Non-Radial Oscillation Modes of Superfluid Neutron Stars Modeled with CompOSE
Abstract
:1. Introduction
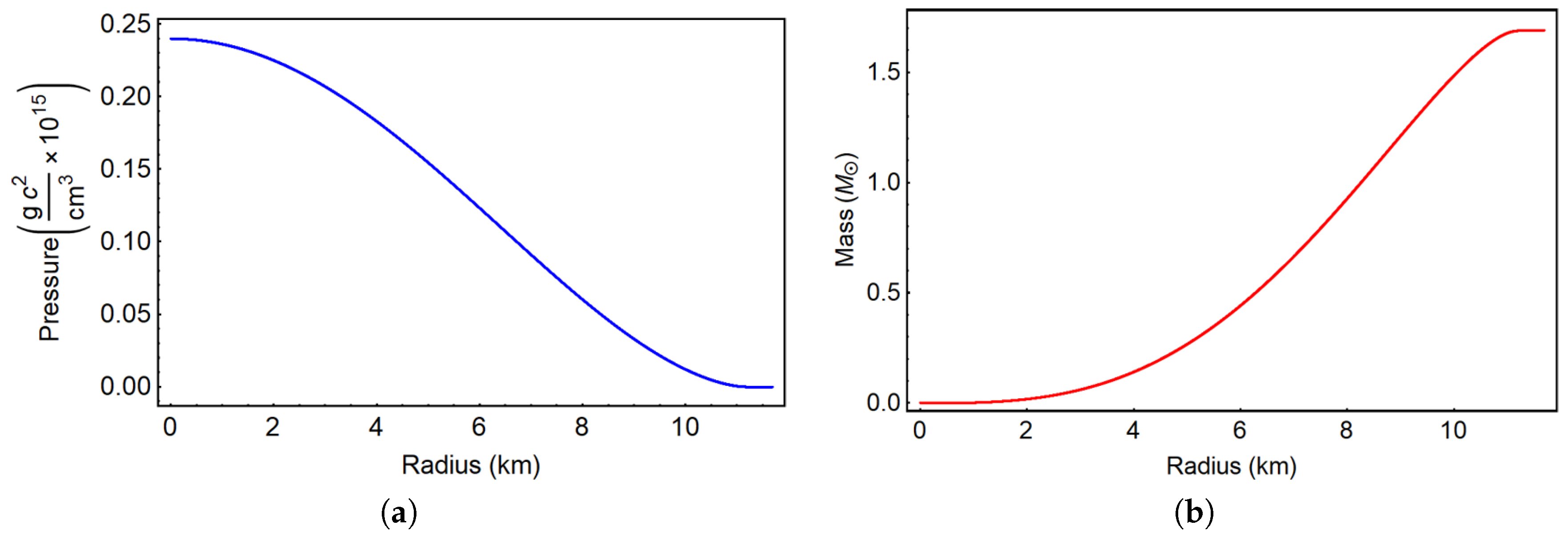
2. EoS Models and Superfluid Neutron Star Structure
3. Fluid Oscillation Equations
3.1. Normal Fluid
3.2. Oscillation Equations: Extension to Superfluidity
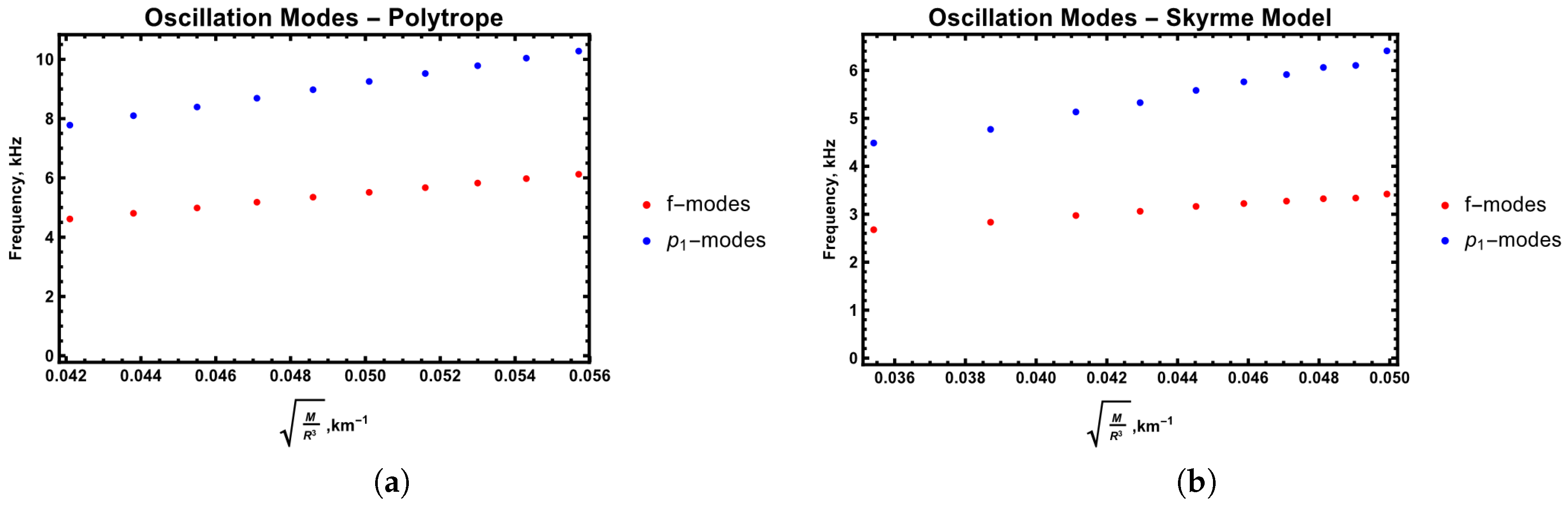
4. Results
- The appearance of a new superfluid mode, while leaving the frequencies of the normal modes almost unchanged, was already noted in [8], but they used a much older EoS [17] based on the Walecka model. We have used the Skyrme EoS which obeys modern constraints from isospin diffusion data and the slope of the symmetry energy. In addition, we employ neutron and proton effective masses that are obtained consistently within the model [7]. This was not the case, for e.g., in all other previous computations of the superfluid oscillation modes [8,16]. This is an important point since the entrainment matrix depends on the effective masses, and different models for the density dependent effective mass yield different numerical values for the modes [8]. In this way, our results are based on an EoS that is built from a unified treatment of terrestrial nuclear experiments and the astrophysics of compact stars, and our results are more consistent from a quantitative standpoint.
- We demonstrate the utility of the CompOSE database in using modern EoS for studies of neutron star oscillations and gravitational waves. The EoS models taken from CompOSE calculate the nucleon effective masses consistently, which is important in superfluid mode calculations. This database also provides easy-to-use interpolation routines that are necessary since the computational grid for the oscillation equations requires more points than are typically provided in tabulated EoS. Readers interested in using the CompOSE repository for compact star and supernova studies may consult the manual [18] or write to the authors of this manuscript.
5. Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EoS | equation of state |
References
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CompStar Online Supernovae Equations of State. Available online: https://compose.obspm.fr/ (accessed on 6 March 2018).
