Abstract
A recent study using weak gravitational lensing revealed that the rotation curves of some isolated galaxies are found at a very large distance from their galactic centres. This may provide strong evidence supporting Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and challenging the standard cold dark matter model. In this article, we propose the possibility that these isolated galaxies are possibly located at the centres of corresponding large dark matter haloes. Using the standard gravitational framework of galaxy groups and galaxy clusters, we show that this scenario can reproduce the observed rotation curves, provided the existence of corresponding hot gas haloes extending beyond 1 Mpc. Therefore, MOND may not be the only solution to the observed rotation curves and the cold dark matter interpretation still remains viable.
Keywords:
dark matter 1. Introduction
Observations of galaxies and galaxy clusters indicate that the enclosed gravitational mass calculated from conventional Newtonian dynamics is much larger than the visible mass observed (i.e., the gravitational mass problem). One possible solution is that there exists a large amount of invisible mass called dark matter [1,2]. Some hypothetical particles like weakly interacting massive particles and axions are proposed to be the candidates of the cosmological dark matter [2]. Nevertheless, there is another way to solve the problem. One can propose a small correction to General Relativity which can mimic the effect of the apparent gravitational mass [1,3]. Some versions of modified gravity have been proposed to mimic the effect of dark matter, such as Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) [3,4] and Emergent Gravity [5]. Therefore, the dark matter model and modified gravity are currently two leading paradigms that are needed when accounting for the gravitational mass problem.
The modified gravity proposal is very attractive because it does not need the additional dark matter component, which has not been discovered so far in collider experiments [6], direct-detection experiments [7], and indirect-detection studies [8,9]. In particular, MOND has provided some successful predictions recently, including the Baryonic Tully–Fisher relation and the radial acceleration relation (RAR) shown in galaxies [10,11,12]. However, at the same time, there is also some negative evidence that opposes the predictions made using MOND. For example, the Milky Way rotation curve seems to be significantly declining at its outer radius which does not agree with the almost flat rotation curve according to MOND’s prediction [13]. Also, the claimed universal nature of RAR is controversial, especially in elliptical galaxies and galaxy clusters [14,15,16,17,18]. On the other hand, some studies have successfully reproduced the RAR in galaxies using the cold dark matter model [19,20]. Therefore, it is still challenging problem for MOND, with other modified gravity theories offering the preferred solutions to the gravitational mass problem.
Recently, a new study using weak gravitational lensing found that there are some isolated galaxies which can manifest rotation curves for very large radii [21]. This may provide new evidence to support the prediction from MOND that the galactic rotation curves should be flat in the deep-MOND regime (i.e., acceleration is much less than the universal acceleration scale ). For the benchmark cold dark matter model, the galactic rotation curves would decline beyond the dark matter scale radii , typically less than 100 kpc. Since [21] claim that the observed rotation curve data generally do not agree with the cold dark matter model’s prediction, this can be used as a piece of evidence to support MOND and challenge the standard cold dark matter model.
In this article, we revisit the case of the isolated galaxies discussed in [21] and show a possible way to give the circular velocities observed in isolated galaxies beyond 1 Mpc. We alternatively propose that those galaxies are located in dark matter haloes with the size of a galaxy group. Using the hydrostatic gas model commonly adopted in galaxy clusters and galaxy groups, one can prove that the outer circular velocities can be almost constant, even extending to 1 Mpc. In other words, the observed circular velocities in those galaxies can still be compatible with the standard cold dark matter model. The purpose of this analysis is not to argue whether the dark matter model or MOND is the correct paradigm. We only aim to show that the recent rotation curve data from the weak lensing reported in [21] is compatible with both the dark matter model and MOND.
