Abstract
The -ray sky above a few tens of megaelectronvolts (MeV) reveals some of the most powerful and energetic phenomena of our Universe. The Astrorivelatore Gamma ad Immagini LEggero (AGILE) Gamma-ray Mission was launched in 2007 with the aim of observing celestial sources by means of three instruments covering a wide range of energies, from hard X-rays up to 30 GeV. Thanks to its wide field of view, AGILE set to observe and detect emission from pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, gamma-ray bursts, active galactic nuclei, fast radio bursts, terrestrial gamma-ray flashes, and the electromagnetic counterparts of neutrinos and gravitational waves. In particular, the fast on-ground processing and analysis chain allowed the AGILE team to promptly respond to transient events, and activate or participate in multiwavelength observing campaigns. Eventually, after 17 years of operations, the AGILE Italian scientific satellite re-entered the atmosphere on 14 February 2024, ending its intense activity as a hunter of some of the most energetic cosmic sources in the Universe that emit X and -rays. We will review the most relevant AGILE results to date and their impact on the advancements of theoretical models.
1. Introduction
The -ray sky at high energies (HE, MeV) has been investigated since the beginning of the 1960s. On 27 April 1961, the EXPLORER XI (1961) satellite [1] was launched with the aim of producing an all-sky survey at energies above a few tens of MeV.
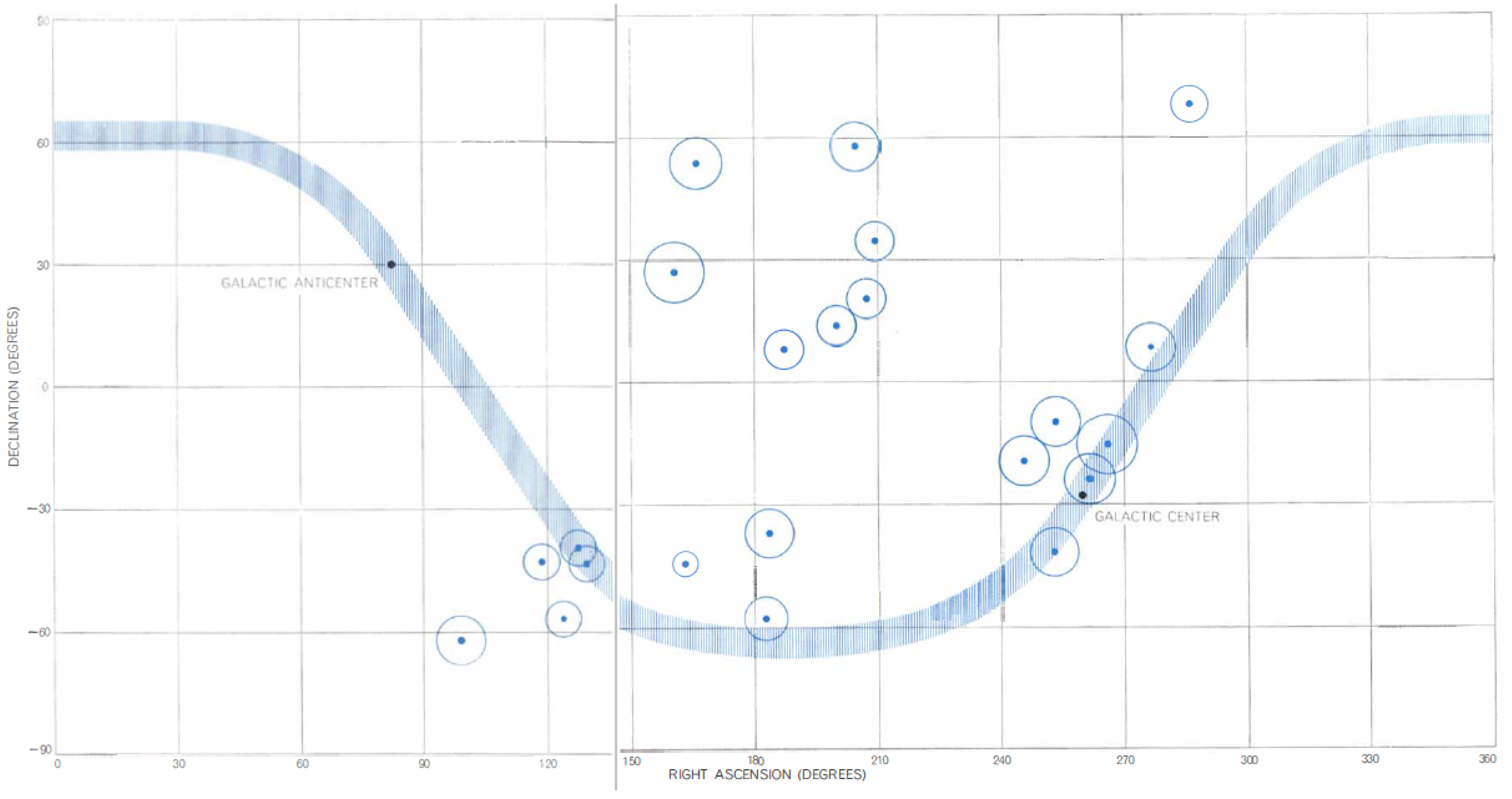
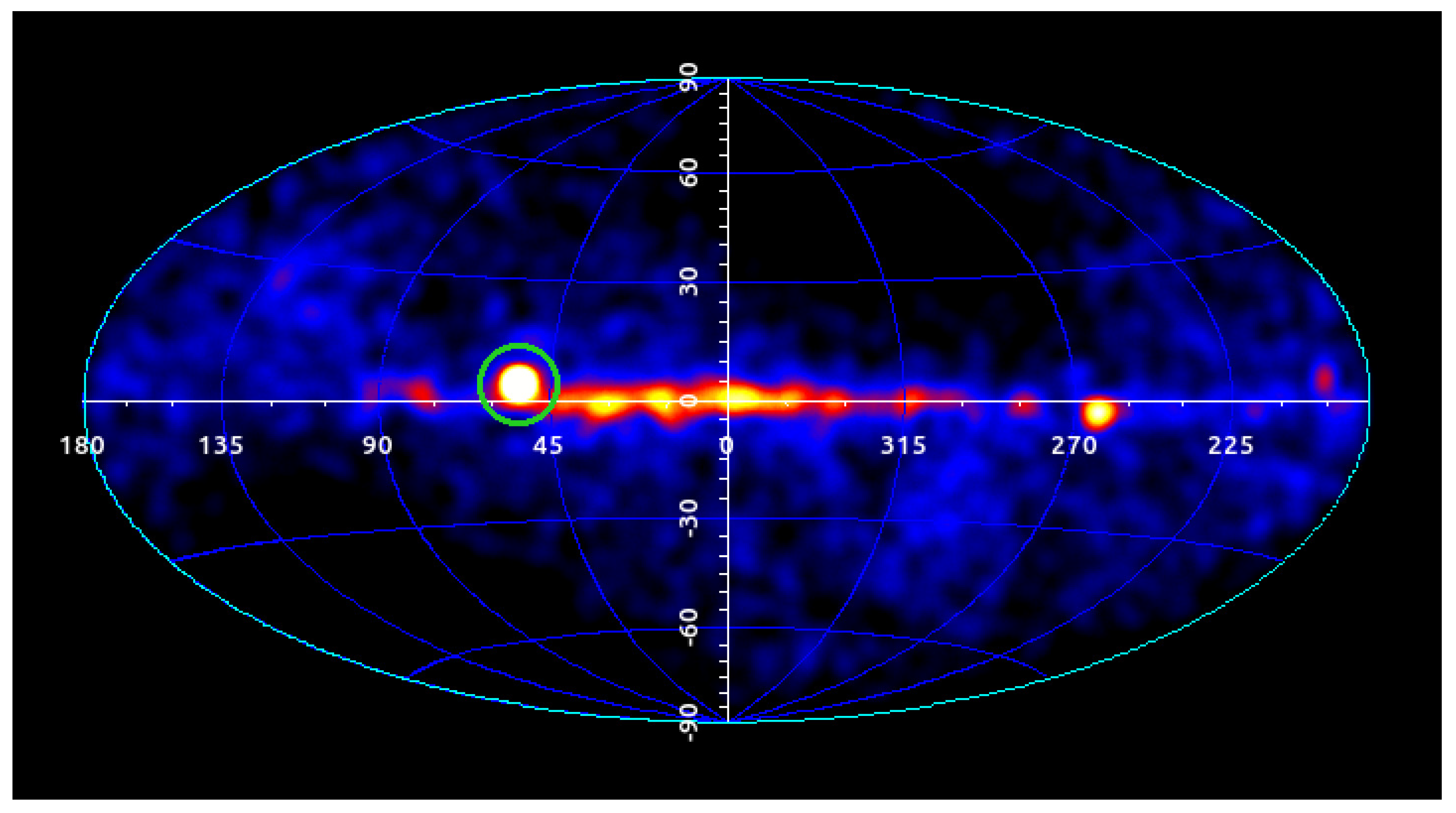
Despite the very limited number of fairly certain -rays, as the authors note, and no certain sources detected, this may mark the beginning of studies of -ray astrophysics with space satellites1. Figure 1 shows the sky distribution of the 22 photons detected by the EXPLORER XI satellite in its early months.
Figure 1.
The -ray sky as seen by the EXPLORER XI satellite. The x-axis is the RA (deg); the y-axis is the Dec (deg). The shaded stripe represents the galactic plane in celestial coordinates. The blue dots mark the position of the 22 detected -rays. The circles are proportional to the scanned time length in that particular region of the sky. From [1].
The first confirmed -ray-emitting regions were detected by the OSO-3 (1967–1969) satellite [2]. OSO-3 reported -ray emission with energies above 50 MeV from the galactic disk with peak intensity towards the galactic center. The first two pointlike sources, Crab and Vela (both pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe)), were detected by the SAS-2 (1972–1973) satellite [3].
A further improvement was achieved with the COS-B (1975–1982) satellite, which detected 25 sources, reported in [4]. We note that only 4 sources were identified: Crab, Vela, Oph, and the first extragalactic one, the blazar 3C 273.
Among the SAS-2 and COS-B unidentified -ray sources, one deserves a special mention, 195 + 5, in the Gemini constellation. This may represent the first example of a multiwavelength campaign to identify a newly discovered -ray source, as described in [5]. Nowadays, this source is commonly known as Geminga.
A remarkable step ahead was obtained in the 1990s, with the launch of the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, hosting on board the EGRET (1991–2000) telescope [6]. EGRET detected more than 270 sources, both galactic and extragalactic. Many of them were unidentified at the time, as reported in the Third EGRET Catalog (3EGC) [7]. 3EGC was instrumental in performing the first population studies of different source types and helped plan observations and target definitions for future HE space missions, e.g., [8] for the study of the -ray AGN duty cycle.
AGILE was a step forward with respect to previous -ray satellites under several aspects. Thanks to its silicon-based -ray tracker, it improved the angular resolution near 100 MeV by at least a factor of 2–3 compared with EGRET. The AGILE field of view (FoV) was about five times larger, improving the transient source detection and obtaining broad-band spectral information by including large FoV detectors in the MeV and X-ray energy ranges. These characteristics, combined with a rapid quick-look analysis of the -ray data and a fast dissemination of results, allowed the AGILE collaboration to provide alerts, stimulating efficient multifrequency programs.
In the next sections, we describe the AGILE Mission, its concepts, and the major scientific results obtained so far. We show how the AGILE Mission has been able to overcome some of the bottlenecks of the previous -ray missions by dramatically improving the ground segment efficiency, which allowed a rapid analysis of -ray data and dissemination of the results. Finally, we would like to note that this review cannot be a compilation of all the AGILE scientific results that the AGILE collaboration obtained during its 17 years of operation.
2. The AGILE Mission
The Astrorivelatore Gamma ad Immagini LEggero (AGILE2) satellite [9] (2007–2024) was a mission of the Italian Space Agency (ASI) devoted to high-energy astrophysics. It was launched on 23 April 2007 by the Indian PSLV-C8 rocket from the Sriharikota ISRO base (India). It ceased its operations on 18 January 2024 and subsequently re-entered the Earth’s atmosphere on 14 February 2024 [10]. The AGILE scientific instrument combined four active detectors yielding broad-band coverage from hard X-ray to -ray energies: a silicon tracker [ST; 30 MeV–50 GeV] [11], a coaligned coded-mask hard X-ray imager, Super-AGILE [SA; 18–60 keV] [12], a nonimaging CsI mini-calorimeter [MCAL; 0.3–100 MeV] [13], and a segmented anticoincidence system [ACS] [14]. Any -ray detection was obtained by the combination of ST, MCAL, and ACS; these three detectors formed the AGILE gamma-ray imaging detector (GRID). The coaligned detectors, the silicon-strip-based tracker, a wide FoV -ray imager, and the fast-reaction ground segment were the AGILE innovative solutions with respect to the previous generation of -ray satellites.
Table 1 shows the main AGILE scientific performance. In addition to these figures, we note that AGILE had the possibility of jointly monitoring celestial sources both in the X-ray and in the -ray energy bands, as well as quickly reacting to fast transients.

Table 1.
The AGILE scientific performance.
The AGILE satellite was in a low-Earth equatorial orbit with an inclination of about 2.5 degrees, with an initial average altitude of about 500 km. AGILE raw telemetry level-0 (LV0) data were downlinked every ∼100 min to the ASI Malindi ground station in Kenya and transmitted, through the fast ASINET network provided by ASI, first to the Telespazio Mission Control Center at Fucino in Italy and then to the AGILE Data Center3 (ADC, Italy), part of the ASI multimission Space Science Data Center (SSDC), min after the end of each contact downlink. The ADC is in charge of all the scientific operations: data management, archiving, distribution of AGILE data and scientific software, and user support. Its main activities and architecture are described in [15].
A ground segment alert system allowed the AGILE team to perform the full AGILE-GRID data reduction and the preliminary quick-look scientific analysis for a fast reaction to high-energy transients [15,16].
3. The Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula (G184.6−5.8) is an expanding remnant of a supernova explosion (SN1054) recorded by Japanese and Chinese astronomers in 1054 A.D., located at an estimated distance of 2 kpc from Earth [17]. The Crab Nebula [18] is a complex pulsar wind nebula (PWN) system, powered by a powerful rotating neutron star, a pulsar of spin-down luminosity PSR = 5 × 1038 erg , and spin period = 33 ms. Observations of the nebula have been carried out at every accessible wavelength, from radio up to very high energy (VHE) [19]. In the last decades, almost all high-energy (EGRET, Fermi-LAT, AGILE) and very-high-energy (H.E.S.S., MAGIC, VERITAS, HAWC, Tibet AS-, LHAASO) instruments provided invaluable information up to PeV energies. Moreover, in recent years, the first detection at TeV energies from the Crab Nebula by a dual-mirror Schwarzschild–Couder configuration Čherenkov telescope was reported by the 4 m ASTRI-Horn telescope, operated on Mt. Etna, Italy, and developed in the context of the Čherenkov Telescope Array Observatory (CTAO) preparatory phase [20]. Recently, the Crab was also observed with the Large-Sized Telescope Prototype of the Čherenkov Telescope Array LST-1 [21]. The results of the observations with high significance of the Crab Nebula in the energy ranges 10–100 TeV and >100 TeV were reported by the HAWC Collaboration [22] and by the LHAASO Collaboration using the first 5 months of the hybrid extensive air shower (EAS) half-array LHAASO-KM2A data [23].
Local variations in the inner nebula showing distinctive optical and X-ray features aligned with the pulsar jet (“wisps”, “knots”, and the “anvil”) [24,25,26,27] have been attributed to enhancements of the synchrotron emission produced by instabilities or shocks in the pulsar wind outflow. However, when averaged over the whole inner region, the overall high-energy flux resulting from the unpulsed synchrotron radiation of the Crab Nebula has been considered essentially stable. Concerning the Crab Nebula variability, before 2010, only possible long-term nebular hard X-ray flux changes on a timescale of a few years have been reported. The X-ray variability has been observed to occur with an apparent relative amplitude of a few percent on timescales of ∼3 years [28,29,30]. The Crab was thus regarded as a nearly constant source at a level of a few percent from optical to -ray energies and used as a calibration source, a “standard candle” in astrophysics, up to very high energies [31].
In September 2010, thanks to its rapid alert system [15,16], AGILE detected a fast -ray flare above 100 MeV from the Crab Nebula over a daily timescale (see Flare F7 in Figure 2, left panel) and made the first public announcement on 22 September 2010 [32,33]. This finding was confirmed the following day by the Fermi satellite [34].
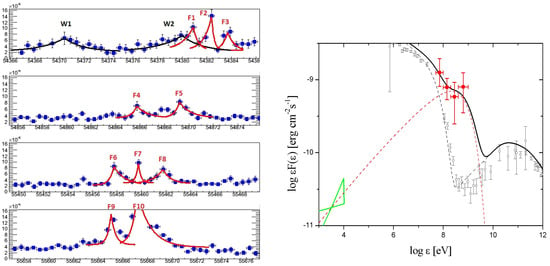
Figure 2.
