Abstract
Computer modeling of the outflow from Be stars is performed. In our approach, processes of turbulence excitation and turbulent viscosity are added to the conventional model of the radiation driven winds. The objective of our study is to reproduce from the first principles the main features of the outflow from Be stars: a fast polar wind and a slow viscous Keplerian disk at the equator. At sub-critical velocity of rotation up to 0.999 of the critical velocity, our model reproduces the formation of the fast polar wind together with a slow highly turbulent outflow at the equatorial region. This outflow, however, does not reassemble a Keplerian disk. We link this to the absence of the angular moment transfer from the star to the disk. This process provides an increase of the angular momentum of the disk matter with radius. We consider a star with super critical rotation as the simplest way to supply the angular momentum to the disk. In this case, the star surface has a higher azimuthal speed than the matter at the inner edge of the disk. The angular momentum transfer becomes unavoidable. Already at rotation velocity 0.5% above the critical one, a quasi Keplerian disk at the equator is formed with size ∼10 stellar radius. At rotation 1% higher than the critical speed, the disk reaches ∼15 stellar radius. The main conclusion following from our work is that the conventional model of the radiation driven winds is able to reproduce the main features of the outflow from Be stars provided that the process of turbulence excitation and a process of angular momentum supply of the disk from the central source are added in to this model.
1. Introduction
The physics of Be stars remains a hot topic in astrophysics for a century since the discovery of these objects. It is firmly established that the outflow from Be stars consists of a fast polar wind and a Keplerian disk at the equator [1,2], but we still have no answer for a key question of the physics of Be stars: how does it happen that powerful stellar radiation forms fast wind in the polar region while a Keplerian disk with very low radial velocity appears at the equator? The main reason is that our knowledge about Be stars is rather poor. We obtain some information about the Be star outflows from observations. However, to a large extent, the phenomenology of these sources is based on a simplified model that can not be justified by observations. Numerical modeling of outflows from Be stars provides a way to improve the situation, but up to now, all attempts to reproduce the basic observational properties of the outflow from Be stars, fast polar wind and Keplerian outflow at the equator, in one physical picture were not successful.
There is a common consent regarding physics of the polar wind. Polar outflows from Be stars are line-driven winds, i.e., ions in the wind are accelerated by the radiation pressure provided by absorption lines. The radiative force provides a high velocity of the wind and a high mass loss rate in agreement with observations. The polar wind has been modeled in many works under different assumptions [3,4,5]. While the key observation properties of the polar winds, e.g., their termination speed and mass loss rate, are reproduced in many simulations, none has succeeded with modeling of the Keplerian disk formation. The reason for that might be quite obvious.
Theoretical arguments [3,4,5] and observations [6,7,8] say in favor a viscous quasi Keplerian disk ([9,10,11,12,13]) (hereafter the decretion disk) around Be stars. In this disk, transport of the angular momentum from the rotating star to the outer edge of the disk is provided by turbulent viscosity, which is the key physical process in the disk. It is obvious that any model of the plasma outflow from the Be star that neglects the process of turbulence generation and viscosity has no chance to reproduce a viscous Keplerian decretion disk. Nevertheless, some other processes might also be important for the disk formation. They lead to the slower and denser flow at the equator such as bi-stability [14], wind compression [15] or effects of finite disk size and rotation [16]. All these processes facilitate formation of the Keplerian disks. Some of them are used in this work.
This work is additionally motivated by discovery of transient radiation from binary systems containing a massive Be star and a pulsar or a black hole [17]. Binary system is one of the representatives of such objects. It consists of a pulsar and massive O-type companion ([18,19,20]). Interaction of the pulsar wind with the outflow from the Be star leads to radiation in the range from radio to hard gamma rays with photon energy at least 10 TeV ([21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]). GeV flares 30–60 days after the passage of the periastron in 2010 [30], 2014 [29], 2017 [31,32] and in 2021 [33] are one of the most spectacular phenomena in this system. The luminosity of the system during these flares is comparable with the total rotational losses of the pulsar PSR 1259-63. So far, the physics of the flares is not clear [34,35,36]. However, its repetitive nature suggests that the hydrodynamics of the pulsar–stellar winds interaction plays a key role in understanding this phenomenon. This clearly shows how much we need a reliable model of the outflow from Be stars that could be able to reproduce simultaneously so different structures: fast polar wind and the decretion disk.
We have started a series of works in which we study the disk formation with computational models that include the process of generation of the hydrodynamic turbulence [37,38]. We also include the numerical model conventional processes: gravity, thermal pressure, rotation of the star, oblateness of the stellar surface due to rotation, acceleration of the wind due to scattering of the stellar radiation in lines of ions and impact of the finite size of the star on the radiative force.
This work is a direct continuation of our previous studies, in which we presented the results of the numerical simulation of the turbulent outflow from a fast rotating star neglecting the radiative acceleration [37] and taking into account the radiative acceleration [38]. It was found that a turbulent slow disk-like flow is formed at the equator at the typical velocity of rotation of the star close to 80% of the critical one. However, in contrast to our expectations, the properties of the revealed flow are quite different from the Keplerian disk. In particular, the angular momentum of gas elements is conserved, i.e., there is no angular momentum transport through the flow. The objective of the present work is to determine conditions or mechanisms that should be added to the model to provide formation of the Keplerian viscous disk. In this work, we modify the model as follows:
- The radiative force was corrected taking into account the finite size of the star. This correction is crucially important for the radiative winds. Without this correction the steady state solution crossing all the critical points [39] does not exist for rapidly rotating stars [16,40]. According to [16,40,41], adding a correction factor to the radiative force produces new solutions and allows the flow to pass though the new critical points.
