Abstract
Dust storms, observed in all seasons, are among the most momentous of Mars’ atmospheric activities. The Entry–Descent–Landing (EDL) activity of a Martian landing mission is influenced by local atmospheric conditions, especially the probability of dust storm activity. Chryse Planitia, featuring many of the largest and most prominent outflow channels and possible mud volcanoes, is an important target site for current and future Mars landing missions. It is of great significance to understand that a Mars landing probe may encounter a dust storm situation during EDL season in the Chryse Planitia. In this study, based on four Martian years, Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) Mars Daily Global Maps (MDGMs), 1172 dust storms were identified within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring. Secondly, the daily mean dust storm probability was calculated, binned by 1° of solar longitude in the Chryse landing area. The two active periods of dust storm activity are Ls = 177–239° and Ls = 288–4°, with an average daily mean dust storm probability of 9.5% and 4.1%. Dust storm activity frequency is closely interrelated with the seasonal ebb and flow of the north polar ice cap; consequently, most dust storms occur in either the cap’s growth or recession phase. We divided the Chryse landing area into square grids of 0.5° and computed the average probability of dust storm occurrence in each grid, which ranged from 0.19% to 2.42%, with an average of 1.22%. The dust storm activity probability in space was also inhomogeneous—low in the west and south but high in the east and north—which was mainly affected by the origin and the path of dust storm sequences. Based on empirical orthogonal function (EOF) analysis of storms in the Chryse area, 40.5% are cap-edge storms in the northern hemisphere. Finally, we concluded that the preferred time of a Mars landing mission is Ls = 18–65° in the Chryse Planitia, and three preferred landing areas were selected with low dust storm probability.
1. Introduction
The atmospheric surface pressure on Mars is about 1% of that on Earth, but Mars is not short of dynamics. Dust storms, observed in all seasons, are one of the most momentous of Mars’ atmospheric activities in both spacecraft- and Earth-based observations [1,2,3,4,5]. The atmospheric thermal and dynamic structures, and the transport of aerosols and chemical species, are all strongly dependent on the dust’s spatio-temporal distribution, particle sizes, and optical properties [6]. Dust storms on Mars absorb solar radiation and affect the atmospheric thermal structure and dynamics, which show great variability in time and space [7]. According to previous Earth-based and spacecraft observations, three significant characteristics of the Martian climatic system were revealed: (1) seasonal polar cap growth and decline recurring year after year [8,9]; (2) large-scale local and global dust storms expanding stochastically to a greater or lesser extent in the period of a half year known as the typical “dust storm season” [10]; (3) the preferred origin regions of dust storms (Acidalia, Utopia, Arcadia, Hellas, etc.) in both southern and northern hemispheres [11].
Fonseca et al. [12] used the Mars implementation of the Planet Weather Research and Forecasting model (MarsWRF) to simulate the Entry–Descent–Landing (EDL) vertical profiles from Mars past missions, and compare the results with observed results. They found that MarsWRF had a trend to underestimate the temperature and overestimate the density for heights above 15 km, which could be due to an incorrect description of the observed dust loading. Thus, dust storm activity can affect the precision and success during EDL season for a Martian landing mission [13,14,15]. The Spirit and Opportunity rovers landed just in the southern summer dust storm season, contributing to their landing sites being 10.1 km and 24.6 km away from the center of the landing ellipses [16]. The Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) evaluated the atmospheric risks, including the dust storm activity in the landing area of EDL season (near Gale Crater) in advance with the result that the landing position was only 2.4 km away from the center of the landing ellipse [17].
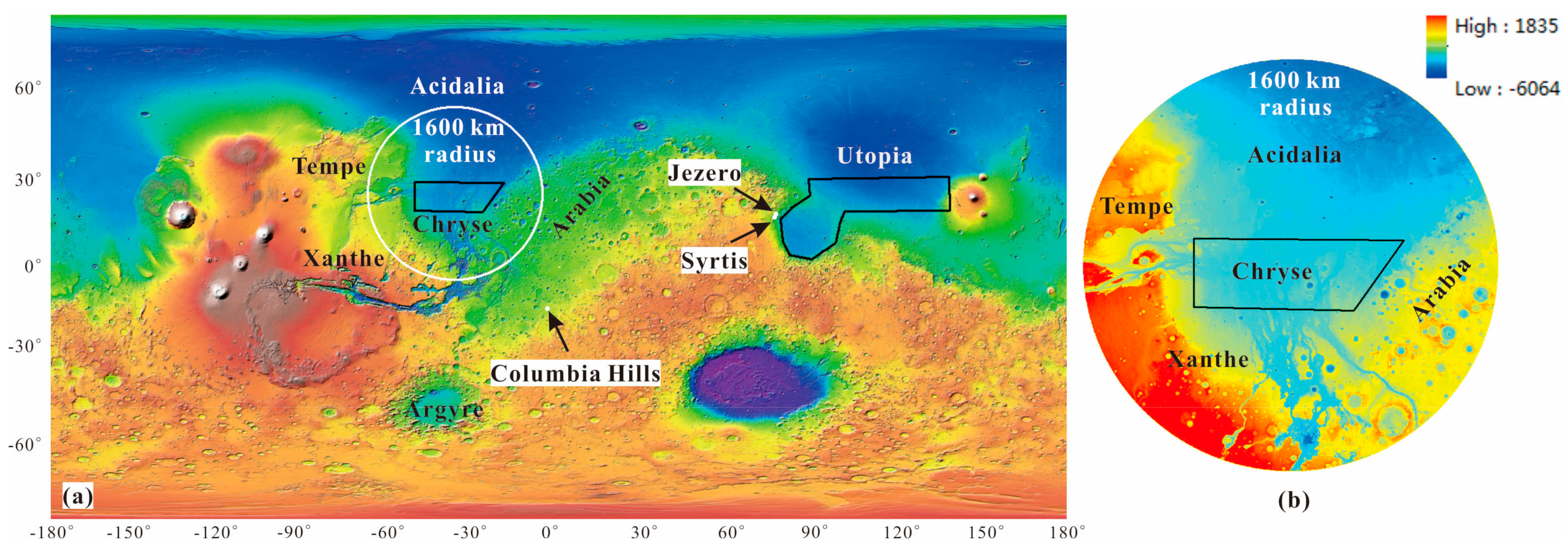
China’s first Mars probe mission (Tianwen-1) landed in southern Utopia Planitia on 15 May 2021 and carried out detailed investigations of the landing area using the Zhurong rover, with high accuracy and resolution. Before launching the Tianwen-1 probe, two tentative landing areas (Chryse and southern Utopia Planitia) were chosen in the latitude range of 5–30° (Figure 1a) by considering several factors, such as the topographic slope, latitude, geographic elevation, coverage of dust, distribution of rocks, local wind speed and visibility. Southern Utopia Planitia is close to the Jezero site of Perseverance (Figure 1a). Cantor et al. [18] employed MRO MARCI images (MY 28-MY 34) to look into dust storm activity in Syrtis and the Columbia Hills, and found that the dust storm activity probability was about 1.6% in the Columbia Hills and 3.2% at the Syrtis site. Yao et al. [19] studied the average daily probability of dust storm activity in southern Utopia Planitia, with a range of 0% to 14.13%, and selected five preferred landing areas with the spatial probability of dust storm <3%. Hence, this paper intends to study the dust storm activity probability in Chryse Planitia, and within its 1600 km-radius monitoring ring (Figure 1a). Small edifice features in Chryse Planitia were identified as mud volcanism using the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) images [20]. It is very important to study the geological background, structural features, the formation and evolution of aquifers in Chryse Planitia, which is an important target site for current and future Mars landing missions.
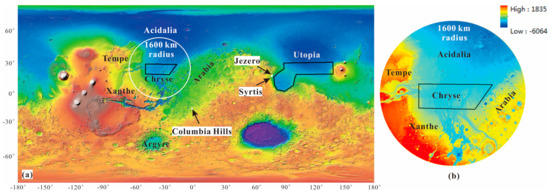
Figure 1.
(a) Two tentative landing areas of Tianwen-1 mission on an elevation rendering map from Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbit Laser Altimeter (MOLA) DEM data with a simple cylindrical projection. The black polygons show the two tentative landing areas and the black arrows denote the NASA Mars 2020 candidate landing sites, respectively. The white circle is Chryse’s 1600 km-radius monitoring ring. (b) The elevation map within the 1600 km-radius monitoring ring of the Chryse landing area.
According to previous work, Chryse Planitia is an important dust storm activity origin area in the northern hemisphere of Mars, and it lies to the south of Acidalia and the north of Argyre (Figure 1a). Acidalia and Argyre are also frequent dust storm origin areas, with dust storm sequences occurring most intensively at Acidalia. Moreover, two dust storm sequences pass through the Chryse landing area. One comes from Acidalia, traveling towards the south, and the other comes from Argyre, traveling towards the north [11]. We focus on dust storms during EDL season for the Chryse landing area, considering both time and space.
In this paper, we used imagery from the Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) onboard the Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) to: (1) identify the dust storms within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring and extract their shape parameters, such as center, range and area; (2) calculate the daily mean dust storm probability binned by 1° of solar longitude; (3) divide the study area into square grids of 0.5° and compute the mean occurrence probability of dust storms in each grid during the EDL season for Tianwen-1; (4) employ empirical orthogonal function (EOF) analysis to find out the leading causes, and separate dust storm occurrence in space in 0.5-degree grids within the Chryse area and the seasonal cycle.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. MOC Mars Daily Global Maps
MGS was the first successful NASA mission to Mars after the Viking mission in 1976, and it went silent in November 2006. The MGS MOC aimed at acquiring daily global images to study temporal and spatial models of the Martian atmosphere over the course of one Martian year. The MGS MOC science investigation used 3 instruments: two wide-angle (WA) cameras with red (580–620 nm) and blue (400–450 nm) band passes (WAR and WAB), with a maximum resolution of ~230 m/pixel and a narrow-angle camera for obtaining gray (black and white) high-definition images (usually 1.5 to 12 meters per pixel). Each WA camera contains a single linear CCD array (3456 pixels across) with a “fish-eye” lens providing a 140° field of view. The WA cameras provide the planetary edge view from 12:17 to 15:43 LMST, with an intrinsic resolution of about 230 m−1 at the lowest point and 1.5 km−1 at the edge. Low-resolution observations of MOC can be made in every orbit, such that in a single 24-hour period a complete global picture of the planet can be assembled at a resolution of at least 7.5 km/pixel. Of course, because the Mars Observer orbit is Sun-synchronous, this global picture shows how each part of Mars appears at approximately 1400 local solar time [21]. MOC has sent back more than 2.4 million images spanning 4.8 Martian years. With their “daily global map” mode running, the WA cameras continuously map the Mars surface at a constant resolving power of 3.75 or 7.5 km per pixel. The Mars daily global map (MDGM) is a global image mosaic with 13 single MOC wide-angle mapping blocks, covering almost a complete Mars Day [22]. The MDGMs have a resolution of 0.1 × 0.1° (~6 km/pixel at the equator); these were archived in 4 mission sub-phases and can be downloaded from https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/WWRT1V (accessed on 20 August 2021).