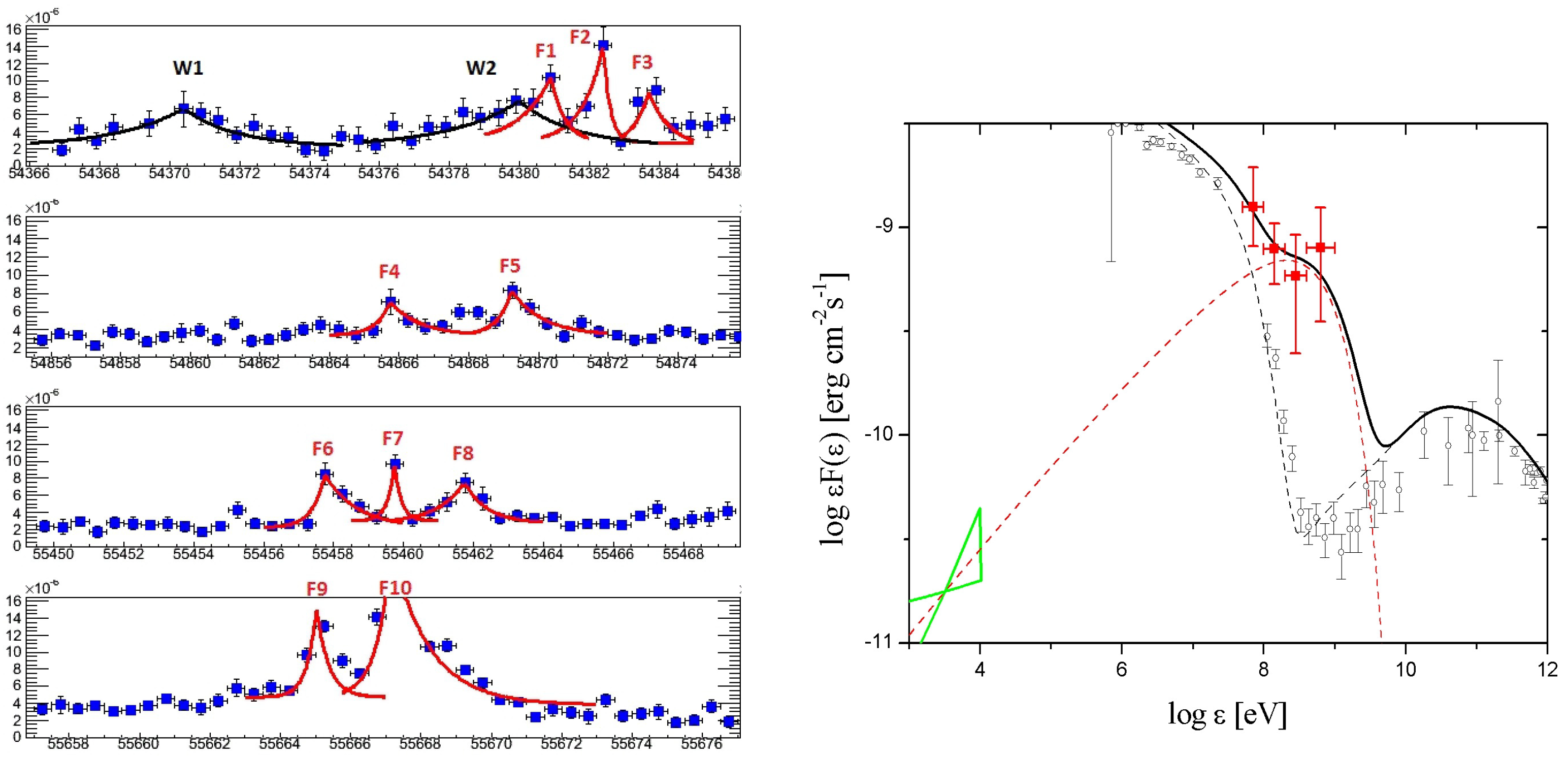
Left panel: decomposition of the multiyear Crab light curve in “waves” (W) and “flares” (F) according to [35], represented with exponential fits (see Table 1 in [35] for detailed fitting parameters). The x-axis is the date in MJD; the y-axis is the flux in units of photons . Right panel: AGILE (filled squares) 48 h averaged data of the September 2010 -ray flare. The black line represents the 48 h averaged synchrotron emission model of the September 2010 flare summed with the standard nebular emission. The dashed red curve shows the flaring component averaged over 48 h. Open circles mark the standard average Crab Nebula spectrum, modeled by the dashed black curve. The green bow tie marks the X-ray data. Further details in [36].
The surprising discovery by AGILE of variable -ray emission from the Crab Nebula started a new era of investigation of this system. As a consequence, the 2012 Bruno Rossi International Prize was awarded to the principal investigator (PI), Marco Tavani, and the AGILE team for this important and unexpected discovery. The detailed and exciting story that led to the AGILE discovery has been very well described in the article “The Crab that Roared” [37].
The interest in the discovery triggered several prompt multifrequency observations (from radio to TeV). However, no enhancement was detected at any of these energies, indicating that the flaring episode happened only in the -ray band. Moreover, no variations were detected in the pulsed emission, leaving out any interpretation in terms of magnetospheric origin near the Crab pulsar. AGILE had also previously detected a giant flare from the Crab in October 2007 during the initial science verification period of the satellite; furthermore, the first AGILE catalog paper [38] reported that anomalous episodic high-flux values observed from the Crab in 2007 were under investigation. Several major -ray flares from the Crab Nebula were detected by the AGILE-GRID and Fermi-LAT in the following years, with an approximate rate of one every few years (see Table 2), as well as more frequent enhanced -ray weeklong activity of lower intensity (the so-called “waves”, W) [35], as shown in Figure 2, left panel, and as can be seen in [35], Figure 7.

Table 2.
AGILE-GRID and Fermi-LAT Crab flares.
During the flaring states, -ray spectra above 100 MeV have cutoff energies below a few GeVs, and the data are compatible with the observation of a new, almost monochromatic -ray spectral component evolving during the flare [36], as shown in Figure 2, right panel. The -ray flux can increase up to a factor of 8 over timescales of days [39], and drop below the average flux within a similar timescale [40]. -ray data provide evidence for particle acceleration mechanisms in nebular shock regions more efficient than previously expected from theoretical models, as discussed in [41] in a recent review.
4. Probes for Cosmic-Ray Acceleration
Understanding the escape of accelerated particles from expanding spherical shocks is a key ingredient to establish a connection between supernova remnants (SNRs) and the origin of galactic cosmic rays (CR). Moreover, SNRs are excellent laboratories to investigate the hadronic scenario as the main emission model in astrophysical sources [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. In this section, we describe a few AGILE results on this topic.
4.1. W28
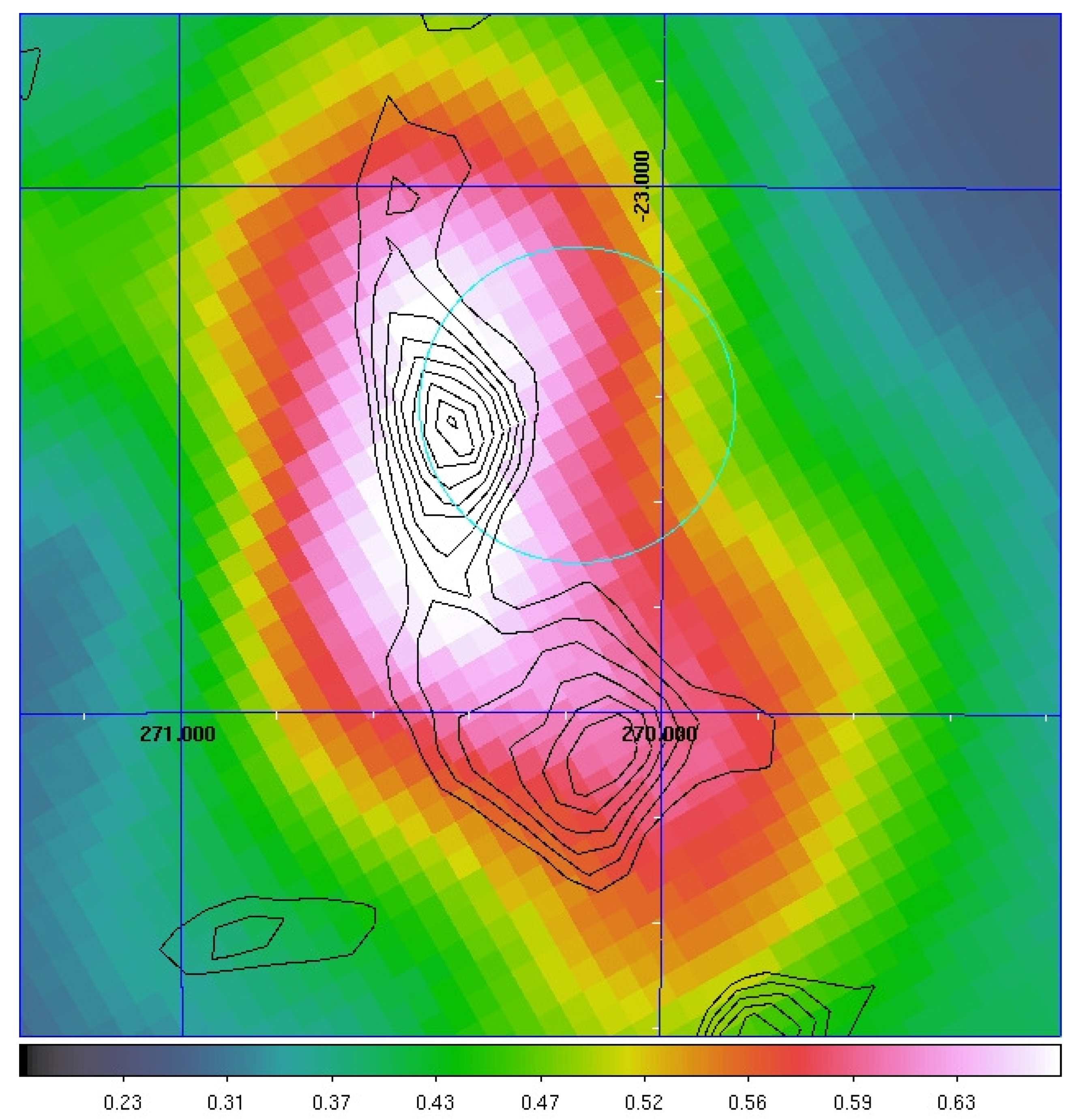
W28 is a middle-aged SNR with an age of at least 35,000 years. It is surrounded by molecular clouds [50], located at a projected distance of 10–20 pc from the SNR shell and detected by the High Energy Stereoscopic System (H.E.S.S.) up to several TeVs [51]. AGILE investigated W28 by means of -ray data accumulated during the “pointing observing mode” (2007–2009) [52], when it detected this source with a flux of photons . Two ingredients are fundamental in this investigation. The first one is an accurate modeling of the diffuse galactic -ray background, as presented in [53]. The second is the multiwavelength study of the region around this source. For this reason, the AGILE collaboration made use of 12CO () molecular line observations taken by the NANTEN telescope, which detected a system of molecular clouds (cloud-N and cloud-S, respectively) associated with W28 [50], complemented with VHE observation by H.E.S.S. [51]. Figure 3 shows the AGILE-GRID data ( GeV, Gaussian-smoothed map) with the superimposed 12CO contours (black lines) and the position of W28 (cyan circle).
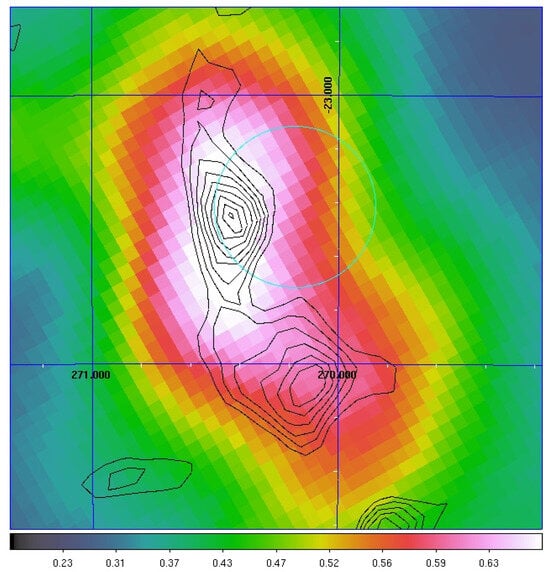
Figure 3.
AGILE-GRID data ( GeV, Gaussian-smoothed map) with the superimposed 12CO contours (black lines) and the position of W28 (cyan circle). The grid represents celestial (RA, Dec) coordinates. Cloud-N and cloud-S are located at (RA, Dec) = (270.4°, −23.4°) and (RA, Dec) = (270.2°, −24.1°), respectively. Further details are available in [52].
A broad-band spectral energy distribution (SED) of the nonsimultaneous AGILE and H.E.S.S. data allowed us to model the observed data in terms of hadronic-induced interaction with the two molecular clouds adjacent to the SNR. This model explains the morphological and spectral features detected by both AGILE in the MeV–GeV energy range and H.E.S.S. in the TeV energy range, i.e., the different emission levels between cloud-N and cloud-S, the former being brighter than the latter at MeV–GeV energies, while the opposite occurs in the TeV energy band.
4.2. W44
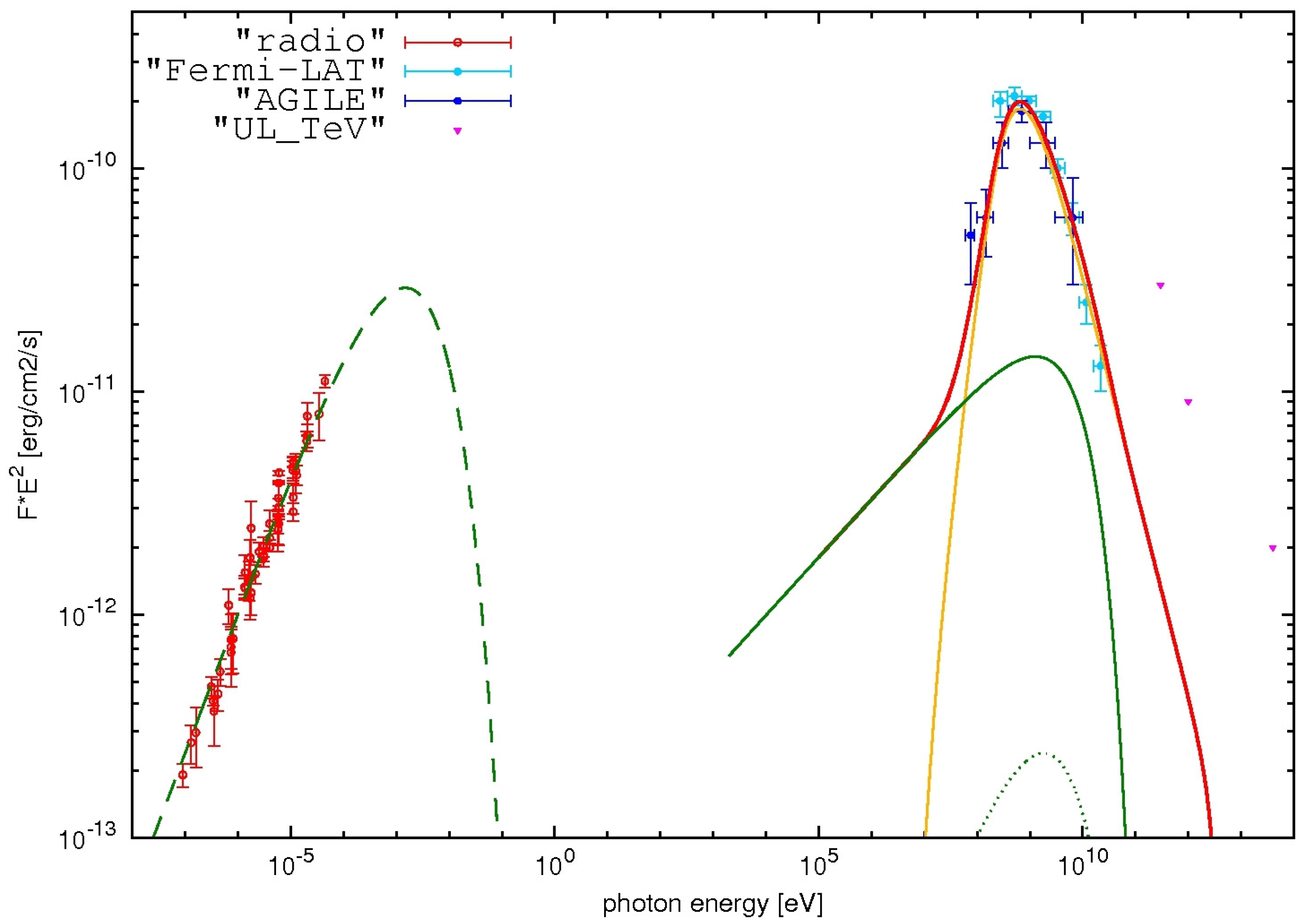
W44 is a middle-aged (∼20,000 yr) SNR located in the galactic disk at a distance of ∼3 kpc from Earth at celestial coordinates (RA, Dec) = (284.04, 1.22)°. A direct proof that SNRs are the origin of cosmic rays can be given by an unambiguous detection of the -ray emission expected from neutral pion decay in hadronic interactions, which is expected to be more evident at low energies (50–100 MeV), where it can be disentangled from the leptonic emission. In this respect, the AGILE-GRID is an excellent detector for investigating emission at such low energies. In [54] and subsequently in [55], the AGILE collaboration discussed the AGILE data accumulated in the period July 2007–April 2011. The -ray flux for energies above 400 MeV (where the AGILE-GRID angular resolution is optimized for the best performance) is photons . Figure 4 shows the first evidence of hadronic cosmic-ray acceleration in the 50–100 MeV energy range. Figure 4 shows the multiwavelength SED of W44 with observations from radio [and references therein] [56] up to TeV [57,58,59]. A model described by a synchrotron, bremsstrahlung, and inverse Compton contributions is shown and constitutes the first evidence of hadronic cosmic-ray acceleration in the 50–100 MeV energy band.
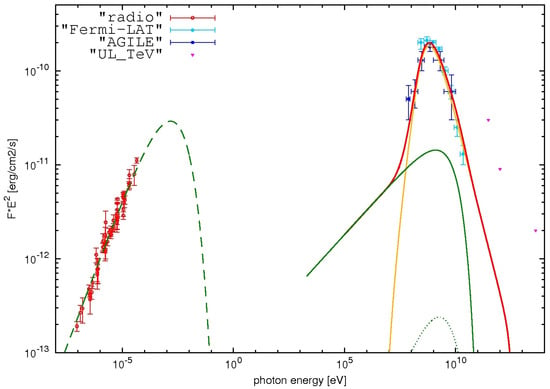
Figure 4.
W44 SED. Red, blue, cyan, and pink points represent the radio, AGILE-GRID, Fermi-LAT, and TeV data, respectively. The yellow curve shows the neutral pion emission from the accelerated proton distribution. The green curves show the electron contribution by synchrotron (dashed curve), bremsstrahlung (solid curve), and inverse-Compton (dotted curve) emissions. The red curve marks the total -ray emission. See [54] for model details.
4.3. IC 433
The intermediate-age SNR IC 443, ∼(1–2) × 104 yr, is located near the galactic anticenter (l = 189°.1, b = 3°.0), and at a close distance from Earth, ∼1.5 kpc. During the first 2 years of operation, AGILE-GRID accumulated about 1 Ms of exposure towards this source [60].
