Abstract
Mrk 783 is a narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxy that possesses a relatively large two-sided radio emission extending up to 14 kpc from the active nucleus possibly connected with a large-scale ionized gas emission. We obtained a deep [O iii] image that revealed an extended system of emission knots and diffuse ionized gas surrounding the main galaxy. The highly-excited gas is related not only to the radio structure, but also to tidal features illuminated by the active nucleus radiation up to the projected distance of 41 kpc as it follows from the emission lines’ intensities and kinematics derived from the long-slit spectroscopic data. Moreover, the part of the disk of the companion galaxy SDSS J130257.20+162537.1, located at ∼99 kpc projected distances to the north of Mrk 783, also falls in the AGN ionizing cone. It is possiblethat Mrk 783 can be considered as ‘Hanny’s Voorwerp precursor’, i.e., a galaxy that demonstrates signs of sequential switching from radio-loud to radio-quiet nuclear activity, in the moment before its ionization luminosity falls.
1. Introduction
Active galactic nucleus (AGN) feedback is important in the coevolution between AGN and its host galaxy. This fundamental physical process has an impact on the interstellar medium and the intergalactic environment, but it has been under debate for a long time and is still not fully understood. Mrk 783 is an interesting example of a galaxy in which we can trace AGN radiation feedback on large spatial scales outside the host galaxy.
Mrk 783 was discovered by Markarian and Lipovetskii [1]; its optical spectra were first defined as the Narrow Line Seyfert 1 galaxy (NLS1) by Osterbrock and Pogge [2]. According to the current point of view, NLS1 is an AGN with a relatively low mass central black hole (10–10 M) and is in an early stage of AGN evolution [3]. Mrk 783 black hole mass M M is at the higher end of NLS1’s distribution; its Eddington ratio is quite low (0.11) and its [O iii] line is quite strong with respect to H [4].
In the radio band, Mrk 783 was extensively investigated by Congiu et al. [5,6]. They have found in the center of galaxy a compact core with a pc-scale jet, as well as a two-sided extended component (up to 14 kpc from the nucleus). The authors stressed that the galaxy ‘is one of the few NLS1s showing such an extended emission at ’. The small-scale jet and the large-scale radio emission are not aligned. Based on these facts, and on the very steep spectral indexes, Congiu et al. [5] concluded that the extended emission observed in Mrk 783 might be a relic and that the radio source might be in a quiescent period of its activity cycle.
No less interesting is that Mrk 783 is in the optical range. A V-band image reveals low surface brightness extended structures on both sides of the galaxy nucleus that look like the tidal tail that is observed in interacting galaxies. The isophotes of the internal part of the galaxy indicate the presence of a second point-like structure, which might be the nucleus of the second galaxy involved in the proposed merging [6]. The optical emission of the ionized gas is far more extended with respect to the radio emission, mostly on the south-east side of the nucleus. The [O iii], H and H lines were tracked up to ∼35 kpc from the nucleus in the spectrum obtained by the 6.5m Magellan telescope, which makes this EELR (extended emission line region) one of the most extended discovered so far [7].
In order to better understand the physics of processes occurring in Mrk 783, we have mapped this galaxy in the [O iii] emission line at the 2.5m telescope of the Caucasus Mountain Observatory (CMO) of the Sternberg Astronomical Institute of Moscow State University (SAI MSU) and also observed it at the 6m telescope of the Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Sciences (SAO RAS) and the 1m Schmidt telescope of the Byurakan Astrophysical Observatory (BAO) of the National Academy of Sciences of Armenia with deep spectral and imaging data. Throughout this study, we adopted the Mrk 738 redshift that gives the standard CDM cosmology (H = 68 km s Mpc, ), a luminosity distance of 318 Mpc, and a scale of 1.35 kpc arcsec, according to the NED database1.
2. Observations and Data Analysis
Images in the [O iii] emission line were obtained in March 2022 by the 2.5m CMO SAI MSU telescope [8] with the tunable filter photometer MaNGaL (Mapper of Narrow Galaxy Lines). This instrument uses a scanning Fabry–Perot interferometer as a narrow-band filter ( Å). The filter was subsequently centered on the redshifted [O iii] emission line and on the continuum shifted in 80 Å from the line. The instrument description and data reduction steps are described by Moiseev et al. [9], and the log of observations is given in Table 1, where , , and represent the total exposure, the seeing value, and the spectral resolution correspondingly. The field-of-view (FoV) was with a scale px. The images obtained on different nights were aligned using the astrometric calibration via the online astrometry.net2 software [10]. The final emission line image after the continuum subtraction is shown in Figure 1. We have mapped the [O iii] emission to the surface brightness ∼ with the signal-to-noise ratio .

Table 1.
Log of optical observations at the 1m (BAO), 2.5m (MaNGaL), and 6m (SCORPIO-2) telescopes.

Figure 1.
DESI Legacy Survey image of Mrk 783 (the combination of images in filters) together with MaNGaL [O iii] map. The SCORPIO-2 slit positions are shown by grey and red lines.
The [O iii] image reveals an extended system of emission knots and diffuse ionized gas surrounding the main galaxy. The brightest external features are (Figure 2): (i) the ‘SE knot’ at the projected distances – from the nucleus, which is a part of the emission ‘tail’; (ii) the ‘E knot’—the bright region at – to the east, which is the root of the ‘tail’; and (iii) the ‘W knot’ at –. Some of the regions listed above are visible in the DESI Legacy Survey [11] as faint blue structures (Figure 1); the SE knot was already found in the Magellan spectra [7]. Also, a significant [O iii] emission was detected in the galaxy SDSS J130257.20+162537.1, located at a projected distance of ∼ (99 kpc) to the north of Mrk 783 (hereafter, SDSS J1302 + 1625 or ‘the satellite’).
