Two Cases of Non-Radial Filament Eruption and Associated CME Deflection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods of Analysis
3. Results
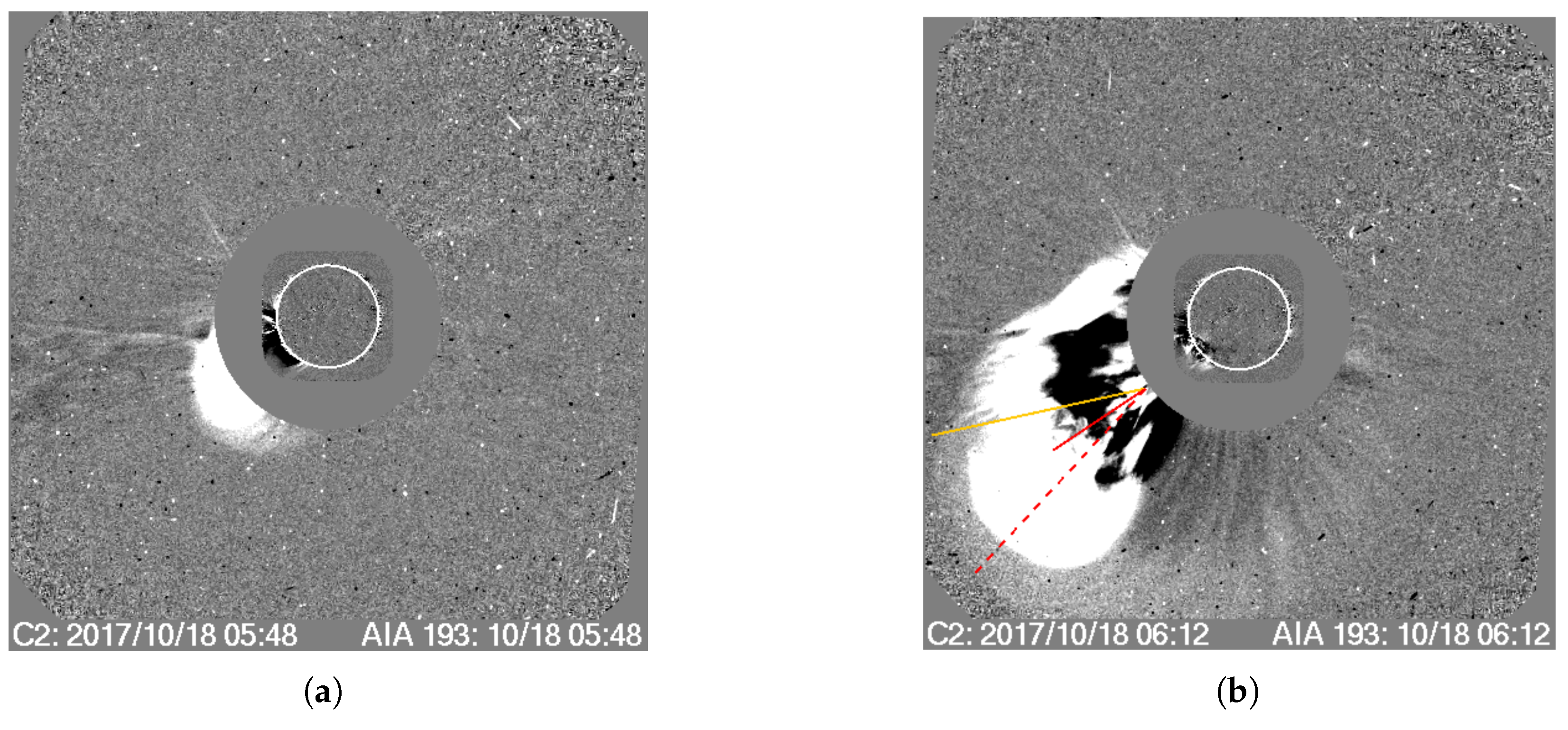
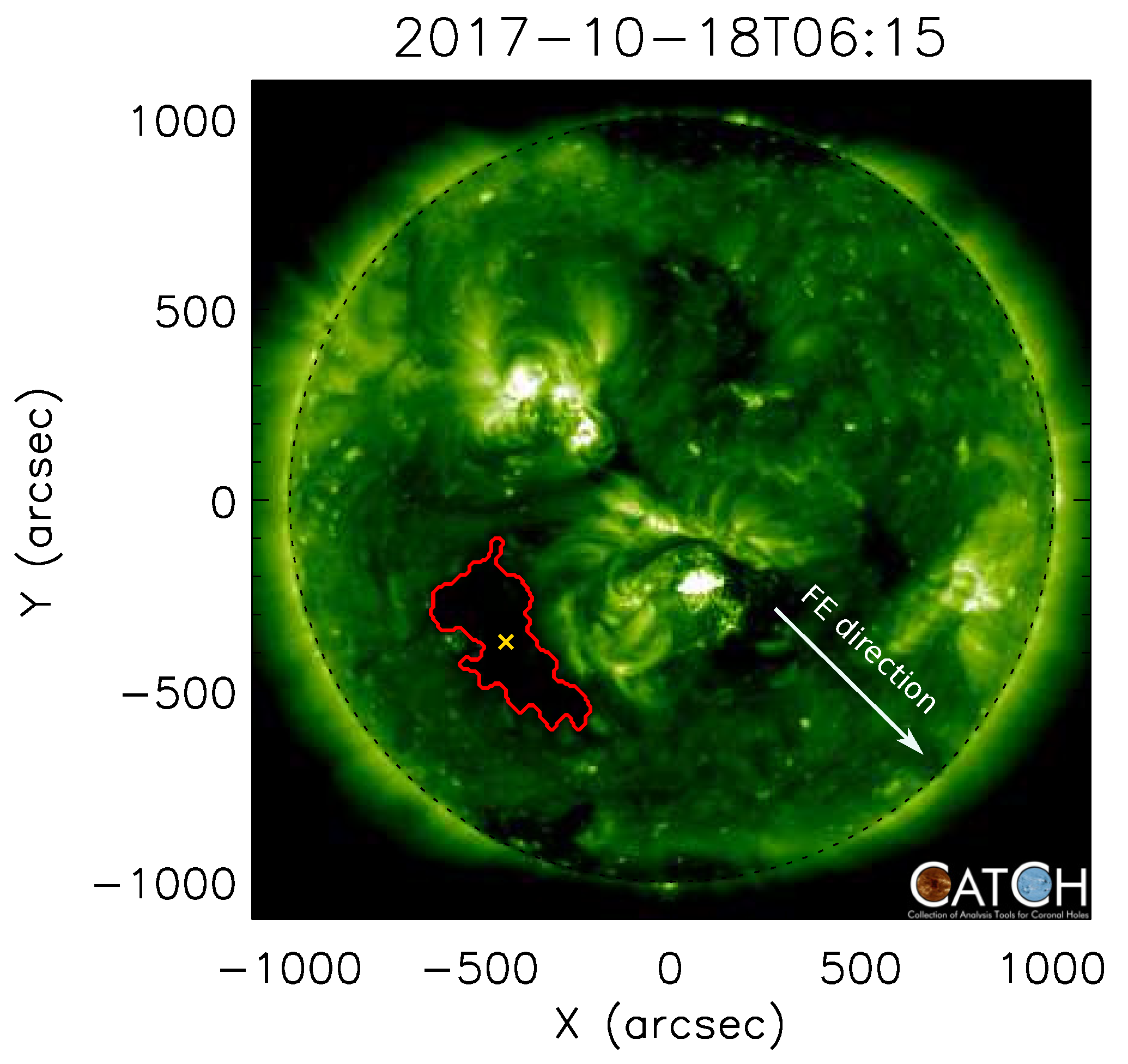
3.1. The 18 October 2017 Event
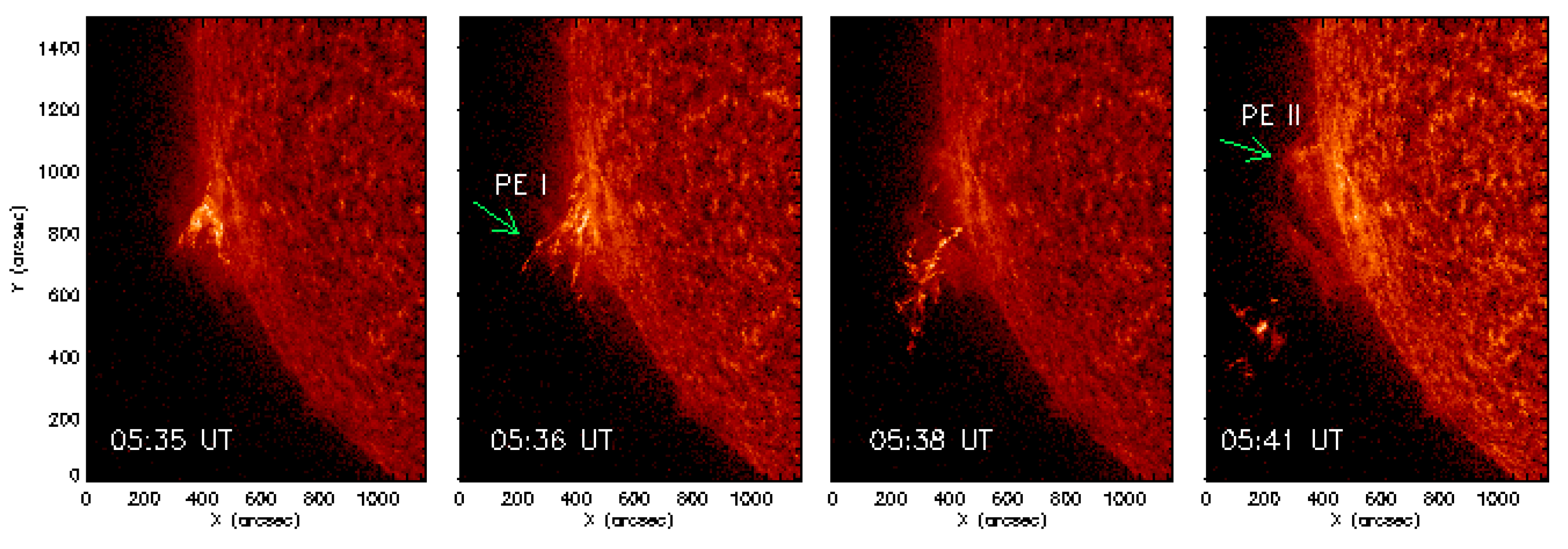
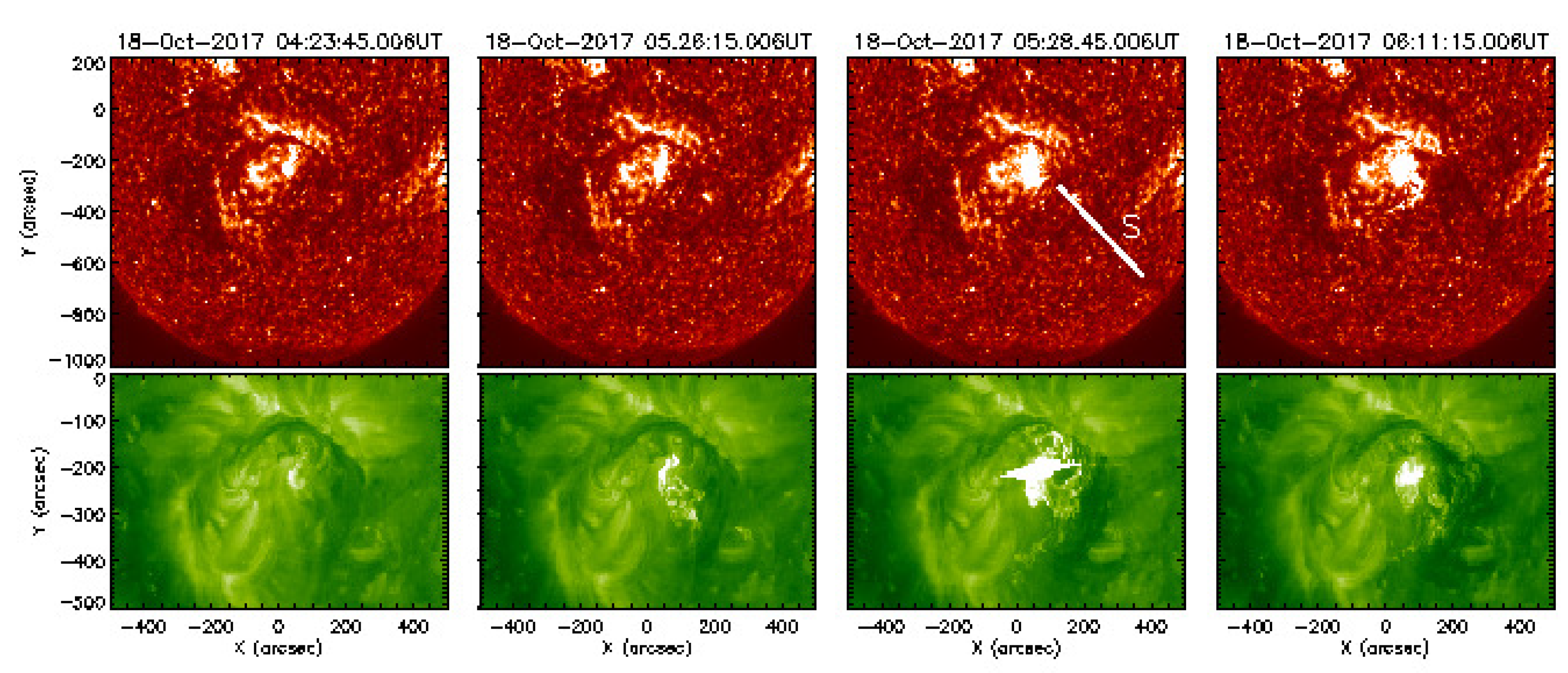
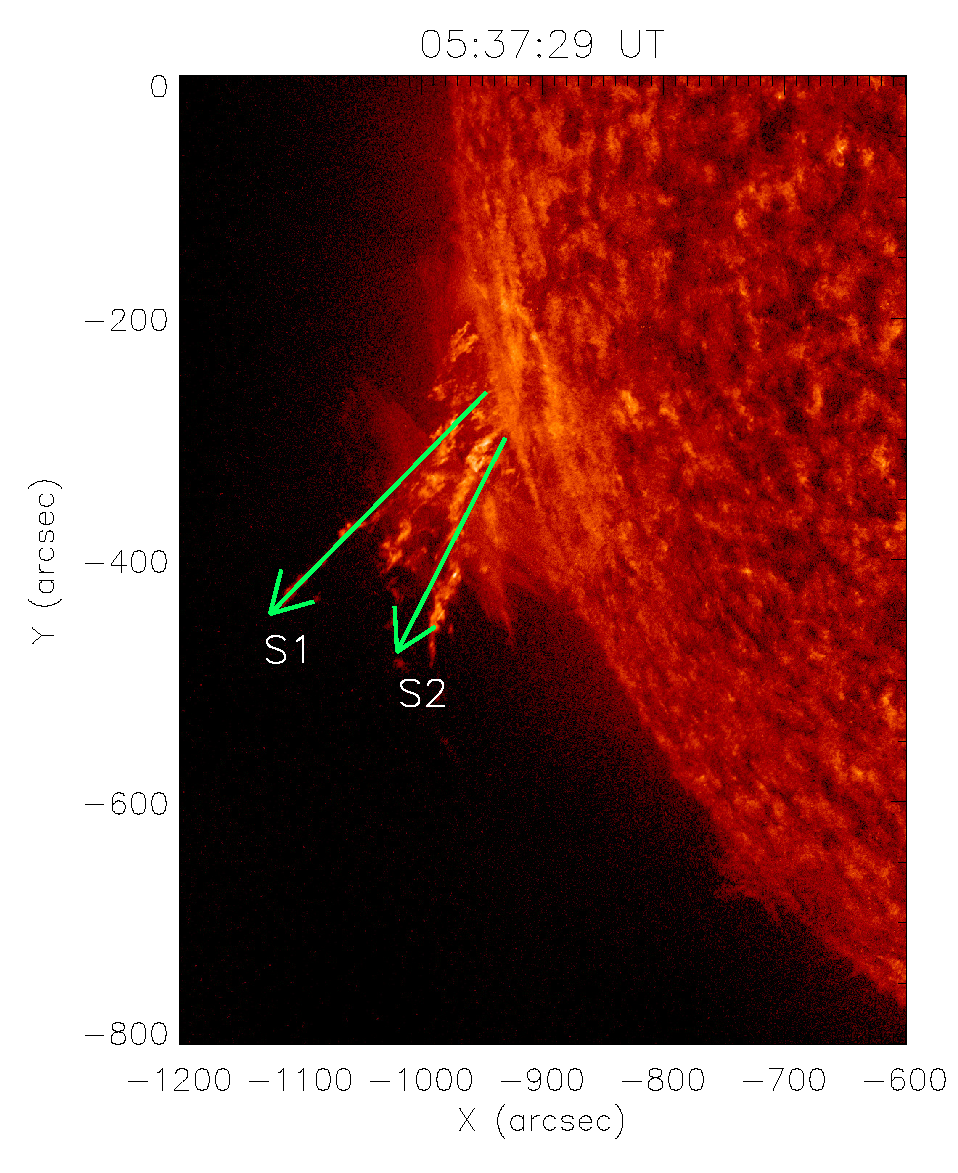
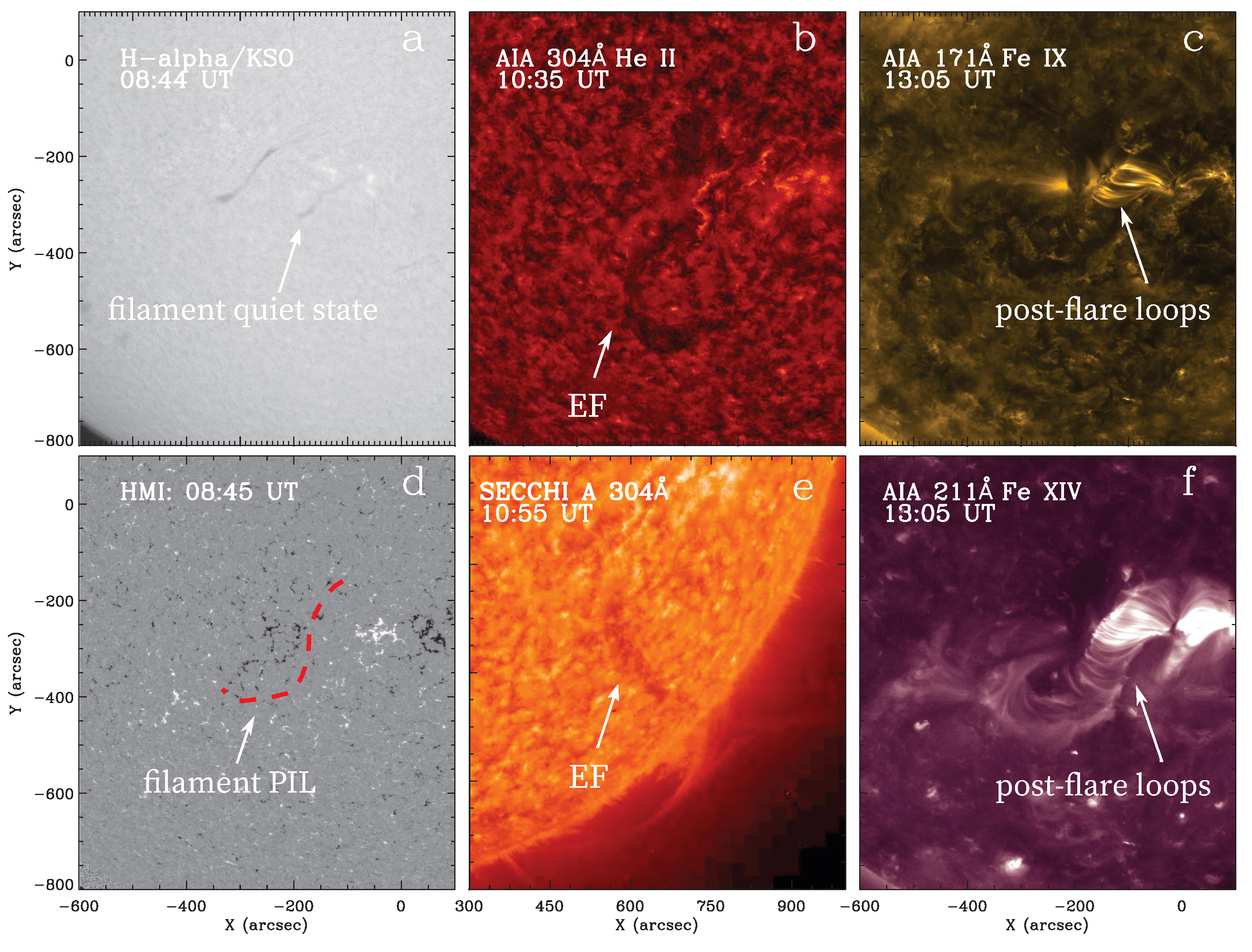
3.1.1. Morphology
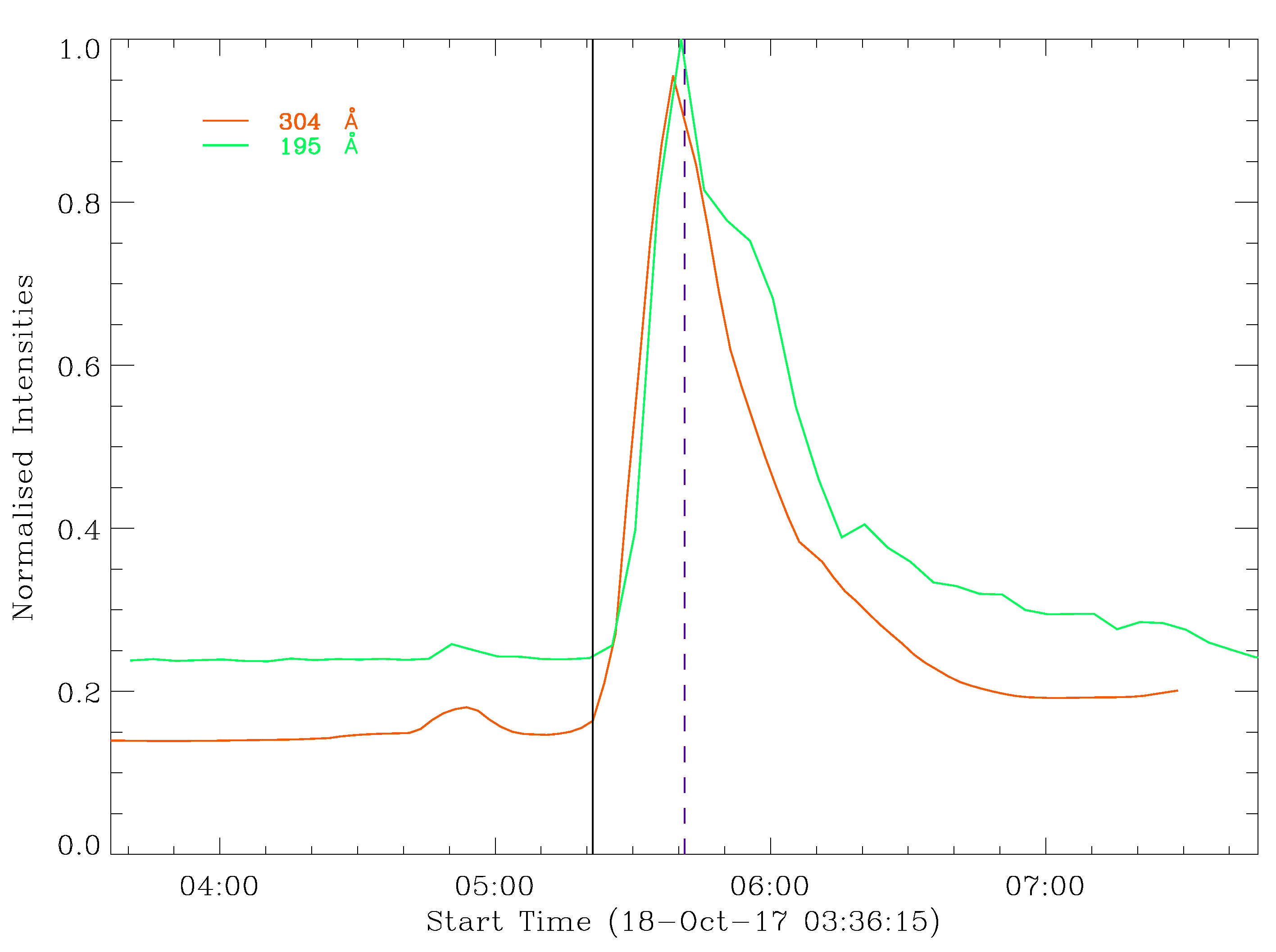
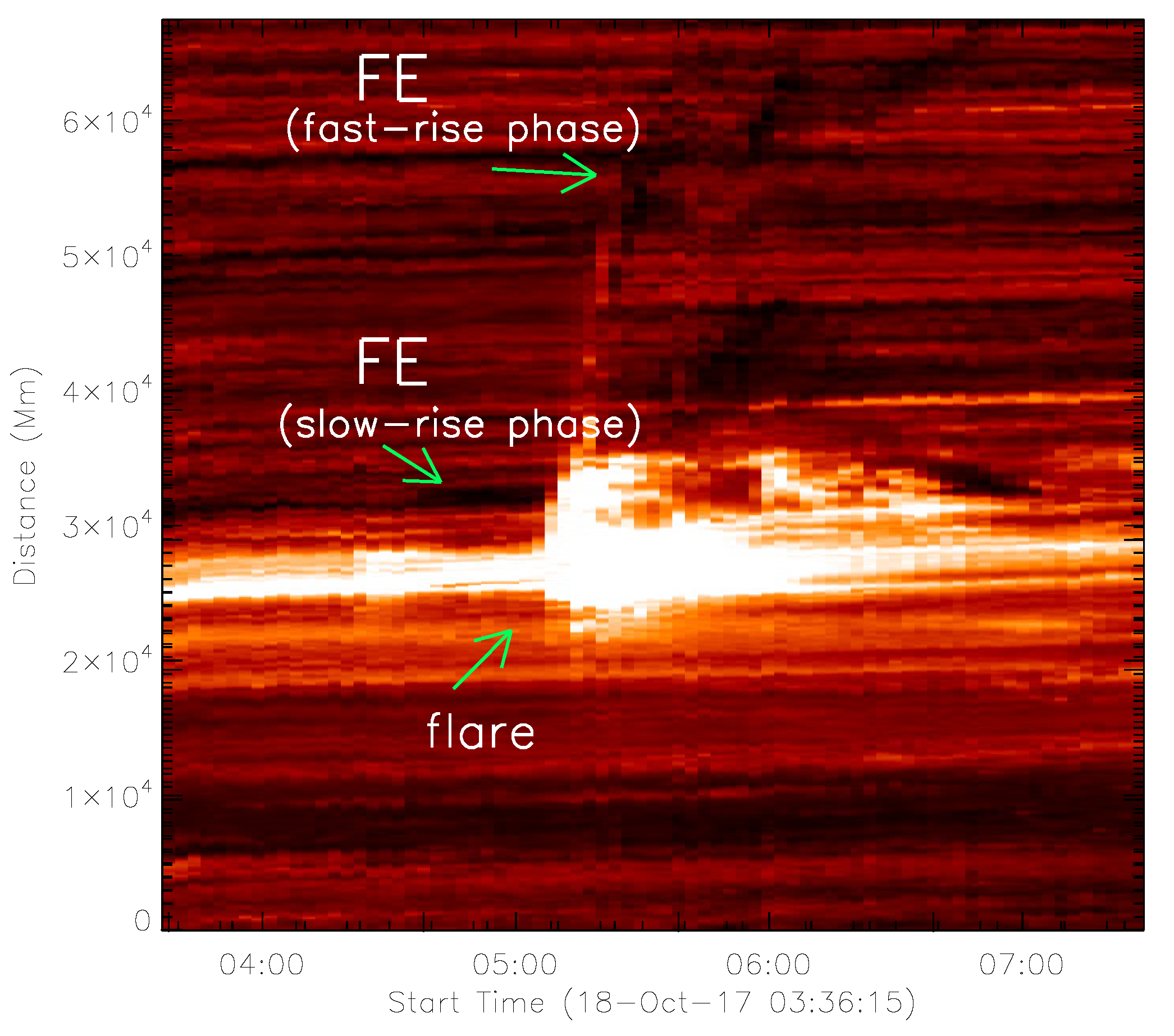
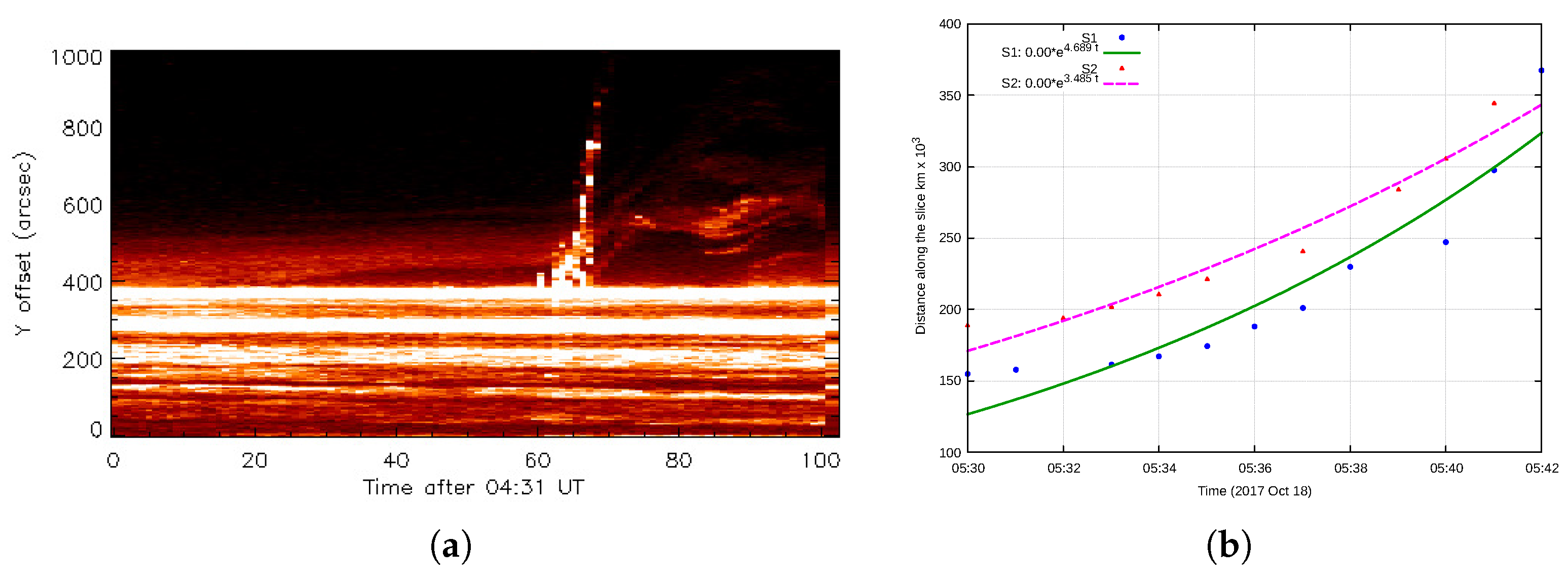
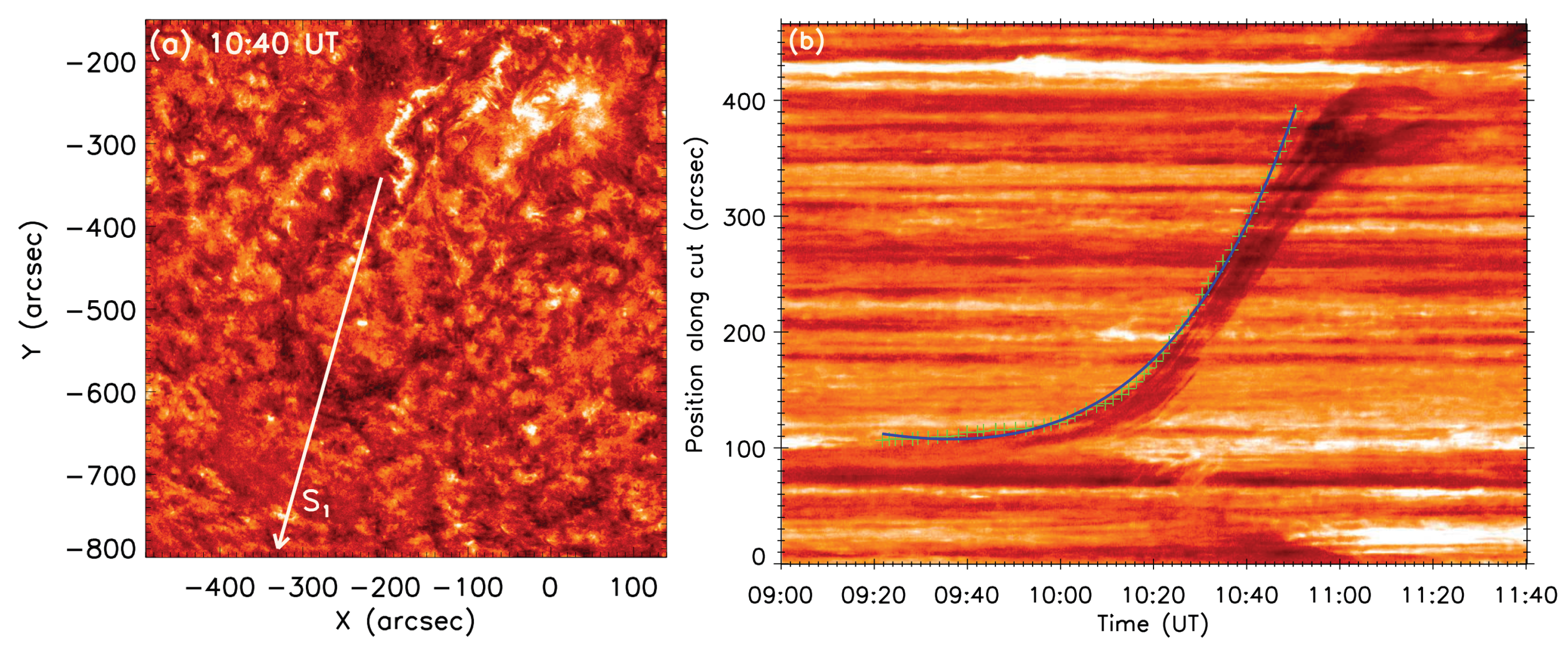
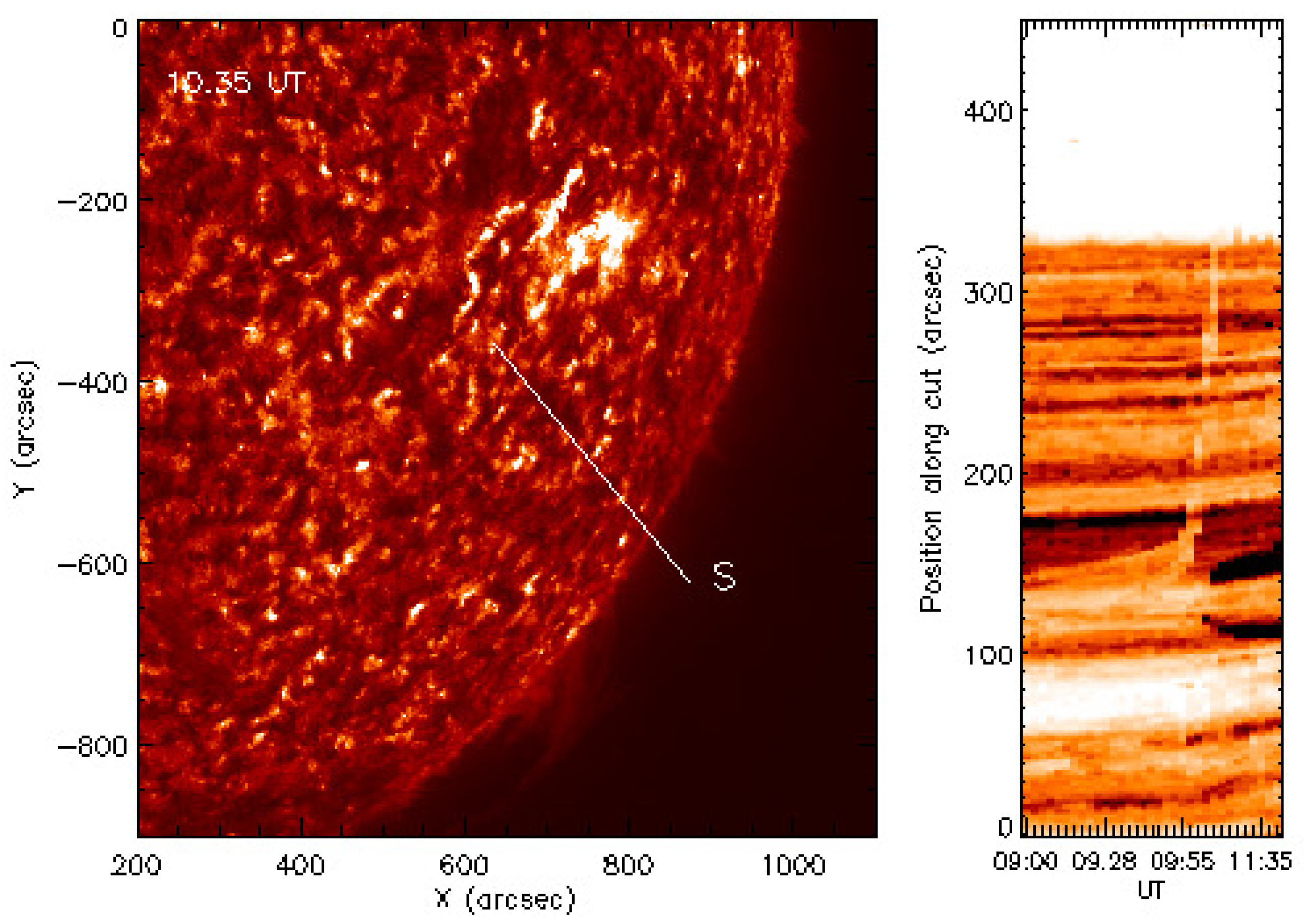
3.1.2. Kinematics
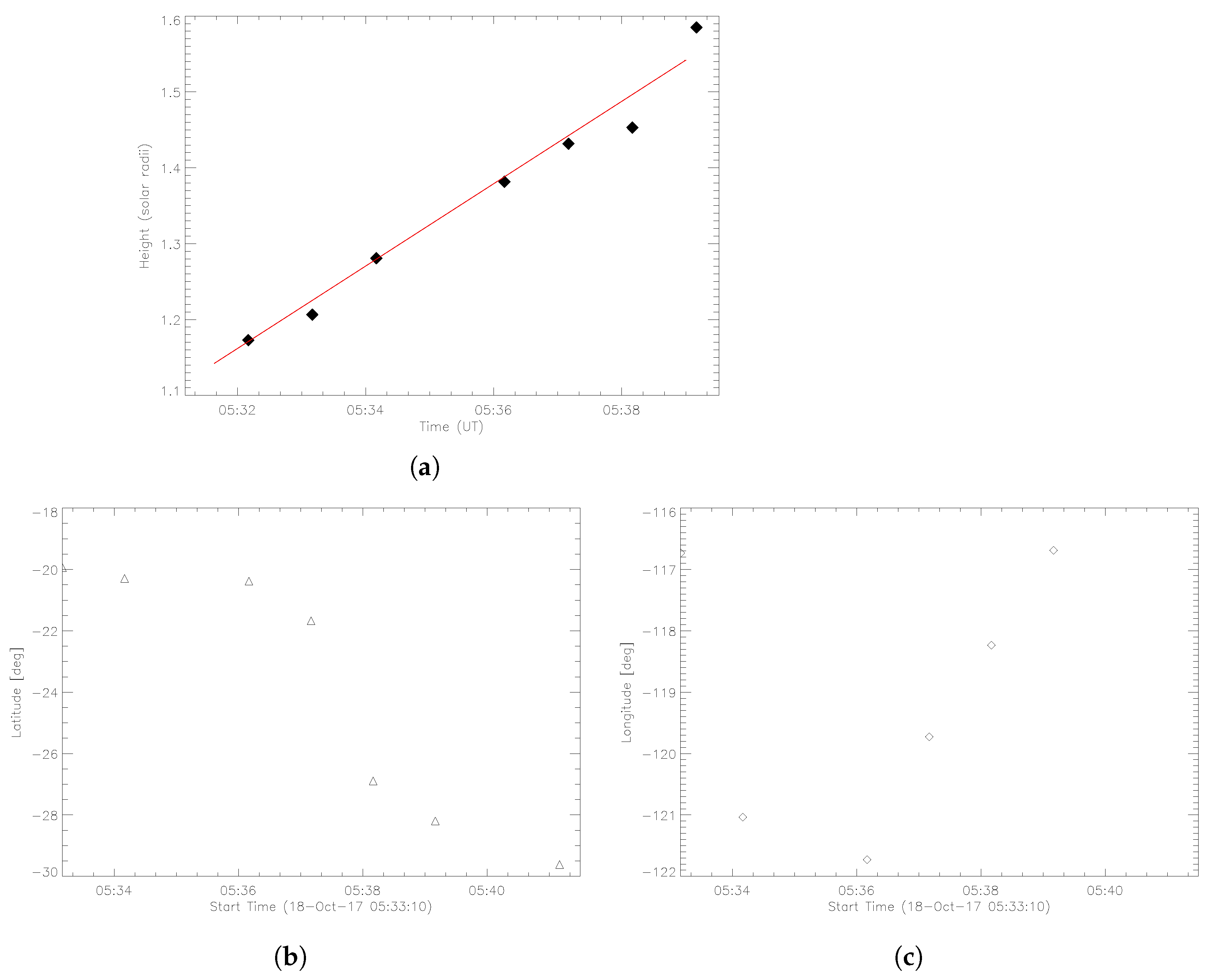
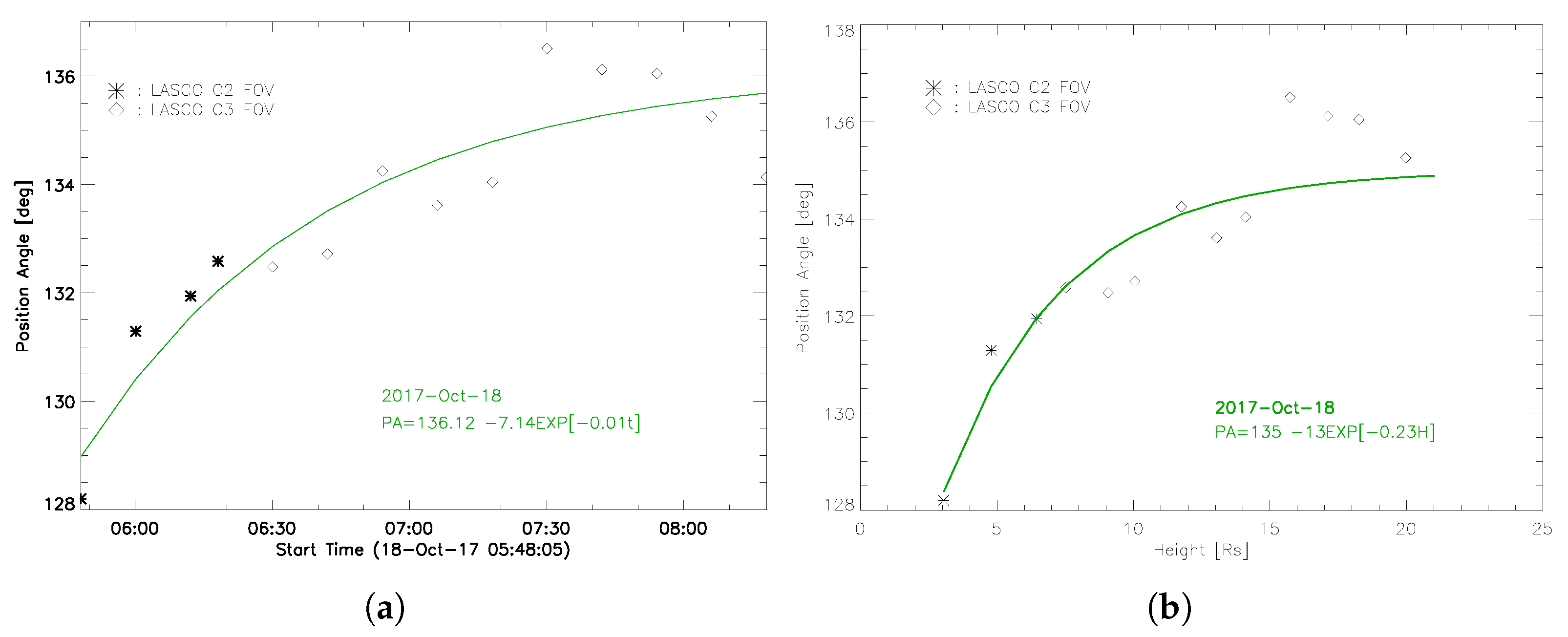
3.1.3. CME Deflection
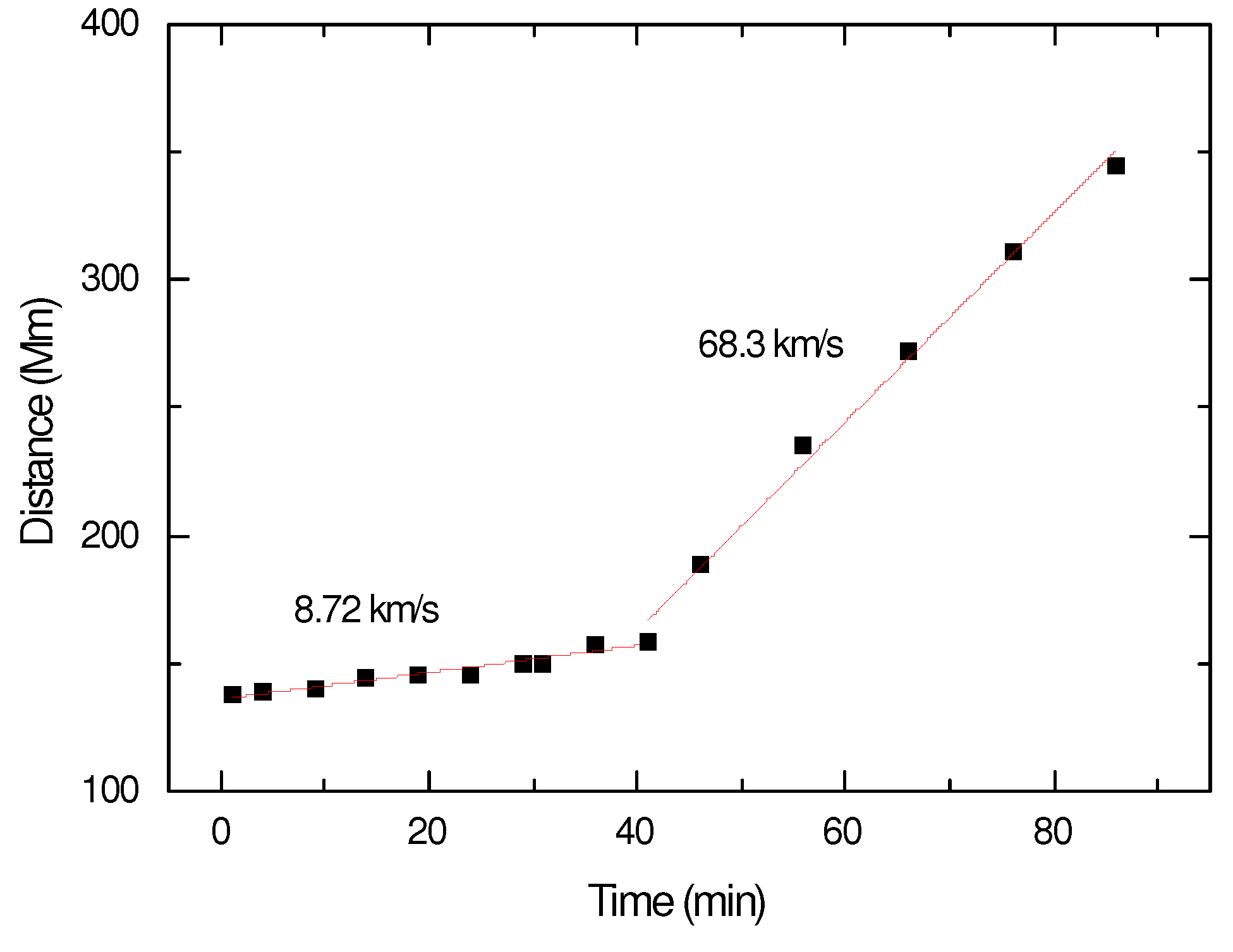
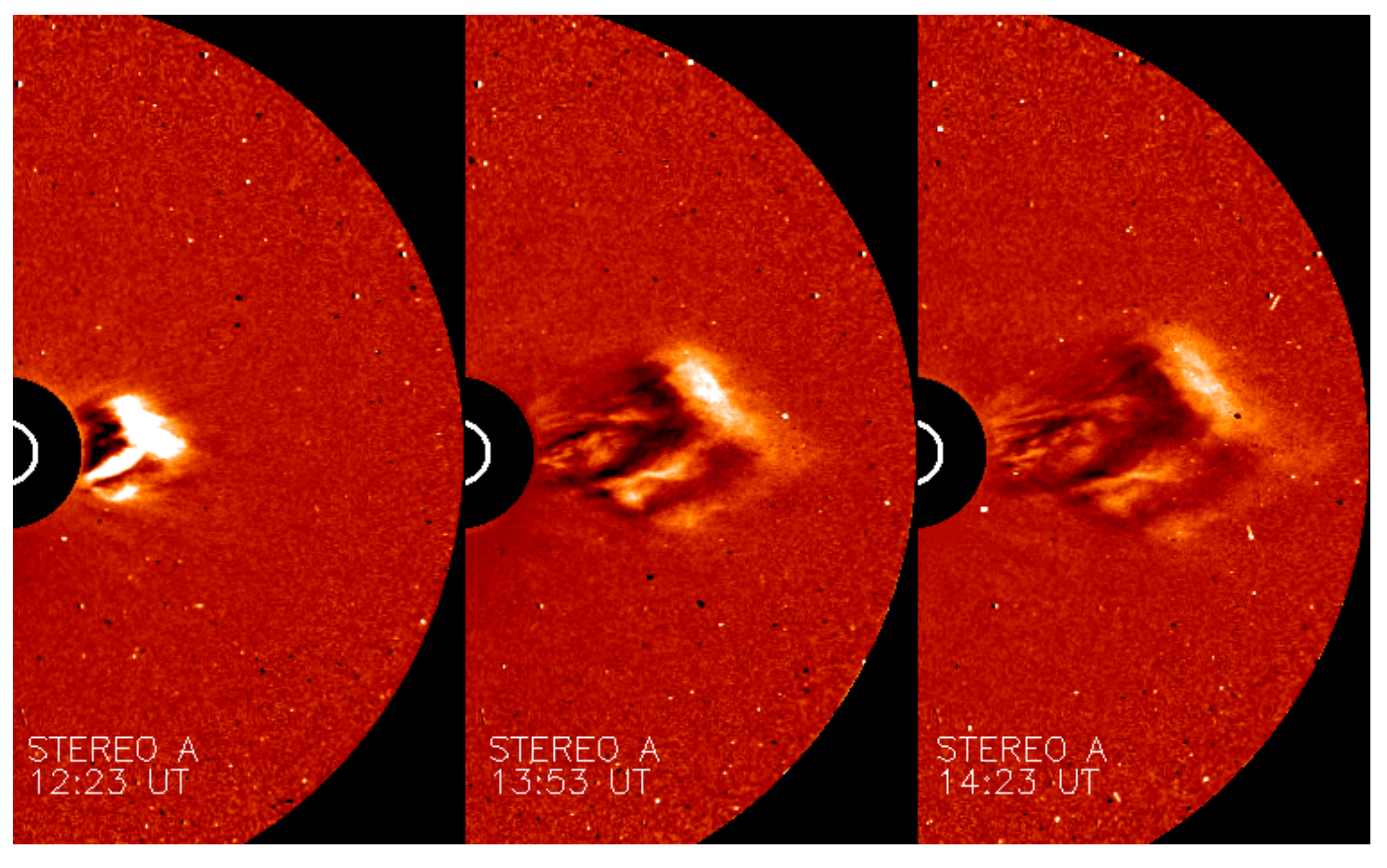
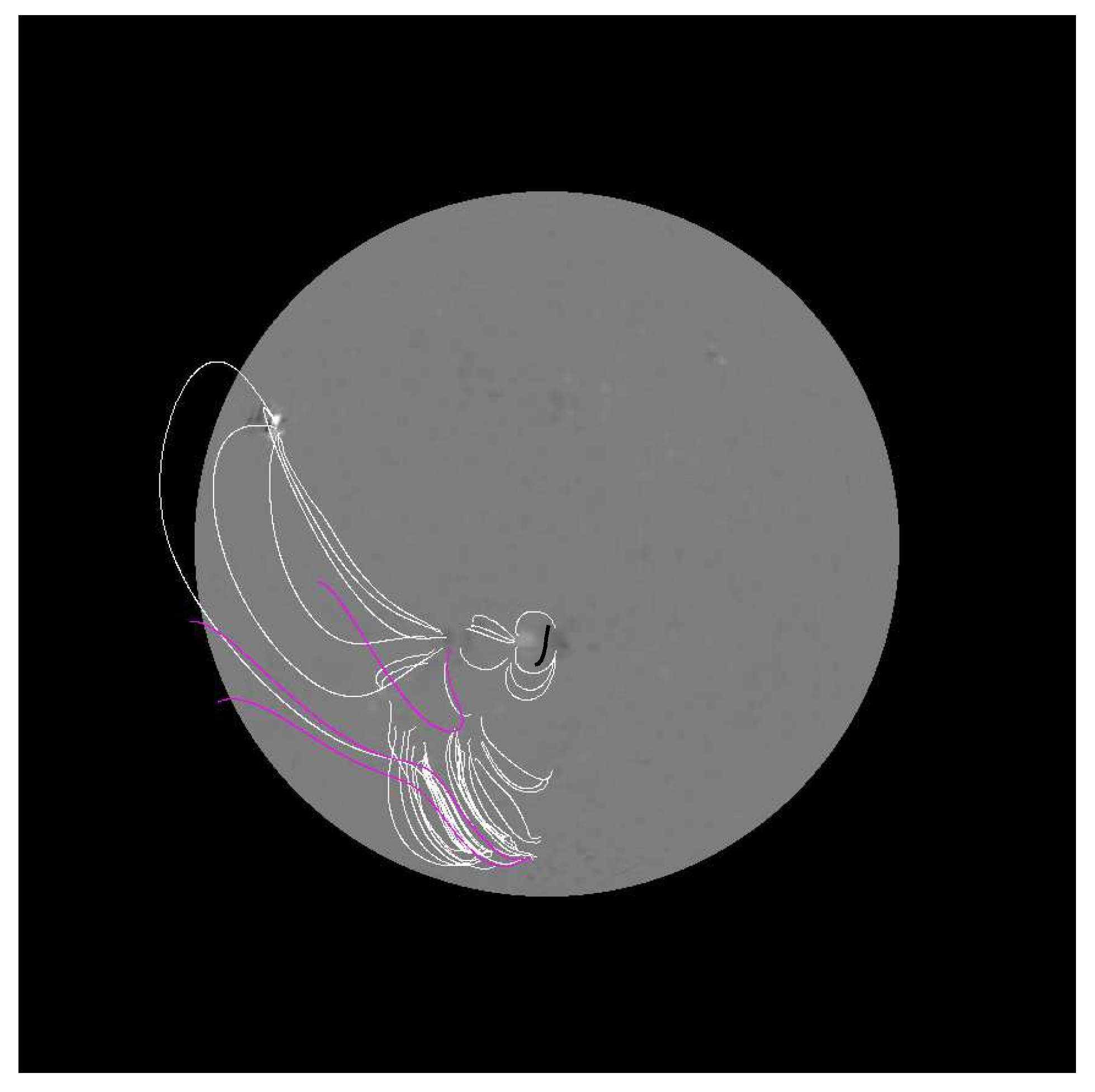
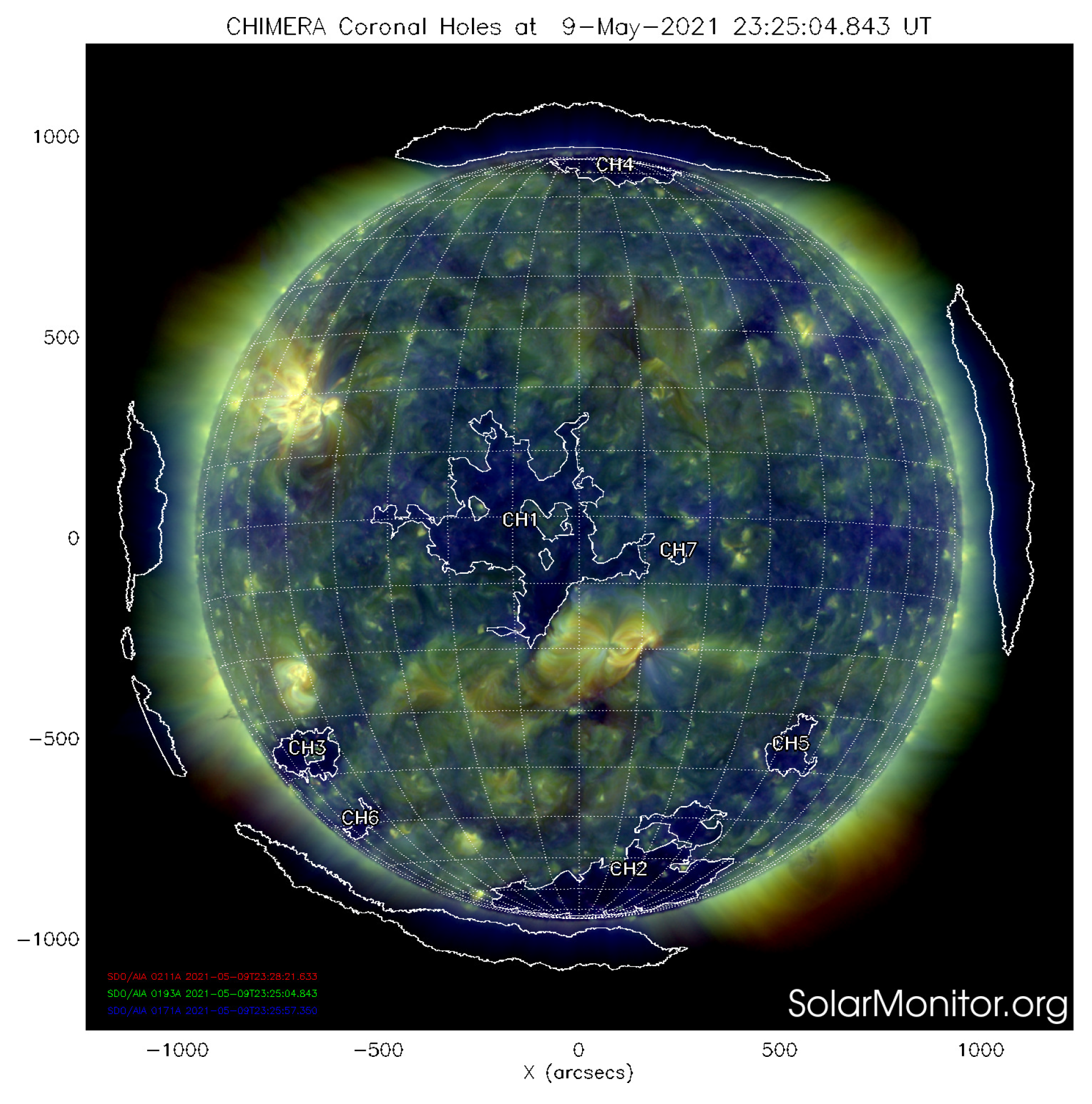
3.2. The 9 May 2021 Event
3.2.1. Morphology
3.2.2. Kinematics
3.2.3. Cme Deflection
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tandberg-Hanssen, E. The Nature of Solar Prominences; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 199. [Google Scholar]
- Labrosse, N.; Heinzel, P.; Vial, J.-C.; Kucera, T.; Parenti, S.; Gunßr, S.; Schmieder, B.; Kilper, G. Physics of solar prominences: I—Spectral diagnostics and non-LTE modelling. Space Sci. Rev. 2010, 243, 243–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, D.H.; Karpen, J.T.; Ballester, J.L.; Schmieder, B.; Aulanier, G. Physics of solar prominences: II—Magnetic structure and dynamics. Space Sci. Rev. 2010, 151, 333–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, S. Solar Prominences: Observations. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2014, 11, 1–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.E. Solar prominences: Theory and models. Fleshing out the magnetic skeleton. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2018, 15, 7–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, H.R.; Alexander, D.; Liu, R. Filament Kinking and Its Implications for Eruption and Re-formation. Sol. Phys. 2007, 245, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, C.J. Driving major solar flares and eruptions: A review. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, A.; Harra, L.; Moore, R. New Evidence for the Role of Emerging Flux in a Solar Filament’s Slow Rise Preceding Its CME-producing Fast Eruption. Astrophys. J. 2007, 669, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, A.; Moore, R.; Freeland, S. Insights into Filament Eruption Onset from Solar Dynamics Observatory Observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 731, L3–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N.; Thompson, B.J. Early life of coronal mass ejections. J. Atmos. -Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2000, 62, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, P.I.; Su, Y.N.; Schanche, N.; Evans, K.E.; Su, C.; McKillop, S.; Reeves, K.K. Prominence and Filament Eruptions Observed by the Solar Dynamics Observatory: Statistical Properties, Kinematics, and Online Catalog. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 1703–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Démoulin, P.; Chandra, R.; Joshi, R.; Schmieder, B.; Joshi, B. Observations of a prominence eruption and loop contraction. Astron. & Astrophys. 2021, 647, A85–A97. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.R.; Török, T.; Démoulin, P.; van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.; Kliem, B. Eruption of a Kink-unstable Filament in NOAA Active Region 10696. Astrophys. J. 2005, 628, L163–L166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F.; Shibata, K. An Emerging Flux Trigger Mechanism for Coronal Mass Ejections. Astrophys. J. 2000, 545, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, R.H.; Gosling, J.T.; Hildner, E.; MacQueen, R.M.; Pol, A.I.; Ross, C.L. The association of coronal mass ejection transients with other forms of solar activity. Sol. Phys. 1979, 61, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Cyr, O.C.; Webb, D.F. Activity Associated with Coronal Mass Ejections at Solar Minimum - Solar Maximum Mission Observations from 1984–1986. Sol. Phys. 1991, 136, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Soon, W.; Baliunas, S.L. Theories of solar eruptions: A review. New Astron. Rev. 2003, 47, 53–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, D.P.; Moore, R.L. Filament eruption without coronal mass ejection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2107–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Schmieder, B.; Mandrini, C.H.; Démoulin, P.; Schmieder, B.; Torok, T.; Chandra, R. Homologous flares and magnetic field topology in active region NOAA 10501 on 20 November 2003. Sol. Phys. 2011, 269, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F. Coronal mass ejections: Models and their observational basis. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2011, 8, 1–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourlidas, A.; Lynch, B.J.; Howard, R.A.; Li, Y. How many CMEs have flux ropes? Deciphering the signatures of shocks, flux ropes, and prominences in coronagraph observations of CMEs. Sol. Phys. 2013, 284, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, B.; Démoulin, P.; Aulanier, G. Solar filament eruptions and their physical role in triggering coronal mass ejections. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, B.; Shen, C.; Wang, Y.; Ye, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X. Quantitative Analysis of CME Deflections in the Corona. Sol. Phys. 2011, 271, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Isavnin, A.; Vourlidas, A.; Kilpua, E.K.J. Three-Dimensional Evolution of Flux-Rope CMEs and Its Relation to the Local Orientation of the Heliospheric Current Sheet. Sol. Phys. 2014, 298, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugaz, N. Accuracy and Limitations of Fitting and Stereoscopic Methods to Determine the Direction of Coronal Mass Ejections from Heliospheric Imagers Observations. Sol. Phys. 2010, 267, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Shen, C.; Shen, F.; Lugaz, N. Deflected propagation of a coronal mass ejection from the corona to interplanetary space. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 5117–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemen, J.R.; Title, A.M.; Akin, D.J.; Boerner, P.F.; Chou, C.; Drake, J.F.; Duncan, D.W.; Edwards, C.G.; Friedlaender, F.M.; Heyman, G.F.; et al. The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Sol. Phys. 2012, 275, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesnell, W.D.; Thompson, B.J.; Chamberlin, P.C. The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Sol. Phys. 2012, 275, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.L.; Kucera, T.A.; Davila, J.M.; St Cyr, O.C.; Guhathakurta, M.; Christian, E. The STEREO Mission: An Introduction. Space Sci. Rev. 2008, 136, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.T.; Davila, J.M.; Fisher, R.R.; Orwig, L.E.; Mentzell, J.E.; Hetherington, S.E.; Derro, R.J.; Federline, R.E.; Clark, D.C.; Chen, P.T.; et al. COR1 inner coronagraph for STEREO-SECCHI. In Innovative Telescopes and Instrumentation for Solar Astrophysics; Proceedings of the SPIE; Stephen, L.K., Sergey, V.A., Eds.; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; Volume 4853, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Brueckner, G.E. The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Sol. Phys. 1995, 162, 357–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashiro, S.; Gopalswamy, N.; Michalek, G.; St Cyr, O.C.; Plunkett, S.P.; Rich, N.B.; Howard, R.A. A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, A07105–A07116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N.; Yashiro, S.; Michalek, G.; Stenborg, G.; Vourlidas, A.; Freeland, S.; Howard, R. The