated neutrons can then be used as the neutron source in future simulations of the detector array. The generation of neutrons from this reaction in the gas cell are shown in Figure 16.
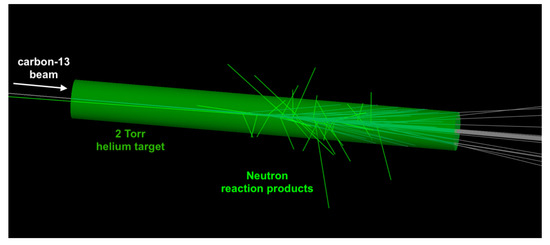
Figure 16.
Neutron production in a helium cell, after the energy loss of an incident 13C beam and the resulting 13C(α,n) reaction.
A phenomenological cross section was used for these simulations. The 13C(α,n) cross section was chosen to be zero, aside from a single Gaussian resonance at 2.25 MeV centre-of-mass energy. The resonance was chosen to have a Full Width at Half Maximum of 20 keV. The uncertainty in the experimental 13C(α,n) cross-section is large in this region, and is an area that is a priority to examine experimentally once the detector is constructed. A 13C beam energy of 10 MeV was chosen and a 2 Torr helium gas pressure means that this beam loses around 1 MeV in the one-metre-long gas cell. Therefore, reactions take place at centre-of-mass energies between 2.12 to 2.35 MeV.
Figure 17 shows the production positions of the neutrons along the helium cell, when the simulation is run with the custom cross section for 13C(α,n). As expected, the simulations show the neutrons being generated around the centre of the detector for 2 Torr of helium, since the resonance energy lies almost directly in between the maximum and minimum centre-of-mass energies traced out by the beam. Based on Figure 16, it is expected that the neutron position reconstruction position resolution will be worsened compared with the results of Section 2.3.4, given that neutrons emitted at scattering angles away from 90° can enter the detector some distance away from the actual interaction point. This could be corrected by introducing neutron collimation, made from borated HDPE. Alternatively, if the detector response is quantified for various neutron interaction positions, and the experimental data have high enough statistics, a cross section unfolding procedure could be applied.
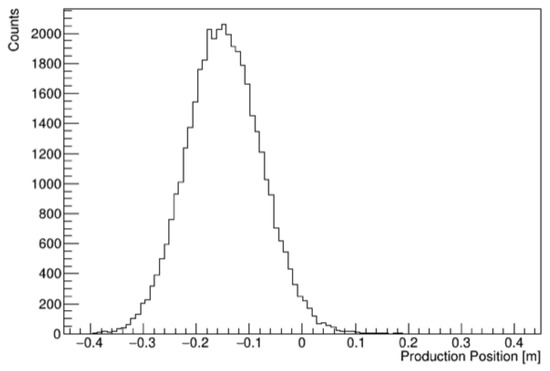
Figure 17.
The emission positions of the neutrons from the 13C(α,n) reaction along the beam path through the 2 Torr helium.
3. Conclusions and Future Work
High quality nuclear data lie at the heart of accurately modelling astrophysical environments and terrestrial nuclear reactors. New, effective neutron detection systems are required for improvements to be made in quantifying the cross sections of certain reactions.
A new low-cost, low-background method of detecting neutrons with position sensitivity has been introduced in the form of ATTIKUS. The ability of the ATTIKUS detector to measure the position of incident neutrons in the 2–4 MeV range was demonstrated. An 8% efficiency and a position resolution of 10 cm were obtained. Although this position resolution is slightly poorer than the design goal, limiting the centre-of-mass energy resolution of the reactions under consideration, some improvements can be made. Reducing the attenuation length of the plastic scintillator, and access to timing information using a higher specification digitiser would improve the situation. In its present form, the design of ATTIKUS is suitable for measuring the 13C(α,n) reaction, a crucial neutron source for the astrophysical s-process in Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) stars. However, the energy range measured in each run would need to be reduced in order to compensate for the poorer resolution. We still deem this technique more efficient than typical experimental runs with many beam energy changes.