2. MOND’s Prediction
MOND suggests that the apparent gravity influenced by the total enclosed mass without dark matter would be modified as [3,22]
where cm/s2 is the acceleration scale and is the conventional Newtonian gravity. Here, the function is the interpolating function (IF) exhibiting the properties when and when . For a sufficiently large distance R from the galactic centre (in cylindrical coordinates), the total enclosed mass would be approximately equal to the total disk mass . The conventional Newtonian gravity influenced by the enclosed disk mass at a particular R is as follows [23,24]:
where , , and are the modified Bessel functions of the nth kind, and a is the galactic disk scale radius. When R is much larger than a (i.e., ), the expression . Therefore, with a large R, the conventional Newtonian gravity would be
In the deep-MOND regime (i.e., R is very large such that ), we have . Therefore, we obtain the galactic circular velocity in the deep-MOND regime as
Since the total disk mass is constant, the galactic circular velocity at a very large R would be close to a constant. In other words, MOND predicts that the galactic rotation curve at very large R would be flat. This prediction has been claimed as one of the major pieces of supporting evidence for MOND because many observed galactic rotation curves are almost flat when R is large [3]. Therefore, the observed rotation curves of the isolated galaxies at very large radii can provide additional evidence on supporting MOND [21]. Moreover, ref. [21] also shows that the conventional cold dark matter model finds it hard to reproduce the rotation curves throughout large ranges of R.
3. The Theoretical Framework Describing a Galaxy Group
Consider the possibility that each of the abovementioned isolated galaxies is indeed located in a large spherical dark matter halo with a size of a galaxy group. There may be other galaxies nearby but these are too dim to be observed. Most of the baryonic matter inside the large dark matter haloes would be in the form of hot gas.
In a galaxy group or galaxy cluster, there is normally a hot gas halo inside [25,26]. The number density of the hot gas halo can be simply modelled by the -model [26]:
where , , and are the central number density, scale radius, and the index parameter of the hot gas. This is the simplest model involving the fewest number of parameters and gives very good likelihood to the X-ray data [25,26].
Now, we assume that the large dark matter haloes containing the abovementioned isolated galaxies are almost identical to that in a galaxy group or galaxy cluster. Considering the hot gas in hydrostatic equilibrium, we have
where P is the gas pressure, is the enclosed total mass profile (including baryonic and dark matter mass), and is the mass density of the hot gas. Recent simulation studies show that the systematic error of assuming hydrostatic equilibrium in galaxy clusters is about 10% only [27,28]. Therefore, Equation (6) is a very good approximation to relate the number density of hot gas with the total enclosed mass. By putting into Equation (6), where T is the hot gas temperature, and combining with Equation (5), we obtain
where is the molecular weight. For , where is the virial radius of a galaxy group, the temperature of the hot gas is almost constant [29], except near the core region for some cool-core clusters [26]. In fact, if there is no large-scale effective heating source (e.g., no Active Galactic Nuclei) in the galaxy group and the conduction of electrons in the hot gas is quite efficient (mean free path∼10 kpc), the temperature of the hot gas would be approximately constant. These conditions can be easily achieved in many of the low-redshift galaxy groups and galaxy clusters [26,29]. Therefore, we simply assume that T is constant throughout the region of interest (i.e., ).
Since the total enclosed mass (dominated by dark matter at large r) is spherical in shape, the rotation velocity is
If the hot gas halo has a small scale radius , for large r such that , the asymptotic rotation velocity is close to a constant: . The data of the rotation velocities of the galaxies in [21] give km/s. Taking the average value of derived from [26], the temperature of the hot gas is 0.05–0.2 keV (i.e., ∼ K), which means that the hot gas Bremsstrahlung emission is mainly in the ultraviolet bands. This temperature is somewhat lower than that in a typical X-ray emitting galaxy cluster ( keV). Therefore, detecting the hot gas emission inside these dark matter haloes would be very challenging because the flux density is very small for the diffused ultraviolet emission.
In Figure 1, we show the predicted rotation velocities for the ‘four galaxies’ (i.e., the four alleged dark matter haloes) using Equation (8). By comparing with the observed rotation velocities using the lensing data, we can see that this scenario generally agrees with the observations. The asymptotic velocities are determined based on the average rotation velocities from the lensing data. Note that the asymptotic velocities v depend on two degenerate empirical parameters and T. Since T is unknown, we arbitrarily use the average value shown in galaxy clusters to model the rotation curves. Using other values of would not change our conclusion because one can change T to match the asymptotic velocities. On the other hand, the scale radius is unknown for all cases. Generally speaking, can range from ∼10 to 500 kpc for galaxy groups and clusters [26]. Nevertheless, since the asymptotic velocities do not depend on , using different values of would not change our conclusion either. The values of only control the positions where would the rotation velocities become flat. Moreover, for small R, the gravitational effect of baryonic matter might be significant, which would affect the best fit . Since the aim of this analysis is to show that our proposed scenario could produce the almost flat asymptotic velocities, we do not perform rigorous fits for the values. In Figure 1, we have set two different values of ( kpc and kpc) for each galaxy for demonstration. Generally speaking, any of the values of kpc can give the same asymptotic velocities.
