The Possibility of Mirror Planet as Planet Nine in the Solar System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mirror Planet in Solar System
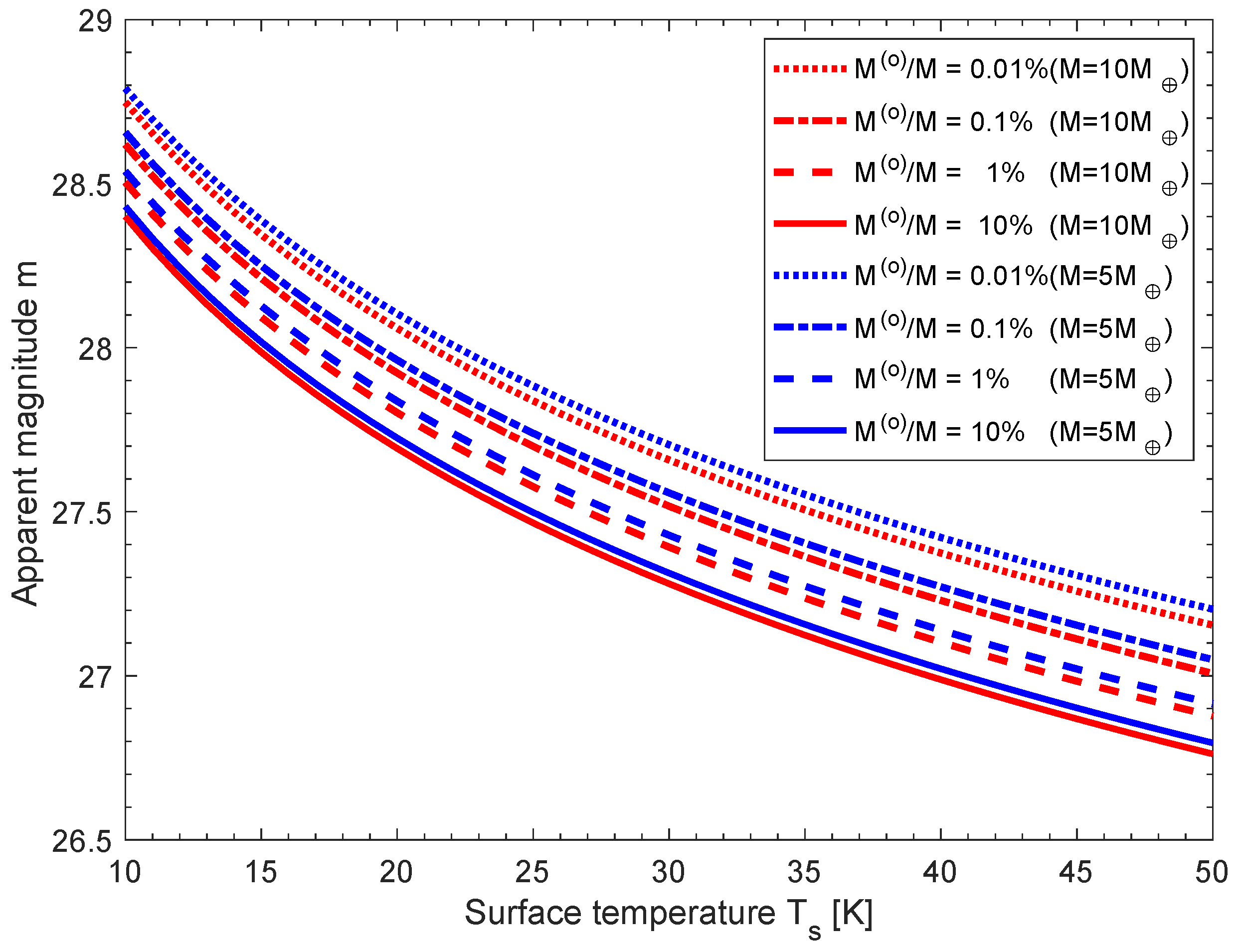
3. Observation of Mirror P9
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, M.E.; Trujillo, C.; Rabinowitz, D. Discovery of a candidate inner Oort cloud planetoid. Astrophys. J. 2004, 617, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, C.A.; Sheppard, S.S. A Sedna-like body with a perihelion of 80 astronomical units. Nature 2014, 507, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batygin, K.; Brown, M.E. Evidence for a distant giant planet in the solar system. Astron. J. 2016, 151, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batygin, K.; Adams, F.C.; Brown, M.E.; Becker, J.C. The planet nine hypothesis. Phys. Rep. 2019, 805, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Adams, F.C. Interaction cross sections and survival rates for proposed solar system member planet nine. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 823, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustill, A.J.; Raymond, S.N.; Davies, M.B. Is there an exoplanet in the Solar system? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2016, 460, L109–L113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.F.; Mordasini, C. Evolution and magnitudes of candidate Planet Nine. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 589, A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J. Measuring the radius and mass of Planet Nine. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2017, 129, 104401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, J.; Unwin, J. What if Planet 9 is a primordial black hole? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 051103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mróz, P.; Udalski, A.; Skowron, J.; Poleski, R.; Kozłowski, S.; Szymański, M.K.; Soszyński, I.; Wyrzykowski, Ł.; Pietrukowicz, P.; Ulaczyk, K.; et al. No large population of unbound or wide-orbit Jupiter-mass planets. Nature 2017, 548, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niikura, H.; Takada, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Sumi, T.; Masaki, S. Constraints on Earth-mass primordial black holes from OGLE 5-year microlensing events. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 083503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabayashi, T. Primordial black holes and mirror dark matter. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.09566. [Google Scholar]
- Tolos, L.; Schaffner-Bielich, J. Dark compact planets. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, R. Mirror dark matter: Cosmology, galaxy structure and direct detection. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2014, 29, 1430013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, R. Have mirror planets been observed? Phys. Lett. B 1999, 471, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Foot, R. Are mirror worlds opaque? Phys. Lett. B 2001, 505, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leung, S.C.; Chu, M.C.; Lin, L.M. Dark-matter admixed neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 107301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, M.Á.; Grigorian, H.; Albertus, C.; Barba, D.; Silk, J. Cooling of Neutron Stars admixed with light dark matter: A case study. Phys. Lett. B 2022, 827, 136937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haensel, P.; Zdunik, J.; Douchin, F. Equation of state of dense matter and the minimum mass of cold neutron stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 385, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.; Setford, J. Signatures of mirror stars. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, F.; Ciarcelluti, P. Effects of mirror dark matter on neutron stars. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 32, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, R.; Ignatiev, A.Y.; Volkas, R. Do “isolated” planetary mass objects orbit mirror stars? Astropart. Phys. 2002, 17, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, A.; Setford, J.; Curtin, D.; Matzner, C.D. How to search for mirror stars with Gaia. J. High Energy Phys. 2022, 2022, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, R.; Silagadze, Z. Do mirror planets exist in our solar system? arXiv 2001, arXiv:astro-ph/0104251. [Google Scholar]
- Foot, R.; Mitra, S. Mirror matter in the solar system: New evidence for mirror matter from Eros. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 19, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Foot, R. The mirror world interpretation of the 1908 Tunguska event and other more recent events. arXiv 2001, arXiv:hep-ph/0107132. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, R.; Gregoire, T.; Hall, L.J. Mirror World at the Large Hadron Collider 2005. Available online: http://xxx.lanl.gov/abs/hep-ph/0509242 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Chacko, Z.; Goh, H.S.; Harnik, R. A Twin Higgs model from left-right symmetry. JHEP 2006, 01, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, Z.; Nomura, Y.; Papucci, M.; Perez, G. Natural little hierarchy from a partially goldstone twin Higgs. JHEP 2006, 01, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kolda, C.; Low, M.; Tsai, Y. Mirror twin Higgs cosmology: Constraints and a possible resolution to the H0 and S8 tensions. J. High Energy Phys. 2022, 2022, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, Z.; Curtin, D.; Geller, M.; Tsai, Y. Direct detection of mirror matter in Twin Higgs models. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, L.; Yuan, G.W.; Feng, L.; Fan, Y.Z. Mirror dark matter and electronic recoil events in XENON1T. Nucl. Phys. B 2021, 965, 115369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beradze, R.; Gogberashvili, M. LIGO signals from the mirror world. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.lsst.org (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Available online: https://www.tmt.org (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Sanders, G.H. The Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT): An International Observatory. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2013, 34, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, W.; Fortney, J.; Lunine, J.; Burrows, A.; Sudarsky, D.; Pinto, P. Theory of extrasolar giant planet transits. Astrophys. J. 2001, 560, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippov, J.; Chobanu, M. Nemesis, Tyche, Planet Nine Hypotheses. I. Can We Detect the Bodies Using Gravitational Lensing? Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2016, 33, e033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Tang, Y.; Zu, L.; Chen, Y.; Feng, L. The Possibility of Mirror Planet as Planet Nine in the Solar System. Universe 2022, 8, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8100523
Wang P, Tang Y, Zu L, Chen Y, Feng L. The Possibility of Mirror Planet as Planet Nine in the Solar System. Universe. 2022; 8(10):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8100523
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pei, Yuchen Tang, Lei Zu, Yuanyuan Chen, and Lei Feng. 2022. "The Possibility of Mirror Planet as Planet Nine in the Solar System" Universe 8, no. 10: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8100523
APA StyleWang, P., Tang, Y., Zu, L., Chen, Y., & Feng, L. (2022). The Possibility of Mirror Planet as Planet Nine in the Solar System. Universe, 8(10), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8100523