- A mechanism of the angular momentum transport from the star to the outflow has been incorporated into the model. To force enabling the angular momentum transport, we adopt the stellar rotation speed slightly above the critical value. In this case, the surface of the star rotates slightly faster than the matter at the Kepler orbit. Angular momentum transfer from the star to the matter becomes unavoidable.
2. Methods
The numerical model was described in [37,38]. In comparison with the previous model, we modified the radiative force taking into account the finite size of the star. For details, we refer the reader to the mentioned works. Here, we discuss only new elements introduced into the model.
2.1. Radiative Acceleration
The line force is taken in the following simple form [16,41,42]:
where , and are force multiplier coefficients. As typical parameters for Be star LS2883, we adopt , and [41]. Modeling is performed only for this set of values. Other sets of parameter values, typically considered as feasible for Be stars, will be considered after developing the final version of the computer model.
We note that can be variable [43,44]. In this version of the model, we neglect this additional freedom of the solution. However, the computer model allows us to take this property into account in the future. is the dilution factor defined as [42]
As in this work, we set the factor to 1. However, we took into account correction of the radiative force due to finite radius of the star. In the limit of the spherically symmetric star, the dependence reduces to the additional correction factor in the radiative force, which has the following form under our approximations [16]:
where
and
In our work, is replaced by the star radius at the pole .
Oblateness of the star and gravity darkening also modify the radiative force [3]. This modification leads to the formation of a faster wind at the pole and slower at the equator. We neglect this effect on the obvious reason. The radiative force is determined basically by derivative . See Equation (1). In the viscous Keplerian disk, is very low compared even with the thermal velocity. The derivative is correspondingly very small as well. The radiative force appears small compared with all other forces in the disk. This explains why the Keplerian disk survive in the very luminous field of radiation of the star. The radiation goes through the disk without interaction with the matter. Therefore, it does not matter for the dynamics of the Keplerian disk if radiation field appears smaller at the equatorial region due to gravity darkening.
2.2. System of Equations
Gravity, rotation of the star, pressure gradients, turbulence and line acceleration are taken into account. Acceleration in continuum is neglected because it is reduced to renormalization of the gravity by a few percents. The problem is solved in the rotating coordinate system. The system of equations is as follows:
These are continuity equation, Navier–Stokes equation [45] and equation for intensity of turbulence k and the rate of the turbulence dissipation in the simplest model of hydrodynamical turbulence [46,47]. Here, is an eddy dynamical viscosity, and p and are the pressure and density. is the effective potential
including the gravitational and centrifugal potentials. Here, is the angular velocity of the star, R and r are the polar and cylindrical radius, is the radius of the star at the pole, is the mass of the star, G is the gravitational constant, , is the turbulent viscosity , are model constants [46,47]. We assume that gas is isothermal with the equation of state in the form , where C is the constant sound velocity, which is connected with the effective temperature of the star as follows , where is the Boltzmann constant, is mass of the particles of the wind.
2.3. Dimensionless Variables
As in our previous work [38], we consider the problem in dimensionless variables. Velocities are expressed in —Kepler velocity at the pole of the star, the distance is measured in radius of the star at the pole , density is measured in units of typical density of Be stars at the photosphere and dimensionless mass flow rate of the wind is defined as
where is the rate of mass loss.
Parameters of Be star in the binary system are given in [20,48] and [49] in a rather wide range. For definiteness, we use the following dimensionless squared sound velocity and [38].
It is convenient to represent the line radiative force in dimensionless form as well. According to [50], radially expanding cold wind driven only by radiation and gravitation has the following relationship between mass flow rate and luminosity of the star :
In [38], we introduced a dimensionless mass flow rate as . The physical sense of is evident. This is the dimensionless mass loss rate that a non-rotating star of a given mass and luminosity could create under assumption of a point source of radiation and neglecting thermal pressure. Then, the line radiative force in dimensionless variables can be rewritten as
The critical rotation speed of the star is determined by the condition when the stellar surface at the equator moves with the Keplerian speed. Taking into account the oblateness of the star due to rotation, one finds that [2].
2.4. Boundary Conditions
The system of Equations (6)–(9) is solved under axisymmetric approximation in a two-dimensional plane (r,z). The computational domain includes only the upper hemisphere. The oblateness of the star [2] has been taken into account. The star surface coincides with one of the lines where the effective potential is constant. At the surface of the star, we specify only the dimensionless density equal to 1. Taking into account that the star surface cannot coincide exactly with the line of the constant potential , we specify a more general condition at the star surface in the form
We set the effective potential to be 0 at the pole. Temperature is defined by constant . We do not fix the velocity of plasma at the stellar surface. The value and direction of the plasma velocity are determined in the process of solution. The density of the mass flux from every point of the stellar surface is determined by the solution.
The outer boundary of the computational domain is a sphere with radius 30 polar stellar radii, which greatly exceeds the radius of the critical points [39] in the flow. The velocity at this boundary has been determined at the simulation.
3. Results
3.1. Motivation of Consideration of the Supercritical Rotation
At the very beginning of our study, we assumed that introduction of the turbulence into the conventional model of radiation driven winds will automatically give us a viscous Keplerian disk. However, reality appeared more complicated.
