Abstract
In this brief review, I summarize our basic knowledge about different types of isolated neutron stars. I discuss radio pulsars, central compact objects in supernova remnants, magnetars, nearby cooling neutron stars (also known as the magnificent seven), and sources of fast radio bursts. Several scenarios of magneto-rotational evolution are presented. Recent observational data, such as the discovery of long-period radio pulsars, require the non-trivial evolution of magnetic fields, the spin periods of neutron stars, or both. In some detail, I discuss different models of magnetic field decay and interactions of young neutron stars with fallback matter.
1. Introduction
Neutron stars (NSs) are very fascinating objects. The more we study them, the more interesting they seem to be.
There are numerous types of sources related to NSs. Many of them contain a NS as a member of a binary system. These are X-ray binaries with accretion on the compact object. The first discovery (but not identification) of such a source, Sco X-1, occurred in 1962 [1]. The first robust identification of a NS in an accreting binary, Cen X-3, occurred a few years later due to observations on-board the UHURU satellite [2].
Even as accreting objects, NSs in closed binary systems can appear as sources with very different properties. This is possible because binary evolution provides many possibilities to obtain systems with various parameters [3].
In low-mass X-ray binaries (LMXBs), mass transfer from a low-mass component spins up the NS. This can result in the formation of a millisecond radio pulsar (mPSR) [4]. The first mPSR was discovered in 1982 [5]. Spin up in a binary system was confirmed after identification of so-called transitional mPSRs [6]. Such NSs are characterized by very short spin periods (∼1–10 ms) and low magnetic fields (∼– G). The latter leads to large characteristic ages, a few billion years, a and long life time.
Some PSRs (ordinary and mPSRs) are found in binary systems with other NSs [7]. There are several evolutionary channels which can result in the formation of such systems [8]. Some of these binary NSs are doomed to end their lives in a spectacular coalescence accompanied by a short gamma-ray burst (sGRB), a gravitational wave burst, and a kilonova [9].
NSs are usually found in binary systems due to their own activity (as in the case of PSRs), or due to their interaction with their companion (accretion or coalescence). However, recently, several candidates to inactive/non-interacting NSs in binaries have been reported on the basis of astrometric and spectroscopic data, see [10] and references therein for other proposed candidates.
Observations of binary systems provide a plethora of data on NSs. Still, in many cases, it is necessary to study isolated NSs, as in this case, properties of compact objects are not modified by the presence of a companion. In this review, I focus on different types of isolated (mostly young) NSs and their evolution.
2. Main Species in the Zoo
Observations in the whole range of electromagnetic waves, from radio to gamma, demonstrate very different phenomena related to isolated NSs. Various observational appearances and intrinsic properties (spin period, magnetic field, surface temperature, etc.) result in the classification of isolated NSs into several main types; see Figure 1. In this Section 1 briefly present descriptions of them.
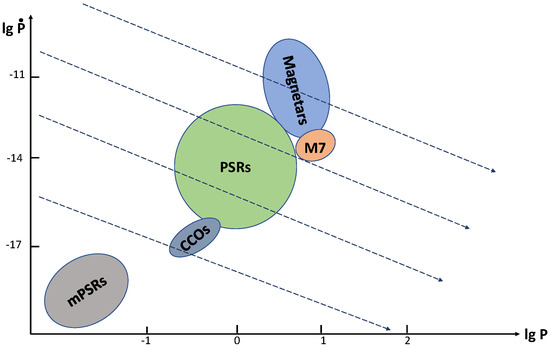
Figure 1.
P– diagram. The main types of young isolated NSs are shown together with recycled mPSRs (lower left part of the plot) and the simplest tracks corresponding to Equation (1) with a constant magnetic field. Scales on axes are approximate.
2.1. Radio Pulsars
Radio pulsars (PSRs) are the best-known (and the most numerous, referring to observed objects) type of isolated NS. They were discovered 55 years ago [11] through detection of their periodic radio pulses. The periodicity is due to the rotation of these compact objects. Spin periods cover the range of –100 s. Presently, the ATNF catalog1 contains ∼3000 of these sources [12]. Magnetic fields determined from the standard spin-down equation are in the range of ∼– G. These are dipolar fields on magnetic poles. On the equator, the field it twice as small: . Non-dipolar components might also exist, but their determination in the case of radio pulsars is not possible with any confidence, at least for now.
Low fields together with small spin periods correspond to old “recycled” mPSRs originating from LMXBs. In this section, we do not discuss them, focusing on young “normal” PSRs (in many respects, a group of so-called rotating radio transients (RRATs; see [13]) can be unified with PSRs, as they share main properties).
Radio emissions of PSRs are generated in magnetospheric processes which are not completely understood yet (see a review and references to early studies in [14]). Magnetospheric emissions might have a very wide spectrum. In some cases, e.g., the Crab pulsar, it is observed in the whole spectral range: from radio to gamma rays.
The energy reservoir is related to rotation of a PSR. This helps to relate key properties of a NS with observed parameters in a simplified magneto-dipole formula:
Here, I is the moment of inertia of a NS, is spin frequency, is the magnetic moment, and c is the speed of light. is the NS radius. Detailed calculations broadly confirm this equation [15]; however, alternative views also exist, e.g., [16].
Different studies indicate that the majority of young NSs pass through the stage of a PSR. Thus, the birth rate of PSRs is not much smaller than the birth rate of NSs in general. The latter, in its turn, is not much smaller than the rate of core-collapse supernovae (CCSN), which is about 1/60 yr−1 [17]. All of these numbers are known with an uncertainty that is smaller than a factor of ∼2. Let us assume for a simple estimate that the birth rate of PSRs is 1/100 yr−1. Near the so-called “death line”, where the number of observed pulsars in the P– diagram drops (this might be related to a drop in efficiency of -pair production in the magnetosphere), a typical pulsar has s and s/s. Then, its characteristic age is about yrs. Thus, the total number of PSRs in the galaxy is ∼. As radio emissions from PSRs are significantly beamed, just a small fraction (about 10%, [18]) of them can be observed even with infinite sensitivity. At the moment, the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) is the most sensitive instrument looking for new PSRs [19,20]. It is expected that SKA will allow us to detect most galactic pulsars that are potentially visible from Earth [21].
PSRs are characterized by large spatial velocities, ∼a few hundred km s−1, which are about an order of magnitude larger than in the case of their progenitors [22]. Additional velocity, kick, is received by a NS during a SN explosion [23]. For young NSs, spatial velocity does not change significantly. Thus, there are hopes that the properties of velocity distributions of different subpopulations of isolated NSs can shed light on their origin and causes of diversity in their properties. However, it seems that velocities of different types of isolated NSs are similar to each other.
Young ages of normal PSRs are confirmed by their associations with supernova remnants (SNRs) [24] and spiral arms [25]. Some types of isolated NSs that will be discussed are even younger on average and are associated with SNRs by definition.
2.2. Central Compact Objects
Central compact objects in SNRs (CCOs for short) are young NSs observed due to their thermal emission inside supernova remnants. Known CCOs are not numerous, there about a dozen of them2 [26,27]. However, their very small ages, about a few thousand years, point to a significant birth rate. Thus, this is a non-negligible subpopulation of isolated NSs.
CCOs can be an inhomogeneous group of sources united by their appearance inside SNRs and absence of any traces of radio pulsar activity. These objects are observed as soft X-ray sources with a thermal spectrum [28]. The origin of emissions is attributed to hot areas of a NS surface with a typical temperature of ∼ K. As the sources are young (ages are ∼few thousand years), the most obvious source of energy is residual heat. This assumption corresponds with the modeling of thermal evolution of NSs [29,30]. However, at least in a few cases, an additional source of energy is suspected.
Standard cooling is determined by neutrino emissions from the interior and photon emissions from the surface [31]. At the early stage of evolution, typically up to – yrs, the neutrino emissions prevail. The neutrino emissivity strongly depends on the NS mass: low-mass objects can stay hot for a longer time. Still, residual heat can explain only temperatures of ≲ K for ages yrs and ≲ K for ages yrs. Larger temperatures at young ages are typically explained by magnetic energy release, e.g., [32]. Measurable temperature in mature NSs (e.g., [33]) can be explained by chemical [34] or rotochemical heating [35].
In three CCOs, spin periods and their derivatives are measured due to X-ray flux variability. Periods ∼ –0.4 s and s/s, according to the magneto-dipole formula, correspond to fields ∼ – G. Because of their position in the P– diagram, these CCOs are often called “antimagnetars”. Still, some CCOs can be real magnetars.
Analysis of the light curve of PSR J1852+0040 in the SNR, Kes 79, allowed Shabaltas and Lai [36] to state that large pulse fractions observed in this source require a crustal field of the magnetar scale (see also [37]). Additional energy release due to field decay in the crust, or modification of the surface temperature distribution due to the influence of the magnetic field on heat transfer, might be responsible for the small emitting area in the PSR, J1852+0040, which may help to explain large pulsations of flux in the presence of the light bending effect in strong gravitational fields of compact objects. As no magnetospheric activity was ever observed from this source, it was proposed in [36] that the NS is a “hidden” magnetar, i.e., the strong field is “screened” by the matter that falls back onto the NS soon after the SN explosion (see [38] and references therein to early papers regarding this scenario).
