Magnetar Wind-Driven Shock Breakout Emission after Double Neutron Star Mergers: The Effect of the Anisotropy of the Merger Ejecta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Model
2.1. Anisotropic Merger Ejecta
2.2. Magnetar Wind
2.3. Shock Dynamics and Breakout Emission
2.4. Integration over the Emission Surface
3. Results
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Here, the shocked energy is considered to distribute approximately uniformly behind the shock, which is different from [25], where the shocked energy is assumed to be concentrated within a thin shell immediately behind the shock front. |
| 2 | An exact expression of had been given by Mihalas [85] as
|
References
- Li, L.X.; Paczyński, B. Transient Events from Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 1998, 507, L59–L62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Martínez-Pinedo, G.; Darbha, S.; Quataert, E.; Arcones, A.; Kasen, D.; Thomas, R.; Nugent, P.; Panov, I.V.; Zinner, N.T. Electromagnetic counterparts of compact object mergers powered by the radioactive decay of r-process nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 2650–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.F.; Kasen, D.; Lee, W.H.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. Electromagnetic Transients Powered by Nuclear Decay in the Tidal Tails of Coalescing Compact Binaries. Astrophys. J. 2011, 736, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.; Kasen, D. Effect of a High Opacity on the Light Curves of Radioactively Powered Transients from Compact Object Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2013, 775, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasen, D.; Badnell, N.R.; Barnes, J. Opacities and Spectra of the r-process Ejecta from Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2013, 774, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Hotokezaka, K. Radiative Transfer Simulations of Neutron Star Merger Ejecta. Astrophys. J. 2013, 775, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Gravitational Waves and Gamma-Rays from a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcavi, I.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Howell, D.A.; McCully, C.; Poznanski, D.; Kasen, D.; Barnes, J.; Zaltzman, M.; Vasylyev, S.; Maoz, D.; et al. Optical emission from a kilonova following a gravitational-wave-detected neutron-star merger. Nature 2017, 551, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, D.A.; Foley, R.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Simon, J.D.; Ulloa, N.; Kasen, D.; et al. Swope Supernova Survey 2017a (SSS17a), the optical counterpart to a gravitational wave source. Science 2017, 358, 1556–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Berger, E.; Villar, V.A.; Metzger, B.D.; Nicholl, M.; Chornock, R.; Blanchard, P.K.; Fong, W.; Margutti, R.; Soares-Santos, M.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. II. UV, Optical, and Near-infrared Light Curves and Comparison to Kilonova Models. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.A.; Cenko, S.B.; Kennea, J.A.; Emery, S.W.K.; Kuin, N.P.M.; Korobkin, O.; Wollaeger, R.T.; Fryer, C.L.; Madsen, K.K.; Harrison, F.A.; et al. Swift and NuSTAR observations of GW170817: Detection of a blue kilonova. Science 2017, 358, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholl, M.; Berger, E.; Kasen, D.; Metzger, B.D.; Elias, J.; Briceño, C.; Alexander, K.D.; Blanchard, P.K.; Chornock, R.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. III. Optical and UV Spectra of a Blue Kilonova from Fast Polar Ejecta. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J.; Chen, T.W.; Jerkstrand, A.; Coughlin, M.; Kankare, E.; Sim, S.A.; Fraser, M.; Inserra, C.; Maguire, K.; Chambers, K.C.; et al. A kilonova as the electromagnetic counterpart to a gravitational-wave source. Nature 2017, 551, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares-Santos, M.; Holz, D.E.; Annis, J.; Chornock, R.; Herner, K.; Berger, E.; Brout, D.; Chen, H.Y.; Kessler, R.; Sako, M.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. I. Discovery of the Optical Counterpart Using the Dark Energy Camera. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, N.R.; Levan, A.J.; González-Fernández, C.; Korobkin, O.; Mandel, I.; Rosswog, S.; Hjorth, J.; D’Avanzo, P.; Fruchter, A.S.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. The Emergence of a Lanthanide-rich Kilonova Following the Merger of Two Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Search for Post-merger Gravitational Waves from the Remnant of the Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817. Astrophys. J. 2017, 851, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.W.; Zhang, B.; Gao, H. Bright “Merger-nova” from the Remnant of a Neutron Star Binary Merger: A Signature of a Newly Born, Massive, Millisecond Magnetar. Astrophys. J. 2013, 776, L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Piro, A.L. Optical and X-ray emission from stable millisecond magnetars formed from the merger of binary neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 3916–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.W.; Liu, L.D.; Dai, Z.G. A Long-lived Remnant Neutron Star after GW170817 Inferred from Its Associated Kilonova. Astrophys. J. 2018, 861, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Liu, L.D.; Yu, Y.W.; Zhang, B. What Powered the Optical Transient AT2017gfo Associated with GW170817? Astrophys. J. 2018, 861, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Fujibayashi, S.; Hotokezaka, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Tanaka, M. Modeling GW170817 based on numerical relativity and its implications. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 123012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Thompson, T.A.; Quataert, E. A Magnetar Origin for the Kilonova Ejecta in GW170817. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Shibata, M.; Tanaka, M. Radiative Transfer Simulation for the Optical and Near-infrared Electromagnetic Counterparts to GW170817. Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Yu, Y.W. Shock Breakout Driven by the Remnant of a Neutron Star Binary Merger: An X-ray Precursor of Mergernova Emission. Astrophys. J. 2016, 819, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Ding, X.; Wu, X.F.; Dai, Z.G.; Zhang, B. GRB 080503 Late Afterglow Re-brightening: Signature of a Magnetar-powered Merger-nova. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Ciolfi, R. Electromagnetic Emission from Long-lived Binary Neutron Star Merger Remnants. I. Formulation of the Problem. Astrophys. J. 2016, 819, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Ciolfi, R. Electromagnetic Emission from Long-lived Binary Neutron Star Merger Remnants. II. Lightcurves and Spectra. Astrophys. J. 2016, 819, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, B.; Lü, H.J.; Li, Y. Searching for Magnetar-powered Merger-novae from Short GRBS. Astrophys. J. 2017, 837, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollaeger, R.T.; Fryer, C.L.; Fontes, C.J.; Lippuner, J.; Vestrand, W.T.; Mumpower, M.R.; Korobkin, O.; Hungerford, A.L.; Even, W.P. Impact of Pulsar and Fallback Sources on Multifrequency Kilonova Models. Astrophys. J. 2019, 880, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.W.; Chen, A.; Li, X.D. X-ray Transients from the Accretion-induced Collapse of White Dwarfs. Astrophys. J. 2019, 877, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Lin, D.B.