The Equation of State of Novel Double-Field Pure K-Essence for Inflation, Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Equations of Motion
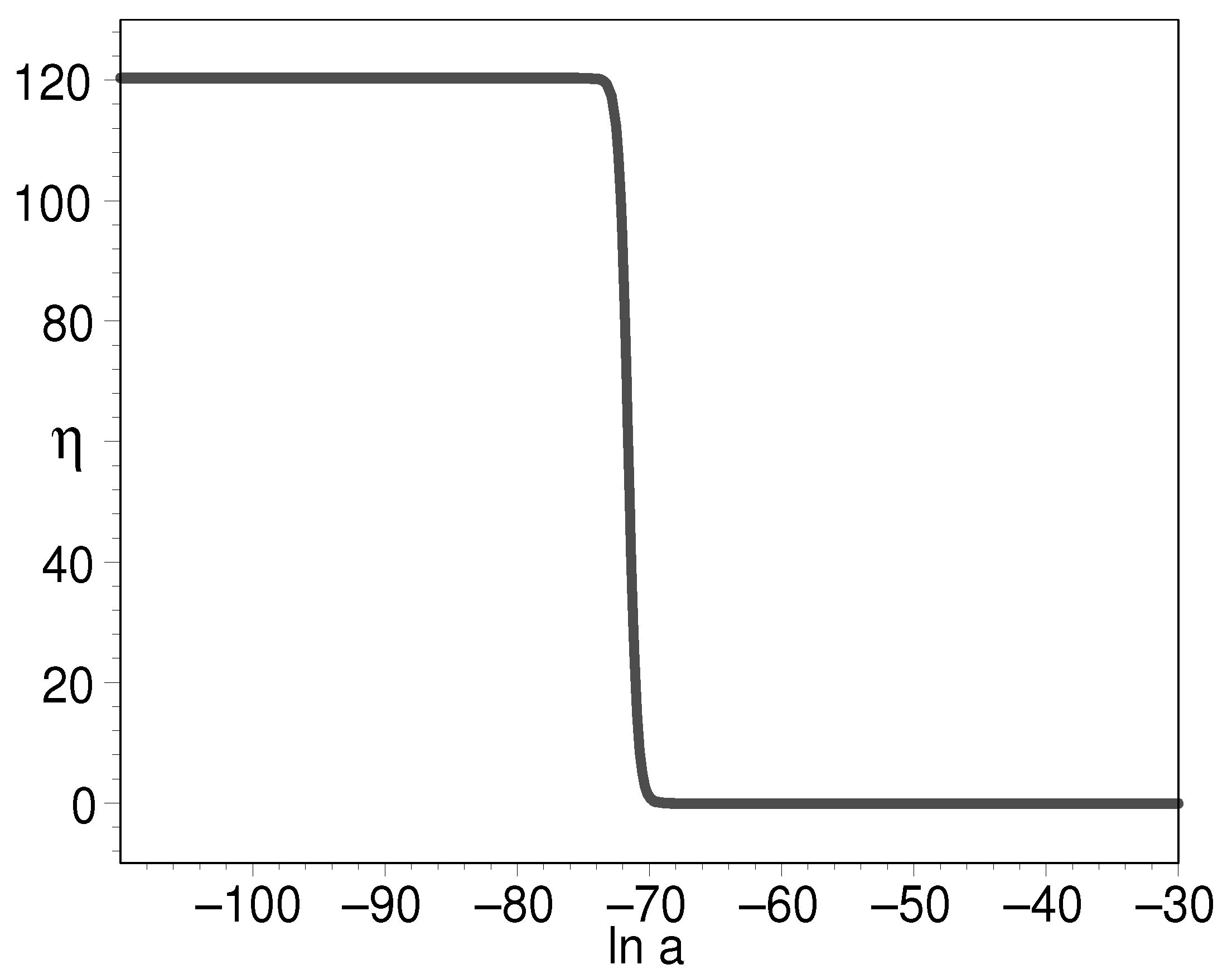
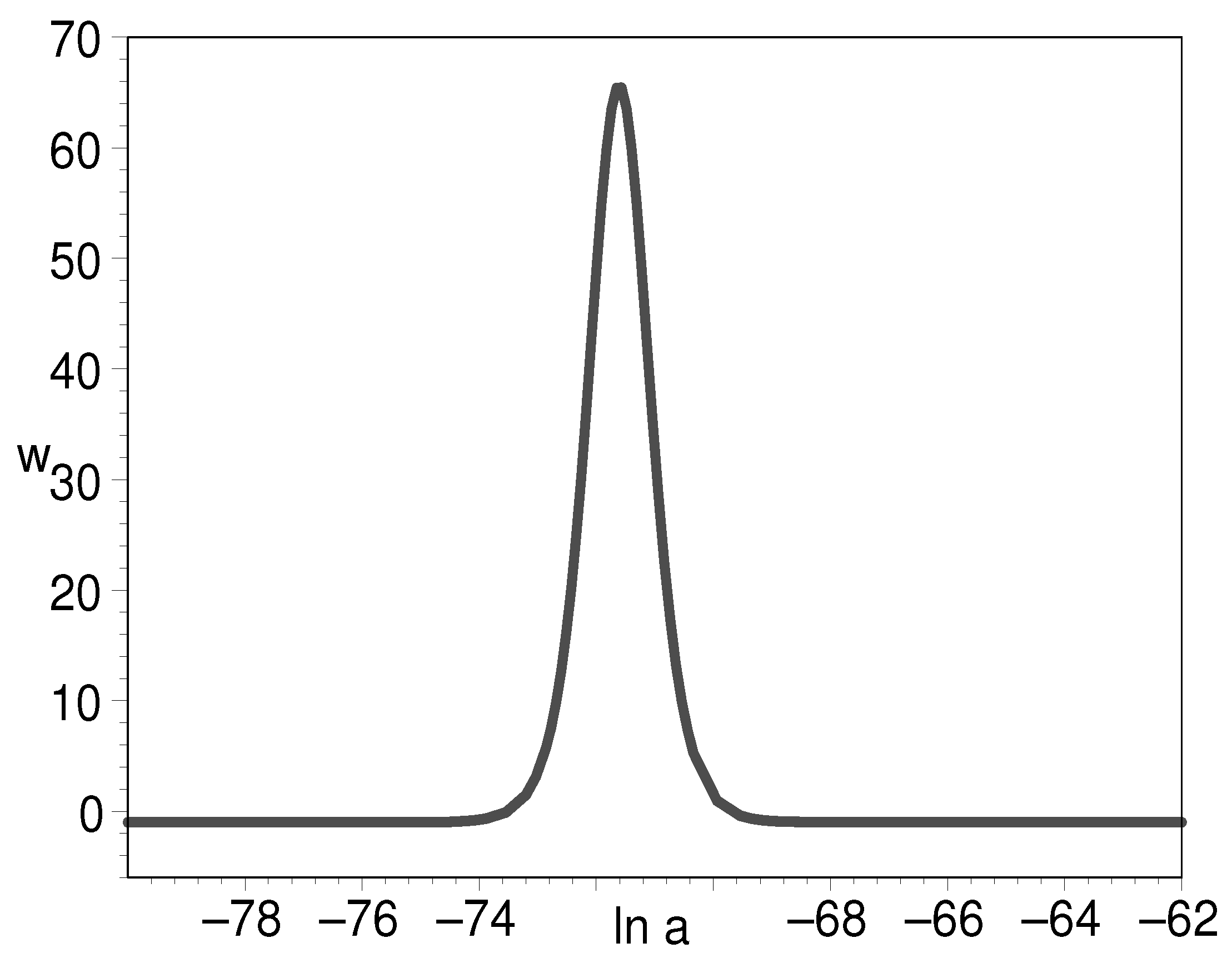
3. Cosmic Evolution
3.1. Cosmological Equations of Motion
3.2. Motivation: The Power of Double-Field Pure K-Essence
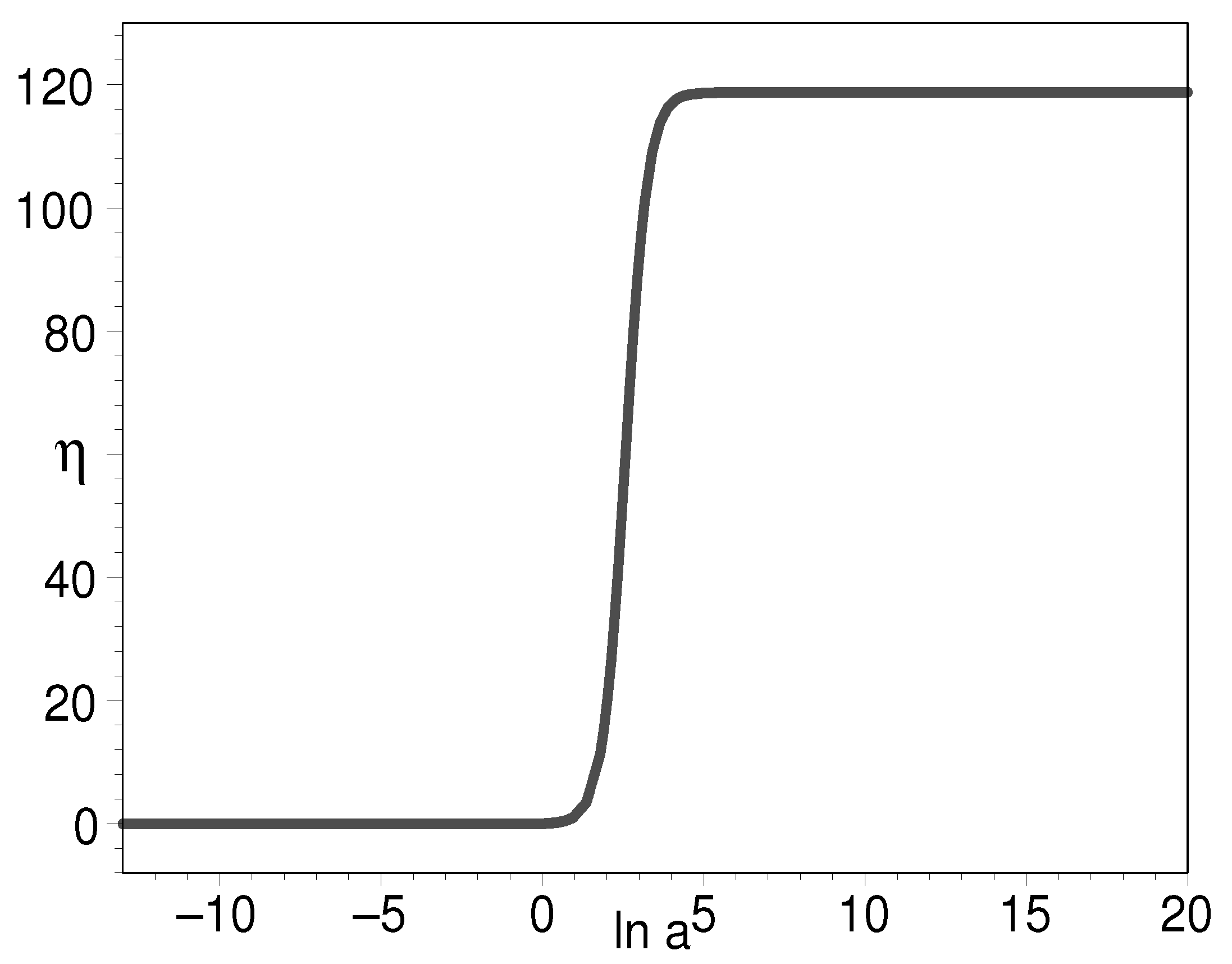
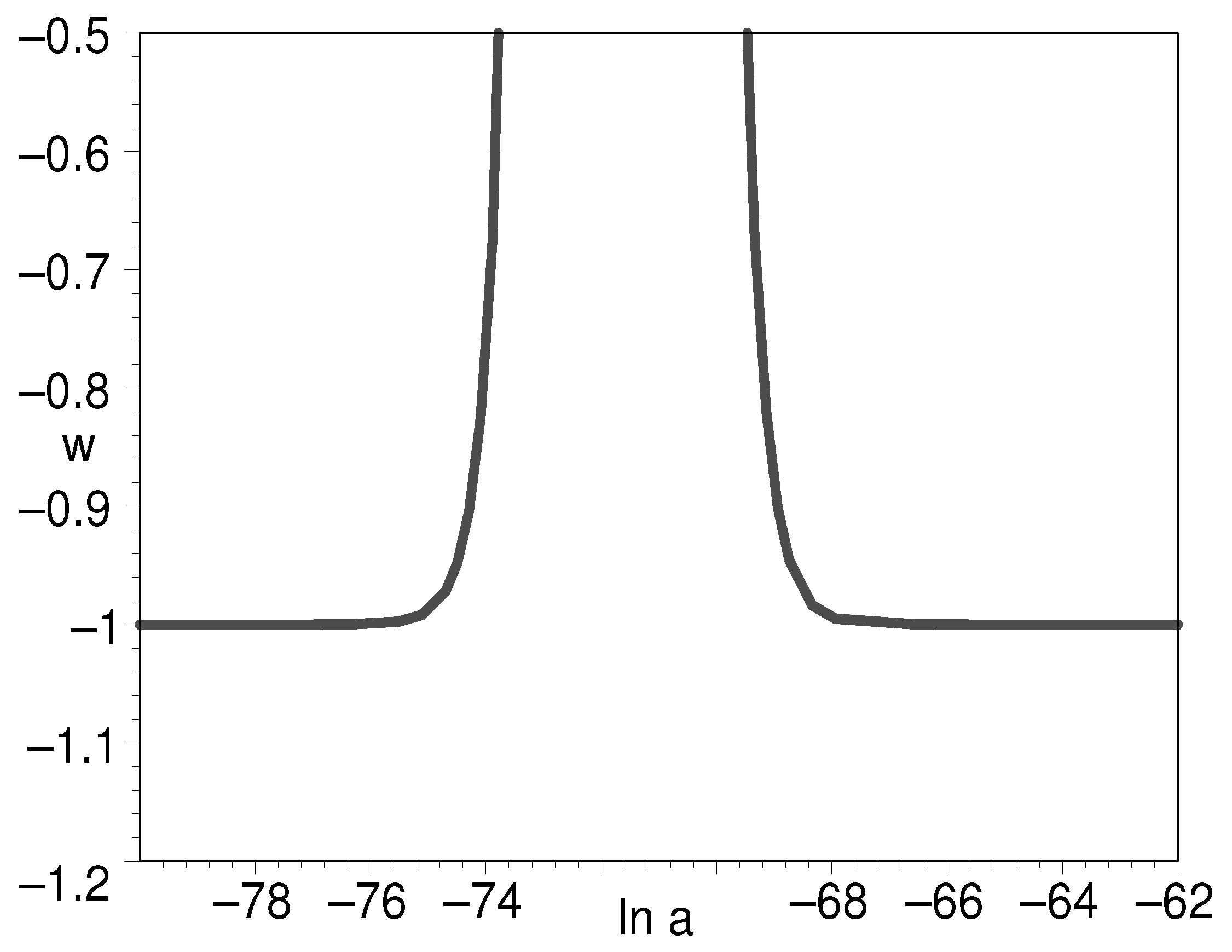
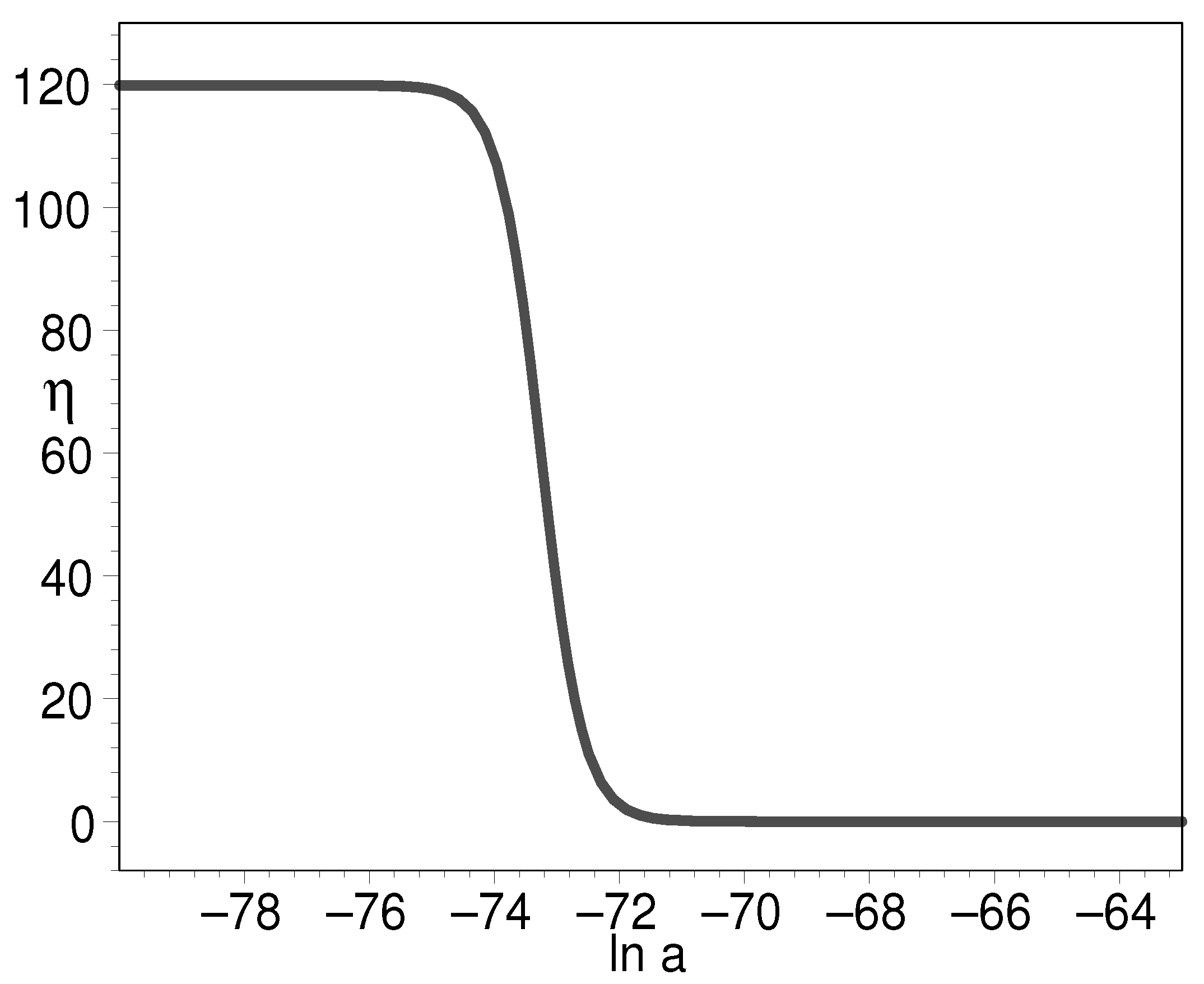
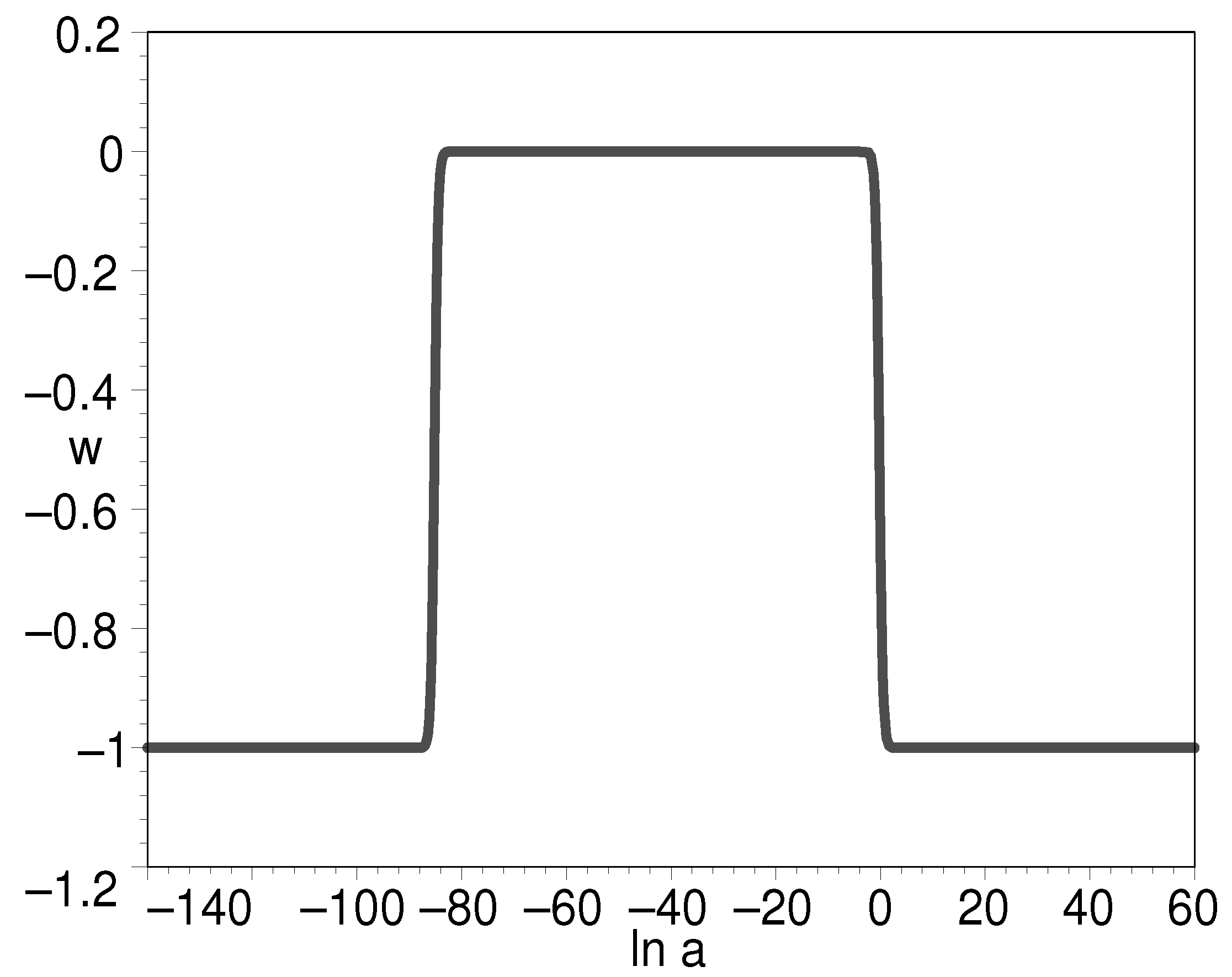
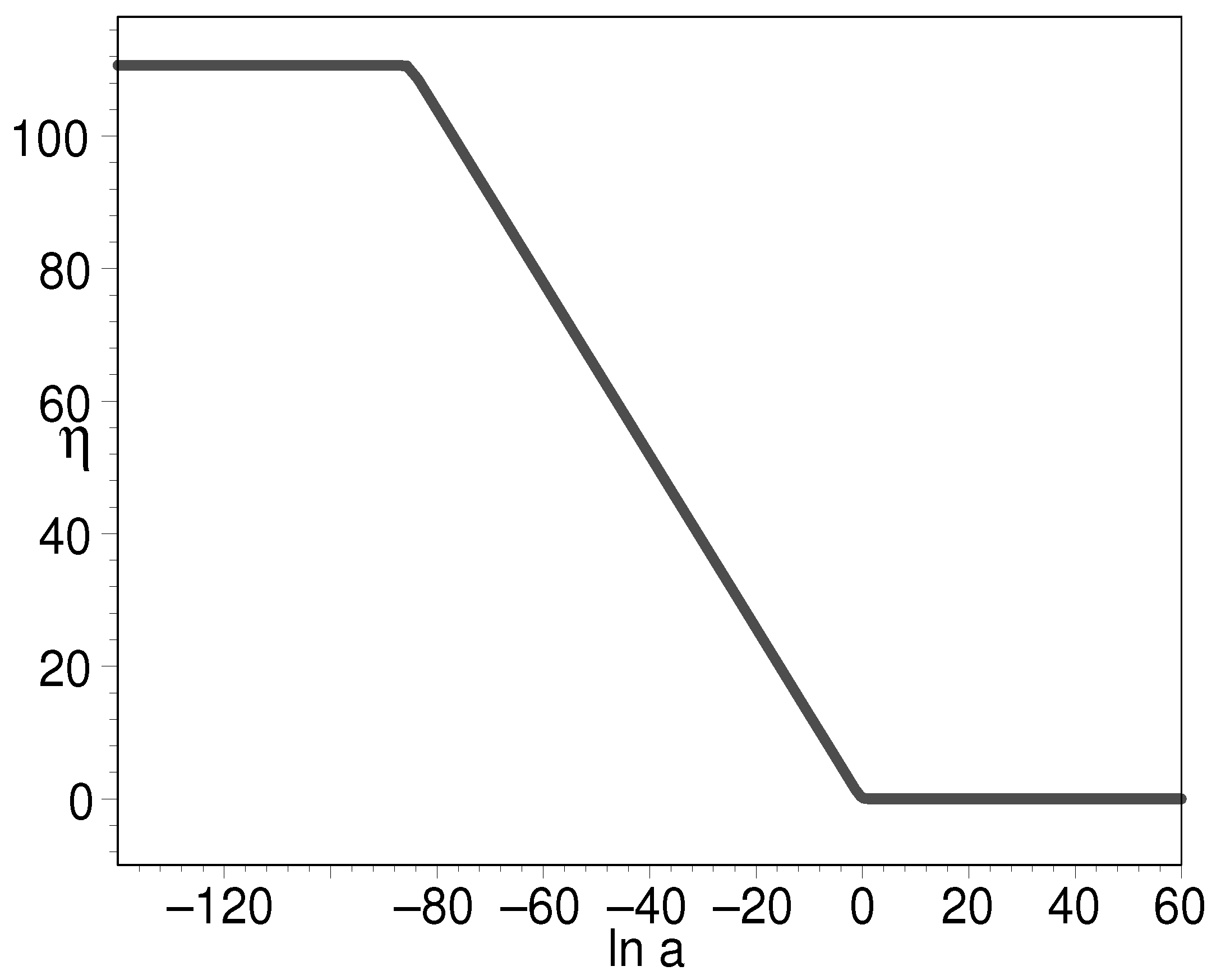
3.2.1. Dynamical Cosmological Constant
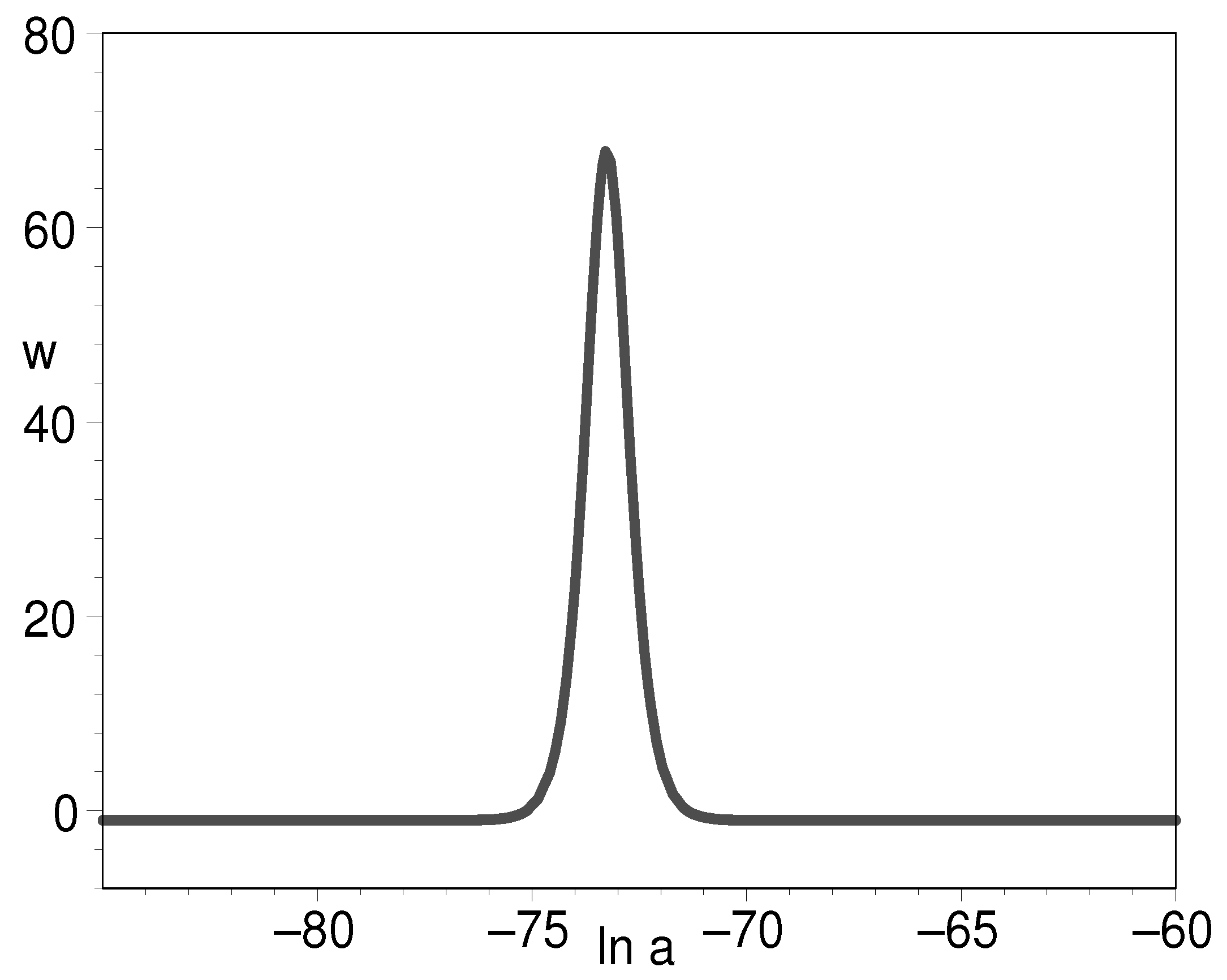
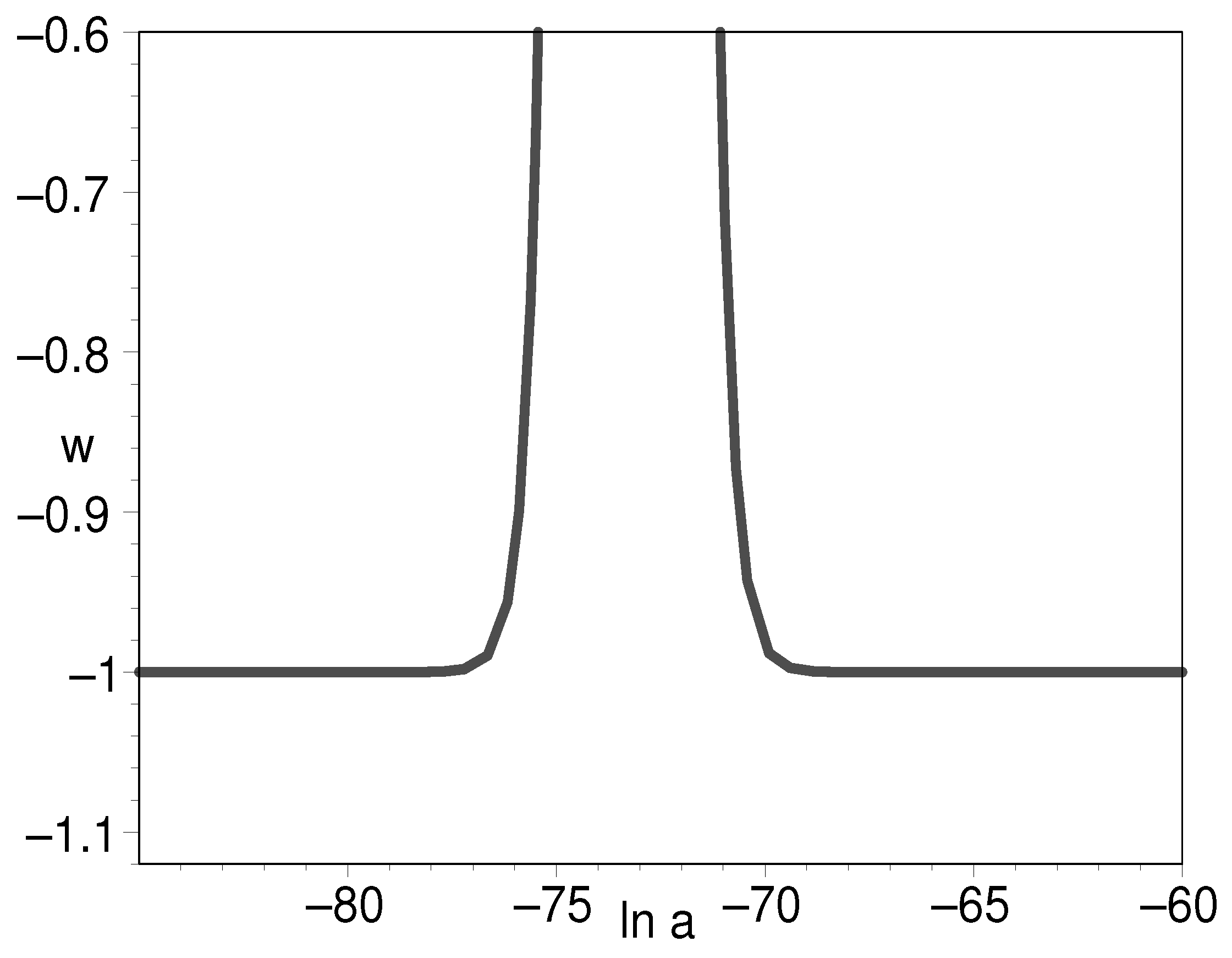
3.2.2. Constant Equation of State
3.2.3. Generalized Chaplygin Gas
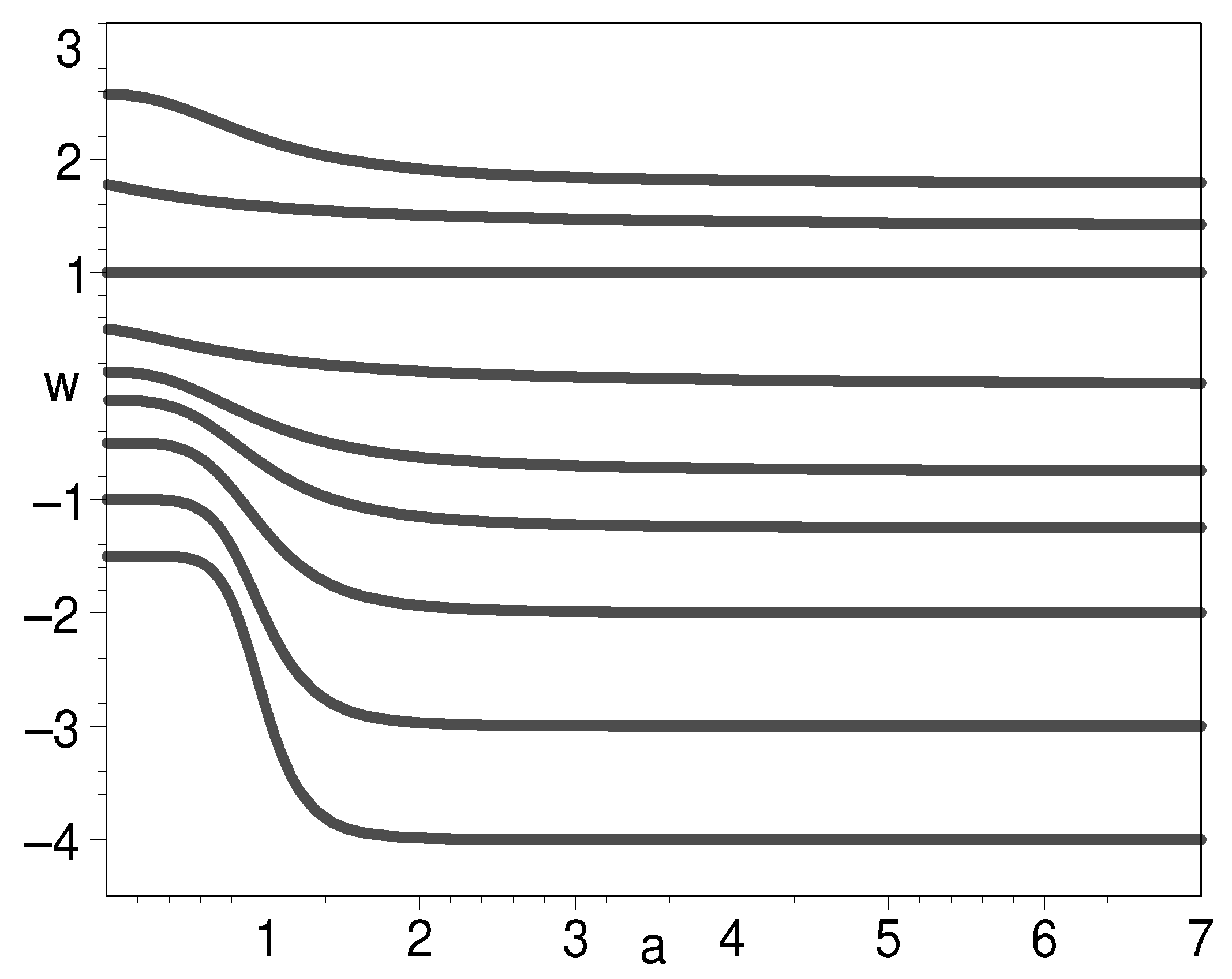
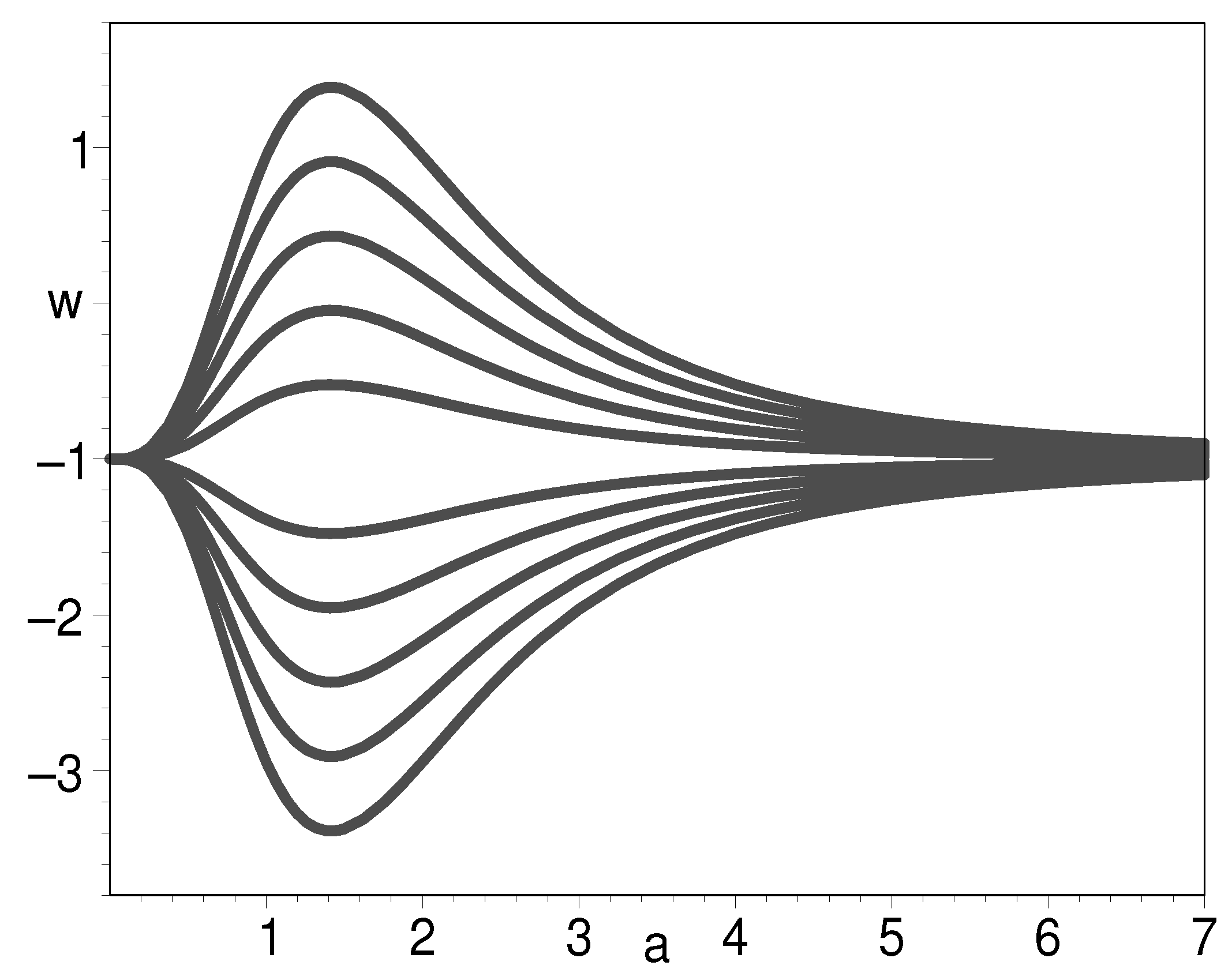
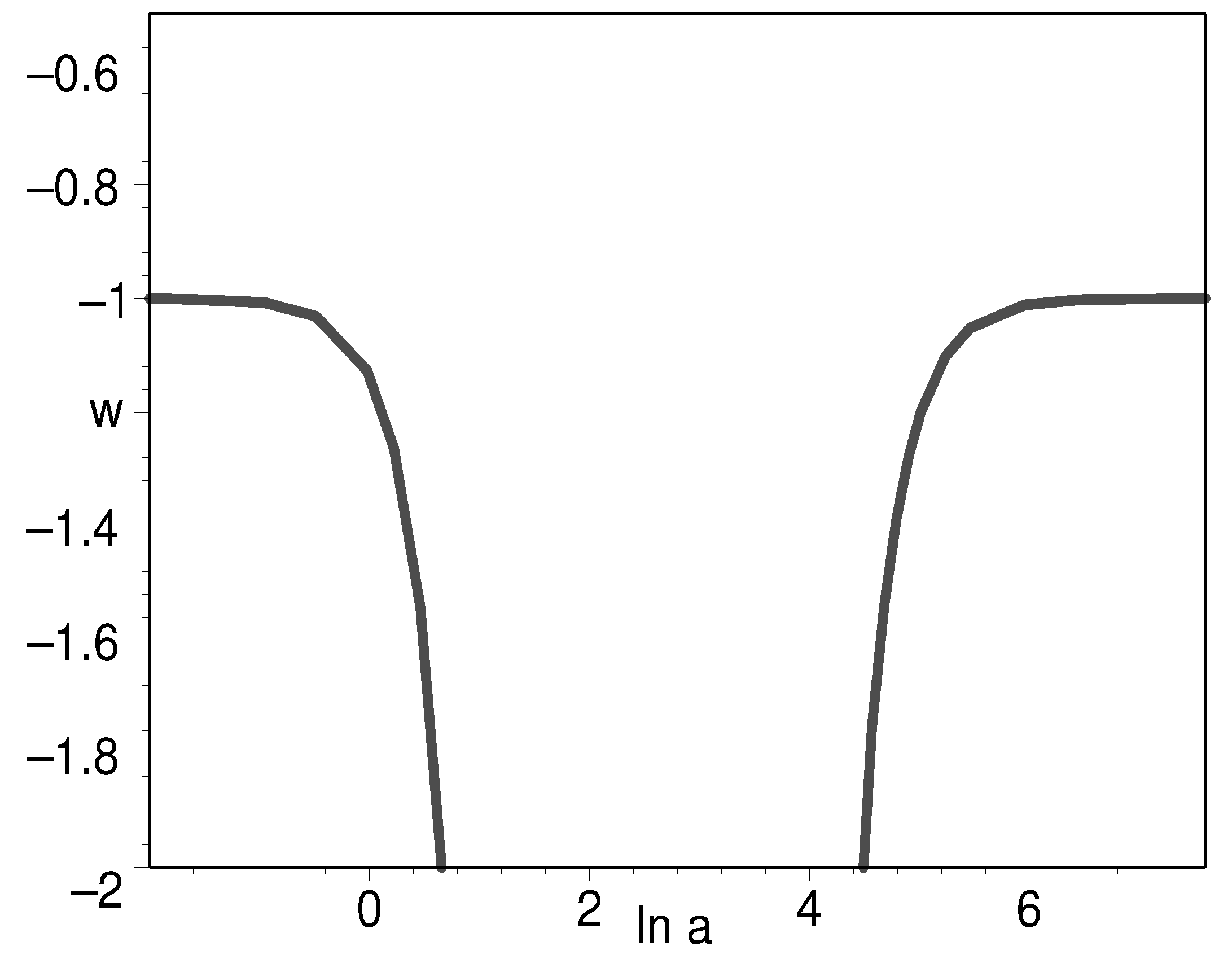
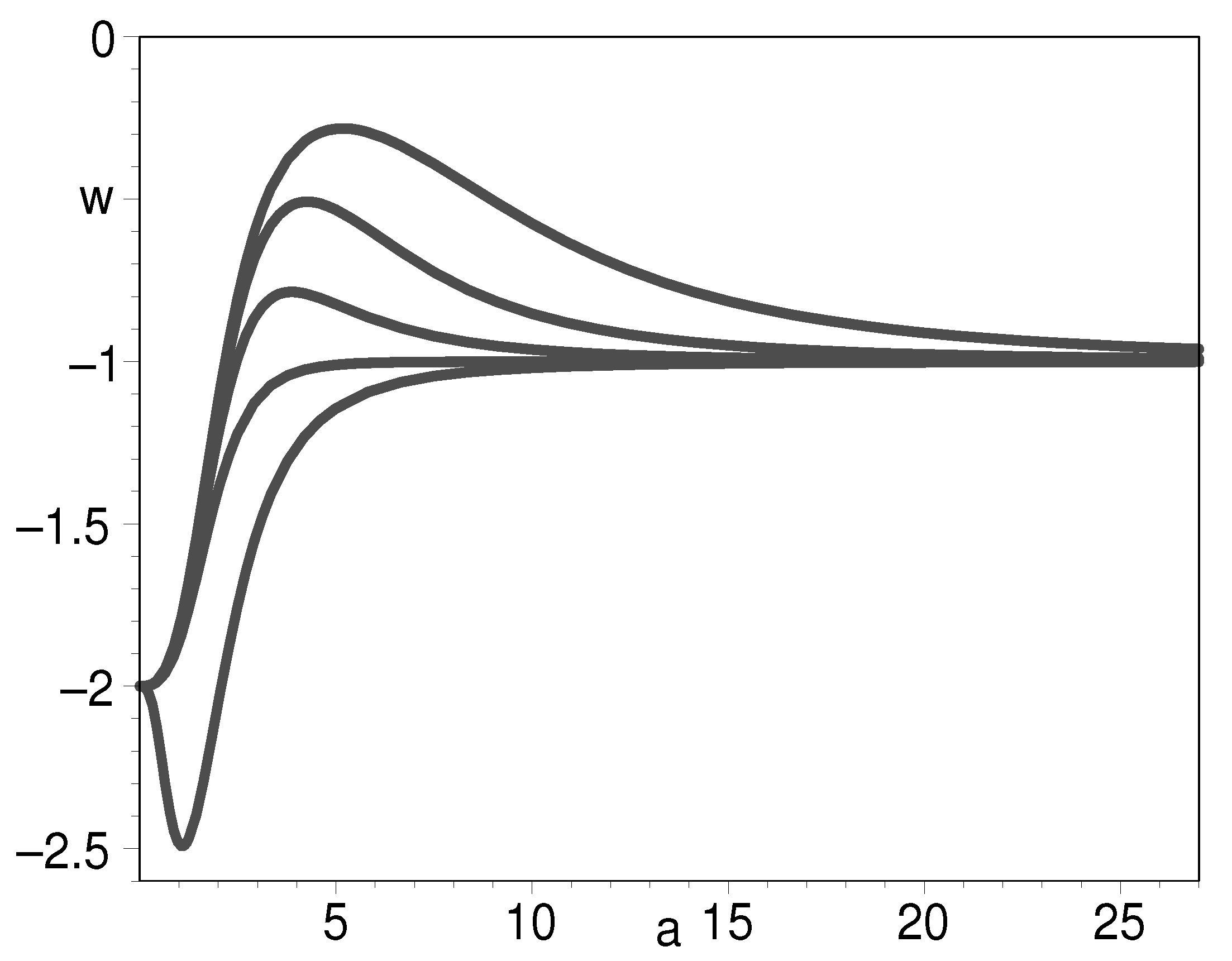
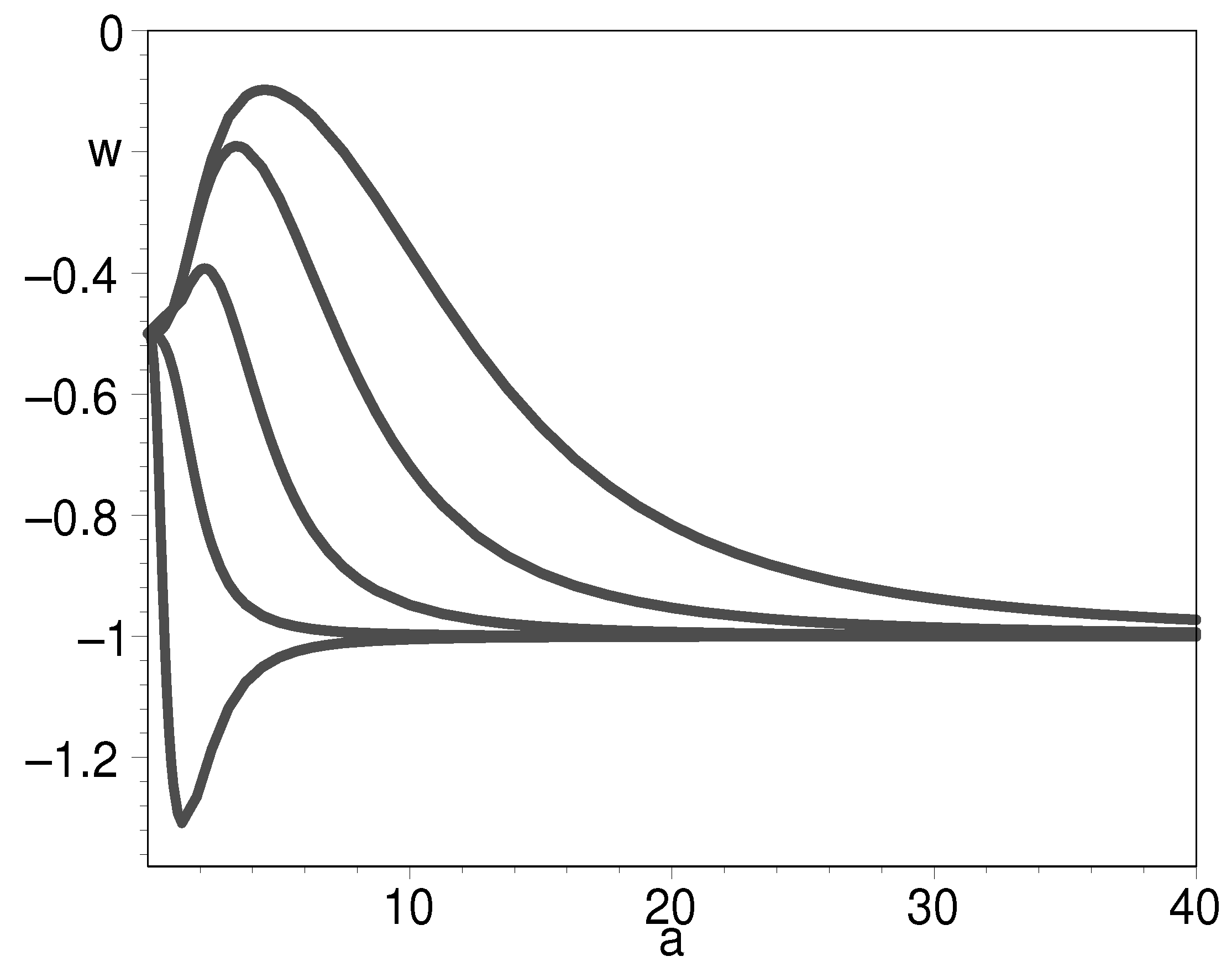
3.3. Some Unconventional EOSs
3.3.1. The Case of
3.3.2. The Case of
3.3.3. The Case of
3.3.4. The Case of
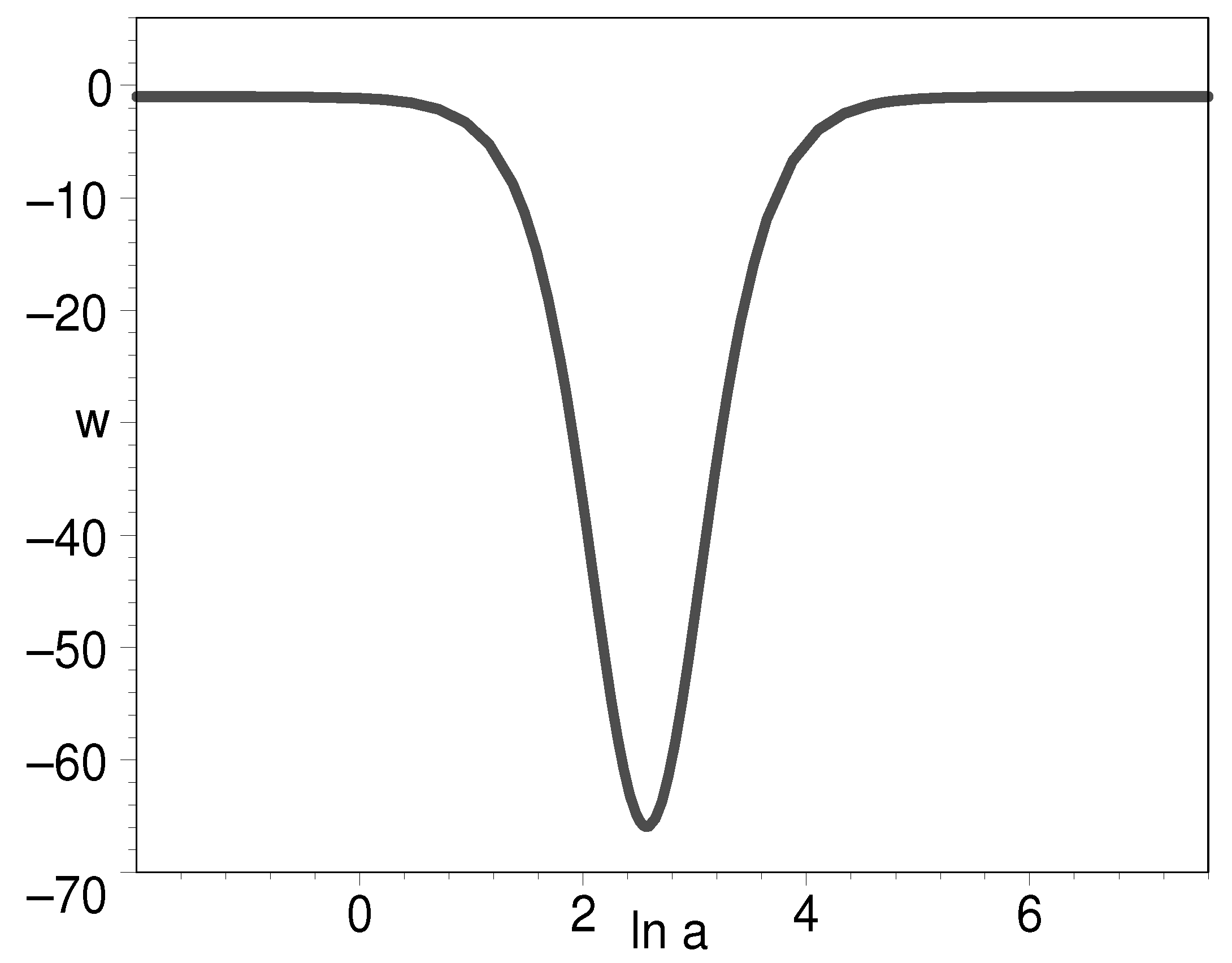
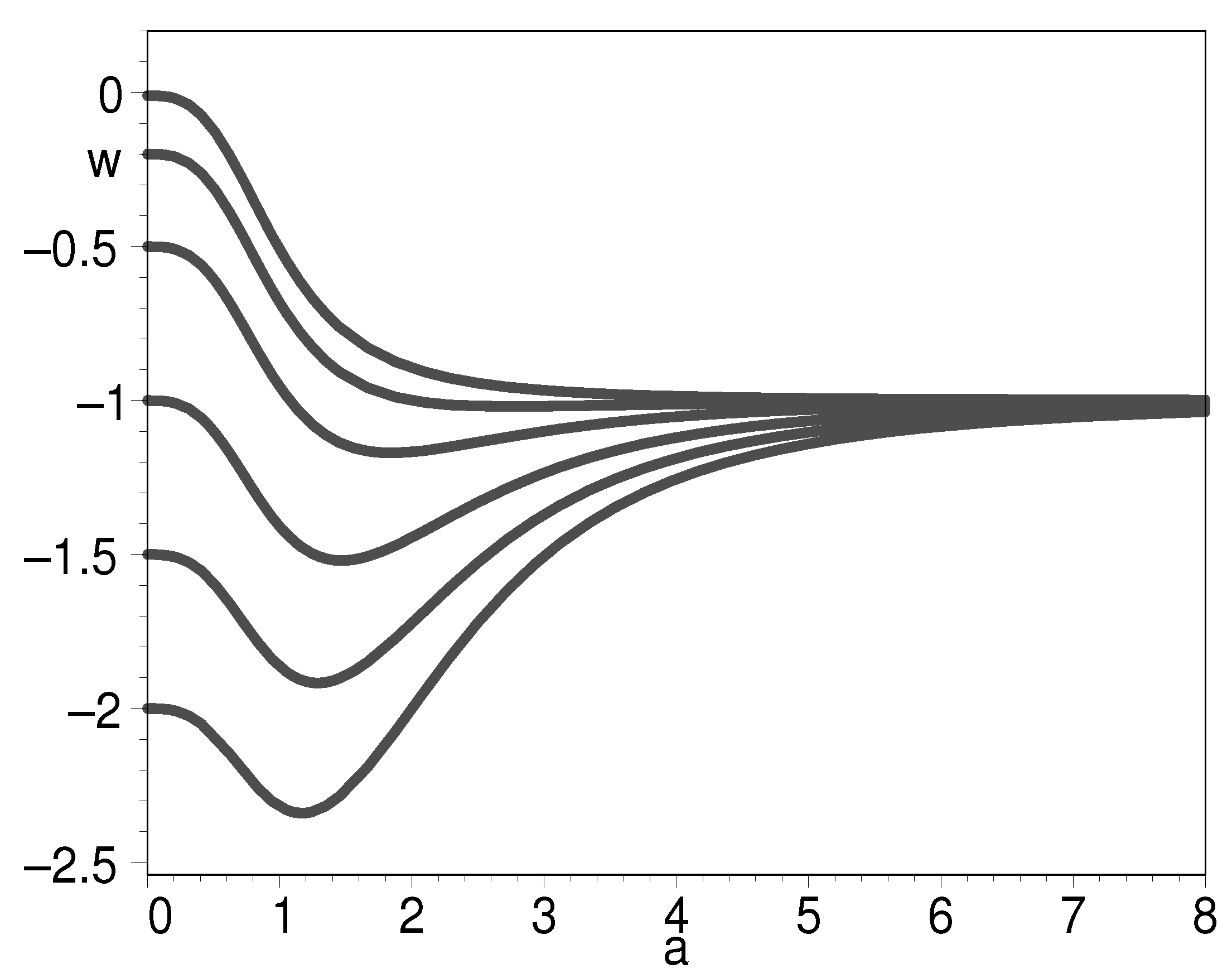
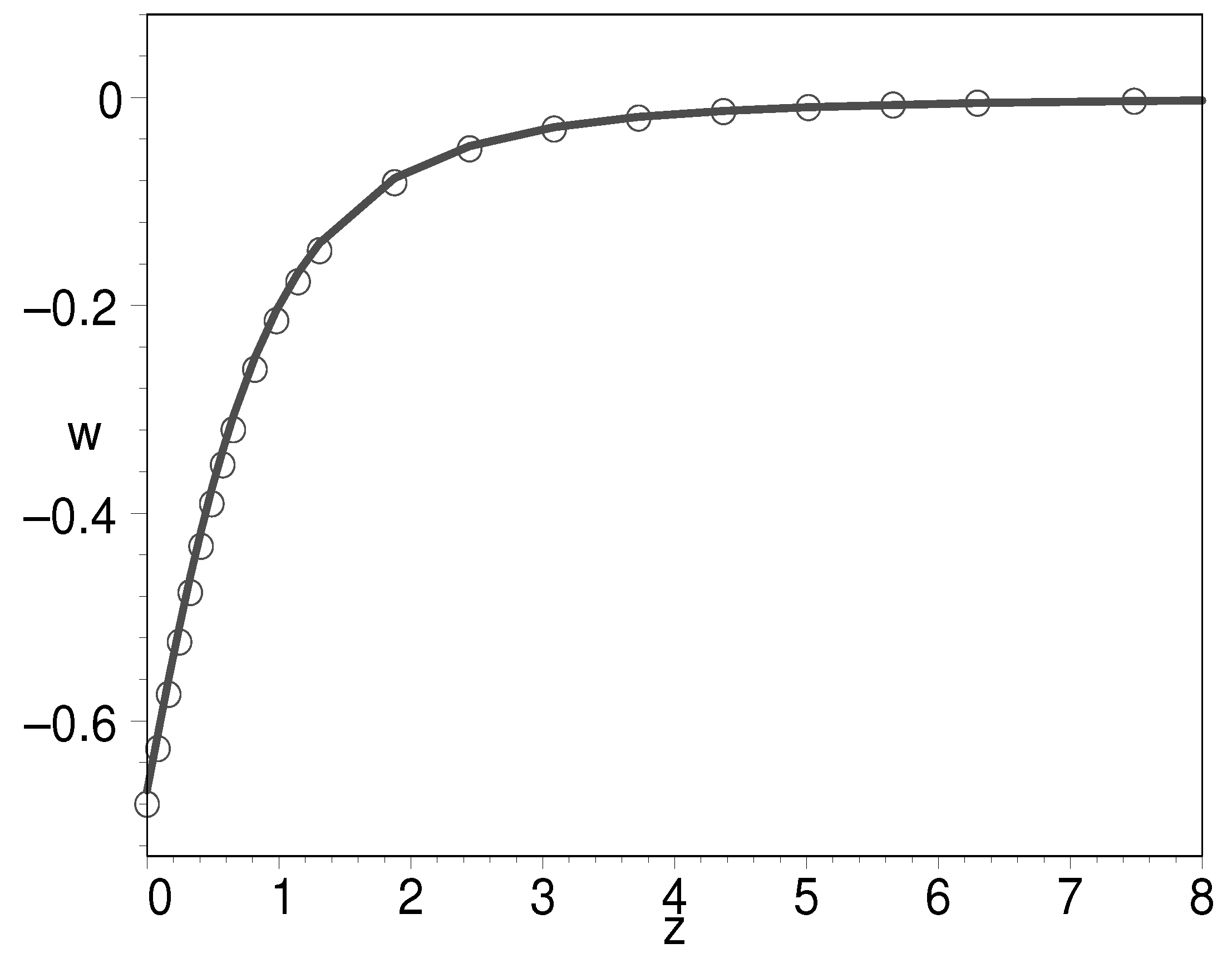
4. Stability Analysis