Another magnetar among CCOs is the famous NS inside the RCW 103 remnant. This source was discovered years ago at the Einstein observatory [39]. A prominent feature of the central source, which is its variability on a time scale of about a few years, was successfully described in the model of magnetic energy release in the crust [40], and it was suspected that the source can also belong to the class of “hidden” magnetars. However, it was soon demonstrated that it is not so hidden. Bright, short, high-energy bursts, quite similar to the bursts of soft gamma-ray repeaters, were detected from this source [41,42]. This clearly points toward the magnetar nature of the source. In addition, the 6.67 h spin period was measured for the NS in RCW103 [43]. Such long spin periods in young, presently non-accreting objects can be explained in a model where a strong magnetic field of the NS interacts with a fallback disc [44].
Despite that the majority of CCOs demonstrate only surface thermal emission, at least in a few cases can CCOs have an additional source of energy: its magnetic field, i.e., they can be related to magnetars.
2.3. Magnetars
A NS is called a magnetar if its observational appearance is mainly due to magnetic energy release. There are two main manifestations of these sources: high-energy bursts and surface thermal emissions. Often, magnetars are considered as the most extreme and interesting type of NSs. Their unusual properties manifest themselves in spectacular observational appearance, unfamiliar to other types of compact objects. During the hyperflare of SGR 1806-20 in 2004, the peak luminosity was above erg s−1, and the total energy release in the event was ∼ erg [45]. This tremendous burst demonstrates that magnetic energy in NSs can reach very large values and can be rapidly released in a huge quantity.
It is not easy to say exactly when magnetars were discovered. The most reasonable approach may be to attribute it to the identification of the source, which was called, in 1979, “X-ray burster 0525.9-66.1” [46,47], and which is now mostly known as SGR 0525-66. Observations with gamma-ray detectors demonstrated the existence of subsequent powerful flares from the same source, including one giant flare with erg s−1. A stable period of ∼8 s was found, and the object was localized in a SNR in the Large Magellanic cloud (LMC). Now, the McGill catalog of magnetars3 lists about 30 sources [48]. They belong to two main subclasses: anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs) and soft gamma-ray repeaters (SGRs). A recent review with a large bibliography dedicated specifically to these types of sources can be found in [49].
Initially, the division into AXPs and SGRs was very clear. Anomalous X-ray pulsars were characterized by relatively stable X-ray emissions with luminosity ∼ erg s−1 (i.e., substantially smaller than in most accreting X-ray pulsars in binary systems); they had spin periods of about a few seconds, which were always increasing, and they did not have any optical or IR counterparts. Soft gamma-ray repeaters were characterized by intense bursts observed in the hard X-ray, in soft gamma-ray, or in both ranges, whereas AXPs did not show this type of activity. However, step by step, it became clear that AXPs and SGRs share similar properties. During active periods SGRs often resemble AXPs, and in 2002, Gavriil et al. demonstrated that well-known AXPs can have bursting activity identical to that of SGRs [50].
Typical spin periods of magnetars are about a few seconds. However, there are several important examples of outliers. A high-B young pulsar in the Crab-like plerion PSR J1846-0258, which started to demonstrate SGR-like flares, ref. [51] has a spin period of 0.327 s. Oppositely, the source 1E 161348-5055 in the SNR RCW 103 (which I described above) has a spin period of ∼ h.
The situation regarding magnetic fields is also not so univocal. “Classical” magnetars have fields of ∼– G. However, there are several so-called “low-field magnetars”. Up to now, three objects have been reported (see a review in [52]). According to estimates, based on the usual magneto-dipole equation, these sources have dipole fields well below G, but phase-resolved spectroscopy has demonstrated the existence of proton cyclotron lines that indicate local surface fields of ∼– G [53,54]. These might be small-scale, non-dipolar components of the magnetic field.
The best definition of a magnetar involves magnetic field dissipation. That is, a magnetar is not just a NS with a large field, but a compact object with a magnetic energy release that dominates its luminosity for at least some period of time. The total energy budget can be roughly estimated as follows:
Naive estimates of magnetar ages based on the characteristic age are not valid, as this simple equation is written for a constant field. However, the association of some magnetars with SNRs and their position in the galaxy [25] robustly confirm their young ages to be ∼– yrs. The young ages of magnetars indicate that an active period of magnetic energy dissipation does not last long.
Magnetars might constitute a significant fraction of young NSs. Many studies indicate their fraction to be ≲10%; see, e.g., [55] and references therein. However, at least one study suggests a much higher fraction of these objects: ∼40% [56]. The question of the magnetar fraction is closely related to the problem of the formation of these NSs.
It is still unknown what defines if a newborn NSs is a magnetar. In one framework, it is necessary to have a strongly magnetized progenitor [57]. In another, the magnetic field is amplified by several orders of magnitude via a dynamo mechanism operating in a newborn NS [58,59].
In both scenarios, it is quite probable that evolution in binaries can play a role. For example, observations of the magnetic star, Sco, suggest that its magnetic field was substantially increased due to the coalescence of two main sequence stars in a binary, and with magnetic flux conservation, this star can become a magnetar in the future [60]. On the other hand, the evolution in binaries can result in significant spin-up of the stellar core, which might later make the dynamo mechanism efficient enough to produce a magnetar-scale magnetic field [61].
Rapid rotation, which is necessary for the production of large dipolar fields, with the dynamo mechanism [62] can be obtained in different ways. For example, a newborn NS can be spun-up due to fallback accretion [63].
Modeling of the magnetar evolution demonstrates [64,65] that after some time, for example, ∼– yrs, the rate of magnetic energy dissipation decreases, and all types of activity of a NS cease. Thus, magnetars become sources of a different type. One of their descendants are probably X-ray, dim, isolated NSs (XDINS), which are part of the magnificent seven (M7).
2.4. Magnificent Seven
The M7 (or XDINS) is a group of nearby (≲a few hundred pc; see [66]) young, isolated NSs observed due to their thermal surface emissions; see a review in [67,68]. The first member of this class of NSs was discovered in 1996 [69].
The first period in the history of studies of the M7 is dominated by results from the ROSAT satellite; see [70] for an early brief review and discussion (early ideas included, e.g., the possibility that these NSs can be accreting sources with decayed magnetic field [71]). Since then, many observations in different wavelengths have been obtained (in addition to X-rays, many sources are detected as dim optical sources with magnitudes of ∼26–28 as well as in near-UV, near-IR, and in the deep upper limits of radio waves [72,73]).
Now, for all but one of these sources, spin periods and their derivatives are measured; see, e.g., Table 5 in [74]. The magneto-dipole formula provides an estimate of the magnetic field ∼ – G. The observed thermal emissions can be either due to the residual heat, e.g., [75], or to some contribution from magnetic field decay [55].
Evolutionary, M7 might be the descendants of magnetars [55]. It was shown by population synthesis modeling that the population of the M7 originated mainly from the Gould Belt—the local (∼500 pc) star-forming structure [76]. As these NSs are relatively weak (– erg s−1) and soft ( eV), it is difficult to detect such sources at large distances, mostly due to interstellar absorption.
Despite intensive searches (e.g., [77] and references therein), very few NSs similar to the M7 have been found, and none of them ideally resemble the original seven sources. The first one was Calvera, a soft X-ray source high above the galactic plane [78]. However, later, it was shown that this NS has a short spin period (0.06 s), and in some other respects, it is different from the M7 sources [79]. The next one is 2XMM J104608.7-594306 [80]. Again, the spin period (18.6 ms) does not fit the M7 family [81]. Finally, the latest discovery is the source 4XMM J022141.5-735632 [82], which for this object, the spin period has not yet been reported.
There have been hopes that the eROSITA telescope can find more M7-like sources [83,84], but the survey program was terminated after only two years, and these hopes more or less disappeared.
3. Standard Evolution and Its Problems
It is convenient to discuss the evolution of young NSs in terms of P, , and B and to illustrate it with the P– diagram. In the simplest and the most standard way, the evolution is described by Equation (1) for = const. Then, NSs evolve in the P– diagram along strait tracks, as shown in Figure 1.
The absence of significant field decay in normal PSRs is found in many papers, e.g., [85] (see, however, the next section). In addition, in PSRs, we do not see any evidence for the additional release of magnetic energy (the situation with magnetars is drastically different, of course).
Typically, in this standard approach, it is assumed that the initial spin periods are very short. Sometimes, authors can assume that the initial period is close to the limiting rotation (e.g., 1 ms). Sometimes, these initial spin periods are assumed to be close to the initial period of the Crab pulsar. Such assumptions were very popular, for example, in early models of binary population synthesis, e.g., [86]. Due to the gradual progress in our understanding of the initial parameters of NSs, such simplified approaches have been replaced by more advanced ones.
If and the field is constant, then the real age of a pulsar is close to the characteristic age . Population synthesis studies and analysis of young NSs in SNRs with known ages indicate that typical initial periods of the majority of PSRs are of the order of 0.1 s [24,85,87]. Thus, for many standard PSRs with observed s, the assumption of a small initial period can be acceptable. Still, in many cases, this does not work well and the results, e.g., when there is a significant discrepancy between the real age and .
The simplest model of magneto-rotational evolution nearly excludes links between different subpopulations: a CCO cannot become an M7-like object, and a magnetar cannot appear later in its life as a standard radio pulsar. This feature leads to an interesting controversy. The sum of birthrates of different subpopulations is larger than the rate of CCSN [88] (note, in that paper, the authors do not include CCOs in their calculations; with this subpopulation, the problem is even more severe). In addition, in the simplest model, it is difficult to explain the lack of magnetars with periods larger than ∼10 s, e.g., [89]. This includes the absence of descendants of CCOs that might be visible at ages yrs when a SNR is already dissolved [90].
