Abstract
The 760-ton liquid argon ICARUS T600 detector performed a successful three-year physics run at the underground LNGS laboratories, studying in particular neutrino oscillations with the CNGS neutrino beam from CERN. This detector has been moved in 2017 to Fermilab after a significant overhauling and will be exposed soon to the Booster Neutrino Beam acting as the far station to search for sterile neutrinos within the SBN program. The contribution addresses the developed methods and the results of an analysis to identify and reconstruct atmospheric neutrino interactions collected by ICARUS T600 in the underground run at LNGS. Despite the limited statistics, this search demonstrates the excellent quality of the detector reconstruction and the feasibility of an automatic search for the electron neutrino CC interactions in the sub-GeV range, as required for the study of the BNB neutrinos at FNAL.
1. The ICARUS T600 Detector and the Next SBN Experiment at Fermilab
A very promising detection technique for the study of rare events like neutrino interactions is based on the Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber (LArTPC). First proposed by C. Rubbia in 1977 [1], these fully-electronic detectors blend together the imaging capabilities of the famous bubble chambers with the excellent energy measurement of homogeneous calorimeters: for this reason, they are particularly well suited to investigate a large variety of physical events, spanning a wide energy spectrum (from a few keV to several hundreds of GeV). The LArTPC is a continuously-sensitive and self-triggering detector, characterized by high granularity and spatial resolution: it provides a 3D imaging of any ionizing event starting from the electrons produced by each ionizing event taking place in highly purified LAr ionization. These ionization electrons can be transported by a uniform electric field and can be collected by three parallel wire planes, placed at the end of the drift path with wires oriented in different directions. Moreover, thanks to the excellent calorimetric measurement provided, this detector can provide an efficient particle identification based on the density of the energy deposition.
The state of the art of this technique is represented by the ICARUS T600 detector, which has been operated in Hall B of the Gran Sasso underground National Laboratory of the Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (I.N.F.N.). The construction and successful operation of this detector finalized many years of R&D studies: this detector with a total active mass of 476 t of LAr is the major milestone towards the realization of a multi-kiloton LArTPC detector. From October 2010 to December 2012, ICARUS has collected about 3000 neutrino events from the CNGS CERN to Gran Sasso neutrino beam corresponding to 8.6 × 10 protons on target. Neutrino events in the 10–30-GeV energy range have been recorded with unprecedented details, demonstrating the high level of technical performances and the physical potentialities of this telescope. Cosmic rays were also collected to study the detector’s capability with respect to atmospheric neutrinos, as described in the next section, and for the proton decay search.
The ICARUS T600 detector is composed of two identical adjacent “T300” half-modules filled with liquid argon (internal dimensions: 3.6-m width, 3.9-m height, and 19.9-m length). Two Time Projection Chambers (TPCs) with a common cathode placed in the middle, the electric field shaping system, and Photo-Multiplier Tubes (PMTs) are enclosed in each half-module, and along the longest side walls (left and right) of each half-module, three parallel planes of anode wires are placed. By appropriate voltage biasing, the first two planes facing toward the drift region (induction planes) provide signals in a non-destructive way, and the charge is collected in the last wire plane, called collection view. The signals coming from each wire are continuously read and digitized every 400 ns and recorded in the event when a trigger signal is provided. A more detailed description of the ICARUS T600 detector can be found in [2,3,4].
The main ICARUS T600 trigger system is based on the scintillation light signal collected by the PMTs located behind the wire planes [5]. In particular, during the Gran Sasso run, the analog sum of the signals from PMTs in the same chamber was used, with a defined photo-electron discrimination threshold for each TPC chamber (∼100 phe in the west cryostat and ∼200 phe in the east cryostat), and the trigger was provided by the coincidence of the PMT sum signals of the two adjacent chambers in the same module. In the particular case of the CNGS neutrino events, thanks to the Early Warning Signal sent from CERN to LNGS 80 ms before each proton extraction, the trigger was generated when the PMT sum signal was present in at least one TPC chamber within a 60-s gate opened at the expected neutrino arrival time.
One of the most important results obtained by the ICARUS T600 detector is related to the search for the anomalous LSND-like appearance of electron neutrinos [6,7,8] in the CNGS beam, in order to verify the possible existence of a fourth sterile neutrino flavor with a mass ∼1 eV/. In total, 2650 neutrino events, corresponding to 7.9 × 10 protons on target, have been visually studied to identify the electron neutrino events. Only the events with an energy deposition smaller than 30 GeV have been selected for further analysis, in order to strongly reduce the intrinsic contamination from the tiny (∼1%) electron neutrino component in the CNGS beam. The muon neutrino CC events have been identified and rejected, requiring the presence of a track from the primary vertex without any hadronic interaction and a visible length greater than 2.5 m. Finally, an event has been identified as an electron neutrino if a charged track from the primary vertex presents a dE/dx compatible with a m.i.p. and subsequently builds up into a shower isolated from other ionizing tracks near the vertex in at least one of the TPC views. Electron neutrino recognition efficiency has been also studied using Monte Carlo events reproducing in every detail the signals from wire planes. As a result, seven events have been identified as electron neutrino CC interactions with an expected background from conventional sources of 8.5 ± 1.1 events. This negative result allowed defining a very small parameter region, around , in agreement with all published experimental measurements.