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | But Lee et al. [19] proved that the EOS (equation of state) of dark energy and the present-day Hubble parameter are anti-correlated in K-essence theories. So, K-essence acting as late-time dark energy may make the Hubble tension even worse. The reason for this is that if the K-essence scalar does not rest at the minimum of the potential, the present-day Hubble parameter would be decreased. |
References
- Armendariz-Picon, C.; Damour, T.; Mukhanov, V. k-Inflation. Phys. Lett. B 1999, 458, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga, J.; Mukhanov, V.F. Perturbations in k-inflation. Phys. Lett. B 1999, 458, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Okabe, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Kinetically driven quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 023511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendariz-Picon, C.; Mukhanov, V.; Steinhardt, P.J. Dynamical solution to the problem of a small cosmological constant and late-time cosmic acceleration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendariz-Picon, C.; Mukhanov, V.; Steinhardt, P.J. Essentials of k-essence. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 63, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T. Tracking k-essence. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 063514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimento, L.P.; Feinstein, A. Power-low expansion in k-essence cosmology. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2004, 19, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimento, L.P. Extended tachyon field, Chaplygin gas, and solvable k-essence cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 123517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malquarti, M.; Copeland, E.J.; Liddle, A.R. K-essence and the coincidence problem. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 023512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, R.J. Purely kinetic k essence as unified dark matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimento, L.P.; Lazkoz, R. Atypical k-essence cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 023505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramo, L.R.; Pinto-Neto, N. Stability of phantom k-essence theories. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 063522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvin, C.; Caprini, C.; Durrer, R. No-go theorem for k-essence dark energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 081303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, N.; Majumdar, A.S. K-essence