Thus, it is necessary to consider more complicated evolutionary paths.
4. Double Nature and Non-Standard Evolution
In this section, I discuss two possible features of NS evolution: magnetic field decay and fallback. Simplified tracks are shown in Figure 2. In addition, I present several examples of sources that absolutely do not fit the simplified NS evolution but that require either field decay, fallback, or both.
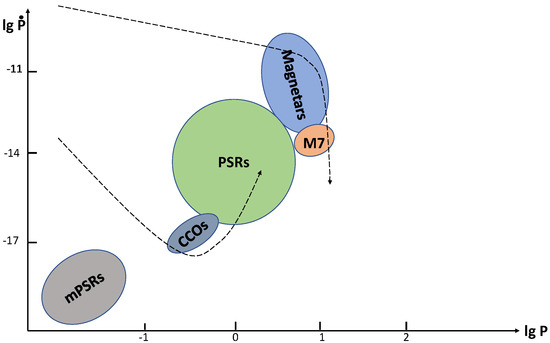
Figure 2.
The same as in Figure 1, but with evolutionary tracks corresponding to field decay in magnetars and re-emerging fields in CCOs.
4.1. Magnetic Field Decay
It is quite natural to expect that magnetic fields of NSs might decay in time. In addition to obvious arguments about general physics that electric currents that are responsible for the magnetic field might decay due to finite conductivity in the crust (and maybe due to other processes, such as transport of magnetic flux tubes from the core to the crust, e.g., [91]), there are observational arguments. The existence of low fields in old NSs was demonstrated, e.g., through the discovery of mPSRs [5].
The theory of magnetic field decay in NSs and related observational data have been reviewed many times, see e.g., [64,65] and references therein. Here, I briefly mention several basic features.
A magnetic field can exist in the solid NS crust, in the liquid (and, most probably, superconducting) core, or in both. In the first case, the magnetic field is produced by electric currents. In the second, the field is confined in magnetic flux tubes, as the core is expected to be a type II superconductor, see e.g., [92]. Thus, the physics of the field evolution is very different in these two cases.
The physics of the core is much less understood, partly because only the field evolution in the crust is considered. The basics of crustal field evolution are perfectly described in [93]. The two main time scales can be defined as the Ohmic () and the Hall ().
The Ohmic scale can be written as:
Here, is conductivity, and L is a length scale in the crust.
The Ohmic time scale depends on the temperature of the crust, as electrons can scatter off phonons, as well as on crustal composition (impurities). For usual field configurations, L is sufficiently large enough (∼a few hundred meters in deeper layers, comparable to the crust thickness; see [93]) to make the time scale relatively long. In young hot NSs, can be about yrs; see, e.g., Figure 4 in [94]. In older cold NSs, this time scale is long, at ∼ yrs.
The rapid release of magnetic energy can proceed via the Hall cascade [95]. This is a non-dissipative process, but it reconfigures the field such that L decreases, such that the field can now decay faster. The time scale of this process is:
where e is the elementary charge, and is the concentration of electrons. For fields ∼ G, it can be as small as ∼100 yrs, e.g., [32]. However, the value of is not well known, and it can be two orders of magnitude larger for the same field at G. It is widely accepted that magnetar activity is related to the Hall cascade in the crust of NSs.
The evolution of magnetic fields in the core is described in a more complicated way (see a brief review in Section 3.2 in [65]). Recently, Gusakov, Kantor, and Ofengeim developed a new approach to calculate field behavior in superconducting cores [96,97]. In particular, their results suggest that in the vicinity of the crust, the time scale can be as short as ∼100 yrs [98]. This is intriguing, as it potentially gives an opportunity to explain magnetar activity in the framework of the evolution of the core’s field.
From an observational point of view, there are many arguments in favor of decaying fields in young NSs of different types. Magnetar activity provides evidence for field decay, as the magnetic energy is released in bursts and is responsible for the heating of the crust. The active lifetime of magnetars might be short, as it comes from the independent age estimates of these sources (SNR and kinematic ages, associations with clusters of young stars, etc.). However, bursts can also be produced by older NSs, but they are more seldom [99].
The thermal properties of NSs also provide arguments in favor of field decay. For example, Pons et al. [100] demonstrated that, typically, a high-B NS cannot have a low surface temperature due to additional heating related to the magnetic energy release in the crust.
Analysis of the properties of high-mass X-ray binaries (HMXBs) showed that the distribution of magnetic fields of NSs in these systems is compatible with models of crustal field evolution [101].
Finally, even for normal PSRs, some modeling favored a decaying field alongside their evolution; see, e.g., [102] and references therein. A different conclusion was made in [103]. These authors constructed a modified model of a so-called “pulsar current” [104,105] and concluded that a significant fraction of normal pulsars experiences an episode of field decay with a time scale of ∼ yrs at ages of ≲ yrs. Later, this decay might be terminated. This points to Ohmic decay due to electron scattering off phonons, as this type of decay disappears when a NS becomes sufficiently cold. This happens at the ages of ≲ yrs even for low-mass objects. In the same framework, anomalous braking indices of PSRs can be explained as well [106].
To summarize, magnetic field decay in NSs is now a standard ingredient for modeling their evolution. Different modes of decay with different time scales are possible. Thus, presently, the situation is far from being clear, which is why observations of peculiar objects are important. I discuss these some of these observations in the following subsection.
4.2. Werewolves and Secret Agents
Until the beginning of this century, it was possible to attribute each young NS to some well-defined category (PSR, AXP, SGR, CCO, M7, etc.). In 2002, the discovery of SGR-like bursts from an AXP was announced [50]. That was the first, but not very prominent, example of “double nature”. It was not so prominent because for some time, it had already been suspected that AXPs and SGRs form the same family of objects—magnetars. SGRs may be slightly younger and thus more active. However, later on, more pronounced examples of transitions from one subpopulation to the other were found. Here, I give some examples.
PSR 1846-0258 is observed only as an X-ray source; the radio beam does not point toward Earth. The NS has G and the largest rotational energy losses among PSRs. A plerion and a SNR have been observed around the source. The characteristic age is ∼884 yrs. The spin period is ∼ s. Thus, it resembled a Crab-like PSR, with an order-of-magnitude large field and an order-of-magnitude longer period. However, in 2008, magnetar-like activity was reported from this object [51,107]. The X-ray luminosity of the PSR significantly increased, and it started to produce SGR-like bursts. This came to be the first example of a radio pulsar becoming a magnetar.
Another example of a pulsar → magnetar transition is PSR 1622-4950. It has a s and a large period derivative corresponding to G. Since its discovery, it has been suspected [108] that the source can be a magnetar in a quiescent state. In 2017, the source re-activated [109]. Its X-ray luminosity significantly increased; however, no bursts were detected.
I have already described a very peculiar source in the SNR RCW 103, which initially resembled an atypical CCO but then appeared to be an active magnetar. Its activity continued in 2016 with an outburst [110] that then decayed following the general scenario of crustal magnetic energy release.
PSR J1852+0040 in Kes 79 has also been previously mentioned. It is a candidate for “hidden” magnetars, i.e., a magnetar covered during a fallback episode such that only its crustal (but not magnetospheric) activity can be visible. This NS has a spin period of ∼ s [111]. If we assume that the magnetar scale field was buried by fallback, then the initial episode has been very rapid such that the NS had no time to increase the spin period due to the interaction with the fallback flow (as what most probably happened in RCW 103). Then, the spin period of PSR J1852+0040 could be “frozen”. Thus, the present-day value could be similar to the initial spin. This means that magnetar formation does not necessarily require rotation with a rate much smaller than 0.1 s [112]. It is tempting to say that a compact remnant of SN 1987A can also be a “hidden” magnetar [40], as its progenitor was a product of a coalescence of two massive stars in a binary system [113]. This coalescence could enhance the spin rate and magnetic field of the stellar core of the progenitor. The discovery of more “frozen” magnetars can shed light on their initial rotation rate and thus on the mechanism of magnetar formation.
After a fallback episode, the field is expected to diffuse out on a time scale of ∼– yrs [114]. While the field is diffusing out, its external structure can be changed, which can prevent the appearance of radio pulsar emissions [115]. Still, there is a possibility of observing a PSR on the stage of field re-emergence. Then, it might have a very non-standard track in the P– diagram. Such objects are known. The most famous example is PSR 1734-3333 [116]. This is a standard PSR, but its period derivative is rapidly increasing. The rate corresponds to a braking index of ∼1, (the standard Equation (1) corresponds to ). With s and a large period derivative s/s, it can after some time, e.g., ∼20–30 kyrs, enter the region of magnetars; see [116].
Finally, it is necessary to say a few words about low-field magnetars, which have also been mentioned above. As proposed in [117], these sources can form a significant subpopulation of relatively old magnetars. These sources might demonstrate very seldom activity and have low quiescent luminosities. Their existence points to the possibility of a quasistationary configuration of magnetic fields with a relatively low dipolar component. In the following subsection, I discuss a recently proposed stable field configuration—the Hall attractor.
4.3. Fallback and Hall Attractor
Examples of the peculiar sources described above suggest that NS field evolution can follow non-standard routes. In this subsection, I consider two important features of such evolution: fallback and the Hall attractor.
The idea that some fraction of matter ejected after a bounce in a SN explosion can later fallback onto the NS was proposed in the early 1970s (see a brief historical review in the introductory section of [118]). In 1995, Muslimov and Page [119] suggested that fallback can significantly influence the external magnetic field of NSs and delay the switching-on of the radio pulsar emission mechanism.