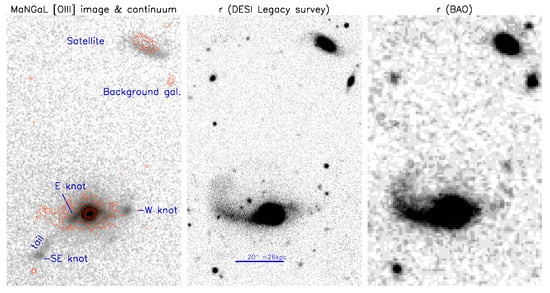
Figure 2.
Mrk 783 with the satellite SDSS J130257.20+162537.1. From left to right: the [O iii] emission line map with contours of the MaNGaL image in the continuum; the main emission knots are labeled; the DESI Legacy Survey r-band image; deep r-band image from the 1m BAO telescope.
In order to study the faint stellar structures on the outskirts of Mrk 783 in detail, we performed deep imaging in the r-SDSS filter with the 1m Schmidt telescope of the BAO3. The updated 4 K × 4 K Imaging Systems Inc (Concord, MA, USA) liquid-cooled CCD camera was used as a detector with a pixel scale and an FoV of ∼. The detailed description of the telescope, the photometer, and the data reduction steps are given by Dodonov et al. [12]. The r-band image was calibrated to the magnitudes by using the DESI Legacy Survey’s DR10 on-line photometric catalogue4 of sources in the observed field. At the signal to noise value we reached the surface brightness limit that is on ∼ mag deeper than r-band DESI Legacy Survey image (Figure 2).
The spectral observations were carried out as the prime focus of the SAO RAS 6m telescope in the long-slit mode of the SCORPIO-2 focal reducer [13] providing the spatial scale px along the slit. Other parameters are listed in Table 1. We put the slit along the most interesting features appearing in [O iii] map: the slit with position angle crossed the possible companion galaxy SDSS J1302 + 1625 and fainter red galaxy SDSS J130256.50+162521.8, the slit with crossed the Mrk 783 nucleus together with W and E knots, whereas the slit exposed the tail with E and SE knots (see Figure 1). The spectrophotometric calibration was based on the observations of the standard star BD + 75,325. Also the spectrum of this O-type star was used to correction of the galaxy spectra on the telluric absorption: O B-band (686–698 nm) and H2O band at 710–730 nm. The last one affects the [S ii] redshifted lines of Mrk 783.
3. Ionized Gas Properties
The integrated spectra of the emission knots mentioned above, together with the nuclei of both galaxies, are shown in Figure 3. The nuclear spectrum demonstrates the same properties detected in previous studies, including SDSS archival data5: a broad blue-shifted component of the Balmer emission lines and the Sy-like flux ratio without bright iron emission. Both low- and high-excitation emission lines in external knots are narrow with a single-component structure. Also, we detected here highly-excited He ii emission with a relative intensity that is similar to the nuclear source: He ii/H . Figure 4 clearly demonstrates the extended emission in He ii along the SE gaseous tail up to the projected distance (41 kpc). The spectrum of the satellite (Figure 3, bottom panel) corresponds to intermediate objects between AGN and starburst (see Section 4) with narrow Balmer, [S ii], [N ii], and [O iii] lines without helium emission.
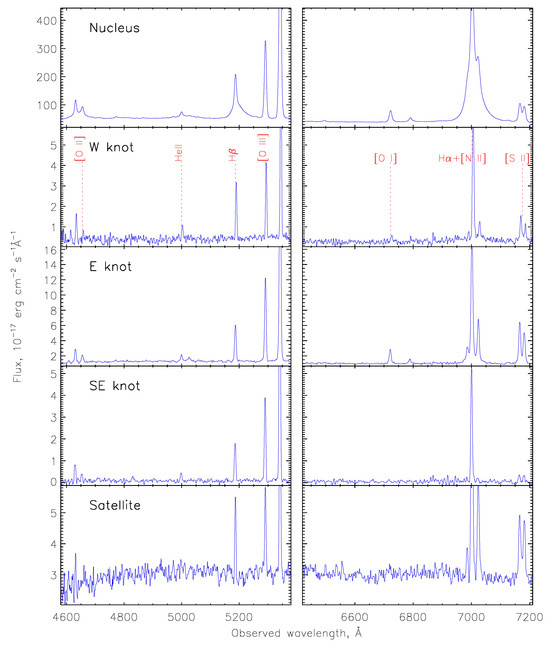
Figure 3.
SCORPIO-2 spectra of the Mrk 783 nucleus, W, E, and SE emission knots, and the satellite. All spectra are integrated in the aperture. The main emission lines are labeled.
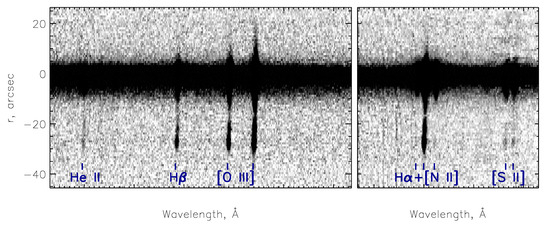
Figure 4.
Fragments of the 2D spectrum along in the blue and red ranges binned to a scale of 0.8/px.
The parameters of the emission lines after subtraction of continuum interpolated by a cubic spline (integrated flux, line-of-sight velocity, and velocity dispersion corrected on the instrumental broadening) were estimated using a single-Gaussian fitting and are shown in the Figure 5.
