Abstract
In the last 20 years, modern wide-field surveys discovered a new class of peculiar transients, which lie in the luminosity gap between standard supernovae and classical novae. These transients are often called “intermediate luminosity optical transients” or “gap transients”. They are usually distinguished in subgroups based on their phenomenology, such as supernova impostors, intermediate luminosity red transients, and luminous red novae. In this review, we present a brief overview of their observational features and possible physical scenarios to date, in the attempt to understand their nature.
1. Introduction
Beyond supernovae (SNe), few cosmic events can release an amount of kinetic energy of the order of 10 erg (1 foe). On the higher end of the energy spectrum, we find Superluminous SNe (SL SNe; e.g., [1,2,3,4]), which are extreme examples of stellar explosions, and in some cases, Fast Blue Optical Transients (FBOTs; e.g., [5,6,7,8,9,10]) can even exceed the energy released by SL SNe. On the other hand, a growing number of stellar transients release less kinetic energy than the typical SNe, while still being more luminous than classical Novae. The names Intermediate luminosity optical transients [11,12,13] or gap transients refer to such underluminous events. The early discoveries of gap transients were made a few decades ago (e.g., M31-RV, SN 1997bs; see [14,15]); today, after the introduction of wide-field synoptic surveys, such as the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF; e.g., [16]), the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS; e.g., [17]), and the Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System (Pan-STARRS; e.g., [18]), the number of transients populating this luminosity gap keeps growing: it is time to provide a clearer picture of these phenomena.
In the poorly known luminosity range known as the “gap” [19], we find several types of stellar transients with heterogeneous observational properties and various physical origins. This luminosity gap contains the giant eruptions of massive stars including luminous blue variables (LBVs), intermediate-luminosity red transients (ILRTs), and luminous red novae (LRNe) (see Figure 1). Although these gap transients belong to different subtypes, their observational features are often similar; hence, their classification can be challenging. They also share physical characteristics, such as being on the Optical Transient Stripe (see e.g., [20,21,22,23]). This motivated us to systematically summarise their observations and physics to date.
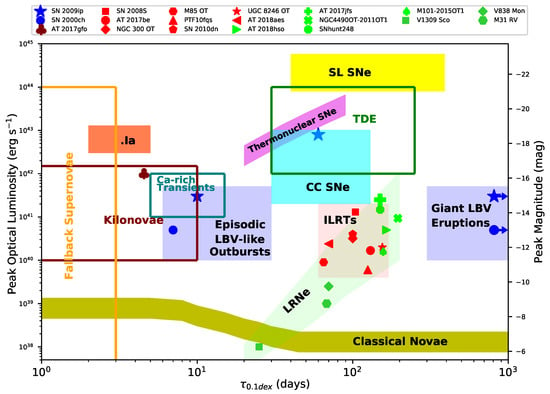
Figure 1.
Peak optical luminosity vs. characteristic time (defined as the time for a luminosity decline of 0.1 dex) for optical transients in the local Universe. Various regions, marked by different colours and shapes, indicate the general location of some representative classes of transients (e.g., superluminous SNe (SL SNe), tidal disruption event (TDE), Thermonuclear and core-collapse SNe (CC SNe), classical novae, Ca-rich transients, SNe .Ia, Kilonovae, fallback SNe, events from LBVs, ILRTs, LRNe). Figure adapted from Rau et al. [24], Kasliwal et al. [25].
2. Supernova Impostors
Massive (≥40 ) stars close to the end of their evolutionary paths can experience luminous, non-terminal eruptions, in which they can lose from tenths to tens of solar masses [26]. Because their spectra and photometric properties mimic those of genuine Type-IIn SNe [27,28], but the progenitors survived the events, these gap transients are often dubbed as “Supernova impostors” [14,29]. These events are usually associated with Luminous Blue Variables (LBVs; [30]). LBVs are a short phase in the final evolution of evolved and massive stars [31], during which they can reach and exceed a luminosity of 10 . In recent times a lot of effort has been devoted to solve the disagreement regarding the ‘sociality’ of LBVs, i.e., if they tend to be isolated stars or confined in binary systems, and whether they are associated or not with other young massive stars (see, e.g., [32,33,34,35], for discording results). This discrepancy has profound implications on their evolution, both regarding their mass loss history and age.
LBVs can experience bright and years-long “giant eruptions”, the most famous example being the luminous event from the Galactic LBV Carinae (see the left panel of Figure 2) in the middle of 19th century [30,36,37], during which the star reached an impressive absolute magnitude of −14 mag [38,39], shortly becoming the second brightest star in the night sky and releasing an amount of energy comparable to that of an SN event [26]; however, it survived the event. Smith [40] proposed a model in which a violent collision of stars in an eccentric binary system at the periastron may have been the cause of the Great Eruption of Carinae around the 1840s. Another Galactic star recognised as an LBV is P Cygni (in which the homonym spectral line profile was firstly observed), which experienced repeated outbursts around four centuries ago [41]. Interestingly, P Cygni was also suggested to be a binary system [42]. During the great eruptions, the star’s mass loss rate increases significantly, becoming greater than 10/10 Myr [43], even of the order of 10 Myr for Carinae, and several to tens of solar masses are expelled during its entire duration ([44], from the mass of the Homunculus Nebula, created after the 1843 Event).
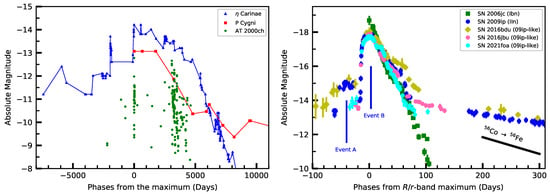
Figure 2.
Left panel: -band absolute light curves of historical LBV eruptions. Right panel: -band absolute light curves of SN2009ip-like objects with pre-supernova outbursts. The light curve peaks of SN 2009ip, indicated as ‘Event A’ and ‘B’, are marked. The expected decline rate from the radioactive decay of Co into Fe is also reported. The late-time decline rate of the light curves is shallower than the one expected from simple Co decay, therefore suggesting the presence of an additional powering source in the form of CSM interaction. Data from Smith and Frew [39], Frew [45], Foley et al. [46], Smith et al. [47], Pastorello et al. [48,49,50,51], Fraser et al. [52,53], Brennan et al. [54, 55], Reguitti et al. [56].
Occasionally, extragalactic giant eruptions can be observed in external nearby galaxies, such as AT 2000ch [57], a well-known LBV in the galaxy NGC 3432, which generated multiple bright outbursts (up to ∼ mag) since its discovery (see the left panel of Figure 2), most notably in 2008 and 2009 [49]. Other relevant examples include the SN 1954J [58] and SN 2002kg [59] events, identified as major brightenings of two known LBVs in the galaxy NGC 2403 [60,61], and SN 1997bs [14], an analogue of the Carinae eruption in M66. In some occasions, isolated outbursts from massive hypergiants/LBVs are also observed [62,63].
The spectra of such events reveal narrow (∼10–10 , [64]) emission lines from the Balmer series on top of blue continua (see some important examples in Figure 3). The narrow emission lines result from the photoionization of the unshocked circumstellar medium (CSM) surrounding the star [65]. It is still unclear how major mass-loss episodes can be triggered. Stellar encounters in close binary systems is a viable explanation for some Giant Eruptions, as Carinae itself is in a binary system [66]. For single stars, instead, extreme super-Eddington continuum-driven winds have also been invoked [67], although it is unknown what can lead to a sudden and conspicuous excess in the star’s Eddington luminosity/mass limit (see also [68]). One possibility is a variation in opacity at the helium peak beneath the surface [69].
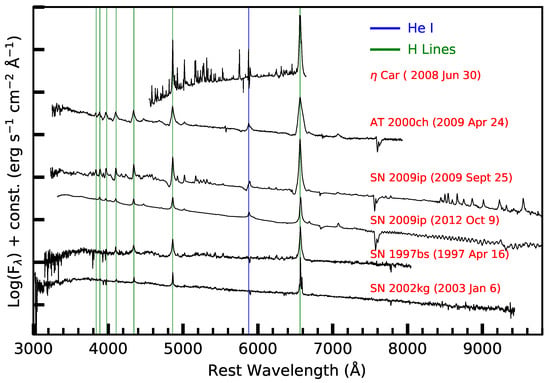
Figure 3.
Spectra of LBV eruptions and SN impostors at different phases. All the spectra show a blue continuum and narrow H emission lines, often with P Cygni profiles. Sometimes, He I lines are also identified. The principal lines from H and He are marked with vertical lines.
