Radio Pulsars in an Electromagnetic Universe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Solution of Maxwell’S Equations for Stationary Magnetic Fields around Rotating Dipolar Magnetized NSs in the Electromagnetic Universe
2.1. Spacetime around NSs in the Electromagnetic Universe
2.2. An Exact Solution of Maxwell Equations for Magnetic Fields
3. Goldreich–Julian Charge Density
4. Solutions of Poisson Equations
4.1. Accelerating Parallel Electric Field in Near Zone
4.2. The Parallel Electric Field in Far Zone
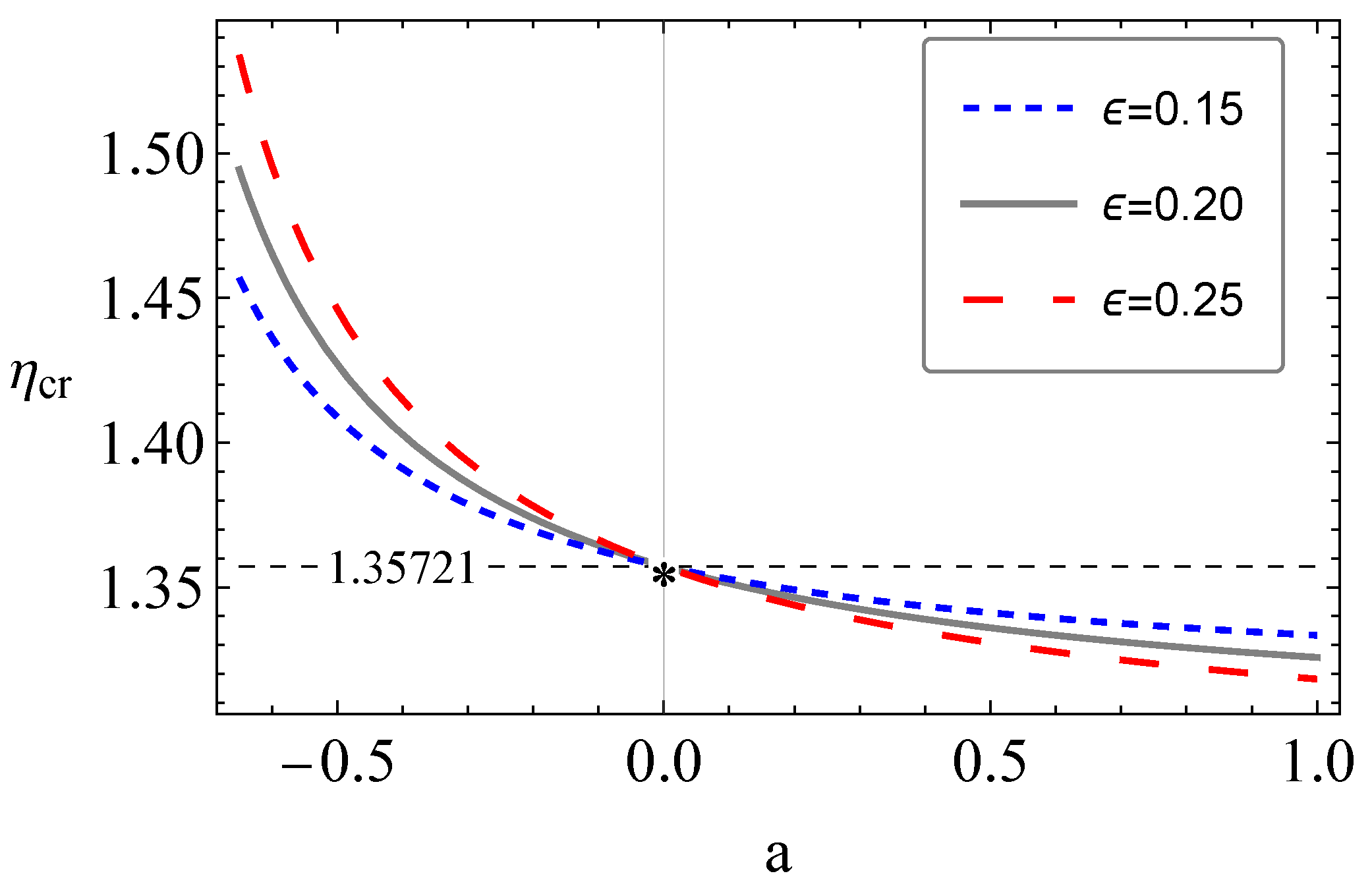
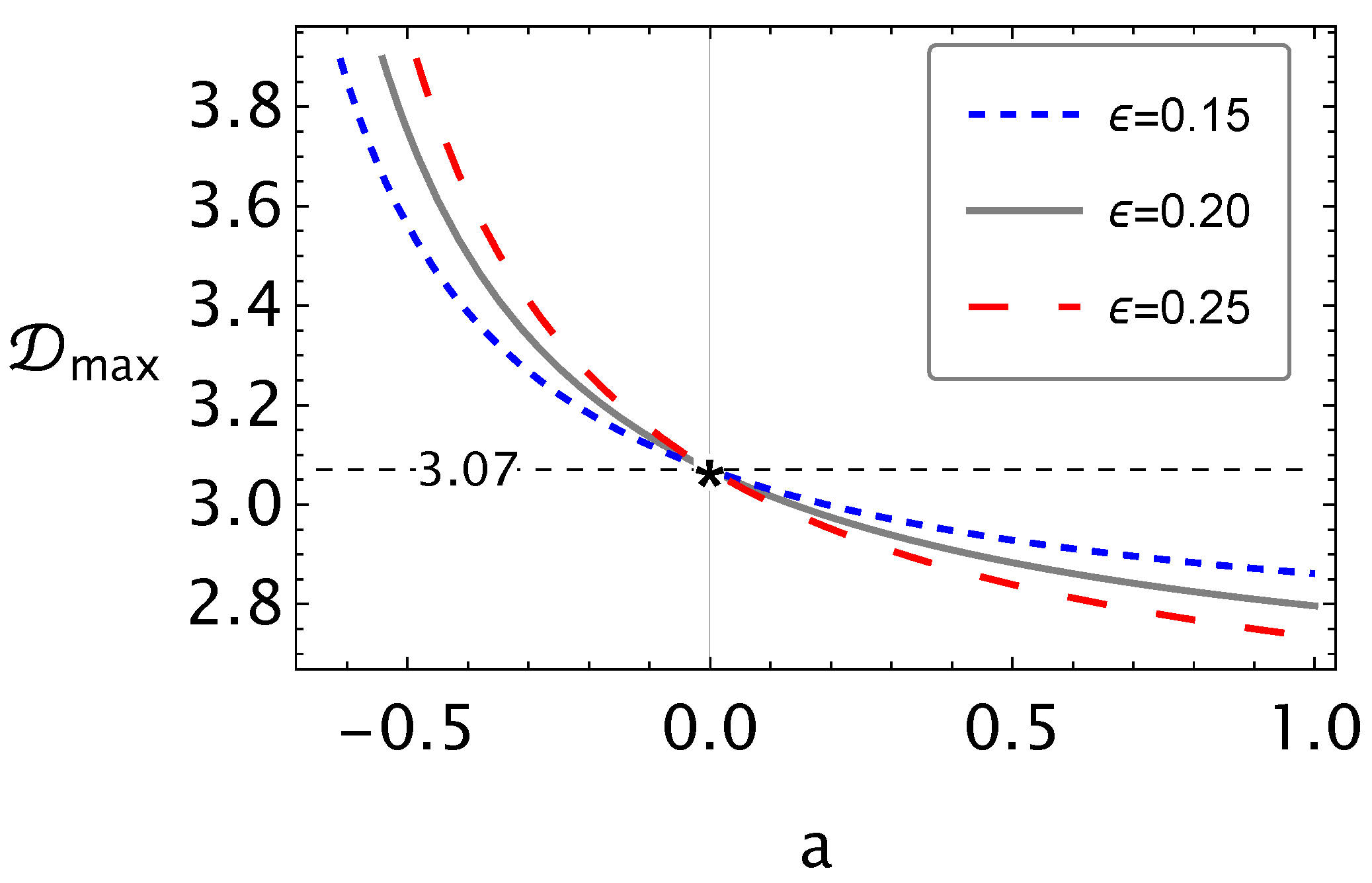
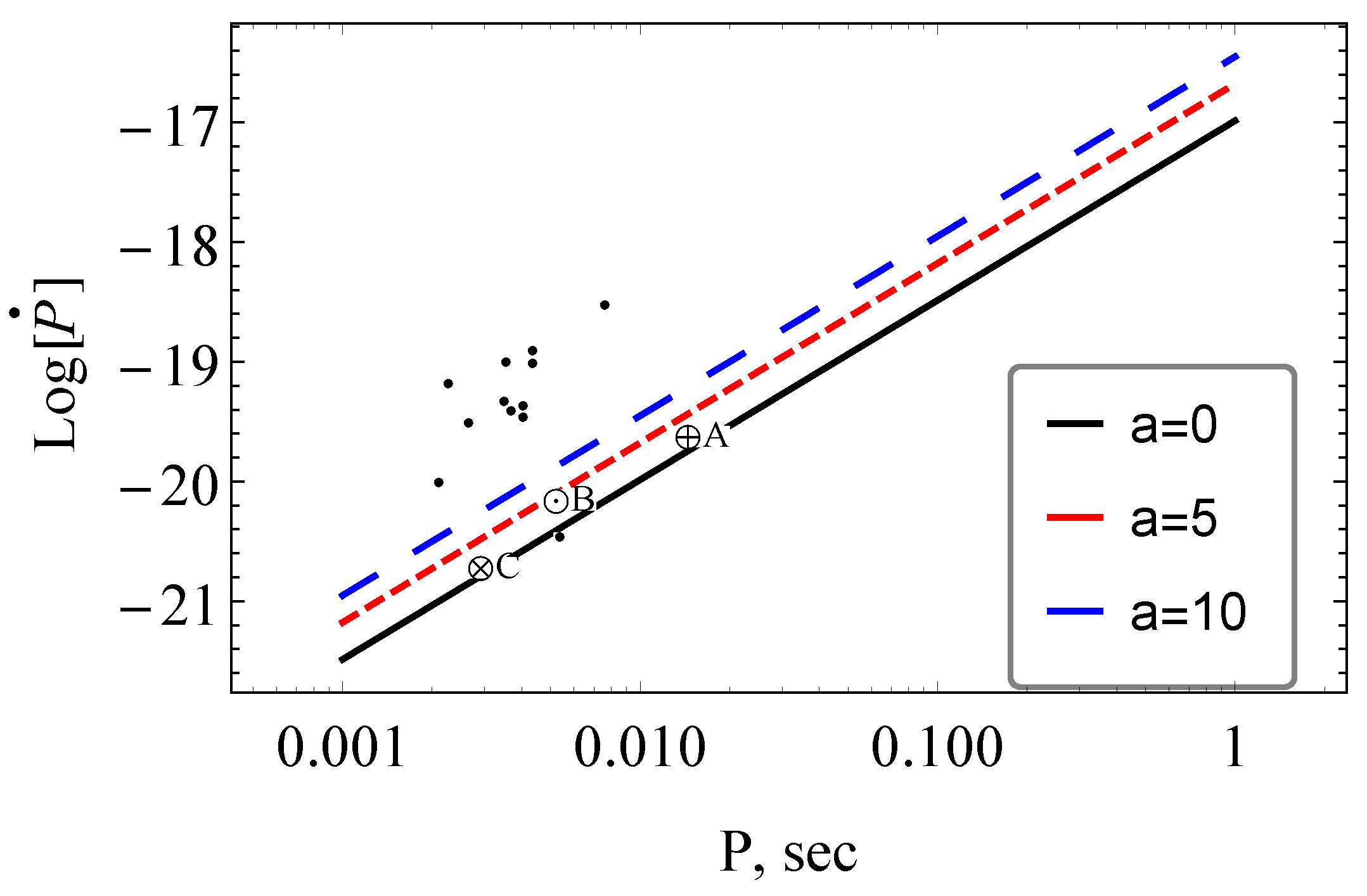