In our previous study, we modeled the turbulent outflow from Be star at the angular velocity close to 70–90% of the critical angular velocity. We have obtained relatively slow turbulent outflow at the equator while the fast polar wind is formed in the polar region. The flow at the equatorial region was not steady state. It was variable with a small time scale. In this study, we take into account correction of the radiative force due to the finite size of the star. After that the solution becomes a steady state. However, in all cases, the equatorial flow does not converge to the Keplerian disk as we expected to obtain. Even in the limiting case, when we set the stellar angular speed to 0.999 of the critical one, the outflow at the equatorial plane remains non-Keplerian. Figure 1 demonstrates a poloidal cut of the velocity distribution in such a flow. The flow consists of two parts: fast polar wind accelerated by the radiation and the slow wind at the equatorial plane. Figure 2 shows density distribution in the poloidal plane. Density at the equator evidently essentially exceeds the density in the polar region. The disk-like outflow at the equator looks like a viscous disk. Nevertheless, this is not a Keplerian disk. The flow at the equator occurs with practically constant angular momentum along flow lines. It follows from Figure 3 that close to the star the angular momentum even slightly decreases.
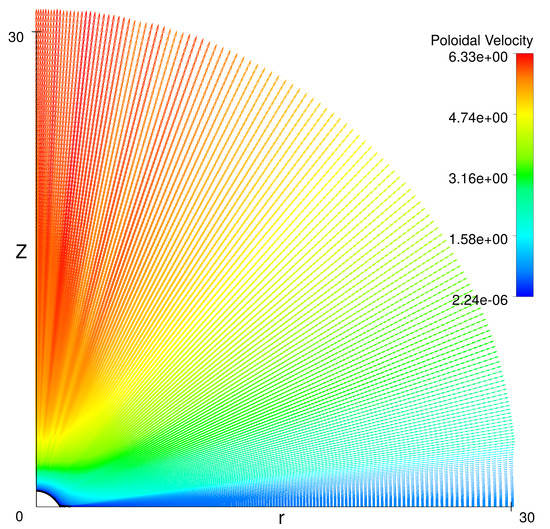
Figure 1.
The field of velocity in the poloidal plane at . Thick black solid line at the star surface—sound line for the poloidal velocity.
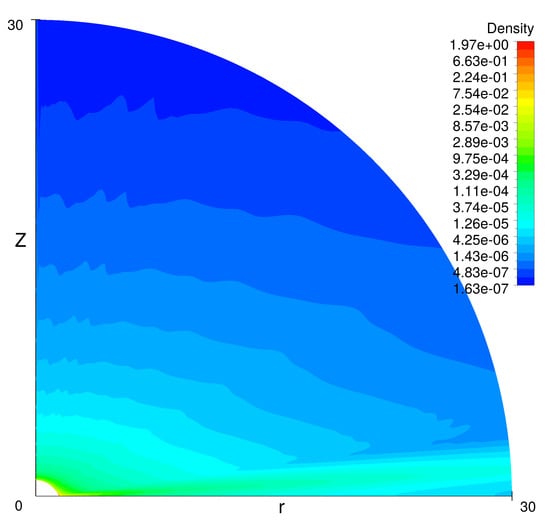
Figure 2.
The density at .
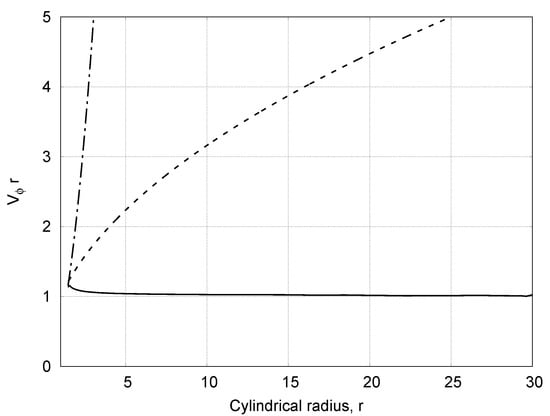
Figure 3.
Distribution of the angular momentum of the flow at the equatorial plane (solid line). Dashed line—angular momentum at the Keplerian rotation, and dashed-dotted line—angular momentum at the rigid rotation. The equatorial flow at remains non-Keplerian.
Thus, adding turbulence alone to the conventional model of the radiation driven winds does not result in the formation of a Keplerian disk. Our analysis has shown why this happens. The Keplerian decretion disk can exist only if the angular momentum from the central star is permanently transported due to turbulent viscosity to the outer edge of the disk [9]. Although turbulence is excited in the equatorial region, the angular momentum transfer from the star to the outflowing plasma is absent because the star that rotates slower than the inner edge of the disk is not able to transfer its angular momentum to the matter rotating on Keplerian orbit faster than the star. To create a viscous Keplerian disk, it is necessary incorporate into the model a physical mechanism that provides a transfer of the angular momentum from the star to the outflowing matter. The nature of this mechanism is not important for characteristics of disks. They are determined only by one parameter—the angular momentum that every particle of the outflow carries out from the star. This value also determines the size of the disk [9].
We expect that the most realistic mechanism for the process of the angular momentum transfer is the magnetic field. We already mentioned that a relatively weak chaotic magnetic field ∼ 10–20 can provide the mechanism for corotation of the plasma together with the star up to the distance where the toroidal velocity will reach or even exceed the Keplerian velocity. This magnetic field should be rather weak [38]. It is well below the typical upper limits on the magnetic field at the surface of Be stars [51,52]. This assumption does not contradict the observations.
At present, we have not in our hand a numerical code for simulation of the process of corotation of the outflowing plasma due to the magnetic field. However, we can verify our assumption by another way. We can consider a case when the star rotates slightly faster than the critical speed. If our assumption is correct, then the angular momentum transfer should allow the formation of a viscous Keplerian disk. Below, we consider two cases of the supercritical rotation assuming the shape of the star corresponding to the star rotating with angular velocity .