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, T.; Lu, R.J.; Wang, X.G.; Liang, E.W. A Pulsar Wind Nebula Embedded in the Kilonova AT 2017gfo Associated with GW170817/GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. 2019, 885, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Dai, Z.G. Broad-band emission from a kilonova ejecta-pulsar wind Nebula system: Late-time X-ray afterglow rebrightening of GRB 170817A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 512, 5572–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.L.; Yu, Y.W.; Zhu, J.P. Does a long-lived remnant neutron star exist after short gamma-ray burst GRB 160821B? Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 654, A124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, Z. Engine-fed Kilonovae (Mergernovae)—I. Dynamical Evolution and Energy Injection / Heating Efficiencies. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.03045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasen, D.; Metzger, B.D.; Bildsten, L. Magnetar-driven Shock Breakout and Double-peaked Supernova Light Curves. Astrophys. J. 2016, 821, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.D.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.F.; Yang, S. Magnetar-driven Shock Breakout Revisited and Implications for Double-peaked Type I Superluminous Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2021, 911, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.D.; Yu, Y.W.; Liu, L.D. The effects of a magnetar engine on the gamma-ray burst-associated supernovae: Application to double-peaked SN 2006aj. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.11092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.B.; Benz, W.; Piran, T.; Thielemann, F.K. Merging Neutron Stars. I. Initial Results for Coalescence of Noncorotating Systems. Astrophys. J. 1994, 431, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffert, M.; Janka, H.T.; Schaefer, G. Coalescing neutron stars—A step towards physical models. I. Hydrodynamic evolution and gravitational-wave emission. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 311, 532–566. [Google Scholar]
- Rosswog, S.; Liebendörfer, M.; Thielemann, F.K.; Davies, M.B.; Benz, W.; Piran, T. Mass ejection in neutron star mergers. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 341, 499–526. [Google Scholar]
- Rosswog, S.; Davies, M.B.; Thielemann, F.K.; Piran, T. Merging neutron stars: Asymmetric systems. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 360, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ruffert, M.; Janka, H.T. Coalescing neutron stars—A step towards physical models. III. Improved numerics and different neutron star masses and spins. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 380, 544–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobkin, O.; Rosswog, S.; Arcones, A.; Winteler, C. On the astrophysical robustness of the neutron star merger r-process. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 426, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piran, T.; Nakar, E.; Rosswog, S. The electromagnetic signals of compact binary mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 430, 2121–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosswog, S.; Piran, T.; Nakar, E. The multimessenger picture of compact object encounters: Binary mergers versus dynamical collisions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 430, 2585–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauswein, A.; Goriely, S.; Janka, H.T. Systematics of Dynamical Mass Ejection, Nucleosynthesis, and Radioactively Powered Electromagnetic Signals from Neutron-star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Okawa, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.i.