2.2. Dust Storm Detection
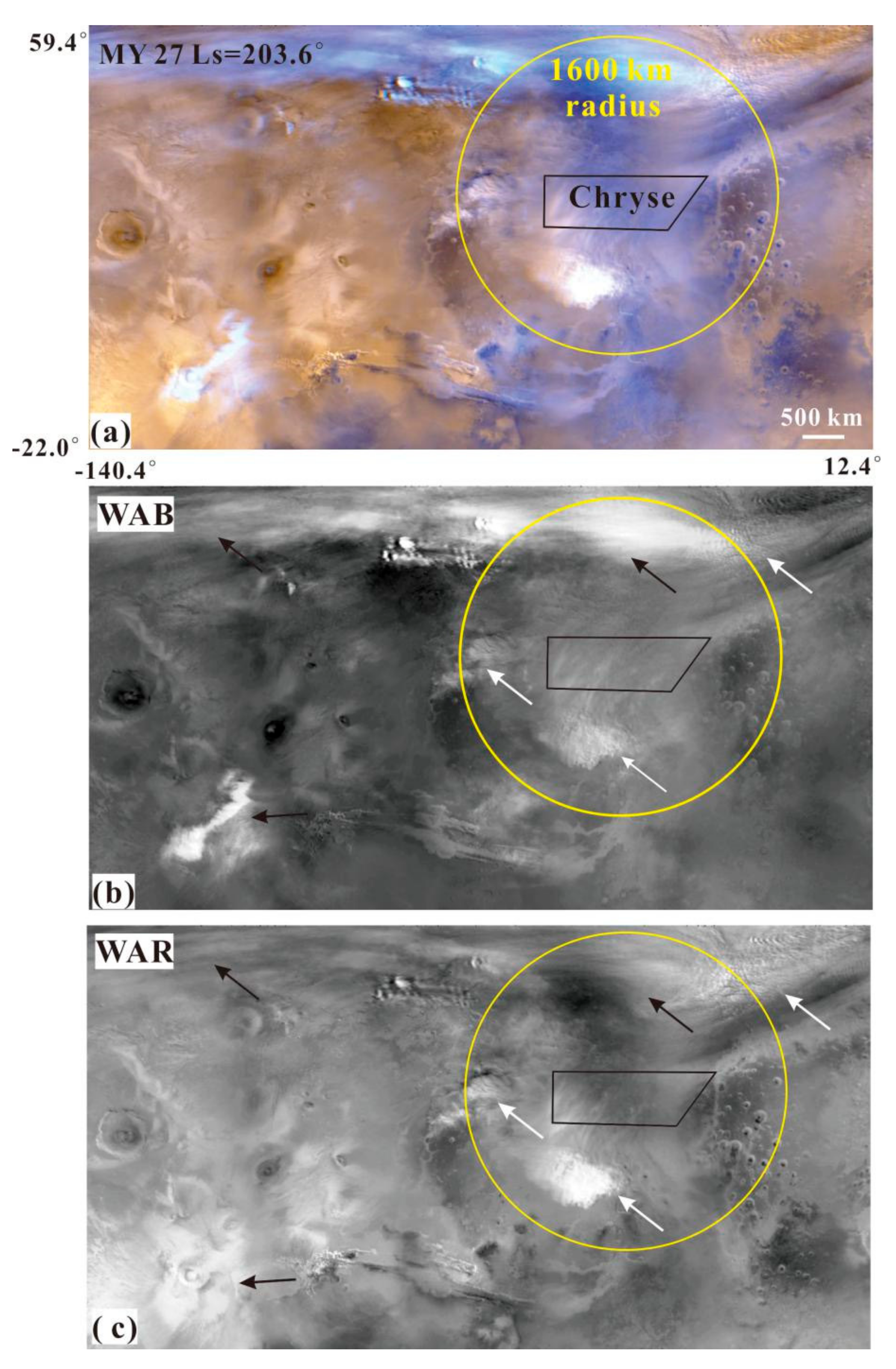
In MOC MDGMs, the Martian surface covered by dust storms appears yellow, while the exposed rocks usually appear black (Figure 2a). As a result of atmospheric dynamics, the Martian surface covered by meteorological phenomena, such as dust storms and clouds, appears white or has visible structures (Figure 2). In this paper, dust storms were identified via the visual detection procedures described in detail in [4]. Condensation clouds (ice) have a higher single-scattering albedo than dust storms in the WAB band pass of MOC, and so are more uniformly white [23] and brighter in blue bands than red bands (black arrows in Figure 2b,c). The opposite is true for dust storms (white arrows in Figure 2b,c). We can discriminate between dust storms and condensation clouds depending on the contrast between the WAR and WAB images of the same MOC.
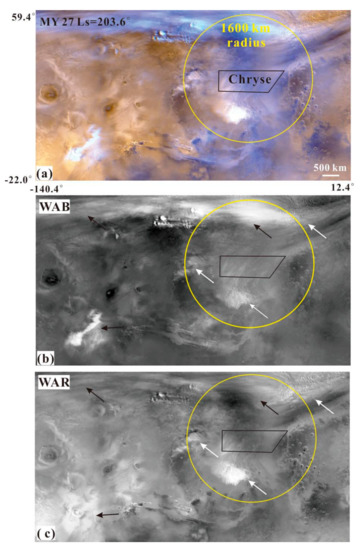
Figure 2.
(a) Example of a MOC MDGM section (MY 27, Ls = 203.6°) in Chryse Planitia. (b,c) are the blue and red bands of this image. These two wavelengths can discriminate between clouds (black arrows) and dust storm activity (white arrows). The black polygon and yellow circles are the Chryse landing area and its 1600 km-radius monitoring ring, respectively.
There are two kinds of dust storms that can reach or appear at Chryse Planitia. One is from the northern polar region and then moves southward to Chryse Planitia after 1–2 sols. The other are local dust storms because Chryse Planitia is the main dust storm source area in the northern hemisphere. According to the above-mentioned dust storm detection methods, 1172 dust storms were observed within the 1600 km-radius monitoring ring. The longitude and latitude, Martian year and Ls of 1172 dust storms identified in the study area were contained in Table S1. Dust storms can be recognized as textured and untextured depending on whether they have textures. The textured dust storms show visible structures on their cloud tops that are indicative of active dust lifting. While the untextured dust storms are classified as discrete clouds of dust with clearly defined borders without distinct topside visible texture. Then, each identified dust storm was vectorized as a polygon feature with the GIS software, and its shape parameters were extracted and measured, including center, area and range. Lambert Conformal Conic Projection was adopted to reduce projection deformation, ensuring these measurements’ accuracy. This projection was based on the Esri GCS_Mars_2000 (a geographic coordinate system), the data of which are Esri D_Mars_2000.
2.3. Planet-Encircling Dust Event
The solar longitude Ls is the Mars–Sun angle, measured from the Northern Hemisphere spring equinox where Ls = 0°. Ls = 90° thus corresponds to northern summer solstice, just as Ls = 180° marks the northern autumn equinox and Ls = 270° the northern winter solstice. There was only one planet-encircling dust event (PEDE) in the four Martian years for which the MGS was investigating, starting at Ls = 184.7° in MY 25 (26 June 2001) and receding to around Ls = 200.4°, with a duration of 120 sols or so [5]. By 2019, only seven confirmed PEDEs had been observed, occurring in 1956, 1971–1972, 1973, two in 1977, 2001, 2007 and 2018 [3,6,10,24,25,26,27,28,29]. In line with the predecessors’ observations, two characteristics of PEDEs were revealed: (1) the onset of PEDEs usually occurs in the southern spring and summer seasons [3]; (2) PEDEs were observed to originate in three main areas—the northwest of Hellas, the west, the south, and the southeast of Solis Planum and Claritas Fossae, and Isidis [5]. The Chryse region is not included in the above three. As non-universal phenomena [30], dust storms in PEDEs produce deviations that affect the prediction of the spatial and temporal probability of dust storm activity in the Chryse Planitia. Therefore, the dust storms that occurred during the PEDE in 2001 were not considered or identified in this paper.
3. Temporal Probability of Dust Storm Activity in Chryse
Dust storm events have seasonal patterns, recurring year after year, and so we can estimate dust storm activities in the EDL season [14,31]. It is extremely important to understand dust storm probability during EDL season to improve the landing safety and accuracy, and thus ensure the landing mission’s success.
3.1. Dust Storm Activity of a Martian Year
According to the work of [18], the daily mean probability P(T) of a dust storm considering both time probability P(d) and area probability P(A) can be calculated as follows:
In Equation (2), i is the index of the four Martian years in MGS MOC observations, N(i, d) is the number of dust storms identified on a sol (d) of the given Mars year (i), A(i, d) is the fraction of the area covered by a dust storm on the sol (d) of the Mars year i. n(d) is the sum of dust storms identified on the same sol of four Martian years. In Equation (3), P(d) is the probability of dust storms recurring on the same sol (d) in four Martian years. Is(i, d) indicates whether there is a dust storm on sol (d) of Martian year (i). If dust storms occur on sol (d) of Martian year (i), the Is(i, d) is 1, while if there is no dust storm, the Is(i, d) is 0.
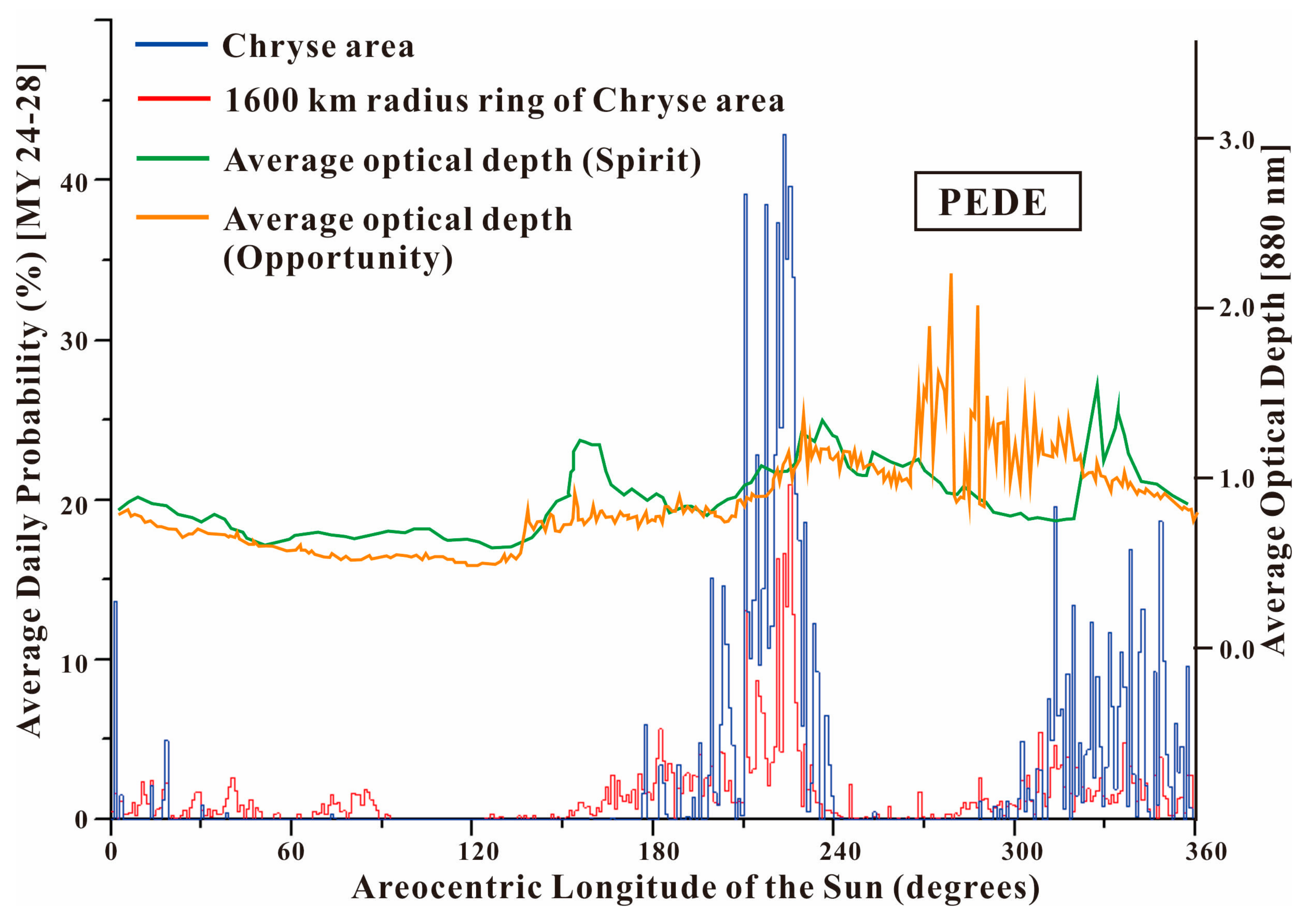
According to Equation (1), the daily mean dust storm probability in the Chryse landing area and within its 1600 km-radius ring is shown in Figure 3.