3.2. Rotation on 0.5% Faster Than Critical One
In Figure 4 and Figure 5, the field of velocity and density are shown for the rotation with . All the rest of parameters are the same like in the previous section. At first glance, there is no crucial difference in compare with the flow with . Only the slow turbulent region at the equator occupies larger cone and the zone of subsonic flow at the equator extends to a larger distance. However, inspection of Figure 6 shows that in this case, the flow becomes Keplerian up to the distance polar radius of the star. Our assumption is fully confirmed. Even exceeding the critical speeding by 0.5% activates the mechanism of the angular momentum transfer. After that, the turbulent viscosity provides transport of the angular momentum along the flow to the outer parts of the outflow.
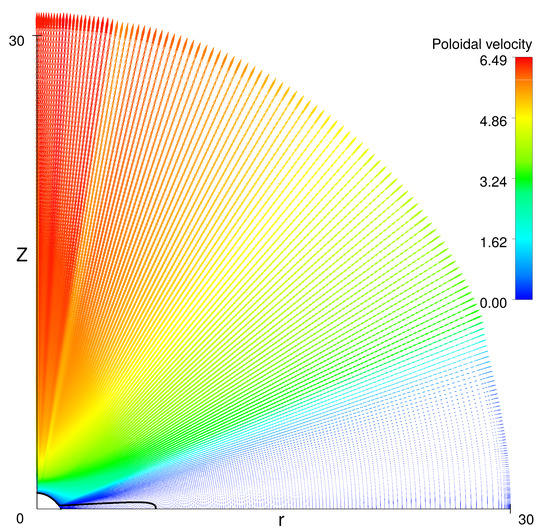
Figure 4.
The field of velocity in the poloidal plane at . Thick black solid line—sound line for the poloidal velocity.
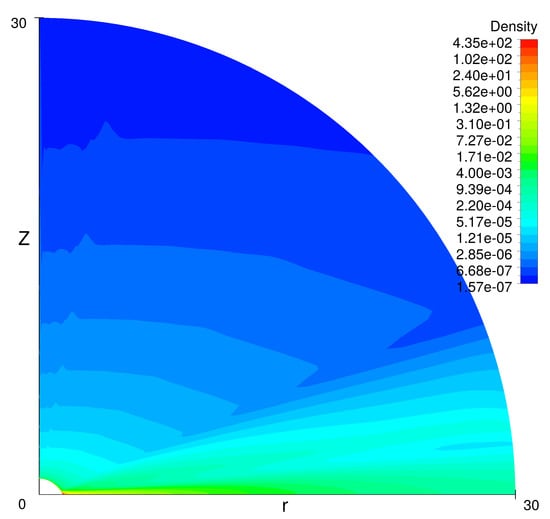
Figure 5.
The density in the poloidal plane at .
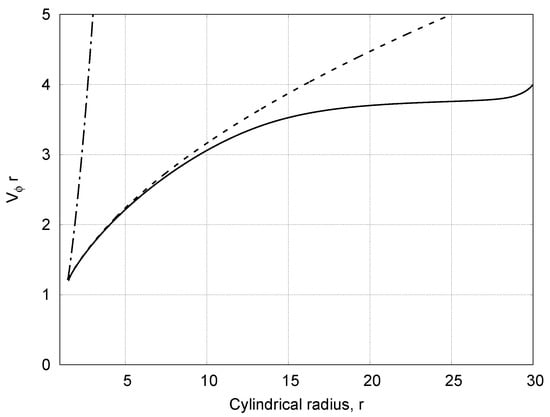
Figure 6.
Distribution of the angular momentum of the flow at the equatorial plane (solid line). Dashed line—angular momentum at the Keplerian rotation and dashed-dotted line—angular momentum at the rigid rotation. The equatorial flow at becomes Keplerian.
It follows from Figure 7 that in the polar region, we have fast polar wind accelerated by radiation. Very slow radial flow in the quasi-Keplerian disk takes place at the equator.
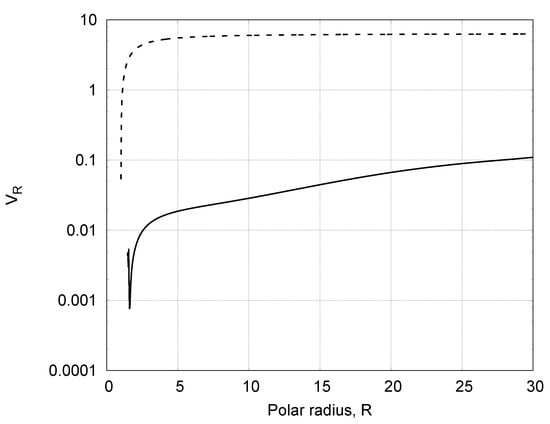
Figure 7.
Dependence of the poloidal velocity on the polar radius R at the equator (solid line) and at the axis of rotation (dashed line), .
3.3. Rotation on 1% Faster Than Critical One
An increase of the rotation velocity by additional 0.5% makes the picture more interesting. In Figure 8 and Figure 9, the field of velocity and density are shown for the rotation with . The cone of the slow turbulent flow at the equator increases even more with sudden expansion at ∼15 stellar radius. According to Figure 10, the radius of the viscous Kepler disk reaches 15–20 stellar radius. The size of the Keplerian disk evidently increases. According to Figure 11, the radial velocity of the flow at the equator is much smaller than at the pole. The radial velocity is even smaller than the same velocity in the case of .
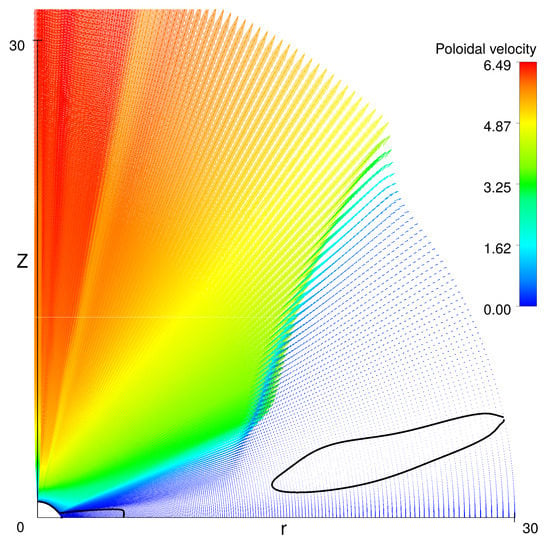
Figure 8.