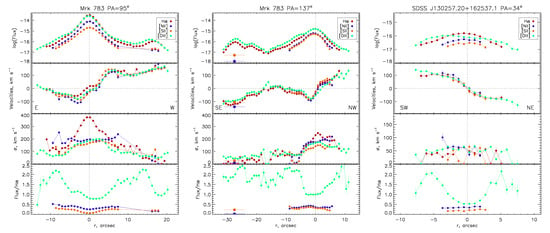
Figure 5.
The changes of the main emission lines parameters along (left) and (center) and (right). From top to bottom: the surface brightness, line-of-sight velocities (the systemic velocity 20,100 and 20,038 were subtracted for the Mrk 738 and SDSS J1302+1625 correspondingly), velocity dispersion corrected on the instrumental width, and flux ratio relative to the H. The largest symbols in the central panel correspond to the integrated values in the SE knot. The point corresponds to the maximal emission in the stellar continuum.
In the inner few kpc (), our long-slit data reveal features probably related to the AGN outflow influence on the surrounding gas: a high velocity dispersion in the H line (including a spread of light from the broad line region), a significant difference between velocities in the forbidden and Balmer lines at ( in , see Figure 5), and a peak of negative velocities near the E-knot ( in ). In contrast with a circumnuclear region, the external gas in and around Mrk 783 is dynamically cold: the observed velocities in the forbidden and Balmer lines are in good agreement within the errors; the typical velocity dispersion is –. The line-of-sight velocity curve along at seems like a typical flat rotation curve of a disk galaxy (the slit lies near its photometric major axis). In this case, the falling velocities in the opposite (eastern) side of this curve should correspond to rotation in the stellar tidal tail that is clearly visible in broad-band images, which can be partly off-plane. The amplitude of observed velocities along is about , which is in agreement with gas rotation on orbits that are slightly inclined to the main galaxy disk.
The [O iii] to H flux ratio along has a more or less constant value [O iii]/H in a very large distant range , implying the same source of the gas excitation along the SE tail. Figure 6 shows the diagnostic emission-line flux ratio diagrams (BPT, after Baldwin et al. [14]) for the Mrk 783 EELR. In contrast with the previous spectroscopic observations [7], where only upper limits for the [N ii]/H ratio were presented for the most distant SE-knot, we were able to detect in this region both relatively faint [N ii] and [S ii] doublets of emission lines (Figure 4).
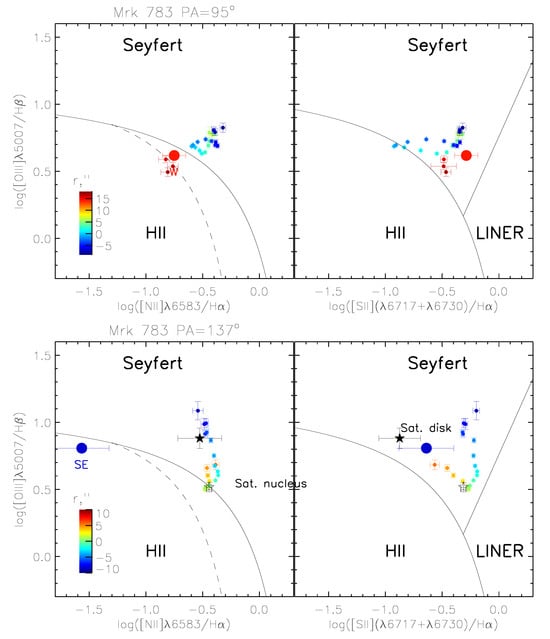
Figure 6.
Line ratio (BPT) diagrams for the binned spectra along (top) and (bottom). Dividing lines between HII regions, AGN, and the composite nucleus are taken from Kewley et al. [15] and Kauffmann et al. [16]. Different colors correspond to radial distances along the slit according to the scale box. Large red and blue points correspond to the integrated values for the W and SE knots. The open and filled black stars in the bottom panels show line ratios for the nuclear and external regions of the satellite.
On the diagram [O iii]/H vs. [S ii]/H (Figure 6, right), all points occupied an area corresponding to the AGN-type ionization, whereas in the case of [O iii]/H vs. [N ii]/H plot (Figure 6, left), the most distant regions are located near the border between the H ii and composite excitation (W knot) or even in the H ii area (SE knot). On the other hand, the high value of the He ii/H lines ratio in these regions suggest (as well as in a bulk of EELR) the photoionization by the hard UV continuum from AGN than by young OB stars. In this case, a decrease of the [N ii]/H ratio for the external regions could be caused by a relatively low gas chemical abundance. Indeed, numerical calculations by Bennert et al. [17] for the typical NLR exhibit a similar behaviour of points on the BPT-diagrams, if we accept metal abundance values for the W-knot and for the NW-knot.
Therefore, the observed emission line ratios (He ii/H and BPT diagrams) suggest that AGN radiation is the dominant source of the gas ionization up to a projected distance of 41 kpc from the nucleus.
4. The Galaxy Environment and the Satellite
As we have already noted in Section 1, Mrk 783 was considered an interacting galaxy with a tidal tail and a possible secondary nucleus. The SCORPIO-2 spectrum along reveals that the brightest and nearest candidate to a possible companion—the galaxy SDSS J1302 + 1625 (‘the satellite’)—has a systemic velocity 20,038 that deviates only on from the velocity of Mrk 783 nucleus according to our estimations along (20,100 , it is a mean value in the H, [N ii] and [O iii] lines) or on if we accepted the velocity of the Mrk 783 nucleus according to SDSS data in NED. This small velocity difference implies that Mrk 783 and SDSS J130257.20+162537.1 is a gravitationally bound pair. The slit also crossed a smaller galaxy in 20 from the satellite—J130256.50+162521.8, its spectrum corresponds to a distant galaxy redshifted at . It is marked in Figure 2 as a ‘background galaxy’. We also found no other Mrk 783 companions by looking at the list of spectral and photometric redshifts for all NED objects up to a projected distance of 500 kpc ().