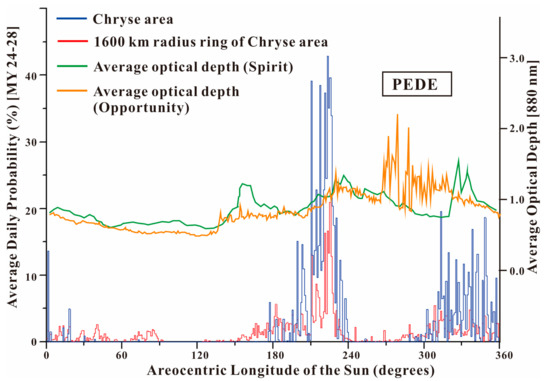
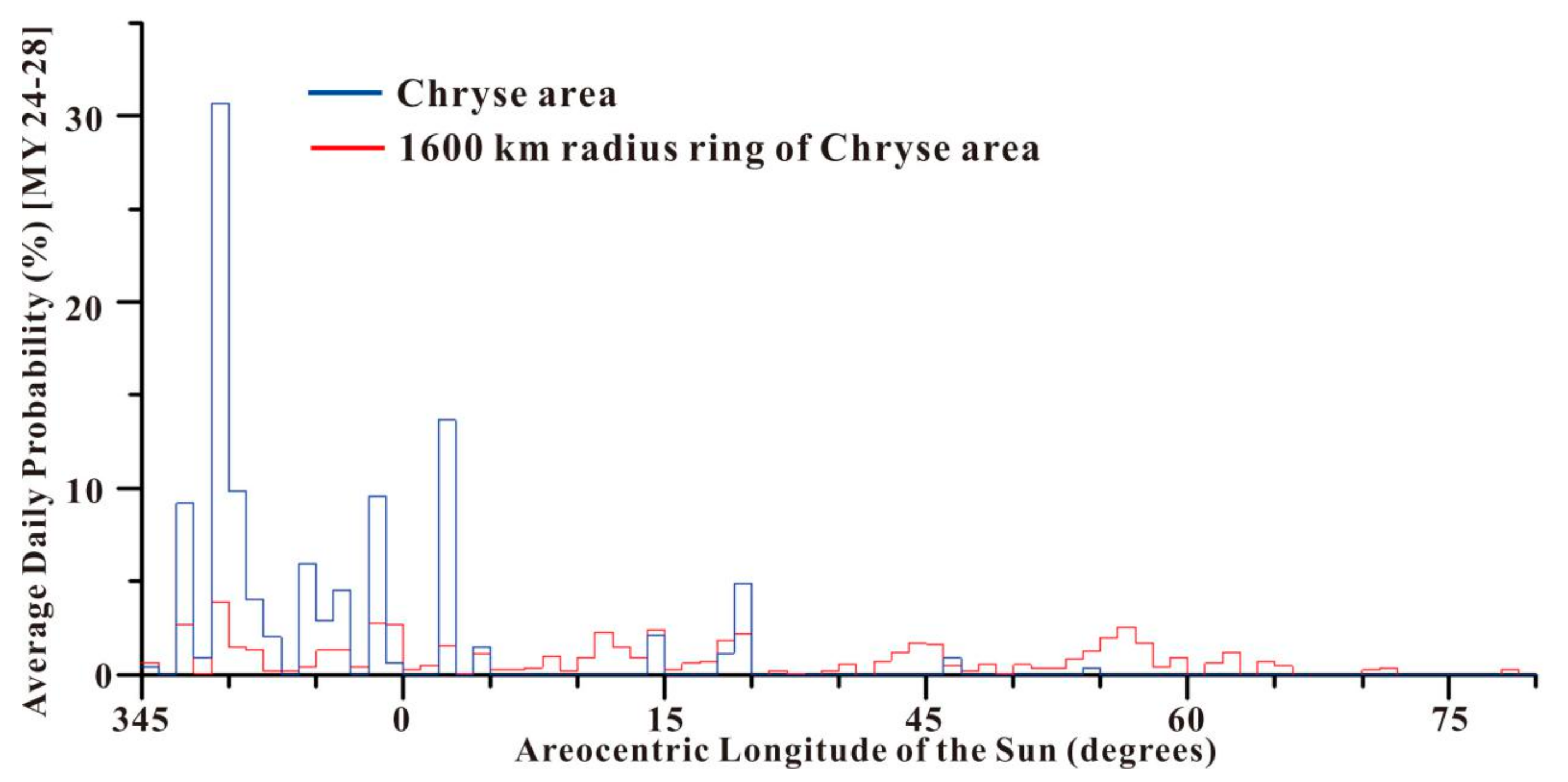
Figure 3.
Daily mean dust storm frequency is proportional to the Ls of the Chryse area (blue color) and within its 1600 km-radius ring (red color) in 1° of Ls. The green and orange curves show the average optical depths gauged by the Spirit Rover and opportunity Rover [32] in 2.5° of Ls.
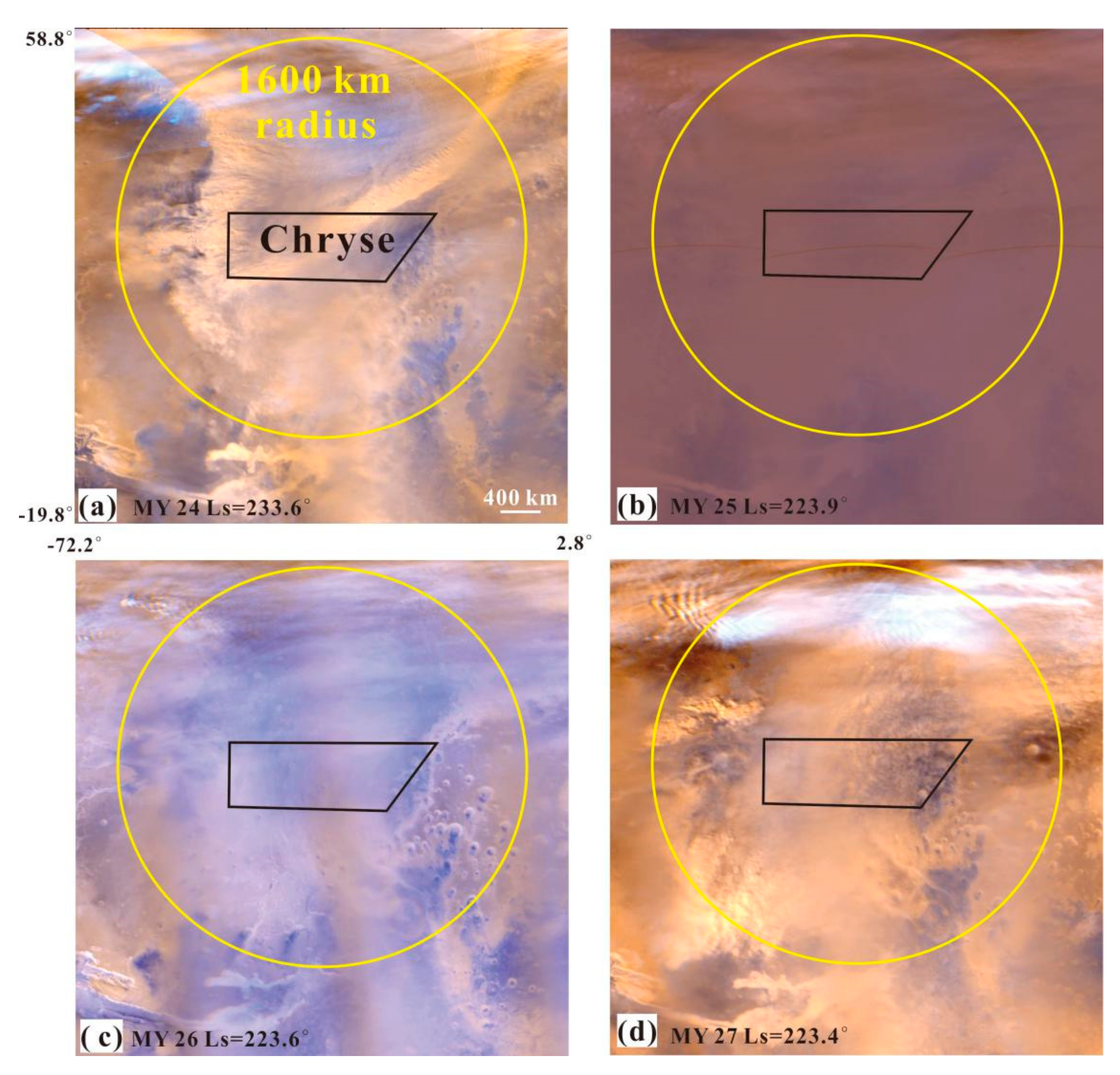
(1) As shown in Figure 3, the P(T) in the Chryse area, shown in blue, and within its 1600 km-radius ring, shown in red, peaked at 42.9% with Ls = 223° and 20.9% with Ls = 225°, respectively. The minimum P(T) in Chryse and within its 1600 km-radius ring was 0. For example, during Ls = 39–72°, no dust storm was identified in the four Martian years of MOC MDGMs in the Chryse area. The P(T) in the Chryse area and within its 1600 km-radius ring was one order of magnitude higher than that (the maximum was 5%) calculated by [11] at candidate landing sites for the NASA Mars 2020 Rover mission. The four Martian years of MOC MDGMs at Ls = 223° in the Chryse area are shown in Figure 4. At Ls = 223° for MY 24 and MY 27, the dust storms almost covered the whole Chryse area (Figure 4a,d), while at Ls = 223° for MY 25, the dust storms were excluded because of the PEDE; at Ls = 223° for MY 26, there was no dust storm in the Chryse area (Figure 4b,c). As a result, we can conclude that the Chryse area had a large P(T) (42.9%) at Ls = 223° for MY 24–28. In addition, Adp_ds in the Chryse area was higher than that within its 1600 km-radius ring at the same sol, which may be due to the fact that the area of the latter (8.04 × 106 km2) is larger than that of the former (1.03 × 106 km2).
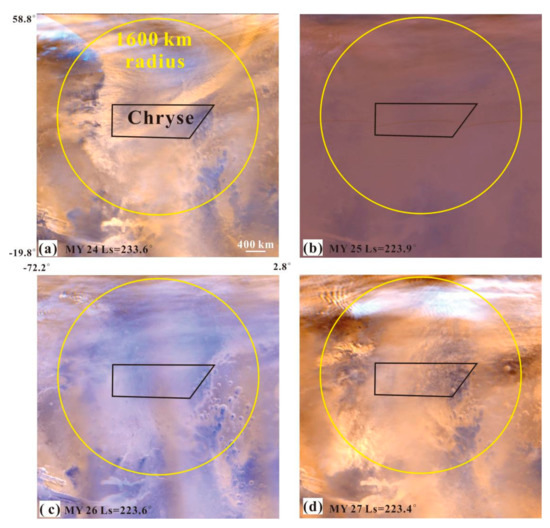
Figure 4.
The MOC MDGMs at Ls = 223° of the Chryse area in four Martian years. The black polygon and yellow circle are the Chryse and its 1600 km-radius monitoring ring, respectively. (a) is the MOC MDGM at Ls = 223.6° in MY 24. (b) is the MOC MDGM at Ls = 223.9° in MY 25 and shows the PEDE. (c) is the MOC MDGM at Ls = 223.6° in MY 26. (d) is the MOC MDGM at Ls = 223.4° in MY 27.