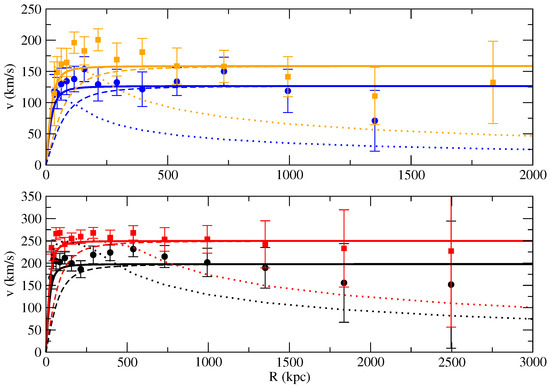
Figure 1.
The upper and lower graphs show the rotation curves for the four galaxies extending to Mpc (two in each graph). The solid lines and dashed lines represent the predictions using the galaxy group model with kpc and kpc, respectively. We have assumed for all cases. The dotted lines represent the rotation curves predicted by the conventional NFW model (with Keplerian decline outside the virial radius). Each color in the graphs represents the data and the predicted rotation curves for each galaxy. The data points with error bars (based on the weak lensing measurement) are extracted from [21].
Moreover, we also compare our results with the conventional predictions using the cold dark matter model. In galaxies, the cold dark matter model predicts that the dark matter density would follow the Navarro–Frenk–White (NFW) profile [30]. The rotation velocity in a galaxy would be given by [31]
where and are the scale density and scale radius of the NFW profile, respectively. Using the abundance matching framework in [32] and the mass–concentration relation (WMAP5) in [33], one can obtain the virial mass and the concentration parameters of the ‘four galaxies’. These values can transform to the scale density and scale radius for each galaxy. Outside the virial radius of each galaxy, the rotation velocity would follow the ‘Keplerian decline’ as
Comparing the conventional NFW rotation curves with the data in Figure 1, although the error bars are quite large for kpc, the NFW rotation curves show some significant disagreements in the region of kpc. This is the reason why the conventional NFW model cannot provide good accounts for the data [21]. Nevertheless, our proposed scenario assumes that those galaxies are located inside dark matter halos with the size of a galaxy group, which can provide an alternative possible explanation using the cold dark matter paradigm to account for the observed rotation velocities of galaxies at large R. Therefore, MOND is not the only solution to account for the observed rotation curves at large R. The observed data are also compatible with the dark matter paradigm, but not using the conventional NFW model.
4. Discussion
In this article, we discuss the possibility that the isolated galaxies in [21] are indeed located inside the dark matter haloes with the size of a galaxy group. By using the standard gravitational framework used in galaxy groups and galaxy clusters, we show that it provides a viable solution to the observed rotation curves of galaxies at large R, provided the hot gas profiles extend beyond 1 Mpc. Also, in this scenario, the hot gas profile would be different from the galactic scaling relation applied in [21]. Therefore, whether the results are consistent with the baryonic Tully–Fisher relation is unknown. The correlation between the rotation curves and the Baryonic Tully–Fisher relation in galaxies is indeed theory-laden. Overall speaking, MOND is not the only solution for these observed results. The standard cold dark matter interpretation still remains viable. Although the conventional NFW model fails to account for the rotation curve data, our proposed scenario (the galaxy group model) following the cold dark matter paradigm can provide a satisfactory solution.