A conclusive experiment, capable of providing a definitive answer at the 5 level on the existence of sterile neutrinos, is now under preparation within the Short Baseline Neutrino program (SBN) [9] at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, exploiting three liquid-Argon TPC detectors (SBND, MicroBooNE, ICARUS-T600) exposed to the Booster muon neutrino beam (average MeV). The use of similar detectors in different positions (110, 470, 600 m from the target, respectively) along the beam line will allow strongly reducing the systematics and studying both the appearance and the disappearance channels, providing a full coverage of the LSND parameter region with 5 significance in three years of data-taking (6.6 × protons on target).
In order to prepare the detector for this new experimental phase, starting from December 2014, the ICARUS T600 detector underwent an intensive overhauling phase at CERN: in particular, a new scintillation light collection system [10] and new higher performance read-out electronics [11,12] have been introduced. The two T600 modules have been then transported to FNAL in July 2017 and are currently being installed in the far position at the FNAL Booster beam: in particular, the detector commissioning is expected to start at the beginning of 2019.
2. Atmospheric Neutrino Search in the T600 Detector
Starting from 2019, the T600 detector at Fermilab will take data at a shallow depth, protected only by a 3-m concrete overburden, facing more challenging experimental conditions with respect to its previous operation in the Gran Sasso underground laboratory: in the previous run, a single prompt trigger has always corresponded to a single interaction event within the detector, whose time determines unambiguously the track position along the drift coordinate. At Fermilab, even if the presence of the concrete shielding will suppress the hadronic component in cosmic rays and reduce cosmic muons by ∼30%, ∼11 additional cosmic muons are expected to randomly overlap any triggered event within the 1-ms drift time window, challenging the disentangling and reconstruction of the interesting neutrino events. This condition makes it necessary to deploy suitable automatic tools for the identification, selection, and measurement of the neutrino events among the millions of events triggered by cosmics.
A fundamental test for the development of these tools can be done using the cosmic ray events collected during the Gran Sasso run. In fact, the recorded atmospheric neutrino events cover the same energy range expected for the SBN experiment, and they should be automatically identified among the ∼3000 cosmic ray events per day recorded during the run. For these reasons, the cosmic ray events collected have been analyzed using a fully-automatic procedure in order to identify atmospheric neutrino CC interactions and to reject the main source of backgrounds for this analysis related in particular to the cosmic ray events containing single muon tracks crossing the detector. First of all, in each TPC wire plane, the physical signals (“hits”) are automatically identified in all the wires and then grouped into “clusters” on the basis of their relative distance. The charge current neutrino candidates are then identified studying the geometrical and calorimetric properties of the largest cluster in the collection wires’ planes: since in the events collected during the Gran Sasso run, usually a single cosmic muon track or a single neutrino interaction is recorded, the study of the largest cluster ensures the study of the physical activity inside the detector. In particular, the selection criteria have been optimized in order to obtain a strong rejection for the cosmic muon tracks, resulting in being very straight in the collection view, and to maximize the efficiency for the identification of the e.m. showers in the events. The filter procedure has been applied to a sample of Monte Carlo events in order to evaluate the identification efficiency for neutrino interactions with a deposited energy larger than 200 MeV. The global filter efficiencies turn out to be ∼81% for the electron neutrinos and ∼26% for the muon neutrino CC interactions. The procedure was optimized to select the electron neutrino events, while the tight requests applied to cope with the incoming cosmic muon flux resulted in a smaller efficiency for CC, whose primary muon in some cases can be misidentified as an incoming cosmic ray.
The tuned automatic procedure has been then applied to all the events triggered outside of the CNGS beam arrival gate and collected during the 2012–2013 run (total exposure of 0.43 kton y): the incoming cosmic rays events containing a single cosmic muon track crossing the detector have been reduced by a factor of ∼100 (cosmic muon rejection efficiency of ∼99%), and the selected CC neutrino event candidates have been then visually studied to identify the genuine neutrino interactions. In particular, the electron neutrino events have been recognized requiring the presence of a clear e.m. shower from the primary vertex with a dE/dx in the first wires fully compatible with a minimum ionizing particle, while the muon neutrino CC events have been selected requiring the presence of a long track (at least 1 m) from the primary vertex. In addition, only events with a deposited energy larger than 200 MeV and with the primary vertex at a distance of at least 5 cm from each side of the active volume have been selected.