(2) The P(T) in the Chryse area and within its 1600 km-radius ring showed obvious inhomogeneity and seasonality within a Martian year. In the Chryse area, dust storm activity was the most frequent from the northern hemisphere autumnal equinox (Ls = 177°) to the end of autumn (Ls = 239°), with an average P(T) of 9.5%. Another period with high P(T) in the Chryse area was from the northern hemisphere winter solstice (Ls = 288°) to the next spring (Ls = 4°), with an average P(T) of 4.1%. The active periods of these two dust storm activities within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring were longer than those in the Chryse area. Their duration ranged from Ls = 152° to 247° and from Ls = 269° to Ls = 92°, with mean P(T)values of 2.9% and 1.0%, respectively. This was not due to the study area’s growth, but the northward movement of the 1600 km-radius ring near the seasonal cover edge in the northern hemisphere, where dust storms occurred frequently [4,5]. Moreover, a small number of dust storms occurred during Ls = 93–123° within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring.
(3) The green and orange curves show the average optical depths provided by the Spirit and Opportunity Rovers during the mission, with increments of 2.5° Ls. Excluding PEDEs, the average optical depths peaked at 1.0 (Ls = ~160°), 1.2 (Ls = ~240°) and 1.45 (Ls = ~330°). The elevated optical depths obtained by the two rovers were related to storm activity observations in the Chryse area and its 1600 km-radius ring, except for the first peak (Ls = ~160°) (Figure 3). Chryse and the two rovers were located in different parts of Mars (far away from each other), but the dust storm curves and optical depths they both obtained were similar in terms of laws and shapes. Dust storms at the end of summer in the northern hemisphere (Ls = ~160°) mainly occurred at the edge of the southern polar cap, which recedes seasonally, while the edge of the northern polar cap recedes toward the north pole at 75° N. The Spirit Rover was located in the southern hemisphere of Mars (14.6° S), and was closer to the south polar cap edge than the Chryse area, which would be deeply affected by storms traveling from the south polar cap’s edge around Ls = 160°. However, the Chryse area was far away from both south and north polar caps at Ls = 160°, and there were almost no dust storms.
(4) The dust storm activity in both Chryse and within its 1600 km-radius ring mainly occurred during the period from Ls = 180° to Ls = 240°. We deemed that these storms originated in the Acidalia–Chryse channel. The Acidalia–Chryse channel was the most common development mode of dust storm sequences, and each sequence propagated along the same path, lasting for at least five sols. This seemed to have a bearing on the frequent frontal eruptions (or the “pumping” of storms by frontal systems) in the high latitudes of the northern hemisphere. In each sol, one or more dust storms appeared in the Acidalia–Chryse channel during Ls = 214–228° in MY 27 [11].
3.2. Latitudinal Distribution of Dust Storms within Chryse’s 1600 km-Radius Ring
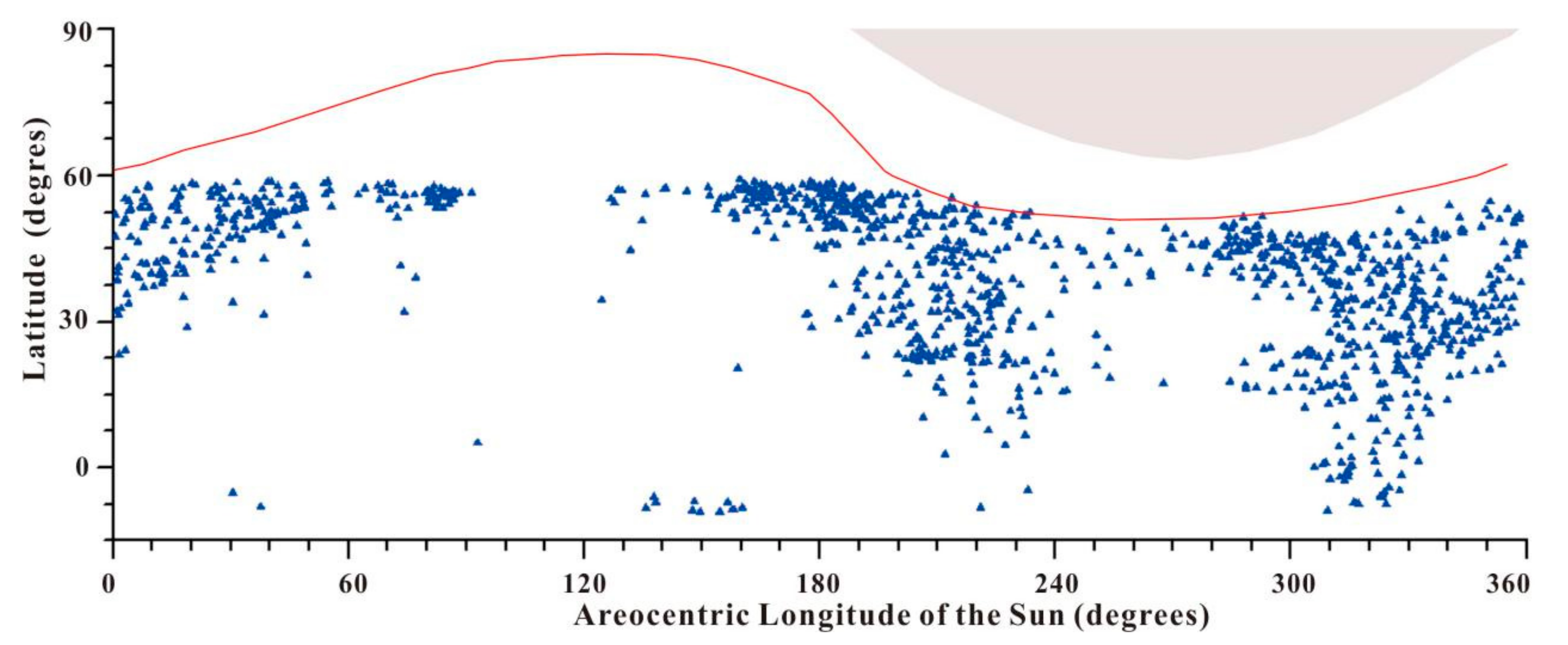
In order to study the relationship between the location (latitude) and time of dust storm occurrence within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring, we made a 2D scatter map, which took the central latitude and sol of dust storm activity for use as the Y- and X-axis (Figure 5).
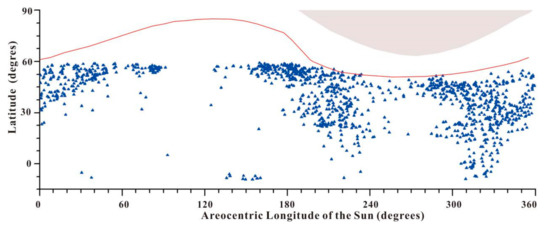
Figure 5.
Dust storm latitude distribution, observed within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring for every 1° solar longitude. The red curve indicates the mean latitude of the north polar cap edge, while the gray area at the top shows the terminator. The blue triangles are the centers of dust storm events.
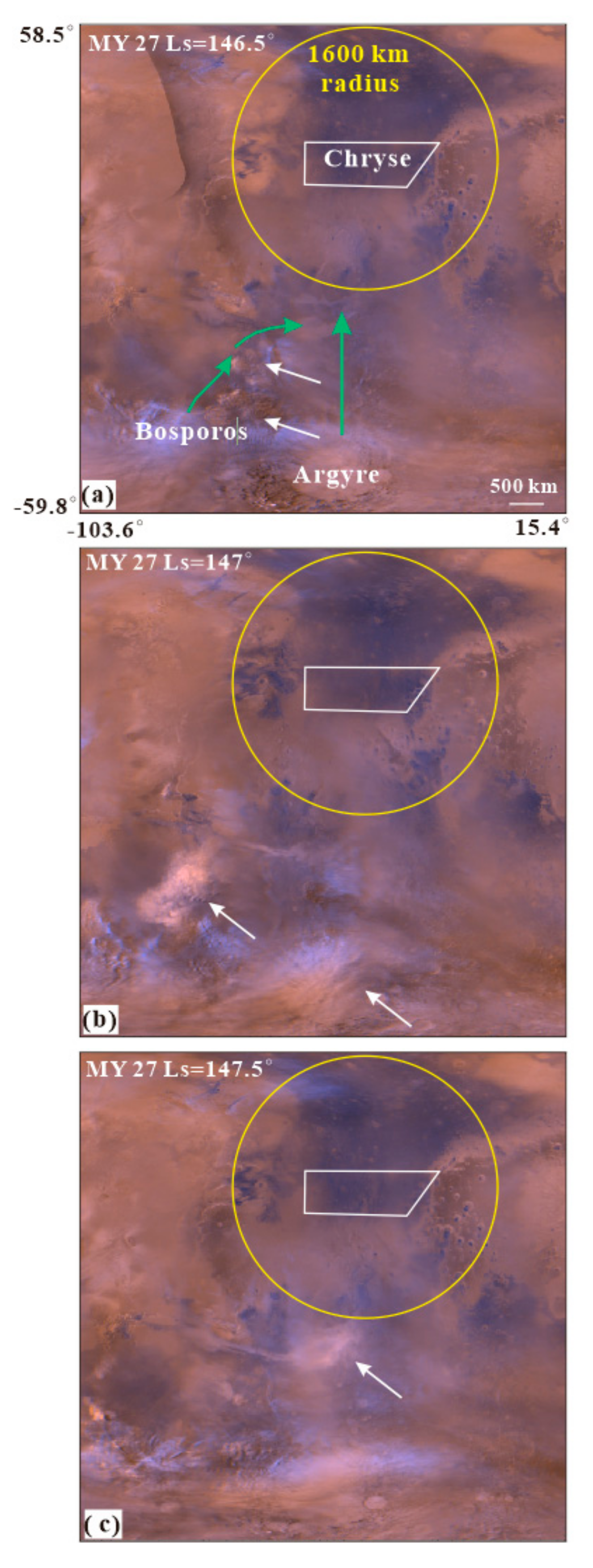
The latitude of Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring ranges from 60° N to 20° S. Major storm activity in the Chryse monitoring area occurred early in the Martian year (Ls = 0°), originating along the north polar cap edge, the north of the Chryse, which recedes seasonally. From Ls = 0° to 90°, as the dust storm centers gradually moved northward, the dust storm in the south of the Chryse gradually disappeared, with the seasonal north polar cap edge having receded poleward to 83° N. As Ls increased, the quantities of dust storms decreased until Ls = 90°, when no dust storms occur in the monitoring area. From the beginning of the northern summer solstice (Ls = 90°) until Ls = 130°, the northern hemisphere dust storm activity disappeared in the Chryse landing area, only occurring once near the equator. There was no dust storm activity in Chryse’s 1600 km area at the end of the northern spring, which may be caused by: (1) a longitudinal offset in the Acidalia storm zone [33], where the northern hemisphere’s spring dust storm activity is initiated; (2) the continued northward regression of the north polar cap’s edge, which is usually followed by Martian storms [4,34]; (3) the period of minimum storm activity in most parts of Mars (including Chryse) is regarded as the solstice minimum (Ls = 90°) [35]. As the storm activity increased again around mid-summer (Ls = 135°), some of the storms were initiated in the southern hemisphere, starting in the northern Argyre and Bosporos Straits during Ls = 135–160° (Figure 6a). These storms moved north toward the south of the Chryse landing area, but they had small sizes and a narrow impact range (Figure 6b,c).

Figure 6.
