Shape Invariant Potentials in Supersymmetric Quantum Cosmology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics
2.1. Hamiltonian Formulation of Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics
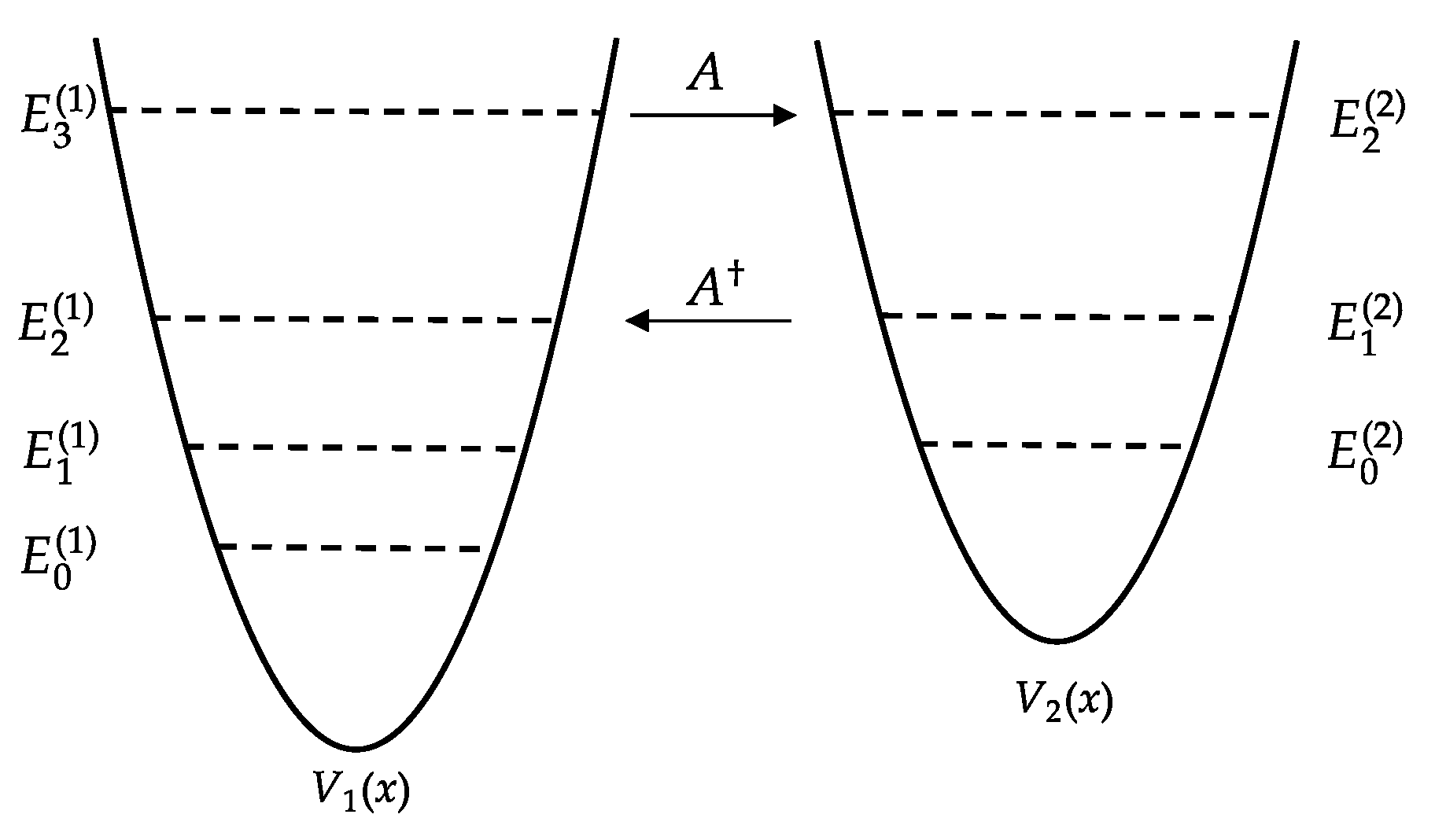
2.2. Shape Invariance and Solvable Potentials
3. SUSY Quantum Cosmology
3.1. A Case Study: Classical Setting
3.2. Quantization
3.3. Supersymmetric Quantization
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | In [37], the excited wave functions have also been studied. More concretely, instead of the choice of a nonsingular superpotential that is based on the ground state wave function , a generalized procedure was presented to construct all possible superpotentials. |
| 2 | Cf. next subsection, concretely about Equation (28). |
| 3 | Throughout this paper we work in natural units where . |
| 4 | Adler–Deser–Misner (ADM); see [56] for more details. |
| 5 | |
| 6 | “Ah, but a man’s reach should exceed his grasp, Or what’s a heaven for?”, Robert Browning (in ‘Andrea del Sarto’ l. 97 (1855)). |
References
- Cooper, F.; Ginocchio, J.N.; Wipf, A. Supersymmetry, operator transformations and exactly solvable potentials. J. Phys. A 1989, 22, 3707–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyaya, A.; Mallow, J.V.; Sukhatme, U.P. Shape invariance and its connection to potential algebra. In Supersymmetry and Integrable Models; Aratyn, H., Imbo, T.D., Keung, W.Y., Sukhatme, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 502, pp. 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balantekin, A.B. Algebraic approach to shape invariance. Phys. Rev. A 1998, 57, 4188–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyaya, A.; Mallow, J.V.; Sukhatme, U.P. Broken supersymmetric shape invariant systems and their potential algebras. Phys. Lett. A 2001, 283, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.D.; Xuan, P.C. Exactly solvable potentials of the Klein Gordon equation with the supersymmetry method. Phys. Lett. A 2006, 352, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, A.; Bhaduri, R.K. Supersymmetry, shape invariance and exactly solvable noncentral potentials. Am. J. Phys. 1994, 62, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesne, C. Deformed Shape Invariant Superpotentials in Quantum Mechanics and Expansions in Powers of ℏ. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, V.K. A relation between Z3-graded symmetry and shape invariant supersymmetric systems. J. Phys. A 2014, 47, 435304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bazeia, D.; Das, A. Supersymmetry, shape invariance and the Legendre equations. Phys. Lett. B 2012, 715, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stahlhofen, A. Remarks on the equivalence between the shape-invariance condition and the factorisation condition. J. Phys. A 1989, 22, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarizadeh, M.A.; Fakhri, H. Supersymmetry and shape invariance in differential equations of mathematical physics. Phys. Lett. A 1997, 230, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, A.; Ghorbanpour, H. Supersymmetry Approach and Shape Invariance for Pseudo-harmonic Potential. Acta Phys. Pol. B 2012, 43, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Jalalzadeh, S.; Moniz, P.V. Classical Universe emerging from quantum cosmology without horizon and flatness problems. Eur. Phys. J. C 2016, 76, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalzadeh, S.; Rostami, T.; Moniz, P.V. On the relation between boundary proposals and hidden symmetries of the extended pre-big bang quantum cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, T.; Jalalzadeh, S.; Moniz, P.V. Quantum cosmological intertwining: Factor ordering and boundary conditions from hidden symmetries. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 023526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalzadeh, S.; Moniz, P.V. Dirac observables and boundary proposals in quantum cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 083504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalzadeh, S.; Rostami, T.; Moniz, P.V. Quantum cosmology: From hidden symmetries towards a new (supersymmetric) perspective. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2016, 25, 1630009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniz, P.V. Quantum Cosmology—The Supersymmetric Perspective—Vol. 1; Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniz, P.V. Quantum Cosmology—The Supersymmetric Perspective—Vol. 2; Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniz, P.V. Origin of structure in supersymmetric quantum cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 57, R7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, C.; Lück, T.; Moniz, P.V. Semiclassical approximation to supersymmetric quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, R.; Granados, V.D.; Mota, R.D. Novel Complete Non-Compact Symmetries for the Wheeler–DeWitt Equation in a Wormhole Scalar Model and Axion-Dilaton String Cosmology. Class. Quant. Grav. 2011, 28, 185002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, R.; Mota, R.D. New exact supersymmetric wave functions for a massless scalar field and axion–dilaton string cosmology in a FRWL metric. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.S.G.; Reyes, M.A.; Mora, C.V.; Pozo, E.C. Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics: Two Factorization Schemes and Quasi-Exactly Solvable Potentials. In Panorama of Contemporary Quantum Mechanics-Concepts and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, R.K.; Sakhr, J.; Sprung, D.W.L.; Dutt, R.; Suzuki, A. Shape invariant potentials in SUSY quantum mechanics and periodic orbit theory. J. Phys. A 2005, 38, L183–L189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougie, J.; Gangopadhyaya, A.; Mallow, J.V. Method for generating additive shape-invariant potentials from an Euler equation. J. Phys. A 2011, 44, 275307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, E.D.; Ribeiro, M.A.C. Generalized Ladder Operators for Shape-invariant Potentials. Phys. Scripta 2001, 64, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyaya, A.; Mallow, J.V.; Rasinariu, C.; Bougie, J. Exactness of SWKB for shape invariant potentials. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougie, J.; Gangopadhyaya, A.; Mallow, J.; Rasinariu, C. Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics and Solvable Models. Symmetry 2012, 4, 452–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariñena, J.F.; Ramos, A. Shape-invariant potentials depending on n parameters transformed by translation. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2000, 33, 3467–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.C. Shape invariant potentials in second-order supersymmetric quantum mechanics. J. Phys. Math. 2011, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.H. Factorization Method in Quantum Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasuda, Y.; Sawado, N. SWKB Quantization Condition for Conditionally Exactly Solvable Systems and the Residual Corrections. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.12567. [Google Scholar]
- Gangopadhyaya, A.; Mallow, J.V.; Rasinariu, C. Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics: An Introduction; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, F.; Ginocchio, J.N.; Khare, A. Relationship Between Supersymmetry and Solvable Potentials. Phys. Rev. D 1987, 36, 2458–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutt, R.; Khare, A.; Sukhatme, U.P. Supersymmetry, shape invariance, and exactly solvable potentials. Am. J. Phys. 1988, 56, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, F.; Khare, A.; Sukhatme, U. Supersymmetry and quantum mechanics. Phys. Rept. 1995, 251, 267–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.M. Relationship Between Supersymmetry and the Inverse Method in Quantum Mechanics. Phys. Lett. B 1984, 145, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursey, D.L. Isometric operators, isospectral Hamiltonians, and supersymmetric quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. D 1986, 33, 2267–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gel’fand, I.M.; Levitan, B.M. On the determination of a differential equation from its spectral function. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Ser. Mat. 1951, 15, 309–360. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, P.B.; Moses, H.E. Changes in potentials due to changes in the point spectrum: Anharmonic oscillators with exact solutions. Phys. Rev. A 1980, 22, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kac, V.G. A sketch of Lie superalgebra theory. Comm. Math. Phys. 1977, 53, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendenshtein, L.E. Derivation of Exact Spectra of the Schrodinger Equation by Means of Supersymmetry. JETP Lett. 1983, 38, 356–359. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger, E. A Method of Determining Quantum-Mechanical Eigenvalues and Eigenfunctions. Proc. R. Ir. Acad. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1940, 46, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Infeld, L.; Hull, T.E. The Factorization Method. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1951, 23, 21–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, A. Supersymmetry in quantum mechanics. Pramana-J. Phys. 1997, 49, 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, E. Further Studies on Solving Eigenvalue Problems by Factorization. Proc. R. Ir. Acad., A Math. phys. sci. 1940, 46, 183–206. [Google Scholar]
- Darboux, G. On a proposition relative to linear equations. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 1882, 94, 1456–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Luban, M.; Pursey, D.L. New Schrödinger equations for old: Inequivalence of the Darboux and Abraham-Moses constructions. Phys. Rev. D 1986, 33, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arancibia, A.; Plyushchay, M.S.; Nieto, L.-M. Exotic supersymmetry of the kink-antikink crystal, and the infinite period limit. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 83, 065025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, J.; Tsulaia, M. A Note on Shape Invariant Potentials for Discretized Hamiltonians arXiv 2022, arXiv. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.10100. [Google Scholar]
- Cariñena, J.F.; Plyushchay, M.S. Ground-state isolation and discrete flows in a rationally extended quantum harmonic oscillator. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariñena, J.F.; Inzunza, L.; Plyushchay, M.S. Rational deformations of conformal mechanics. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 026017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancibia, A.; Plyushchay, M.S. Chiral asymmetry in propagation of soliton defects in crystalline backgrounds. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, T.; Aizawa, N. Shape-invariant potentials and an associated coherent state. Phys. Lett. A 1993, 180, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalzadeh, S.; Moniz, P.V. Challenging Routes in Quantum Cosmology; World Scientific: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Saba, N.; Farhoudi, M.; Marto, J.; Moniz, P. Inflationary universe in deformed phase space scenario. Ann. Phys. 2018, 393, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Pacheco, R.; Sakellariadou, M.; Moniz, P. Late time cosmic acceleration in modified Sáez–Ballester theory. Phys. Dark Univ. 2020, 27, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.M.M. Noncommutativity, Saez-Ballester Theory and Kinetic Inflation. Universe 2022, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Farhoudi, M.; Khosravi, N. Horizon problem remediation via deformed phase space. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2011, 43, 2895–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rasouli, S.M.M.; Moniz, P.V. Noncommutative minisuperspace, gravity-driven acceleration, and kinetic inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 083533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Ziaie, A.; Jalalzadeh, S.; Moniz, P. Non-singular Brans–Dicke collapse in deformed phase space. Ann. Phys. 2016, 375, 154–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.M.M.; Vargas Moniz, P. Gravity-Driven Acceleration and Kinetic Inflation in Noncommutative Brans-Dicke Setting. Odessa Astron. Pub. 2016, 29, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Marto, J.; Moniz, P. Kinetic inflation in deformed phase space Brans–Dicke cosmology. Phys. Dark Univ. 2019, 24, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, T.; Tucker, R.W. Signature dynamics in general relativity. Class. Quant. Grav. 1993, 10, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, T.; Onder, M.; Tucker, R.W. Signature transitions in quantum cosmology. Class. Quant. Grav. 1993, 10, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalzadeh, S.; Ahmadi, F.; Sepangi, H.R. Multidimensional classical and quantum cosmology: Exact solutions, signature transition and stabilization. J. High Energy Phys. 2003, 2003, 012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, N.; Jalalzadeh, S.; Sepangi, H.R. Quantum noncommutative multidimensional cosmology. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2007, 39, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram, P.; Jalalzadeh, S. Quantum cosmology with varying speed of light: Canonical approach. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 660, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bina, A.; Atazadeh, K.; Jalalzadeh, S. Noncommutativity, generalized uncertainty principle and FRW cosmology. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2008, 47, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jalalzadeh, S.; Vakili, B. Quantization of the interior Schwarzschild black hole. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2012, 51, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, N.; Jalalzadeh, S.; Sepangi, H.R. Non-commutative multi-dimensional cosmology. J. High Energy Phys. 2006, 2006, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, B.; Pedram, P.; Jalalzadeh, S. Late time acceleration in a deformed phase space model of dilaton cosmology. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 687, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, F. Large scale—Small scale duality and cosmological constant. Phys. Lett. A 1999, 259, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Darabi, F.; Rastkar, A. A quantum cosmology and discontinuous signature changing classical solutions. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2006, 38, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalzadeh, S.; Rashki, M.; Abarghouei Nejad, S. Classical universe arising from quantum cosmology. Phys. Dark Univ. 2020, 30, 100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrup, H.A. A new look at the quantum mechanics of the harmonic oscillator. Ann. Phys. 2007, 519, 439–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Malik, R.P. Supersymmetric Oscillator: Novel Symmetries. EPL 2012, 98, 11002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Eath, P.D. Supersymmetric Quantum Cosmology; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniz, P.V. Supersymmetric quantum cosmology: Shaken, not stirred. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 1996, 11, 4321–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniz, P.V. Quantum Cosmology: Meeting SUSY. In Progress in Mathematical Relativity, Gravitation and Cosmology; García-Parrado, A., Mena, F.C., Moura, F., Vaz, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Compeán, H.; Obregón, O.; Ramírez, C. Topics in Supersymmetric and Noncommutative Quantum Cosmology. Universe 2021, 7, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniz, P.V. Supersymmetric quantum cosmology: A ‘Socratic’ guide. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2014, 46, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Obregón, O. Supersymmetric quantum matrix cosmology. Class. quant. grav. 2015, 32, 235014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregon, O.; Ramirez, C. Dirac-like formulation of quantum supersymmetric cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 57, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bene, J.; Graham, R. Supersymmetric homogeneous quantum cosmologies coupled to a scalar field. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 49, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csordas, A.; Graham, R. Supersymmetric minisuperspace with nonvanishing fermion number. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, A.; Koehn, M.; Nicolai, H. Supersymmetric quantum cosmological billiards. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 061701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, A.; Mielke, E.W.; Socorro, J. Supersymmetric quantum cosmology for Bianchi class A models. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 1998, 7, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damour, T.; Spindel, P. Quantum supersymmetric cosmology and its hidden Kac–Moody structure. Class. Quant. Grav. 2013, 30, 162001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kiefer, C. Quantum Gravity; International Series of Monographs on Physics; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 2004; Volume 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G. Quantum Gravity, Quantum Cosmology and Lorentzian Geometries; Lecture Notes in Physics Monographs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagni, G. Classical and Quantum Cosmology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojowald, M. Quantum Cosmology: A Fundamental Description of the Universe; Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidsey, J.E. Quantum cosmology of generalized two-dimensional dilaton-gravity models. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 51, 6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidsey, J.E.; Moniz, P.V. Supersymmetric quantization of anisotropic scalar-tensor cosmologies. Class. Quant. Grav. 2000, 17, 4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R. Supersymmetric Bianchi type IX cosmology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidsey, J.E. Scale factor duality and hidden supersymmetry in scalar-tensor cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 52, R5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, V.; Rosales, J.; Obregón, O. Supersymmetric action for Bianchi type models. Class. Quant. Grav. 1996, 13, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, O.; Rosales, J.; Tkach, V. Superfield description of the FRW universe. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 53, R1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, E. Dynamical breaking of supersymmetry. Nucl. Phys. B 1981, 188, 513–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jalalzadeh, S.; Rasouli, S.M.M.; Moniz, P. Shape Invariant Potentials in Supersymmetric Quantum Cosmology. Universe 2022, 8, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8060316
Jalalzadeh S, Rasouli SMM, Moniz P. Shape Invariant Potentials in Supersymmetric Quantum Cosmology. Universe. 2022; 8(6):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8060316
Chicago/Turabian StyleJalalzadeh, Shahram, Seyed Meraj M. Rasouli, and Paulo Moniz. 2022. "Shape Invariant Potentials in Supersymmetric Quantum Cosmology" Universe 8, no. 6: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8060316
APA StyleJalalzadeh, S., Rasouli, S. M. M., & Moniz, P. (2022). Shape Invariant Potentials in Supersymmetric Quantum Cosmology. Universe, 8(6), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8060316