If the galaxies are actually located inside dark matter haloes with the size of a galaxy group, there may exist some ultra-faint dwarf galaxies nearby which have not been observed or other galazies where their formation has failed. In fact, there is a problem called the missing satellites problem, which states that there are too few galaxies observed around massive galaxies [34]. However, when the resolution and sensitivity of observations have been improved, more faint dwarf galaxies have been observed so that the missing satellite problem is generally alleviated [35,36,37]. For example, in our galaxy, some ultra-faint galaxies such as Willman 1 and Segue 1 were observed in the past two decades [37,38,39]. Some recent simulations even suggest that our Milky Way might contain ∼1000 ultra-faint dwarf galaxies, which is much more than our expectation [40]. Therefore, the suggestion of having some unobserved dwarf galaxies surrounding those isolated galaxies is a reasonable guess. If this suggested possible scenario is true, we expect that we may be able to observe some ultra-faint dwarf galaxies around these isolated galaxies in the future. High-sensitivity optical, infrared, and radio telescopes are required to search for the alleged dwarf galaxies to test our proposed scenario.
Author Contributions
M.H.C. conceived the study and performed the analysis. Y.Z. performed the derivations and checking. A.D.P. performed the posterior analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Dean’s Research Fund from The Education University of Hong Kong (IRS-2) and a grant from the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China (Project No. EdUHK 18300922).
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the reviewers for providing useful comments and feedback.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bertone, G.; Tait, T.M.P. A new era in the search for dark matter. Nature 2018, 562, 51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cirelli, M.; Strumia, A.; Zupan, J. Dark matter. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.01705. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, R.H.; McGaugh, S.S. Modified Newtonian Dynamics as an alternative to dark matter. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 40, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Milgrom, M. A modification of the Newtonian dynamics as a possible alternative to the hidden mass hypothesis. Astrophys. J. 1983, 270, 365. [Google Scholar]
- Verlinde, E.P. Emergent gravity and the dark universe. SciPost Phys. 2017, 2, 016. [Google Scholar]
- Abercrombie, D.; Akchurin, N.; Akilli, E.; Maestre, J.A.; Allen, B.; Gonzalez, B.A.; Andrea, J.; Arbey, A.; Azuelos, G.; Azzi, P.; et al. Dark matter benchmark models for early LHC run-2 searches: Report of the ATLAS/CMS dark matter forum. Phys. Dark Universe 2020, 27, 100371. [Google Scholar]
- Aprile, E.; Aalbers, J.; Agostini, F.; Alfonsi, M.; Althueser, L.; Amaro, F.D.; Anthony, M.; Arneodo, F.; Baudis, L.; Bauermeister, B.; et al. Dark matter search results from a one ton-year exposure of XENON1T. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 111302. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, M.H.; Lee, C.M. A new method to constrain annihilating dark matter. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 524, L61. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, G.; Sarkis, M. Galaxy clusters in high definition: A dark matter search. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 023006. [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh, S.S.; Lelli, F.; Schombert, J.M. Radial acceleration relation in rotationally supported galaxies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 201101. [Google Scholar]
- Lelli, F.; McGaugh, S.S.; Schombert, J.M.; Desmond, H.; Katz, H. The baryonic Tully-Fisher relation for different velocity definitions and implications for galaxy angular momentum. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 484, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, K.-H.; Bernardi, M.; Sanchez, H.D.; Sheth, R.K. On the presence of a universe acceleration scale in elliptical galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2020, 903, L31. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, M.H.; Law, K.C. A severe challenge to the Modified Newtonian Dynamics phenomenology in our Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2023, 957, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.H.; Del Popolo, A. The radial acceleration relation in galaxy clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.H.; Desai, S.; Del Popolo, A. There is no universal acceleration scale in galaxies. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2022, 74, 1441. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Umetsu, K.; Ko, C.-M.; Donahue, M.; Chiu, I.N. The radial acceleration relation in CLASH galaxy clusters. Astrophys. J. 2020, 896, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Gopika, K.; Desai, S. A test of constancy of dark matter halo surface density and radial acceleration relation in relaxed galaxy groups. Phys. Dark Universe 2021, 33, 100874. [Google Scholar]