The dust storm activity of the southern hemisphere (Argyre and Bosporos) in northern summer season (Ls = 135–160°) within the monitoring area of Chryse. (a–c) are MOC MDGMs at Ls = 146.5–147.5° of MY 27, a simple cylindrical projection with a resolution of 6 km/pixel. The white and green arrows denote the dust storm events and the southern dust storm sequences [11], respectively. The white polygon and yellow circle represent the Chryse landing area and its 1600 km-radius monitoring area.
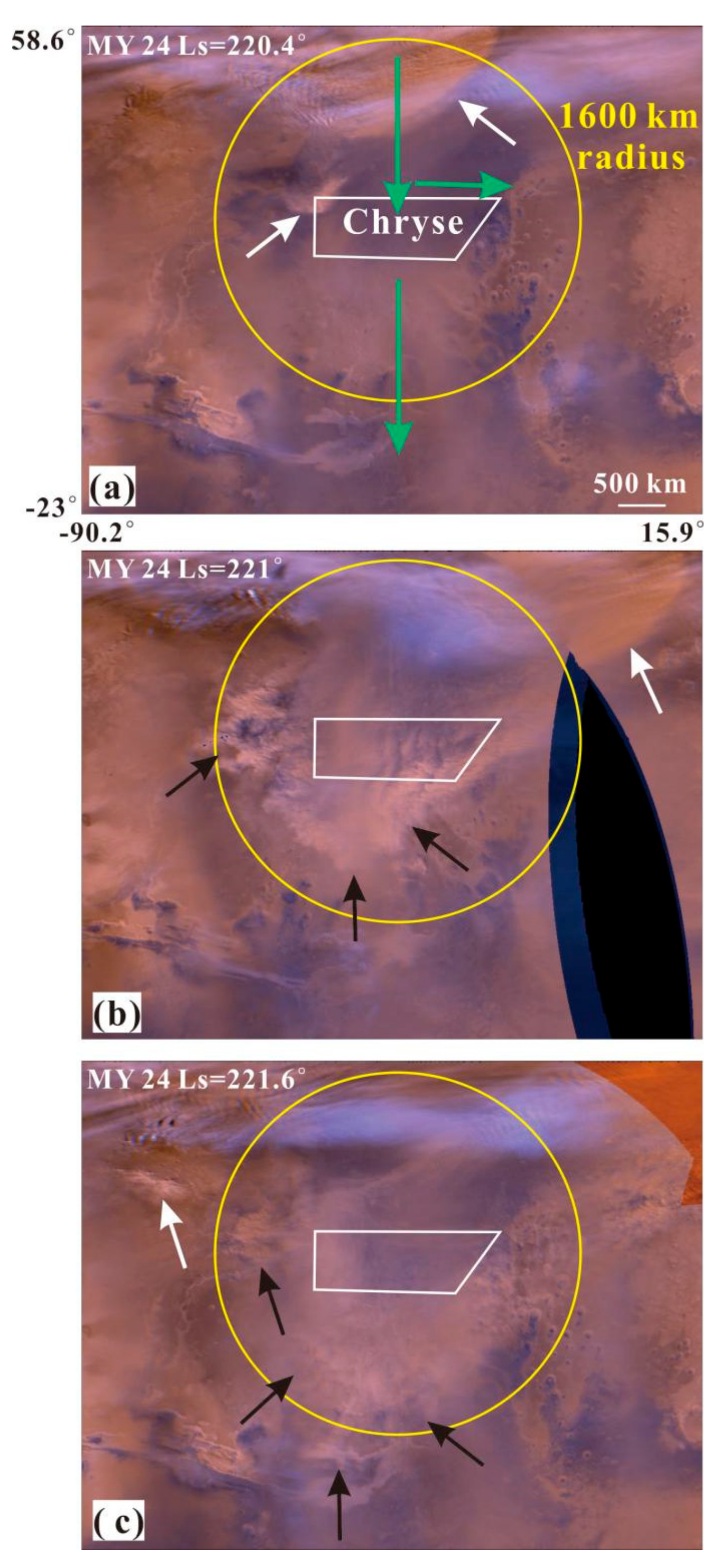
The storm activity became active in the north polar and Chryse regions with the arrival of the northern autumnal equinox (Ls = 180°) and the expansion of the seasonal north polar cap edge. During Ls = 180–250°, the scale and range of dust storm activity gradually increased, as it moved southward. Most dust storm activity originated from the Chryse landing area or north of it, as observed in the MOC MDGMs for four Martian years. These included not only local dust storms (white arrows in Figure 7) originating in the Chryse landing area but also multiple frontal/flushing dust storms (black arrows in Figure 7) moving along the Acidalia cross-equatorial storm-track (green arrows in Figure 7). As the seasonal north polar cap edge had moved towards the equator by 55° N at the end of the northern autumnal season (Ls = 250–280°), the frequency and scope of dust storm activity reached their minimum. About half a month after the winter solstice in the northern hemisphere (Ls = 270°), dust storm activities recurred in the monitoring area and were mainly distributed at the edge of the north polar cap and the north of Chryse. There were also some small-scale dust storms in the southern hemisphere, originating from Argyre and Bosporos. These Chryse and north polar cap edge storms lasted from Ls = 270° until the next northern spring equinox, respectively.
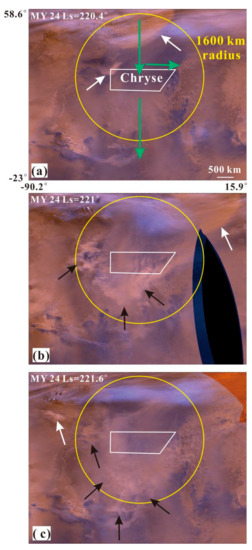
Figure 7.
The dust storm activity in northern hemisphere’s autumn (Ls = 180–250°) within 1600 km-radius ring of the Chryse landing area. (a–c) are the MOC MDGMs at Ls = 220.4–221.6° of MY 24, a simple cylindrical projection with a resolving power of 6 km/pixel. The white, black and green arrows are the local, frontal/flushing dust storm event and the northern Acidalia dust storm sequences [11], respectively. The white polygon and yellow circle represent the Chryse landing area and its 1600 km-radius monitoring area.
The latitudinal distribution of dust storm centers in the monitoring area in every 1° of solar longitude (Figure 5) showed seasonal and spatial heterogeneity. Firstly, the dust storm activity frequency was closely related to the seasonal waxing and waning of the north polar ice cap. Dust storms within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring mostly arose during the rise or decay of the polar cap, rather than in its quiescent stage, when the cap’s change rate approached the minimum. In the northern hemisphere, the dust storm activity at the edge of the cap was almost at a standstill before or on the northern summer solstice, and this stagnation lasted for a long time (Ls = 90–120°). Secondly, the dust storm activity within the monitoring area mainly came from the north polar cap, Acidalia and Chryse, and a small number of events arose from the southern hemisphere (Argyre and Bosporos) northward. Nevertheless, the dust storms in the southern hemisphere were much smaller and much less frequent than the ones in the northern hemisphere.
3.3. Dust Storm Probability during the EDL Season of Mars Landing Missions
In this section, we take the EDL seasons of the Tianwen-1 and the Perseverance as examples to analyze the probability of dust storm activities in the Chryse Planitia and select the appropriate landing time.Tianwen-1 was launched on 23 July 2020, and its EDL season was around April–June 2021 (MY 36, Ls = 25.1–65.4°) [36], which is different from that of the Perseverance (Ls = 345–25°). Consequently, this study set the EDL season as Ls = 345–65°, in agreement with the Mars missions of China and NASA in 2020. According to Equation (1) and Figure 3, the P(T) during EDL season in Chryse and within its 1600 km-radius ring were determined and are shown in Figure 8.
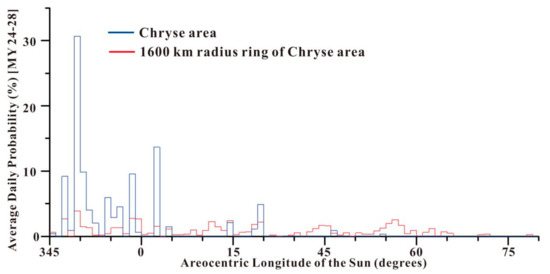
Figure 8.
Daily mean dust storm probability in the Chryse landing area (blue color) and within its 1600 km-radius ring (red color) between Ls = 345 and 65° (EDL season) with the increment of Ls = 1°.
(1) As shown in Figure 8, the P(T)of the MOC MDGMs of MY 24-MY 28 in Chryse (blue color) peaked at 30.6% (Ls = 348°) during EDL season. The dust storm activity in the Chryse landing area is discontinuous and large, but it is continuous in the range of Ls = 345–3°, with an average P(T) of 4.8%. After this, the dust storm activity recurred from Ls = 13° to 18°, but was very weak, with an average P(T) of 1.3%. As to dust storm activity within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring, the P(T) peak decreased to 3.9% at Ls = 3.8° and continued almost throughout the EDL season (Ls = 345–49°) with an average P(T) of 0.9%.
(2) When the seasonal northern polar cap edge retreated northward from 58° N to 65° N, it had an impact on the probability of dust storm activity in Chryse, which resulted from the northward movement of the cap edge dust storm activity. During the warm season in the northern hemisphere (Ls = 345–5°), the north polar cap began to sublime, and a great quantity of carbon dioxide was released into the Martian atmosphere. As the north polar cap edge receded northward, cap-edge storms occurred and moved southward. These cap-edge storms move southward through the Chryse landing area along the Acidalia storm track [11]. In late northern spring (Ls = 45–80°), as it receded, the northern polar cap moved far away from Chryse, and the change rate of the north polar cap’s size was near the minimum, thus the dust storm activity probability was the lowest within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring.
(3) Success and accuracy during EDL season are decided by Chryse’s atmospheric conditions, especially the dust storm activity probability. It is best to complete the landing procedure during the period with the lowest P(T) in EDL season, so as to reduce the risk. In EDL season, the dust storm lasts throughout Ls = 345–3° and 13–18° in the Chryse landing area, which is thus not the best time for a landing mission. While during Ls = 18–65°, dust storm activity was found in only five sols, the P(T) was around ≤1.6% with an average of 0.15%. The probabilities mentioned above are consistent with the estimate of an MSL candidate landing site at less than 3%: 0.1% for the actual Gale site [14], and ranging from 1.6% in the Columbia Hills to 3.2% at the Syrtis site for NASA’s 2020 Mars mission [17]. We can conclude that dust storms will not give rise to major hazards between Ls = 18°and 65° in the EDL season.
4. Spatial Distribution of Dust Storm Activity in the Chryse Planitia
The dust storm activity on Mars is characterized by obvious spatiotemporal heterogeneity. In this section, we study the average spatial probability of dust storm activity in the Chryse landing area, ascertaining the most suitable landing area for future Mars landing probes. For the sake of calculating the P(S) in different areas, the research area was divided into a regular grid, with each grid’s side length being 0.5° in this paper. According to [18], the P(S) in each 0.5° grid in a whole Martian year can be calculated by:
While the P(S) in 0.5° grids during the EDL season can be calculated by:
where N(i, g) is the number of dust storms identified in a given grid (g) of the given Mars year (i), and A(i, g) is the total dust storm area identified in a given grid (g) of the given Mars year (i) divided by the given grid area, which is the percentage of dust storm area in a given grid (g) of the i Mars year. n(g) is the total number of dust storms in the given grid (g) of four Martian years. The Martian year and EDL season can be divided into 36 and 9 segments, binned by 10° of Ls, separately. s is the index of the segment, and Is(s, g) indicates whether there is a dust storm in segment (s) of a given grid (g). According to Equations (4) and (5), the P(S) in the 0.5° grids during the Martian year and EDL season are shown in Figure 9.