5. Death Line of Radio Pulsars
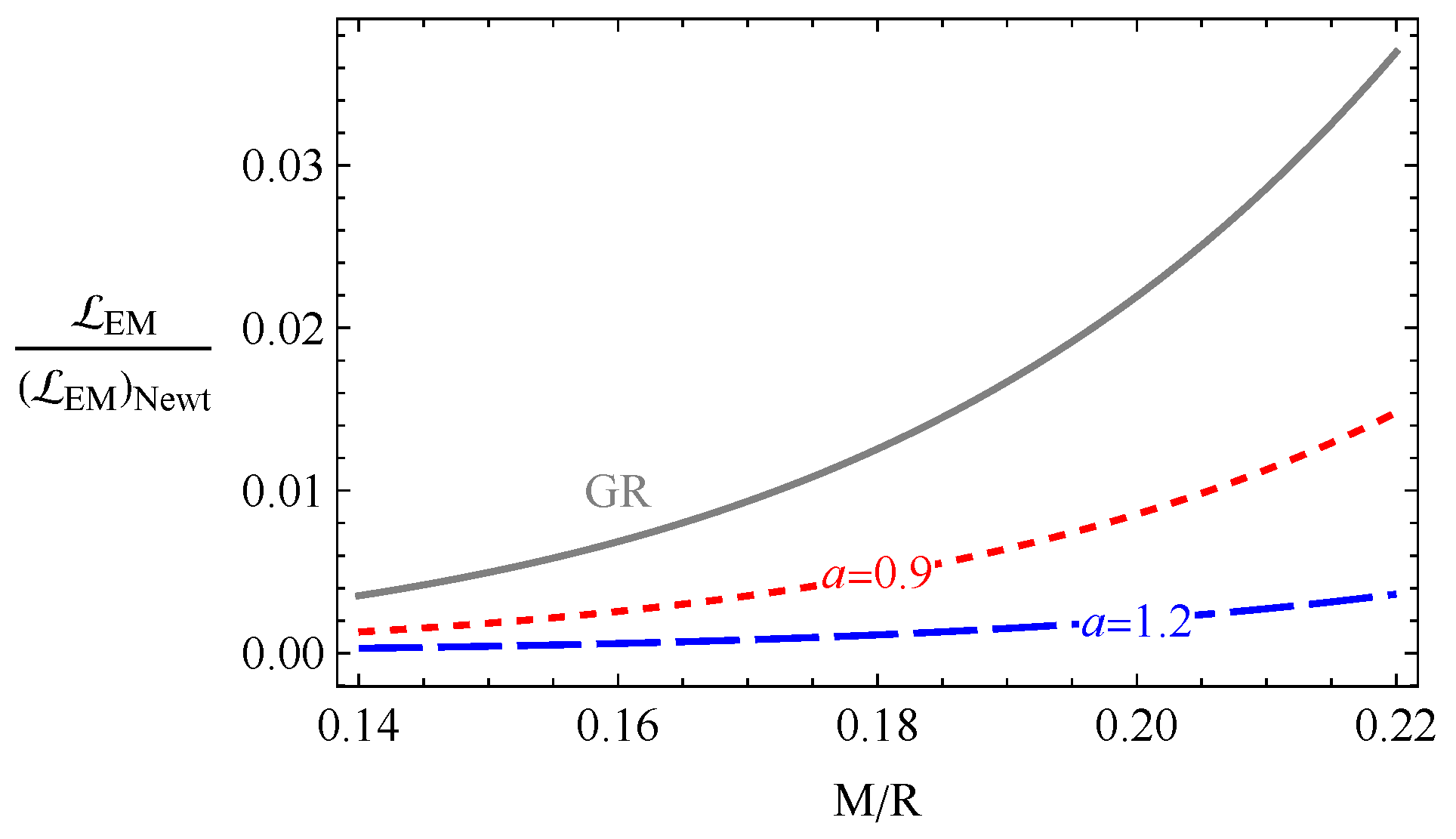
6. Energy Losses
6.1. Energy Losses by Magnetodipolar Radiations
6.2. Energy Losses through Plasma Magnetospheric Radiations
7. Conclusions
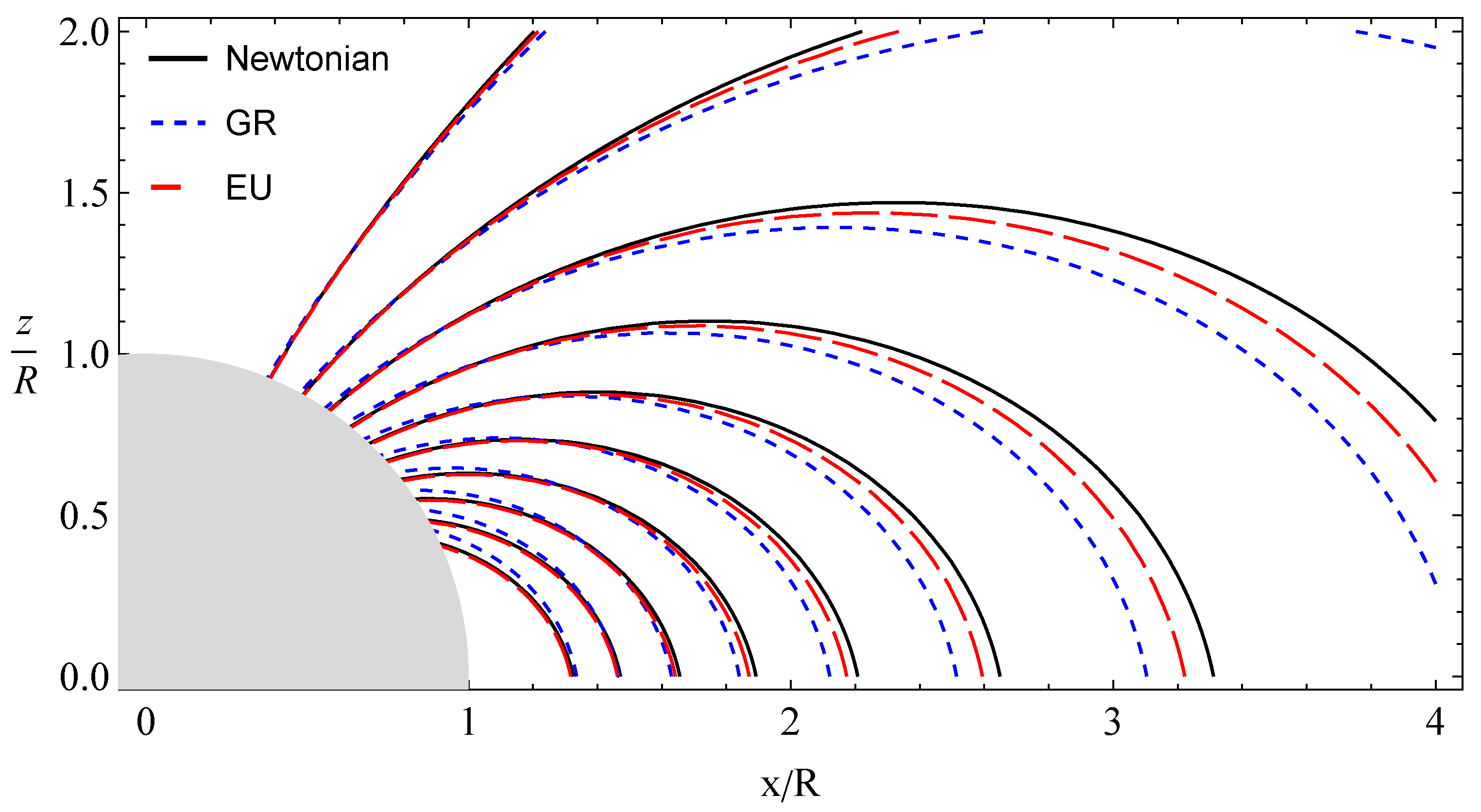
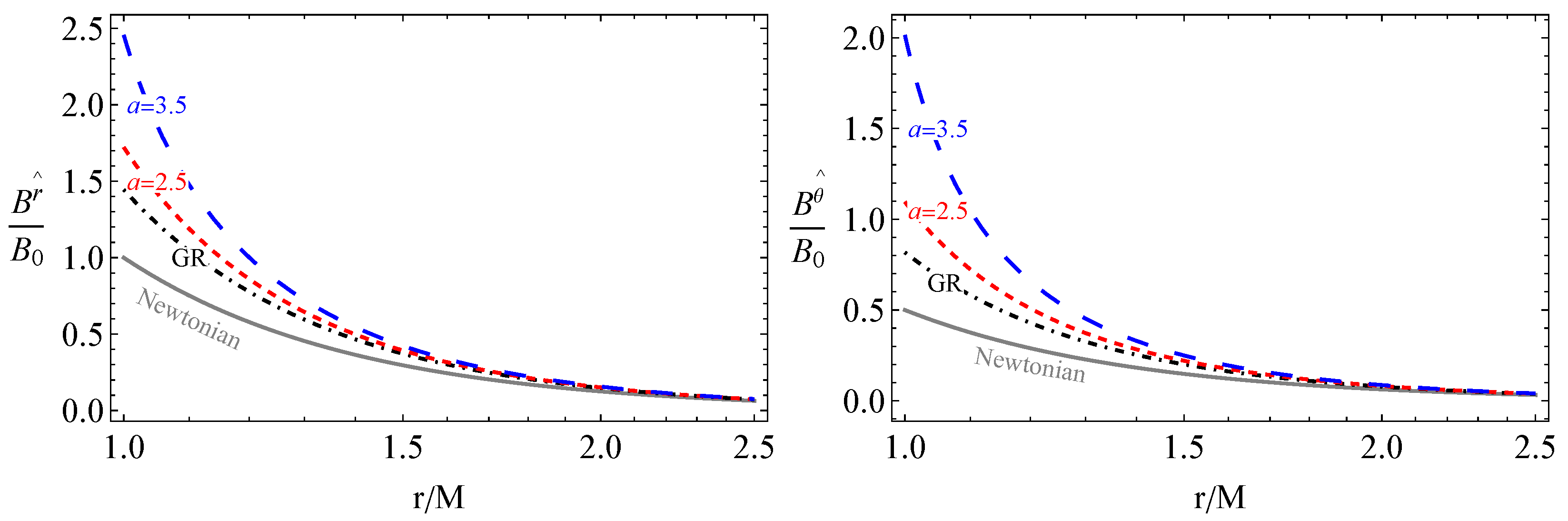