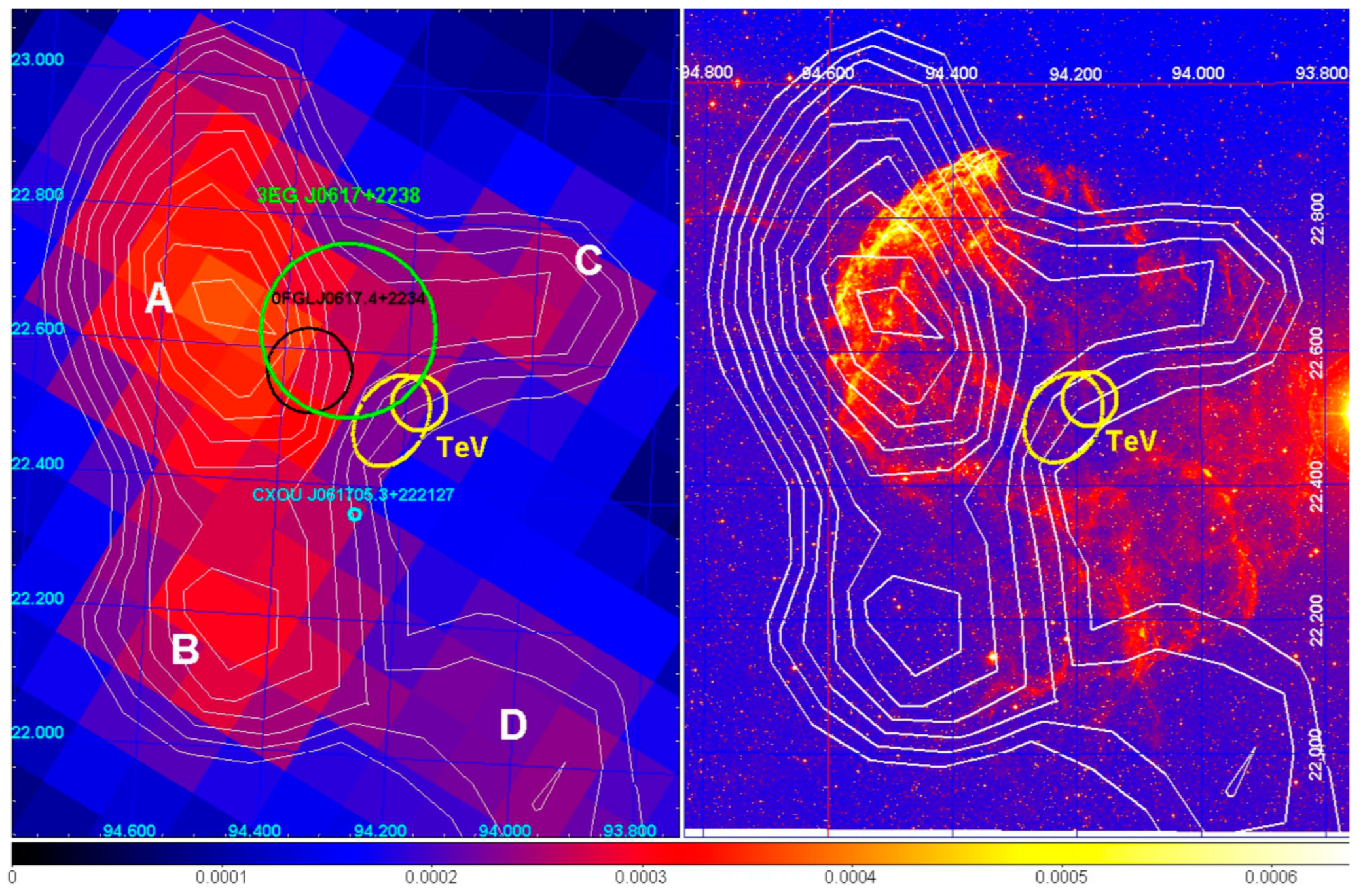
Figure 5 shows the AGILE-GRID data and the different sources in the IC 433 region. The AGILE-GRID data show four possible excesses (A–D). The -ray flux above 100 MeV of excess-A is of photons .
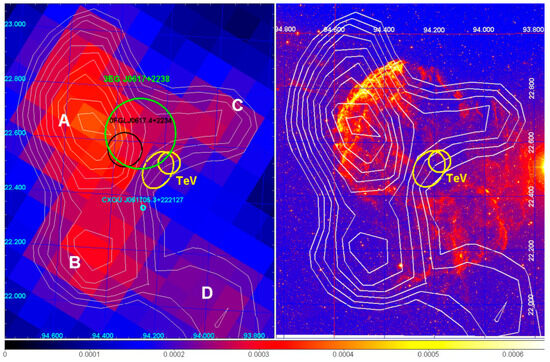
Figure 5.
Left panel: AGILE -ray intensity map above 400 MeV centered on IC 443. White contour levels mark the -ray intensity. The green and black circles mark the 95% error boxes of the EGRET (3EG J0617+2238) and Fermi-LAT (0FGL J0617.4+2234) sources, respectively. The position of the TeV source associated with IC 443 is marked by a yellow circle and ellipse that give the 95% confidence level error boxes determined by MAGIC and VERITAS. The X-ray Chandra source CXOU J061705.3+222127 is marked by a cyan circle. Right panel: optical image of IC 443 (Palomar Digitized Sky Survey) superimposed with the AGILE -ray intensity contours above 400 MeV (same as the left panel). Further details are reported in [60].
From the AGILE-GRID observations, and from the lack of detectable diffuse TeV emission, it was demonstrated that electrons cannot be the main emitters of -rays in the range 0.1–10 GeV at the site of the strongest SNR shock. The intensity, spectral characteristics, and location of the most prominent -ray emission together with the absence of cospatial detectable TeV emission are consistent only with a hadronic model of cosmic-ray acceleration in the SNR.
5. The Cygnus Region
The Cygnus region () is a site hosting bright diffuse emission, both transient and persistent pointlike and extended sources. The AGILE-GRID detected several sources in this region [38,61,62]. The most prominent persistent -ray pointlike sources are the three pulsars: PSR J2021+3651 (2AGL J2021+3654), PSR J2021+4026 (2AGL J2021+4029), and PSR J2032+4127 (2AGL J2032+4135). Moreover, three microquasars were detected in this region with variable -ray emission: Cygnus X-1 [63,64], Cygnus X-3 [65,66,67,68], and V404 Cygni [69]. Last but not least, the analysis of the AGILE-GRID data allowed the discovery of a Be-type star with a black hole companion in MWC 656 (AGL J2241+4454) [70]. This region is shining both above a few hundred of GeV [see the H.E.S.S. Galactic Plane Survey] [71] and in the TeV–PeV energy band, as reported in the first LHAASO catalog [72].
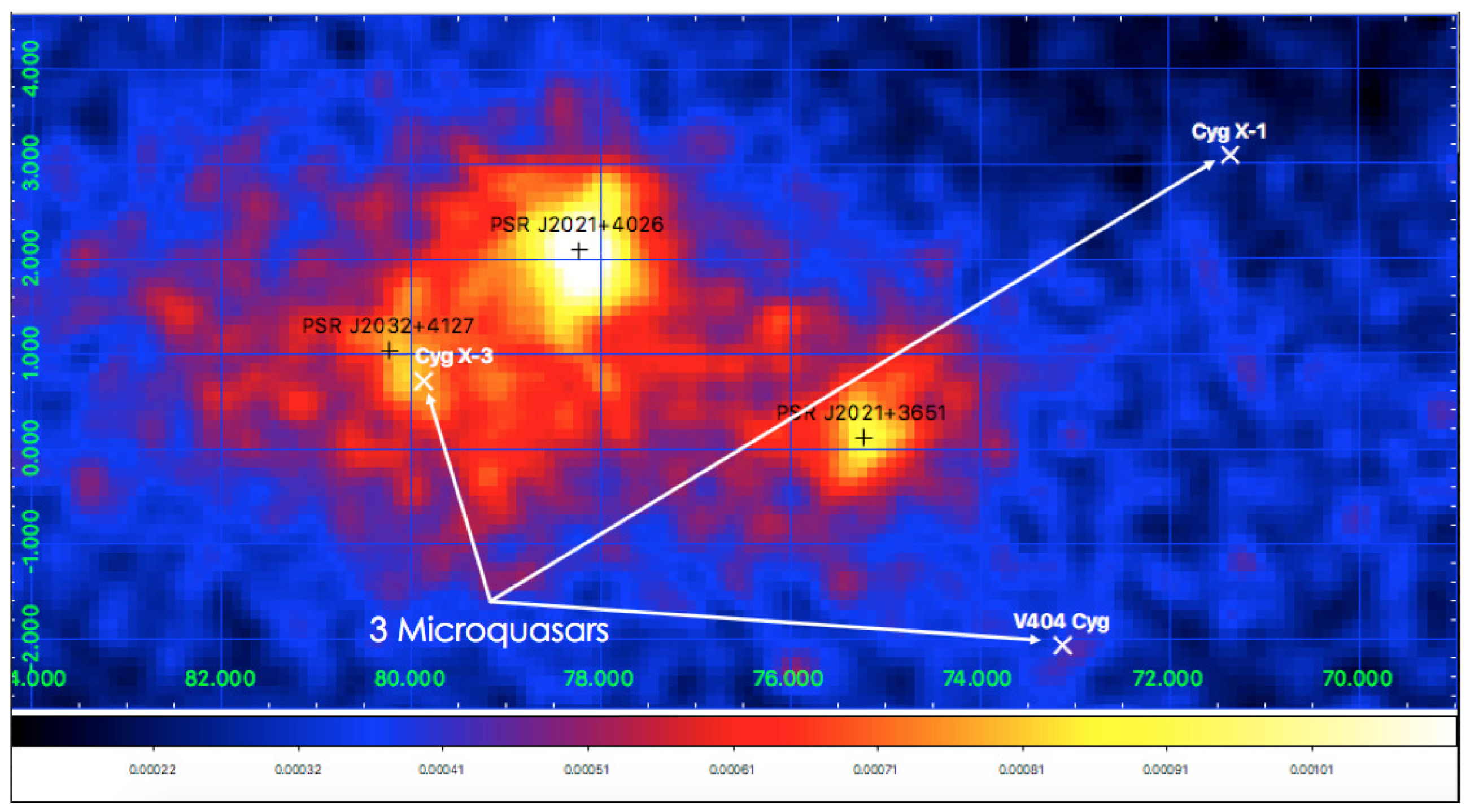
Figure 6 shows the AGILE-GRID count map ( MeV) centered on the Cygnus region. The positions of the three PSRs and of the three microquasars are marked with black and white crosses, respectively.
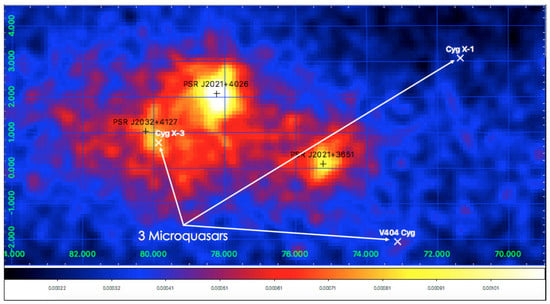
Figure 6.
AGILE-GRID count map ( MeV) centered on the Cygnus region. The positions of three PSRs and of the three microquasars are marked with black and white crosses, respectively. [G. Piano, Priv. Comm.].
Table 3 shows the principal properties of the three microquasars detected by the AGILE-GRID.

Table 3.
Principal properties of the three microquasars detected by the AGILE-GRID. Data are drawn from [63,64,65,66,67,69] and references therein.
AGILE extensive monitoring of Cyg X-1 in the energy range 100 MeV–3 GeV during the period July 2007–October 2009 confirmed the existence of a spectral cutoff between 1 and 100 MeV during the typical hard spectral state of the source. However, on 15–16 October 2009, the AGILE-GRID detected Cyg X-1 at a flux of photons in the energy range 100 MeV–3 GeV [63], which demonstrates that Cyg X-1 is capable of producing episodes of extreme particle acceleration on 1-day timescales.
On the contrary, the AGILE-GRID detected Cyg X-3 flaring events several times in the period February 2008–July 2009 [65,67]. The typical flare has a -ray flux of about one order of magnitude larger than its steady flux, photons . The -ray flares seem to occur in anticorrelation with hard X-ray emission, during soft X-ray spectral state, and a few days before major radio flares. This picture seems to indicate that quenched states are a key condition for -ray flares [65].
The AGILE “spinning” observing mode4 allowed the detection of a -ray flare from V404 Cygni, after more than a quarter of a century of quiescence, coincident with outbursts in radio, hard X-ray, and soft -ray (continuum and 511 keV annihilation line), as reported in [69] and references therein. The AGILE-GRID detected V404 Cygni on 24–26 June 2015 in the energy band (50–400) MeV with a flux of photons . The AGILE observations are compatible with a microquasar scenario in which plasmoid ejections in a lepton-dominated transient jet are responsible for the high-energy -ray emission.
Finally, another transient source in the Cygnus region, namely, AGL J2241+4454, was detected by the AGILE-GRID on July 2010 at a flux of photons [73]. The combination of this detection with optical observations allowed the firm discovery of a black hole of (3.8–6.9), which orbits the Be star MWC 656, counterpart of AGL J2241+4454 [70].
6. The Crazy Diamond 3C 454.3
The renown flat-spectrum radio quasar (FSRQ) 3C 454.3 () was originally detected in the -ray energy band by EGRET [74,75]. In 2005, 3C 454.3 underwent a major flaring activity at almost all energy bands and caused the start of a multiwavelength campaign, e.g., [76,77,78]. One interesting piece of evidence is a clear signature of the accretion disk in low states. 3C 454.3 was the first blazar detected in a flaring state by AGILE in 2007 [79]. Subsequently, it also became the brightest -ray source in the AGILE sky above 100 MeV, thus earning the nickname Crazy Diamond because of its prolonged and fast variability, resembling a diamond lit by light.
AGILE performed several multiwavelength campaigns on 3C 454.3, which enabled the study of the different SED and the discussion of innovative theoretical models to account for different flaring activity periods. Between July 2007 and October 2009, a long-term observing campaign [80] was performed during which fast -ray variability ( d) was recorded, with almost no time lag with respect to the optical one.
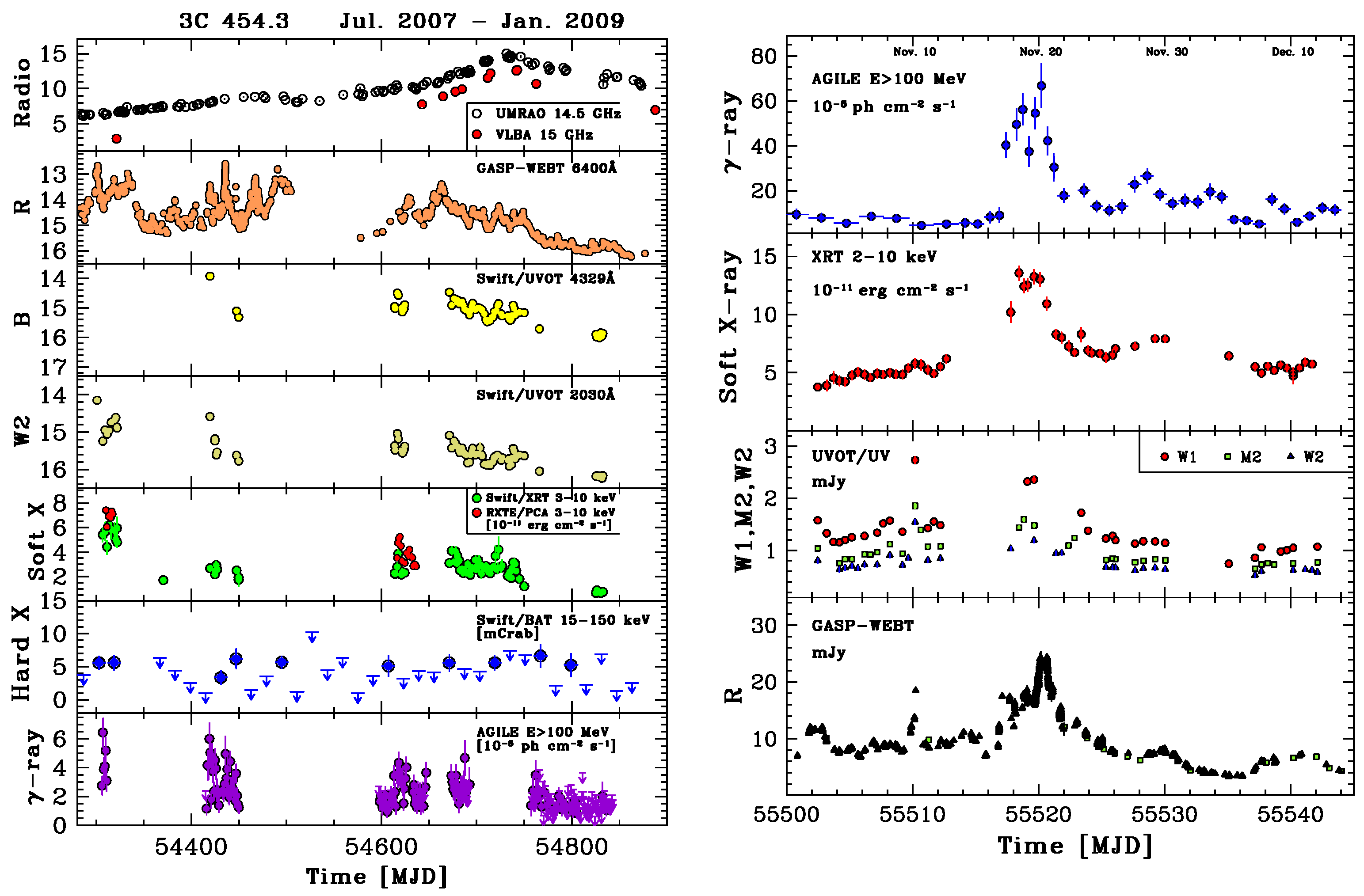
Figure 7 (left) shows the 18-month multiwavelength light curves that display how the radio band presents a markedly distinct behavior from the higher-frequency bands.
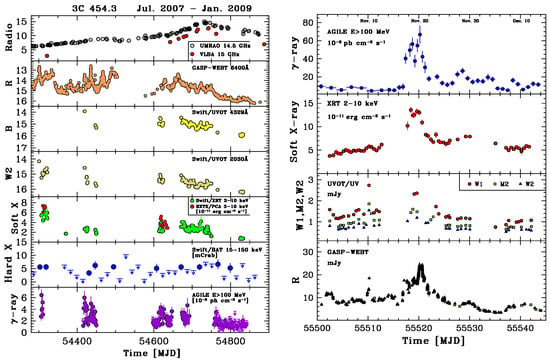
Figure 7.
Left panel: 3C 454.3 light curves at different energies, covering about 18 months of monitoring. Data from [80]. Right panel: from top to bottom, AGILE ( MeV), Swift/XRT (2–10 keV), Swift/UVOT (, , ), and GASP-WEBT (R) light curves obtained during the November 2010 flare. Data from [81].
Thanks to this long timescale multiwavelength coverage, the AGILE collaboration was able to uncover a slow, nearly constant increase of the 15 GHz flux uncorrelated with other wavebands. This different behavior of the light curves at different wavelengths could be interpreted in terms of a changing of the jet geometry between 2007 and 2008.