The field of velocity in the poloidal plane at . Thick black solid line—sound line for the poloidal velocity.
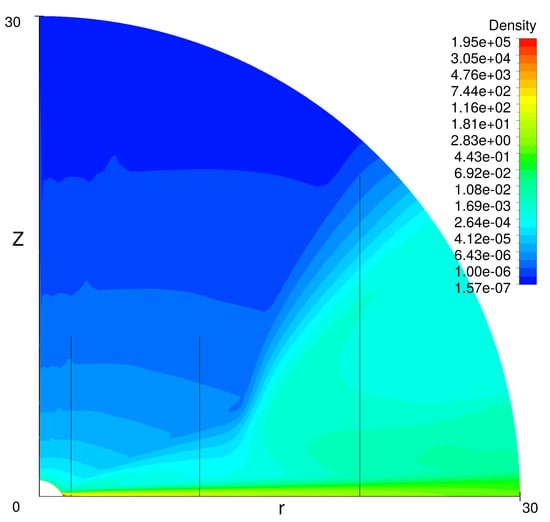
Figure 9.
The density at .
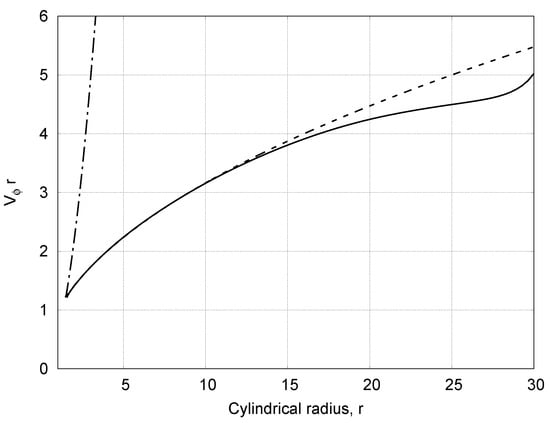
Figure 10.
Distribution of the angular momentum of the flow at the equatorial plane (solid line). Dashed line—angular momentum at the Keplerian rotation, and dashed-dotted line—angular momentum at the rigid rotation. The equatorial flow at is Keplerian up to 15 stellar radius.
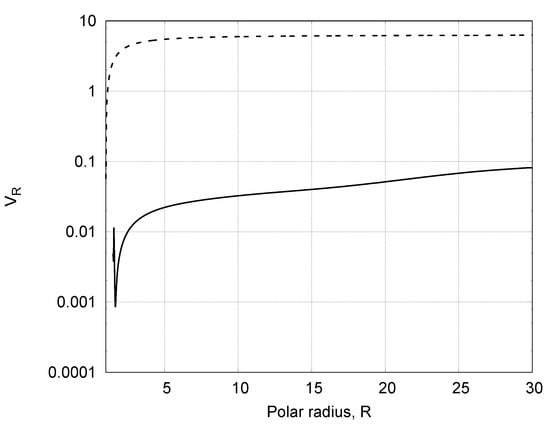
Figure 11.
Dependence of the poloidal velocity on the polar radius R at the equator (solid line) and at the axis of rotation (dashed line), .
The new feature of the flow at is the sudden expansion of the equatorial flow at . Figure 12 shows density distributions along lines perpendicular to the equator located at different distances from the star: 2, 10 and 20 radius of the star. They are shown in Figure 9 by thin vertical lines. The disk survives at least up to the distance of 20 stellar radii. This is a very thin and dense structure. In all cases, the density falls down with the height above the equatorial plane on a few orders of magnitude. In contrast, at larger distances, the distributions have rather wide wings, especially at distance 20. In the last case, the wing is produced by the wind from the disk. Formation of the wind from the disk supports the basic idea of the work [53].
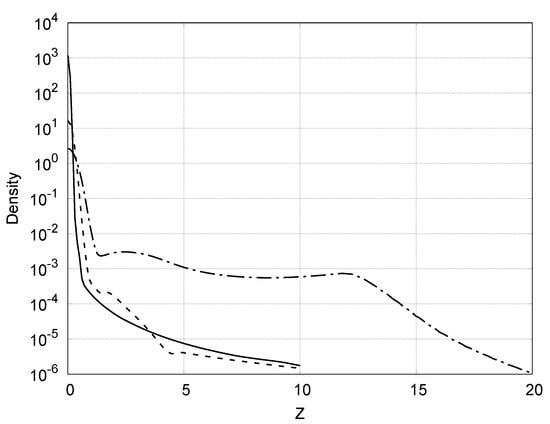
Figure 12.
Distribution of density across the disk at distance 2 (solid line), 10 (dashed line) and 20 stellar radius (dashed-dotted line) at .
An unusual property of the disk is high density of the disk at the stellar surface. Recall that the boundary condition at the star specified a constant density equal to 1. For sub-critical rotation speed, Equation (14) provides this condition. However, at a supercritical rotation Equation (14) leads to a huge density on the surface of the star at the equator. Figure 13 explains why this happens. Thick lines show the surface of the star for . Thin lines show the contours of the efficient potential . For clarity, the efficient potential is presented at . At a sub-critical rotation the surface of the star coincides with one of the contours of . At the supercritical rotation, the contour lines from the internal part of the star (where the density is high) cross the star surface at the equatorial region. Taking into account that this leads to the exponentially large growth of the density at the equator.