Can the satellite SDSS J1302 + 1625 create the observed peculiar morphology of Mrk 783? The most prominent tidal tail expands in E and NE directions up to a projected distance of (35 kpc) from the Mrk 783 center. Both the DESI Legacy Survey and deep BAO images (Figure 2) demonstrate an absence of any faint tidal structures between the main galaxy and the satellite at least up to a surface brightness in the r-band (Section 2). The comparison of SDSS DR18 red magnitudes of Mrk 783 (, ) with those for the satellite (, ) gives the ratio in their luminosity and hence a stellar mass of –. This low ratio corresponds to the case of minor merging without significant perturbation of the main galaxy. Moreover, in contrast with the main galaxy, the satellite seems unperturbed in both morphology and internal kinematics: it has a symmetrical rotation curve of the ionized gas (Figure 5). All the facts listed above, together with a possible sign of the secondary nucleus [6], suggest that the observed peculiar morphology of Mrk 783 was caused by a previous external event (merging with a companion) rather than by the low-massive satellite ∼100 kpc away.
The ionized gas properties of the satellite are intriguing. As we already mentioned in Section 3, its nuclear spectrum corresponds to a starburst galaxy. The emission line ratios correspond to the border between AGN and HII regions in BPT diagrams (open black star in Figure 6, bottom panels). However, the excitation of the [O iii] emission to the galaxy outskirts increases dramatically—the ratio [O iii]/H reaches , which is similar to the Mrk 783 EELR (Figure 5, bottom). The corresponding points on the BPT-diagrams move upward in the AGN area, in the region occupied by Mrk 785 EELR (the filled black star in Figure 6, bottom). This fact implies that the outer part of the satellite disk is also ionized by the Mrk 783 AGN.
The second argument in favour of the external origin of the gas ionization in the satellite disk comes from the [O iii] emission distribution according to the MaNGaL data (Figure 2). It is clearly seen that the highly ionized gas in the satellite is placed asymmetrically relative to its nucleus—we observed it mostly on the side nearest to the Mrk 783.
We tried to estimate the electron density from the density-sensitive [S ii] doublet flux ratio [S ii][S ii]) using the diagnostic equations from [18] for K. The values of R derived from the integrated spectra of W-knot, SE-knot, and the outer part of SDSS J1302 + 1625 (in the range –) are , and that corresponds to , and with the level. Preliminary, we can conclude that the ionized gas density is significantly higher in the SDSS J1302 + 1625 disk than in Mrk 783 EELR, but the uncertainty in estimation is too great for a more detailed analysis. New deeper spatially-resolved spectroscopic data are needed to better understand the ionization properties of the SDSS J1302 + 1625 outskirts.
5. The Energetic Budget
External EELRs are considered a good probe with which to study the history of AGN radiative output on the time scale – yr (it corresponds to light-travel time to the gaseous clouds). The well-known prototype is Hanny’s Voorwerp, a cloud of highly ionized gas near the spiral galaxy IC 2497. The detailed comparison of the ionized gas properties and AGN luminosity clearly demonstrates that the radiation associated with a nuclear activity significantly fall at least two orders in the last yr [19,20,21]. New examples of ‘fading’ AGNs were discovered in follow-up spectroscopic observations of EELR candidates found in SDSS broad-band images by volunteers of the Galaxy Zoo citizen-science project [22,23], as well as in the data collected in surveys based on narrow-band [O iii] imaging [24] or integral-field spectroscopy [25]. The ionized gas clouds around Mrk 783 including the disk of the companion galaxy allows as to use the same technique for estimation of its ionization budget.
We calculated the ionizing luminosity () required to creation the distant emission knots with the current bolometric luminosity of AGN () using the approach proposed in the paper cited above and briefly described below. The upper limit of the AGN flux absorbed by dust was estimated as a sum of fluxes in the far infrared (FIR, the wavelength range 42–122) according the Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) point-source catalogue data [26] and mid-infrared (MIR, the wavelength range 3.4–42) data from the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, [27]). We evaluated the IRAS luminosity () using a standard linear combination of the flux in the 60 and 100 bands in a similar way as described in Keel et al. [22]. For the WISE luminosity (), we used a low-power approximation of the flux values obtained from the NED in the four bands 3.4, 4.6, 11.6, and 22.08 in the same manner as by Keel et al. [23]. For the unobscured AGN luminosity, we used an empirical equation from [24]: , where is a nuclear luminosity in the [O iii] emission line based on the nuclear flux derived from a 2D Moffat fitting of the MaNGaL image. In this case:
The lower limit of the nuclear source luminosity required for the ionization of the gas region with the H flux F(H) and occupying an angle was estimated according to the equation proposed in [22]:
where z is a galaxy redshift and is a projection of a solid angle under which the considered region is viewed from the nucleus. Here, r is a projected distance from the nucleus, whereas W is a radius of this region.
The quantities related to the energy balance based on Equations (1) and (2) are listed in Table 2. For the SE-knot, we integrated the H flux from the SCORPIO-2 spectra along in the range –, is half of the slit width. Equation (1) is written for the slit oriented radially to the AGN, which is true for . But it is not valid for the slit orientation , passing through the satellite. To account for this, we used the same technique as described by Keel et al. [24] for the similar observations of the external gas cloud near NGC 5514, i.e., we multiply the square of the emission edge of the satellite disk according [O iii] MaNGaL map (Figure 2, left) on the mean surface brightness of the external part of the disk at from the satellite nucleus according to spectra along . In this case, (the radius of the emission region) and (the distance from the AGN).