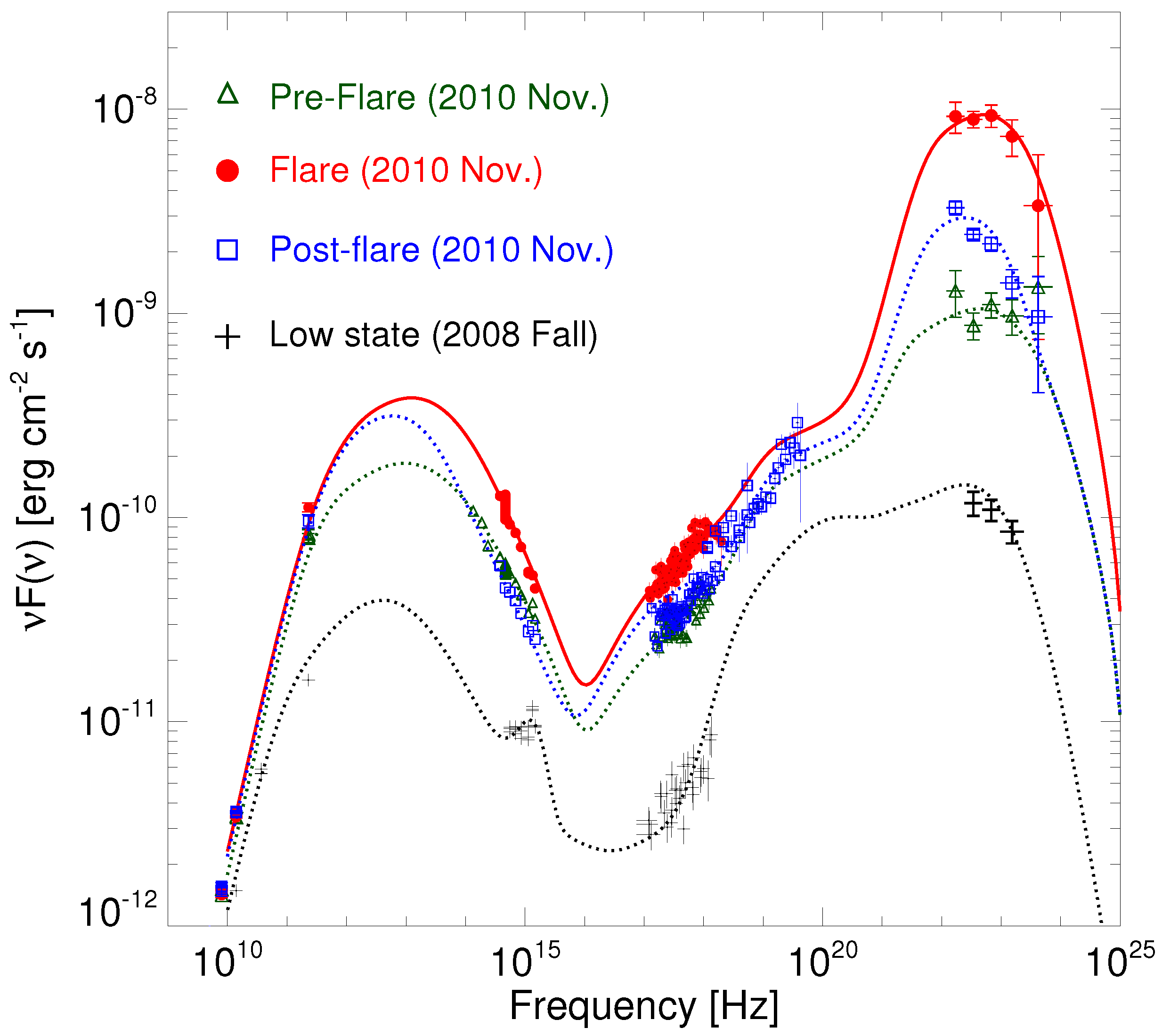
On the other hand, as shown in Figure 7 (right), the -ray flare that occurred on 20 November 2010 [81] showed some peculiar behaviors, among which was a -ray-orphan optical flare, which may challenge the model of a uniform external photon field responsible for the high-energy emission. Figure 8 shows three SEDs of 3C 454.3 obtained in November 2010, when the source was in a -ray-enhanced and flaring state [81]. In particular, preflare, flare, and postflare states can be distinguished, with remarkably different -ray flux levels and a Compton dominance reaching up to a factor of 20. The figure also shows, as a comparison, a SED for a very low -ray state for this source obtained 2 years earlier [80]. The AGILE team presented many observational and theoretical results on this source throughout the mission; see [79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86] and references therein.
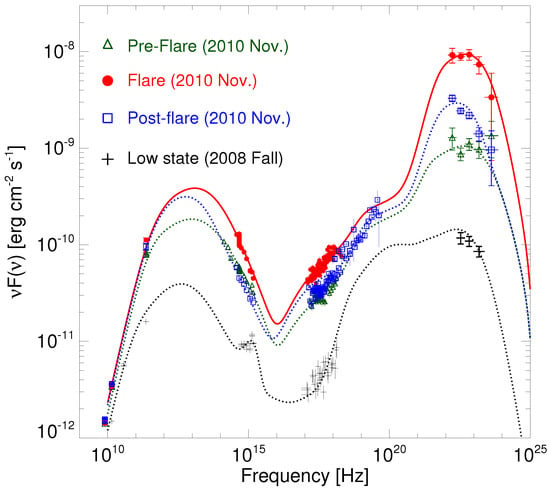
Figure 8.
SED of the flat-spectrum radio quasar 3C 454.3 accumulated during the November 2010 flare in colors, data from [81] compared with a SED accumulated during a particularly low -ray state during fall 2008 in black, data from [80].
7. High-Redshift Sources
High-redshift () blazars have a SED whose inverse Compton peak usually lies in the MeV–GeV energy range (see [87] for a seminal study of high-redshift -ray sources at ). In a recent paper, [88] considered the extragalactic sources listed in the Fermi-LAT 4FGL-DR2 catalog [89], selected those outside the galactic plane (), and reclassified them from the spectroscopic point of view. Out of 2980 sources, 1465 have spectroscopically determined redshift, and among them, 102 have . The majority of these high-redshift jetted sources are FSRQ (95, 93%), while BLLAC (5, 5%) and CLAGN5 (2, 2%) are marginal. We focus on two high-redshift sources that have been investigated with AGILE.
7.1. 4C +71.07
The flat-spectrum radio quasar 4C+71.07 is a high-redshift (), -ray loud blazar whose optical emission is dominated by thermal radiation from the accretion disk. In [90], the AGILE collaboration reported on the high -ray activity of this source in the period October–November 2015. AGILE detected two separate flares (F1 and F2) with fluxes photons between 26 October 2015 and 1 November 2015 and photons between 7 November 2015 and 13 November 2015, respectively. The AGILE collaboration activated a multiwavelength campaign involving the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory (Swift) [91] narrow field instruments, the X-ray Telescope [XRT] [92] and the UV/Optical Telescope [UVOT] [93], and the GLAST-AGILE Support Program of the Whole Earth Blazar Telescope [GASP/WEBT] [94], with a coverage from the radio (5 GHz) up to GeV energy bands.
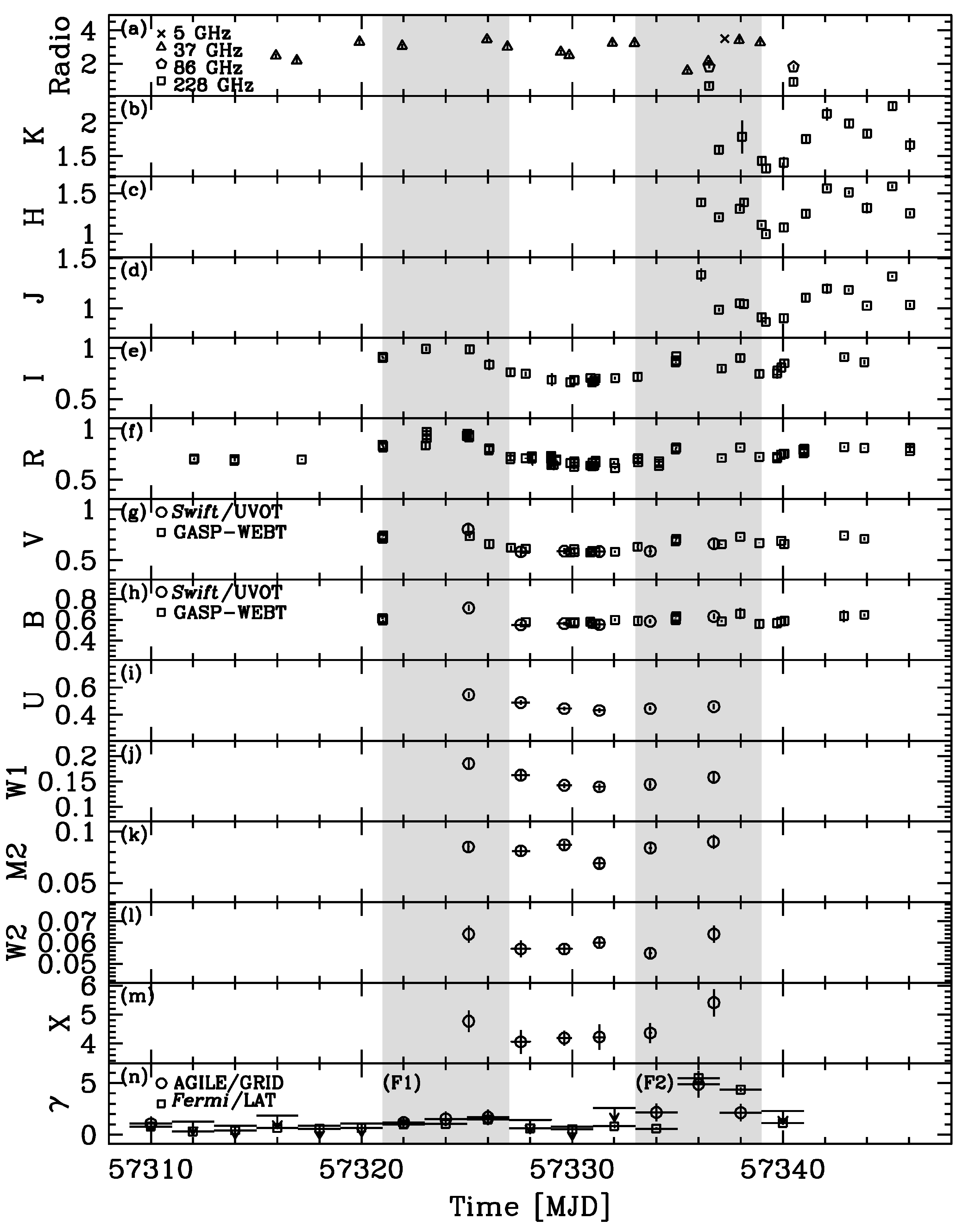
Figure 9 shows the multiwavelength campaign light curves, from the radio to the -ray energy band. In particular, the second and most prominent -ray flare (F2) has a much richer multiwavelength coverage, including the mm and the near-infrared wavelengths.
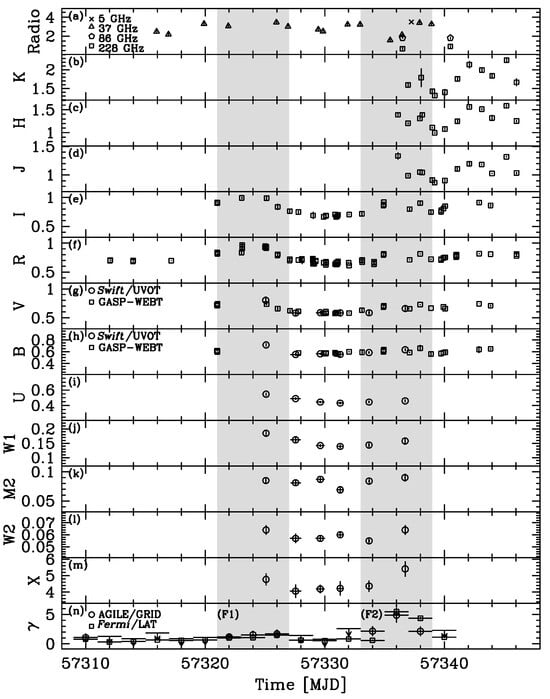
Figure 9.
Multiwavelength light curves for the observing campaign on 4C+71.07. Panel (a): GASP-WEBT 5 GHz (cross sign), 37 GHz (triangles), 86 GHz (diamonds), and 228 GHz (squares) data [Jy]. Panels (b–h): K, H, J, I, R, V, B bands (open squares, [mJy]). Panels (g–l): Swift/UVOT v, b, u, , , bands (open circles, [mJy]). Panel (m): Swift/XRT 0.3–10 keV observed flux [ erg ]. Panel (n): AGILE/GRID (circles) and Fermi-LAT (squares) data ( MeV, [ photons ]). The gray-dashed areas mark the time intervals F1 (MJD 57,321.0–57,327.0) and F2 (MJD 57,333.0–57,339.0) used to accumulate the almost simultaneous SEDs. Data from [90].
7.2. PKS 1830−211
PKS 1830−211 is a -ray-emitting, high-redshift (z ), lensed flat-spectrum radio quasar (see [95]). Recently, Ref. [96] investigated the -ray flare detected by AGILE/GRID and Fermi/LAT of PKS 1830−211.
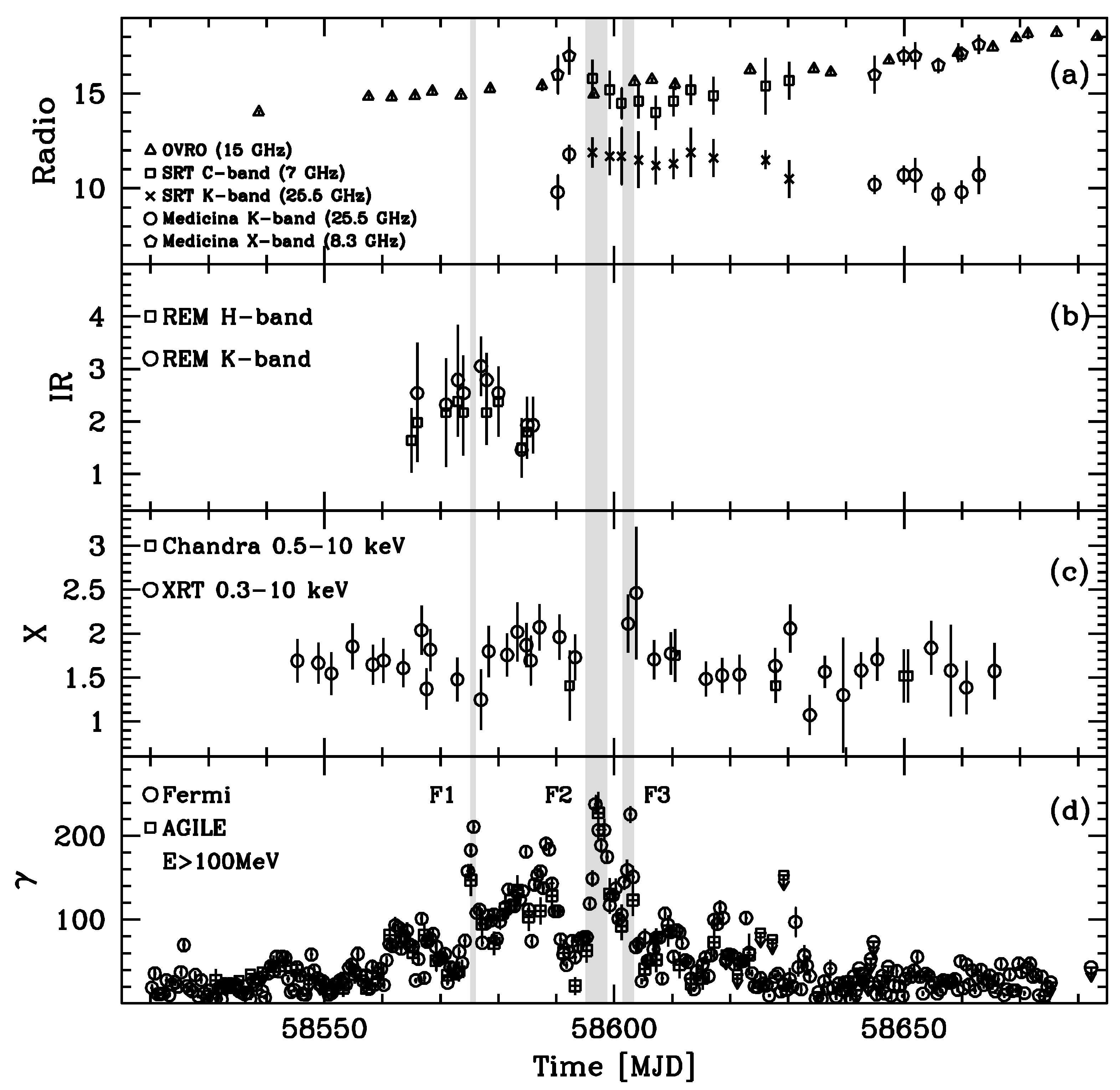
Figure 10 shows the multiwavelength light curves from radio (5 GHz) to -ray ( MeV). The source reached its maximum flux above 100 MeV ( photons ) around 24 April 2019 (MJD ), as shown in panel (d). This flux level is unprecedented for this source, and it is one of the largest ever detected in -rays from blazars at redshift .
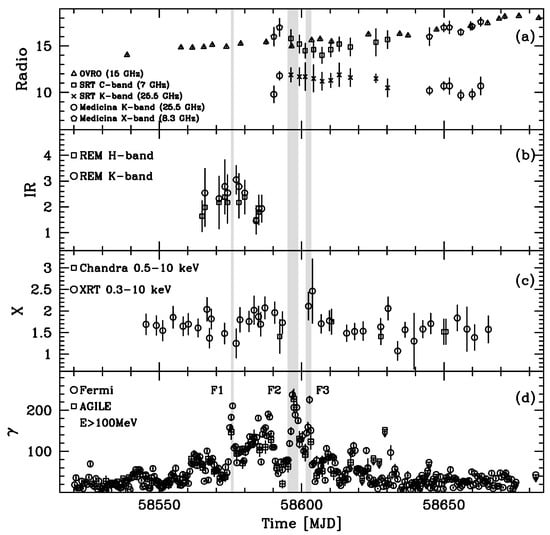
Figure 10.
PKS 1830−211 multiwavelength light curves. Panel (a): radio (7, 8.3, 15, 25.5) GHz [Jy]. Panel (b): IR (H-band, K-band [ erg ]). Panel (c): X-ray [ erg ]. Panel (d): -ray (E > 100 MeV [ photons ]) data. The shaded areas correspond to the major -ray flares F1, F2, and F3, when the spectral energy distributions were computed. Arrows mark upper limits. Data from [96].
