Abstract
Femtoscopy is a unique tool to investigate the space-time geometry of the matter created in ultra-relativistic collisions. If the probability density distribution of hadron emission is parametrized, then the dependence of its parameters on particle momentum, collision energy, and collision geometry can be given. In recent years, several measurements came to light that indicated the adequacy of assuming a Lévy-stable shape for the mentioned distribution. In parallel, several new phenomenological developments appeared, aiding the interpretation of the experimental results or providing tools for the measurements. In this paper, we discuss important aspects of femtoscopy with Lévy sources in light of some of these advances, including phenomenological and experimental ones.
1. Introduction
In high-energy physics, femtoscopy [1,2] is the most important way to gain information about the space-time geometry of the particle-emitting source (the probability density of particle creation in an infinitesimal interval in phase-space). Historically, the phenomenon on which this technique is based was discovered by R. Hanbury Brown and R. Q. Twiss in astronomy in two-photon correlations [3]. Hence, measurements in this field are often labeled “HBT-correlations”. Independently, G. Goldhaber and collaborators investigated proton–proton collisions and observed the correlations of identical pions [4]. Our current understanding suggests that both phenomena are based on the wave-like nature of light and pions, or alternatively (starting from the quantum nature of particle detection) on the Bose–Einstein symmetrization of pair wavefunctions. See, for example, the introduction of Refs. [5,6] for details.
Two-particle momentum correlations (or Bose–Einstein correlations) are defined as
where and are the momenta of the two particles, is the invariant pair-momentum distribution, while and are the invariant momentum distributions of the particles 1 and 2 (for identical particles, these distributions are of course also identical). In general, there are several reasons for correlated particle production (i.e., ): for example, collective flow, jets, resonance decay, and conservation laws. In the case of high-multiplicity heavy-ion collisions, the main source of correlations is the HBT effect mentioned above, and they appear mostly at small relative momenta, where , or if one introduces and , the criterion may be given. It turns out that in the absence of final-state interactions and multiparticle-correlations, a simple relation can be established [7,8,9] between the measured momentum correlation and the spatial pair-distribution (or pair source) (indicating the probability density of creating a pair in an infinitesimal interval around distance r and mean momentum K), given as
where denotes the Fourier-transform of the pair source in its first variable (see a comprehensive overview of this result in Ref. [8]). It is characteristic to sources in heavy-ion collisions that the dependence of and, hence, of on K is smoother than on q; this property is often called the “smoothness approximation” [2]. One may furthermore note that several phenomena may decrease the strength of the correlation functions: decays of long-lived resonances [10], coherence [11], and quasi-random electromagnetic fields [12]. Taking these into account, the above equation is modified as
where is the correlation strength parameter in the core–halo model [10] identified with the squared fraction of primordial pions amongst all produced pions.
Suppose one aims to characterize the geometry of the (pair) source. In that case, one often assumes a parametrization of it, in such a way that the source shape is a parametric distribution as a function of r, and its parameters depend on the pair momentum K. A usual assumption (see e.g., [13]) is that of a Gaussian source, in which case
where is the momentum-dependent width of the source (here, a factor of 2 would appear in the denominator for the single-particle source, which then cancels from the pair source), which can also be called the HBT or femtoscopic size. This would lead to a correlation function of
This HBT radius is of high relevance in terms of the physics of the quark–gluon plasma, as (especially if measured in multiple dimensions) it sheds light on transverse expansion or details of the phase diagram, as indicated, e.g., in Refs. [14,15,16,17,18]. We note here that, usually instead of pair momentum K, pair transverse mass is defined (in units), where is the transverse component of K, and m is the mass of the particle being investigated.
Note finally that the above is true for non-interacting particles. However, even pions undergo electromagnetic final-state interactions. The effect of these is usually handled via the so-called Coulomb-correction [8]. At the same time, the strong interaction of pions is usually negligible [19], but is much more important for baryons and in case of non-identical correlations [20,21].
2. Basics of Femtoscopy with Lévy Sources
As mentioned above, a usual assumption for the shape of the (pair or single-particle) source is the Gaussian distribution. However, the observation of a long tail on the reconstructed source shape suggested [22,23] that for an adequate description, one can and should go beyond the Gaussian approximation. A plausible generalization is to utilize Lévy-stable distributions, as introduced in Ref. [24] and utilized, for example, in Ref. [6]. These appear when the conditions of the Central Limit Theorem are not met, particularly when the independent and identically distributed random variables (the sum of which we investigate) do not have a finite mean or variance. In this case, the Generalized Central Limit Theorem applies [25], and the limiting distributions are the so-called Lévy-stable distributions [26]. The spherically symmetric Lévy-stable distributions (or Lévy distributions for short) are defined as
where is the spatial vector, the variable of the distribution, and is the Lévy exponent, characterizing the shape of the distribution; the stability criterion (i.e., the limiting nature of the distribution) is met if . Furthermore, R is the spatial scale of the distribution, characterizing its size (even if the variance or root-mean-square is infinity) and corresponding to the HBT or femtoscopic radius in our case. Let us note here that if , then the distribution exhibits a power-law tail in , with . Its angle-averaged version behaves as , underlining the fact that these distributions have no finite variance for , and r has no finite mean for (clearly, the mean of is zero, due to spherical symmetry).