Table 2.
The energy balance between observed AGN output and required photoionization to power the emission clouds.
The ratio could be considered an indicator of a long-term fading of AGN radiation or a difference of dust obscuration of this radiation between the direction to an observer and to EELR. Usually, a fading AGN has [22,24]. However, in the Mrk 783 this value is significantly smaller: in the SE-knot and even 0.12 in the outer disk of the companion galaxy. Of course, the real value could be higher, because the Equation (1) gives an upper bound of the active nucleus infrared luminosity and includes a fraction related with a dust heated by a star formation in the galaxy, whereas Equation (2) gives a low bound of the ionizing flux absorbed by the clouds, because it depends on spatial resolution and optical thickness in the Lyman continuum (see the discussion in [21]). A real spatial geometry of the system is unknown. Nevertheless, we have no arguments in favour of significant fall in AGN radiation in the last 0.1–0.3 Myr, which corresponds to a projection of travel-light time from the Mrk 783 nucleus to the SE-knot and to the disk of SDSS J1302 + 1625.
6. Discussion
It is generally accepted that large-scale EELRs around AGN can be formed in two main ways: via nuclear outflow driven by the kinetic power of a radio jet and/or superwind in radio-loud AGN [28,29] or as a result of the ionization of the pre-existing gas surrounding radio-quiet Seyfert galaxies [22,24]. The combination of both cases is also possible, including relic structures from the previous activity episodes [30]. The radio-to-optical luminosity ratio puts the Mrk 783 between radio-quiet and radio-loud AGN; the galaxy contains both an inner jet and an extended diffuse radio structure [5]. What is the origin of this EELR?
Our spectroscopic data clearly manifest that the possible sign of jet outflow in the ionized gas kinematics appears only in the circumnuclear region ( kpc, Section 3), whereas the more external gas exhibits properties similar to those of the external off-plane gas and tidal debris ionized by AGN in other galaxies ([21,24], and references therein):
- The flux ratio of the most indicative emission lines (BPT-diagrams, high He ii/H) corresponds to the ionization by UV-continuum of AGN rather than by shocks related to jet or outflow.
- The quiet kinematics of gas clouds (rotation on circular orbits, relatively low velocity dispersion) also indicates tidal-induced motions or an external gas accretion.
In their paper based on Magellan spectroscopy Congiu et al. [7] assumed that the ionized gas excitation in the Mrk 783 EELR is related to the extended radio structure. However, the comparison of their synchrotron radio isocontours with the MaNGaL [O iii] image manifests that only SE and E knots are more or less aligned with a direction of central radio structure, wheres the W-knot and the surrounding gas do not coincide with the radio contours (Figure 7). On the other hand, the gas excitation and kinematics are similar in all considered structures, which implies a common source of its ionization. In Figure 7, we draw a location of possible bi-symmetric ionization cones with axes aligned to according to a large-scale jet orientation [5]. Most of the EELR structure lies inside the cones if we accept the projected value of the cone’s open angle . This value is in agreement with the mean value of for other ionization cones [31] if the projection effect is taken into account.
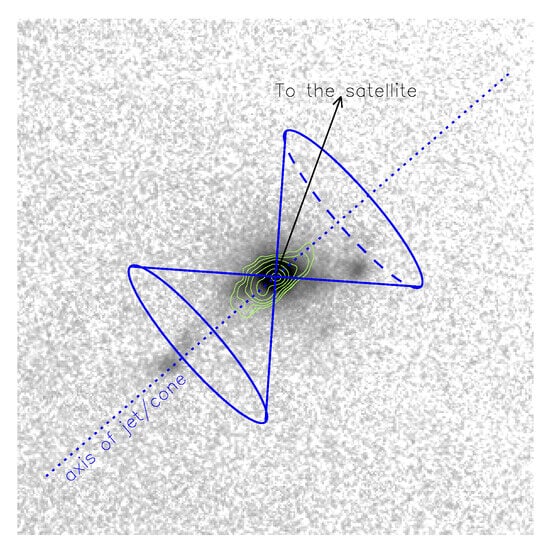
Figure 7.
The [O iii] emission line image with contours of radio continuum at 5 GHz according to Congiu et al. [5]. Proposed orientation of the ionization cone is shown.
The proposed orientation of the AGN cones allows us to explain the ionization of the external parts of the gaseous disk in the satellite galaxy (see the arrow in Figure 7). A minimum of half of its disk, which is close to the Mrk 783, is also ionized by the AGN. The effect of cross-ionization by the companion’s AGN has already been found in several galactic pairs; however, the characteristic separation was about 15–20 kpc [31,32,33]. In the case of the Mrk 783 system, the projected distance between the companion’s nuclei is about 100 kpc, which is perhaps the largest known today.
In Section 4, we presented arguments that the disturbed morphology of Mrk 783 and its tidal structures is not related to a distant companion galaxy. It is most likely that we are observing the result of merging with a gas-rich dwarf galaxy. In this case, most of the external gas in EELR came from a tidal-destroyed low-metallicity companion (– according to the low [N ii]/H ratio, Section 3). The stellar tidal structure is aligned with the gaseous one on the west from the galaxy, but the NE emission tail has no stellar counterpart. This stellar-gaseous spatial misalignment is also observed in some AGN interacting galaxies in which EELRs that are not spatial coincide with stellar tidal structures (for instance, NGC 5278/9 [31] or a spectacular local example—NGC 5194/95 [34]). It is not surprising, because in [O iii] we have detected only a highly-ionized fraction of a whole gaseous structure, whereas a distribution of cold H i can be revealed only by radio observations.