7.3. SED Comparison
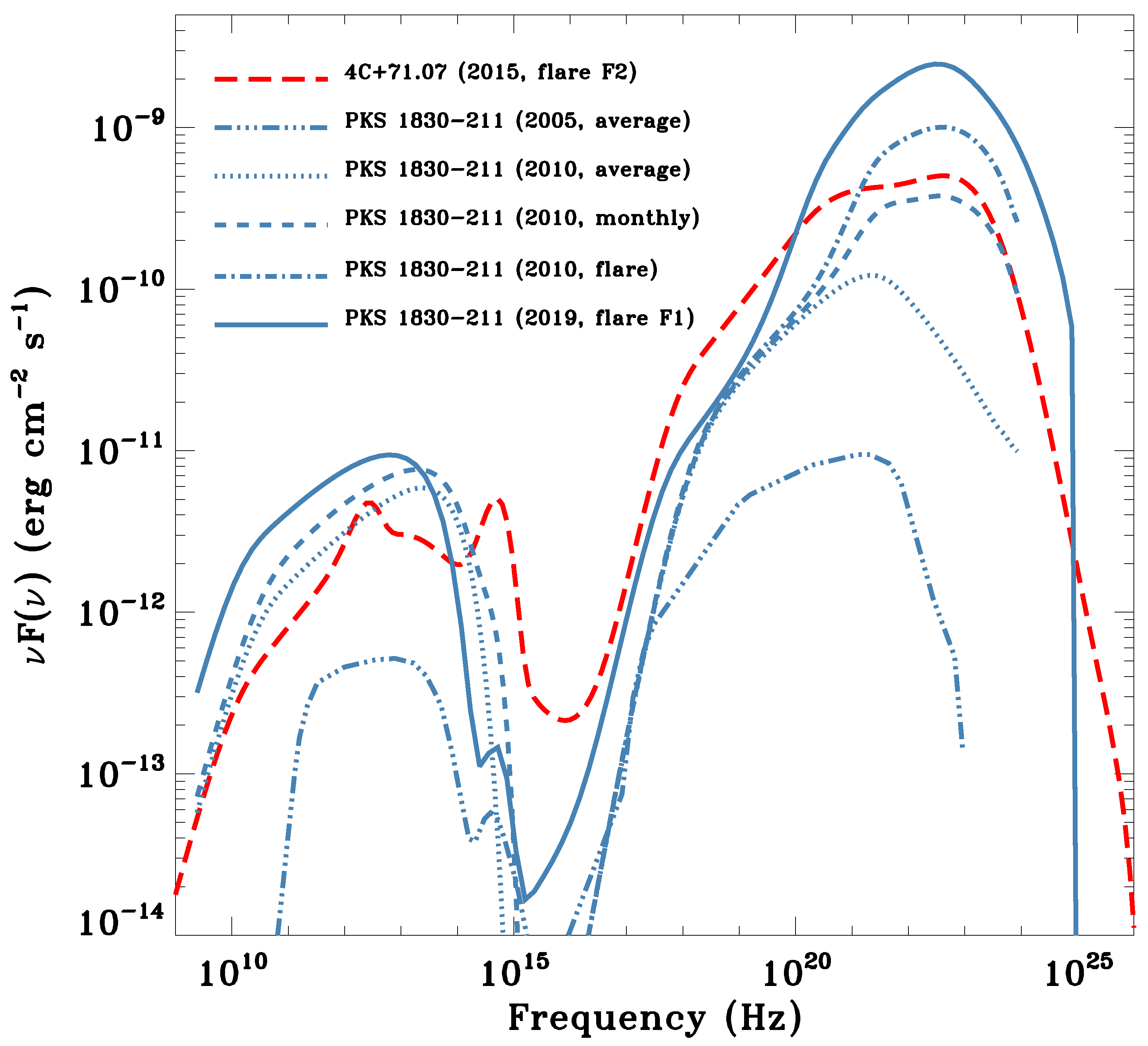
We can now compare the SEDs of these two sources. Figure 11 shows the SEDs for both 4C+71.07 and PKS 1830−211, the latter in different epochs and emission states.
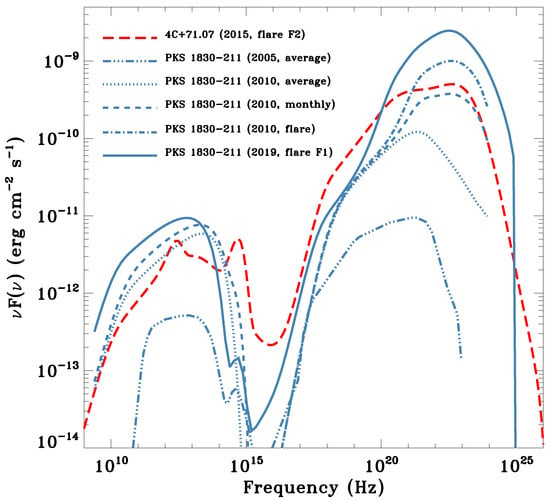
Figure 11.
Comparison of the 4C+71.07 and PKS 1830−211 SEDs. Only the sum of different emission components is reported. Data drawn from 4C+71.07 (2015) [90], PKS 1830−211 (2005) [97], PKS 1830−211 (2010, three distinct states) [95], and PKS 1830−211 (2019) [96].
We note that, during the flaring states, both sources are within a factor of about 10 in flux. In particular, the isotropic -ray luminosity for 4C+71.07 at its maximum is erg , while the Eddington luminosity is erg , assuming a black hole mass of M⊙, as computed in [98]. For PKS 1830−211, the AGILE collaboration similarly obtains erg , while erg , where for the latter, the value of the black hole mass reported in [99], M⊙, was assumed. A notable difference between the flaring and the average state of PKS 1830−211 is the value of the Compton dominance (CD), i.e., the ratio between the inverse Compton and the synchrotron peaks. During the average 2005 state, the CD is of the order of ≈20, rising to ≈100 in 2010 and topping at >200 in 2019. Such high CD values may challenge the canonical one-component emission model, requiring alternative models to explain this remarkable SED, such as the “mirror model” [100,101] or the “jet-cloud interaction model” [86,102].
8. From MeV to TeV
The search for possible very-high-energy blazar candidates was also one of the BeppoSAX legacies, as discussed in [103] and recently updated, taking advantage of the Fermi-LAT all-sky -ray survey applied to the ROMA-BZCAT and sedentary survey samples [104]. Since the beginning of observations of the sky with both imaging atmospheric Čherenkov telescopes and extended air-shower arrays, jetted extragalactic sources started to emerge as a TeV-emitting class. In 1992, the Whipple telescope detected Mrk 421 [105], while a few years later, it also detected Mrk 501 [106]. An important recent result is the detection [107] of FSRQ OP 313 by means of the Čherenkov Telescope Array Observatory (CTAO) large-sized telescope (LST) prototype LST-1 [21]. This source, at a redshift of , is the most distant blazar ever detected by a Čherenkov telescope. LST-1 detected OP 313 during a target of opportunity repointing on 11–14 December 2023, with an integrated flux, above 100 GeV, of % of the flux of the Crab Nebula in the same energy band.
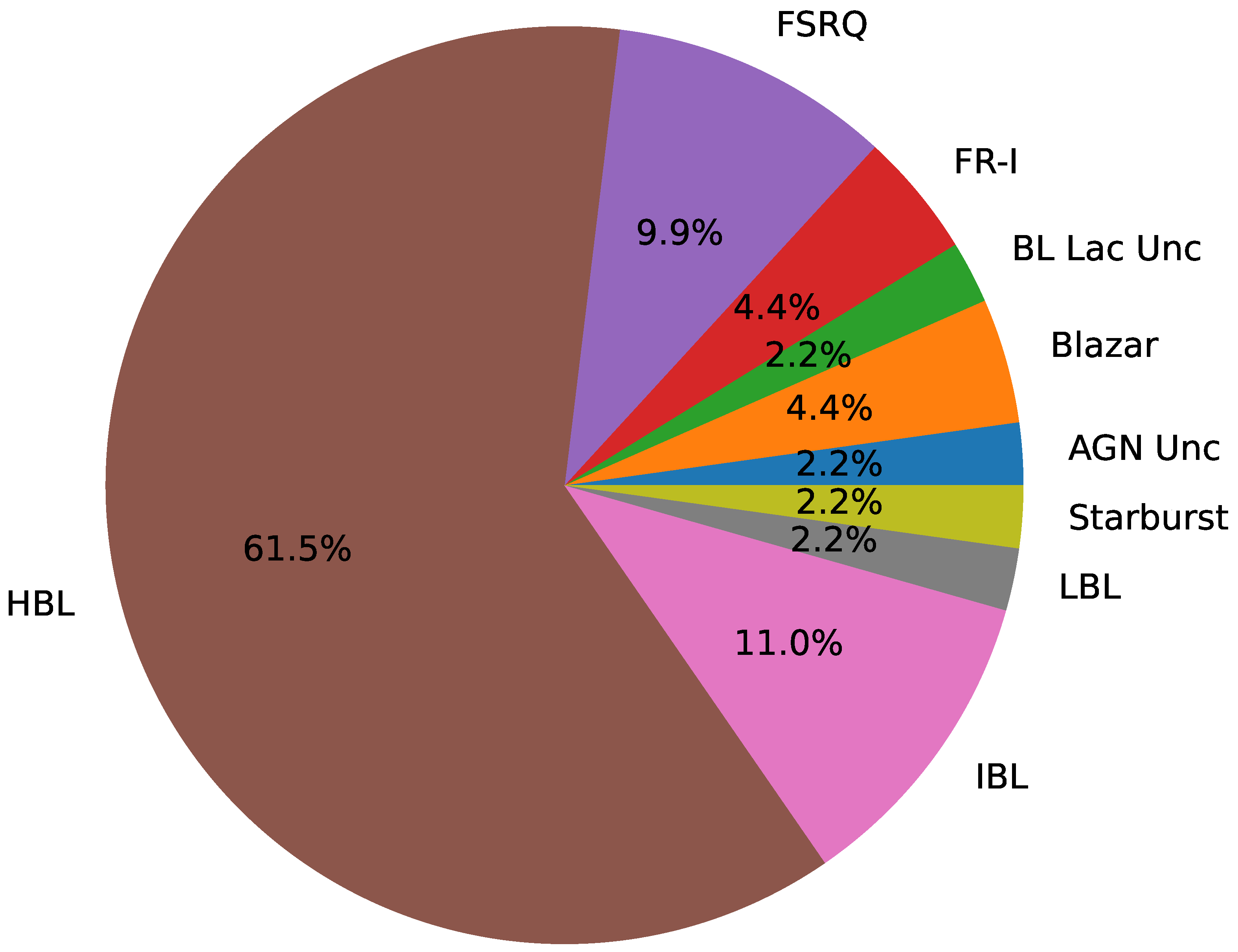
Currently, the number of extragalactic jetted sources is about 90, as reported by the TeVCat [108] website6. Figure 12 shows the fraction of extragalactic jetted sources divided according to the TeVCat nomenclature.
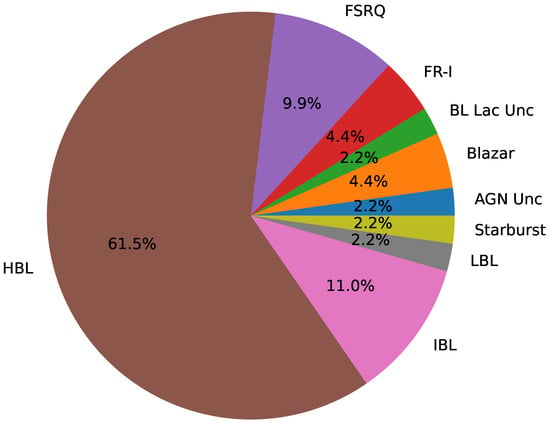
Figure 12.
Fraction of jetted sources detected above ≈100 GeV by imaging atmospheric Čherenkov telescopes and extended air-shower arrays according to the TeVCat nomenclature. Data from the TeVCat website.
The majority of TeV-detected extragalactic jetted sources are high-peaked BL Lac objects (HBLs), accounting for more than 60% of the entire sample.
8.1. Search for MeV–GeV Counterparts of TeV Sources
A preliminary yet comprehensive analysis of the MeV-GeV search for AGILE counterparts of TeV extragalactic jetted sources is reported in [109]. The authors focused on the period 9 July 2007–18 October 2009, during which the AGILE satellite operated in the nominal pointing mode. During this period, the satellite was mainly pointed to observe two regions near the galactic plane: towards the Cygnus region (l ≈ 90°) and the Vela region (l ≈ 270°). These observations, therefore, are suboptimal to investigate extragalactic sources. The counterpart search was performed using the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) described in [110] on the data accumulated in the period MJD (54,290.5–55,122.5). The AGILE collaboration used as input sources those reported in [38,61,66]. When the analysis was performed, TeVCat contained a lower number of sources than the current one, and the analysis was performed on 152 TeV sources.
Table 4 shows the extragalactic TeV sources listed in TeVCat that have been detected by AGILE in the period 9 July 2007–18 October 2009. Among them, there are five HBLs, two IBLs, two LBLs, two FSRQs, and two FR-I galaxies.

Table 4.
TeVCat sources detected by AGILE in the period 9 July 2007–18 October 2009.
8.2. The Multiwavelength View of TeV Sources: W Comae and Mrk 421
In addition to the sources listed in Table 4, AGILE performed multiwavelength studies on some peculiar TeV sources and, among them, W Comae and Mrk 421.
W Comae (, IBL) was detected by AGILE on June 9–15 2008 as a follow-up observation [111] of the detection at VHE by VERITAS [112] on 7–8 June 2008 with a flux of photons . This value is about three times brighter than the flux detected by VERITAS in March 2008, when the sources were discovered as a VHE emitter [113]. AGILE detected W Comae with a flux of photons , which was, at that time, a factor of 1.5 higher than any -ray emission detected by both EGRET and Fermi-LAT. A multiwavelength campaign was immediately activated, as reported in [114]. Figure 13 (left panel) shows the almost-simultaneous multiwavelength light curves covering W Comae HE and VHE flare from the radio up to the GeV energy bands from MJD 54622 to MJD 54636. The SED was accumulated during the high-state period MJD 54624–54626, and fit with both a pure synchrotron self-Compton (SSC) model and an SSC plus external Compton (EC) one. The latter model fits the observed data better, in particular the near-infrared bump (see Figure 5 in [114]), suggesting a dusty molecular torus as a possible source of seed photons for the EC component.
Mrk 421 (, HBL) is a well-known TeV emitter. AGILE detected Mrk 421 both by means of its onboard hard X-ray detector, Super-AGILE, on 10 June 2008 [115] and in the -ray energy band [116], by integrating in the period 9–15 June 2008. In the period 9–15 June 2008, Mrk 421 reached a flux in the hard X-ray energy band of mCrab ( erg ) and a -ray flux of photons [117]. Figure 13, right panel, illustrates the Mrk 421 light curves at different energies, showing the broad-band coverage for this flaring event. The X-ray and HE/VHE correlated variability points towards a possible SSC modeling of the SED. In particular, the decreasing trend in the R-band data, not followed by a similar trend in the X-ray energy band, may suggest a scenario in which the inner jet region would produce the X-rays while the outer region can only produce lower-frequency emission; see, e.g., [118,119].
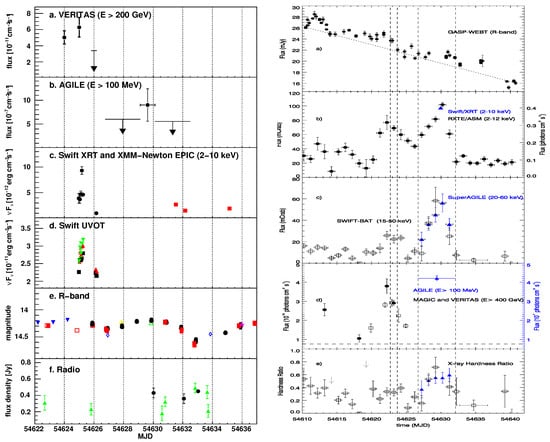
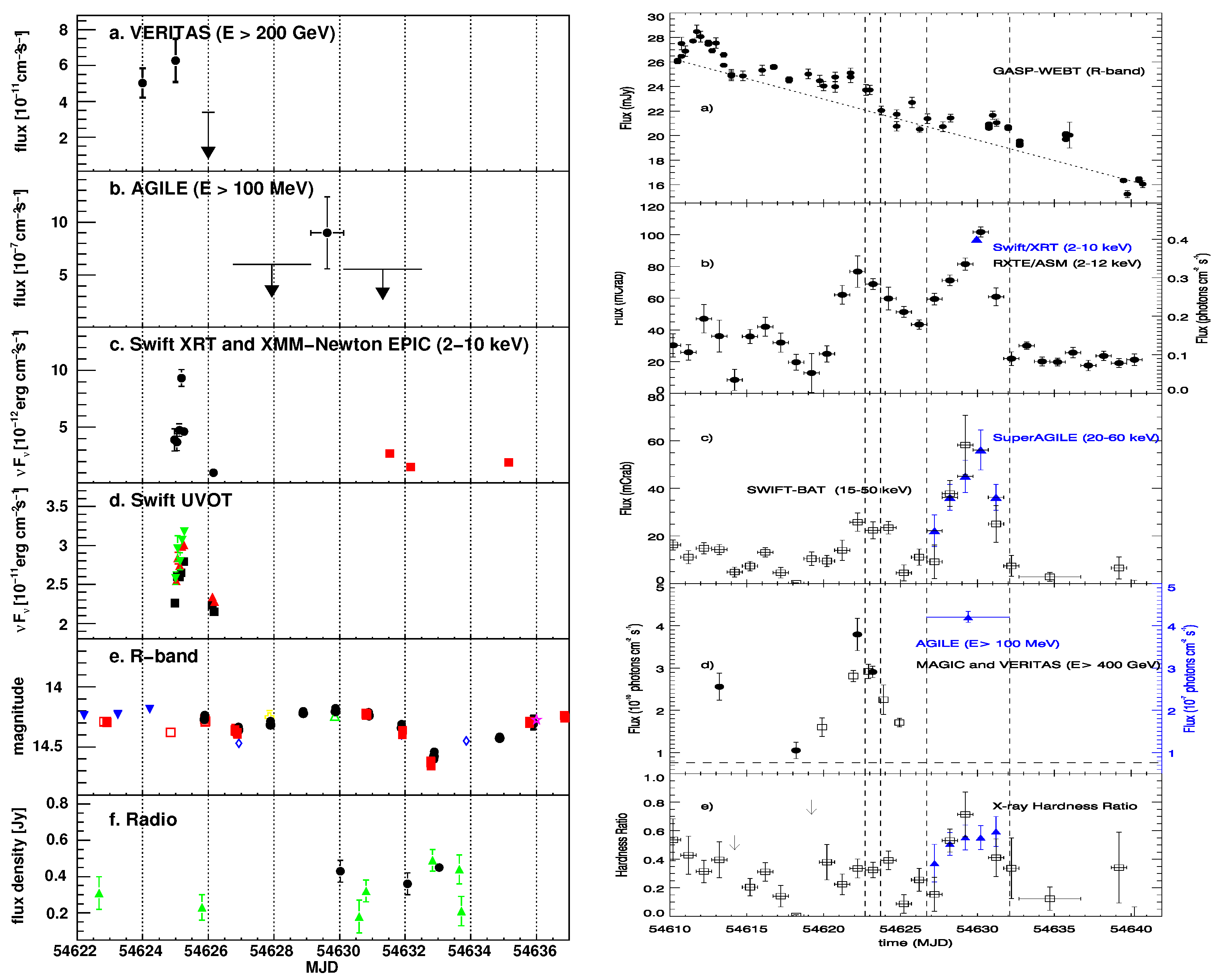

Figure 13.
Left panel: W Comae multiwavelength light curve covering the HE and VHE flare from the radio up to the GeV energy bands. The x-axis is the date in MJD. Panel (a): VERITAS -ray ( GeV) light curve. Panel (b): AGILE-GRID -ray ( MeV) light curve. Panel (c): 2–10 keV Swift-XRT (circles) and XMM-Newton (squares) X-ray light curves. Panel (d): Swift-UVOT (UVW1: squares; UVM2: downward-pointing triangles; UVW2: upward-pointing triangles) light curves. Panel (e): GASP/WEBT R-band light curves. Panel (f): radio light curve (circles: UMRAO 14.5 GHz; triangles: Metsähovi 37 GHz). Downward-pointing arrows indicate 99% C.L. upper limits. Right panel: Mrk 421 multiwavelength light curve covering the HE and VHE flare from the optical up to the GeV energy bands. The x-axis is the date in MJD. Panel (a): R-band GASP/WEBT optical light curve. Panel (b): RXTE/ASM (2–12 keV) daily binned light curve and Swift/XRT (2–10 keV) light curve (blue triangle). Panel (c): Super-AGILE (20–60 keV, blue triangles; photons ) and the Swift Burst Alert Telescope [BAT,][15–50 keV] [120] (empty black squares; photons ). Panel (d): MAGIC, VERITAS ( GeV, empty black squares, and black circles, respectively), and AGILE ( MeV, blue triangles); the horizontal dashed line marks the 1 Crab flux level at GeV. Panel (e): hardness ratio computed using the Super-AGILE (or Swift/BAT) and RXTE/ASM data for each day. Vertical dashed lines represent two distinct time periods, P1 (6 June 2008) and P2 (9–15 June 2008). Further details are available in [W Comae] [114] and [Mrk 421] [117].