Pre-Supernova Outbursts
In an increasing number of cases, one or more SN impostors were observed a few months to years before the explosion of a real SN (e.g., [70,71,72] and references therein). Most of these SNe belong to the class of type IIn [27,28], whose spectra are dominated by a blue continuum, superimposed by narrow (FWHM of some 10 , up to a few 10 ) emission lines of H, features are also common in Supernova Impostors spectra. These lines are indicative of interaction of fast SN ejecta with slow-moving H-rich CSM ejected shortly before (tens to thousands of years [73]) the SN explosion ([74], for a review of the ejecta-CSM interaction theory).
The most important object with multiple outbursts preceding a SN IIn is SN 2009ip [75,76]. It was discovered on August 2009 at an absolute magnitude of mag, but despite the name, the 2009 event was not a terminal one. The progenitor was recovered months after, and other luminous episodes were seen in 2011 (see the right panel of Figure 2). On July 2012, another outburst reaching the same luminosity level as the 2009 one (∼) was observed. Finally, on October 2012, the brightest and much more luminous brightening occurred, with an absolute −18 mag. Then, its luminosity has been declining ever since, and no other major outbursts have been detected. In fact, nowadays SN 2009ip is even fainter than the quiescent progenitor [77] identified by Foley et al. [78] at an absolute magnitude of −10 (consistent with a star of 50–60 M) in archival HST (Hubble Space Telescope) images taken years before the 2009 event. Soker and Kashi [79] suggested that the progenitor of SN 2009ip was a massive binary system where the primary star was a massive LBV of 60–100 M with a much lighter main-sequence star as a companion.
There has been some debate regarding the nature of the two events of SN 2009ip observed in 2012, using the terminology in Pastorello et al. [50]; they are called ‘Event A’ and ‘Event B’, respectively. Mauerhan et al. [80] and Graham et al. [81] argue that ‘Event A’ was a true SN event, and the strong interaction of the fast ejecta that collided with a pre-existing shell of CSM material ejected during the previous LBV-like eruptive episodes powered ‘Event B’. This scenario has been recently modelled by Chugai [82]. However, Fraser et al. [52] and Pastorello et al. [50] disagree on that: while ejecta velocities of 10 are normal in CCSNe, they also observed material moving at 13,000 during the 2011 event, which was surely not the end of the progenitor star. In addition, the ‘Event A’ luminosity was exceptionally dim for a true SN (but see [83]), and no newly synthesized material was seen. Instead, they suggest that the ‘Event A’ was powered by the Pulsational Pair Instability mechanism [83,84], followed by collision with pre-existing CSM sustaining the ‘Event B’, and the star may ultimately have survived. Finally, another model proposed by Kashi et al. [85] for the outbursts of SN 2009ip is a repeated binary interaction at periastron passages, with the two stars finally merging during the second 2012 outburst [79], in a similar fashion as the Smith [40] model for Carinae.
In the years since, other objects with photometric and spectroscopic similarities to SN 2009ip (dubbed as ’SN 2009ip-like’ objects) have been discovered [51,54,55,86,87,88,89], and recently even a transitional object between SN 2009ip-like and Ibn SNe [56], but the relatively high rate of these objects has raised the question if all those transients are indeed produced by massive stars [55]. Recently, very late-time observations of SN 2009ip-like events SN 2015bh [90] and SN 2016jbu [91] revealed that the transients are now much fainter than their progenitors, supporting the idea that SN 2009ip-like objects are indeed genuine, albeit strange, terminal SNe.
Nonetheless, SN impostors are not only observed before a type-IIn SN or from LBVs. For instance, in at least one case, a pre-SN outburst was spotted before a type-Ibn SN. A ∼ mag outburst was observed 2 years prior to the appearance of the type-Ibn SN 2006jc [46,48], see Figure 4. Differently from type-IIn SNe, SNe Ibn present no H lines, but narrow He emission lines instead [92]. The precursor event was likely produced by a Wolf–Rayet star during an episode of intense mass-loss, and it created a dense He-rich CSM around the progenitor, with which the ejecta from the SN later interacted.
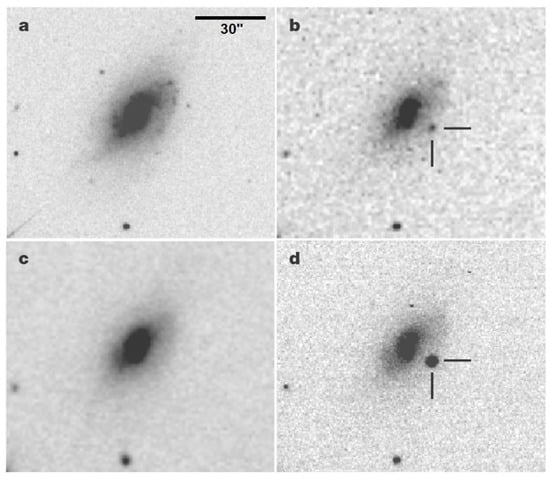
Figure 4.
(a) A Sloan Digital Sky Survey image of UGC 4904 (host galaxy of SN 2006jc) obtained in 2001. No transient is visible. (b) The faint transient UGC 4904-V1 on 16 October 2004. (c) The same field on 21 September 2006. No transient is visible. (d) SN 2006jc on 2006 October 29. The position of UGC 4904-V1 is coincident with that of SN 2006jc, making it an SN impostor prior to the real SN event. Figure from Pastorello et al. [48].
Bright outbursts immediately before an SN explosion are not predicted by current models of stellar evolution, as late evolutionary stages are difficult to simulate. Nonetheless, a few physical mechanisms have been proposed to explain pre-SN eruptions, such as violent convection and unstable late nuclear burnings [93,94,95].
With the study of pre-SN outbursts and the comprehension of which processes are their drivers, it will be possible to establish if these events can herald the imminent core-collapse of massive stars.
3. Intermediate Luminosity Red Transients
Intermediate Luminosity Red Transients (ILRTs) are a class of poorly studied gap transients that sparked debate over their origin and interpretation. While some authors invoked non-terminal outbursts of post main sequence stars to explain the observed data (e.g., [96,97]), ILRTs are among the most promising candidates for being Electron Capture Supernova (EC SN) events (see, e.g., [19,98,99,100]). Their light curves are reminiscent of classical SNe (see the left panel of Figure 5), with a single peak and a late-time linear decline in magnitudes compatible with Ni decay [98,99,100]. Indeed, long-term mid-infrared monitoring displayed that two ILRTs (NGC300 2008OT-1 and SN 2008S) became fainter than their progenitors years after their peak luminosity, corroborating the scenario of a terminal explosion rather than an eruptive event [101].
Despite the indicators that ILRTs are indeed the result of a stellar explosion, differentiating between a faint Fe CC event [102,103,104,105] and an EC SN [106,107,108,109,110] is not an easy task. First of all, EC SNe are expected to be weak explosions following the collapse of an O–Ne–Mg core, therefore yielding low peak luminosity as well as slowly expanding ejecta, compared to standard SN events [111]. Lying within the luminosity gap, ILRTs easily fulfill the condition of being low-energy explosions. Additionally, EC SNe should synthesize only few 10 M of Ni [112], which, again, is consistent with observational constraints obtained for ILRTs [98,100]. Finally, the progenitor star of an EC SN is expected to be a ∼9 M luminous super-Asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star, which, during its evolution, will develop a degenerate O–Ne–Mg core [107]. This is a key condition, but at the same time, it is the most difficult to probe, given that only for targets closer than ∼10 Mpc is it possible to study the progenitor star in archival images. In the few cases of ILRT with a successful detection in archival images, the results are encouraging: the progenitor stars of NGC 300 2008OT-1 and SN 2008S were identified as extreme AGB stars, enshrouded in dust and with masses between 8 and 12 M [113]. While such detailed identification was impossible for the progenitor of AT 2019abn, the results and upper limits obtained were still compatible with a super-AGB star [114]. It is also worth noticing that the estimated rate of ILRTs is ∼8% of the total core collapse events, perfectly in line with what is expected for EC SNe [100].