The scenario of magnetic field submergence due to fallback became popular when it was applied to CCOs by Ho [114] and then by Vigano and Pons [120]. These authors demonstrated that for a realistic fallback amount (), the magnetic field can be significantly submerged and diffuses out on a time scale of ∼– yrs. This perfectly fits the properties of CCOs and explains why “evolved CCOs” are not observed as purely thermal emitters with s, e.g., [90].
Bernal et al. presented 2D and 3D simulations of magnetic field submergence due to fallback [38]. They modeled the dynamics of interactions between falling matter and magnetic fields on the scale of ≲100 ms for different fallback rates. The authors showed that for rates of yr−1, total submergence happens, and for lower rates, the field is just partially submerged. Such rates are realistic at early stages of fallback; thus, in some fraction of young NSs, the external magnetic field can be smaller than the crustal field by several orders of magnitude.
Fallback can be prevented by activity of the central source. This possibility has been neglected in, e.g., [38], but later, it was studied by a group of Japanese researchers [121,122]. These authors attribute the diversity of young NSs mainly to different amounts of fallback. In particular, in [121], they define the criteria according to which, in a simplified 1D model for a given fallback rate, a NS becomes a CCO, a PSR, or a magnetar, depending on its spin and magnetic field. In [122], the same situation was studied in more detail with a numerical approach, but again in the 1D approximation and without accounting for instabilities.
Advanced fallback calculations were performed in a framework of SN explosion modeling [123]. A specific feature of this modeling is the motion of the NS relative to the ejecta. It was shown that this results in spin-up of a newborn NS due to fallback and spin–velocity alignment. In this framework, a NS’s spin in mostly determined by the fallback (and not by the spin rate of the progenitor).
The influence of fallback on the spin of a newborn NS was also studied in [63]. In this scenario, a NS formed from a slowly rotating progenitor star can be spun-up significantly enough that conditions necessary for magnetar formation are fulfilled. Thus, in this model, fallback also produces rapidly rotating compact objects. An opposite situation is also possible in other scenarios.
The interaction between a fallback disc and magnetic field of a magnetar can result in significant spin-down of the NS. This possibility was recently analyzed in [44]. The disc can penetrate the light cylinder within a wide range of realistic fallback rates. Thus, the NS enters the propeller stage of magneto-rotational evolution. At this stage, a compact object can spin-down rapidly. Periods of ∼– s can be easily reached even within the lifetime of the SNR (≲ yrs). This scenario is applicable for recently discovered long-period pulsars, which are discussed in the following section.
Long-spin periods can also be reached if the magnetic field remains large for a long time. This is possible if the Hall cascade in a magnetar crust is terminated or is at least significantly slowed down. Such a situation has been found numerically, and the stage was named “the Hall attractor” [124,125]. Later, it was confirmed in [126,127].
In their original paper [125], the authors obtained that the attractor is reached in ≲1 Myr for initial fields of ∼ G. For larger fields, it is reached faster. At the attractor stage, the dipolar field is about , where is the initial field. The details significantly depend on the model, in particular, on the initial conditions (see a review of magnetic field evolution in NSs in [65]). The bottom line is the following: the rapid initial Hall evolution of large magnetic fields can be significantly slowed; this potentially allows for the existence of NSs with relatively large fields at ages of at least ∼1 Myr (which is also important for the explanation of magnetar candidates in accreting binary systems [128]). In this case, such objects can reach relatively large spin periods due to standard losses. This can help to explain some sources discussed in the next section.
5. New Puzzle, New Tracks
Recent discoveries of long-spin period pulsars demand new non-trivial evolutionary tracks in comparison with those shown in Figure 2.
MeerKAT observations allowed Caleb et al. to discover a radio pulsar PSR J0901-4046 with a record-long spin period of 76 s [129]. With s s−1, the source has the characteristic age of 5.3 Myr. The magneto-dipole field estimate provides a value of G. In the standard scenario of magneto-rotational evolution, such a combination of parameters is impossible due to short initial spin periods and the rapid decay of large magnetic fields.
GLEAM-X J162759.5-523504.3 is even more exotic, with the period of pulsations of its radio emissions at ∼18 min [130]. This object was discovered with help from the Murchison Widefield Array. The period derivative has not been measured yet. This prevents robust determination of the source’s nature. Still, it is probably a NS and not a WD; see discussion and references in [131]. Moreover, it might be a magnetar, as an upper limit on s s−1 provides that the observed luminosity is larger than the rotational energy losses. Thus, an additional source of energy is necessary, and it can be magnetic energy of the magnetar.
If of GLEAM-X J162759.5-523504.3 is close to the upper limit, then the dipolar field is ∼ G. Such values have been never observed. The characteristic age for such a field is yrs, which is significantly larger that the expected time scale of the Hall cascade for such huge fields. If s s−1, then the field is ∼ G and yrs. Again, such a combination is not a part of the standard scenario of NS evolution.
Possible solutions are related to physical processes discussed in the previous section. Either the real ages of both objects are much smaller than their characteristic ages due to large initial spin periods or the dipolar magnetic field in both cases could survive for a very long time, much longer than the initial time scale of the Hall cascade. In Figure 3, we show the tracks with large initial spin periods (3a,b,c). The initial short-dashed part of the tracks pointing toward PSR J0901-4046 (tracks 3b,c) and GLEAM-X J162759.5-523504.3 (track 3a) corresponds to a rapid spin-down from a short period, just after the core collapse, to longer periods, e.g., due to interactions with the fallback disc (of course, this spin-down does not proceed with a constant period derivative, and thus, we do not take this part of the tracks literally). For PSR J0901-4046, two variants of further evolution are shown: standard field decay and stalled decay.
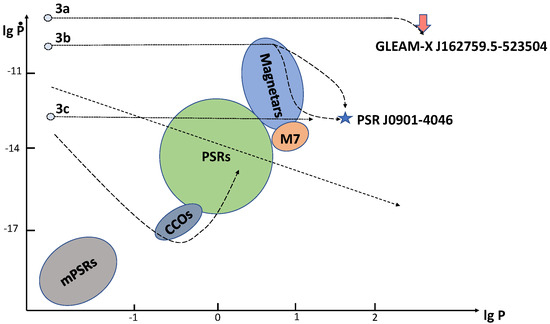
Figure 3.
The same as in Figure 2, but with recently discovered long-period pulsars (the star symbol represents PSR J0901-4046, the arrow corresponds to the spin period and the upper limit on the period derivative of GLEAM-X 162759.5-523504) and tracks that can illustrate their evolution; see the text for details.
Note that above I discussed only the scenarios involving single stars. Evolution in a binary system can open an additional channel of producing long spin periods of NSs. If a NS in a HMXB system rapidly starts to accrete [132], or at least reaches the propeller stage, then its period can be rapidly increased up to hundreds or thousand of seconds in the case of large magnetic fields and accretion from a stellar wind; see a catalog of HMXBs in [133]. If this happens close to the moment of explosion of the secondary component, then we can expect a “birth” of an isolated NS with a large spin period.
NSs that can rapidly reach long spin periods (and that probably save a large value of their dipolar magnetic fields for a long time) can be of special interest for the long-term evolution of NSs. I discuss this in the following section.
6. Toward Accretion from the ISM
Already more than 50 years ago, it was suggested that isolated NSs can sooner or later start to accrete gas from the interstellar medium (ISM) [134,135]. More than 30 years ago, it was proposed that, e.g., ROSAT can detect thousands of accreting isolated NSs (AINSs) [136], but none have been found. This was explained in [137] as an evolutionary effect: most of isolated NSs under the standard assumptions cannot reach a stage of accretion during the lifetime of the galaxy. In addition, the rate of accretion onto the surface of a NS can be much lower than the standard Bondi value due to magnetic inhibition [138]. In the formula, v is the NS velocity relative to the ISM, and is the ISM density, while the coefficient depends on the details of the accretion flow around the NS.
Velocity distribution is an important ingredient of isolated NS evolution modeling, as interactions of a compact object with the interstellar medium strongly depend on this parameter. In addition, the initial velocity distribution determines the spatial distribution of NSs in the galaxy; see, e.g., [139]. Already, early observations have demonstrated that NSs can have spatial velocities that are significantly larger than their progenitors [140]. It is assumed that NSs obtain additional velocity at birth (so-called “kick”). The origin of kick, the shape of the velocity distribution, and the possible correlations of the kick velocity with other parameters are not yet completely understood. During last ≲50 yrs, many attempt have been made to derive the kick velocity distribution from observations or to obtain it from theoretical considerations, e.g., SN explosion models (see a brief review and references to early studies in the introductory part of [141]). It is quite popular to use bimodal velocity distributions, as they fit better various data on radio pulsars and X-ray binaries (especially those with a Be-star donor). Recently, in [142], the authors presented a new analysis where they investigated the properties of radio pulsars and HMXBs. Their best fit was a bimodal distribution with 30–70 km s−1 and km s−1, where 10–30% of NSs come from a low-velocity component. If isolated, such NSs can become potentially observable accreting sources within the galactic lifetime.
NSs with larger magnetic fields can start to accrete faster. This was studied in detail in [143]. The problem of low accretion luminosity can be solved in the settling accretion scenario [144]. In this framework, an accreting isolated NS can be observed as a relatively bright (e.g., using eROSITA) transient source [145]. However, the number of isolated accretors is still not expected to be very high, which makes these searches problematic.