- Dabringhausen, J.; Kroupa, P. The integrated galaxy-wide stellar initial mass function over the radial acceleration range of early-type galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 526, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, C.; Courteau, S. The intrinsic scatter of the radial acceleration relation. Astrophys. J. 2019, 882, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Paranjape, A.; Sheth, R.K. The radial acceleration in a ΛCDM universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 507, 632. [Google Scholar]
- Mistele, T.; McGaugh, S.; Lelli, F.; Schombert, J.; Li, P. Indefinitely flat circular velocities and the Baryonic Tully-Fisher relation from weak lensing. Astrophys. J. 2024, 969, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, A.A.; Macció, A.V.; Obreja, A.; Buck, T. NIHAO-XVII. Origin of the MOND phenomenology of galactic rotation curves in a ΛCDM universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 485, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, K.C. On the disks of spiral and S0 galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1970, 160, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofue, Y. Grand rotation curve and dark matter halo in the Milky Way Galaxy. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 64, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiprich, T.H.; Böhringer, H. The mass function of an X-ray flux-limited sample of galaxy clusters. Astrophys. J. 2001, 567, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Reiprich, T.H.; Böhringer, H.; Ikebe, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y. Statistics of X-ray observables for the cooling-core and non-cooling galaxy clusters. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 466, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, V.; Borgani, S.; Murante, G.; Rasia, E.; Planelles, S.; Granato, G.L.; Ragone-Figueroa, C.; Back, A.M.; Gaspari, M.; Dolag, K. On the nature of hydrostatic equilibrium in galaxy clusters. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, C.H.A.; Maughan, B.J.; Diaferio, A.; Duffy, R.T.; Geller, M.J.; Rines, K.; Sohn, J. Chandra follow-up of the Hectospec Cluster Survey: Comparison of caustic and hydrostatic masses and constraints on the hydrostatic bias. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 665, A124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiprich, T.H.; Basu, K.; Ettori, S.; Israel, H.; Lovisari, L.; Molendi, S.; Pointecouteau, E.; Roncarelli, M. Outskirts of galaxy clusters. Sp. Sci. Rev. 2013, 177, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. The structure of cold dark matter halos. Astrophys. J. 1996, 462, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-N.; Li, X. The dark matter profiles in the Milky Way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 5679. [Google Scholar]
- Kravtsov, A.V.; Vikhlinin, A.A.; Meshcheryakov, A.V. Stellar mass-halo mass relation and star formation efficiency in high-mass halos. Astron. Lett. 2018, 44, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Macciò, A.V.; Dutton, A.A.; van den Bosch, F.C. Concentration, spin and shape of dark matter haloes as a function of the cosmological model: WMAP1, WMAP3 and WMAP5 results. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, B.; Ghigna, S.; Governato, F.; Lake, G.; Quinn, T.; Stadel, J.; Tozzi, P. Dark matter substructure within galactic halos. Astrophys. J. 1999, 524, L19. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, J.D.; Geha, M. The kinematics of the ultra-faint Milky Way satellites: Solving the missing satellite problem. Astrophys. J. 2007, 670, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, E.A.K.; Giovanelli, R.; Haynes, M.P. A catalog of ultra-compact high velocity clouds from the ALFALFA survey: Local Group galaxy candidates? Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Peter, A.H.G.; Hargis, J.R. Missing satellites problem: Completeness corrections to the number of satellite galaxies in the Milky Way are consistent with cold dark matter predictions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 211302. [Google Scholar]
- Belokurov, V.; Zucker, D.B.; Evans, N.W.; Kleyna, J.T.; Koposov, S.; Hodgkin, S.T.; Irwin, M.J.; Gilmore, G.; Wilkinson, M.I.; Fellhauer, M.; et al. Cats and dogs, hair and a hero: A quintet of new Milky Way companions. Astrophys. J. 2007, 654, 897. [Google Scholar]
- Willman, B.; Geha, M.; Strader, J.; Strigari, L.E.; Simon, J.D.; Kirby, E.; Ho, N.; Warres, A. Willman 1—A probable dwarf galaxy with an irregular kinematic distribution. Astron. J. 2011, 142, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, T.; Bullock, J.S.; Garrison-Kimmel, S.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Graus, A.S. Phat ELVIS: The inevitable effect of the Milky Way’s disc on its dark matter subhaloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 4409. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).