The long delay between the initial fast neutron pulse and capture pulse will require long time windows (1000 μs) for the digitiser in an experimental set-up. This affects the permitted count rate for the detector, given that in a high-flux neutron setting, pile-up of events may occur. This is not a problem for typical astrophysical reaction measurements, where a maximum of a few neutrons counts per second are expected. The pile-up probability is 0.1% for 0.2 n/s count rate, 1% for 2 n/s and 5% for 10 n/s.
Measurements of astrophysical nuclear reactions, such as 13C(α,n) are typically sensitive to the effects of backgrounds given that low neutron count rates are expected. As such, influences from common environmental gamma-rays, such as the 1461 keV from potassium-40 may become important. The influence of background gamma rays will be suppressed by the coincidence trigger, which will only apply to neutrons. However, it is possible that a gamma-ray could interact in the plastic scintillator layer, giving rise to a measurable signal, followed by a neutron, which has not interacted in the plastic scintillator, being captured by the Li:ZnS. This would mimic the triggering conditions. This possibility has been explored for a typical background gamma flux in a nuclear laboratory setting [25]. Given the low efficiency for 1461 keV gamma interactions in the plastic scintillator layer and the efficiency for neutron absorption (for 2–4 MeV neutrons it is 18%) a 0.2% contribution from background gamma-rays was calculated.
The performance of the detector during the Monte-Carlo simulations has also demonstrated that this type of detector could be used for low-background neutron spectroscopy with a traditional experimental set-up. By surrounding a solid 13C target with the detectors, while it is bombarded with an α-particle beam, angular distributions for the 13C(α,n) reaction could be measured by aligning the detectors into a wall arrangement. This is topical, since recent experiments [20] have highlighted significant discrepancies. Such an experiment would complement the planned TTIK measurements.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.; methodology, J.P.S., R.S. and L.F.T.; software, J.P.S.; validation, J.P.S., R.S. and D.B.; formal analysis, J.P.S., R.S. and D.B.; investigation, J.P.S. and R.S.; resources, R.S. and L.F.T.; data curation, J.P.S. and R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S. and J.P.S.; writing—review and editing, R.S., J.P.S., L.F.T. and D.B.; visualization, J.P.S. and R.S.; project administration, R.S.; funding acquisition, R.S. and L.F.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded under the £46m Advanced Fuel Cycle Programme as part of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy’s (BEIS) £505m Energy Innovation Programme. The output of this article was also supported by the UK STFC under grant number ST/V001086/1.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Burbidge, E.M.; Burbidge, G.R.; Fowler, W.A.; Hoyle, F. Synthesis of the elements in stars. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1957, 29, 547–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallmeister, K.; Mosel, U.; Weil, J. Neutrino-induced reactions on nuclei. Phys. Rev. C 2016, 94, 035502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifarth, R.; Erbacher, P.; Fiebiger, S.; Göbel, K.; Heftrich, T.; Heil, M.; Käppeler, F.; Klapper, N.; Kurtulgil, D.; Langer, C.; et al. Neutron-induced cross sections. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiescher, M.; Köppeler, F.; Langanke, K. Critical reactions in contemporary nuclear astrophysics. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 50, 165–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfs, C.; Rodney, W.S. Cauldrons in the Cosmos; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Aprahamian, A.; Langanke, K.; Wiescher, M. Nuclear structure aspects in nuclear astrophysics. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2005, 54, 535–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.S. Nuclear Data Relevant for Astrophysics. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2002, 39, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L.A.; Brown, D.A.; Koning, A.J.; Rearden, B.T.; Romano, C.E.; Sonzogni, A.A.; Younes, W. Our future nuclear data needs. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2019, 69, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plompen, A.J.; Cabellos, O.; De Saint, Jean, C.; Fleming, M.; Algora, A.; Angelone, M.; Žerovnik, G. The joint evaluated fission and fusion nuclear data library, JEFF-3.3. Eur. Phys. J. A 2020, 56, 1–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomp, S.; Bartlett, D.T.; Mayer, S.; Reitz, G.; Röttger, S.; Silari, M.; Smit, F.D.; Vincke, H.; Yasuda, H. High-energy quasi-monoenergetic neutron fields: Existing facilities and future needs. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 161, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślak, M.J.; Gamage, K.A.A.; Glover, R. Critical Review of Scintillating Crystals for Neutron Detection. Crystals 2019, 9, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastaniah, S.D.; Sellin, P.J. Digital techniques for n/γ pulse shape discrimination and capture-gated neutron spectroscopy using liquid scintillators. Nucl. Instruments Meth. Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2004, 517, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitseva, N.; Rupert, B.L.; Pawełczak, I.; Glenn, A.; Martinez, H.P.; Carman, L.; Payne, S. Plastic scintillators with efficient neutron/gamma pulse shape discrimination. Nucl. Instruments Meth. Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2012, 668, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, A.; Torresi, D.; Zadro, M.; Cosentino, L.; Ducoin, C.; Figuera, P.; Strano, E. The inverse kinematics thick target scattering method as a tool to study cluster states in exotic nuclei. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 366, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciani, G.F.; Csedreki, L.; Rapagnani, D.; Aliotta, M.; Balibrea-Correa, J.; Barile, F.; Bemmerer, D.; Best, A.; Boeltzig, A.; Broggini, C.; et al. Direct Measurement of the 13C(α,n)16O Cross Section into the s-Process Gamow Peak. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 152701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatari, M.; Gallino, R.; Heil, M.; Wiescher, M.; Käppeler, F.; Herwig, F.; Bisterzo, S. The weak s-process in massive stars and its dependence on the neutron capture cross sections. Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisterzo, S.; Gallino, R.; Käppeler, F.; Wiescher, M.; Imbriani, G.; Straniero, O.; Cristallo, S.; Görres, J.; Deboer, R.J. The branchings of the main s-process: Their sensitivity to α-induced reactions on 13C and 22Ne and to the uncertainties of the nuclear network. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 506–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courcelle, A. Need for 16O(n,α) Measurement and Evaluation in the Range 2.5 to 10 MeV. 2005. Available online: http://www.nea.fr/html/dbdata/hprl/ (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Giorginis, G.; Khryachkov, V.; Corcalciuc, V.; Kievets, M. The cross section of the 16O(n,α)13C reaction in the MeV energy range. In International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2007; pp. 525–528. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmukhanbetova, A.K.; Goldberg, V.Z.; Nauruzbayev, D.K.; Rogachev, G.V.; Golovkov, M.S.; Mynbayev, N.A.; Artemov, S. Thick target inverse kinematics approach for neutron emission. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 032036. [Google Scholar]
- Ashenfelter, J.; Balantekin, A.B.; Band, H.R.; Bass, C.D.; Bergeron, D.E.; Berish, D.; Bowden, N.S. Performance of a segmented 6Li-loaded liquid scintillator detector for the PROSPECT experiment. J. Instrum. 2018, 13, P06023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steer, C.; Stowell, J.P.; Thompson, L. CRESTA: Cosmic rays for Engineering, Scientific, and Technology Applications. Available online: https://gitlab.com/cosmicraysim/cresta (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Agostinelli, S.; GEANT4 Collaboration. GEANT4–A simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2003, 506, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetter, S.; Dwyer, D.; Jiang, W.Q.; Liu, D.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, Z.M.; Wen, L.J. PMT waveform modeling at the daya bay experiment. Chin. Phys. C 2012, 36, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gran Sasso Malczewski, D.; Kisiel, J.; Dorda, J. Gamma background measurements in the Gran Sasso National Laboratory. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2013, 295, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).