SOHO/LASCO CME Catalog. Earth Moon Planets 2009, 104, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Kliem, B.; Török, T.; Xing, C.; Zhou, Z.J.; Inhester, B.; Ding, M.D. Initiation and Early Kinematic Evolution of Solar Eruptions. Astrophys. J. 2020, 894, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, A.W.; Priest, E.R. Thermal Nonequilibrium—A Trigger for Solar Flares. Sol. Phys. 1981, 73, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremades, H.; Bothmer, V. On the three-dimensional configuration of coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 422, 307–322. [Google Scholar]
- Michalek, G.; Gopalswamy, N.; Yashiro, S.; Koleva, K. A Statistical Analysis of Deflection of Coronal Mass Ejections in the Field of View of LASCO Coronagraphs. Astrophys. J. 2023, 956, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N.; Mäkelä, P.; Xie, H.; Akiyama, S.; Yashiro, S. CME nteractions with coronal holes and their interplanetary consequences. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, A00A22–A00A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremades, H.; Bothmer, V.; Tripathi, D. Properties of structured coronal mass ejections in solar cycle 23. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 38, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpua, E.; Pomoell, J.; Vourlidas, A.; Vainio, R.; Luhmann, J.; Li, Y.; Schroeder, P.; Galvin, A.B.; Simunac, K. STEREO observations of interplanetary coronal mass ejections and prominence deflection during solar minimum period. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 4491–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, P.; Gopalswamy, N.; Xie, H.; Mohamed, A.A.; Akiyama, S.; Yashiro, S. Coronal Hole Influence on the Observed Structure of Interplanetary CMEs. Sol. Phys. 2013, 284, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahade, A.; Cécere, M.; Krause, G. Influence of Coronal Holes on CME Deflections: Numerical Study. Astrophys. J. 2020, 896, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cécere, M.; Sieyra, M.V.; Cremades, H.; Mierla, M.; Sahade, A.; Stenborg, G.; Costa, A.; West, M.J.; D’Huys, E. Large non-radial propagation of a coronal mass ejection on 2011 January 24. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, C.; Opher, M.; Evans, R.M. Global Trends of CME Deflections Based on CME and Solar Parameters. Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.D.; Dai, X.; Yang, Z.; Huang, C.; Hu, H. The Role of Active Region Coronal Magnetic Field in Determining Coronal Mass Ejection Propagation Direction. Astrophys. J. 2015, 814, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N.; Yashiro, S.; Kaiser, M.L.; Howard, R.A.; Bougeret, J.L. Radio Signatures of Coronal Mass Ejection Interaction: Coronal Mass Ejection Cannibalism? Astrophys. J. 2001, 584, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, S.G.; Temmer, M.; Heinemann, N.; Dissauer, K.; Samara, E.; Jerčić, V.; Hofmeister, S.J.; Veronig, A.M. Statistical Analysis and Catalog of Non-polar Coronal Holes Covering the SDO-Era Using CATCH. Sol. Phys. 2019, 294, 144–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
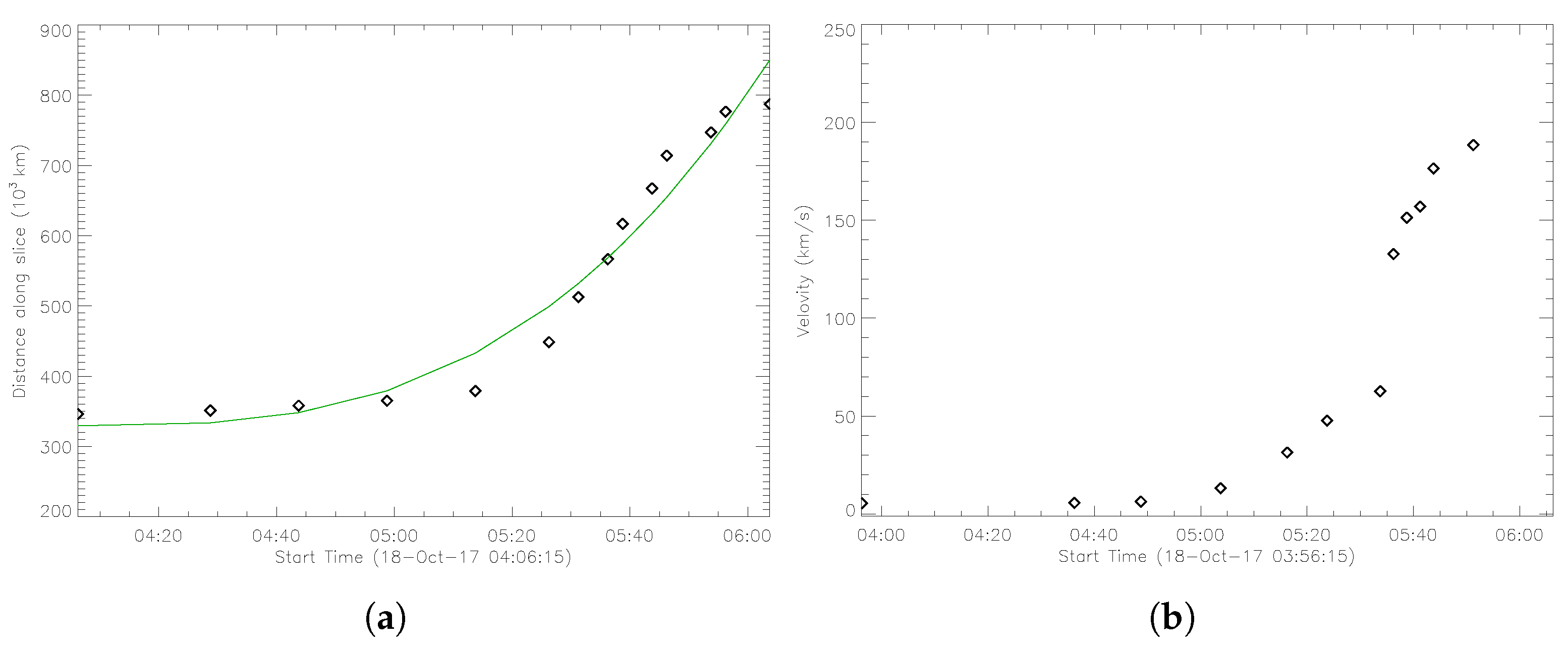