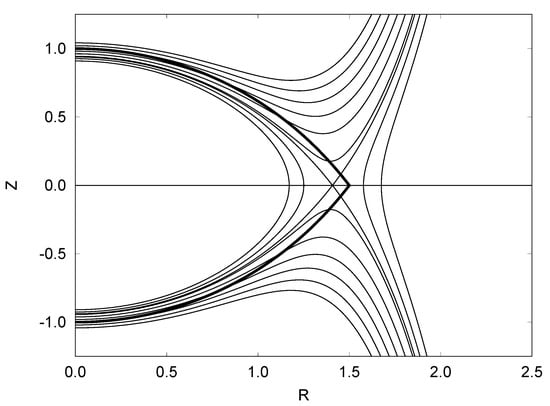
Figure 13.
The shape of the star surface at (thick solid line) and lines of the constant values of the effective potential (thin lines) at .
Due to this, we obtain in our model extremely dense Keplerian disks.
4. Discussion
In our previous work [38], we have obtained fast polar wind and slow equatorial flow considering subcritical rotation of the star, at = 0.8–0.9. The revealed equatorial flow appeared to be quite turbulent. The turbulence is excited at the equator due to stresses arising in the flow. According to the present work, this equatorial flow also remains non-Keplerian for very fast subcritical rotations, up to . The matter in the flow at the equator moves with the constant angular momentum. This shows that adding turbulence alone to the model of radiation driven winds does not lead to formation of the Keplerian decretion disk. We present the results obtained with the simplest model of turbulence. However, we tested another two parameter models of turbulence. The results are similar.
It is well known that Keplerian decretion disks can exist only if the angular momentum from the central source is transported along the disk to its outer edge [9,54]. We have turbulent viscosity in the model to transport the angular momentum along the disk. However, the mechanism of the angular momentum transfer from the central source to the inner edge of the disk is absent. There is no source of the angular momentum. The star rotating at 80–90% of the critical velocity is not able to transfer the angular momentum to the matter rotating at the Kepler orbit faster than the surface of the star. Thus, for formation of the disk, we need to add this mechanism.
The mechanisms of the angular momentum transfer by waves [55] or by magnetic field [56,57] were already considered. We also assume that the best candidate for this is a magnetic field, chaotic or regular. A magnetic field provides conventional mechanism for the angular momentum loss for a wide range of astrophysical objects starting with young stars and finishing by rotation powered pulsars. It would be natural if, in Be stars, magnetic fields allow angular momentum transfer as well. Magnetic fields are not conventionally detected at the surface of Be stars. Observations give only the upper limit on the magnetic field of the order of ∼100 G [51,52]. According to our estimates, the value of the magnetic field necessary to provide corotation of the plasma in the disk with the star at the distance ∼1.5 is close to 10 G [38]. In this case, our assumption does not contradict to observations. Detailed discussion of these estimates is outside the scope of our present work and will be given elsewhere.
It is worth mentioning that in a number of works, the impact of the regular magnetic field on the radiation driven wind has been considered [58,59,60]. The impact of the dipole magnetic field on the Keplerian disk has been considered in [61]. It is interesting that in the last work a ∼10 G magnetic field appears marginal. This field still does not destroy the disk, but its influence on the disk dynamics becomes noticeable.
The assumption about the impact of a weak magnetic field on the angular momentum transfer from the star to the disk deserves a special analysis in the future. At the present status of our understanding of the physics of the decretion disk formation, we have to ask the following questions. Will it be sufficient to add to the model a mechanism of the angular momentum transfer from the star to disk to obtain the Keplerian disk? Did we not again oversee something critical?
To answer on these questions it is necessary to perform modeling of the outflow from the rotating star with an enabled mechanism of the angular momentum supply. The nature of this mechanism is not so important. This mechanism has to provide a relatively large angular momentum per particle in the equatorial flow. If so, we can consider any physically reasonable (even if only theoretically) mechanism that can supply the disk with the angular momentum. As a temporal measure, we use here supercritical rotation of the star as such a mechanism. The idea is simple. The star inevitably has to transfer the angular momentum to the outflowing matter if it rotates slightly faster than the critical velocity of rotation. Our modeling of the plasma outflow at the supercritical rotation demonstrates the formation of the Keplerian disk at the equatorial plane already at 0.5% excess above the critical velocity. It is the first case when in one model taking into account all main physical processes we have obtained the fast polar wind and viscous Keplerian disk at the equator. This is the main result of our work. Now we know how the same physical processes can lead to the formation of so different outflows as the radiation driven wind at the pole and viscous Keplerian disk at the equator.