- Chandrasekhar, S. An Introduction to the Study of Stellar Structure; Dover Publications, Incorporated: Mineola, NY, USA, 1967; ISBN 13: 9780486604138. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, B.K.; Shlomo, S.; Kim Au, V. Determination of the parameters of a Skyrme type effective interaction using the simulated annealing approach. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 72, 014310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulminelli, F.; Raduta, A.R. Unified treatment of subsaturation stellar matter at zero and finite temperature. Phys. Rev. C 2015, 92, 055803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, B.K.; Shlomo, S.; Kim Au, V. Nuclear matter incompressibility coefficient in relativistic and nonrelativistic microscopic models. Phys. Rev. C 2003, 68, 031304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamel, N. Two-fluid models of superfluid neutron star cores. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 388, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, L.; Mendell, G. The oscillations of superfluid neutron stars. Astrophys. J. 1994, 421, 689–704. [Google Scholar]
- Gualtieri, L.; Kantor, E.M.; Gusakov, M.E.; Chugunov, A.I. Quasinormal modes of superfluid neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 024010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, N.; Comer, G.L. Entropy entrainment and dissipation in superfluid Helium. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2011, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, A.F.; Bashkin, E.P. Three-velocity hydrodynamics of superfluid solutions. Sov. Phys. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 1976, 42, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, N.; Comer, G.L.; Glampedakis, K. How viscous is a superfluid neutron star core? Nucl. Phys. A 2005, 763, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, L.; Mendell, G. R-modes in superfluid neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 61, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdermott, P.N.; Van Horn, H.M.; Hansen, C.J. Nonradial oscillations of neutron stars. Astrophys. J. 1988, 325, 725–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbell, J.L. Non-Radial Fluid Pulsation Modes of Compact Stars. Master’s Thesis, California State University, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, U. Nonradial oscillations of neutron stars with the superfluid core. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 303, 515–525. [Google Scholar]
- Serot, B.D. A relativistic nuclear field theory with π and ρ mesons. Phys. Lett. B 1979, 86, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Typel, S.; Oertel, M.; Klähn, T. CompOSE CompStar online supernova equations of state; harmonising the concert of nuclear physics and astrophysics compose.obspm.fr. Phys. Part. Nucl. 1979, 46, 633–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusakov, M.E.; Kantor, M.; Haensel, P. The relativistic entrainment matrix of a superfluid nucleon-hyperon mixture at zero temperature. Phys. Rev. C 2009, 79, 055806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, N.; Kokkotas, K.D. Pulsation modes for increasingly relativistic polytropes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 297, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.V.; Lugones, G. Constraining color flavor locked strange stars in the gravitational wave era. Phys. Rev. C 2017, 95, 025808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mode | Polytrope | Model A | Model B | Model C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4 | ||||
| f | 4.77 | 2.74 (2.73) | 2.69 (2.69) | 2.41 (2.41) |
| p | 8.34 | 4.42 (4.40) | 4.29 (4.27) | 3.98 (3.97) |
| s | – | 3.66 | 3.59 | 3.34 |
| 1.8 | ||||
| f | 5.67 | 2.91 (2.88) | 2.87 (2.85) | 2.55 (2.54) |
| p | 9.52 | 5.05 (5.02) | 4.96 (4.94) | 4.76 (4.74) |
| s | – | 4.21 | 4.18 | 3.87 |
| 2.2 | ||||
| f | 6.26 | 3.52 (3.50) | 3.37 (3.34) | 3.05 (3.03) |
| p | 10.55 | 6.28 (6.24) | 6.18 (6.15) | 5.66 (5.65) |
| s | – | 5.13 | 5.07 | 4.75 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaikumar, P.; Klähn, T.; Monroy, R. Non-Radial Oscillation Modes of Superfluid Neutron Stars Modeled with CompOSE. Universe 2018, 4, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe4030053
Jaikumar P, Klähn T, Monroy R. Non-Radial Oscillation Modes of Superfluid Neutron Stars Modeled with CompOSE. Universe. 2018; 4(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe4030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaikumar, Prashanth, Thomas Klähn, and Raphael Monroy. 2018. "Non-Radial Oscillation Modes of Superfluid Neutron Stars Modeled with CompOSE" Universe 4, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe4030053
APA StyleJaikumar, P., Klähn, T., & Monroy, R. (2018). Non-Radial Oscillation Modes of Superfluid Neutron Stars Modeled with CompOSE. Universe, 4(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe4030053