- We found the vacuum solutions of the Maxwell equations for electromagnetic fields of slowly rotating magnetized NSs. The effects of the EU parameter on magnetic field components are obtained. It is also shown that the presence of the EU field makes the field lines denser and stronger near the star in comparison with GR.
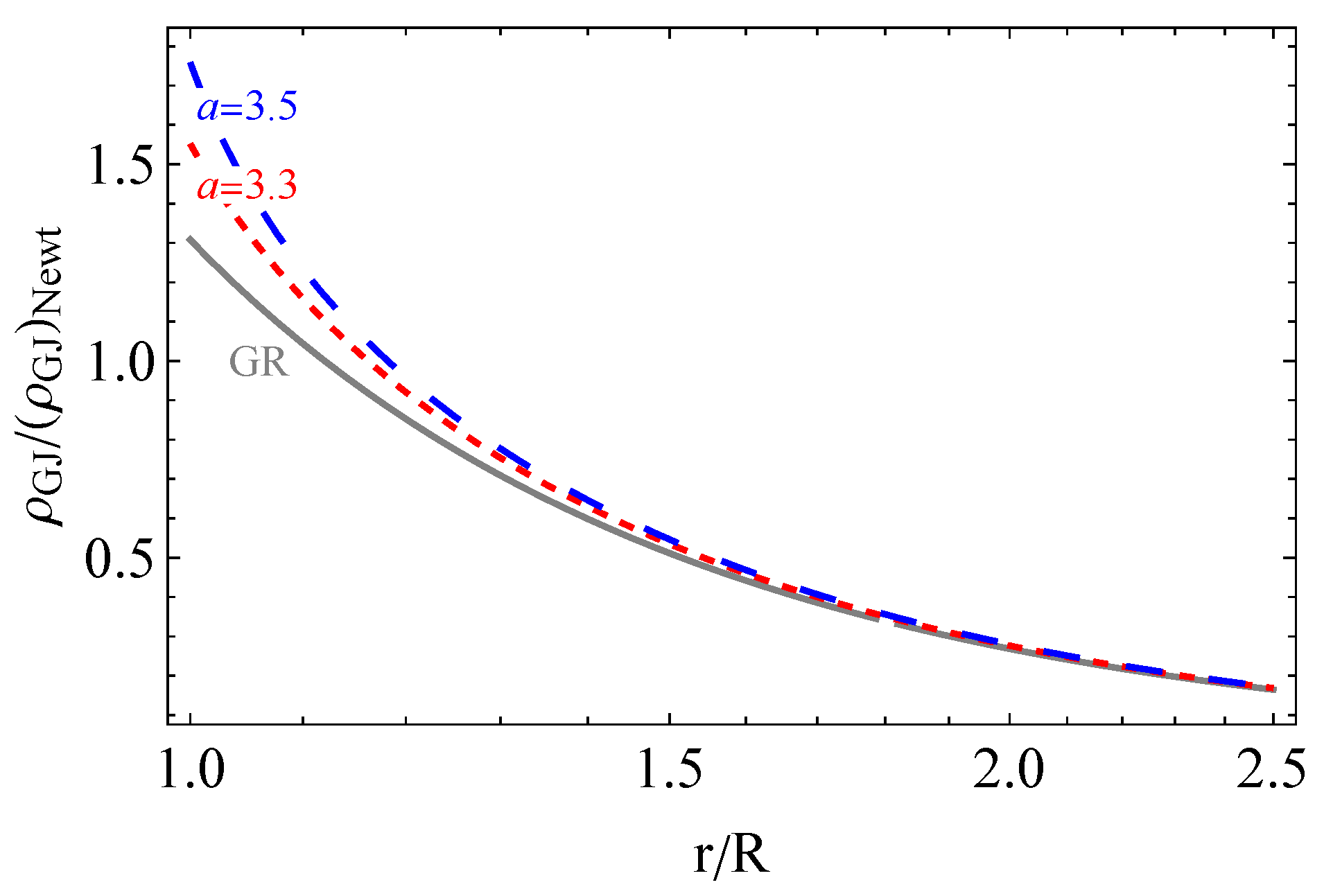
- We calculated the Goldreich–Julian charge density, which is responsible for the source of the induced electric field. The analyses of the effects of the EU parameter on the GJ charge density show that the charge density increases with an increase in the EU parameter.