It is interesting to note that many properties of Mrk 783 are similar to those observed in IC 2497 with Hanny’s Voorwerp nebula (Section 5): both are post-interacting disk galaxies having detached AGN-ionized EELR at the spatial scale of tens of kpc and a relic structure traces the previous phase of radio jet activity. This means that we possibly caught both galaxies after the switching between different types of activity [30,35]: radio-loud (i.e., kinetic) mode and radio-quiet (i.e., radiation) mode. However, in IC 2497, the radio outburst occurred 100 Myr ago [36], whereas a significant shortfall of AGN ionizing radiation traced in Hanny’s Voorwerp nebula is dated as ∼–0.2 Myr ago [19,21]. In Mrk 783, the age of the relic radio structure was not evaluated, whereas our calculations of the energetic budget (Section 5) presented no evidence for a significant decrease of AGN radiation in the last 0.1–0.3 Myr. Comparing these time scales, we can speculate that the Mrk 783 AGN ionizing radiation will be turned off in the near future. In other words, it can be considered ‘Hanny’s Voorwerp precursor’. However, a more in-depth study of the ionization balance in the disk of the Mrk783 companion is needed to prove this conclusion, because in the present work we operated only with the integrated spectrum of the SDSS J1302+1625 outskirts having a low surface brightness. Now we have performed only the first attempt to estimation of in the EELR and the satellite disk, whereas the spatial resolution is crucial for using Equation (2), see Keel et al. [22,23]. Moreover, Congiu et al. [6] found in Mrk 783 an inner pc-scale radio jet that is significantly misaligned with a kpc-scale structure. For the explanation, they proposed two scenarios: a jet precession or reactivation after a period of inactivity. In this case, the composition of recent activity episodes in Mrk 783 may be even more complex.
7. Conclusions
Based on new optical spectral and imaging observations, we have studied the distribution, kinematics, and excitation of the ionized gas in the giant EELR of the Mrk 783 galaxy as well as the properties of its environment. The deepest spectra of this area to date allow us to consider the gas ionization conditions up to 41 kpc from the galactic nucleus. Moreover, its ionization trace was found in the disk of the satellite galaxy. The main results are as follows:
- Mrk 783 forms a gravitationally bound pair with SDSS J130257.20+162537.1 (the projected distance between their nucleus is kpc). However, the disturbed morphology and tidal structures are most likely caused by merging with another pre-existing companion—a gas-rich dwarf galaxy.
- Most of the gaseous structures detected in the emission lines are ionized by the AGN radiation but not by the radio jet.
- Part of the gas illuminated by the cone belongs to the stellar tidal structure, but the most distant SE-knot is a part of the external gaseous structure without a stellar counterpart. Gas in this region has a low metallicity (– according to the low [N ii]/H ratio).
- External regions of the satellite gaseous disk at the nearest side to Mrk 783 fall into the ionizing cone from the main galaxy’s active nucleus. This fact makes the Mrk 783 system perhaps the most extreme example among nearby AGN galaxies of the cross-ionization of a galactic disk by a companion.
- A comparison of the ionizing luminosity required to create the most distant emission knots (including the satellite’s disk) with the current bolometric luminosity of the nucleus indicates that there has been no significant decreasing ionizing radiation during the last 0.1–0.3 Myr.
- Mrk 783 can be considered a ‘Hanny’s Voorwerp precursor’, i.e., a galaxy that demonstrates signs of sequential switching from kinematics (radio-dominated) to radiation (ionization-dominated) AGN modes, in the moment before its ionization luminosity falls.
We hope that new multi-wavelength observations, first of all H i mapping in a radio domain and deep optical integral-field mapping of the both galaxies in the pair, will allow us to better understand the spatial structure and evolution of this galactic system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.V.M. and A.A.S.; methodology, A.V.M.; formal analysis, A.V.M., A.A.S. and T.A.M.; investigation, A.V.M. and A.A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.V.M.; writing—review and editing, A.V.M., A.A.S. and T.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was performed as part of the SAO RAS government contract approved by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in this study are openly available in the General observation data archive of SAO RAS: https://www.sao.ru/oasis/fetch.html (accessed on 1 April 2023). The reduced data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We obtained the observed data on the unique scientific facility “Big Telescope Alt-azimuthal” of SAO RAS. The renovation of telescope equipment is currently provided within the national project “Science and Universities”. We thank Roman Uklein and Dmitry Oparin who performed observations at the 2.5m and 6m telescopes. Some of the data presented in this paper were obtained from the Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes (MAST). This research has made use of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED), which is funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and operated by the California Institute of Technology. The work used the public data of the Legacy Surveys accessed on 1 April 2023 (http://legacysurvey.org), that consists of three individual and complementary projects: the Dark Energy Camera Legacy Survey (DECaLS; Proposal ID -0404; PIs: David Schlegel and Arjun Dey), the Beijing-Arizona Sky Survey (BASS; NOAO Prop. ID -0801; PIs: Zhou Xu and Xiaohui Fan), and the Mayall z-band Legacy Survey (MzLS; Prop. ID -0453; PI: Arjun Dey). DECaLS, BASS and MzLS together include data obtained, respectively, at the Blanco telescope, Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, NSF’s NOIRLab; the Bok telescope, Steward Observatory, University of Arizona; and the Mayall telescope, Kitt Peak National Observatory, NOIRLab. The Legacy Surveys project is honored to be permitted to conduct astronomical research on Iolkam Duág (Kitt Peak), a mountain with particular significance to the Tohono Oódham Nation. This project used data obtained with the Dark Energy Camera (DECam), which was constructed by the Dark Energy