Several (competing) physical phenomena may cause the appearance of Lévy distributions in high-energy physics:
- Anomalous diffusion [27,28], or Lévy-flight, probably due to hadronic rescattering; if this happens in the hadronic stage, then an ordering of the Lévy exponent is expected as , due to the cross-section and, hence, mean free path of the given particle species [28].
- Jet fragmentation [29], where the fractal nature of the process creates the Lévy distribution; this may be a dominant effect in collisions [30].
- Second-order phase transitions [31], where the correlation length diverges near the critical point, and at the critical point, the spatial correlations exhibit a power-law tail with exponent ; this is one of the critical exponents, and its value is suggested to be [32] for the 3D Ising model, or for the random external field 3D Ising model [33]—QCD is expected to be in the same universality class as one of them [34,35].
- Resonance decays [9,28,36], where the power-law tail is generated by the set of resonances decaying into pions (or the given investigated particle species); this phenomenon is similar to the decay heat of used fuel rods in power plants, see Figure 1 of Ref. [37]. Note that the simulations of Refs. [9,36] indicate Lévy distributions in EPOS even before resonance decays; hence (at least in EPOS), these cannot be the only reason for the appearance of Lévy distributions.
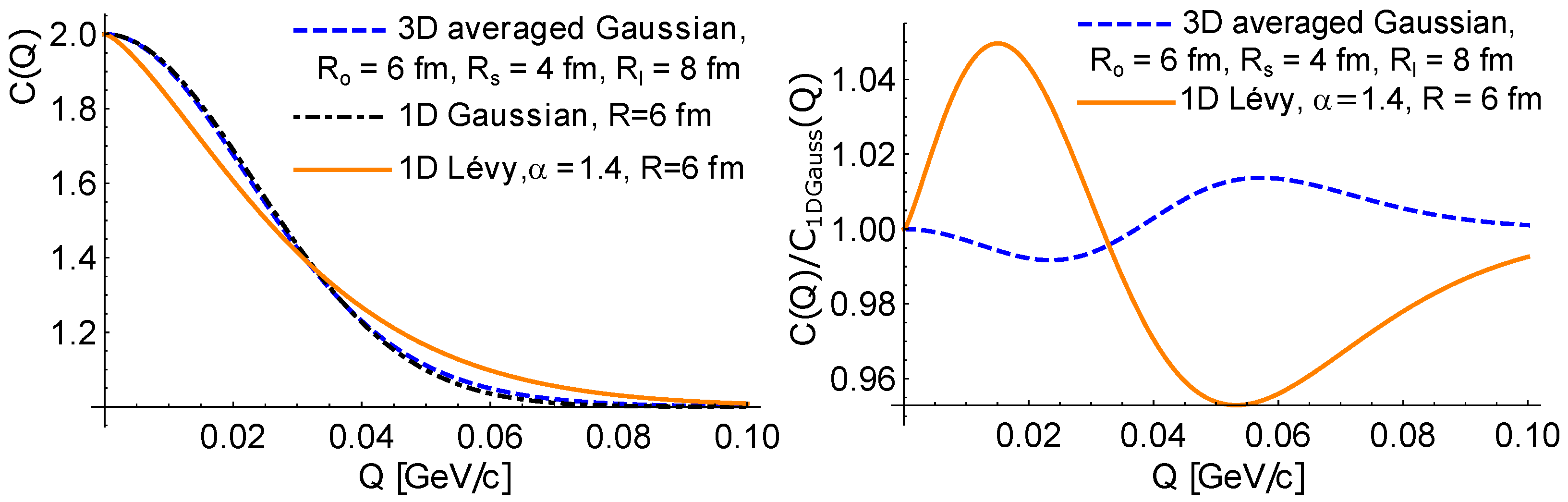
Further ideas have been promoted recently, for example, event averaging and angular averaging, see Refs. [38,39]. Note that in Refs. [9,36], source shapes from the EPOS model have been analyzed on an event-by-event basis, and Lévy distributions appeared in individual events as well. Note furthermore that while a non-spherical Gaussian source is clearly exhibiting a non-Gaussian shape when measured in an angle-averaged fashion, a spherically symmetric Lévy distribution leads to quite different correlation functions, as illustrated in Figure 1. This shows that a 3D angle-averaged Gaussian (with radii fm, fm, and fm in the Bertsch–Pratt frame [40,41]) source leads to a non-Gaussian 1D correlation function. However, this apparent “non-Gaussianity” is distinctly different from a 1D (or spherically symmetric) correlation function based on a Lévy distribution. With respect to this, it shall also be noted that 3D HBT measurements in the longitudinally comoving system (LCMS) have been performed in PHENIX [42] and the resulting exponent appeared to be the same as the one from the 1D analysis at [6], indicating that it is not non-sphericality that causes the appearance of Lévy distributions. Note that a further difference between 1D and 3D analyses is that, in 1D, one cannot easily make the transformation from the LCMS to the pair rest frame, where the Coulomb correction is calculated (the two-particle Schrödinger equation is a good approximation to the given problem only in this frame, where the nonrelativistic formulas may be utilized). However, in Ref. [7], simple but adequate approximation formulas were found, particularly for the source radius to be used in the Coulomb correction calculation.