To better understand the observational properties of these transients, it is useful to discuss the case of the closest ILRT ever studied, NGC 300 2008OT-1, which is located at less than 2 Mpc from the Milky Way and proves to be a valuable benchmark for the whole class of objects [11,97,115]. The light curve of NGC 300 2008OT-1 is missing the rising phase due to solar conjunction, but its overall shape is similar to the light curves of SNe IIP, with a slow decline in the first phases followed by a sharper drop in luminosity, and finally, a linear decline compatible with Ni decay. The spectra are dominated by narrow Balmer emission lines, with a full width at half maximum of ∼1000 km s. Ca lines are also prominent spectral features, both in absorption, such as Ca H&K at early phases, and in emission, such as the forbidden [Ca II] doublet and Ca Near-Infrared (NIR) triplet. In particular, the [Ca ii] doublet ( 7291, 7324) feature, which is visible at all phases, is a characteristic signature for ILRTs1 (see the right panel of Figure 5). The study of the spectral continuum over time reveals that the emitting source is monotonously cooling after maximum luminosity. NIR observations suggest the presence of thermal emission from dust grains, which formed once the temperature in the expanding gas became sufficiently low to allow condensation [117,118]. An additional dust component, cooler and more distant from the transient, has been identified [97], possibly pre-existing dust that survived the explosion. The geometry of dust has been discussed in detail for SN 2008S, which displayed similar observables, but more generally, dust formation appears to be a ubiquitous characteristic in ILRTs [98,100]. Thanks to its proximity, NGC 300 2008OT-1 was also studied through high-resolution spectroscopy, revealing narrow (∼40 km s) absorption lines superimposed to the H line and Ca NIR triplet, suggesting the presence of slowly moving gas shells around the transient [11]. Other identified lines include Fe II and He I, as well as narrow O I and Na I. The complete absence of a P-Cygni profile, even at high resolution, indicates that we are only probing the CSM, which displays only moderate expansion velocity, while the higher-velocity ejecta are hidden by this optically thick gas.
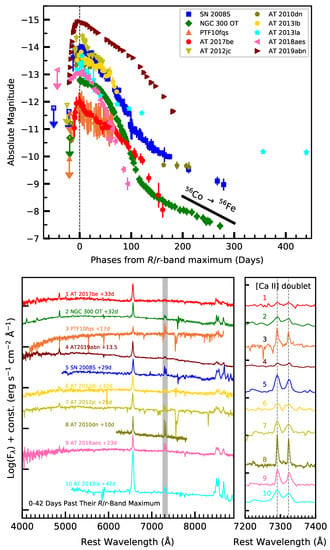
Figure 5.
Top panel: -band absolute light curves of ILRTs. Bottom panel: spectral comparison of ILRTs, along with the [Ca II] region which is marked in grey. Their [Ca II] lines ( 7291, 7324) are enlarged on the right of this panel. Data from Kasliwal et al. [25], Humphreys et al. [97], Botticella et al. [98], Cai et al. [99,100], Bond et al. [115], Williams et al. [119], Stritzinger et al. [120].
As mentioned above, it is plausible that ILRTs are EC SNe arising from super-AGB stars, but there is no consensus on this topic yet. Due to this fundamental uncertainty the theoretical modelling of these object is still in a preliminary stage. Different mechanisms have been suggested to power the ILRTs, including mass accretion on a main sequence star [121], a failed supernova due to fallback on a black hole [122] and jets interacting with CSM [13]. Some of these models envision ILRTs and LRNe arising from the same physical phenomenon. In any case, no model has been systematically used to describe ILRTs. On the other hand, EC SN models are in a more advanced stage: thanks to simulations accounting for hydrodynamics and radiation transfer in the ejecta, recent studies are able to provide predictions for key observables of EC SNe, in particular, broad band light curves (e.g., [123]). So far, however, the results of such studies are more compatible with low-luminosity SNe IIP rather than with ILRTs. One key detail that may be lacking to explain ILRTs as EC SN, in the context of these theoretical models, is the presence of thick CSM surrounding the exploding star. Further studies both on the theoretical and the observational side are required to reach a better understanding of these transients.
4. Luminous Red Novae
Luminous red novae (LRNe) are another important subclass of gap transients. In the past few years, we have observed about 20 extragalactic events. The remarkable cases of this class are as follows: M31-RV, NGC4490-2011OT1, NGC3437-2011OT1, UGC12307-2013OT1, AT 2014ej, SNhunt248 2, M31-LRN2015, AT 2015dl/M101-2015OT1, AT 2017jfs, AT 2018bwo, AT 2018hso, AT 2019zhd, AT 2020hat, AT 2020kog, AT 2020hat, AT 2021biy, AT 2021afy and AT 2021blu [14,15,116,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142]. Most LRNe are located in spiral to irregular galaxies.
The Galactic luminous red nova V1309 Sco (e.g., [127,133,143,144]) was shown to be a short-period contact binary before its outburst, displaying a slow rise superposed on a periodic modulation (P∼1.4 days) between 2002 and mid-2007 [145]. This period decreased with time as a consequence of the loss of orbital angular momentum [143]. Then, its luminosity started to decline following an exponential law from late 2007 to early 2008, along with the disappearance of period variability. This is likely due to the orbital shrinking of the two stars which were therefore engulfed in a common envelope [143,146]. Soon after this minimum, the light curve experiences a steep rise with a ∼3.5 mag brightening within ∼5 months (from March to late August 2008), which can be associated with the ejection of the common envelope. The 7-year pre-outburst light curve of V1309 Sco observed by OGLE survey is well matched with the predictions for a contact binary. Unfortunately, extra-Galactic LRNe usually lack of deep photometry observations during the pre-outburst phases. So far, only two Galactic luminous red novae (V1309 Sco ([143], see their Figure 1) and V838 Mon ([147], see their Figure 1)) have been relatively well-monitored during the pre-outburst phases. Finally, a huge brightening of ∼3.5 mag in less than two weeks was observed for V1309 Sco. Subsequently, these transients display a double-hump light curve typical of most LRNe (see the left panel of Figure 6). The early short-duration peak, usually with a blue colour, is then followed by the second broad peak (or a plateau), characterised with a progressively redder colour. Afterwards, LRNe light curves usually experience a fast luminosity drop in all bands. Occasionally, a very late-time bump in the light curves can be observed for some LRNe (e.g., AT 2017jfs, AT 2021biy; [135,141]). Nonetheless, the theoretical mechanisms regulating the structured light curve of LRNe is still very poorly understood. In analogy to the plateau feature in Type IIP SNe [148], hydrogen recombination might be the reason to stabilise the luminosity (e.g., [149,150]). However, recombination energy cannot give a major contribution to the first blue peak, as mentioned by MacLeod et al. [151]. Instead, Metzger and Pejcha [152] propose that the two-part structure light curve originates from the interaction between a fast ejected shell and a pre-existing equatorial wind. Recently, Matsumoto and Metzger [153] presented a new one-dimensional model of LRN light curves, which accounts for various effects of opacities, radiation, gas pressure, and the hydrogen recombination. This model can be applied to LRNe to infer the ejecta properties, such as ejecta mass, ejecta velocity, and launching radius. High-dimension hydrodynamical simulations will be a powerful tool to solve these puzzles.
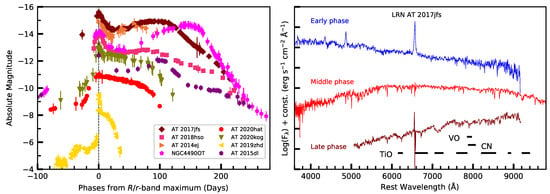
Figure 6.
Left panel: -band absolute light curves of LRNe. Right panel: spectral evolution of a remarkable LRN AT 2017jfs at early, middle, and late phases. Data from Cai et al. [116], Smith et al. [133], Blagorodnova et al. [134], Pastorello et al. [135], Stritzinger et al. [137], Pastorello et al. [138,139].
During the pre-outburst phase, LRNe have never been observed in spectroscopy. Fortunately, some LRNe (e.g., NGC4490-2011OT1, AT 2017jfs, AT 2021biy) are well-monitored in optical spectroscopy during the major outburst phase in which they show similar spectral properties. Specifically, early-time (during the first peak) spectra show a blue continuum dominated by prominent H lines in emission, resembling those of other gap transients. During the second peak or plateau phase, the spectral continuum becomes progressively redder, similar to that of a K-type star. The weaker H and a forest of narrow metal lines in absorption are observed in LRNe by that time. At very late phase, the spectra show an extremely red continuum resemble that of an M-type star. H becomes prominent again in pure emission, and the characterising molecular features (e.g., TiO, VO) emerge at such late phase. This dramatic spectral evolution behaviour (see the right panel of Figure 6) can be a diagnostic tool to discriminate LRNe from other gap transients, such as LBV outbursts and ILRTs.
Several authors (e.g., [136,139,140,142,144,154,155]) looked for the possible correlations among the photometric and spectroscopic observables for LRNe. They obtained similar results: higher-luminosity events have longer evolution; hotter, larger, and higher-velocity photospheres; along with luminous H lines. In addition, the quiescent progenitors of bright events are generally more massive than dim ones. (see their Equations (2) and (3), Cai et al. [141]) obtained an empirical relation between the progenitor mass and the V-band absolute magnitudes at the second peak or plateau, which can be used for roughly inferring the progenitor mass of LRNe which lack detection of the progenitor in pre-explosion images. Robust correlations in observational parameters can be provided with the expanding LRNe sample in future surveys.