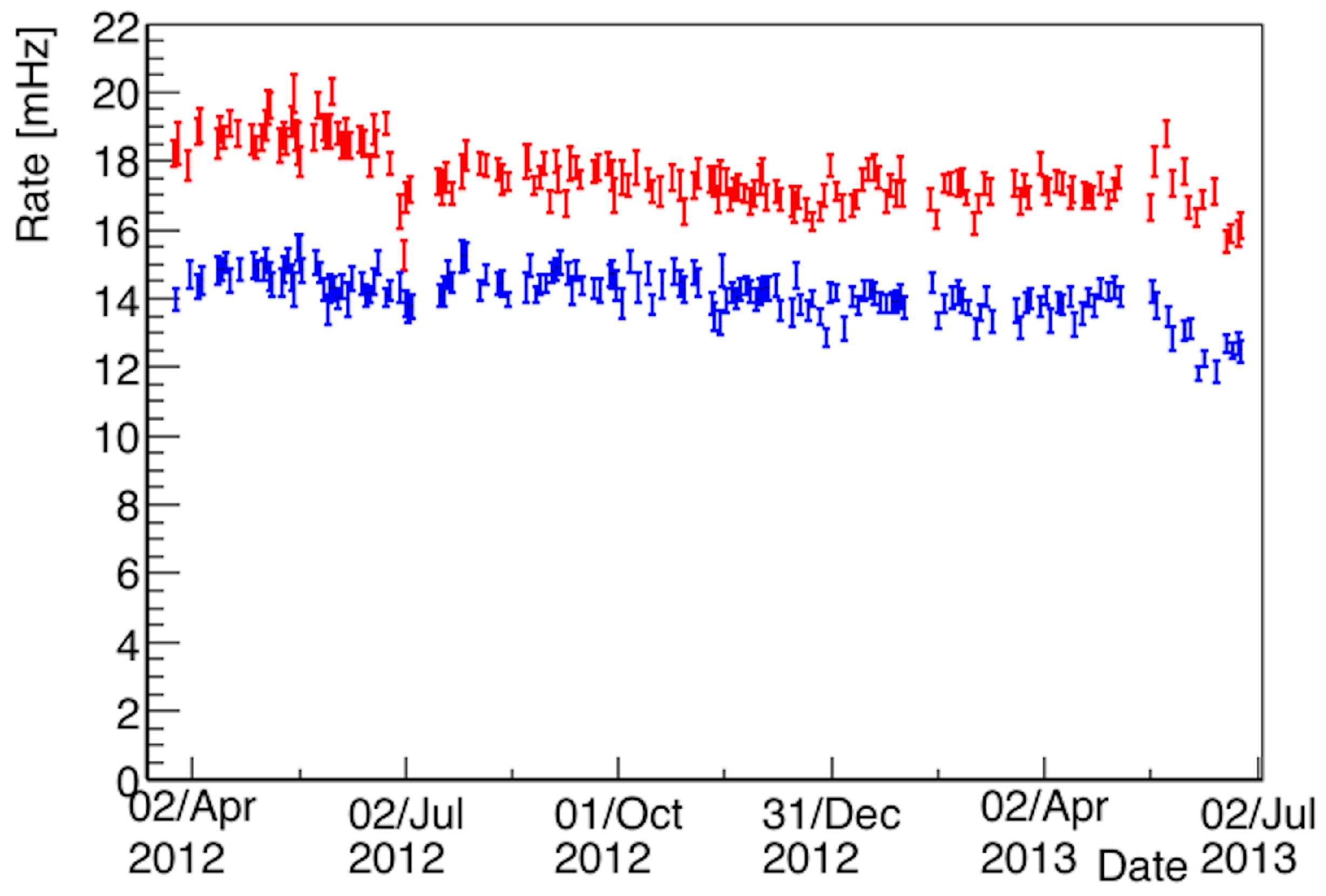
Finally, a dedicated study has been performed in order to evaluate the expected number of atmospheric neutrino interactions in the studied statistics. In particular, the passing cosmic muon tracks rejected by the filter have been used to evaluate the trigger efficiency as a function of the energy and to evaluate possible differences in the efficiency in the two different modules, related to the different number of PMTs installed (a more detailed analysis on the trigger efficiency can be found in [5]). In fact, as shown in Figure 1, since in the east module, a larger number of PMTs were installed, the rate of cosmic ray muons collected results in being higher: this different behavior is included in the analysis. In addition, in order to determine the selection efficiency based on the final visual scanning, a sample of MC events selected by the automatic filter has been studied, providing a ∼80% scanning efficiency for both and CC interactions. In particular, the combined application of the filter procedure and of the visual study of the selected events allow fully rejecting the backgrounds related to the incoming cosmic muon tracks and providing the final identification of the neutrino type. Globally, 14 CC neutrino interactions have been identified and fully reconstructed: some examples of the recognized events are shown in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. This number of events must be compared with a preliminary evaluation of the expected number of neutrino interactions in the studied exposure, which results in 17.7 events, as shown in Table 1. The distribution of the deposited energy of the selected events has been also evaluated, resulting in being roughly in agreement with the expected distribution from Monte Carlo events, as shown in Figure 5.