Figure 13.
Left panel: W Comae multiwavelength light curve covering the HE and VHE flare from the radio up to the GeV energy bands. The x-axis is the date in MJD. Panel (a): VERITAS -ray ( GeV) light curve. Panel (b): AGILE-GRID -ray ( MeV) light curve. Panel (c): 2–10 keV Swift-XRT (circles) and XMM-Newton (squares) X-ray light curves. Panel (d): Swift-UVOT (UVW1: squares; UVM2: downward-pointing triangles; UVW2: upward-pointing triangles) light curves. Panel (e): GASP/WEBT R-band light curves. Panel (f): radio light curve (circles: UMRAO 14.5 GHz; triangles: Metsähovi 37 GHz). Downward-pointing arrows indicate 99% C.L. upper limits. Right panel: Mrk 421 multiwavelength light curve covering the HE and VHE flare from the optical up to the GeV energy bands. The x-axis is the date in MJD. Panel (a): R-band GASP/WEBT optical light curve. Panel (b): RXTE/ASM (2–12 keV) daily binned light curve and Swift/XRT (2–10 keV) light curve (blue triangle). Panel (c): Super-AGILE (20–60 keV, blue triangles; photons ) and the Swift Burst Alert Telescope [BAT,][15–50 keV] [120] (empty black squares; photons ). Panel (d): MAGIC, VERITAS ( GeV, empty black squares, and black circles, respectively), and AGILE ( MeV, blue triangles); the horizontal dashed line marks the 1 Crab flux level at GeV. Panel (e): hardness ratio computed using the Super-AGILE (or Swift/BAT) and RXTE/ASM data for each day. Vertical dashed lines represent two distinct time periods, P1 (6 June 2008) and P2 (9–15 June 2008). Further details are available in [W Comae] [114] and [Mrk 421] [117].

9. Gamma-ray Bursts and Multimessenger Astrophysics
An important contribution of the AGILE team has been to alert the community for short timescale (seconds/minutes/hours) transients, such as gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), through dedicated channels, such as the General Coordinates Network7 (GCN) and the Astronomer’s Telegram8 (ATel), and to perform the follow-up of gravitational wave (GW) events, cosmic neutrinos, fast radio bursts (FRB), and other bursting events.
The efficient real-time analysis (RTA) system developed for the AGILE space mission to detect transient sources on short timescales has been presented in [121]. Two types of pipelines were implemented. The first one executed automated analyses as soon as new AGILE data were available, sharing the detection of sources with the community (more than 90 automated notices have been sent to the GCN since May 2019). The other pipeline reacted to external science alerts (GRBs from other missions, neutrinos, GW, etc.) to search for electromagnetic counterparts in the AGILE data. The AGILE alert system is also considered a heritage for the development of future RTA systems of the next generation of space and ground-based -ray observatories. Here, we present a short summary of selected results.
9.1. The AGILE-GRID View of GRBs and the Exceptional GRB 221009A
Following the EGRET seminal detections of GRBs above a few tens of MeVs in the early 1990s, in 2008, AGILE detected its first GRB with photons of energy above several tens of MeVs [GRB 080514B] [122]. The hard X-ray emission observed by Super-AGILE lasted about 7 s, while the emission observed by the AGILE-GRID above 30 MeV had almost twice the duration (at least 13 s). Prior to AGILE, such behavior regarding a possible longer-lasting high-energy component had only been hypothesized from a few other GRBs observed with EGRET. However, EGRET measurements were affected by instrumental deadtime effects, resulting in only lower limits to the GRB intensity. Thanks to the small deadtime of the AGILE-GRID and the unique simultaneous hard X-ray/-ray AGILE capability, for the first time, it could be assessed that the arrival times of the high-energy photons detected with the AGILE-GRID do not coincide with the brightest peaks seen in hard X-rays. Three high-energy photons are concentrated within 2 s at the beginning of the burst, while the next ones arrive only when the X-ray emission has returned to a level consistent with the background (7 s after the beginning of the burst). This implies a rapid time evolution of the -ray to X-ray flux ratio, although a quantitative assessment of this variability is hampered by the small statistics.
The AGILE and Fermi satellites have since then increased the sample of GRBs detected at -ray energies above 100 MeV to a couple of hundreds [123] with a rate of ∼10–17 GRBs per year. Most of them are are long bursts with typical prompt durations above 2 s, probably associated with stellar explosions of massive stars. However, they still represent a small fraction (<5%) of the GRB samples detected in the X-ray band.
AGILE and Fermi also contributed to the detection of short GRBs, characterized by durations below 2 s, which are usually spectrally hard compared to the average properties of GRBs and are believed to be associated with the coalescence of neutron star binaries. While Fermi detected the first short GRB in the -ray energy band, GRB 081024B [124,125], AGILE contributed to the science of short GRBs with the detection of GRB 090510 [126] (also observed by Fermi [127]), which provided the first case of a short GRB with delayed -ray emission. Indeed, Ref. [126] reported a delay of 0.2 s between the AGILE-GRID data with respect to the AGILE-MCAL ones (see their Figure 2). The short GRB 090510 is now considered a reference for potential electromagnetic -ray emission that could be associated with a gravitational wave event, and its light curve has been used as a possible high-energy template counterpart of GW events [128,129].
Now, this interesting and unexpected finding that for some GRBs the GeV emission starts with a delay after the MeV emission has become an often revealed trait. GRB 190114C was the first GRB with delayed emission ever detected above 300 GeV, a breakthrough discovery reported by MAGIC [130]. The sub-MeV/MeV data of the prompt and early afterglow emissions of GRB 190114C as detected by AGILE and Konus-Wind have been presented in [131]. In that AGILE paper, the first ∼200 s of the early afterglow of GRB 190114C have been carefully analyzed, and a previously unnoticed flux temporal break near T0+100 s was identified. Such a break is incompatible with the commonly assumed adiabatic evolution of a fireball in a constant-density medium, and it has been tentatively interpreted as a consequence of radiative evolution of the early afterglow from a fireball expanding in a wind-like circumburst medium.
Among the exceptional events observed, the long-duration GRB 221009A needs to be mentioned, as it was the brightest and most energetic GRB ever recorded, hence named brightest of all time or the “BOAT”. During this unprecedented event, AGILE detected an extraordinary incoming flux of hard X-ray and high-energy -ray photons.
Figure 14 shows the AGILE-GRID sky count map accumulated during the first 48 h after the GRB 221009A onset. The BOAT clearly outshines all other -ray sources active at that time. The high-energy emission has been observed with an almost-continuous time coverage, from ∼200 s up to ∼20 ks after the GRB onset [132]. AGILE observations provide crucial flux and spectral -ray information regarding the early phases of GRB 221009A, during which emission in the TeV range was reported together with the first detection of photons above 10 TeV from GRBs [133]. The AGILE data suggest a dramatic transition between prompt and afterglow emission with a peculiar phase of coexistence of MeV and GeV emissions with very different spectral properties. A general review on the main discoveries about GRB science can be found in [134].
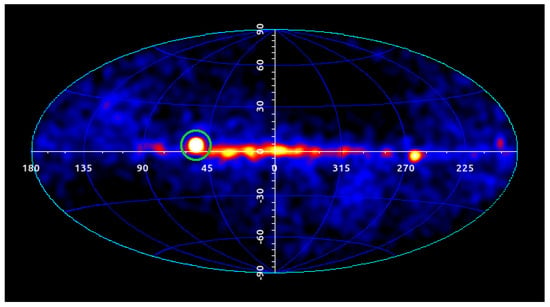
Figure 14.
Sky count map above 100 MeV in galactic coordinates of the AGILE-GRID -ray detector during the time interval [ hr]. The -ray source associated with GRB 221009A is shown inside the green circle. The darkened sky regions are due to seasonal lack of exposure of the AGILE-GRID detector due to solar panel constraints. Further details in [132].
9.2. AGILE and Other Transients
The AGILE space mission, with its fast ground segment alert system and its unique observing capability to cover about 80% of the sky in ∼7 min in the so-called “spinning observing mode”, provided crucial contribution in follow-up observations of multiwavelength and multimessenger transients, such as gravitational wave events, cosmic neutrinos, and fast radio bursts.
A detailed report on these significant results that involved all AGILE payload instruments (GRID, MCAL, and AC system) on timescales ranging from sub-milliseconds to tens to hundreds of seconds goes beyond the scope of this paper. In this section, we briefly present a list of AGILE main publications on these topics.
- AGILE and GWs: AGILE follow-up observations have provided in general the fastest response and the most significant upper limits above 100 MeV on all GW events detected by the Ligo–Virgo–Kagra Collaboration up to now [129,135,136,137].
- AGILE and neutrinos: AGILE published results from follow-up observations of IceCube neutrinos range from the first (still unconfirmed) tentative discovery of a -ray precursor in 2017 [138] to the systematic search for transient -ray sources temporally and spatially coincident with ten high-energy neutrino IceCube events published up to August 2018 [139], and the AGILE detection of the flaring blazar TXS 0506+056 in 2017, following the most interesting neutrino event detected to date [140].
- AGILE and FRBs: FRBs are millisecond radio pulses originating from powerful sources of unknown origin at extragalactic distances. AGILE observations in a multiwavelength context provide important constraints on the prompt (millisecond and hundreds of millisecond timescales) emission in the sub-MeV–MeV range. AGILE also studied the persistent long timescale -ray emission above 30 MeV from repeating FRBs [141,142,143,144]. A breakthrough in FRB science happened in 2020, with the AGILE detection of an X-ray burst from the galactic magnetar SGR 1935+2154 [145], an important finding that supports magnetar models and sheds light on the understanding of the physical mechanism of FRBs.
AGILE also produced important results on terrestrial gamma-ray flashes and solar flares, with the publication of dedicated catalogs, as described in Section 10.
10. The AGILE Legacy: The Catalogs
In this section, we present a summary of the main AGILE catalogs published at the time of writing (January 2024). Our goal is to provide a centralized source of information, which allows the reader to easily access online catalogs and their references, as reported in Table 5. The AGILE catalogs cover both celestial (including GRBs and solar flares) and terrestrial events (TGFs). This shows the AGILE versatility, which, thanks to the information collected by its detectors, could detect steady, flaring, and transient events from 20 keV up to 30 GeV.

Table 5.
List of AGILE catalogs up to January 2024. References: (a) Pittori et al. [38]; (b) Feroci et al. [146]; (c) Galli et al. [147]; (d) Verrecchia et al. [61]; (e) Marisaldi et al. [148]; (f) Marisaldi et al. [149]; (g) Rappoldi et al. [109]; (h) Bulgarelli et al. [62];
(i) Marisaldi et al. [150]; (j) https://www.ssdc.asi.it/mcal3tgfcat/ (accessed on 18 March 2024); (k) Ursi et al. [151]; (l) Ursi et al. [152].
11. Conclusions
The AGILE mission has been a first of its kind. It was selected by ASI as the first among the small mission programs in 1998. It was the first HE mission to have a hard X-ray monitor on board. For the first time in the -ray energy range, a fast ground segment allowed the dissemination of flaring events and the activation of the target of opportunity observations with other observatories. AGILE provided the first evidence of hadronic cosmic-ray acceleration in supernova remnants. For the first time, a -ray mission devoted to the observations of the sky became an asset in the study of terrestrial -ray flashes. Last, but not least, AGILE discovered, for the first time, flux variability in the Crab Nebula, previously considered to be a “standard candle” in the energy range (0.1–10) GeV. This discovery allowed the AGILE team to be awarded in 2012 with the Bruno Rossi Prize9 of High Energy Astrophysics Division of the American Astronomical Society.
After 17 years of thriving operations, the AGILE Italian scientific satellite re-entered the atmosphere on 14 February 2024, thus ending its intense activity as a hunter of some of the most energetic cosmic sources in the Universe that emit X and -rays [10]. With AGILE’s re-entry, the in-orbit operational phase comes to a close, but a new phase of scientific work on the satellite legacy data archive opens.
Currently, only Fermi-LAT is acquiring -ray data. In the future, ASTROGAM, a proposed observatory space mission dedicated to the study of the nonthermal Universe in the photon energy range from 0.3 MeV to 3 GeV [153,154], could provide important information not only above a few hundreds of MeV but also at lower energies. Furthermore, the Compton Spectrometer and Imager [COSI] [155] should be launched in 2027. It is designed as a soft -ray survey telescope sensitive in the 0.2–5 MeV energy band, performing studies of -ray polarization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.V., C.P. and M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.V. and C.P.; writing—review and editing, S.V., C.P. and M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying this review are publicly available from their archives and processed with publicly available software.
Acknowledgments
This paper is written on behalf of the AGILE collaboration. Part of this work is based on archival data, software, or online services provided by the ASI–Space Science Data Center (SSDC). This research has made use of the TeVCat online source catalog (http://tevcat.uchicago.edu) (accessed on 18 March 2024). The scientific research carried out for the project has been partially supported under the grants ASI-I/R/045/04, ASI-I/089/06/0, and ASI-I/028/12/0 and subsequent grants and addenda. S.V. acknowledges partial financial contribution from the agreement ASI–INAF n.2017-14-H.0.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 3EG | third EGRET catalog |
| ACS | anticoincidence system |
| ADC | AGILE data center |
| AGILE | Astrorivelatore Gamma ad Immagini LEggero |
| AGN | active galactic nuclei |
| ASI | Agenzia spaziale Italiana |
| ATel | Astronomer’s Telegram |
| BH | black hole |
| C.L. | confidence limit |
| CLAGN | changing-look AGN |
| COSI | Compton spectrometer and imager |
| CR | cosmic ray |
| CsI | cesium iodide |
| CTAO | Čherenkov Telescope Array Observatory |
| EAS | extensive air shower |
| EC | external Compton |
| EGRET | Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope |
| FR | Fanaroff–Riley galaxies |
| FoV | field of view |
| FRB | fast radio burst |
| FSRQ | flat-spectrum radio quasar |
| FWHM | full-width half maximum |
| FWZI | full-width zero intensity |
| GASP | GLAST-AGILE Support Program |
| GCN | general coordinates network |
| GRB | gamma-ray burst |
| GRID | gamma-ray imaging detector |
| GW | gravitational wave |
| HBL | high-peaked BL Lacs |
| HE | high energy |
| HMXB | high-mass X-ray binary |
| IBL | intermediate-peaked BL Lacs |
| LAT | large area telescope |
| LBL | low-peaked BL Lacs |
| LST | large-sized telescope |
| LMXB | low-mass X-ray binary |
| MCAL | mini-calorimeter |
| MJD | Modified Julian Day |
| NS | neutron star |
| PI | principal investigator |
| PSR | pulsar |
| RTA | real-time analysis |
| SA | Super-AGILE |
| SED | spectral energy distribution |
| S/N | signal-to-noise |
| SNR | supernova remnant |
| SSC | synchrotron self-Compton |
| SSDC | space science data center |
| ST | silicon tracker |
| TGF | terrestrial gamma-ray flashes |
| WEBT | whole-earth blazar telescope |
Notes
| 1 | We do not discuss here the large number of balloon-based instruments. |
| 2 | http://agile.rm.iasf.cnr.it/ (accessed on 18 March 2024). |
| 3 | https://agile.ssdc.asi.it/ (accessed on 18 March 2024). |
| 4 | On 2009 November 4 the AGILE scientific operations were reconfigured following a malfunction of the unique rotation wheel. See, https://agile.asdc.asi.it/news.html#115 and https://agile.asdc.asi.it/news.html#117 (accessed on 18 March 2024). Since then, the satellite started operating in a controlled “spinning observing mode”, with the solar panels pointing at the Sun and the instrument axis sweeping the accessible sky with an angular speed of about 0.8 deg . In spinning mode AGILE was able to survey a large fraction (about 80%) of the sky each day. |
| 5 | We note that changing-look AGN, CLAGN, are sources changing from one type to another, and vice versa. |
| 6 | http://tevcat.uchicago.edu/ (accessed on 18 March 2024). |
| 7 | https://gcn.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 18 March 2024). |
| 8 | https://www.astronomerstelegram.org/ (accessed on 18 March 2024). |
| 9 | https://head.aas.org/rossi/rossi.recip.html#AB (accessed on 18 March 2024). |
References