Survey (DES) collaboration. Funding for the DES Projects has been provided by the U.S. Department of Energy, the U.S. National Science Foundation, the Ministry of Science and Education of Spain, the Science and Technology Facilities Council of the United Kingdom, the Higher Education Funding Council for England, the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, the Kavli Institute of Cosmological Physics at the University of Chicago, Center for Cosmology and Astro-Particle Physics at the Ohio State University, the Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics and Astronomy at Texas A&M University, Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos, Fundacao Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo, Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos, Fundacao Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnologico and the Ministerio da Ciencia, Tecnologia e Inovacao, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Collaborating Institutions in the Dark Energy Survey. The Collaborating Institutions are Argonne National Laboratory, the University of California at Santa Cruz, the University of Cambridge, Centro de Investigaciones Energeticas, Medioambientales y Tecnologicas-Madrid, the University of Chicago, University College London, the DES-Brazil Consortium, the University of Edinburgh, the Eidgenossische Technische Hochschule (ETH) Zurich, Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, the Institut de Ciencies de l’Espai (IEEC/CSIC), the Institut de Fisica de Altes Energies, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, the Ludwig Maximilians Universitat Munchen and the associated Excellence Cluster Universe, the University of Michigan, NSF’s NOIRLab, the University of Nottingham, the Ohio State University, the University of Pennsylvania, the University of Portsmouth, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University, the University of Sussex, and Texas A&M University. BASS is a key project of the Telescope Access Program (TAP), which has been funded by the National Astronomical Observatories of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (the Strategic Priority Research Program ‘The Emergence of Cosmological Structures’ Grant #XDB09000000), and the Special Fund for Astronomy from the Ministry of Finance. The BASS is also supported by the External Cooperation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant # 114A11KYSB20160057), and Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (Grant # 11433005). The Legacy Survey team makes use of data products from the Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE), which is a project of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology. NEOWISE is funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. The Legacy Surveys imaging of the DESI footprint is supported by the Director, Office of Science, Office of High Energy Physics of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH1123; by the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, a DOE Office of Science User Facility under the same contract; and by the U.S. National Science Foundation, Division of Astronomical Sciences under Contract No. AST-0950945 to NOAO.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AGN | Active galaxy nucleus |
| EELR | Extended emission-line region |
| FWHM | Full width at half-maximum |
| LINER | Low-ionization nuclear emission-line region |
| SAO RAS | Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Sciences |
Notes
| 1 | http://ned.ipac.caltech.edu/, accessed on 20 November 2023 |
| 2 | |
| 3 | The galaxy Mrk 783 was discovered with this telescope in 1976 [1] |
| 4 | |
| 5 | https://dr18.sdss.org/optical/spectrum/view?plateid=2603&mjd=54479&fiberid=259, accessed on 20 November 2023 |
References
- Markarian, B.E.; Lipovetskii, V.A. Galaxies with ultraviolet continuum. VIII. Astrofizika 1976, 12, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterbrock, D.E.; Pogge, R.W. The spectra of narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1985, 297, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S. Narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies and the evolution of galaxies and active galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 314, L17–L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton, M.; Foschini, L.; Ciroi, S.; Cracco, V.; La Mura, G.; Lister, M.L.; Mathur, S.; Peterson, B.M.; Richards, J.L.; Rafanelli, P. Parent population of flat-spectrum radio-loud narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 578, A28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congiu, E.; Berton, M.; Giroletti, M.; Antonucci, R.; Caccianiga, A.; Kharb, P.; Lister, M.L.; Foschini, L.; Ciroi, S.; Cracco, V.; et al. Kiloparsec-scale emission in the narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxy Mrk 783. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congiu, E.; Kharb, P.; Tarchi, A.; Berton, M.; Caccianiga, A.; Chen, S.; Crepaldi, L.; Di Mille, F.; Järvelä, E.; Jarvis, M.; et al. The radio structure of the narrow-line Seyfert 1 Mrk 783 with VLBA and e-MERLIN. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 3149–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congiu, E.; Contini, M.; Ciroi, S.; Cracco, V.; Di Mille, F.; Berton, M.; Frezzato, M.; La Mura, G.; Rafanelli, P. Extended Narrow-Line Region in Seyfert Galaxies. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2017, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatsky, N.; Belinski, A.; Dodin, A.; Zheltoukhov, S.; Kornilov, V.; Postnov, K.; Potanin, S.; Safonov, B.; Tatarnikov, A.; Cherepashchuk, A. The Caucasian Mountain Observatory of the Sternberg Astronomical Institute: First Six Years of Operation. In Proceedings of the Ground-Based Astronomy in Russia. 21st Century, Nizhny Arkhyz, Russia, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseev, A.; Perepelitsyn, A.; Oparin, D. Mapper of Narrow Galaxy Lines (MaNGaL): New tunable filter imager for Caucasian telescopes. Exp. Astron. 