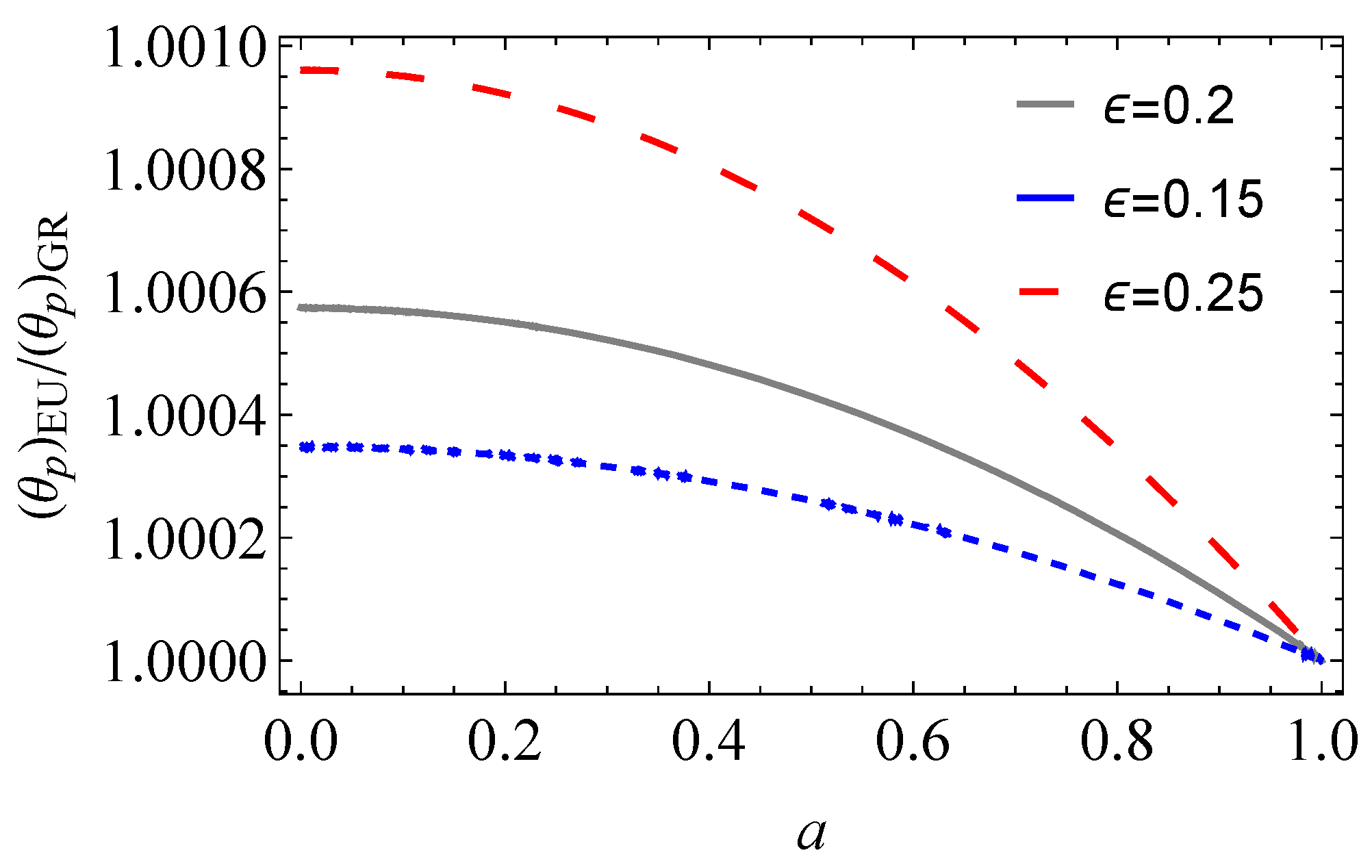
- The effects of the EU field on the size of the polar caps of NSs are also explored. It is found that the size decreases due to the presence of the EU.
- Solutions of the Poisson equation for the scalar electric field, which is parallel to the magnetic field lines, are also obtained at near and far zones in small-angle approximation by separating the variables and performing the Fourier–Bessel transformations, and it is observed that the parallel accelerating electric field increases in the presence of the EU.
- We also analyzed the effects of the EU on the death line conditions for radio pulsars, corresponding to the plasma magnetospheric radiations through inverse Compton scattering processes, and show that the position of the death line in the diagram shifts up, causing a pulsar which lies on the death line to become invisible.
- Using the death line condition for radio pulsars, and observational data from the pulsars, we found that the upper limits for the EU parameter for the pulsar J 2145-0750 is , while for the pulsars J 0024-7204 D and J 0024-7204 H, and .
