Neutron Star Binary Mergers: The Legacy of GW170817 and Future Prospects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Long Quest for the Short GRB Progenitor
- No core-collapse supernova is typically found to be associated with short GRBs, even for the most nearby ones: this strongly disfavours any origin linked to the gravitational collapse of massive stars.
- The position of short GRBs within the host galaxy typically tracks the outermost regions rather than central, bright, star-forming ones. Such a spatial distribution is more consistent with an old stellar population that had enough time to migrate far from its formation region, rather than with a young, short-lived one [42].
- A further clue in favour of an older progenitor is based on the mixed type of short GRB host galaxies, with about half of them being elliptical and the other half being forming galaxies, depending on the merger time delay [43].
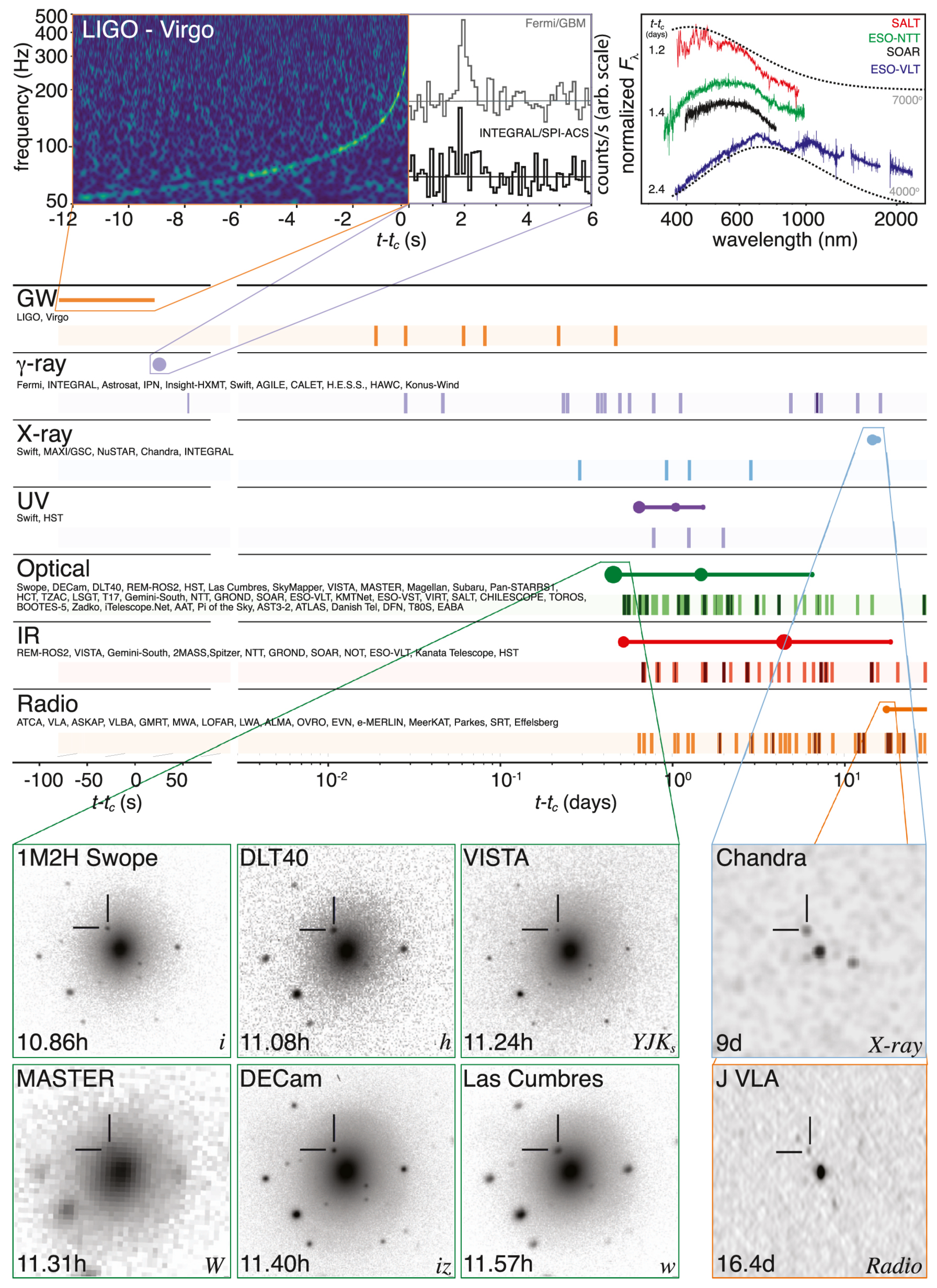
- Finally, in some short GRBs, a rising thermal optical/near-infrared emission was detected and identified with kilonova emission.