Sana et al. [156] provide an estimation that over 70% of massive stars interact with their companions and finally give rise to a binary merger with a ratio of about 30% of them. As presented by Kochanek et al. [154], the stellar merger rate in the Galaxy is at the order of 0.5 yr for events more luminous than mag, while brighter events ( mag) have a much lower rate with ∼0.03 yr. Recently, Howitt et al. [157] estimated a Galactic rate of an LRNe of about 0.2 yr and a volumetric LRNe rate of about 8 × 10 Mpcyr in the local Universe. Although the precise LRNe rate is still not available, we are confident that the intrinsic rate of LRNe is strongly dependent on their luminosity function and the mass of the progenitor binary system (e.g., [139,154,156,157]).
There are several scenarios to interpret the LRN phenomenon: the thermonuclear runaway occurred on a low-mass degenerate dwarf was proposed to explain M31 RV by Iben and Tutukov [158] or post-AGB star helium flash scenario (see e.g., [159,160]). Pastorello et al. [136] also summarised several scenarios for the LRNe phenomenon, in which the major instabilities of single massive stars and the common envelope ejection followed by a stellar merger scenario are two popular ones. The watershed event is the Galactic LRN V1309 Sco which provided the strongest evidence that LRNe originate from the mergers of non-degenerate binaries (e.g., [127,143]). For example, V838 Mon has been proposed to be a merger of two main sequence stars by Soker and Tylenda [161]. On the other hand, the post-outburst outcome is still debated, as it can either result in a core-collapse SN event, or the system could survive as close binary stars (e.g., see [134,136]). Very late-time photometry, in particular the IR observations, and spectroscopy will be needed to unveil the mystery.
5. Unknown Transients
Modern, wide-field, time-domain surveys launched an upheaval in the astronomical field of studying transients, such as the discovery of kilonovae, the electromagnetic counterpart of the merger of binary neutron stars (e.g., [162,163,164,165]). These surveys allow us to explore new regimes in the transients phase space represented in Figure 1, which may also challenge the existing models for stellar evolution and explosions. Along with SN impostors, ILRTs, and LRNe, we are prepared to identify any possible transients lying in this luminosity gap, such as very faint and failed SNe (e.g., [166]).
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Although significant progress has been made in both the follow-up and theoretical modelling for gap transients, our study is still in its early stages. The major obstacles are the small sample size and the lack of wavelength coverage in domains outside the optical and NIR ones. However, both issues will be soon effectively tackled: with the inauguration of the Vera C. Rubin Observatory (e.g., [167,168,169]), the sample size problem will be immediately solved, thanks to the large amount of data that this survey will provide. On the other hand, with the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope [170], it will be possible to investigate in the infrared domain in an unprecedented fashion, unveiling the secrets of the dust that is such a key component for many of these gap transients. In addition, comparing archival pre-outburst images at the transient site with ones taken several years after will discriminate whether the gap transients are non-terminal events or final explosions. With the advent of new facilities, high-cadence observations can help to cover their entire evolution. In particular, deeper photometry and intermediate-resolution spectroscopy performed on 2–4 m mid-size class telescopes are key for achieving such a goal. Late-time spectra obtained from 10 m class telescopes are another powerful tool to probe the physics of these events. On the other hand, the development of theoretical models will give helpful elements to understand the physical mechanisms and provide observational predictions for known and unknown transients in the gap. All of these efforts will allow us to better comprehend the nature of gap transients.
Author Contributions
Y.C. is the first author who is responsible for this paper; A.R. contributed to the Section of Supernova Impostors; G.V. contributed to the Section of Intermediate Luminosity Red Transients; X.W. supervised/supported Y.C. for this paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Y.C. is funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant no. 2021M691821). This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC grants 12033003, 11633002), the Scholar Program of Beijing Academy of Science and Technology (DZ:BS202002), and the Tencent Xplorer Prize. A.R. acknowledges support from ANID BECAS/DOCTORADO NACIONAL 21202412.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Some data are obtained from the Weizmann Interactive Supernova Data Repository (WISeREP) at https://wiserep.weizmann.ac.il/ (accessed on 6 July 2022). Some data used in this work are available from the published literature.
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly thank the referees and the academic editor for their helpful comments and suggestions, that allowed us to improve the quality of the paper. Y.C. thanks the instructive comments from the former PhD supervisor A. Pastorello.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| SNe | Supernovae |
| SL SNe | Superluminous SNe |
| CC SNe | Core-collapse supernovae |
| EC SNe | Electron Capture Supernovae |
| TDE | Tidal Disruption Event |
| LBVs | Luminous Blue Variables |
| ILRTs | Intermediate-luminosity red transients |
| LRNe | Luminous red novae |
| AGB | Asymptotic giant branch |
| FWHM | Full-width at half-maximum |
| CSM | Circumstellar material |
| HST | Hubble Space Telescope |
| NIR | Near Infrared |
| ZTF | Zwicky Transient Facility |
| ATLAS | Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System |
| Pan-STARRS | Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System |
| OGLE | Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment |
Notes
| 1 | However, weak [Ca II] lines were also detected in the spectra of the LRN AT 2018hso [116]. |
| 2 | SNhunt248 is a LRN candidate whose nature is debated [124]. |
References
- Inserra, C. Observational properties of extreme supernovae. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Yam, A. The Most Luminous Supernovae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 305–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Yan, L.; Kangas, T.; Lunnan, R.; Schulze, S.; Sollerman, J.; Perley, D.A.; Chen, T.W.; Gal-Yam, A.; Wang, X.F.; et al. The Hydrogen-Poor Superluminous Supernovae from the Zwicky Transient Facility Phase-I Survey: I. Data. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.02059. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.H.; Yan, L.; Kangas, T.; Lunnan, R.; Sollerman, J.; Schulze, S.; Perley, D.A.; Chen, T.W.; Gal-Yam, A.; Wang, X.F.; et al. The Hydrogen-Poor Superluminous Supernovae from the Zwicky Transient Facility Phase-I Survey: II. Light Curve Modeling and Analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.02060. [Google Scholar]
- Drout, M.R.; Chornock, R.; Soderberg, A.M.; Sanders, N.E.; McKinnon, R.; Rest, A.; Foley, R.J.; Milisavljevic, D.; Margutti, R.; Berger, E.; et al. Rapidly Evolving and Luminous Transients from Pan-STARRS1. Astrophys. J. 2014, 794, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margutti, R.; Metzger, B.D.; Chornock, R.; Vurm, I.; Roth, N.; Grefenstette, B.W.; Savchenko, V.; Cartier, R.; Steiner, J.F.; Terreran, G.; et al. An Embedded X-Ray Source Shines through the Aspherical AT 2018cow: Revealing the Inner Workings of the Most Luminous Fast-evolving Optical Transients. Astrophys. J. 2019, 872, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.Y.Q.; Perley, D.A.; Gal-Yam, A.; Lunnan, R.; Sollerman, J.; Schulze, S.; Das, K.K.; Dobie, D.; Yao, Y.; Fremling, C.; et al. The Photometric and Spectroscopic Evolution of Rapidly Evolving Extragalactic Transients in ZTF. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.08811. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, M.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Brennan, S.J.; Pastorello, A.; Cai, Y.; Piro, A.L.; Ashall, C.; Brown, P.; Burns, C.R.; Elias-Rosa, N.; et al. SN 2021csp—The explosion of a stripped envelope star within a H and He-poor circumstellar medium. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07278. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, D.; Wang, X.; Lin, W.; Mo, J.; Lin, H.; Burke, J.; Hiramatsu, D.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Howell, D.A.; McCully, C.; et al. The Peculiar Transient AT2018cow: A Possible Origin of a Type Ibn/IIn Supernova. Astrophys. J. 2021, 910, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D. Luminous Fast Blue Optical Transients and Type Ibn/Icn SNe from Wolf-Rayet/Black Hole Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2022, 932, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.; Soderberg, A.M.; Chevalier, R.A.; Fransson, C.; Foley, R.J.; Leonard, D.C.; Debes, J.H.; Diamond-Stanic, A.M.; Dupree, A.K.; Ivans, I.I.; et al. An Intermediate Luminosity Transient in NGC 300: The Eruption of a Dust-Enshrouded Massive Star. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, 1850–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N.; Kashi, A. Formation of Bipolar Planetary Nebulae by Intermediate-luminosity Optical Transients. Astrophys. J. 2012, 746, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N.; Kaplan, N. Explaining recently studied intermediate luminosity optical transients (ILOTs) with jet powering. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 21, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Peng, C.Y.; King, J.Y.; Filippenko, A.V.; Treffers, R.R.; Li, W.; Richmond, M.W. SN 1997bs in M66: Another Extragalactic η Carinae Analog? Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2000, 112, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschi, F.; Munari, U. M 31-RV evolution and its alleged multi-outburst pattern. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 418, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Graham, M.J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Bellm, E.C.; Adams, S.M.; Barbarino, C.; Blagorodnova, N.; Bodewits, D.; Bolin, B.; Brady, P.R.; Cenko, S.B.; et al. The Zwicky Transient Facility: Science Objectives. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2019, 131, 078001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonry, J.L.; Denneau, L.; Heinze, A.N.; Stalder, B.; Smith, K.W.; Smartt, S.J.; Stubbs, C.W.; Weiland, H.J.; Rest, A. ATLAS: A High-cadence All-sky Survey System. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2018, 130, 064505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, K.C.; Magnier, E.A.; Metcalfe, N.; Flewelling, H.A.; Huber, M.E.; Waters, C.Z.; Denneau, L.; Draper, P.W.; Farrow, D.; Finkbeiner, D.P.; et al. The Pan-STARRS1 Surveys. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.05560. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M. Supernova impostors and other gap transients. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, A.; Soker, N. Common Powering Mechanism of Intermediate Luminosity Optical Transients and Luminous Blue Variables. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1011.1222. [Google Scholar]
