Polarization Transfer Rates by Isotropic Collisions between Astrophysical SiO Molecule and Electrons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definitions and Numerical Calculations
- –
- E being the collision energy;
- –
- is the SiO spin;
- –
- N is the rotational momentum of the SiO;
- –
- ,
- –
- quantifies the angular momentum exchange between the molecular states at the time of the collision;
- –
- is the SiO lower electronic state and is the upper electronic state. In this work, = X and represents the , , and states, respectively.
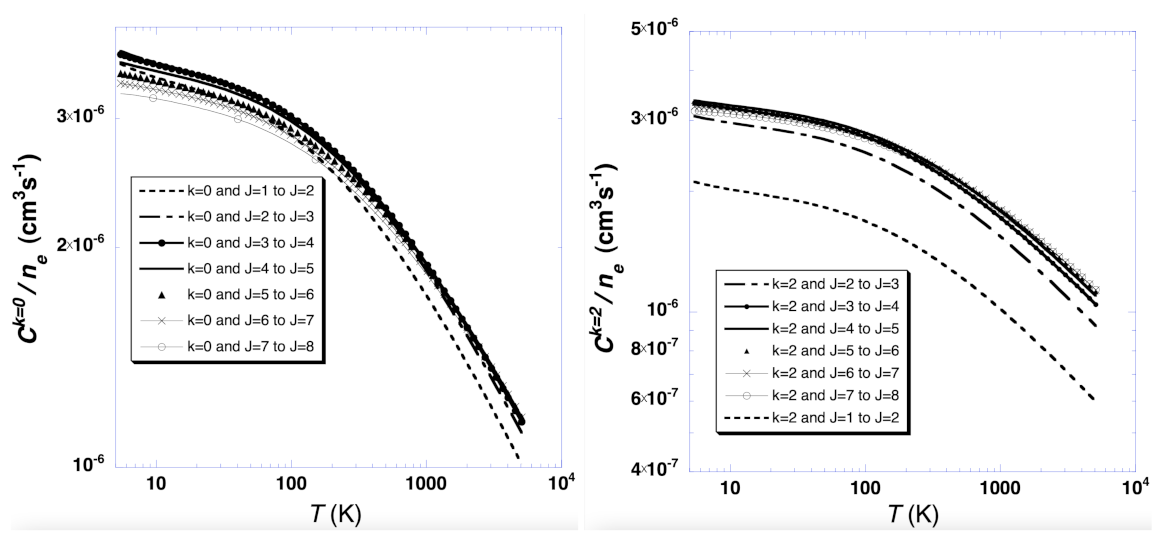
3. Rotational Rates
4. Astrophysical Implications
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elitzur, M. Polarization of Astronomical Maser Radiation. III. Arbitrary Zeeman Splitting and Anisotropic Pumping. Astrophys. J. 1996, 457, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio Ramos, A.; Landi Degl’Innocenti, E.; Trujillo Bueno, J. Dichroic Masers Due to Radiation Anisotropy and the Influence of the Hanle Effect on the Circumstellar SiO Polarization. Astrophys. J. 2005, 625, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, M.; Ukita, N.; Winnberg, A.; Johansson, L.E.B. SiO maser emission from OH/IR stars close to the galactic centre. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 250, 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist, M.; Habing, H.J.; Winnberg, A. OH/IR stars close to the galactic centre. II. Their spatial and kinematics properties and the mass distribution within 5–100 PC from the galactic centre. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 259, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kemball, A.J.; Diamond, P.J. Imaging the Magnetic Field in the Atmosphere of TX Camelopardalis. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1997, 481, L111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmurs, J.F.; Bujarrabal, V.; Colomer, F.; Alcolea, J. VLBA observations of SiO masers: Arguments in favor of radiative pumping mechanisms. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 360, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Derouich, M. Collisional depolarization of molecular lines. Application to the SiO+H isotropic collisions. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 449, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Derouich, M.; Sahal-Bréchot, S.; Barklem, P.S.; O’Mara, B.J. Semi-classical theory of collisional depolarization of spectral lines by atomic hydrogen I. Application to p states of neutral atoms. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 404, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouich, M. Comprehensive Data for Depolarization of the Second Solar Spectrum by Isotropic Collisions with Neutral Hydrogen. Astrophys. J. 2020, 247, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi Degl’Innocenti, E.; Landolfi, M. Polarization in Spectral Lines; Astrophysics and Space Library: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 307. [Google Scholar]
- Sahal-Bréchot, S. Calculation of the polarization degree of the infrared lines of Fe XIII of the solar corona. Astrophys. J. 1977, 213, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.; Tennyson, J.; Faure, A. Calculated electron impact spin-coupled rotational cross-sections for 2S+1Σ+ linear molecules: CN as an example. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2012, 45, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, G.C.; Smith, A.D. Classical theory of collisional depolarization and rotational relaxation in open-shell diatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83, 5663–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qutub, S.; Derouich, M.; Kalugina, Y.N.; Asiri, H.; Lique, F. Effect of isotropic collisions with neutral hydrogen on the polarization of the CN solar molecule. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 491, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouich, M.; Badruddin, B.; Alruhaili, A.; Qutub, S. Are collisions with electrons important for modeling the polarization of the lines of the C2 solar molecule? Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 7, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, H.M.; Poynter, R.L.; Cohen, E.A.; Delitsky, M.L.; Pearson, J.C.; Müller, H.S.P. Submillimeter, millimeter and microwave spectral line catalog. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1998, 60, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varambhia, H.N.; Gupta, M.; Faure, A.; Baluja, K.L.; Tennyson, J. Electron collision with the silicon monoxide (SiO) molecule using the R-matrix method. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2009, 42, 095204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, D. Molecular Collisions in the Interstellar Medium; Cambridge Astrophysics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Derouich, M.; Alruhaili, A.; Badruddin, B. Polarization and isotropic collisions with electrons in the solar atmosphere. New Astron. 2019, 71, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, R.H.; Chackerian, C., Jr. Vibration-rotation intensities of SiO. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1981, 88, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommier, V.; Sahal-Brechot, S.; Leroy, J.L. The linear polarization of hydrogen H-beta radiation and the joint diagnostic of magnetic field vector and electron density in quiescent prominences. I—The magnetic field. II—The electron density. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 156, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | Derouich (2006) [7] found that collisions of the SiO in the X state with the hydrogen atom in its ground state arise with a transfer of polarization rate of ∼ 10 cm s for j ≤ 8 and for the vibrational level v = 0. |
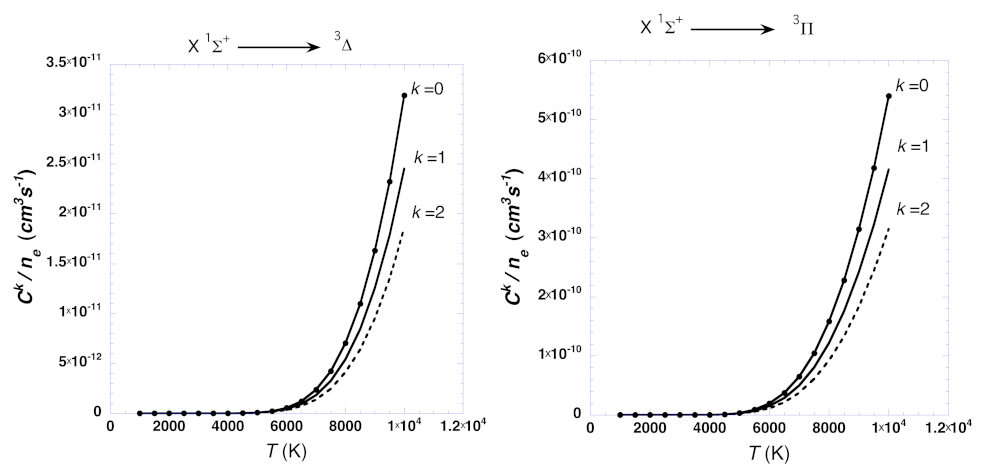
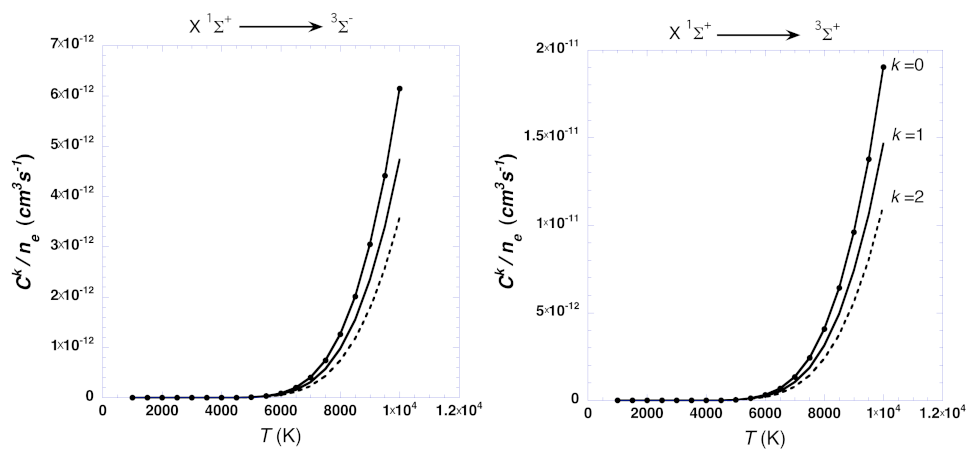
| k | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | ||||||
| → | ||||||
| 0 | −1.5428 | 1.7377 | −4.1598 | −2.5952 | 1.0604 | |
| 1 | −1.1882 | 1.3382 | −3.2035 | −1.9986 | 0.8166 | |
| 2 | −0.9006 | 1.0144 | −2.4282 | −1.5149 | 0.619 | |
| X | ||||||
| → | ||||||
| 0 | 7.1625 | −1.202 | 6.5227 | −1.4116 | 1.0631 | |
| 1 | 5.5158 | −0.9257 | 5.0231 | −1.0871 | 0.8187 | |
| 2 | 4.1809 | −0.7017 | 3.8075 | −0.8240 | 0.62055 | |
| X | ||||||
| → | ||||||
| 0 | 9.8049 | −1.7041 | 9.5997 | −2.1515 | 1.6715 | |
| 1 | 7.5508 | −1.3124 | 7.3928 | −1.6569 | 1.2873 | |
| 2 | 5.7234 | −0.9947 | 5.6036 | −1.2559 | 0.9757 | |
| X | ||||||
| → | ||||||
| 0 | 2.8107 | −4.5924 | 2.416 | −5.0649 | 3.6956 | |
| 1 | 2.1646 | −3.5367 | 1.8606 | −3.9005 | 2.846 | |
| 2 | 1.6407 | −2.6807 | 1.4103 | −2.9565 | 2.1572 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Derouich, M.; Zaheer Ahmad, B.; Alruhaili, A.; Qutub, S. Polarization Transfer Rates by Isotropic Collisions between Astrophysical SiO Molecule and Electrons. Universe 2022, 8, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8030140
Derouich M, Zaheer Ahmad B, Alruhaili A, Qutub S. Polarization Transfer Rates by Isotropic Collisions between Astrophysical SiO Molecule and Electrons. Universe. 2022; 8(3):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8030140
Chicago/Turabian StyleDerouich, Moncef, Badruddin Zaheer Ahmad, Aied Alruhaili, and Saleh Qutub. 2022. "Polarization Transfer Rates by Isotropic Collisions between Astrophysical SiO Molecule and Electrons" Universe 8, no. 3: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8030140
APA StyleDerouich, M., Zaheer Ahmad, B., Alruhaili, A., & Qutub, S. (2022). Polarization Transfer Rates by Isotropic Collisions between Astrophysical SiO Molecule and Electrons. Universe, 8(3), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8030140