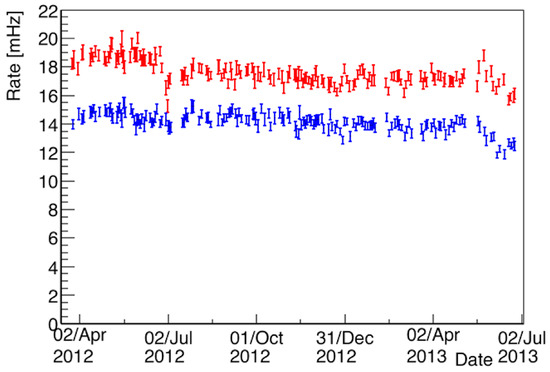
Figure 1.
Rates of the cosmic ray events collected on the west (blue) and on the east (red) cryostat, in the period analyzed for the atmospheric neutrino search. The difference between the two modules is related to the different number of PMTs installed: in the east module 54, PMTs were present, while in the west module, only 20 PMT were installed.
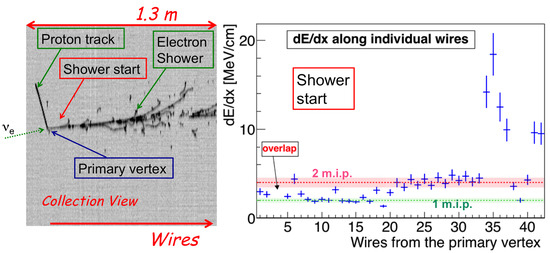