- Kashi, A.; Soker, N. Operation of the jet feedback mechanism (JFM) in intermediate luminosity optical transients (ILOTs). Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, A.; Soker, N. An intermediate luminosity optical transient (ILOTs) model for the young stellar object ASASSN-15qi. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, 4938–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N.; Kashi, A. Explaining two recent intermediate-luminosity optical transients (ILOTs) by a binary interaction and jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rau, A.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Law, N.M.; Bloom, J.S.; Ciardi, D.; Djorgovski, G.S.; Fox, D.B.; Gal-Yam, A.; Grillmair, C.C.; Kasliwal, M.M.; et al. Exploring the Optical Transient Sky with the Palomar Transient Factory. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2009, 121, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasliwal, M.M.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Arcavi, I.; Quimby, R.M.; Ofek, E.O.; Nugent, P.; Jacobsen, J.; Gal-Yam, A.; Green, Y.; Yaron, O.; et al. PTF 10fqs: A Luminous Red Nova in the Spiral Galaxy Messier 99. Astrophys. J. 2011, 730, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Owocki, S.P. On the Role of Continuum-driven Eruptions in the Evolution of Very Massive Stars and Population III Stars. Astrophys. J. 2006, 645, L45–L48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, E.M. A new subclass of Type II supernovae? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1990, 244, 269–271. [Google Scholar]
- Filippenko, A.V. Optical Spectra of Supernovae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 35, 309–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R.; Smartt, S.J.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Pastorello, A.; Nelemans, G.; Bresolin, F.; Patat, F.; Gilmore, G.F.; Benn, C.R. Faint supernovae and supernova impostors: Case studies of SN 2002kg/NGC 2403-V37 and SN 2003gm. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 369, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K. The luminous blue variables: Astrophysical geysers. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1994, 106, 1025–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, A.; Conti, P.S. Massive Star Populations in Nearby Galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 32, 227–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Tombleson, R. Luminous blue variables are antisocial: Their isolation implies that they are kicked mass gainers in binary evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 598–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghakhanloo, M.; Murphy, J.W.; Smith, N.; Hložek, R. Modelling luminous-blue-variable isolation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Weis, K.; Davidson, K.; Gordon, M.S. On the Social Traits of Luminous Blue Variables. Astrophys. J. 2016, 825, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadland, E.; Massey, P.; Neugent, K.F.; Drout, M.R. Shedding Light on the Isolation of Luminous Blue Variables. Astrophys. J. 2018, 156, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N. A model for the strings of η Carinae. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 377, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N. The departure of η Carinae from axisymmetry and the binary hypothesis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 325, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Humphreys, R.M. The Great Eruption of η Carinae. Nature 2012, 486, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Frew, D.J. A revised historical light curve of Eta Carinae and the timing of close periastron encounters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Explosions triggered by violent binary-star collisions: Application to Eta Carinae and other eruptive transients. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 2020–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, M. The most luminous stars in the universe. Ir. Astron. J. 1988, 18, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kashi, A. An indication for the binarity of P Cygni from its 17th century eruption. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 405, 1924–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, N.; Hartigan, P. Infrared [Fe II] Emission from P Cygni’s Nebula: Atomic Data, Mass, Kinematics, and the 1600 AD Outburst. Astrophys. J. 2006, 638, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Gehrz, R.D.; Hinz, P.M.; Hoffmann, W.F.; Hora, J.L.; Mamajek, E.E.; Meyer, M.R. Mass and Kinetic Energy of the Homunculus Nebula around η Carinae. Astrophys. J. 2003, 125, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, D.J. The Historical Record of η Carinae I. The Visual Light Curve, 1595–2000. J. Astron. Data 2004, 10, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, R.J.; Smith, N.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Li, W.; Chornock, R.; Filippenko, A.V. SN 2006jc: A Wolf-Rayet Star Exploding in a Dense He-rich Circumstellar Medium. Astrophys. J. 2007, 657, L105–L108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Li, W.; Silverman, J.M.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Filippenko, A.V. Luminous blue variable eruptions and related transients: Diversity of progenitors and outburst properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 773–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Smartt, S.J.; Mattila, S.; Eldridge, J.J.; Young, D.; Itagaki, K.; Yamaoka, H.; Navasardyan, H.; Valenti, S.; Patat, F.; et al. A giant outburst two years before the core-collapse of a massive star. Nature 2007, 447, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Botticella, M.T.; Trundle, C.; Taubenberger, S.; Mattila, S.; Kankare, E.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Benetti, S.; Duszanowicz, G.; Hermansson, L.; et al. Multiple major outbursts from a restless luminous blue variable in NGC 3432. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 408, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Cappellaro, E.; Inserra, C.; Smartt, S.J.; Pignata, G.; Benetti, S.; Valenti, S.; Fraser, M.; Takáts, K.; Benitez, S.; et al. Interacting Supernovae and Supernova Impostors: SN 2009ip, is this the End? Astrophys. J. 2013, 767, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Kochanek, C.S.; Fraser, M.; Dong, S.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Filippenko, A.V.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Tomasella, L.; Drake, A.J.; et al. Supernovae 2016bdu and 2005gl, and their link with SN 2009ip-like transients: Another piece of the puzzle. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.; Inserra, C.; Jerkstrand, A.; Kotak, R.; Pignata, G.; Benetti, S.; Botticella, M.T.; Bufano, F.; Childress, M.; Mattila, S.; et al. SN 2009ip à la PESSTO: No evidence for core collapse yet. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 433, 1312–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.; Kotak, R.; Pastorello, A.; Jerkstrand, A.; Smartt, S.J.; Chen, T.W.; Childress, M.; Gilmore, G.; Inserra, C.; Kankare, E.; et al. SN 2009ip at late times—An interacting transient at +2 years. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 3886–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brennan, S.J.; Fraser, M.; Johansson, J.; Pastorello, A.; Kotak, R.; Stevance, H.F.; Chen, T.W.; Eldridge, J.J.; Bose, S.; Brown, P.J.; et al. Photometric and spectroscopic evolution of the interacting transient AT 2016jbu(Gaia16cfr). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 5642–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, S.J.; Fraser, M.; Johansson, J.; Pastorello, A.; Kotak, R.; Stevance, H.F.; Chen, T.W.; Eldridge, J.J.; Bose, S.; Brown, P.J.; et al. Progenitor, environment, and modelling of the interacting transient AT 2016jbu (Gaia16cfr). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 5666–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguitti, A.; Pastorello, A.; Pignata, G.; Fraser, M.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Brennan, S.J.; Cai, Y.Z.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Fugazza, D.; Gutierrez, C.P.; et al. SN 2021foa, a transitional event between a Type IIn (SN 2009ip-like) and a Type Ibn supernova. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 662, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.M.; Vrba, F.J.; Henden, A.A.; Canzian, B.; Luginbuhl, C.B.; Filippenko, A.V.; Chornock, R.; Li, W.; Coil, A.L.; Schmidt, G.D.; et al. Discovery and Evolution of an Unusual Luminous Variable Star in NGC 3432 (Supernova 2000ch). Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2004, 116, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G.A.; Sandage, A. The Stellar Content and Distance of the Galaxy NGC 2403 IN the M81 Group. Astrophys. J. 1968, 151, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K.; Bomans, D.J. SN 2002kg—The brightening of LBV V37 in NGC 2403. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 429, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Chornock, R.; Li, W.; Challis, P.M. Supernova 1954J (Variable 12) in NGC 2403 Unmasked. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2005, 117, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Gordon, M.S. A Tale of Two Impostors: SN2002kg and SN1954J in NGC 2403. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, L.; Pastorello, A.; Taubenberger, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Maund, J.R.; Benetti, S.; Boles, T.; Bufano, F.; Duszanowicz, G.; Elias-Rosa, N.; et al. Interacting supernovae and supernova impostors. SN 2007sv: The major eruption of a massive star in UGC 5979. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, L.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Pastorello, A.; Benetti, S.; Taubenberger, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Cortini, G.; Granata, V.; Ishida, E.E.O.; Morales-Garoffolo, A.; et al. The Supernova Impostor PSN J09132750+7627410 and Its Progenitor. Astrophys. J. 2016, 823, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Interacting Supernovae: Types IIn and Ibn. In Handbook of Supernovae; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; p. 403. ISBN 978-3-319-21845-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugai, N.N.; Danziger, I.J. SN 1988Z: Low-mass ejecta colliding with the clumpy wind? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 268, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damineli, A. The 5.52 Year Cycle of Eta Carinae. Astrophys. J. 1996, 460, L49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.P.; Gayley, K.G.; Shaviv, N.J. A Porosity-Length Formalism for Photon-Tiring-limited Mass Loss from Stars above the Eddington Limit. Astrophys. J. 2004, 616, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, H.J.G.L.M.; Fitzpatrick, E.L. The Relationship between the Eddington Limit, the Observed Upper Luminosity Limit for Massive Stars, and the Luminous Blue Variables. Astrophys. J. 1988, 324, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Cantiello, M.; Bildsten, L.; Quataert, E.; Blaes, O.; Stone, J. Outbursts of luminous blue variable stars from variations in the helium opacity. Nature 2018, 561, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, E.O.; Sullivan, M.; Shaviv, N.J.; Steinbok, A.; Arcavi, I.; Gal-Yam, A.; Tal, D.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Nugent, P.E.; Ben-Ami, S.; et al. Precursors Prior to Type IIn Supernova Explosions are Common: Precursor Rates, Properties, and Correlations. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguitti, A.; Pastorello, A.; Pignata, G.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Turatto, M.; Agliozzo, C.; Bufano, F.; Morrell, N.I.; Olivares E., F.; et al. Signatures of an eruptive phase before the explosion of the peculiar core-collapse SN 2013gc. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 2750–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotjohann, N.L.; Ofek, E.O.; Gal-Yam, A.; Bruch, R.; Schulze, S.; Shaviv, N.; Sollerman, J.; Filippenko, A.V.; Yaron, O.; Fremling, C.; et al. Bright, Months-long Stellar Outbursts Announce the Explosion of Interaction-powered Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2021, 907, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Mass Loss: Its Effect on the Evolution and Fate of High-Mass Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 487–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.A.; Fransson, C. Emission from circumstellar interaction in normal Type II supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1994, 420, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Miller, A.; Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V.; Silverman, J.M.; Howard, A.W.; Nugent, P.; Marcy, G.W.; Bloom, J.S.; Ghez, A.M.; et al. Discovery of Precursor Luminous Blue Variable Outbursts in Two Recent Optical Transients: The Fitfully Variable Missing Links UGC 2773-OT and SN 2009ip. Astrophys. J. 2010, 139, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margutti, R.; Milisavljevic, D.; Soderberg, A.M.; Chornock, R.; Zauderer, B.A.; Murase, K.; Guidorzi, C.; Sanders, N.E.; Kuin, P.; Fransson, C.; et al. A Panchromatic View of the Restless SN 2009ip Reveals the Explosive Ejection of a Massive Star Envelope. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Andrews, J.E.; Filippenko, A.V.; Fox, O.D.; Mauerhan, J.C.; Van Dyk, S.D. SN 2009ip after a decade: The luminous blue variable progenitor is now gone. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.02896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, R.J.; Berger, E.; Fox, O.; Levesque, E.M.; Challis, P.J.; Ivans, I.I.; Rhoads, J.E.; Soderberg, A.M. The Diversity of Massive Star Outbursts. I. Observations of SN2009ip, UGC 2773 OT2009-1, and Their Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2011, 732, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N.; Kashi, A. Explaining the Supernova Impostor SN 2009ip as Mergerburst. Astrophys. J. 2013, 764, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mauerhan, J.C.; Smith, N.; Silverman, J.M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Morgan, A.N.; Cenko, S.B.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Clubb, K.I.; Bloom, J.S.; Matheson, T.; et al. SN 2011ht: Confirming a class of interacting supernovae with plateau light curves (Type IIn-P). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 2599–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.L.; Sand, D.J.; Valenti, S.; Howell, D.A.; Parrent, J.; Halford, M.; Zaritsky, D.; Bianco, F.; Rest, A.; Dilday, B. Clues to the Nature of SN 2009ip from Photometric and Spectroscopic Evolution to Late Times. Astrophys. J. 2014, 787, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugai, N. Supernova 2009ip outbursts in 2012: From scenario to model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.05204. [Google Scholar]
- Woosley, S.E.; Blinnikov, S.; Heger, A. Pulsational pair instability as an explanation for the most luminous supernovae. Nature 2007, 450, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woosley, S.E. Pulsational Pair-instability Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, A.; Soker, N.; Moskovitz, N. Powering the second 2012 outburst of SN 2009ip by repeating binary interaction. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 2484–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessi, T.; Prieto, J.L.; Monard, B.; Kochanek, C.S.; Bock, G.; Drake, A.J.; Fox, O.D.; Parker, S.; Stevance, H.F. Unveiling the Nature of SN 2011fh: A Young and Massive Star Gives Rise to a Luminous SN 2009ip-like Event. Astrophys. J. 2022, 928, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias-Rosa, N.; Pastorello, A.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Taubenberger, S.; Terreran, G.; Fraser, M.; Brown, P.J.; Tartaglia, L.; Morales-Garoffolo, A.; et al. Dead or Alive? Long-term evolution of SN 2015bh (SNhunt275). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, 3894–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thöne, C.C.; de Ugarte Postigo, A.; Leloudas, G.; Gall, C.; Cano, Z.; Maeda, K.; Schulze, S.; Campana, S.; Wiersema, K.; Groh, J.; et al. SN 2015bh: NGC 2770’s 4th supernova or a luminous blue variable on its way to a Wolf-Rayet star? Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 599, A129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, L.; Pastorello, A.; Sullivan, M.; Baltay, C.; Rabinowitz, D.; Nugent, P.; Drake, A.J.; Djorgovski, S.G.; Gal-Yam, A.; Fabrika, S.; et al. Interacting supernovae and supernova impostors. LSQ13zm: An outburst heralds the death of a massive star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jencson, J.E.; Sand, D.J.; Andrews, J.E.; Smith, N.; Strader, J.; Aghakhanloo, M.; Pearson, J.; Valenti, S. Hubble Space Telescope Imaging Reveals that SN 2015bh is Much Fainter than its Progenitor. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.02816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, S.J.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Fraser, M.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Lyman, J.D. The impostor revealed: SN 2016jbu was a terminal explosion. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.06365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Quimby, R.M.; Smartt, S.J.; Mattila, S.; Navasardyan, H.; Crockett, R.M.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Mondol, P.; Wheeler, J.C.; Young, D.R. Massive stars exploding in a He-rich circumstellar medium—II. The transitional case of SN 2005la. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 389, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, W.D.; Meakin, C. Turbulent Cells in Stars: Fluctuations in Kinetic Energy and Luminosity. Astrophys. J. 2011, 741, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quataert, E.; Shiode, J. Wave-driven mass loss in the last year of stellar evolution: Setting the stage for the most luminous core-collapse supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, L92–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiode, J.H.; Quataert, E. Setting the Stage for Circumstellar Interaction in Core-Collapse Supernovae. II. Wave-driven Mass Loss in Supernova Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, A.; Frankowski, A.; Soker, N. NGC 300 OT2008-1 as a Scaled-down Version of the Eta Carinae Great Eruption. Astrophys. J. 2010, 709, L11–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Bond, H.E.; Bedin, L.R.; Bonanos, A.Z.; Davidson, K.; Berto Monard, L.A.G.; Prieto, J.L.; Walter, F.M. The Photometric and Spectral Evolution of the 2008 Luminous Optical Transient in NGC 300. Astrophys. J. 2011, 743, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticella, M.T.; Pastorello, A.; Smartt, S.J.; Meikle, W.P.S.; Benetti, S.; Kotak, R.; Cappellaro, E.; Crockett, R.M.; Mattila, S.; Sereno, M.; et al. SN 2008S: An electron-capture SN from a super-AGB progenitor? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 398, 1041–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M.; Botticella, M.T.; Gall, C.; Arcavi, I.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Harmanen, J.; et al. AT 2017be—A new member of the class of intermediate-luminosity red transients. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 3424–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M.; Botticella, M.T.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Wang, L.Z.; Kotak, R.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Turatto, M.; et al. Intermediate-luminosity red transients: Spectrophotometric properties and connection to electron-capture supernova explosions. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 654, A157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.M.; Kochanek, C.S.; Prieto, J.L.; Dai, X.; Shappee, B.J.; Stanek, K.Z. Almost gone: SN 2008S and NGC 300 2008OT-1 are fainter than their progenitors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Zampieri, L.; Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Meikle, W.P.S.; Benetti, S.; Branch, D.; Baron, E.; Patat, F.; Armstrong, M.; et al. Low-luminosity Type II supernovae: Spectroscopic and photometric evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 347, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, S.; Pastorello, A.; Pumo, M.L.; Zampieri, L.; Turatto, M.; Smartt, S.J.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Valenti, S.; Agnoletto, I.; et al. Low luminosity Type II supernovae—II. Pointing towards moderate mass precursors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 2873–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguitti, A.; Pumo, M.L.; Mazzali, P.A.; Pastorello, A.; Pignata, G.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Prentice, S.J.; Reynolds, T.; Benetti, S.; Rodrìguez, O.; et al. Low-luminosity Type II supernovae—III. SN 2018hwm, a faint event with an unusually long plateau. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 501, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerin, G.; Pumo, M.L.; Pastorello, A.; Reguitti, A.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Gútierrez, C.P.; Kankare, E.; Fraser, M.; Mazzali, P.A.; Howell, D.A.; et al. Low luminosity Type II supernovae—IV. SN 2020cxd and SN 2021aai, at the edges of the sub-luminous supernovae class. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 4983–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, K. Evolution of 8-10 solar mass stars toward electron capture supernovae. I—Formation of electron-degenerate O + Ne + Mg cores. Astrophys. J. 1984, 277, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelarends, A.J.T.; Herwig, F.; Langer, N.; Heger, A. The Supernova Channel of Super-AGB Stars. Astrophys. J. 2008, 675, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumo, M.L.; Turatto, M.; Botticella, M.T.; Pastorello, A.; Valenti, S.; Zampieri, L.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Patat, F. EC-SNe from Super-Asymptotic Giant Branch Progenitors: Theoretical Models Versus Observations. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, L138–L142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, T.J.; Tominaga, N.; Langer, N.; Nomoto, K.; Blinnikov, S.I.; Sorokina, E.I. Electron-capture supernovae exploding within their progenitor wind. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 569, A57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, C.L.; Gil-Pons, P.; Siess, L.; Lattanzio, J.C.; Lau, H.H.B. Super- and massive AGB stars—IV. Final fates—Initial-to-Final mass relation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 446, 2599–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, H.T.; Müller, B.; Kitaura, F.S.; Buras, R. Dynamics of shock propagation and nucleosynthesis conditions in O-Ne-Mg core supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 485, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanajo, S.; Nomoto, K.; Janka, H.T.; Kitaura, F.S.; Müller, B. Nucleosynthesis in Electron Capture Supernovae of Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars. Astrophys. J. 2009, 695, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.A.; Prieto, J.L.; Stanek, K.Z.; Kistler, M.D.; Beacom, J.F.; Kochanek, C.S. A New Class of Luminous Transients and a First Census of their Massive Stellar Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 1364–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jencson, J.E.; Adams, S.M.; Bond, H.E.; van Dyk, S.D.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Bally, J.; Blagorodnova, N.; De, K.; Fremling, C.; Yao, Y.; et al. Discovery of an Intermediate-luminosity Red Transient in M51 and Its Likely Dust-obscured, Infrared-variable Progenitor. APJ 2019, 880, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, H.E.; Bedin, L.R.; Bonanos, A.Z.; Humphreys, R.M.; Monard, L.A.G.B.; Prieto, J.L.; Walter, F.M. The 2008 Luminous Optical Transient in the Nearby Galaxy NGC 300. Astrophys. J. 2009, 695, L154–L158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M.; Prentice, S.J.; Reynolds, T.M.; Cappellaro, E.; Benetti, S.; Morales-Garoffolo, A.; Reguitti, A.; Elias-Rosa, N.; et al. The transitional gap transient AT 2018hso: New insights into the luminous red nova phenomenon. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 632, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, J.L.; Sellgren, K.; Thompson, T.A.; Kochanek, C.S. A Spitzer/IRS Spectrum of the 2008 Luminous Transient in NGC 300: Connection to Proto-Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, R.; Sakon, I.; Onaka, T.; Tanaka, M.; Moriya, T.; Nozawa, T.; Maeda, K.; Nomoto, K.; Tominaga, N.; Usui, F.; et al. Observations of the Optical Transient in NGC 300 with AKARI/IRC: Possibilities of Asymmetric Dust Formation. Astrophys. J. 2010, 718, 1456–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.C.; Jones, D.; Pessev, P.; Geier, S.; Corradi, R.L.M.; Hook, I.M.; Darnley, M.J.; Pejcha, O.; Núñez, A.; Meingast, S.; et al. AT 2019abn: Multi-wavelength observations over the first 200 days. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 637, A20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stritzinger, M.D.; Taddia, F.; Fraser, M.; Tauris, T.M.; Suntzeff, N.B.; Contreras, C.; Drybye, S.; Galbany, L.; Holmbo, S.; Morrell, N.; et al. The Carnegie Supernova Project II. Observations of the intermediate-luminosity red transient SNhunt120. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 639, A103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N.; Kashi, A. The energy source of intermediate luminosity optical transients. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1107.3454. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuna, D.; Ishii, A.; Kuriyama, N.; Kashiyama, K.; Shigeyama, T. Intermediate Luminosity Red Transients by Black Holes Born from Erupting Massive Stars. Astrophys. J. 2020, 897, L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyreva, A.; Baklanov, P.; Jones, S.; Stockinger, G.; Janka, H.T. Synthetic observables for electron-capture supernovae and low-mass core collapse supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 503, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankare, E.; Kotak, R.; Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M.; Mattila, S.; Smartt, S.J.; Bruce, A.; Chambers, K.C.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Flewelling, H. On the triple peaks of SNHunt248 in NGC 5806. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 581, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Hu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Modjaz, M.; Leonard, D.C. A Hubble Space Telescope Snapshot Survey of Nearby Supernovae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2002, 114, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, R.B.; Rizzi, L.; Shaya, E.J.; Courtois, H.M.; Makarov, D.I.; Jacobs, B.A. The Extragalactic Distance Database. Astrophys. J. 2009, 138, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, E.; Diaz, M.; Williams, R.E.; Preston, G.; Bensby, T. The peculiar nova V1309 Scorpii/nova Scorpii 2008. A candidate twin of V838 Monocerotis. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 516, A108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlafly, E.F.; Finkbeiner, D.P. Measuring Reddening with Sloan Digital Sky Survey Stellar Spectra and Recalibrating SFD. Astrophys. J. 2011, 737, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorce, J.G.; Tully, R.B.; Courtois, H.M.; Jarrett, T.H.; Neill, J.D.; Shaya, E.J. From Spitzer Galaxy photometry to Tully-Fisher distances. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 444, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.M.; Kochanek, C.S. LOSS’s first supernova? New limits on the ‘impostor’ SN 1997bs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauerhan, J.C.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Graham, M.L.; Zheng, W.; Clubb, K.I.; Filippenko, A.V.; Valenti, S.; Brown, P.; Smith, N.; Howell, D.A.; et al. SN Hunt 248: A super-Eddington outburst from a massive cool hypergiant. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goranskij, V.P.; Barsukova, E.A.; Spiridonova, O.I.; Valeev, A.F.; Fatkhullin, T.A.; Moskvitin, A.S.; Vozyakova, O.V.; Cheryasov, D.V.; Safonov, B.S.; Zharova, A.V.; et al. Photometry and spectroscopy of the luminous red nova PSNJ14021678+5426205 in the galaxy M101. Astrophys. Bull. 2016, 71, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Andrews, J.E.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Mauerhan, J.C.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Bond, H.E.; Filippenko, A.V.; Clubb, K.I.; Graham, M.L.; Perley, D.A.; et al. Massive star mergers and the recent transient in NGC 4490: A more massive cousin of V838 Mon and V1309 Sco. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagorodnova, N.; Kotak, R.; Polshaw, J.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Cao, Y.; Cody, A.M.; Doran, G.B.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Fraser, M.; Fremling, C.; et al. Common Envelope Ejection for a Luminous Red Nova in M101. Astrophys. J. 2017, 834, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Chen, T.W.; Cai, Y.Z.; Morales-Garoffolo, A.; Cano, Z.; Mason, E.; Barsukova, E.A.; Benetti, S.; Berton, M.; Bose, S. The evolution of luminous red nova AT 2017jfs in NGC 4470. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 625, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Mason, E.; Taubenberger, S.; Fraser, M.; Cortini, G.; Tomasella, L.; Botticella, M.T.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Kotak, R.; Smartt, S.J.; et al. Luminous red novae: Stellar mergers or giant eruptions? Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 630, A75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stritzinger, M.D.; Taddia, F.; Fraser, M.; Tauris, T.M.; Contreras, C.; Drybye, S.; Galbany, L.; Holmbo, S.; Morrell, N.; Pastorello, A.; et al. The Carnegie Supernova Project II. Observations of the luminous red nova AT 2014ej. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 639, A104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M.; Valerin, G.; Reguitti, A.; Itagaki, K.; Ochner, P.; Williams, S.C.; Jones, D.; Munday, J.; Smartt, S.J.; et al. Forbidden hugs in pandemic times. I. Luminous red nova AT 2019zhd, a new merger in M 31. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 646, A119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Valerin, G.; Fraser, M.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Valenti, S.; Reguitti, A.; Mazzali, P.A.; Amaro, R.C.; Andrews, J.E.; Dong, Y.; et al. Forbidden hugs in pandemic times. II. The luminous red nova variety: AT 2020hat and AT 2020kog. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 647, A93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagorodnova, N.; Klencki, J.; Pejcha, O.; Vreeswijk, P.M.; Bond, H.E.; Burdge, K.B.; De, K.; Fremling, C.; Gehrz, R.D.; Jencson, J.E.; et al. The luminous red nova AT 2018bwo in NGC 45 and its binary yellow supergiant progenitor. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 653, A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M.; Wang, X.F.; Filippenko, A.V.; Reguitti, A.; Patra, K.C.; Goranskij, V.P.; Barsukova, E.A.; Brink, T.G.; et al. Observations of the luminous red nova AT 2021biy in the nearby galaxy NGC 4631. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.00734. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorello, A.; Valerin, G.; Fraser, M.; Reguitti, A.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Filippenko, A.V.; Rojas-Bravo, C.; Tartaglia, L.; Reynolds, T.M.; Valenti, S.; et al. Panchromatic evolution of three luminous red novae: Forbidden hugs in pandemic times—IV. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.02782. [Google Scholar]
- Tylenda, R.; Hajduk, M.; Kamiński, T.; Udalski, A.; Soszyński, I.; Szymański, M.K.; Kubiak, M.; Pietrzyński, G.; Poleski, R.; Wyrzykowski, Ł.; et al. V1309 Scorpii: Merger of a contact binary. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 528, A114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejcha, O. Burying a Binary: Dynamical Mass Loss and a Continuous Optically thick Outflow Explain the Candidate Stellar Merger V1309 Scorpii. Astrophys. J. 2014, 788, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejcha, O.; Metzger, B.D.; Tomida, K. Cool and luminous transients from mass-losing binary stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 4351–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejcha, O.; Metzger, B.D.; Tomida, K. Binary stellar mergers with marginally bound ejecta: Excretion discs, inflated envelopes, outflows, and their luminous transients. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, 2527–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goranskij, V.P.; Shugarov, S.Y.; Barsukova, E.A.; Kroll, P. V838 Mon Before and After Its Outburst. Inf. Bull. Var. Stars 2004, 5511, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, D.V. An Analytical Model for the Plateau Stage of Type II Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1993, 414, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.; Justham, S.; Avendano Nandez, J.L.; Lombardi, J.C. Identification of the Long-Sought Common-Envelope Events. Science 2013, 339, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipunov, V.M.; Blinnikov, S.; Gorbovskoy, E.; Tutukov, A.; Baklanov, P.; Krushinski, V.; Tiurina, N.; Balanutsa, P.; Kuznetsov, A.; Kornilov, V. MASTER OT J004207.99+405501.1/M31LRN 2015 luminous red nova in M31: Discovery, light curve, hydrodynamics and evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, M.; Macias, P.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Grindlay, J.; Batta, A.; Montes, G. Lessons from the Onset of a Common Envelope Episode: The Remarkable M31 2015 Luminous Red Nova Outburst. APJ 2017, 835, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Pejcha, O. Shock-powered light curves of luminous red novae as signatures of pre-dynamical mass-loss in stellar mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 471, 3200–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Metzger, B.D. Light Curve Model for Luminous Red Novae and Inferences about the Ejecta of Stellar Mergers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.10478. [Google Scholar]
- Kochanek, C.S.; Adams, S.M.; Belczynski, K. Stellar mergers are common. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauerhan, J.C.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Johansson, J.; Fox, O.D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Graham, M.L. The dusty aftermath of SN Hunt 248: Merger-burst remnant? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, H.; de Mink, S.E.; de Koter, A.; Langer, N.; Evans, C.J.; Gieles, M.; Gosset, E.; Izzard, R.G.; Le Bouquin, J.B.; Schneider, F.R.N. Binary Interaction Dominates the Evolution of Massive Stars. Science 2012, 337, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitt, G.; Stevenson, S.; Vigna-Gómez, A.; Justham, S.; Ivanova, N.; Woods, T.E.; Neijssel, C.J.; Mandel, I. Luminous Red Novae: Population models and future prospects. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 3229–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iben, I., Jr.; Tutukov, A.V. Rare Thermonuclear Explosions in Short-Period Cataclysmic Variables, with Possible Application to the Nova-like Red Variable in the Galaxy M31. Astrophys. J. 1992, 389, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, U.; Henden, A.; Kiyota, S.; Laney, D.; Marang, F.; Zwitter, T.; Corradi, R.L.M.; Desidera, S.; Marrese, P.M.; Giro, E.; et al. The mysterious eruption of V838 Mon. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 389, L51–L56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimeswenger, S.; Lederle, C.; Schmeja, S.; Armsdorfer, B. The peculiar variable V838 Mon. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 336, L43–L47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soker, N.; Tylenda, R. Main-Sequence Stellar Eruption Model for V838 Monocerotis. Astrophys. J. 2003, 582, L105–L108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcavi, I.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Howell, D.A.; McCully, C.; Poznanski, D.; Kasen, D.; Barnes, J.; Zaltzman, M.; Vasylyev, S.; Maoz, D.; et al. Optical emission from a kilonova following a gravitational-wave-detected neutron-star merger. Nature 2017, 551, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J.; Chen, T.W.; Jerkstrand, A.; Coughlin, M.; Kankare, E.; Sim, S.A.; Fraser, M.; Inserra, C.; Maguire, K.; Chambers, K.C.; et al. A kilonova as the electromagnetic counterpart to a gravitational-wave source. Nature 2017, 551, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, F.W.; Wang, Y.Z.; Shen, Z.Q.; Liang, Y.F.; Li, X.; Liao, N.H.; Jin, Z.P.; Yuan, Q.; Zou, Y.C.; et al. The GW170817/GRB 170817A/AT 2017gfo Association: Some Implications for Physics and Astrophysics. Astrophys. J. 2017, 851, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Liu, L.D.; Dai, Z.G.; Wu, X.F. Afterglows and Kilonovae Associated with Nearby Low-luminosity Short-duration Gamma-Ray Bursts: Application to GW170817/GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, L41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovegrove, E.; Woosley, S.E. Very Low Energy Supernovae from Neutrino Mass Loss. Astrophys. J. 2013, 769, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.B.; Ivezić, Ž.; Jones, R.L.; Graham, M.L.; Marshall, P.; Saha, A.; Strauss, M.A.; Yoachim, P.; Ribeiro, T.; Anguita, T.; et al. Optimization of the Observing Cadence for the Rubin Observatory Legacy Survey of Space and Time: A Pioneering Process of Community-focused Experimental Design. ApJS 2022, 258, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breivik, K.; Connolly, A.J.; Ford, K.E.S.; Jurić, M.; Mandelbaum, R.; Miller, A.A.; Norman, D.; Olsen, K.; O’Mullane, W.; Price-Whelan, A.; et al. From Data to Software to Science with the Rubin Observatory LSST. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.02781. [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton, K.M.; Bianco, F.B.; Street, R.; Bell, K.; Buckley, D.; Graham, M.; Hernitschek, N.; Lund, M.B.; Mason, E.; Pepper, J.; et al. Rubin Observatory LSST Transients and Variable Stars Roadmap. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.04499. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, J.P.; Mather, J.C.; Clampin, M.; Doyon, R.; Greenhouse, M.A.; Hammel, H.B.; Hutchings, J.B.; Jakobsen, P.; Lilly, S.J.; Long, K.S.; et al. The James Webb Space Telescope. Space Sci. Rev. 2006, 123, 485–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).