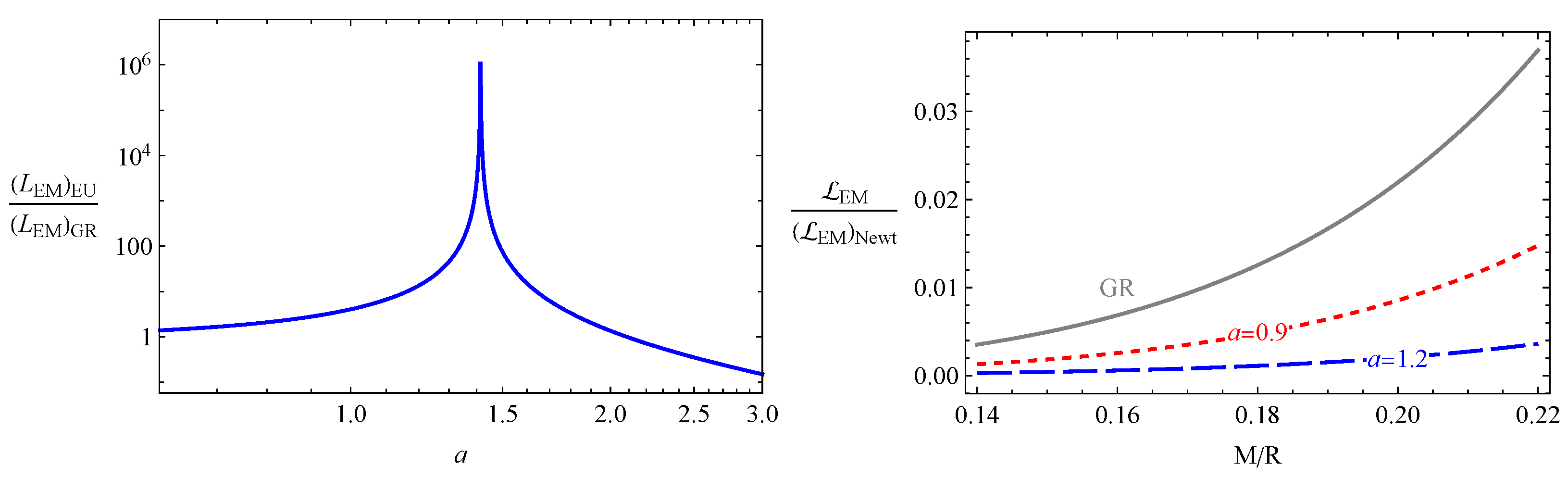
- Finally, we investigated magnetodipolar and plasma magnetospheric energy losses of rotating NSs. It is obtained that with the increase in the EU parameter, the magnetodipolar radiation luminosity decreases, while the luminosity of plasma magnetospheric radiations increases sufficiently. Moreover, at a critical value of the EU parameter, the electromagnetic radiations of magnetospheric radiation increase about times, and the critic value depends on the compactness parameter.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Solution of Poisson Equation
References
- Hewish, A.; Bell, S.J.; Pilkington, J.D.H.; Scott, P.F.; Collins, R.A. Observation of a Rapidly Pulsating Radio Source. Nature 1968, 217, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, F. Rotating Neutron Stars, Pulsars and Supernova Remnants. Nature 1968, 219, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, T. Rotating Neutron Stars as the Origin of the Pulsating Radio Sources. Nature 1968, 218, 731–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, A.J. The electromagnetic field of an idealized star in rigid rotation in vacuo. Ann. D’Astrophys. 1955, 18, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Muslimov, A.G.; Tsygan, A.I. Electric Fields Generated by a Rotating Neutron Star in a Vacuum with Allowance for Gtr Effects. Sov. Astonomy 1986, 30, 567. [Google Scholar]
- Konno, K.; Kojima, Y. General Relativistic Modification of a Pulsar Electromagnetic Field. Prog. Theor. Phys. 2000, 104, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Ahmedov, B.J.; Miller, J.C. General relativistic electromagnetic fields of a slowly rotating magnetized neutron star—I. Formulation of the equations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 322, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Ahmedov, B.J.; Miller, J.C. Stationary Electromagnetic Fields of a Slowly Rotating Magnetized Neutron Star in General Relativity. Found. Phys. 2001, 31, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedov, B.J.; Fattoyev, F.J. Magnetic fields of spherical compact stars in a braneworld. Rhys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 047501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimov, A.; Abdujabbarov, A.; Ahmedov, B. Magnetic fields of spherical compact stars in modified theories of gravity: F(R) type gravity and Hořava-Lifshitz gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 024008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turimov, B.V.; Ahmedov, B.J.; Hakimov, A.A. Stationary electromagnetic fields of slowly rotating relativistic magnetized star in the braneworld. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turimov, B.; Ahmedov, B.; Abdujabbarov, A.; Bambi, C. Electromagnetic fields of slowly rotating magnetized compact stars in conformal gravity. Phis. Rev. D 2018, 97, 124005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayimbaev, J.; Turimov, B.; Marcos, F.; Palvanov, S.; Rakhmatov, A. Particle acceleration and electromagnetic field of deformed neutron stars. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 35, 2050056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldreich, P.; Julian, W.H. Pulsar Electrodynamics. Astrophys. J. 1969, 157, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimov, A.G.; Tsygan, A.I. General relativistic electric potential drops above pulsar polar caps. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1992, 255, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, V.S.; Ahmedov, B.J. Quantum Interference Effects in Slowly Rotating Nut Space-Time. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2009, 18, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedov, B.J.; Fattoyev, F.J. Quasi-Stationary Electromagnetic Effects in Conductors and Superconductors in Schwarzschild Space-Time. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2005, 14, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayimbaev, J.R.; Ahmedov, B.J.; Juraeva, N.B.; Rakhmatov, A.S. Plasma magnetosphere of deformed magnetized neutron star. Astrophys. Space Sc. 2015, 356, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayimbaev, J.; Turimov, B.; Ahmedov, B. Braneworld effects in plasma magnetosphere of a slowly rotating magnetized neutron star. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1950128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayimbaev, J.; Turimov, B.; Palvanov, S. Plasma magnetosphere of slowly rotating magnetized neutron star in branewold. Int. J. Mod. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 49, 1960019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedov, B.J.; Khugaev, A.V.; Abdujabbarov, A.A. External electromagnetic fields of a slowly rotating magnetized star with gravitomagnetic charge. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2012, 337, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedov, B.J.; Abdujabbarov, A.A.; Fayzullaev, D.B. Plasma magnetosphere and spin down of rotating magnetized strange stars in general relativity. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2013, 346, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedov, B.J.; Morozova, V.S. Plasma magnetosphere formation around oscillating magnetized neutron stars. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2009, 319, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, V.S.; Ahmedov, B.J.; Zanotti, O. Explaining the subpulse drift velocity of pulsar magnetosphere within the space-charge limited flow model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 444, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdikamalov, E.B.; Ahmedov, B.J.; Miller, J.C. The magnetosphere of oscillating neutron stars in general relativity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 395, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mofiz, U.A.; Ahmedov, B.J. Plasma Modes along the Open Field Lines of a Neutron Star. Astrophys. J. 2000, 542, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rezzolla, L.; Ahmedov, B.J. Electromagnetic fields in the exterior of an oscillating relativistic star—I. General expressions and application to a rotating magnetic dipole. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 352, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rezzolla, L.; Ahmedov, B.J. Electromagnetic fields in the exterior of an oscillating relativistic star—II. Electromagnetic damping. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 4144–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halilsoy, M.; Al-Badawi, A. Metric for a static mass coupled to a stationary electromagnetic field. Class. Quantum Gravity 1995, 12, 3013–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, B. Uniform Electromagnetic Field in the Theory of General Relativity. Phys. Rev. 1959, 116, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Badawi, A.; Owaidat, M.Q.; Tarawneh, S. The geodesics structure of Schwarzschild black hole immersed in an electromagnetic universe. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2017, 26, 1750169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimov, A.; Harding, A.K. Toward the Quasi–Steady State Electrodynamics of a Neutron Star. Astrophys. J. 1997, 485, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippov, A.A.; Cerutti, B.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Spitkovsky, A. Ab Initio Pulsar Magnetosphere: The Role of General Relativity. Astrophys J. 2015, 815, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, J.K.; Harding, A.K. Electromagnetic cascades in pulsars. APJ 1982, 252, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, V.V.; Melrose, D.B. Pulsars with strong magnetic fields: Polar gaps, bound pair creation and nonthermal luminosities. Aust. J. Phys. 1995, 48, 571–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomiashvili, D.; Machabeli, G.; Malov, I. On the Nature of Radio Pulsars with Long Periods. Astrophys. J. 2006, 637, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kantor, E.M.; Tsygan, A.I. The Death Lines of Radio Pulsars for Dipolar and Asymmetric Magnetic Fields. Astron. Rep. 2004, 48, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Freire, P.C.; Camilo, F.; Kramer, M.; Lorimer, D.R.; Lyne, A.G.; Manchester, R.N.; D’Amico, N. Further results from the timing of the millisecond pulsars in 47 Tucanae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 340, 1359–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, J.; Ray, P.S.; Taylor, G.B.; Blythe, J.N.; Clarke, T.; Craig, J.; Ellingson, S.W.; Helmboldt, J.F.; Henning, P.A.; Lazio, T.J.W.; et al. Detection and Flux Density Measurements of the Millisecond Pulsar J2145-0750 below 100 MHz. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 775, L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskin, V.S. General Relativity Effects on Electrodynamic Processes in Radio Pulsars. Sov. Astron. Lett. 1990, 16, 286. [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty, J.K.; Harding, A.K. Gamma-Ray Pulsars: Emission from Extended Polar CAP Cascades. Astrophys. J. 1996, 458, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.P.; Zhang, B. Fast Radio Bursts and Their High-energy Counterparts from Magnetar Magnetospheres. Astrophys. J. 2021, 919, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyutikov, M. Escape of Fast Radio Bursts from magnetars’ magnetospheres. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.08435. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rayimbaev, J.; Jumaniyozov, S.; Umaraliyev, M.; Abdujabbarov, A. Radio Pulsars in an Electromagnetic Universe. Universe 2022, 8, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8100496
Rayimbaev J, Jumaniyozov S, Umaraliyev M, Abdujabbarov A. Radio Pulsars in an Electromagnetic Universe. Universe. 2022; 8(10):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8100496
Chicago/Turabian StyleRayimbaev, Javlon, Shokhzod Jumaniyozov, Maksud Umaraliyev, and Ahmadjon Abdujabbarov. 2022. "Radio Pulsars in an Electromagnetic Universe" Universe 8, no. 10: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8100496
APA StyleRayimbaev, J., Jumaniyozov, S., Umaraliyev, M., & Abdujabbarov, A. (2022). Radio Pulsars in an Electromagnetic Universe. Universe, 8(10), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8100496