3. GW170817/GRB 170817A: Observations and Implications
3.1. The Gravitational-Wave Signal
3.2. The Electromagnetic Signal
3.3. Implications of Multi-Messenger Data Analysis Results
3.3.1. Propagation Speed of Gravitational Waves
3.3.2. Short GRB Jet Structure
3.3.3. Cosmology
3.3.4. Heavy Element Formation
4. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | This is given by , where and are the NS rotational angular momentum and mass, respectively, and c and G are the speed of light and the gravitational constant, respectively. |
| 2 | https://observing.docs.ligo.org/plan/ (accessed date 15 June 2022). |
References
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] Advanced LIGO. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 074001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acernese, F.; Agathos, M.; Agatsuma, K.; Aisa, D.; Allemandou, N.; Allocca, A.; Amarni, J.; Astone, P.; Balestri, G.; Ballardin, G.; et al. Advanced Virgo: A second-generation interferometric gravitational wave detector. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GWTC-1: A Gravitational-Wave Transient Catalog of Compact Binary Mergers Observed by LIGO and Virgo during the First and Second Observing Runs. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 031040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] Gravitational Waves and Gamma-rays from a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Veres, P.; Burns, E.; Briggs, M.S.; Hamburg, R.; Kocevski, D.; Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Preece, R.D.; Poolakkil, S.; Roberts, O.J.; et al. An Ordinary Short Gamma-Ray Burst with Extraordinary Implications: Fermi-GBM Detection of GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, V.; Ferrigno, C.; Kuulkers, E.; Bazzano, A.N.G.E.L.A.; Bozzo, E.; Brandt, S.; Chenevez, J.; Courvoisier, T.L.; Diehl, R.; Domingo, A.; et al. INTEGRAL Detection of the First Prompt Gamma-Ray Signal Coincident with the Gravitational-wave Event GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, V.A.; Guillochon, J.; Berger, E.; Metzger, B.D.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Nicholl, M.; Alexander, K.D.; Blanchard, P.K.; Chornock, R.; Eftekhari, T.; et al. The Combined Ultraviolet, Optical, and Near-infrared Light Curves of the Kilonova Associated with the Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817: Unified Data Set, Analytic Models, and Physical Implications. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 851, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pian, E.; D’Avanzo, P.; Benetti, S.; Branchesi, M.; Brocato, E.; Campana, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Covino, S.; D’Elia, V.; Fynbo, J.P.U.; et al. Spectroscopic identification of r-process nucleosynthesis in a double neutron-star merger. Nature 2017, 551, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smartt, S.J.; Chen, T.W.; Jerkstrand, A.; Coughlin, M.; Kankare, E.; Sim, S.A.; Fraser, M.; Inserra, C.; Maguire, K.; Chambers, K.C.; et al. A kilonova as the electromagnetic counterpart to a gravitational-wave source. Nature 2017, 551, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattimer, J.M.; Schramm, D.N. Black-Hole-Neutron-Star Collisions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1974, 192, L145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, D.; Livio, M.; Piran, T.; Schramm, D.N. Nucleosynthesis, neutrino bursts and γ-rays from coalescing neutron stars. Nature 1989, 340, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GWTC-2: Compact Binary Coalescences Observed by LIGO and Virgo During the First Half of the Third Observing Run. Phys. Rev. X 2021, 11, 021053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GWTC-2.1: Deep Extended Catalog of Compact Binary Coalescences Observed by LIGO and Virgo During the First Half of the Third Observing Run. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.01045. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GWTC-3: Compact Binary Coalescences Observed by LIGO and Virgo During the Second Part of the Third Observing Run. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03606. [Google Scholar]
- Akutsu, T.; Ando, M.; Arai, K.; Arai, Y.; Araki, S.; Araya, A.; Aritomi, N.; Aso, Y.; Bae, S.; Bae, Y.; et al. Overview of KAGRA: Detector design and construction history. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2021, 2021, 05A101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitz, A.H.; Nielsen, A.B.; Capano, C.D. Potential Gravitational-wave and Gamma-ray Multi-messenger Candidate from 2015 October 30. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 876, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackay, B.; Venumadhav, T.; Dai, L.; Roulet, J.; Zaldarriaga, M. Highly spinning and aligned binary black hole merger in the Advanced LIGO first observing run. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 023007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venumadhav, T.; Zackay, B.; Roulet, J.; Dai, L.; Zaldarriaga, M. New binary black hole mergers in the second observing run of Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 083030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitz, A.H.; Dent, T.; Davies, G.S.; Kumar, S.; Capano, C.D.; Harry, I.; Mozzon, S.; Nuttall, L.; Lundgren, A.; Tápai, M. 2-OGC: Open Gravitational-wave Catalog of binary mergers from analysis of public Advanced LIGO and Virgo data. Astrophys. J. 2020, 891, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackay, B.; Dai, L.; Venumadhav, T.; Roulet, J.; Zaldarriaga, M. Detecting gravitational waves with disparate detector responses: Two new binary black hole mergers. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 063030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitz, A.H.; Dent, T.; Davies, G.S.; Harry, I. A Search for Gravitational Waves from Binary Mergers with a Single Observatory. Astrophys. J. 2020, 897, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitz, A.H.; Capano, C.D.; Kumar, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Kastha, S.; Schäfer, M.; Dhurkunde, R.; Cabero, M. 3-OGC: Catalog of Gravitational Waves from Compact-binary Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2021, 922, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, S.; Oganesyan, G.; Branchesi, M.; Ciolfi, R. Electromagnetic counterparts of compact binary mergers. J. Plasma Phys. 2021, 87, 845870102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GW190425: Observation of a Compact Binary Coalescence with Total Mass ∼3.4M⊙. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 892, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] Observation of Gravitational Waves from Two Neutron Star–Black Hole Coalescences. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 915, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GW190814: Gravitational Waves from the Coalescence of a 23 Solar Mass Black Hole with a 2.6 Solar Mass Compact Object. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 896, L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley, K.; Amati, L.; Barbieri, C.; Bauer, F.E.; Benetti, S.; Bernardini, M.G.; Bhirombhakdi, K.; Botticella, M.T.; Branchesi, M.; Brocato, E.; et al. Observational constraints on the optical and near-infrared emission from the neutron star-black hole binary merger candidate S190814bv. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 643, A113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.L.; Dichiara, S.; Troja, E.; Chase, E.A.; Sánchez-Ramírez, R.; Piro, L.; Fryer, C.L.; Butler, N.R.; Watson, A.M.; Wollaeger, R.T.; et al. A search for optical and near-infrared counterparts of the compact binary merger GW190814. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 3868–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. The Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts; University of Nevada, Las Vegas: Reno, NV, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burns, E. Neutron star mergers and how to study them. Living Rev. Relativ. 2020, 23, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebesadel, R.W.; Strong, I.B.; Olson, R.A. Observations of Gamma-Ray Bursts of Cosmic Origin. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1973, 182, L85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouveliotou, C.; Meegan, C.A.; Fishman, G.J.; Bhat, N.P.; Briggs, M.S.; Koshut, T.M.; Paciesas, W.S.; Pendleton, G.N. Identification of Two Classes of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1993, 413, L101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaev, P.Y.; Pozanenko, A.S. The Ep,I-Eiso correlation: Type I gamma-ray bursts and the new classification method. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 1919–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boella, G.; Butler, R.C.; Perola, G.C.; Piro, L.; Scarsi, L.; Bleeker, J.A.M. BeppoSAX, the wide band mission for X-ray astronomy. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1997, 122, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrels, N.; Swift Team. The Swift γ-ray burst mission. New Astron. Rev. 2004, 48, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galama, T.J.; Vreeswijk, P.M.; van Paradijs, J.; Kouveliotou, C.; Augusteijn, T.; Böhnhardt, H.; Brewer, J.P.; Doublier, V.; Gonzalez, J.F.; Leibundgut, B.; et al. An unusual supernova in the error box of the γ-ray burst of 25 April 1998. Nature 1998, 395, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, J.; Sollerman, J.; Møller, P.; Fynbo, J.P.U.; Woosley, S.E.; Kouveliotou, C.; Tanvir, N.R.; Greiner, J.; Andersen, M.I.; Castro-Tirado, A.J.; et al. A very energetic supernova associated with the γ-ray burst of 29 March 2003. Nature 2003, 423, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E. Short-Duration Gamma-Ray Bursts. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 43–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.; Berger, E. The Locations of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts as Evidence for Compact Object Binary Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2013, 776, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, W.; Berger, E.; Chornock, R.; Margutti, R.; Levan, A.J.; Tanvir, N.R.; Tunnicliffe, R.L.; Czekala, I.; Fox, D.B.; Perley, D.A.; et al. Demographics of the Galaxies Hosting Short-duration Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2013, 769, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannarale, F.; Ohme, F. Prospects for Joint Gravitational-wave and Electromagnetic Observations of Neutron-star-Black-hole Coalescing Binaries. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 791, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastinejad, J.C.; Gompertz, B.P.; Levan, A.J.; Fong, W.; Nicholl, M.; Lamb, G.P.; Malesani, D.B.; Nugent, A.E.; Oates, S.R.; Tanvir, N.R.; et al. A Kilonova Following a Long-Duration Gamma-Ray Burst at 350 Mpc. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.10864. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, A.; Rothberg, B.; Palazzi, E.; Kann, D.A.; D’Avanzo, P.; Amati, L.; Klose, S.; Perego, A.; Pian, E.; Guidorzi, C.; et al. The Peculiar Short-duration GRB 200826A and Its Supernova. Astrophys. J. 2022, 932, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] Properties of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Zhang, B.; Sun, H.; Lei, W.H.; Gao, H.; Li, Y.; Shao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.D.; Lü, H.J.; et al. A peculiar low-luminosity short gamma-ray burst from a double neutron star merger progenitor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, G.; Burns, E.; Canton, T.D.; Dent, T.; Eggenstein, H.B.; Nielsen, A.B.; Prix, R.; Was, M.; Zhu, S.J. Coincident detection significance in multimessenger astronomy. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, D.A.; Foley, R.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Simon, J.D.; Ulloa, N.; Kasen, D.; et al. Swope Supernova Survey 2017a (SSS17a), the optical counterpart to a gravitational wave source. Science 2017, 358, 1556–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troja, E.; Piro, L.; van Eerten, H.; Wollaeger, R.T.; Im, M.; Fox, O.D.; Butler, N.R.; Cenko, S.B.; Sakamoto, T.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. The X-ray counterpart to the gravitational-wave event GW170817. Nature 2017, 551, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, B.; Troja, E. Continued Chandra monitoring of GW170817 at 4.8 yr post-merger. GRB Coord. Netw. 2022, 32065, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, R.; O’Connor, B.; Troja, E. VLA observations of GW170817 at 4.8 years after the merger. GRB Coord. Netw. 2022, 32094, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mooley, K.P.; Nakar, E.; Hotokezaka, K.; Hallinan, G.; Corsi, A.; Frail, D.A.; Horesh, A.; Murphy, T.; Lenc, E.; Kaplan, D.L.; et al. A mildly relativistic wide-angle outflow in the neutron-star merger event GW170817. Nature 2018, 554, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooley, K.P.; Deller, A.T.; Gottlieb, O.; Nakar, E.; Hallinan, G.; Bourke, S.; Frail, D.A.; Horesh, A.; Corsi, A.; Hotokezaka, K. Superluminal motion of a relativistic jet in the neutron-star merger GW170817. Nature 2018, 561, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghirlanda, G.; Salafia, O.S.; Paragi, Z.; Giroletti, M.; Yang, J.; Marcote, B.; Blanchard, J.; Agudo, I.; An, T.; Bernardini, M.G.; et al. Compact radio emission indicates a structured jet was produced by a binary neutron star merger. Science 2019, 363, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.; DuÅ£an, I.; Köhn, C.; Mizuno, Y. PIC methods in astrophysics: Simulations of relativistic jets and kinetic physics in astrophysical systems. Living Rev. Comput. Astrophys. 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, B.F. Determining the Hubble Constant from Gravitational Wave Observations. Nature 1986, 323, 310–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, D.E.; Hughes, S.A. Using gravitational-wave standard sirens. Astrophys. J. 2005, 629, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Holz, D.E.; Hughes, S.A.; Jain, B. Short grb and binary black hole standard sirens as a probe of dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 063006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissanke, S.; Holz, D.E.; Hughes, S.A.; Dalal, N.; Sievers, J.L. Exploring short gamma-ray bursts as gravitational-wave standard sirens. Astrophys. J. 2010, 725, 496–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration and The Virgo Collaboration; The 1M2H Collaboration; The Dark Energy Camera GW-EM Collaboration and the DES Collaboration; The DLT40 Collaboration; The Las Cumbres Observatory Collaboration; The VINROUGE Collaboration; The MASTER Collaboration. A gravitational-wave standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant. Nature 2017, 551, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perego, A.; Radice, D.; Bernuzzi, S. AT 2017gfo: An Anisotropic and Three-component Kilonova Counterpart of GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasen, D.; Metzger, B.; Barnes, J.; Quataert, E.