- Kraushaar, W.L.; Clark, G.W. GAMMA RAY ASTRONOMY. Sci. Am. 1962, 206, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraushaar, W.L.; Clark, G.W.; Garmire, G.P.; Borken, R.; Higbie, P.; Leong, V.; Thorsos, T. High-Energy Cosmic Gamma-ray Observations from the OSO-3 Satellite. Astrophys. J. 1972, 177, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtel, C.E.; Hartman, R.C.; Kniffen, D.A.; Thompson, D.J.; Bignami, G.F.; Ögelman, H.; Özel, M.E.; Tümer, T. High-energy gamma-ray results from the second Small Astronomy Satellite. Astrophys. J. 1975, 198, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanenburg, B.N.; Bennett, K.; Bignami, G.F.; Buccheri, R.; Caraveo, P.; Hermsen, W.; Kanbach, G.; Lichti, G.G.; Masnou, J.L.; Mayer-Hasselwander, H.A.; et al. Second COS-B catalogue of high-energy gamma-ray sources. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1981, 243, L69–L73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, G.F.; Caraveo, P.A. Geminga: Its Phenomenology, Its Fraternity, and Its Physics. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 34, 331–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbach, G.; Bertsch, D.L.; Fichtel, C.E.; Hartman, R.C.; Hunter, S.D.; Kniffen, D.A.; Hughlock, B.W.; Favale, A.; Hofstadter, R.; Hughes, E.B. The project EGRET (energetic gamma-ray experiment telescope) on NASA’s Gamma-ray Observatory GRO. Space Sci. Rev. 1989, 49, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, R.C.; Bertsch, D.L.; Bloom, S.D.; Chen, A.W.; Deines-Jones, P.; Esposito, J.A.; Fichtel, C.E.; Friedlander, D.P.; Hunter, S.D.; McDonald, L.M.; et al. The Third EGRET Catalog of High-Energy Gamma-ray Sources. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1999, 123, 79–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellone, S.; Soldi, S.; Chen, A.W.; Tavani, M. On the duty-cycle of γ-ray blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 353, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tavani, M.; Barbiellini, G.; Argan, A.; Boffelli, F.; Bulgarelli, A.; Caraveo, P.; Cattaneo, P.W.; Chen, A.W.; Cocco, V.; Costa, E.; et al. The AGILE Mission. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 502, 995–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Addis, A.; Argan, A.; Antonelli, L.A.; Auricchio, N.; Barbiellini, G.; Baroncelli, L.; Basset, M.; Boffelli, F.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. The AGILE satellite ceased operations and re-entered today into the atmosphere. Astron. Telegr. 2024, 16450, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Prest, M.; Barbiellini, G.; Bordignon, G.; Fedel, G.; Liello, F.; Longo, F.; Pontoni, C.; Vallazza, E. The AGILE silicon tracker: An innovative /γ-ray instrument for space. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. 2003, 501, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroci, M.; Costa, E.; Soffitta, P.; Del Monte, E.; di Persio, G.; Donnarumma, I.; Evangelista, Y.; Frutti, M.; Lapshov, I.; Lazzarotto, F.; et al. SuperAGILE: The hard X-ray imager for the AGILE space mission. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. 2007, 581, 728–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labanti, C.; Marisaldi, M.; Fuschino, F.; Galli, M.; Argan, A.; Bulgarelli, A.; Di Cocco, G.; Gianotti, F.; Tavani, M.; Trifoglio, M. Design and construction of the Mini-Calorimeter of the AGILE satellite. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. 2009, 598, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotti, F.; Fiorini, M.; Incorvaia, S.; Mattaini, E.; Sant’Ambrogio, E. The AGILE anticoincidence detector. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. 2006, 556, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittori, C.; The Agile-Ssdc Team. The AGILE data center and its legacy. Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. Nat. 2019, 30, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, A.; Trifoglio, M.; Gianotti, F.; Tavani, M.; Parmiggiani, N.; Fioretti, V.; Chen, A.W.; Vercellone, S.; Pittori, C.; Verrecchia, F.; et al. The AGILE Alert System for Gamma-ray Transients. Astrophys. J. 2014, 781, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, V. Motions and Structure of the Filamentary Envelope of the Crab Nebula. Astron. J. 1968, 73, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.J. The Crab Nebula: An astrophysical chimera. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 46, 127–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekes, T.C.; Cawley, M.F.; Fegan, D.J.; Gibbs, K.G.; Hillas, A.M.; Kowk, P.W.; Lamb, R.C.; Lewis, D.A.; Macomb, D.; Porter, N.A.; et al. Observation of TeV Gamma Rays from the Crab Nebula Using the Atmospheric Cerenkov Imaging Technique. Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, S.; Catalano, O.; Scuderi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Pareschi, G.; Antolini, E.; Arrabito, L.; Bellassai, G.; Bernlöhr, K.; Bigongiari, C.; et al. First detection of the Crab Nebula at TeV energies with a Cherenkov telescope in a dual-mirror Schwarzschild-Couder configuration: The ASTRI-Horn telescope. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 634, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Abe, K.; Abe, S.; Aguasca-Cabot, A.; Agudo, I.; Alvarez Crespo, N.; Antonelli, L.A.; Aramo, C.; Arbet-Engels, A.; Arcaro, C.; et al. Observations of the Crab Nebula and Pulsar with the Large-sized Telescope Prototype of the Cherenkov Telescope Array. Astrophys. J. 2023, 956, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysekara, A.U.; Albert, A.; Alfaro, R.; Alvarez, C.; Álvarez, J.D.; Camacho, J.R.A.; Arceo, R.; Arteaga-Velázquez, J.C.; Arunbabu, K.P.; Avila Rojas, D.; et al. Measurement of the Crab Nebula Spectrum Past 100 TeV with HAWC. Astrophys. J. 2019, 881, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; An, Q.; Axikegu; Bai, L.X.; Bai, Y.X.; Bao, Y.W.; Bastieri, D.; Bi, X.J.; Bi, Y.J.; Cai, H.; et al. Observation of the Crab Nebula with LHAASO-KM2A - a performance study. Chin. Phys. C 2021, 45, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scargle, J.D. Activity in the Crab Nebula. Astrophys. J. 1969, 156, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.J.; Scowen, P.A.; Sankrit, R.; Burrows, C.J.; Gallagher, J.S.; Holtzman, J.A.; Watson, A.; Trauger, J.T.; Ballester, G.E.; Casertano, S.; et al. WFPC2 Studies of the Crab Nebula. I. HST and ROSAT Imaging of the Synchrotron Nebula. Astrophys. J. 1995, 448, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.J.; Mori, K.; Burrows, D.; Gallagher, J.S.; Graham, J.R.; Halverson, M.; Kader, A.; Michel, F.C.; Scowen, P. Hubble Space Telescope and Chandra Monitoring of the Crab Synchrotron Nebula. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2002, 577, L49–L52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Hester, J.J.; Tennant, A.F.; Elsner, R.F.; Schulz, N.S.; Marshall, H.L.; Karovska, M.; Nichols, J.S.; Swartz, D.A.; Kolodziejczak, J.J.; et al. Discovery of Spatial and Spectral Structure in the X-ray Emission from the Crab Nebula. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 536, L81–L84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiveldinger, C.; Aschenbach, B. Temporal Variability of the X-ray Emission of the Crab Nebula Torus. Astrophys. J. 1999, 510, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.C.; Wheaton, W.A. Gamma-ray Spectra and Variability of the Crab Nebula Emission Observed by BATSE. Astrophys. J. 2003, 598, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Cherry, M.L.; Case, G.L.; Baumgartner, W.H.; Beklen, E.; Narayana Bhat, P.; Briggs, M.S.; Camero-Arranz, A.; Chaplin, V.; Connaughton, V.; et al. When a Standard Candle Flickers. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 727, L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Horns, D.; Zechlin, H.S. The Crab Nebula as a standard candle in very high-energy astrophysics. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 523, A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Striani, E.; Bulgarelli, A.; Gianotti, F.; Trifoglio, M.; Pittori, C.; Verrecchia, F.; Argan, A.; Trois, A.; de Paris, G.; et al. AGILE detection of enhanced gamma-ray emission from the Crab Nebula region. Astron. Telegr. 2010, 2855, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tavani, M.; Bulgarelli, A.; Vittorini, V.; Pellizzoni, A.; Striani, E.; Caraveo, P.; Weisskopf, M.C.; Tennant, A.; Pucella, G.; Trois, A.; et al. Discovery of Powerful Gamma-ray Flares from the Crab Nebula. Science 2011, 331, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, R.; D’Ammando, F.; Hays, E. Fermi LAT confirmation of enhanced gamma-ray emission from the Crab Nebula region. Astron. Telegr. 2010, 2861, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Striani, E.; Tavani, M.; Vittorini, V.; Donnarumma, I.; Giuliani, A.; Pucella, G.; Argan, A.; Bulgarelli, A.; Colafrancesco, S.; Cardillo, M.; et al. Variable Gamma-ray Emission from the Crab Nebula: Short Flares and Long “Waves”. Astrophys. J. 2013, 765, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittorini, V.; Tavani, M.; Pucella, G.; Striani, E.; Donnarumma, I.; Caraveo, P.; Giuliani, A.; Mereghetti, S.; Pellizzoni, A.; Trois, A.; et al. Spectral Evolution of the 2010 September Gamma-ray Flare from the Crab Nebula. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 732, L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharje, Y. Crab That Roared. Science 2013, 341, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittori, C.; Verrecchia, F.; Chen, A.W.; Bulgarelli, A.; Pellizzoni, A.; Giuliani, A.; Vercellone, S.; Longo, F.; Tavani, M.; Giommi, P.; et al. First AGILE catalog of high-confidence gamma-ray sources. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 506, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, R.; Scargle, J.D.; Blandford, R.D.; Baldini, L.; Baring, M.G.; Belfiore, A.; Charles, E.; Chiang, J.; D’Ammando, F.; Dermer, C.D.; et al. Gamma-ray Activity in the Crab Nebula: The Exceptional Flare of 2011 April. Astrophys. J. 2012, 749, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, P.K.H.; Horns, D. Fermi Large Area Telescope observations of the fast-dimming Crab Nebula in 60-600 MeV. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 638, A147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, E.; Olmi, B. The Crab Pulsar and Nebula as Seen in Gamma-rays. Universe 2021, 7, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.; Eichler, D. Particle acceleration at astrophysical shocks: A theory of cosmic ray origin. Phys. Rep. 1987, 154, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkov, M.A.; Drury, L.O. Nonlinear theory of diffusive acceleration of particles by shock waves. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2001, 64, 429–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, S.P. Supernova remnants at high energy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 46, 89–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Aye, K.M.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Berghaus, P.; Bernlöhr, K.; Bolz, O.; et al. High-energy particle acceleration in the shell of a supernova remnant. Nature 2004, 432, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; Borrel, V.; et al. Primary particle acceleration above 100 TeV in the shell-type supernova remnant <ASTROBJ>RX J1713.7-3946</ASTROBJ> with deep HESS observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 464, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; Borrel, V.; et al. H.E.S.S. Observations of the Supernova Remnant RX J0852.0-4622: Shell-Type Morphology and Spectrum of a Widely Extended Very High Energy Gamma-ray Source. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dermer, C.D.; Powale, G. Gamma rays from cosmic rays in supernova remnants. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, G.; Aharonian, F. Probing the galactic cosmic-ray density with current and future γ-ray instruments. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 659, A57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, A.; Fukui, Y. Physical properties of molecular clouds as revealed by NANTEN CO survey: From the galactic center to the galactic warp. In Proceedings of the 5th Boston University Astrophysics Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 15–17 June 2003; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Behera, B.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; et al. Discovery of very high energy gamma-ray emission coincident with molecular clouds in the W 28 (G6.4-0.1) field. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 481, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, A.; Tavani, M.; Bulgarelli, A.; Striani, E.; Sabatini, S.; Cardillo, M.; Fukui, Y.; Kawamura, A.; Ohama, A.; Furukawa, N.; et al. AGILE detection of GeV γ-ray emission from the SNR W28. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 516, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, A.; Chen, A.; Mereghetti, S.; Pellizzoni, A.; Tavani, M.; Vercellone, S. Gamma-ray emission from the Galaxy: A new model for AGILE. Mem. Della Soc. Astron. Ital. Suppl. 2004, 5, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, A.; Cardillo, M.; Tavani, M.; Fukui, Y.; Yoshiike, S.; Torii, K.; Dubner, G.; Castelletti, G.; Barbiellini, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. Neutral Pion Emission from Accelerated Protons in the Supernova Remnant W44. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 742, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, M.; Tavani, M.; Giuliani, A.; Yoshiike, S.; Sano, H.; Fukuda, T.; Fukui, Y.; Castelletti, G.; Dubner, G. The supernova remnant W44: Confirmations and challenges for cosmic-ray acceleration. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 565, A74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelletti, G.; Dubner, G.; Brogan, C.; Kassim, N.E. The low-frequency radio emission and spectrum of the extended SNR <ASTROBJ>W44</ASTROBJ>: New VLA observations at 74 and 324 MHz. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 471, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.H.; Akerlof, C.W.; Carter-Lewis, D.A.; Catanese, M.; Cawley, M.F.; Connaughton, V.; Fegan, D.J.; Finley, J.P.; Gaidos, J.A.; Hillas, A.M.; et al. Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from TeV gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 329, 639–658. [Google Scholar]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Beilicke, M.; Bernloehr, K.; Bojahr, H.; Bolz, O.; Boerst, H.; Coarasa, T.; Contreras, J.L.; Cortina, J.; et al. A search for TeV gamma-ray emission from SNRs, pulsars and unidentified GeV sources in the Galactic plane in the longitude range between -2 deg and 85 deg. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 395, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Allen, B.T.; Aune, T.; Berley, D.; Chen, C.; Christopher, G.E.; DeYoung, T.; Dingus, B.L.; Ellsworth, R.W.; Gonzalez, M.M.; et al. Milagro Observations of Multi-TeV Emission from Galactic Sources in the Fermi Bright Source List. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 700, L127–L131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Giuliani, A.; Chen, A.W.; Argan, A.; Barbiellini, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; Caraveo, P.; Cattaneo, P.W.; Cocco, V.; Contessi, T.; et al. Direct Evidence for Hadronic Cosmic-ray Acceleration in the Supernova Remnant IC 443. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 710, L151–L155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Pittori, C.; Chen, A.W.; Bulgarelli, A.; Tavani, M.; Lucarelli, F.; Giommi, P.; Vercellone, S.; Pellizzoni, A.; Giuliani, A.; et al. An updated list of AGILE bright γ-ray sources and their variability in pointing mode. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, A.; Fioretti, V.; Parmiggiani, N.; Verrecchia, F.; Pittori, C.; Lucarelli, F.; Tavani, M.; Aboudan, A.; Cardillo, M.; Giuliani, A.; et al. Second AGILE catalogue of gamma-ray sources. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 627, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, S.; Tavani, M.; Striani, E.; Bulgarelli, A.; Vittorini, V.; Piano, G.; Del Monte, E.; Feroci, M.; de Pasquale, F.; Trifoglio, M.; et al. Episodic Transient Gamma-ray Emission from the Microquasar Cygnus X-1. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 712, L10–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, S.; Tavani, M.; Coppi, P.; Pooley, G.; Del Santo, M.; Campana, R.; Chen, A.; Evangelista, Y.; Piano, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. Gamma-ray Observations of Cygnus X-1 above 100 MeV in the Hard and Soft States. Astrophys. J. 2013, 766, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Bulgarelli, A.; Piano, G.; Sabatini, S.; Striani, E.; Evangelista, Y.; Trois, A.; Pooley, G.; Trushkin, S.; Nizhelskij, N.A.; et al. Extreme particle acceleration in the microquasar CygnusX-3. Nature 2009, 462, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgarelli, A.; Tavani, M.; Chen, A.W.; Evangelista, Y.; Trifoglio, M.; Gianotti, F.; Piano, G.; Sabatini, S.; Striani, E.; Pooley, G.; et al. AGILE detection of Cygnus X-3 γ-ray active states during the period mid-2009/mid-2010. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, A63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, G.; Tavani, M.; Vittorini, V.; Trois, A.; Giuliani, A.; Bulgarelli, A.; Evangelista, Y.; Coppi, P.; Del Monte, E.; Sabatini, S.; et al. The AGILE monitoring of Cygnus X-3: Transient gamma-ray emission and spectral constraints. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 545, A110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koljonen, K.I.I.; Maccarone, T.; McCollough, M.L.; Gurwell, M.; Trushkin, S.A.; Pooley, G.G.; Piano, G.; Tavani, M. The hypersoft state of Cygnus X-3. A key to jet quenching in X-ray binaries? Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 612, A27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, G.; Munar-Adrover, P.; Verrecchia, F.; Tavani, M.; Trushkin, S.A. High-energy Gamma-ray Activity from V404 Cygni Detected by AGILE during the 2015 June Outburst. Astrophys. J. 2017, 839, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares, J.; Negueruela, I.; Ribó, M.; Ribas, I.; Paredes, J.M.; Herrero, A.; Simón-Díaz, S. A Be-type star with a black-hole companion. Nature 2014, 505, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. E. S. S. Collaboration; Abdalla, H.; Abramowski, A.; Aharonian, F.; Ait Benkhali, F.; Angüner, E.O.; Arakawa, M.; Arrieta, M.; Aubert, P.; Backes, M.; et al. The H.E.S.S. Galactic plane survey. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 612, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Aharonian, F.; An, Q.; Axikegu.; Bai, Y.X.; Bao, Y.W.; Bastieri, D.; Bi, X.J.; Bi, Y.J.; Cai, J.T.; et al. The First LHAASO Catalog of Gamma-ray Sources. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, F.; Verrecchia, F.; Striani, E.; Pittori, C.; Tavani, M.; Vercellone, S.; Bulgarelli, A.; Gianotti, F.; Trifoglio, M.; Chen, A.; et al. AGILE detection of the new unidentified gamma-ray source AGL J2241+4454. Astron. Telegr. 2010, 2761, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, R.C.; Bertsch, D.L.; Dingus, B.L.; Fichtel, C.E.; Hunter, S.D.; Kanbach, G.; Kniffen, D.A.; Lin, Y.C.; Mattox, J.R.; Mayer-Hasselwander, H.A.; et al. EGRET Detection of High-Energy Gamma Radiation from the OVV Quasar 3C 454.3. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1993, 407, L41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, M.F.; Marscher, A.P.; Hartman, R.C.; Aller, H.D.; Aller, M.C.; Balonek, T.J.; Begelman, M.C.; Chiaberge, M.; Clements, S.D.; Collmar, W.; et al. Radio to γ-ray observations of 3C 454.3:1993-1995. In Proceedings of the Fourth Compton Symposium, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 27–30 April 1997; pp. 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, P.; Blustin, A.J.; Capalbi, M.; Colafrancesco, S.; Cucchiara, A.; Fuhrmann, L.; Krimm, H.A.; Marchili, N.; Massaro, E.; Perri, M.; et al. Swift and infra-red observations of the blazar 3C 454.3 during the giant X-ray flare of May 2005. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 456, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villata, M.; Raiteri, C.M.; Balonek, T.J.; Aller, M.F.; Jorstad, S.G.; Kurtanidze, O.M.; Nicastro, F.; Nilsson, K.; Aller, H.D.; Arai, A.; et al. The unprecedented optical outburst of the quasar <ASTROBJ>3C 454.3</ASTROBJ>. The WEBT campaign of 2004-2005. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 453, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, E.; Foschini, L.; Beckmann, V.; Soldi, S.; Türler, M.; Gehrels, N.; Ghisellini, G.; Giommi, P.; Maraschi, L.; Pursimo, T.; et al. INTEGRAL observations of the blazar 3C 454.3 in outburst. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 449, L21–L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vercellone, S.; Chen, A.W.; Giuliani, A.; Bulgarelli, A.; Donnarumma, I.; Lapshov, I.; Tavani, M.; Argan, A.; Barbiellini, G.; Caraveo, P.; et al. AGILE Detection of a Strong Gamma-ray Flare from the Blazar 3C 454.3. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 676, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellone, S.; D’Ammando, F.; Vittorini, V.; Donnarumma, I.; Pucella, G.; Tavani, M.; Ferrari, A.; Raiteri, C.M.; Villata, M.; Romano, P.; et al. Multiwavelength Observations of 3C 454.3. III. Eighteen Months of Agile Monitoring of the “Crazy Diamond”. Astrophys. J. 2010, 712, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellone, S.; Striani, E.; Vittorini, V.; Donnarumma, I.; Pacciani, L.; Pucella, G.; Tavani, M.; Raiteri, C.M.; Villata, M.; Romano, P.; et al. The Brightest Gamma-ray Flaring Blazar in the Sky: AGILE and Multi-wavelength Observations of 3C 454.3 During 2010 November. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 736, L38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellone, S.; Chen, A.W.; Vittorini, V.; Giuliani, A.; D’Ammando, F.; Tavani, M.; Donnarumma, I.; Pucella, G.; Raiteri, C.M.; Villata, M.; et al. Multiwavelength Observations of 3C 454.3. I. The AGILE 2007 November campaign on the “Crazy Diamond”. Astrophys. J. 2009, 690, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnarumma, I.; Pucella, G.; Vittorini, V.; D’Ammando, F.; Vercellone, S.; Raiteri, C.M.; Villata, M.; Perri, M.; Chen, W.P.; Smart, R.L.; et al. Multiwavelength Observations of 3C 454.3. II. The AGILE 2007 December Campaign. Astrophys. J. 2009, 707, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacciani, L.; Vittorini, V.; Tavani, M.; Fiocchi, M.T.; Vercellone, S.; D’Ammando, F.; Sakamoto, T.; Pian, E.; Raiteri, C.M.; Villata, M.; et al. The 2009 December Gamma-ray Flare of 3C 454.3: The Multifrequency Campaign. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 716, L170–L175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striani, E.; Vercellone, S.; Tavani, M.; Vittorini, V.; D’Ammando, F.; Donnarumma, I.; Pacciani, L.; Pucella, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; Trifoglio, M.; et al. The Extraordinary Gamma-ray Flare of the Blazar 3C 454.3. Astrophys. J. 2010, 718, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittorini, V.; Tavani, M.; Cavaliere, A.; Striani, E.; Vercellone, S. The Blob Crashes into the Mirror: Modeling the Exceptional γ-ray Flaring Activity of 3C 454.3 in 2010 November. Astrophys. J. 2014, 793, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tagliaferri, G.; Foschini, L.; Ghirlanda, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Della Ceca, R.; Haardt, F.; Volonteri, M.; Gehrels, N. High-redshift Fermi blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 411, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foschini, L.; Lister, M.L.; Andernach, H.; Ciroi, S.; Marziani, P.; Antón, S.; Berton, M.; Dalla Bontà, E.; Järvelä, E.; Marchã, M.J.M.; et al. A New Sample of Gamma-ray Emitting Jetted Active Galactic Nuclei. Universe 2022, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.; Acero, F.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; et al. Fermi Large Area Telescope Fourth Source Catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2020, 247, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellone, S.; Romano, P.; Piano, G.; Vittorini, V.; Donnarumma, I.; Munar-Adrover, P.; Raiteri, C.M.; Villata, M.; Verrecchia, F.; Lucarelli, F.; et al. AGILE, Fermi, Swift, and GASP/WEBT multi-wavelength observations of the high-redshift blazar 4C +71.07 in outburst. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 621, A82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrels, N.; Chincarini, G.; Giommi, P.; Mason, K.O.; Nousek, J.A.; Wells, A.A.; White, N.E.; Barthelmy, S.D.; Burrows, D.N.; Cominsky, L.R.; et al. The Swift Gamma-ray Burst Mission. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, D.N.; Hill, J.E.; Nousek, J.A.; Kennea, J.A.; Wells, A.; Osborne, J.P.; Abbey, A.F.; Beardmore, A.; Mukerjee, K.; Short, A.D.T.; et al. The Swift X-ray Telescope. Space Sci. Rev. 2005, 120, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roming, P.W.A.; Kennedy, T.E.; Mason, K.O.; Nousek, J.A.; Ahr, L.; Bingham, R.E.; Broos, P.S.; Carter, M.J.; Hancock, B.K.; Huckle, H.E.; et al. The Swift Ultra-Violet/Optical Telescope. Space Sci. Rev. 2005, 120, 95–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villata, M.; Raiteri, C.M.; Larionov, V.M.; Kurtanidze, O.M.; Nilsson, K.; Aller, M.F.; Tornikoski, M.; Volvach, A.; Aller, H.D.; Arkharov, A.A.; et al. Multifrequency monitoring of the blazar <ASTROBJ>0716+714</ASTROBJ> during the GASP-WEBT-AGILE campaign of 2007. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 481, L79–L82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnarumma, I.; De Rosa, A.; Vittorini, V.; Miller, H.R.; Popović, L.Č.; Simić, S.; Tavani, M.; Eggen, J.; Maune, J.; Kuulkers, E.; et al. The Remarkable γ-ray Activity in the Gravitationally Lensed Blazar PKS 1830-211. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 736, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellone, S.; Donnarumma, I.; Pittori, C.; Capitanio, F.; De Rosa, A.; Di Gesu, L.; Kiehlmann, S.; Iacolina, M.N.; Pellizzoni, P.A.; Egron, E.; et al. Multiwavelength observations of the lensed quasar PKS 1830-211 during the 2019 γ-ray flare. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 5717–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rosa, A.; Piro, L.; Tramacere, A.; Massaro, E.; Walter, R.; Bassani, L.; Malizia, A.; Bird, A.J.; Dean, A.J. The broad-band X-ray spectrum of the blazar PKS B1830-211 by Chandra and INTEGRAL. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 438, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferri, G.; Ghisellini, G.; Perri, M.; Hayashida, M.; Baloković, M.; Covino, S.; Giommi, P.; Madejski, G.M.; Puccetti, S.; Sbarrato, T.; et al. NuSTAR and Multifrequency Study of the Two High-redshift Blazars S5 0836+710 and PKS 2149-306. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Jin, C.; Garrett, M.A. Helical jet in the gravitationally lensed blazar PKS1830-211. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 362, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Vittorini, V.; Cavaliere, A. An Emerging Class of Gamma-ray Flares from Blazars: Beyond One-zone Models. Astrophys. J. 2015, 814, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittorini, V.; Tavani, M.; Cavaliere, A. Meeting the Challenge from Bright and Fast Gamma-ray Flares of 3C 279. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 843, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araudo, A.T.; Bosch-Ramon, V.; Romero, G.E. Gamma rays from cloud penetration at the base of AGN jets. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 522, A97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamante, L.; Ghisellini, G. TeV candidate BL Lac objects. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 384, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamante, L. TeV-peaked candidate BL Lac objects. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 2771–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punch, M.; Akerlof, C.W.; Cawley, M.F.; Chantell, M.; Fegan, D.J.; Fennell, S.; Gaidos, J.A.; Hagan, J.; Hillas, A.M.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Detection of TeV photons from the active galaxy Markarian 421. Nature 1992, 358, 477–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.; Akerlof, C.W.; Biller, S.; Buckley, J.; Carter-Lewis, D.A.; Cawley, M.F.; Catanese, M.; Connaughton, V.; Fegan, D.J.; Finley, J.P.; et al. Detection of Gamma Rays with E > 300 GeV from Markarian 501. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1996, 456, L83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, J.; CTAO LST Collaboration. First detection of VHE gamma-ray emission from FSRQ OP 313 with LST-1. Astron. Telegr. 2023, 16381, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wakely, S.P.; Horan, D. TeVCat: An online catalog for Very High Energy Gamma-ray Astronomy. Int. Cosm. Ray Conf. 2008, 3, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Rappoldi, A.; Lucarelli, F.; Pittori, C.; Longo, F.; Cattaneo, P.W.; Verrecchia, F.; Tavani, M.; Bulgarelli, A.; Chen, A.W.; Colafrancesco, S.; et al. Search of MeV-GeV counterparts of TeV sources with AGILE in pointing mode. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 587, A93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, A.; Chen, A.W.; Tavani, M.; Gianotti, F.; Trifoglio, M.; Contessi, T. Evaluating the maximum likelihood method for detecting short-term variability of AGILE γ-ray sources. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 540, A79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Gasparrini, D.; Cutini, S.; Preger, B.; Pittori, C.; Colafrancesco, S.; Giommi, P.; Vercellone, S.; Chen, A.; Giuliani, A.; et al. AGILE detection of the blazar W Comae in the gamma-ray energy band. Astron. Telegr. 2008, 1582, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Swordy, S. TeV Outburst from W Comae. Astron. Telegr. 2008, 1565, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Swordy, S. VERITAS discovers TeV gamma rays from W Comae. Astron. Telegr. 2008, 1422, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Acciari, V.A.; Aliu, E.; Aune, T.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Böttcher, M.; Boltuch, D.; Buckley, J.H.; Bradbury, S.M.; Bugaev, V.; et al. Multiwavelength Observations of a TeV-Flare from W Comae. Astrophys. J. 2009, 707, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Del Monte, E.; Donnarumma, I.; Evangelista, Y.; Feroci, M.; Lapshov, I.; Lazzarotto, F.; Pacciani, L.; Rapisarda, M.; Soffitta, P.; et al. SuperAGILE detects enhanced hard X-ray emission from Mkn 421. Astron. Telegr. 2008, 1574, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pittori, C.; Cutini, S.; Gasparrini, D.; Verrecchia, F.; Colafrancesco, S.; Giommi, P.; Vercellone, S.; Chen, A.; Giuliani, A.; Donnarumma, I.; et al. AGILE detection of the blazar Mrk 421. Astron. Telegr. 2008, 1583, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Donnarumma, I.; Vittorini, V.; Vercellone, S.; del Monte, E.; Feroci, M.; D’Ammando, F.; Pacciani, L.; Chen, A.W.; Tavani, M.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. The June 2008 Flare of Markarian 421 from Optical to TeV Energies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 691, L13–L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villata, M.; Raiteri, C.M. Helical jets in blazars. I. The case of MKN 501. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 347, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Villata, M.; Raiteri, C.M.; Kurtanidze, O.M.; Nikolashvili, M.G.; Ibrahimov, M.A.; Papadakis, I.E.; Tosti, G.; Hroch, F.; Takalo, L.O.; Sillanpää, A.; et al. The WEBT <ASTROBJ>BL Lacertae</ASTROBJ> Campaign 2001 and its extension. Optical light curves and colour analysis 1994-2002. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 421, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelmy, S.D.; Barbier, L.M.; Cummings, J.R.; Fenimore, E.E.; Gehrels, N.; Hullinger, D.; Krimm, H.A.; Markwardt, C.B.; Palmer, D.M.; Parsons, A.; et al. The Burst Alert Telescope (BAT) on the SWIFT Midex Mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2005, 120, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmiggiani, N.; Bulgarelli, A.; Ursi, A.; Addis, A.; Baroncelli, L.; Fioretti, V.; Di Piano, A.; Panebianco, G.; Tavani, M.; Pittori, C.; et al. The AGILE real-time analysis software system to detect short-transient events in the multi-messenger era. Astron. Comput. 2023, 44, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, A.; Mereghetti, S.; Fornari, F.; Del Monte, E.; Feroci, M.; Marisaldi, M.; Esposito, P.; Perotti, F.; Tavani, M.; Argan, A.; et al. AGILE detection of delayed gamma-ray emission from GRB 080514B. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 491, L25–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ajello, M.; Arimoto, M.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bellazzini, R.; Bhat, P.N.; Bissaldi, E.; Blandford, R.D.; et al. A Decade of Gamma-ray Bursts Observed by Fermi-LAT: The Second GRB Catalog. Astrophys. J. 2019, 878, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodei, N. Fermi-LAT observation of GRB 081024B. GRB Coord. Netw. 2008, 8407, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Connaughton, V.; Briggs, M. GRB 081024B: Fermi gamma-ray burst monitor detection. GRB Coord. Netw. 2008, 8408, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, A.; Fuschino, F.; Vianello, G.; Marisaldi, M.; Mereghetti, S.; Tavani, M.; Cutini, S.; Barbiellini, G.; Longo, F.; Moretti, E.; et al. AGILE Detection of Delayed Gamma-ray Emission From the Short Gamma-ray Burst GRB 090510. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 708, L84–L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Asano, K.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Baring, M.G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; et al. Fermi Observations of GRB 090510: A Short-Hard Gamma-ray Burst with an Additional, Hard Power-law Component from 10 keV TO GeV Energies. Astrophys. J. 2010, 716, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Albert, A.; Anderson, B.; Arimoto, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; et al. Fermi-LAT Observations of the LIGO Event GW150914. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 823, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Pittori, C.; Verrecchia, F.; Bulgarelli, A.; Giuliani, A.; Donnarumma, I.; Argan, A.; Trois, A.; Lucarelli, F.; Marisaldi, M.; et al. AGILE Observations of the Gravitational-wave Event GW150914. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 825, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAGIC Collaboration; Acciari, V.A.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Engels, A.A.; Baack, D.; Babić, A.; Banerjee, B.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Barrio, J.A.; et al. Observation of inverse Compton emission from a long γ-ray burst. Nature 2019, 575, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursi, A.; Tavani, M.; Frederiks, D.D.; Romani, M.; Verrecchia, F.; Marisaldi, M.; Aptekar, R.L.; Antonelli, L.A.; Argan, A.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. AGILE and Konus-Wind Observations of GRB 190114C: The Remarkable Prompt and Early Afterglow Phases. Astrophys. J. 2020, 904, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Piano, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; Foffano, L.; Ursi, A.; Verrecchia, F.; Pittori, C.; Casentini, C.; Giuliani, A.; Longo, F.; et al. AGILE Gamma-ray Detection of the Exceptional GRB 221009A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 956, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Aharonian, F.; An, Q.; Axikegu; Bai, Y.X.; Bao, Y.W.; Bastieri, D.; Bi, X.J.; Bi, Y.J.; Cai, J.T.; et al. Very high-energy gamma-ray emission beyond 10 TeV from GRB 221009A. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigliano, A.; Longo, F. Gamma-ray Bursts: 50 Years and Counting! Universe 2024, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Tavani, M.; Ursi, A.; Argan, A.; Pittori, C.; Donnarumma, I.; Bulgarelli, A.; Fuschino, F.; Labanti, C.; Marisaldi, M.; et al. AGILE Observations of the Gravitational-wave Source GW170104. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 847, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Tavani, M.; Donnarumma, I.; Bulgarelli, A.; Evangelista, Y.; Pacciani, L.; Ursi, A.; Piano, G.; Pilia, M.; Cardillo, M.; et al. AGILE Observations of the Gravitational-wave Source GW170817: Constraining Gamma-ray Emission from an NS-NS Coalescence. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursi, A.; Verrecchia, F.; Piano, G.; Casentini, C.; Tavani, M.; Bulgarelli, A.; Cardillo, M.; Longo, F.; Lucarelli, F.; Morselli, A.; et al. AGILE Observations of the LIGO-Virgo Gravitational-wave Events of the GWTC-1 Catalog. Astrophys. J. 2022, 924, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, F.; Pittori, C.; Verrecchia, F.; Donnarumma, I.; Tavani, M.; Bulgarelli, A.; Giuliani, A.; Antonelli, L.A.; Caraveo, P.; Cattaneo, P.W.; et al. AGILE Detection of a Candidate Gamma-ray Precursor to the ICECUBE-160731 Neutrino Event. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, F.; Tavani, M.; Piano, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; Donnarumma, I.; Verrecchia, F.; Pittori, C.; Antonelli, L.A.; Argan, A.; Barbiellini, G.; et al. AGILE Detection of Gamma-ray Sources Coincident with Cosmic Neutrino Events. Astrophys. J. 2019, 870, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration; Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; et al. Multimessenger observations of a flaring blazar coincident with high-energy neutrino IceCube-170922A. Science 2018, 361, eaat1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casentini, C.; Verrecchia, F.; Tavani, M.; Ursi, A.; Antonelli, L.A.; Argan, A.; Barbiellini, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; Caraveo, P.; Cardillo, M.; et al. AGILE Observations of Two Repeating Fast Radio Bursts with Low Intrinsic Dispersion Measures. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 890, L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Verrecchia, F.; Casentini, C.; Perri, M.; Ursi, A.; Pacciani, L.; Pittori, C.; Bulgarelli, A.; Piano, G.; Pilia, M.; et al. Gamma-ray and X-ray Observations of the Periodic-repeater FRB 180916 during Active Phases. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 893, L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilia, M.; Burgay, M.; Possenti, A.; Ridolfi, A.; Gajjar, V.; Corongiu, A.; Perrodin, D.; Bernardi, G.; Naldi, G.; Pupillo, G.; et al. The Lowest-frequency Fast Radio Bursts: Sardinia Radio Telescope Detection of the Periodic FRB 180916 at 328 MHz. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 896, L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Casentini, C.; Tavani, M.; Ursi, A.; Mereghetti, S.; Pilia, M.; Cardillo, M.; Addis, A.; Barbiellini, G.; Baroncelli, L.; et al. AGILE Observations of Fast Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2021, 915, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, M.; Casentini, C.; Ursi, A.; Verrecchia, F.; Addis, A.; Antonelli, L.A.; Argan, A.; Barbiellini, G.; Baroncelli, L.; Bernardi, G.; et al. An X-ray burst from a magnetar enlightening the mechanism of fast radio bursts. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroci, M.; Costa, E.; Del Monte, E.; Donnarumma, I.; Evangelista, Y.; Lapshov, I.; Lazzarotto, F.; Pacciani, L.; Rapisarda, M.; Soffitta, P.; et al. Monitoring the hard X-ray sky with SuperAGILE. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 510, A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, M.; Marisaldi, M.; Fuschino, F.; Labanti, C.; Argan, A.; Barbiellini, G.; Bulgarelli, A.; Cattaneo, P.W.; Colafrancesco, S.; Del Monte, E.; et al. AGILE mini-calorimeter gamma-ray burst catalog. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marisaldi, M.; Fuschino, F.; Tavani, M.; Dietrich, S.; Price, C.; Galli, M.; Pittori, C.; Verrecchia, F.; Mereghetti, S.; Cattaneo, P.W.; et al. Properties of terrestrial gamma ray flashes detected by AGILE MCAL below 30 MeV. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 1337–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marisaldi, M.; Argan, A.; Ursi, A.; Gjesteland, T.; Fuschino, F.; Labanti, C.; Galli, M.; Tavani, M.; Pittori, C.; Verrecchia, F.; et al. Enhanced detection of terrestrial gamma-ray flashes by AGILE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9481–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marisaldi, M.; Galli, M.; Labanti, C.; Østgaard, N.; Sarria, D.; Cummer, S.A.; Lyu, F.; Lindanger, A.; Campana, R.; Ursi, A.; et al. On the High-Energy Spectral Component and Fine Time Structure of Terrestrial Gamma Ray Flashes. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 7484–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursi, A.; Romani, M.; Verrecchia, F.; Pittori, C.; Tavani, M.; Marisaldi, M.; Galli, M.; Labanti, C.; Parmiggiani, N.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. The Second AGILE MCAL Gamma-ray Burst Catalog: 13 yr of Observations. Astrophys. J. 2022, 925, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursi, A.; Parmiggiani, N.; Messerotti, M.; Pellizzoni, A.; Pittori, C.; Longo, F.; Verrecchia, F.; Argan, A.; Bulgarelli, A.; Tavani, M.; et al. The First AGILE Solar Flare Catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2023, 267, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Tatischeff, V.; Tavani, M.; Oberlack, U.; Grenier, I.; Hanlon, L.; Walter, R.; Argan, A.; von Ballmoos, P.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. The e-ASTROGAM mission. Exploring the extreme Universe with gamma rays in the MeV-GeV range. Exp. Astron. 2017, 44, 25–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Tatischeff, V.; Argan, A.; Brandt, S.; Bulgarelli, A.; Bykov, A.; Costantini, E.; Silva, R.C.d.; Grenier, I.A.; Hanlon, L.; et al. Gamma-ray astrophysics in the MeV range. Exp. Astron. 2021, 51, 1225–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomsick, J.A.; Boggs, S.E.; Zoglauer, A.; Hartmann, D.; Ajello, M.; Burns, E.; Fryer, C.; Karwin, C.; Kierans, C.; Lowell, A.; et al. The Compton Spectrometer and Imager. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.12362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).