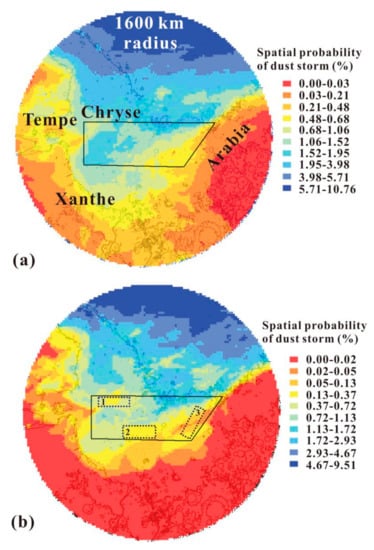
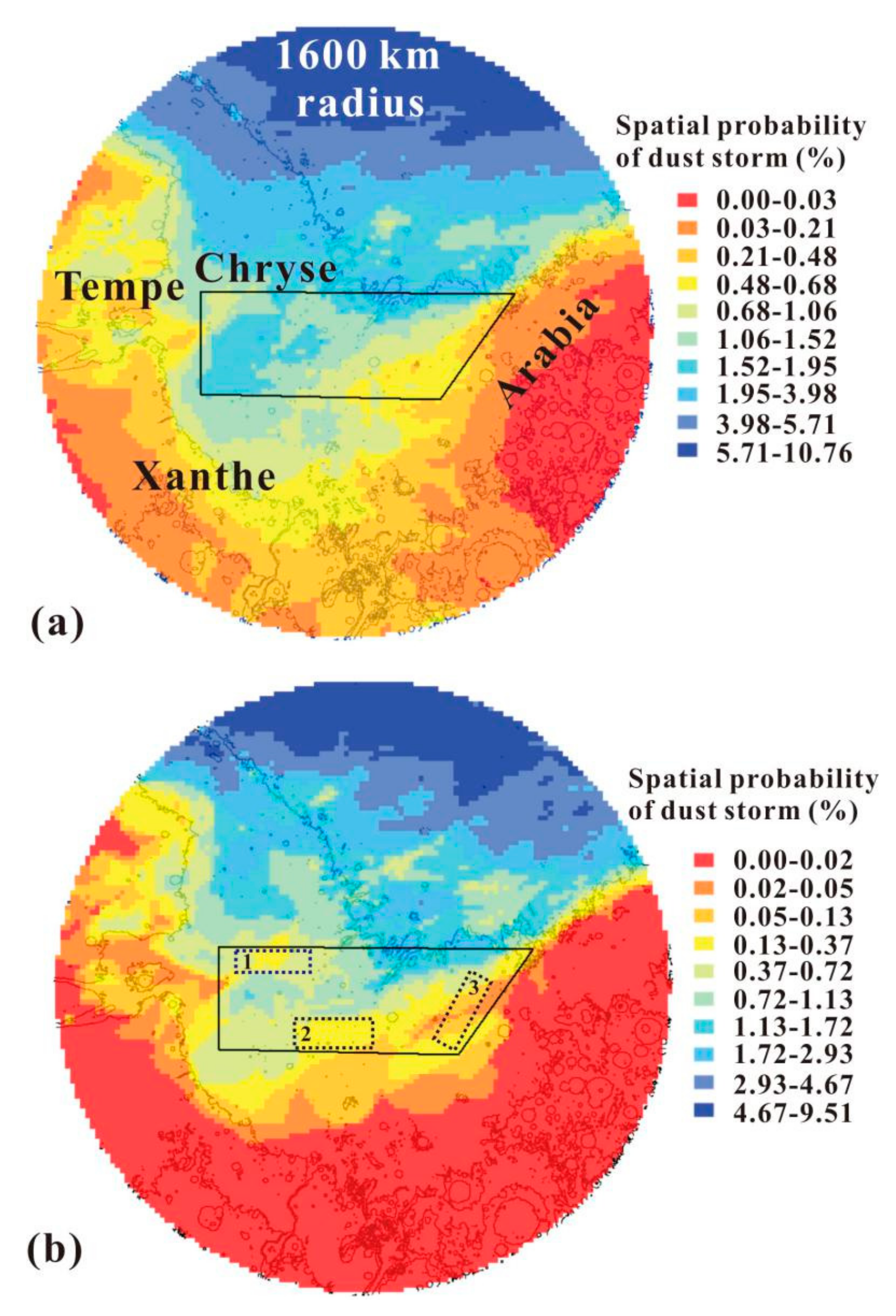
Figure 9.
The dust storm activity probability within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring in MY (a) and EDL season (b) in each 0.5° grid. The black polygon shows the Chryse landing area. Topography is illustrated with black contours (2 km intervals) for reference. The dotted rectangles marked with numbers 1–3 are the PLAs.
(1) In Figure 9a, the P(S) in Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring in a whole Martian year ranged from 0% to 10.8% and showed spatial inhomogeneity. Acidalia, north of Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring, was the region where dust storm activity occurred most frequently, followed by Chryse, Tempe and Arabia, east and west of the monitoring area. Xanthe, south of Chryse, was the region with the lowest P(S). In the Chryse landing area (black polygon), the spatial probability of dust storm activity was also nonuniform, evidenced by the fact that the probability was lower in the west and south and higher in the east and north. The P(S) in the Chryse landing area ranged from 0.19% to 2.42%, with an average of 1.22%.
In Figure 9b, the P(S) of the monitoring area during the EDL season was the highest in the northern area (Acidalia), but this dropped little by little in the southern area and in both the east and west. The dust storm activity probability in the north of Xanthe, east of Tempe and west of Arabia, leveled off to 0, which is lower than that for a whole Martian year (Figure 9a). This is because dust storm activity in the south of the monitoring area mostly occurred in Ls = 135–160° and 305–340°, not during EDL season (Figure 5). The P(S) in the Chryse landing area during the EDL season ranged from 0.03% to 2.03%, with an average of 0.59%. The northeastern part of the Chryse landing area showed the highest P(S), followed by the middle and western parts, while the eastern part had the lowest.
(2) The P(S) distribution in the Chryse landing area can be explained as follows:
(i) Dust storm activity origin. Acidalia is an area where dust storm sequences occur most intensively, and Chryse is one of the origin areas of dust storm activity [11]. According to [37], the following factors can affect regional frontal/flushing dust storms in time and location: conversion among baroclinic wave modes; storm zones and standing waves. In agreement with these observations, Mars GCM simulations have suggested that upwind areas of Acidalia underwent strong surface stresses [38,39]. As a result, Chryse’s northern and central parts showed a higher spatial probability of dust storm activity.
(ii) Routes of dust storm sequences. In the northern hemisphere, there were three main paths from the north to the south, namely, through Acidalia, Utopia and Arcadia [11]. The above-mentioned sequences have manifested numerous frontal/flushing dust storms in previous studies, the large proportion of which dispersed in the northern hemisphere [37,40]. Some Acidalia sequences extend eastward in the southern low latitudes, through the Chryse landing area from east to west (Figure 7a). Hence, the dust storm activity in the east is more intense than that in the west, just as the probability in space in the north is higher than that in the south.
(3) Considering the spatial probability of dust storm activity, the flat 0.5° grids with low probability can be selected as the preferred landing areas (PLAs). In Figure 9b, three PLAs (dotted rectangles marked with numbers 1–3) were labeled. PLAs 1 and 2 were in the west of the Chryse landing area, while PLA 3 was in its eastern section. The areas of the three PLAs were 65856 km2, 84744 km2 and 70242 km2, with average P(S) values of 0.45%, 0.26% and 0.03% during EDL season, respectively.
Finally, Ls = 18–65° can be chosen as the preferred landing time, and the three PLAs in Chryse as the preferred landing areas, for future Mars landing probes.
5. Spatial and Seasonal Pattern of Dust Storm Activity in Chryse
EOF was first applied in geophysics by [41] and has since been used to analyze data with complex spatial and temporal characteristics. In view of EOF, the eigenfunctions, which are empirically found and best describe the information, could be regarded as the best way to decompose data into representative patterns [42]. EOF analysis, one form of principal component analysis, can disassemble the spatiotemporal dataset into a linear combination of spatial function and time function, so as to acquire the association between dust storm spatial mode (the principal component) and time projection (time series). These independent spatial modes give not only the dust storm information in the original study area, but also rank the variance contribution. Hence, it is possible for us to distinguish and explain the dust storm types in the study area via a linear combination of the first several modes. In the light of dust storm frequency as binned by the 0.5° longitude and latitude of Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring, we determine the leading and separate modes of dust storms using EOF. Each 0.5° grid could be regarded as a measuring point in the Chryse area, which can be observed once a Martian day for four Martian years. The final observations could form a spatiotemporal dataset of dust storms in the study area. The main purposes of using EOF to analyze Chryse’s spatio-temporal dust storm dataset are to acquire the space–time distribution pattern of the dust storm; carry out a factor analysis for the association between dust storm modes and the affecting factors; determine the main types of and explanations for dust storms in the study area. The results are shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11.
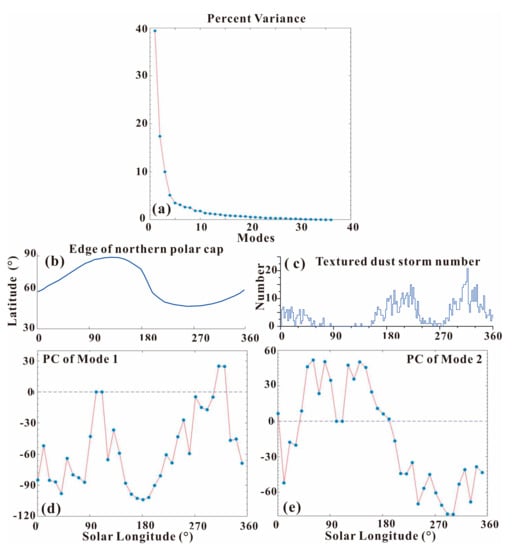
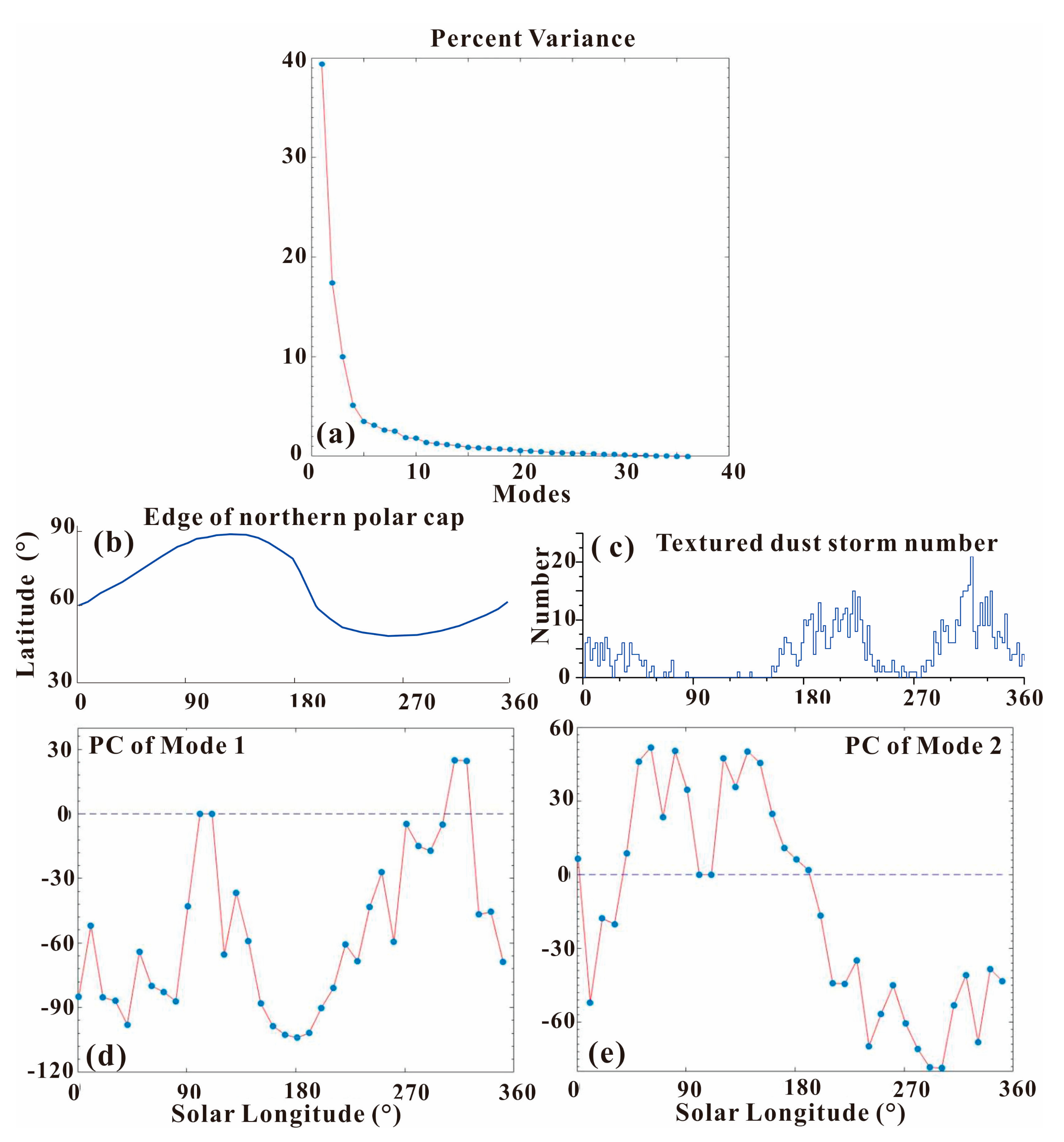
Figure 10.