The discovery of isolated accreting NSs is very much welcomed, as it can open a unique possibility to studying old isolated NSs and can help to learn a lot about their properties and evolution. eROSITA could be a perfect instrument to reach this goal [84]. On the other hand, it is important to provide better estimates of the number of accreting isolated NSs and their properties in order to simplify the identification of these objects.
In the standard approach [137], the main obstacle on the way to accretion is related to relatively slow spin-down of an isolated NS with a standard magnetic field of ∼ G. Recently, it was discovered that young, very long-period NSs are good candidates for reaching the stage of accretion in a relatively short time. Thus, an estimation of the number of such objects is of great interest for long-term NS evolution. Illustrative evolutionary tracks for isolated NSs reaching the stage of accretion are shown in the Figure 4.
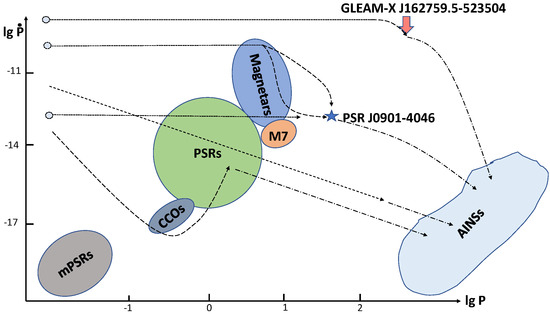
Figure 4.
The same as in Figure 3, but with the addition of the region of AINSs and an illustration of the corresponding evolutionary tracks. See text for details. The position of AINSs is added out of scale.
In general, all NSs with long spin periods, large long-lived magnetic fields, or low spatial velocities (e.g., those born in e−-captured SN) have good chances in reaching the stage of accretion from the ISM.
7. Magnetars and FRBs
Fast radio bursts (FRBs) are millisecond-scale radio transients that were discovered in 2007 [146]; see a recent comprehensive review in [147]. A possible link to NSs, in particular, to magnetars, was proposed in 2007 [148]. In 2020, it was confirmed through the detection of simultaneous radio and high-energy flares from the galactic magnetar, SGR 1935+2154 [149,150,151,152,153,154].
The number of known sources of FRBs is rapidly growing and is now at ∼. About 50 of the known sources demonstrate repeating activity [155], and four of the repeaters show a very high rate of events, producing up to several hundred bursts per hour [156]. In the near future, FRBs might become the most numerous known sources related to NSs, and they are extragalactic up to . Thus, they will be one of the main sources of information regarding the universal population of NSs [157].
NSs that produce FRBs can have different peculiar properties and origin. It is expected that FRB sources are extreme magnetars with large fields that produce hyperflares with a total energy release of ∼ erg and peak luminosities of ∼ erg s−1, which correspond to a millisecond radio burst with erg s−1 with a ratio of (see, e.g., [153]).
Four of the most active FRB sources demonstrate such a huge rate of flares (hundreds per hour) that, from the energetic point of view, such behavior cannot last longer than a few years, as the whole magnetic energy of ≳ erg (see Equation (2)) would be emitted in this period [158]. Such intense outbursts are not observed among galactic magnetars.
Two of the repeating sources of FRBs demonstrate periodicity on the scale of ∼16 [159] and ∼160 [160] days. The origin of this periodicity is unknown. Among the proposed hypotheses, there are the following: binarity [161,162], NS precession [163,164], and extra-long spin periods [165]. All of these opportunities are very intriguing, as we do not have any robust examples of active magnetars in binary systems (see a review in [166]). We have only a few unconfirmed candidates for precessing magnetars (see, e.g., [167] and references therein), and we do not know any examples of such long spin periods of NSs.
The mission mechanism of FRBs has not been discovered yet. Presently, two main frameworks are discussed: magnetospheric emissions and external relativistic shocks; see reviews in [168,169]. A large number of advanced theoretical scenarios have been proposed for both families of models. A growing variety of observational data (including polarization measurements, burst structure, spectra and their evolution during bursts) poses many questions and provides many opportunities to test these model predictions. The observations of simultaneous radio and X/-ray flares from galactic magnetars will probably help in selecting the correct approach. In general, understanding the origin of FRB radiation may shed light on important properties related to NS emission properties.
The galactic population of magnetars is consistent with the assumption that all these sources originated from core-collapsed SN. These NSs demonstrate clear correlations with young stellar populations and are sometimes situated inside standard SNRs; see, e.g., [170] for a review. However, a magnetar (or a NS, in general) can be formed via several other channels. Mostly, they are related to the coalescence of compact objects: NSs and/or WDs.
FRB sources are identified in different types of host galaxies in various environments [171], including in globular clusters [172]. The localization of FRBs at sites of very low star formation points toward alternative evolutionary channels related to old stellar populations. The coalescence NS-NS, NS-WD, and WD-WD altogether can produce NSs with a rate of at most ∼ yrs−1 per Milky-Way-like galaxy (see references in e.g., [157]). Thus, the probability of finding at least one active magnetar with such origins in our galaxy is not high. Observations of FRBs allow us to study these sources, even in different epochs of cosmic history. Moreover, in the near future, new sensitive low-frequency radio telescopes might allow us to observe FRBs from objects originating from Pop III stars.
Understanding the properties of the sources of FRBs can bring us new surprises regarding NS physics and observational appearances.
8. Conclusions
The field of NS astrophysics is actively developing due to the discoveries of new peculiar sources (such as long-spin period pulsars) and to the types of sources (such as FRBs). The phenomenology of NSs has become richer, and this requires more advanced theoretical approaches. We see more and more evolutionary links between the different beasts in the zoo of NSs. Understanding of this diverse population of sources is a fascinating task, and we must continue our research.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to the organizers of the 2nd International Electronic Conference on Universe (ECU 2023) and to Nicholas Chamel for the invitation to present a talk about different types of isolated NSs, which have become the basis for the present review.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AINS | Accreting isolated neutron star |
| AXP | Anomalous X-ray pulsar |
| BH | Blackhole |
| CCO | Central compact object |
| FRB | Fast radio burst |
| HMXB | High-mass X-ray binary |
| ISM | Interstellar medium |
| LMXB | Low-mass X-ray binary |
| M7 | Magnificent seven |
| mPSR | Millisecond radio pulsar |
| NS | Neutron star |
| PSR | Radio pulsar |
| SGR | Soft gamma-ray repeater |
| sGRB | Short gamma-ray burst |
| SN | Supernova |
| SNR | Supernova remnant |
| WD | White dwarf |
| XDINS | X-ray, dim, isolated neutron star |
Notes
| 1 | https:www.atnf.csiro.au/people/pulsar/psrcat/, accessed on 30 May 2023. |
| 2 | See the on-line catalog at http://www.iasf-milano.inaf.it/~deluca/cco/main.htm, accessed on 30 May 2023. Mostly, the parameters of the CCOs mentioned in this subsection refer to this catalog. |
| 3 | http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/~pulsar/magnetar/main.html, accessed on 30 May 2023. |
References
- Giacconi, R.; Gursky, H.; Waters, J.R. Two Sources of Cosmic X-rays in Scorpius and Sagittarius. Nature 1964, 204, 981–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacconi, R.; Gursky, H.; Kellogg, E.; Schreier, E.; Tananbaum, H. Discovery of Periodic X-ray Pulsations in Centaurus X-3 from UHURU. Astrophys. J. 1971, 167, L67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, D.; Schreiber, M.R. Overall Binary Evolution Theory. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisnovatyi-Kogan, G.S.; Komberg, B.V. Possible evolution of a binary-system radio pulsar as an old object with a weak magnetic field. Sov. Astron. Lett. 1976, 2, 130–132. [Google Scholar]
- Backer, D.C.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Heiles, C.; Davis, M.M.; Goss, W.M. A millisecond pulsar. Nature 1982, 300, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papitto, A.; Ferrigno, C.; Bozzo, E.; Rea, N.; Pavan, L.; Burderi, L.; Burgay, M.; Campana, S.; di Salvo, T.; Falanga, M.; et al. Swings between rotation and accretion power in a binary millisecond pulsar. Nature 2013, 501, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, N.; Zhu, X.J.; Thrane, E. The Mass Distribution of Galactic Double Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2019, 876, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauris, T.M.; Kramer, M.; Freire, P.C.C.; Wex, N.; Janka, H.T.; Langer, N.; Podsiadlowski, P.; Bozzo, E.; Chaty, S.; Kruckow, M.U.; et al. Formation of Double Neutron Star Systems. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiotti, L.; Rezzolla, L. Binary neutron star mergers: A review of Einstein’s richest laboratory. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2017, 80, 096901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.J.; Taggart, K.; Foley, R. A Sample of Neutron Star and Black Hole Binaries Detected through Gaia DR3 Astrometry. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.00680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewish, A.; Bell, S.J.; Pilkington, J.D.H.; Scott, P.F.; Collins, R.A. Observation of a Rapidly Pulsating Radio Source. Nature 1968, 217, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchester, R.N.; Hobbs, G.B.; Teoh, A.; Hobbs, M. The Australia Telescope National Facility Pulsar Catalogue. Astron. J. 2005, 129, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.A.; Lyne, A.G.; Lorimer, D.R.; Kramer, M.; Faulkner, A.J.; Manchester, R.N.; Cordes, J.M.; Camilo, F.; Possenti, A.; Stairs, I.H.; et al. Transient radio bursts from rotating neutron stars. Nature 2006, 439, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beskin, V.S. Radio pulsars: Already fifty years! Phys. Uspekhi 2018, 61, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippov, A.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Li, J.G. Time evolution of pulsar obliquity angle from 3D simulations of magnetospheres. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 441, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétri, J. The illusion of neutron star magnetic field estimates. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 485, 4573–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozwadowska, K.; Vissani, F.; Cappellaro, E. On the rate of core collapse supernovae in the milky way. New Astron. 2021, 83, 101498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauris, T.M.; Manchester, R.N. On the Evolution of Pulsar Beams. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 298, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.L.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, T.; Zhou, D.J.; Sun, J.H.; Yan, Y.; Su, W.Q.; Jing, W.C.; Chen, X.; et al. The FAST Galactic Plane Pulsar Snapshot survey: I. Project design and pulsar discoveries. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Qian, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Yan, Z.; Ransom, S.; Lorimer, D.; Li, D.; et al. FAST Globular Cluster Pulsar Survey: Twenty-four Pulsars Discovered in 15 Globular Clusters. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 915, L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.; Armour, W.; Baffa, C.; Barr, E.; Cooper, S.; Eatough, R.; Ensor, A.; Giani, E.; Karastergiou, A.; Karuppusamy, R.; et al. Pulsar Searches with the SKA. In Pulsar Astrophysics the Next Fifty Years; Weltevrede, P., Perera, B.B.P., Preston, L.L., Sanidas, S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; Volume 337, pp. 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyne, A.G.; Lorimer, D.R. High birth velocities of radio pulsars. Nature 1994, 369, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongwathanarat, A.; Janka, H.T.; Müller, E. Three-dimensional neutrino-driven supernovae: Neutron star kicks, spins, and asymmetric ejection of nucleosynthesis products. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 552, A126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Frantsuzova, A.; Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Tsichli, S.; Konstantinou, L.; Popov, S.B. Initial periods and magnetic fields of neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 514, 4606–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrimes, A.A.; Levan, A.J.; Groot, P.J.; Lyman, J.D.; Nelemans, G. The Galactic neutron star population - I. An extragalactic view of the Milky Way and the implications for fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 508, 1929–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A. Central compact objects in supernova remnants. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 932, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Hollerbach, R.; Igoshev, A.P. Powering central compact objects with a tangled crustal magnetic field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 495, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, G.G.; Zavlin, V.E.; Aschenbach, B.; Trümper, J.; Sanwal, D. The Compact Central Object in Cassiopeia A: A Neutron Star with Hot Polar Caps or a Black Hole? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 531, L53–L56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhin, A.Y.; De Luca, A.; Pons, J.A. Neutron Stars—Thermal Emitters. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 191, 171–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhin, A.Y.; Chabrier, G. Magnetic neutron star cooling and microphysics. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.; Lattimer, J.M.; Prakash, M.; Steiner, A.W. Minimal Cooling of Neutron Stars: A New Paradigm. ApJ Suppl. Ser. 2004, 155, 623–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, D.N.; Pons, J.A.; Miralles, J.A. The Impact of Magnetic Field on the Thermal Evolution of Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 673, L167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramkin, V.; Pavlov, G.G.; Shibanov, Y.; Kargaltsev, O. Thermal and Nonthermal Emission in the Optical-UV Spectrum of PSR B0950+08. Astrophys. J. 2022, 924, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, E.M.; Gusakov, M.E. Long-lasting accretion-powered chemical heating of millisecond pulsars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 508, 6118–6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, K.; Nagata, N.; Hamaguchi, K. Cooling theory faced with old warm neutron stars: Role of non-equilibrium processes with proton and neutron gaps. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 5508–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaltas, N.; Lai, D. The Hidden Magnetic Field of the Young Neutron Star in Kesteven 79. Astrophys. J. 2012, 748, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S. Modeling the X-rays from the Central Compact Object PSR J1852+0040 in Kesteven 79: Evidence for a Strongly Magnetized Neutron Star. Astrophys. J. 2014, 790, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, C.G.; Page, D.; Lee, W.H. Hypercritical Accretion onto a Newborn Neutron Star and Magnetic Field Submergence. Astrophys. J. 2013, 770, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuohy, I.; Garmire, G. Discovery of a compact X-ray source at the center of the SNR RCW 103. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1980, 239, L107–L110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Kaurov, A.A.; Kaminker, A.D. Central Compact Objects in Kes 79 and RCW 103 as ‘Hidden’ Magnetars with Crustal Activity. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2015, 32, e018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aì, A.; Evans, P.A.; Burrows, D.N.; Kuin, N.P.M.; Kann, D.A.; Campana, S.; Maselli, A.; Romano, P.; Cusumano, G.; La Parola, V.; et al. Evidence for the magnetar nature of 1E 161348-5055 in RCW 103. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, 2394–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, N.; Borghese, A.; Esposito, P.; Coti Zelati, F.; Bachetti, M.; Israel, G.L.; De Luca, A. Magnetar-like Activity from the Central Compact Object in the SNR RCW103. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 828, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Caraveo, P.A.; Mereghetti, S.; Tiengo, A.; Bignami, G.F. A Long-Period, Violently Variable X-ray Source in a Young Supernova Remnant. Science 2006, 313, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, M.; Rea, N.; Graber, V.; Hurley-Walker, N. Long-period Pulsars as Possible Outcomes of Supernova Fallback Accretion. Astrophys. J. 2022, 934, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, D.M.; Barthelmy, S.; Gehrels, N.; Kippen, R.M.; Cayton, T.; Kouveliotou, C.; Eichler, D.; Wijers, R.A.M.J.; Woods, P.M.; Granot, J.; et al. A giant γ-ray flare from the magnetar SGR 1806-20. Nature 2005, 434, 1107–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazets, E.P.; Golentskii, S.V.; Ilinskii, V.N.; Aptekar, R.L.; Guryan, I.A. Observations of a flaring X-ray pulsar in Dorado. Nature 1979, 282, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedrenne, G.; Zenchenko, V.M.; Kurt, V.G.; Niel, M.; Hurley, K.; Estulin, I.V. Observations of the X-ray burster 0525.9-66.1. Pisma v Astronomicheskii Zhurnal 1979, 5, 588–594. [Google Scholar]
- Olausen, S.A.; Kaspi, V.M. The McGill Magnetar Catalog. ApJ Suppl. Ser. 2014, 212, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, P.; Rea, N.; Israel, G.L. Magnetars: A Short Review and Some Sparse Considerations. Astrophys. Space Sci. Libr. 2021, 461, 97–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriil, F.P.; Kaspi, V.M.; Woods, P.M. Magnetar-like X-ray bursts from an anomalous X-ray pulsar. Nature 2002, 419, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriil, F.P.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Gotthelf, E.V.; Kaspi, V.M.; Livingstone, M.A.; Woods, P.M. Magnetar-Like Emission from the Young Pulsar in Kes 75. Science 2008, 319, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, R.; Esposito, P. Low-Magnetic Magnetars. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2013, 22, 1330024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiengo, A.; Esposito, P.; Mereghetti, S.; Turolla, R.; Nobili, L.; Gastaldello, F.; Götz, D.; Israel, G.L.; Rea, N.; Stella, L.; et al. A variable absorption feature in the X-ray spectrum of a magnetar. Nature 2013, 500, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Castillo, G.A.; Israel, G.L.; Tiengo, A.; Salvetti, D.; Turolla, R.; Zane, S.; Rea, N.; Esposito, P.; Mereghetti, S.; Perna, R.; et al. The outburst decay of the low magnetic field magnetar SWIFT J1822.3-1606: Phase-resolved analysis and evidence for a variable cyclotron feature. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 456, 4145–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Pons, J.A.; Miralles, J.A.; Boldin, P.A.; Posselt, B. Population synthesis studies of isolated neutron stars with magnetic field decay. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 401, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniamini, P.; Hotokezaka, K.; van der Horst, A.; Kouveliotou, C. Formation rates and evolution histories of magnetars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 1426–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, L.; Wickramasinghe, D. Modelling of isolated radio pulsars and magnetars on the fossil field hypothesis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 367, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Duncan, R.C. Neutron Star Dynamos and the Origins of Pulsar Magnetism. Astrophys. J. 1993, 408, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, A.; Urpin, V.; Belvedere, G. Protoneutron star dynamos: Pulsars, magnetars, and radio-silent X-ray emitting neutron stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 451, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.R.N.; Ohlmann, S.T.; Podsiadlowski, P.; Röpke, F.K.; Balbus, S.A.; Pakmor, R.; Springel, V. Stellar mergers as the origin of magnetic massive stars. Nature 2019, 574, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B. Origins of magnetars in binary systems. Astron. Astrophys. Trans. 2016, 29, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, R.; Guilet, J.; Janka, H.T.; Gastine, T. Magnetar formation through a convective dynamo in protoneutron stars. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrère, P.; Guilet, J.; Reboul-Salze, A.; Raynaud, R.; Janka, H.T. A new scenario for magnetar formation: Tayler-Spruit dynamo in a proto-neutron star spun up by fallback. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 668, A79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, J.A.; Viganò, D. Magnetic, thermal and rotational evolution of isolated neutron stars. Living Rev. Comput. Astrophys. 2019, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Popov, S.B.; Hollerbach, R. Evolution of Neutron Star Magnetic Fields. Universe 2021, 7, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posselt, B.; Popov, S.B.; Haberl, F.; Trümper, J.; Turolla, R.; Neuhäuser, R. The Magnificent Seven in the dusty prairie. Astroph. Space Sci. 2007, 308, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, R. Isolated Neutron Stars: The Challenge of Simplicity. Astrophys. Space Sci. Libr. 2009, 357, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhin, A.Y.; Zyuzin, D.A.; Yakovlev, D.G.; Beznogov, M.V.; Shibanov, Y.A. Thermal luminosities of cooling neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 5052–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, F.M.; Wolk, S.J.; Neuhäuser, R. Discovery of a nearby isolated neutron star. Nature 1996, 379, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treves, A.; Popov, S.B.; Colpi, M.; Prokhorov, M.E.; Turolla, R. The Magnificient Seven: Close-by Cooling Neutron Stars? Astron. Soc. Pac. Conf. Ser. 2001, 234, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konenkov, D.Y.; Popov, S.B. RX J0720.4-3125 as a possible example of magnetic field decay in neutron stars. Astron. Lett. 1997, 23, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratiev, V.I.