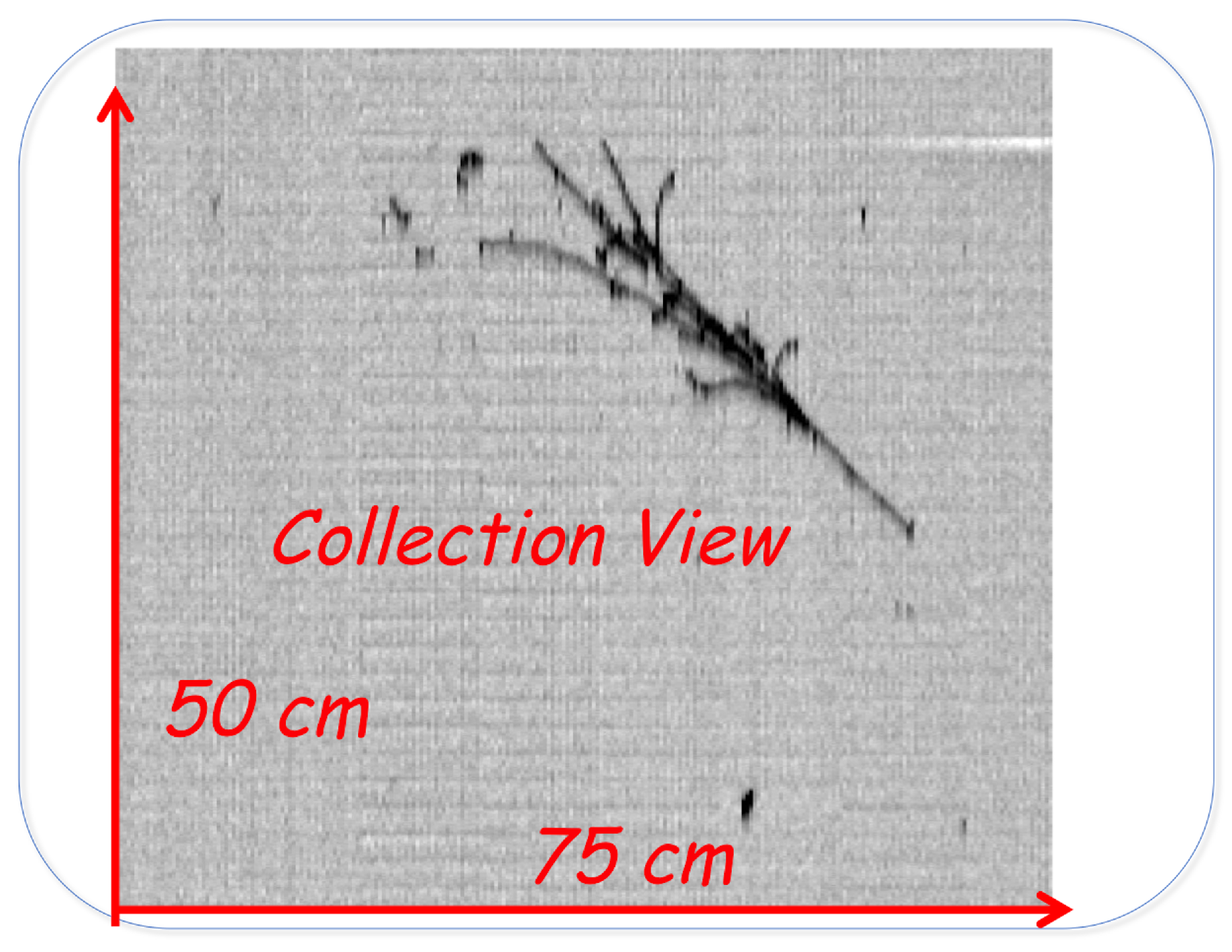
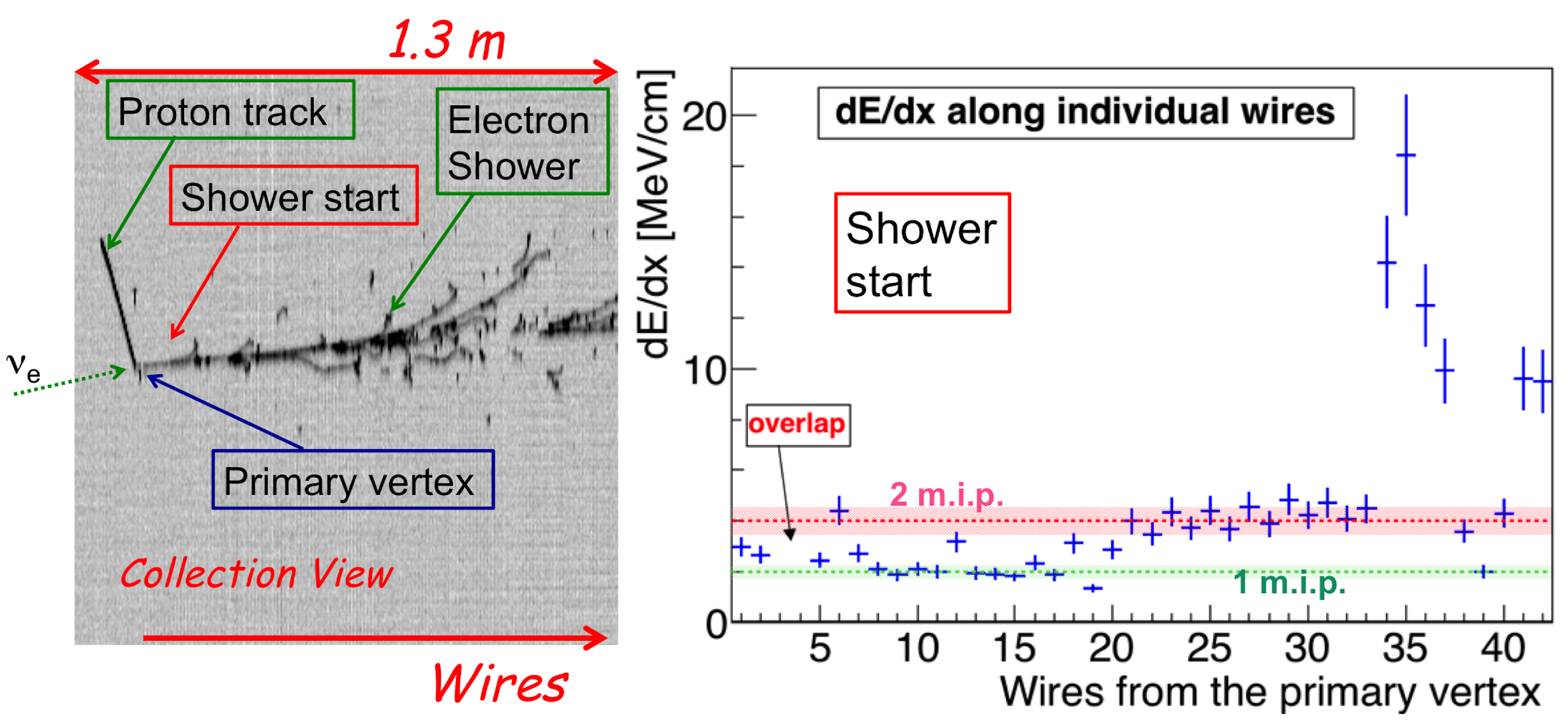
Figure 2.
Zoom view of the interaction vertex of an atmospheric electron neutrino event with a deposited energy of 2.12 GeV (left). The evolution of the ionization density dE/dxin the first wires of the shower is also shown (right), providing a clear signature for the electron identification. A proton track (115 MeV) has been also identified studying the dE/dx versus range relation [13].