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. Origin of the heavy elements in binary neutron-star mergers from a gravitational-wave event. Nature 2017, 551, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanvir, N.R.; Levan, A.J.; Fruchter, A.S.; Hjorth, J.; Hounsell, R.A.; Wiersema, K.; Tunnicliffe, R.L. A ‘kilonova’ associated with the short-duration γ-ray burst GRB 130603B. Nature 2013, 500, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, D.; Hansen, C.J.; Selsing, J.; Koch, A.; Malesani, D.B.; Andersen, A.C.; Fynbo, J.P.U.; Arcones, A.; Bauswein, A.; Covino, S.; et al. Identification of strontium in the merger of two neutron stars. Nature 2019, 574, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] The population of merging compact binaries inferred using gravitational waves through GWTC-3. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03634. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] Search for Gravitational Waves Associated with Gamma-Ray Bursts Detected by Fermi and Swift during the LIGO–Virgo Run O3b. Astrophys. J. 2022, 928, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricelli, B.; Bernardini, M.G.; Mapelli, M.; D’Avanzo, P.; Santoliquido, F.; Cella, G.; Razzano, M.; Cuoco, E. Prospects for multimessenger detection of binary neutron star mergers in the fourth LIGO–Virgo–KAGRA observing run. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 4159–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; Salafia, O.S.; Gabrielli, F.; Ghirlanda, G.; Giacomazzo, B.; Perego, A.; Colpi, M. Multi-messenger observations of binary neutron star mergers in the O4 run. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.07592. [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, B.D. Kilonovae. Living Rev. Rel. 2017, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, I.; Margutti, R.; Salafia, O.S.; Parazin, B.; Villar, V.A.; Coughlin, M.W.; Yoachim, P.; Mortensen, K.; Brethauer, D.; Smartt, S.J.; et al. Target-of-opportunity Observations of Gravitational-wave Events with Vera C. Rubin Observatory. Astrophys. J. Supp. 2022, 260, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscoveanu, S.; Landry, P.; Vitale, S. Population properties and multimessenger prospects of neutron star-black hole mergers following GWTC-3. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.01568. [Google Scholar]
- Punturo, M.; Abernathy, M.; Acernese, F.; Allen, B.; Andersson, N.; Arun, K.; Barone, F.; Barr, B.; Barsuglia, M.; Beker, M.; et al. The Einstein Telescope: A third-generation gravitational wave observatory. Class. Quant. Grav. 2010, 27, 194002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitze, D.; Adhikari, R.X.; Ballmer, S.; Barish, B.; Barsotti, L.; Billingsley, G.; Brown, D.A.; Chen, Y.; Coyne, D.; Eisenstein, R.; et al. Contribution to Gravitational-Wave Astronomy beyond LIGO. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2019, 51, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.M.; Scolnic, D. Large Magellanic Cloud Cepheid Standards Provide a 1% Foundation for the Determination of the Hubble Constant and Stronger Evidence for Physics beyond ΛCDM. Astrophys. J. 2019, 876, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratta, G.; Ciolfi, R.; Amati, L.; Bozzo, E.; Ghirlanda, G.; Maiorano, E.; Nicastro, L.; Rossi, A.; Vinciguerra, S.; Frontera, F.; et al. THESEUS: A key space mission concept for Multi-Messenger Astrophysics. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 662–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; O’Brien, P.; Götz, D.; Bozzo, E.; Tenzer, C.; Frontera, F.; Ghirlanda, G.; Labanti, C.; Osborne, J.P.; Stratta, G.; et al. The THESEUS space mission concept: Science case, design and expected performances. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 191–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stratta, G.; Pannarale, F. Neutron Star Binary Mergers: The Legacy of GW170817 and Future Prospects. Universe 2022, 8, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8090459
Stratta G, Pannarale F. Neutron Star Binary Mergers: The Legacy of GW170817 and Future Prospects. Universe. 2022; 8(9):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8090459
Chicago/Turabian StyleStratta, Giulia, and Francesco Pannarale. 2022. "Neutron Star Binary Mergers: The Legacy of GW170817 and Future Prospects" Universe 8, no. 9: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8090459
APA StyleStratta, G., & Pannarale, F. (2022). Neutron Star Binary Mergers: The Legacy of GW170817 and Future Prospects. Universe, 8(9), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8090459