2020, 50, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, D.; Hogg, D.W.; Mierle, K.; Blanton, M.; Roweis, S. Astrometry.net: Blind Astrometric Calibration of Arbitrary Astronomical Images. Astron. J. 2010, 139, 1782–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Schlegel, D.J.; Lang, D.; Blum, R.; Burleigh, K.; Fan, X.; Findlay, J.R.; Finkbeiner, D.; Herrera, D.; Juneau, S.; et al. Overview of the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys. Astron. J. 2019, 157, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodonov, S.N.; Kotov, S.S.; Movsesyan, T.A.; Gevorkyan, M. One-meter Schmidt telescope of the Byurakan Astrophysical Observatory: New capabilities. Astrophys. Bull. 2017, 72, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasiev, V.L.; Moiseev, A.V. Scorpio on the 6m Telescope: Current State and Perspectives for Spectroscopy of Galactic and Extragalactic Objects. Balt. Astron. 2011, 20, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, J.A.; Phillips, M.M.; Terlevich, R. Classification parameters for the emission-line spectra of extragalactic objects. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1981, 93, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewley, L.J.; Dopita, M.A.; Sutherland, R.S.; Heisler, C.A.; Trevena, J. Theoretical Modeling of Starburst Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2001, 556, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann, G.; Heckman, T.M.; Tremonti, C.; Brinchmann, J.; Charlot, S.; White, S.D.M.; Ridgway, S.E.; Brinkmann, J.; Fukugita, M.; Hall, P.B.; et al. The host galaxies of active galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 346, 1055–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennert, N.; Jungwiert, B.; Komossa, S.; Haas, M.; Chini, R. Size and properties of the NLR in the Seyfert-2 galaxy NGC 1386. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 446, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proxauf, B.; Öttl, S.; Kimeswenger, S. Upgrading electron temperature and electron density diagnostic diagrams of forbidden line emission. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 561, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintott, C.J.; Schawinski, K.; Keel, W.; van Arkel, H.; Bennert, N.; Edmondson, E.; Thomas, D.; Smith, D.J.B.; Herbert, P.D.; Jarvis, M.J.; et al. Galaxy Zoo: ‘Hanny’s Voorwerp’, a quasar light echo? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 399, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schawinski, K.; Evans, D.A.; Virani, S.; Urry, C.M.; Keel, W.C.; Natarajan, P.; Lintott, C.J.; Manning, A.; Coppi, P.; Kaviraj, S.; et al. The Sudden Death of the Nearest Quasar. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 724, L30–L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, W.C.; Lintott, C.J.; Schawinski, K.; Bennert, V.N.; Thomas, D.; Manning, A.; Chojnowski, S.D.; van Arkel, H.; Lynn, S. The History and Environment of a Faded Quasar: Hubble Space Telescope Observations of Hanny’s Voorwerp and IC 2497. Astron. J. 2012, 144, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, W.C.; Chojnowski, S.D.; Bennert, V.N.; Schawinski, K.; Lintott, C.J.; Lynn, S.; Pancoast, A.; Harris, C.; Nierenberg, A.M.; Sonnenfeld, A.; et al. The Galaxy Zoo survey for giant AGN-ionized clouds: Past and present black hole accretion events. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 878–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, W.C.; Lintott, C.J.; Maksym, W.P.; Bennert, V.N.; Chojnowski, S.D.; Moiseev, A.; Smirnova, A.; Schawinski, K.; Sartori, L.F.; Urry, C.M.; et al. Fading AGN Candidates: AGN Histories and Outflow Signatures. Astrophys. J. 2017, 835, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, W.C.; Moiseev, A.; Kozlova, D.V.; Ikhsanova, A.I.; Oparin, D.V.; Uklein, R.I.; Smirnova, A.A.; Eselevich, M.V. The TELPERION survey for distant [O III] clouds around luminous and hibernating AGN. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 510, 4608–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K.D.; Earl, N.; Novack, A.B.; Pardasani, B.; Pillai, V.R.; Tripathi, A.; Verrico, M.E. Fading AGNs in Poststarburst Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2023, 950, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullmer, L.; Londsdale, C.J. Cataloged Galaxies and Quasars Observed in the IRAS Survey; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, E.L.; Eisenhardt, P.R.M.; Mainzer, A.K.; Ressler, M.E.; Cutri, R.M.; Jarrett, T.; Kirkpatrick, J.D.; Padgett, D.; McMillan, R.S.; Skrutskie, M.; et al. The Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE): Mission Description and Initial On-orbit Performance. Astron. J. 2010, 140, 1868–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.M.; Alexander, D.M.; Mullaney, J.R.; Swinbank, A.M. Kiloparsec-scale outflows are prevalent among luminous AGN: Outflows and feedback in the context of the overall AGN population. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 441, 3306–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupke, D.S.N.; Veilleux, S. Integral Field Spectroscopy of Massive, Kiloparsec-scale Outflows in the Infrared-luminous QSO Mrk 231. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 729, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, R. Archaeology of active galaxies across the electromagnetic spectrum. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, W.C.; Bennert, V.N.; Pancoast, A.; Harris, C.E.; Nierenberg, A.; Chojnowski, S.D.; Moiseev, A.V.; Oparin, D.V.; Lintott, C.J.; Schawinski, K.; et al. AGN photoionization of gas in companion galaxies as a probe of AGN radiation in time and direction. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 4847–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, E.C.; Halpern, J.P.; Bothun, G.D.; Becker, R.H. WAS 49: Mirror for a Hidden Seyfert 1 Nucleus. Astron. J. 1992, 104, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merluzzi, P.; Busarello, G.; Dopita, M.A.; Thomas, A.D.; Haines, C.P.; Grado, A.; Limatola, L.; Mercurio, A. An Interacting Galaxy Pair at the Origin of a Light Echo. Astrophys. J. 2018, 852, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A.E.; Mihos, J.C.; Bershady, M.; Harding, P. Discovery of a Vast Ionized Gas Cloud in the M51 System. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 858, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, A.C. Observational Evidence of Active Galactic Nuclei Feedback. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 50, 455–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.J.B.; Krause, M.G.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Drake, A.B. Relic jet activity in ’Hanny’s Voorwerp’ revealed by the LOFAR two metre sky survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 514, 3879–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).