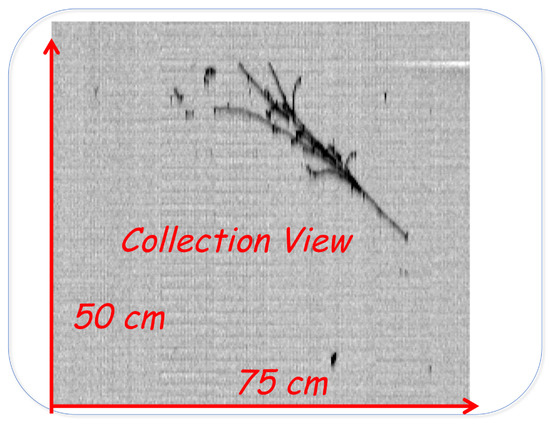

Figure 3.
A quasi-elastic atmospheric electron neutrino interaction with a deposited energy of 0.4 GeV is shown in the 2D collection view of ICARUS-T600. The dE/dx in the first 2.5 cm of the shower results in ∼2 MeV/cm, fully compatible with an m.i.p., as expected for an electron shower.
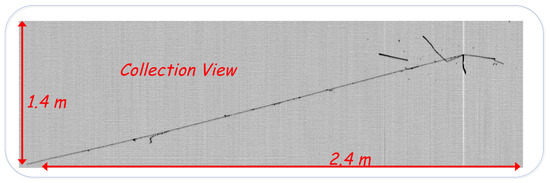
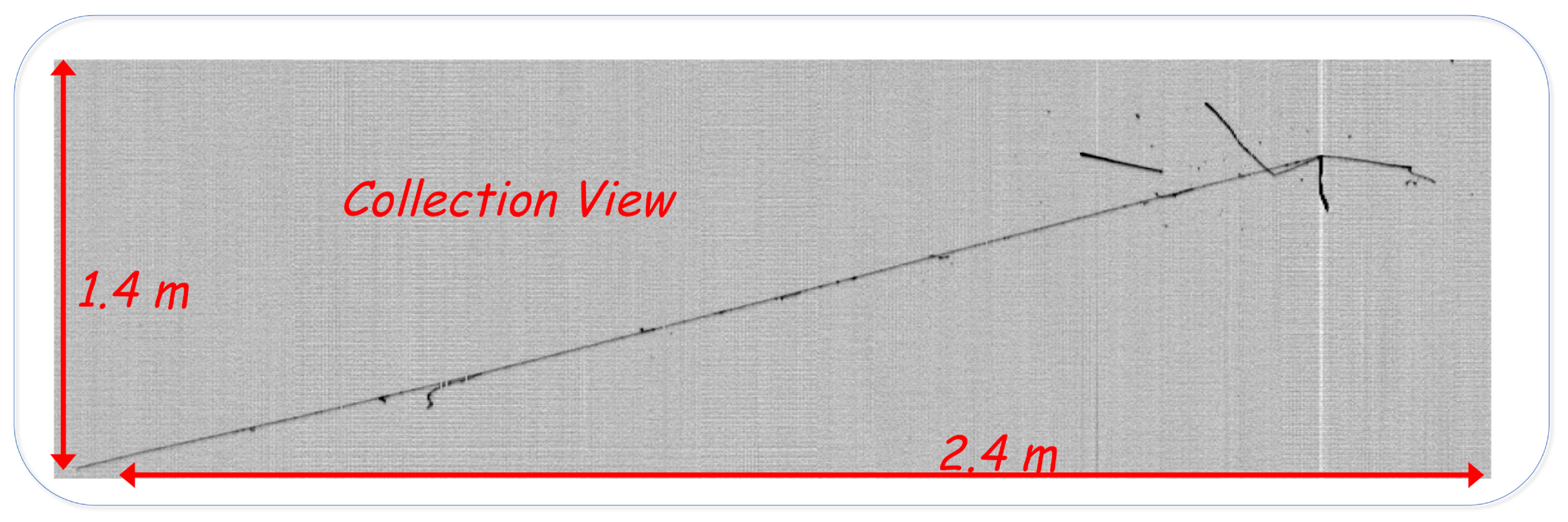
Figure 4.
A clear atmospheric muon neutrino event with a deposited energy of 1.7 GeV is shown in the 2D collection view. The momentum of the 4-m escaping muon has been evaluated using an algorithm based on the multiple Coulomb scattering study [14], providing p = 1.8 ± 0.3 GeV/c. Two protons (deposited energy 250 MeV) and a pion decaying in a muon followed by an electron ( 80 MeV) are produced in the neutrino interaction vertex. A preliminary global reconstruction of the neutrino interaction provides 2 GeV, with a zenith angle of ∼ 78°.

Table 1.