(a) The total variance percentage in dust storm activity within the 1600 km-radius ring of the Chryse Planitia interpreted by every EOF mode. (b) The average latitude of the Arctic polar cap edge in its respective seasons. (c) The daily number of textured dust storms within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring. The principal components of EOF Mode 1 (d) and Mode 2 (e) demonstrate those modes’ seasonality.
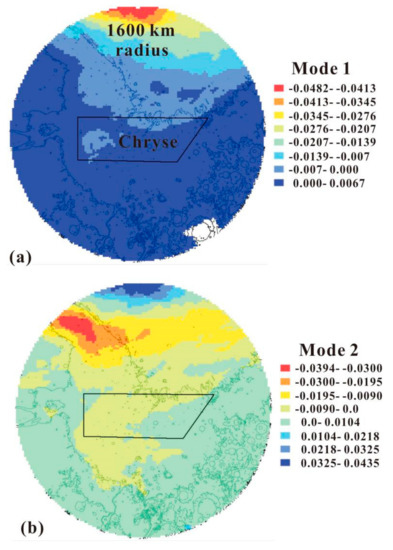
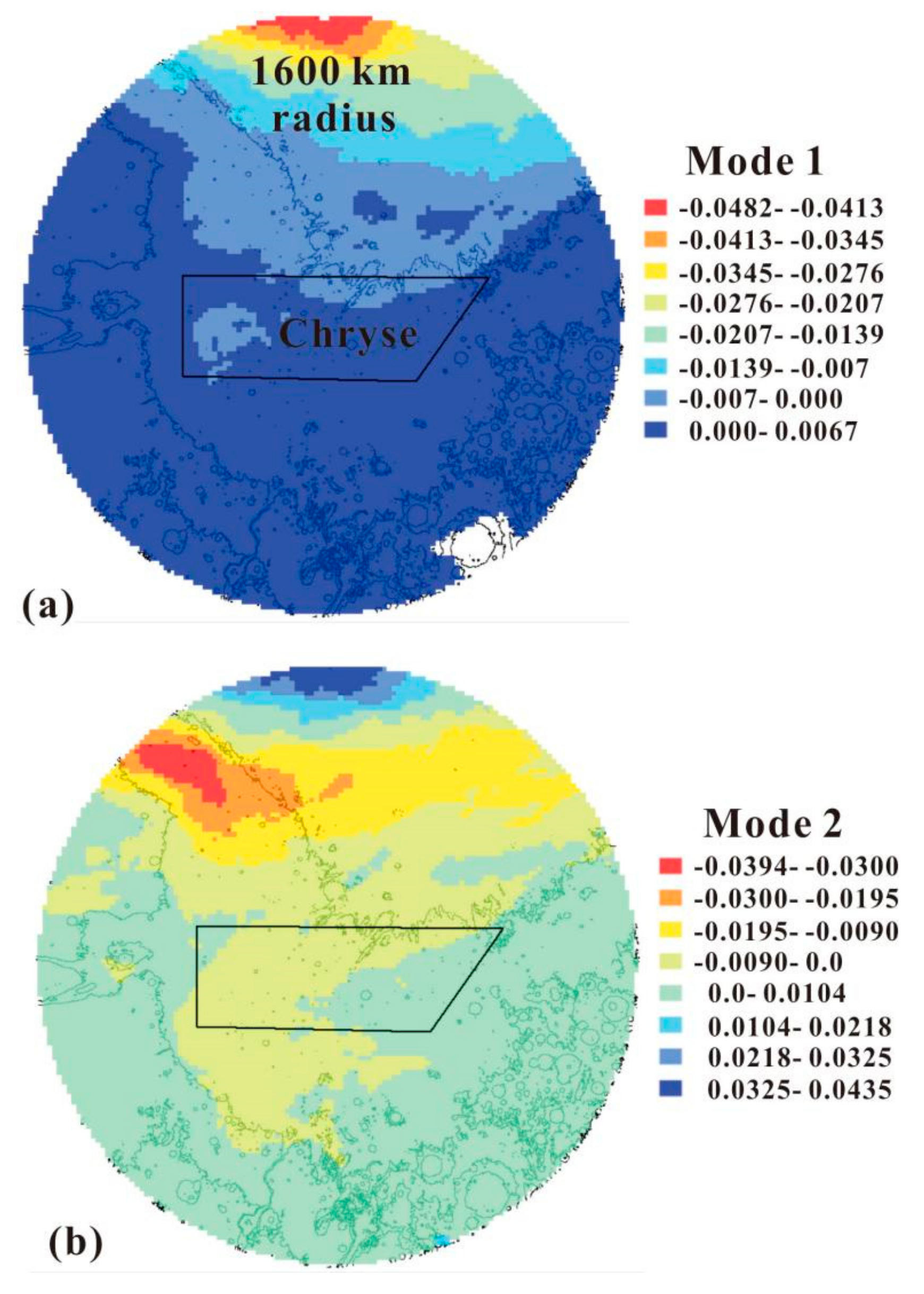
Figure 11.
Eigenvector image patterns for Mode 1 (a) and Mode 2 (b) of temporal variance within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring in 0.5° grids. The black polygon shows the Chryse landing area. The topographic map is shown in black contours (2 km apart) for reference.
Figure 10a shows the variance bound up with every EOF pattern (the eigenvalues) of dust storm activity in the Chryse area. One Martian year can be divided into 36 segments binned by 10° of Ls, in order to obtain 36 EOF modes. It can be seen that the first mode and the second one account for 40.5% and 17.5% of the total variance separately, comprising 58% of the total variance associated with dust storm activity. However, the variance of mode 5–36 is very small. Mode 1 and 2 possessed valuable information, but higher-order modes may be produced by stochastic noise.
The first two EOF modes for dust storm activity within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring are shown in Figure 11. Mode 1 (Figure 11a) is dominated by negative values in the north of the monitoring area, ranging from near 30° to 57° N. There are weak positive values in the south of the monitoring area. Although Mode 2 (Figure 11b) possesses the same spatial model as Mode 1, the negative values shifted southward to near the bottom of the monitoring area. The highest positive values of Mode 2 occurred in the north of the monitoring area. Modes 1 and 2 show enormous vertical variations from the north to the south in the monitoring area. In the northern half of the Chryse Planitia, the two modes were arranged and located differently, but they clearly showed a near north–south frontal feature with an evident gradient.
Figure 10d,e show the principal components of EOF Mode 1 and 2. Mode 1 has a notable seasonal peak, with its positive values occurring only during Ls = 305–325° in the Martian year. For the rest of the Martian year, there is a negative trough at Ls = 180°. In line with the average latitude of the seasonal southern polar cap edge in Figure 10b (the blue curve), Mode 1 is primarily consistent with the seasonal growth and regression of the southern polar cap edge. It has long been known that dust storm origin is related to the polar cap edge. The polar cap edge encourages dust lifting via atmospheric processes along and near the sharp near-surface temperature gradient [43]. This long-known relationship was investigated further in atmospheric circulation and mesoscale models (e.g., [44]), as well as in observations (e.g., [45]). Dust storm activity within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring mostly arose during the growth or regression of the polar cap, rather than in its quiescent stage. In Figure 10d, the two apexes of the principal components in Mode1 are located at Ls = 105° and 315°, which correspond to the northernmost and southernmost edges of the southern polar cap, while the only trough in Mode 1 is located at Ls = 180° when the cap’s change rate approached the minimum. Thus, 40.5% of annual dust storm activity within Chyrse’s 1600 km-radius ring can be regarded as cap edge storms in the northern hemisphere.
In Figure 10e, we see that Mode 2 also has obvious seasonal characteristics, with the positive values lasting mainly from spring to summer in the northern hemisphere and negative values occurring in the rest of the Martian year. The negative eigenvector values occur in the middle of the monitoring area, surrounded by positive values (Figure 11b). Textured dust storms, with visible textures on the cloud tops, are characterized by convection or turbulence. It is speculated that vertical mixing, related to shear cut or convection in the dust column, and the texture on the dust storm top, develop with the occurrence of lifting (e.g., [46,47,48]). There were 764 textured dust storms in 1172 previously identified dust storms. The daily number of textured dust storms within the 1600 km-radius monitoring area is shown in Figure 10c. Based on Figure 10c,e, we discovered that Mode 2 had a negative correlation with the daily frequency of textured dust storms within the monitoring area. The three daily frequency peaks (7 at Ls = 18°, 15 at Ls = 220° and 21 at Ls = 316°) in textured dust storms (Figure 10c) were consistent with the negative values of Mode 2 (Figure 10e). During Ls = 100–110°, the number of textured dust storms reduced to 0, in accord with the positive values of Mode 2 in Figure 10c.
6. Summaries
This paper uses the images of MOC MGS to calculate the daily mean dust storm probability within a 1600 km-radius ring of the Chryse landing area by 1° of solar longitude in order to find out the appropriate period and compute the mean occurrence probability of dust storms in space, helping us to determine suitable landing areas.
(1) The daily mean probability of dust storm activity in the Chryse landing area and within its 1600 km-radius ring peaked at 42.9% (Ls = 223°) and 20.9% (Ls = 225°), respectively. The minimum P(T) in the Chryse monitoring area was 0. The P(T) in the Chryse landing area and within its 1600 km-radius ring showed obvious inhomogeneity and seasonality within a Martian year. In the Chryse landing area, dust storm activity was most frequent from the autumnal equinox (Ls = 177°) to the end of autumn (Ls = 239°) in the northern hemisphere, with an average P(T) of 9.5%. Dust storm activity in the Chryse monitoring area was mainly centered in the period from Ls = 180° to Ls = 240°, and thus we deemed that these storms resulted from the Acidalia–Chryse channel.
(2) The latitudinal distribution of dust storm centers in the monitoring area by 1° of Ls (Figure 5) showed seasonal and spatial heterogeneity. Firstly, the frequency of dust storm activity was closely related to the seasonal waxing and waning of the north polar ice cap. Dust storms within Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring mostly arose during the growth or regression of the polar cap, rather than its quiescent stage, during which the cap’s change rate approached the minimum. In the northern hemisphere, the dust storm activity at the edge of the cap was almost at a standstill before or on the northern summer solstice, and this stagnation lasted for a long time (Ls = 20–80°). Secondly, the dust storm activity within the monitoring area mainly came from the north polar cap region, Acidalia and Chryse, and a small number of events originated from the southern hemisphere (Argyre and Bosporos) before traveling northward. Nevertheless, the dust storms from the southern hemisphere were much smaller and much less frequent than the ones from the northern hemisphere.