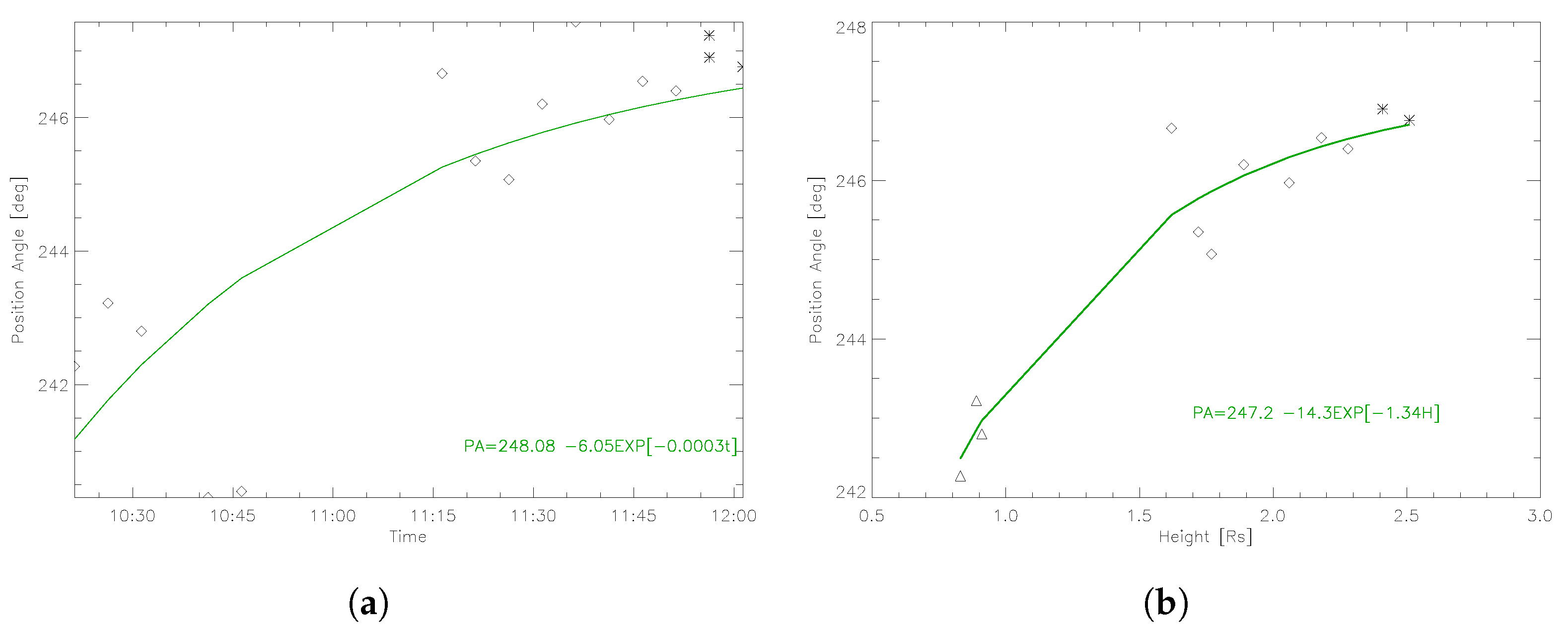
| 18 October 2017 | 9 May 2021 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDO FOV | STA FOV | SDO FOV | STA FOV | |
| Location | SE limb | −38, −223 | −138, −457 | SW limb |
| FE start | 05:32 UT | 05:26 UT | 09:30 UT | 09:40 UT |
| FE velocity: | ||||
| slow phase | – | 5.84 km s−1 | 20 km s−1 | 8.72 km s−1 |
| fast phase | 261 km s−1 | 200 km s−1 | 140 km s−1 | 68.3 km s−1 |
| CME | 05:48 UT | 06:54 (COR2) | No CME associated | 10:21 UT |
| Latitudinal deviation | 1 | - | 2 | |
| Flare (start/maximum) | 05:20/05:41 | spreading ribbons |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koleva, K.; Chandra, R.; Devi, P.; Duchlev, P.; Dechev, M. Two Cases of Non-Radial Filament Eruption and Associated CME Deflection. Universe 2025, 11, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070216
Koleva K, Chandra R, Devi P, Duchlev P, Dechev M. Two Cases of Non-Radial Filament Eruption and Associated CME Deflection. Universe. 2025; 11(7):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070216
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoleva, Kostadinka, Ramesh Chandra, Pooja Devi, Peter Duchlev, and Momchil Dechev. 2025. "Two Cases of Non-Radial Filament Eruption and Associated CME Deflection" Universe 11, no. 7: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070216
APA StyleKoleva, K., Chandra, R., Devi, P., Duchlev, P., & Dechev, M. (2025). Two Cases of Non-Radial Filament Eruption and Associated CME Deflection. Universe, 11(7), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070216