Expected number of neutrino interactions in the studied statistics, compared with the number of events identified by the filter in the collected data. The number of events per kton y has been evaluated assuming the standard 3 neutrino oscillations with m = 2.5 × 10 eV. The filter and scanning efficiency have been obtained using MC events, while the trigger efficiency has been directly evaluated on the cosmic ray events collected [5].
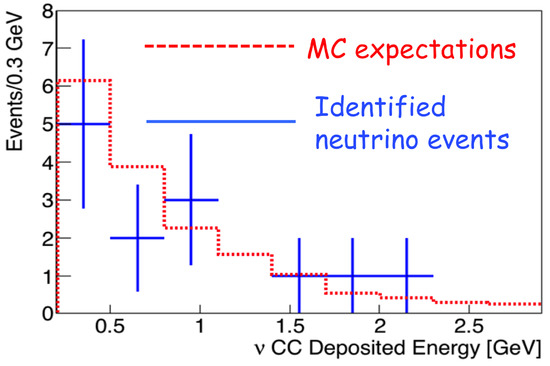
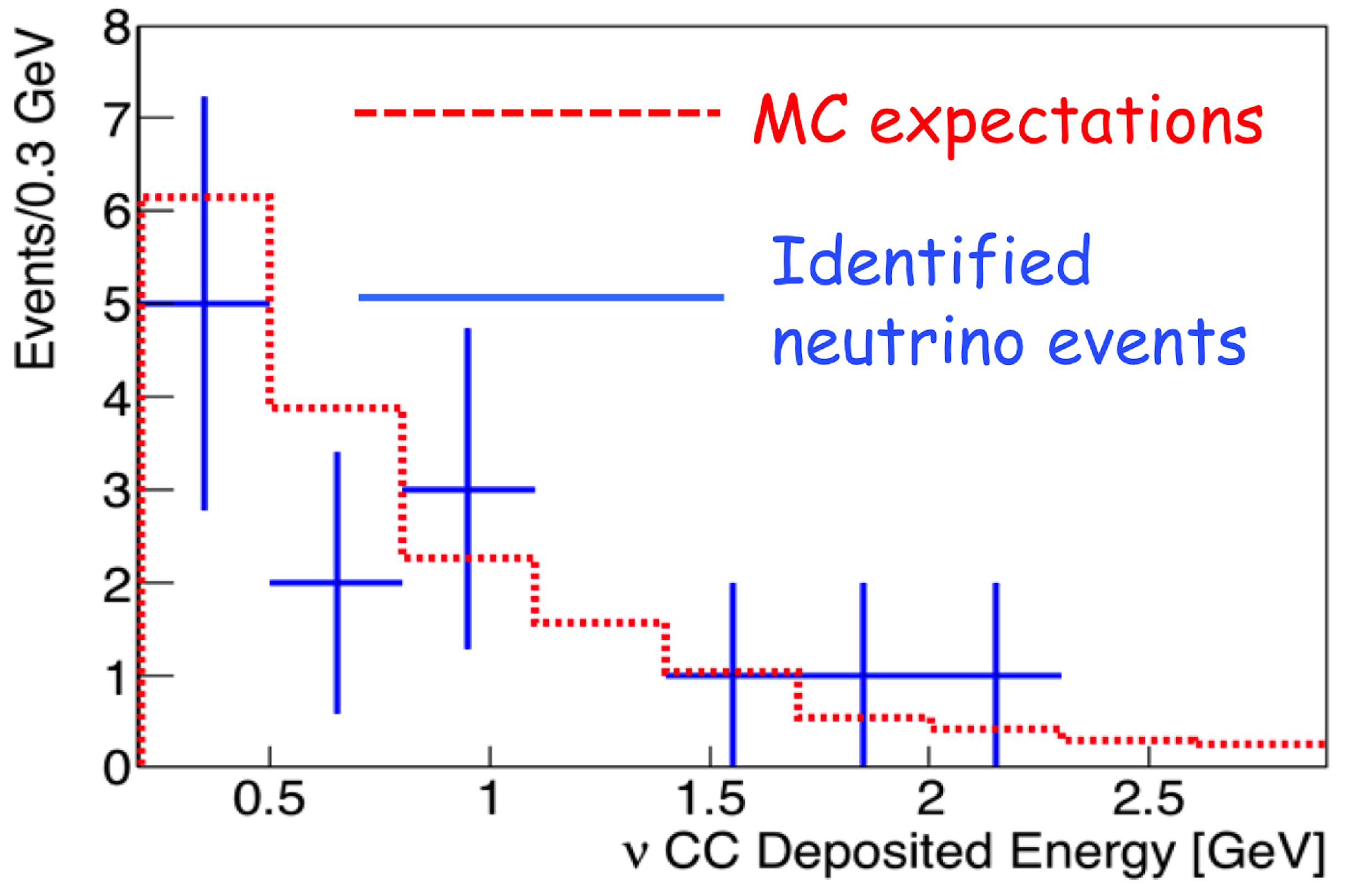
Figure 5.