(3) The spatial probability of dust storm activity in Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring ranged from 0% to 10.8% and showed spatial inhomogeneity. Acidalia, the north of Chryse’s 1600 km-radius ring, was the region where dust storm activity occurred most frequently, followed by Chryse, Tempe and Arabia, to the east and west of the monitoring area. The P(S) of the monitoring area during the EDL season was the highest in the northern area (Acidacia), but it dropped incrementally in the southern area and in both the east and west. The dust storm activity probability in the north of Xanthe, the east of Tempe and the west of Arabia leveled off to 0. The nonuniform distribution of P(S) can be explained by the origin and the route of dust storm sequences.
(4) We sought to determine the leading and separate modes of dust storms in space using EOF. The first and the second modes had 40.5% and 17.5% of the total variance, respectively, comprising 58% of the total variance associated with dust storm activity. Modes 1 and 2 show enormous vertical variations from the north to the south in the monitoring area. In the northern half of the Chryse area, the two modes were arranged and located differently, but they showed an obvious near-north–south frontal feature with an evident gradient. Mode 1 is consistent with the seasonal growth and regression of the Arctic polar cap edge, whereas Mode 2 has an approximate negative correlation with the daily frequency of textured dust storms within the monitoring area.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/universe7110433/s1. Table S1: the longitude and latitude, Martian year and Ls of 1172 dust storms identified in the study area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L.; methodology, B.L.; software, Z.Y.; validation, S.Q., X.F., Z.Y. and Z.L.; formal analysis, B.L. and S.C.; investigation, X.F.; resources, B.L., Z.L. and P.Y.; data curation, S.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, B.L.; writing—review and editing, B.L. and S.C.; visualization, X.F. and S.Q.; supervision, B.L.; project administration, B.L.; funding acquisition, S.C. and X.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Strategic Leading Science and Technology Special Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB41000000, XDB18000000), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2019MD015), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41772346, U1931211), the Pre-research project on Civil Aerospace Technologies No. D020102 was funded by the China National Space Administration (CNSA).
Data Availability Statement
The MDGMs of MGS-MOC from Mars year 24–28 can be downloaded from https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/WWRT1V (accessed on 20 August 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank editors for the suggestions to improve our manuscript. We would like to thank the three anonymous reviewers who provided very helpful and useful suggestions for the manuscript. The efforts of the science and engineering teams that produced all the datasets used in this study, particularly the MGS mission, as well as the MOC WA instruments, are gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gifford, F.A. A study of Martian yellow clouds that display movement. Mon. Weather Rev. 1964, 92, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterfreund, A.R.; Kieffer, H.H. Thermal infrared properties of the martian atmosphere. 3. Local dust storms. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 2853–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, R.W.; Martin, L.J. Interannual variability of planet-encircling dust storms on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 3247–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.A.; James, P.B.; Caplinger, M.; Wolff, M.J. Martian dust storms: 1999 Mars orbiter camera observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 23653–23687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.A. Moc observations of the 2001 mars planet-encircling dust storm. Icarus 2007, 186, 60–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montabone, L.; Forget, F.; Millour, E.; Wilson, R.J.; Wolff, M.J. Eight-year climatology of dust optical depth on mars. Icarus 2015, 251, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heavens, N.G.; McCleese, D.J.; Richardson, M.I.; Kass, D.M.; Kleinböhl, A.; Schofield, J.T. Structure and dynamics of the Martian lower and middle atmosphere as observed by the Mars climate sounder: 2. Implications of the thermal structure and aerosol distributions for the mean meridional circulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, E01010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.A.; Wolff, M.J.; James, P.B.; Higgs, E. Recession of the Martian north polar cap: 1990–1997 Hubble Space Telescope observations. Icarus 1998, 136, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.B.; Cantor, B.A. Martian north polar cap regression: 2000 Mars Orbiter Camera observations. Icarus 2001, 154, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Zurek, R.W. An analysis of the history of dust storm activity on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 3221–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Richardson, M.I. The origin, evolution, and trajectory of large dust storms on mars during mars years 24–30 (1999–2011). Icarus 2015, 251, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.M.; Zorzano, M.-P.; Martín-Torres, J. MARSWRF prediction of entry descent landing profiles: Applications to Mars exploration. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1440–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.A.; Henry, R.M. Mars atmospheric phenomena during major dust storms, as measured at surface. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D. Interannual variability in TES atmospheric observations of mars during 1999–2003. Icarus 2004, 167, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavada, A.R.; Chen, A.; Barnes, J.R.; Burkhart, P.D.; Cantor, B.A.; Dwyer-Cianciolo, A.M.; Fergason, R.L.; Hinson, D.P.; Justh, H.L.; Kass, D.M.; et al. Assessment of environments for mars science laboratory entry, descent, and surface operations. Space Sci. Rev. 2012, 170, 793–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.N.; Knocke, P.C. Mars exploration rovers entry, descent, and landing trajectory analysis. J. Astronaut. Sci. 2007, 55, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Mur, T.J.; Kruizingas, G.L.; Burkhart, P.D.; Wong, M.C.; Abilleira, F. Mars science laboratory navigation results. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium Space Flight Dynamics, Pasadena, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cantor, B.A.; Pickett, N.B.; Malin, M.C.; Lee, S.W.; Wolff, M.J.; Caplinger, M.A. Martian dust storm activity near the mars 2020 candidate landing sites: Mro-marci observations from mars years 28–34. Icarus 2019, 321, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Li, C.; Wang, B.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Ling, Z.; Chen, S. Evaluating the dust storm probability inIsidis-Elysium Planitia, a tentative landing area of China’s first Mars mission (Tianwen-1). Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, G.; Okubo, C.H.; Wray, J.J.; Ojha, L.; Cardinale, M.; Murana, A.; Orosei, R.; Chan, M.A.; Ormö, J.; Gallagher, R. Small edifice features in chryseplanitia, mars: Assessment of a mud volcano hypothesis. Icarus 2016, 268, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin, M.C.; Danielson, G.E.; Ingersoll, A.P.; Masursky, H.; Veverka, J.; Ravine, M.A.; Soulanille, T.A. Mars Observer Camera. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 7699–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ingersoll, A.P. Martian clouds observed by Mars Global Surveyor Mars Orbiter Camera. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.B. Martian local dust storms. In Recent Advances in Planetary Meteorology; Hunt, G., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Shirley, J.H.; Mischna, M.A. Orbit-spin coupling and the interannual variability of global-scale dust storm occurrence on mars. Planet. Space Sci. 2017, 139, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miyamoto, S. The Great Yellow Cloud and the Atmosphere of Mars: Report of Visual Observations during the 1956 Opposition. Contrib. Inst. Astrophys. Kwasan Obs. 1957. Available online: https://books.google.rs/books?id=ze27j5sSJVEC&pg=PA1418&lpg=PA1418&dq=Miyamoto,+S.+The+Great+Yellow+Cloud+and+the+Atmosphere+of+Mars:+Report+of+Visual+Observations+during+the+1956+Opposi-tion.+Contrib.+Inst.+Astrophys.+Kwasan+Obs.+1957&source=bl&ots=4I4fC_QX9y&sig=ACfU3U3Y6SaV5anD8-FG2kbNBpeJXxDf4g&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwi-pqLFypL0AhXB-6QKHcltBgEQ6AF6BAgEEAM#v=onepage&q=Miyamoto%2C%20S.%20The%20Great%20Yellow%20Cloud%20and%20the%20Atmosphere%20of%20Mars%3A%20Report%20of%20Visual%20Observations%20during%20the%201956%20Opposi-tion.%20Contrib.%20Inst.%20Astrophys.%20Kwasan%20Obs.%201957&f=false (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Martin, L.J. The major martian dust storms of 1971 and 1973. Icarus 1974, 23, 108115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J. 1973 dust storm: Maps from hourly photographs. Icarus 1976, 29, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Briggs, G.A.; Baum, W.A.; Barnes, J. Viking orbiter imaging observations of dust in the martian atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 2795–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.A.; Sharman, R.D. Two major dust storms, one Mars year apart: Comparison from Viking data. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 3247–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montabone, L.; Forget, F. On Forecasting Dust Storms on Mars. LPI Contrib. 2016. Available online: https://ttu-ir.tdl.org/bitstream/handle/2346/72982/ICES_2017_175.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Tamppari, L.K.; Barnes, J.; Bonfiglio, E.; Cantor, B.A.; Friedson, A.J.; Ghosh, A.; Grover, M.R.; Kass, D.; Martin, T.Z.; Mellon, M.; et al. Expected atmospheric environment for the Phoenix landing season and location. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.T.; Wolff, M.J.; Bell, J.F., III; Smith, M.D.; Cantor, B.A.; Smith, P.H. Dust aerosol, clouds, and the atmospheric optical depth record over 5 Mars years of the Mars Exploration Rover mission. Icarus 2015, 251, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, J.L.; Haberle, R.M.; Schaeffer, J. Seasonal variations of storm zoneson Mars. Adv. Space Res. 1979, 19, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzewich, S.D.; Toigo, A.D.; Wang, H. An investigation of dust storms observed with the mars color imager. Icarus 2017, 289, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzewich, S.D.; Toigo, A.D.; Kulowski, L.; Wang, H. Mars Orbiter Camera climatology of textured dust storms. Icarus 2015, 258, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.J.; Sun, Z.Z.; Rao, W.; Meng, L.Z. Mission overview and key technologies of the first, Mars probe of China. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2017, 60, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, D.P.; Wang, H. Further observations of regional dust storms andbaroclinic eddies in the northern hemisphere of Mars. Icarus 2010, 206, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.E.; Lewis, S.R.; Read, P.L.; Forget, F. Modeling the martiandustcycle. 2. Multiannual radiatively active dust transport simulations. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 7-1–7-15. [Google Scholar]
- Mulholland, D.P.; Read, P.L.; Lewis, S.R. Simulating the interannual variability ofmajor dust storms on Mars using variable lifting thresholds. Icarus 2013, 223, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zurek, R.W.; Richardson, M.I. Relationship between frontal duststorms and transient eddy activity in the northern hemisphere of Mars asobserved by Mars Global Surveyor. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E. Empirical Orthogonal Functions and Statisticalweather Prediction; Tech. Rep. 1, Statistical Forecasting Project; Department of Meteorology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1956; 49p. [Google Scholar]
- Kaihatu, J.M.; Handler, R.A.; Marmorino, G.O.; Shay, L.K. Empirical orthogonal function analysis of ocean surface currents using complex and real-vector methods. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leovy, C.E.; Zurek, R.W.; Pollack, J.B. Mechanisms for Mars dust storms. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toigo, A.D.; Richardson, M.I.; Wilson, R.J.; Wang, H.; Ingersoll, A.P. A first lookat dust lifting and dust storms near the south pole of Mars with a mesoscalemodel. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fisher, J.A. North polar frontal clouds and dust storms on Marsduring spring and summer. Icarus 2009, 204, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strausberg, M.J.; Wang, H.; Richardson, M.I.; Ewald, S.P.; Toigo, A.D. Observations of the initiation and evolution of the 2001 Mars global dust storm. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, E02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battalio, M.; Wang, H. The Aonia-Solis-Valles dust storm track in the southern hemisphere of Mars. Icarus 2019, 321, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battalio, M.; Wang, H. The Mars Dust Activity Database (MDAD): A comprehensive statistical study of dust storm sequences. Icarus 2021, 354, 114059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).