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Mass ejection from the merger of binary neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Dynamical mass ejection from the merger of asymmetric binary neutron stars: Radiation-hydrodynamics study in general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 124046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucart, F.; O’Connor, E.; Roberts, L.; Kidder, L.E.; Pfeiffer, H.P.; Scheel, M.A. Impact of an improved neutrino energy estimate on outflows in neutron star merger simulations. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 123016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Galeazzi, F.; Lippuner, J.; Roberts, L.F.; Ott, C.D.; Rezzolla, L. Dynamical mass ejection from binary neutron star mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 3255–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, T.; Bernuzzi, S.; Tichy, W. Closed-form tidal approximants for binary neutron star gravitational waveforms constructed from high-resolution numerical relativity simulations. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 121501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, T.; Ujevic, M.; Tichy, W.; Bernuzzi, S.; Brügmann, B. Gravitational waves and mass ejecta from binary neutron star mergers: Effect of the mass ratio. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 024029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Perego, A.; Hotokezaka, K.; Fromm, S.A.; Bernuzzi, S.; Roberts, L.F. Binary Neutron Star Mergers: Mass Ejection, Electromagnetic Counterparts, and Nucleosynthesis. Astrophys. J. 2018, 869, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Fujibayashi, S.; Sekiguchi, Y. Long-term evolution of neutron-star merger remnants in general relativistic resistive magnetohydrodynamics with a mean-field dynamo term. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 063026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oechslin, R.; Janka, H.T.; Marek, A. Relativistic neutron star merger simulations with non-zero temperature equations of state. I. Variation of binary parameters and equation of state. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 467, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L.; Ott, C.D.; Burrows, A.; Rosswog, S.; Livne, E. Neutrino Signatures and the Neutrino-Driven Wind in Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2009, 690, 1681–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, A.; Rosswog, S.; Cabezón, R.M.; Korobkin, O.; Käppeli, R.; Arcones, A.; Liebendörfer, M. Neutrino-driven winds from neutron star merger remnants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 3134–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Perego, A.; Arcones, A.; Thielemann, F.K.; Korobkin, O.; Rosswog, S. Neutrino-driven Winds in the Aftermath of a Neutron Star Merger: Nucleosynthesis and Electromagnetic Transients. Astrophys. J. 2015, 813, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, S.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Kiuchi, K.; Shibata, M. Properties of Neutrino-driven Ejecta from the Remnant of a Binary Neutron Star Merger: Pure Radiation Hydrodynamics Case. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Ciolfi, R.; Rezzolla, L. Magnetically Driven Winds from Differentially Rotating Neutron Stars and X-ray Afterglows of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2014, 785, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, S.; Kiuchi, K.; Nishimura, N.