Zoom of the deposited energy distribution of the identified atmospheric neutrino events, compared with the expected distribution from MC events.
3. Conclusions
The ICARUS T600 detector performed a successful three-year physics run at the underground LNGS laboratories, has been moved in 2017 to Fermilab after a significant overhauling and will be exposed as the far detector to the Booster Neutrino Beam to search for sterile neutrinos within the SBN program.
The events collected during the Gran Sasso run and related to cosmic rays have been used to develop automatic tools for the identification of the atmospheric neutrino interactions, since they cover the energy range expected for the future SBN experiment. Globally, in the studied statistics corresponding to 0.43 kton y 6 CC and 8 CC, atmospheric neutrino events have been identified and reconstructed. This result, roughly in agreement with the expectations, demonstrates that the automatic search for the CC in the sub-GeV range, required for the study of the BNB neutrinos at FNAL, is feasible.
Funding
The costs of the experiment were supported by the funding agencies of the Collaboration Institutes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this proceeding:
| CNGS | CERN Neutrino to Gran Sasso |
| LSND | Liquid Scintillator Neutrino Detector |
| SBN | Short Baseline Neutrino |
| BNB | Booster Neutrino Beam |
| m.i.p. | Minimum ionizing particle |
| e.m. | Electromagnetic |
References
- Rubbia, C. The Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber: A New Concept for Neutrino Detectors; CERN-EP/77-08. 1977. Available online: http://inspirehep.net/record/857394/ (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Rubbia, C.; Antonello, M.; Aprili, P.; Baibussinov, B.; Ceolin, M.B.; Barze, L.; Cavanna, F. Underground operation of the ICARUS T600 LAr-TPC: First results. J. Instrum. 2011, 6, P07011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, M.; Baibussinov, B.; Benetti, P.; Boffelli, F.; Bubak, A.; Calligarich, E.; Cocco, A.G. Experimental observation of an extremely high electron lifetime with the ICARUS-T600 LAr-TPC. J. Instrum. 2014, 9, P12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, M.; Aprili, P.; Baibussinov, B.; Boffelli, F.; Bubak, A.; Calligarich, E.; Cline, D.B. Operation and performance of the ICARUS T600 cryogenic plant at the Gran Sasso underground Laboratory. J. Instrum. 2015, 10, P12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, M.; Baibussinov, B.; Benetti, P.; Boffelli, F.; Bubak, A.; Calligarich, E.; Cocco, A.G. The trigger system of the ICARUS experiment for the CNGS beam. J. Instrum. 2014, 9, P08003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, M.; Baibussinov, B.; Benetti, P.; Calligarich, E.; Canci, N.; Centro, S.; Dabrowska, A. Experimental search for the LSND anomaly with the ICARUS detector in the CNGS neutrino beam. Eur. Phys. J. C 2013, 73, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, M.; Baibussinov, B.; Benetti, P.; Boffelli, F.; Bubak, A.; Calligarich, E.; Cline, D.B. Search for anomalies in the νe appearance from a νμ beam. Eur. Phys. J. C 2013, 73, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnese, C. Some recent results from ICARUS. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1666, 110002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciarri, R.; Adams, C.; An, R.; Andreopoulos, C.; Ankowski, A.M.; Antonello, M.; Baller, B. A Proposal for a Three Detector Short-Baseline Neutrino Oscillation Program in the Fermilab Booster Neutrino Beam. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1503.01520. [Google Scholar]
- Babicz, M.; Bagby, L.; Baibussinov, B.; Bellini, V.; Bonesini, M.; Braggiotti, A.; Farnese, C. Test and characterization of 400 Hamamatsu R5912-MOD photomultiplier tubes for the ICARUS T600 detector. J. Instrum. 2018, 13, P10030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagby, L.; Baibussinov, B.; Bellini, V.; Bonesini, M.; Braggiotti, A.; Castellani, L.; Falcone, A. New read-out electronics for ICARUS-T600 liquid Argon TPC. Description, simulation and tests of the new front-end and ADC system. J. Instrum. 2018, 13, P12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnese, C. The new front end and DAQ of the ICARUS detector. EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 182, 03003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, M.; Baibussinov, B.; Benetti, P.; Calligarich, E.; Canci, N.; Centro, S.; Dabrowska, A. Precise 3D track reconstruction algorithm for the ICARUS T600 liquid argon time projection chamber detector. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2013, 2013, 260820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, M.; Baibussinov, B.; Bellini, V.; Benetti, P.; Boffelli, F.; Bubak, A.; Cieslik, K. Muon momentum measurement in ICARUS-T600 LAr-TPC via multiple scattering in few-GeV range. J. Instrum. 2017, 12, P04010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).