We explored the supercritical rotation to provide the angular momentum supply to the disk only as a “quick fix”. This does not mean that the Keplerian decretion disks are formed only at the supercritical rotation of Be stars. This evidently contradicts to observations and incorrect from the theoretical point of view. This means that search and investigation of the physically reasonable mechanism of the angular momentum supply of the disk by the central star is the key problem for understanding the mechanism of the Be star disk formation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.B.; methodology, S.B.; software, S.B. and M.P.; validation, S.B. and M.P.; formal analysis, S.B. and M.P.; investigation, S.B. and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, S.B.; writing—review and editing, S.B.; visualization, S.B. and M.P.; supervision, S.B.; project administration, S.B.; funding acquisition, S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant number 20-02-00205.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Porter, J.M.; Rivinius, T. Classical Be Stars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2003, 115, 1153–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivinius, T.; Carciofi, A.C.; Martayan, C. Classical Be stars. Rapidly rotating B stars with viscous Keplerian decretion disks. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2013, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranmer, S.R.; Owocki, S.P. The effect of oblateness and gravity darkening on the radiation driving in winds from rapidly rotating B stars. Astrophys. J. 1995, 440, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.P.; Cranmer, S.R.; Gayley, K.G. Inhibition FO Wind Compressed Disk Formation by Nonradial Line-Forces in Rotating Hot-Star Winds. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1996, 472, L115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrenz, P.; Puls, J. 2-D non-LTE models of radiation driven winds from rotating early-type stars. I. Winds with an optically thin continuum. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 358, 956–992. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, J.M. Continuum IR emission of Be star wind-compressed discs. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 324, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Wheelwright, H.E.; Bjorkman, J.E.; Oudmaijer, R.D.; Carciofi, A.C.; Bjorkman, K.S.; Porter, J.M. Probing the properties of Be star discs with spectroastrometry and NLTE radiative transfer modelling: β CMi. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, L11–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Monnier, J.D.; Che, X.; Schaefer, G.; Touhami, Y.; Gies, D.R.; Aufdenberg, J.P.; Baron, F.; Thureau, N.; ten Brummelaar, T.A.; et al. Gas Distribution, Kinematics, and Excitation Structure in the Disks around the Classical Be Stars β Canis Minoris and ζ Tauri. Astrophys. J. 2012, 744, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U.; Osaki, Y.; Saio, H. Viscous excretion discs around Be stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1991, 250, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, A.T.; Negueruela, I. A natural explanation for periodic X-ray outbursts in Be/X-ray binaries. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 377, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.M. On outflowing viscous disc models for Be stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 348, 512–518. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, R.G.; Carciofi, A.C.; Bjorkman, J.E.; Rivinius, T.; Baade, D.; Rímulo, L.R. The life cycles of Be viscous decretion discs: Time-dependent modelling of infrared continuum observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 464, 3071–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U. Viscous Decretion Discs around Rapidly Rotating Stars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 65, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelupessy, I.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M.; Vink, J.S. The radiation driven winds of rotating B[e] supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 359, 695–706. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman, J.E.; Cassinelli, J.P. Equatorial disk formation around rotating stars due to Ram pressure confinement by the stellar wind. Astrophys. J. 1993, 409, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, D.B.; Abbott, D.C. The theory of radiatively driven stellar winds. III—Wind models with finite disk correction and rotation. Astrophys. J. 1986, 311, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubus, G. Gamma-ray binaries and related systems. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2013, 21, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Manchester, R.N.; Lyne, A.G.; Bailes, M.; Kaspi, V.M.; Qiao, G.; D’Amico, N. PSR 1259-63—A binary radio pulsar with a Be star companion. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 387, L37–L41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melatos, A.; Johnston, S.; Melrose, D.B. Stellar wind and stellar disc models of dispersion and rotation measure variations in the PSR B1259-63/SS2883 binary system. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1995, 275, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negueruela, I.; Ribó, M.; Herrero, A.; Lorenzo, J.; Khangulyan, D.; Aharonian, F.A. Astrophysical Parameters of LS 2883 and Implications for the PSR B1259-63 Gamma-ray Binary. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 732, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Manchester, R.N.; McConnell, D.; Campbell-Wilson, D. Transient radio emission from the PSR B1259-63 system near periastron. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 302, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Ball, L.; Wang, N.; Manchester, R.N. Radio observations of PSR B1259-63 through the 2004 periastron passage. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 358, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.G.; Ball, L.; Skjæraasen, O. Inverse Compton emission of TeV gamma rays from PSR B1259-63. Astropart. Phys. 1999, 10, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Aye, K.M.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Berghaus, P.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; et al. Discovery of the binary pulsar PSR B1259-63 in very-high-energy gamma rays around periastron with HESS. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 442, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Anton, G.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Becherini, Y.; Behera, B.; Bernlöhr, K.; Bochow, A.; Boisson, C.; et al. Very high energy γ-ray observations of the binary PSR B1259-63/SS2883 around the 2007 Periastron. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 507, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Allafort, A.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; Bellazzini, R.; Berenji, B.; et al. Discovery of High-energy Gamma-ray Emission from the Binary System PSR B1259-63/LS 2883 around Periastron with Fermi. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 736, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyakova, M.; Abdo, A.A.; Neronov, A.; McSwain, M.V.; Moldón, J.; Ribó, M.; Paredes, J.M.; Sushch, I.; de Naurois, M.; Schwanke, U.; et al. Multiwavelength observations of the binary system PSR B1259-63/LS 2883 around the 2010–2011 periastron passage. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neronov, A.; Chernyakova, M. Radio-to-TeV γ-ray emission from PSR B1259 63. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2007, 309, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyakova, M.; Neronov, A.; van Soelen, B.; Callanan, P.; O’Shaughnessy, L.; Babyk, I.; Tsygankov, S.; Vovk, I.; Krivonos, R.; Tomsick, J.A.; et al. Multi-wavelength observations of the binary system PSR B1259-63/LS 2883 around the 2014 periastron passage. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 454, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliandro, G.A.; Cheung, C.C.; Li, J.; Scargle, J.D.; Torres, D.F.; Wood, K.S.; Chernyakova, M. Gamma-Ray Flare Activity from PSR B1259-63 during 2014 Periastron Passage and Comparison to Its 2010 Passage. Astrophys. J. 2015, 811, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wood, K.S.; Kerr, M.; Corbet, R.H.D.; Cheung, C.C.; Ray, P.S.; Omodei, N. A Luminous and Highly Variable Gamma-Ray Flare Following the 2017 Periastron of PSR B1259-63/LS 2883. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.P.; Ji, L.; Kong, L.D.; Liu, C.Z. The GeV emission of PSR B1259-63 during its last three periastron passages observed by Fermi-LAT. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 18, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.P.; Ji, L.; Kong, L.D.; Wang, P.J. Fermi-LAT Observation of PSR B1259-63 during Its 2021 Periastron Passage. Universe 2021, 7, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khangulyan, D.; Bogovalov, S.V.; Aharonian, F.A. Binary Pulsar System PSR B1259-63/LS2883 as a Gamma-Ray Emitter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 28, 1460169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogovalov, S.V.; Khangulyan, D.; Koldoba, A.; Ustyugova, G.V.; Aharonian, F. Modelling the interaction between relativistic and non-relativistic winds in binary pulsar systems: Strong magnetization of the pulsar wind. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 490, 3601–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khangulyan, D.; Aharonian, F.A.; Bogovalov, S.V.; Ribó, M. Post-periastron Gamma-Ray Flare from PSR B1259-63/LS 2883 as a Result of Comptonization of the Cold Pulsar Wind. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 752, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogovalov, S.V.; Petrov, M.A.; Timofeev, V.A. Winds from fast rotating stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 502, 2409–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogovalov, S.; Petrov, M. Modeling of the Wind/Disk Outflow from Be Stars. Universe 2021, 7, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, D.C. The theory of radiatively driven stellar winds. I. A physical interpretation. Astrophys. J. 1980, 242, 1183–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curé, M. The Influence of Rotation in Radiation-driven Wind from Hot Stars: New Solutions and Disk Formation in Be Stars. Astrophys. J. 2004, 614, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauldrach, A.; Puls, J.; Kudritzki, R.P. Radiation-driven winds of hot luminous stars—Improvements of the theory and first results. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 164, 86–100. [Google Scholar]
- Castor, J.I.; Abbott, D.C.; Klein, R.I. Radiation-driven winds in Of stars. Astrophys. J. 1975, 195, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudritzki, R.P. Line-driven Winds, Ionizing Fluxes, and Ultraviolet Spectra of Hot Stars at Extremely Low Metallicity. I. Very Massive O Stars. Astrophys. J. 2002, 577, 389–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muijres, L.E.; Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A.; Müller, P.E.; Langer, N. Predictions for mass-loss rates and terminal wind velocities of massive O-type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Fluid Mechanics; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Versteeg, H.K.; Malalasekera, W. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics. The Finite Volume Method; Longman Scientific and Technical; Longman Group: Harlow, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, S.; Manchester, R.N.; Lyne, A.G.; D’Amico, N.; Bailes, M.; Gaensler, B.M.; Nicastro, L. Radio observations of PSR B1259-63 around periastron. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 279, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Jones, J.C.A.; Deller, A.T.; Shannon, R.M.; Dodson, R.; Moldón, J.; Ribó, M.; Dubus, G.; Johnston, S.; Paredes, J.M.; Ransom, S.M.; et al. The geometric distance and binary orbit of PSR B1259-63. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 479, 4849–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudritzki, R.P.; Yorke, H.W.; Frisch, H. Radiation in Moving Gaseous Media: Eighteenth Advanced Course of the Swiss Society of Astrophysics and Astronomy; Geneva Observatory: Versoix, Switzerland, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnulo, S.; Landstreet, J.D.; Fossati, L.; Kochukhov, O. Magnetic field measurements and their uncertainties: The FORS1 legacy. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, A129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wade, G.A.; Grunhut, J.H.; MiMeS Collaboration. The MiMeS Survey of Magnetism in Massive Stars. In Proceedings of the Circumstellar Dynamics at High Resolution, Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 27 February–2 March 2012; Carciofi, A.C., Rivinius, T., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series. Volume 464, p. 405. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, N.D.; Kuiper, R. Line-driven ablation of circumstellar discs: IV. The role of disc ablation in massive star formation and its contribution to the stellar upper mass limit. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 4893–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkman, J.E.; Carciofi, A.C. Modeling the Structure of Hot Star Disks. In The Nature and Evolution of Disks Around Hot Stars; Ignace, R., Gayley, K.G., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 337, p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Neiner, C.; Mathis, S.; Saio, H.; Lee, U. Be Star Outbursts: Transport of Angular Momentum by Waves. In Progress in Physics of the Sun and Stars: A New Era in Helio- and Asteroseismology; Shibahashi, H., Lynas-Gray, A.E., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 479, p. 319. [Google Scholar]
- Cassinelli, J.P.; Brown, J.C.; Maheswaran, M.; Miller, N.A.; Telfer, D.C. A Magnetically Torqued Disk Model for Be Stars. Astrophys. J. 2002, 578, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Cassinelli, J.P.; Maheswaran, M. Magnetically Fed Hot Star Keplerian Disks with Slow Outflow. Astrophys. J. 2008, 688, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, D.B.; MacGregor, K.B. Winds from rotating, magnetic, hot stars. I. General model results. Astrophys. J. 1984, 282, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.; Ud-Doula, A. Magnetic Spin-Up of Line-Driven Stellar Winds. In Magnetic Fields in O, B and A Stars: Origin and Connection to Pulsation, Rotation and Mass Loss; Balona, L.A., Henrichs, H.F., Medupe, R., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 305, p. 350. [Google Scholar]
- Ud-Doula, A.; Owocki, S. The Effects of Magnetic Fields on Line-Driven Hot-Star Winds. In Magnetic Fields in O, B and A Stars: Origin and Connection to Pulsation, Rotation and Mass Loss; Balona, L.A., Henrichs, H.F., Medupe, R., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 305, p. 343. [Google Scholar]
- Ud-Doula, A.; Owocki, S.P.; Kee, N.D. Disruption of circumstellar discs by large-scale stellar magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 3049–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).