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M. Mass Ejection from the Remnant of a Binary Neutron Star Merger: Viscous-radiation Hydrodynamics Study. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Metzger, B.D. Three-dimensional GRMHD Simulations of Neutrino-cooled Accretion Disks from Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2018, 858, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Quataert, E.; Foucart, F.; Kasen, D. Long-term GRMHD simulations of neutron star merger accretion discs: Implications for electromagnetic counterparts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 3373–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Metzger, B.D. Delayed outflows from black hole accretion tori following neutron star binary coalescence. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 435, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, O.; Bauswein, A.; Ardevol Pulpillo, R.; Goriely, S.; Janka, H.T. Comprehensive nucleosynthesis analysis for ejecta of compact binary mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 541–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Shibata, M.; Tanaka, M. Diversity of Kilonova Light Curves. Astrophys. J. 2020, 889, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Sub-radian-accuracy gravitational waveforms of coalescing binary neutron stars in numerical relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 084060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakura, H.; Hotokezaka, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M.; Ioka, K. Jet Collimation in the Ejecta of Double Neutron Star Mergers: A New Canonical Picture of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2014, 784, L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.C.; Thompson, C. Formation of Very Strongly Magnetized Neutron Stars: Implications for Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 1992, 392, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.J.; Rosswog, S. Producing Ultrastrong Magnetic Fields in Neutron Star Mergers. Science 2006, 312, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Yu, Y.W. How can Newly Born Rapidly Rotating Neutron Stars Become Magnetars? Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.W.; Cheng, K.S.; Cao, X.F. The Role of Newly Born Magnetars in Gamma-ray Burst X-ray Afterglow Emission: Energy Injection and Internal Emission. Astrophys. J. 2010, 715, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, N.; O’Brien, P.T.; Zhang, B.; Willingale, R.; Troja, E.; Starling, R.L.C. Can X-ray emission powered by a spinning-down magnetar explain some gamma-ray burst light-curve features? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 402, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.J.; Zhang, B. A Test of the Millisecond Magnetar Central Engine Model of Gamma-Ray Bursts with Swift Data. Astrophys. J. 2014, 785, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Lei, W.H.; Li, Y.; Lasky, P.D. The Millisecond Magnetar Central Engine in Short GRBs. Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasen, D.; Bildsten, L. Supernova Light Curves Powered by Young Magnetars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 717, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Li, L.X.; Lin, D.B.; Liang, E.W. Gamma-Ray Emission Produced by r-process Elements from Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2021, 919, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, G.B. Theoretical Methods of Treating Line Formation Problems in Steady-State Extended Atmospheres. Int. Astron. Union Colloq. 1970, 2, 85–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Collins, G.W.I. Further Note on Terminology—Specific Luminosity. Astron. Astrophys. 1973, 26, 315. [Google Scholar]