model of inflation, dark matter, and dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, N.; Majumdar, A.S. Unified model of k-inflation, dark matter, and dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.X.; Zhu, Z.-H. Early dark energy in k-essence. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 043518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Bowers, J.B.; Macri, L.; Zinn, J.C.; Scolnic, D. Cosmic distances calibrated to 1% precision with Gaia EDR3 parallaxes and Hubble Space Telescope photometry of 75 Milky Way Cepheids confirm tension with ΛCDM. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 908, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, W.L. Measurements of the Hubble constant: Tensions in perspective. Astrophys. J. 2021, 919, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-H.; Lee, W.; Colgáin, E.Ó.; Sheikh-Jabbari, M.M.; Thakur, S. Is local H 0 at odds with dark energy EFT? J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 4, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adi, S.A.; Gangopadhyay, M.R.; Sami, M.; Sharma, M.K. Late-time acceleration due to a generic modification of gravity and the Hubble tension. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 103534. [Google Scholar]
- Kehayias, J.; Scherrer, R.J. New generic evolution for k-essence dark energy with w ≈-1. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 023525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Wu, Y.B.; Xu, D.F.; Dong, W.; Zhang, N. Dynamical Stability and Geometrical Diagnostic of the Power Law K-Essence Dark Energy Model with Interaction. Universe 2020, 6, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Wu, Y.B.; Chi, J.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y. The Phase Space Analysis of Interacting K-Essence Dark Energy Models in Loop Quantum Cosmology. Universe 2022, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Rani, S.; Sultan, A.M.; Embreen, K. k-Essence Inflation Evading Swampland Conjectures and Inflationary Parameters. Universe 2022, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socorro, J.; Pérez-Payán, S.; Hernández-Jiménez, R.; Espinoza-García, A.; Díaz-Barrón, L.R. Quintom fields from chiral K-essence cosmology. Universe 2022, 8, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z. Statistics of thawing k-essence dark energy models. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 103533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.L.; Pinto-Neto, J.N.; Zanelli, J. Inflation and late-time accelerated expansion driven by k-essence degenerate dynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 023515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, T. Cosmological constant—The weight of the vacuum. Phys. Rep. 2003, 380, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.C.; Bertolami, O.; Sen, A.A. Generalized Chaplygin gas, accelerated expansion, and dark-energy-matter unification. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 043507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshordi, N.; Chung, D.J.H.; Geshnizjani, G. Causal field theory with an infinite speed of sound. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 083513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehle, F.; Ulbricht, S. Einstein’s basement—A model for dark matter and an expanding universe? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13679. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Raveri, M.; Pogosian, L.; Wang, Y.; Crittenden, R.G.; Handley, W.J.; Percival, W.J.; Beutler, F.; Brinkmann, J.; Chuang, C.; et al. 2017NatAs. 1. 627Z: Dynamical dark energy in light of the latest observations. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.08165v2. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Yang, Y.; Xia, J. Reconstruction of the dark energy equation of state from the latest observations. Astrophys. J. 2018, 857, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Abdalla, E.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Pavon, D. Dark matter and dark energy interactions: Theoretical challenges, cosmological implications and observational signatures. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 096901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unified phantom cosmology: Inflation, dark energy and dark matter under the same standard. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 632, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Kunz, M.; Liddle, A.R.; Parkinson, D. Unified dark energy and dark matter from a scalar field different from quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 043520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kase, R.; Tsujikawa, S. Dark energy in Horndeski theories after GW170817: A review. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1942005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, O.; Barrow, J.D.; Escamilla, L.A.; Vazquez, J.A. Graduated dark energy: Observational hints of a spontaneous sign switch in the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 063528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, O.; Kumar, S.; Ozulker, E.; Vazquez, J.A. Relaxing cosmological tensions with a sign switching cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 123512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennaro, S.D.; Ong, Y.C. Sign switching dark energy from a running barrow entropy. Universe 2022, 8, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, C. The Equation of State of Novel Double-Field Pure K-Essence for Inflation, Dark Matter and Dark Energy. Universe 2024, 10, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10060235
Gao C. The Equation of State of Novel Double-Field Pure K-Essence for Inflation, Dark Matter and Dark Energy. Universe. 2024; 10(6):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10060235
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Changjun. 2024. "The Equation of State of Novel Double-Field Pure K-Essence for Inflation, Dark Matter and Dark Energy" Universe 10, no. 6: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10060235
APA StyleGao, C. (2024). The Equation of State of Novel Double-Field Pure K-Essence for Inflation, Dark Matter and Dark Energy. Universe, 10(6), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10060235