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Lorimer, D.R.; Burgay, M.; Possenti, A.; Turolla, R.; Popov, S.B.; Zane, S. New Limits on Radio Emission from X-ray Dim Isolated Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2009, 702, 692–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Marazuela, I.; Straal, S.M.; van Leeuwen, J.; Kondratiev, V.I. New upper limits on low-frequency radio emission from isolated neutron stars with LOFAR. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.05509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.M.; Haberl, F.; Zavlin, V.E.; Motch, C.; Zane, S.; Hohle, M.M. XMM-Newton reveals a candidate period for the spin of the “Magnificent Seven” neutron star RX J1605.3+3249. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 563, A50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Grigorian, H.; Blaschke, D. Neutron star cooling constraints for color superconductivity in hybrid stars. Phys. Rev. C 2006, 74, 025803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Turolla, R.; Prokhorov, M.E.; Colpi, M.; Treves, A. Young Close-By Neutron Stars: The Gould Belt Vs. The Galactic Disc. Astroph. Space Sci. 2005, 299, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüeros, M.A.; Posselt, B.; Anderson, S.F.; Rosenfield, P.; Haberl, F.; Homer, L.; Margon, B.; Newsom, E.R.; Voges, W. No Confirmed New Isolated Neutron Stars in the SDSS Data Release 4. Astron. J. 2011, 141, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchuk, A.S.H.; Fox, D.B.; Rutledge, R.E. Chandra Observations of 1RXS J141256.0+792204 (Calvera). Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereghetti, S.; Rigoselli, M.; Taverna, R.; Baldeschi, L.; Crestan, S.; Turolla, R.; Zane, S. NICER Study of Pulsed Thermal X-Rays from Calvera: A Neutron Star Born in the Galactic Halo? Astrophys. J. 2021, 922, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.M.; Motch, C.; Turolla, R.; Treves, A.; Popov, S.B. The isolated neutron star candidate 2XMM J104608.7-594306. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 498, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.M.; Motch, C.; Turolla, R.; Popov, S.B.; Schwope, A.D.; Treves, A. New XMM-Newton observation of the thermally emitting isolated neutron star 2XMM J104608.7-594306. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 583, A117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.M.; Motch, C.; Kurpas, J.; Schwope, A.D.; Valdes, F.; Haberl, F.; Traulsen, I.; Tubín, D.; Becker, W.; Comparat, J.; et al. XMM-Newton and SRG/eROSITA observations of the isolated neutron star candidate 4XMM J022141.5−735632. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 666, A148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.M. What will eROSITA reveal among X-ray faint isolated neutron stars? In Pulsar Astrophysics the Next Fifty Years; Weltevrede, P., Perera, B.B.P., Preston, L.L., Sanidas, S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; Volume 337, pp. 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhryakova, A.D.; Biryukov, A.V.; Popov, S.B. Observability of Single Neutron Stars at SRG/eROSITA. Astron. Rep. 2021, 65, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucher-Giguère, C.A.; Kaspi, V.M. Birth and Evolution of Isolated Radio Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2006, 643, 332–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipunov, V.M.; Postnov, K.A.; Prokhorov, M.E. The Scenario Machine: Binary Star Population Synthesis; Harwood Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, S.B.; Turolla, R. Initial spin periods of neutron stars in supernova remnants. Astroph. Space Sci. 2012, 341, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, E.F.; Kramer, M. On the birthrates of Galactic neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpi, M.; Geppert, U.; Page, D. Period Clustering of the Anomalous X-Ray Pulsars and Magnetic Field Decay in Magnetars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 529, L29–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Turolla, R. Initial Parameters of Neutron Stars. Astron. Soc. Pac. Conf. Ser. 2012, 466, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, M.; Zhu, T.; Chen, K. Neutron Star Magnetic Field Evolution, Crust Movement, and Glitches. Astrophys. J. 1998, 492, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baym, G.; Pethick, C.; Pines, D. Superfluidity in Neutron Stars. Nature 1969, 224, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, A.; Arras, P.; Zweibel, E. Magnetic Field Evolution in Neutron Star Crusts Due to the Hall Effect and Ohmic Decay. Astrophys. J. 2004, 609, 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Popov, S.B. Magnetic field decay in normal radio pulsars. Astron. Nachrichten 2015, 336, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldreich, P.; Reisenegger, A. Magnetic Field Decay in Isolated Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 1992, 395, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusakov, M.E.; Kantor, E.M.; Ofengeim, D.D. Evolution of the magnetic field in neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 103012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusakov, M.E.; Kantor, E.M.; Ofengeim, D.D. Magnetic field evolution time-scales in superconducting neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 4561–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofengeim, D.D.; Gusakov, M.E. Fast magnetic field evolution in neutron stars: The key role of magnetically induced fluid motions in the core. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 043007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, R.; Pons, J.A. A Unified Model of the Magnetar and Radio Pulsar Bursting Phenomenology. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 727, L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, J.A.; Link, B.; Miralles, J.A.; Geppert, U. Evidence for heating of neutron stars by magnetic-field decay. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 071101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chashkina, A.; Popov, S.B. Magnetic field estimates for accreting neutron stars in massive binary systems and models of magnetic field decay. New Astron. 2012, 17, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonthier, P.L.; Ouellette, M.S.; Berrier, J.; O’Brien, S.; Harding, A.K. Galactic Populations of Radio and Gamma-Ray Pulsars in the Polar Cap Model. Astrophys. J. 2002, 565, 482–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Popov, S.B. Modified pulsar current analysis: Probing magnetic field evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 444, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, E.S.; Blandford, R.D. Analysis of the pulsar P-P-prime distribution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981, 194, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanand, M.; Narayan, R. A new look at pulsar statistics—Birthrate and evidence for injection. J. Astrophys. Astron. 1981, 2, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Popov, S.B. Braking indices of young radio pulsars: Theoretical perspective. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 2826–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeev Kumar, H.; Safi-Harb, S. Variability of the High-Magnetic Field X-ray Pulsar PSR J1846-0258 Associated with the Supernova Remnant Kes 75 as Revealed by the Chandra X-ray Observatory. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0802.1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.; Bailes, M.; Bates, S.; Bhat, N.D.R.; Burgay, M.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; D’Amico, N.; Johnston, S.; Keith, M.; Kramer, M.; et al. A Radio-loud Magnetar in X-ray Quiescence. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 721, L33–L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilo, F.; Scholz, P.; Serylak, M.; Buchner, S.; Merryfield, M.; Kaspi, V.M.; Archibald, R.F.; Bailes, M.; Jameson, A.; van Straten, W.; et al. Revival of the Magnetar PSR J1622-4950: Observations with MeerKAT, Parkes, XMM-Newton, Swift, Chandra, and NuSTAR. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, P.; De Luca, A.; Turolla, R.; Coti Zelati, F.; Hummel, W.; Tiengo, A.; Israel, G.L.; Rea, N.; Mignani, R.P.; Borghese, A. Long X-ray flares from the central source in RCW 103. XMM-Newton and VLT observations in the aftermath of the 2016 outburst. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 626, A19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, J.P.; Gotthelf, E.V. Spin-Down Measurement of PSR J1852+0040 in Kesteven 79: Central Compact Objects as Anti-Magnetars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 709, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B. Origin of Magnetar-Scale Crustal Field in PSR J1852+0040 and ’Frozen’ Magnetars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2013, 30, e045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, T.; Podsiadlowski, P. The Triple-Ring Nebula Around SN 1987A: Fingerprint of a Binary Merger. Science 2007, 315, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.C.G. Evolution of a buried magnetic field in the central compact object neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 2567–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Elfritz, J.G.; Popov, S.B. Post-fall-back evolution of multipolar magnetic fields and radio pulsar activation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 3689–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, C.M.; Lyne, A.G.; Kramer, M.; Manchester, R.N.; Kaspi, V.M. The Braking Index of PSR J1734-3333 and the Magnetar Population. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 741, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, N.; Viganò, D.; Israel, G.L.; Pons, J.A.; Torres, D.F. 3XMM J185246.6+003317: Another Low Magnetic Field Magnetar. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 781, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.A. Neutron Star Accretion in a Supernova. Astrophys. J. 1989, 346, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimov, A.; Page, D. Delayed Switch-on of Pulsars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 440, L77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viganò, D.; Pons, J.A. Central compact objects and the hidden magnetic field scenario. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 425, 2487–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeyama, T.; Kashiyama, K. Repulsion of fallback matter due to central energy source in supernova. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 70, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Kashiyama, K.; Shigeyama, T.; Takasao, S. A Necessary Condition for Supernova Fallback Invading Newborn Neutron-star Magnetosphere. Astrophys. J. 2021, 917, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, H.T.; Wongwathanarat, A.; Kramer, M. Supernova Fallback as Origin of Neutron Star Spins and Spin-kick Alignment. Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Cumming, A.; Reisenegger, A.; Armaza, C.; Lyutikov, M.; Valdivia, J.A. Hall equilibria with toroidal and poloidal fields: Application to neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 434, 2480–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Cumming, A. Hall attractor in axially symmetric magnetic fields in neutron star crusts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, T.S.; Hollerbach, R. Three Dimensional Simulation of the Magnetic Stress in a Neutron Star Crust. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 191101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bransgrove, A.; Levin, Y.; Beloborodov, A. Magnetic field evolution of neutron stars - I. Basic formalism, numerical techniques and first results. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 2771–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Popov, S.B. How to make a mature accreting magnetar. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 3204–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caleb, M.; Heywood, I.; Rajwade, K.; Malenta, M.; Stappers, B.W.; Barr, E.; Chen, W.; Morello, V.; Sanidas, S.; van den Eijnden, J.; et al. Discovery of a radio-emitting neutron star with an ultra-long spin period of 76 s. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley-Walker, N.; Zhang, X.; Bahramian, A.; McSweeney, S.J.; O’Doherty, T.N.; Hancock, P.J.; Morgan, J.S.; Anderson, G.E.; Heald, G.H.; Galvin, T.J. A radio transient with unusually slow periodic emission. Nature 2022, 601, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniamini, P.; Wadiasingh, Z.; Hare, J.; Rajwade, K.M.; Younes, G.; van der Horst, A.J. Evidence for an abundant old population of Galactic ultra-long period magnetars and implications for fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 520, 1872–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhriakova, A.D.; Popov, S.B. Origin of young accreting neutron stars in high-mass X-ray binaries in supernova remnants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 511, 4447–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, F.; García, F.; Simaz Bunzel, A.; Chaty, S. A catalogue of high-mass X-ray binaries in the Galaxy: From the INTEGRAL to the Gaia era. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 671, A149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostriker, J.P.; Rees, M.J.; Silk, J. Some Observable Consequences of Accretion by Defunct Pulsars. Astrophys. Lett. 1970, 6, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Shvartsman, V.G. Ionization Zones around Neutron Stars: Hα Emission, Heating of the Interstellar Medium, and the Influence on Accretion. Sov. Astron. 1971, 14, 662. [Google Scholar]
- Treves, A.; Colpi, M. The observability of old isolated neutron stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 241, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, S.B.; Colpi, M.; Treves, A.; Turolla, R.; Lipunov, V.M.; Prokhorov, M.E. The Neutron Star Census. Astrophys. J. 2000, 530, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropina, O.D.; Romanova, M.M.; Toropin, Y.M.; Lovelace, R.V.E. Magnetic Inhibition of Accretion and Observability of Isolated Old Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2003, 593, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, D.; Tuthill, P.; Sharma, S.; Hirai, R. The Galactic underworld: The spatial distribution of compact remnants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 516, 4971–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shklovskii, I.S. Possible Causes of the Secular Increase in Pulsar Periods. Sov. Astron. 1970, 13, 562. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, M.S.B.; Burrows, A. Kicks and induced spins of neutron stars at birth. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 517, 3938–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Chruslinska, M.; Dorozsmai, A.; Toonen, S. Combined analysis of neutron star natal kicks using proper motions and parallax measurements for radio pulsars and Be X-ray binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 508, 3345–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldin, P.A.; Popov, S.B. The evolution of isolated neutron stars until accretion: The role of the initial magnetic field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 407, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.; Postnov, K.; Kochetkova, A.; Hjalmarsdotter, L. Theory of quasi-spherical accretion in X-ray pulsars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 216–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Postnov, K.A.; Shakura, N.I. Settling accretion on to isolated neutron stars from interstellar medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 2817–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorimer, D.R.; Bailes, M.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Narkevic, D.J.; Crawford, F. A Bright Millisecond Radio Burst of Extragalactic Origin. Science 2007, 318, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. The Physics of Fast Radio Bursts. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.03972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Postnov, K.A. Hyperflares of SGRs as an engine for millisecond extragalactic radio bursts. arXiv 2007, arXiv:0710.2006. [Google Scholar]
- CHIME/FRB Collaboration; Andersen, B.C.; Bandura, K.M.; Bhardwaj, M.; Bij, A.; Boyce, M.M.; Boyle, P.J.; Brar, C.; Cassanelli, T.; Chawla, P.; et al. A bright millisecond-duration radio burst from a Galactic magnetar. Nature 2020, 587, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, C.D.; Ravi, V.; Belov, K.V.; Hallinan, G.; Kocz, J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; McKenna, D.L. A fast radio burst associated with a Galactic magnetar. Nature 2020, 587, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.K.; Lin, L.; Xiong, S.L.; Ge, M.Y.; Li, X.B.; Li, T.P.; Lu, F.J.; Zhang, S.N.; Tuo, Y.L.; Nang, Y.; et al. HXMT identification of a non-thermal X-ray burst from SGR J1935+2154 and with FRB 200428. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereghetti, S.; Savchenko, V.; Ferrigno, C.; Götz, D.; Rigoselli, M.; Tiengo, A.; Bazzano, A.; Bozzo, E.; Coleiro, A.; Courvoisier, T.J.L.; et al. INTEGRAL Discovery of a Burst with Associated Radio Emission from the Magnetar SGR 1935+2154. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 898, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridnaia, A.; Svinkin, D.; Frederiks, D.; Bykov, A.; Popov, S.; Aptekar, R.; Golenetskii, S.; Lysenko, A.; Tsvetkova, A.; Ulanov, M.; et al. A peculiar hard X-ray counterpart of a Galactic fast radio burst. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Casentini, C.; Ursi, A.; Verrecchia, F.; Addis, A.; Antonelli, L.A.; Argan, A.; Barbiellini, G.; Baroncelli, L.; Bernardi, G.; et al. An X-ray burst from a magnetar enlightening the mechanism of fast radio bursts. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The CHIME/FRB Collaboration; Andersen, B.C.; Bandura, K.; Bhardwaj, M.; Boyle, P.J.; Brar, C.; Cassanelli, T.; Chatterjee, S.; Chawla, P.; Cook, A.M.; et al. CHIME/FRB Discovery of 25 Repeating Fast Radio Burst Sources. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.08762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.R.; Huang, Y.F. A Comprehensive Analysis on Repeating Fast Radio Bursts. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.05242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Pshirkov, M.S. Future of Neutron Star Studies with Fast Radio Bursts. Particles 2023, 6, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Cao, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Qu, Y.H.; Niu, J.R.; Zhu, W.W.; Han, J.L.; et al. FAST Observations of FRB 20220912A: Burst Properties and Polarization Characteristics. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.14665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chime/Frb Collaboration; Amiri, M.; Andersen, B.C.; Bandura, K.M.; Bhardwaj, M.; Boyle, P.J.; Brar, C.; Chawla, P.; Chen, T.; Cliche, J.F.; et al. Periodic activity from a fast radio burst source. Nature 2020, 582, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajwade, K.M.; Mickaliger, M.B.; Stappers, B.W.; Morello, V.; Agarwal, D.; Bassa, C.G.; Breton, R.P.; Caleb, M.; Karastergiou, A.; Keane, E.F.; et al. Possible periodic activity in the repeating FRB 121102. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 495, 3551–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyutikov, M.; Barkov, M.V.; Giannios, D. FRB Periodicity: Mild Pulsars in Tight O/B-star Binaries. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 893, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkov, M.V.; Popov, S.B. Formation of periodic FRB in binary systems with eccentricity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 515, 4217–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanazzi, J.J.; Lai, D. Periodic Fast Radio Bursts with Neutron Star Free Precession. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 892, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, Y.; Beloborodov, A.M.; Bransgrove, A. Precessing Flaring Magnetar as a Source of Repeating FRB 180916.J0158+65. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 895, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniamini, P.; Wadiasingh, Z.; Metzger, B.D. Periodicity in recurrent fast radio bursts and the origin of ultralong period magnetars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 3390–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B. High magnetic field neutron stars and magnetars in binary systems. IAU Symp. 2023, 363, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makishima, K.; Enoto, T.; Yoneda, H.; Odaka, H. A NuSTAR confirmation of the 36 ks hard X-ray pulse-phase modulation in the magnetar 1E 1547.0-5408. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 502, 2266–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. The physical mechanisms of fast radio bursts. Nature 2020, 587, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B. FRB emission mechanisms vs. observations. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.14268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, R.; Zane, S.; Watts, A.L. Magnetars: The physics behind observations. A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 116901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.C.; Fong, W.F.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Eftekhari, T.; Leja, J.; Prochaska, J.X.; Nugent, A.E.; Bhandari, S.; Blanchard, P.K.; Caleb, M.; et al. The Demographics, Stellar Populations, and Star Formation Histories of Fast Radio Burst Host Galaxies: Implications for the Progenitors. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.05465. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsten, F.; Marcote, B.; Nimmo, K.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Bhardwaj, M.; Tendulkar, S.P.; Keimpema, A.; Yang, J.; Snelders, M.P.; Scholz, P.; et al. A repeating fast radio burst source in a globular cluster. Nature 2022, 602, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).