- Kandel, R.S. Note on Terminology—Specific Luminosity. Astron. Astrophys. 1973, 22, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Rybicki, G.B.; Hummer, D.G. The specific luminosity of a three-dimensional medium in terms of the escape probability. Astrophys. J. 1983, 274, 380–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, E. Remarks on the Schwarzschild-Milne model of the outer layers of a star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1930, 90, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Radiative Transfer; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalas, D. Stellar Atmospheres; W.H. Freeman & Co.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1978; pp. 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bronstein, M. Zum Strahlungsgleichgewichtsproblem von Milne. Zeitschrift fur Physik 1929, 58, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, G.; van Eerten, H.; Piro, L.; Troja, E. Gamma-Ray Burst Afterglows in the Multimessenger Era: Numerical Models and Closure Relations. Astrophys. J. 2020, 896, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W. The Einstein Probe mission. In Proceedings of the 44th COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Athens, Greece, 16–24 July 2022; Volume 44, p. 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.Q.; Zheng, X.C.; Li, Y.; Brandt, W.N.; Zhang, B.; Luo, B.; Zhang, B.B.; Bauer, F.E.; Sun, H.; Lehmer, B.D.; et al. A magnetar-powered X-ray transient as the aftermath of a binary neutron-star merger. Nature 2019, 568, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Irwin, J.A.; Berger, E.; Nguyen, R. Discovery of Three Candidate Magnetar-powered Fast X-ray Transients from Chandra Archival Data. Astrophys. J. 2022, 927, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirola-Vásquez, J.; Bauer, F.E.; Jonker, P.G.; Brandt, W.N.; Yang, G.; Levan, A.J.; Xue, Y.Q.; Eappachen, D.; Zheng, X.C.; Luo, B. Extragalactic fast X-ray transient candidates discovered by Chandra (2000–2014). Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 663, A168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Early X-ray and Optical Afterglow of Gravitational Wave Bursts from Mergers of Binary Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 763, L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
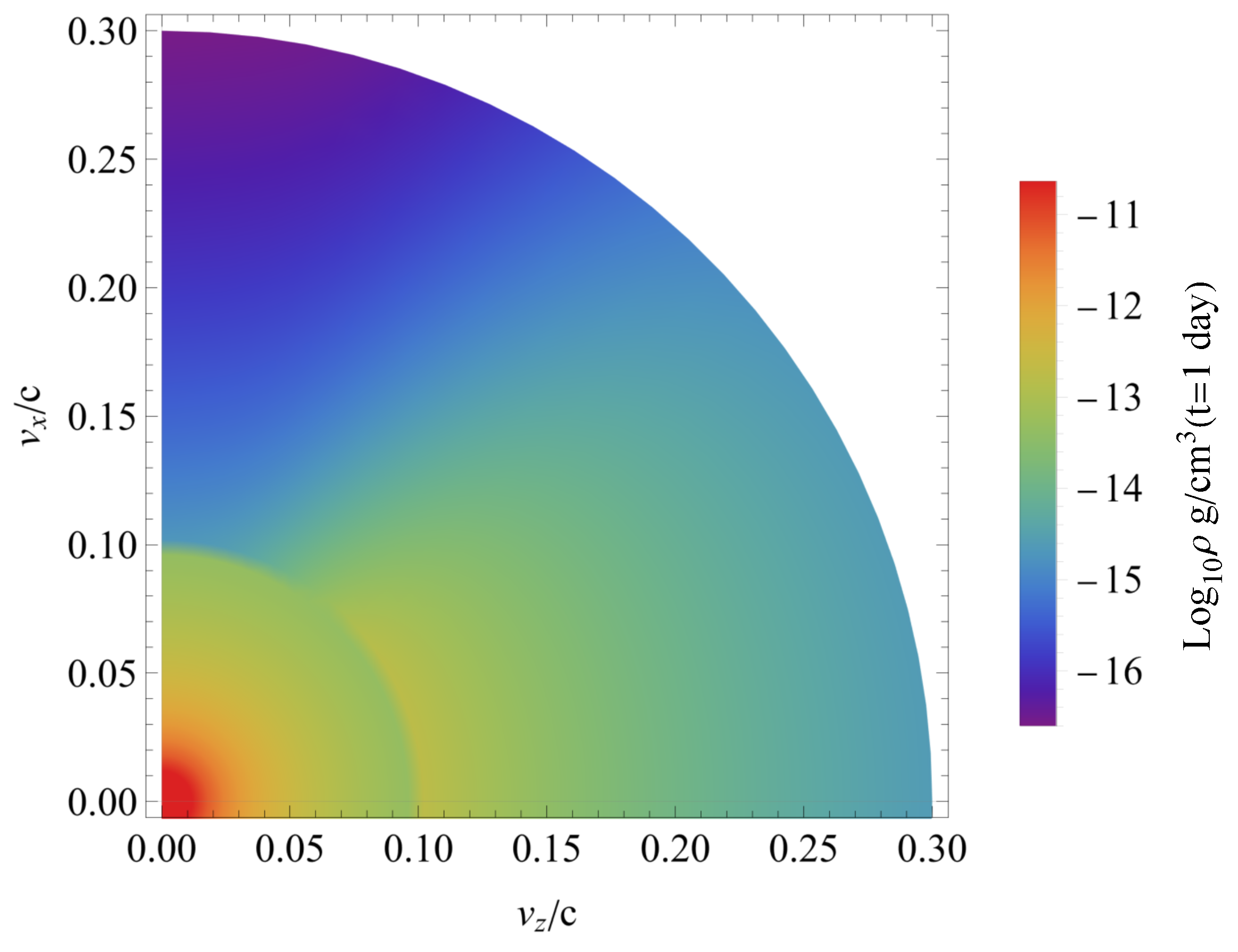

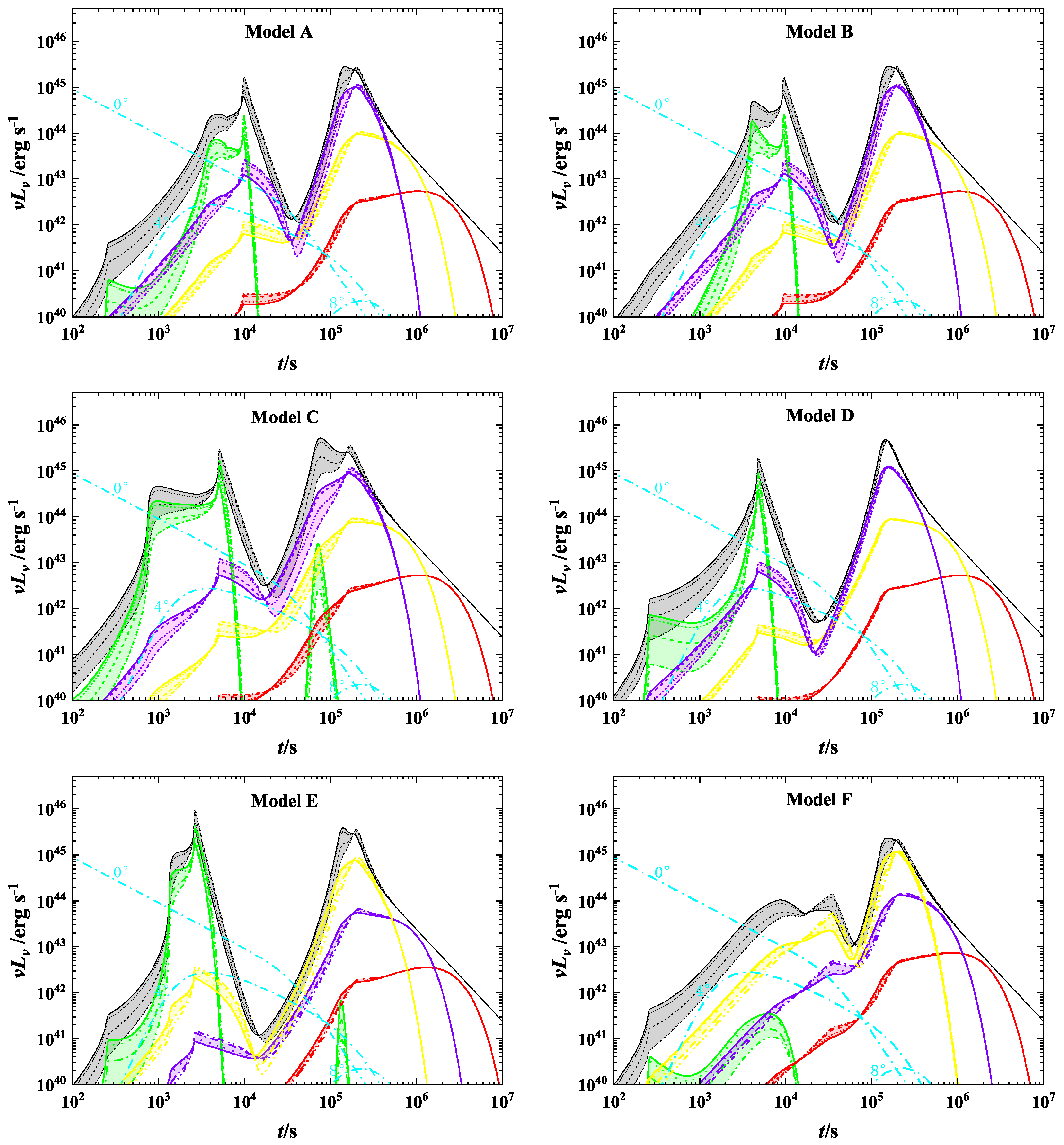

| Model | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 1 | ||||||
| 10 | ||||||
| f | ||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.-L.; Yu, Y.-W.; Li, S.-Z. Magnetar Wind-Driven Shock Breakout Emission after Double Neutron Star Mergers: The Effect of the Anisotropy of the Merger Ejecta. Universe 2022, 8, 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8120633
Wu G-L, Yu Y-W, Li S-Z. Magnetar Wind-Driven Shock Breakout Emission after Double Neutron Star Mergers: The Effect of the Anisotropy of the Merger Ejecta. Universe. 2022; 8(12):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8120633
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guang-Lei, Yun-Wei Yu, and Shao-Ze Li. 2022. "Magnetar Wind-Driven Shock Breakout Emission after Double Neutron Star Mergers: The Effect of the Anisotropy of the Merger Ejecta" Universe 8, no. 12: 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8120633
APA StyleWu, G.-L., Yu, Y.-W., & Li, S.-Z. (2022). Magnetar Wind-Driven Shock Breakout Emission after Double Neutron Star Mergers: The Effect of the Anisotropy of the Merger Ejecta. Universe, 8(12), 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8120633