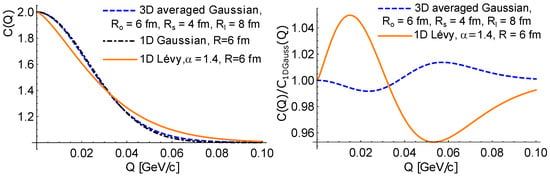
Figure 1.
The (left plot) shows correlation functions (equivalent to as denoted in the text) based on various source geometries: a 3D angle-averaged Gaussian with fm, fm, and fm, a spherically symmetric (‘1D’) Gaussian with fm, and an also spherically symmetric (‘1D’) Lévy with and fm. The (right plot) shows the ratio of the correlation functions based on a 3D Gaussian source and the spherically symmetric Lévy source, divided by the spherically symmetric Gaussian source.
3. Measures of the Source Extent
As discussed above, the source may exhibit various shapes, and even in the absence of a finite variance, one is interested in finding an “assumption-independent” measure of the source extent. One of these may be the half with at half maximum (HWHM), the distance (from the origin or center) where the probability density decreases to half of the maximal value (admitted at the origin or center usually). Another such measure may be the half width at half-integral, i.e., the radius of the region from where half of the particles are emitted. In the case of a Gaussian, the HWHM of the single-particle source can be readily calculated as
which is valid for both 1D and 3D Gaussian distributions with width R. The HWHI value for a 1D Gaussian is
while for the 3D Gaussian, it can be given implicitly in terms of solving
and the numerical value of the solution is
The above results can be understood for a Lévy distribution with . However, these values strongly depend on , as illustrated by Figure 2. This means that either HWHI or HWHM can change due to either of the following:
- A change in size (i.e., the scale);
- A change in shape.
This means that if one is interested in a size change, then one may not be able to access this by investigating any of the “assumption-independent” measures (note furthermore that in order to experimentally access either HWHI or HWHM, one may need to extrapolate to large sizes, a region not accessible even via the so-called imaging technique [22,43]), but one needs to investigate the shape as well. This statement, of course, depends on what one regards as “size”, but the above details underline the fact that any size measure may be entangled with the shape measure, and to extract size information, one may need to be able to quantify the shape of the source as well.
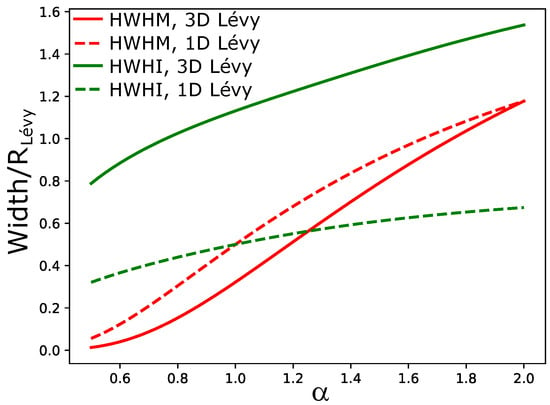
Figure 2.
Two “model-independent” source measures, scaled by the Lévy radius (): half width at half maximum (HWHM, red lines) and half width at half integral (HWHI, green lines) are shown, for 1D and 3D sources (dashed and solid lines, respectively), as a function of the Lévy-exponent .
Figure 2.
Two “model-independent” source measures, scaled by the Lévy radius (): half width at half maximum (HWHM, red lines) and half width at half integral (HWHI, green lines) are shown, for 1D and 3D sources (dashed and solid lines, respectively), as a function of the Lévy-exponent .
4. Signs of the Critical Point in Femtoscopy
As noted above, the Lévy exponent was identified in Ref. [31] with the critical exponent of spatial correlations, usually denoted by . It was furthermore suggested that, while far from the critical point, may be of a value close to 2, closer to the critical point, or it may decrease to the above-mentioned values, close to or below 0.5. This behavior may be blurred by finite size effects; however, Refs. [44,45] found that the correlation exponent is largely unchanged by finite size effects in the 3D Ising model and also in the random field 3D Ising model. This suggests that it is not a priori impossible to search for the critical point via the measurement of . Furthermore, discussed, e.g., in Ref. [14], femtoscopic radii may be interpreted as signaling the vicinity of the critical point. Finally, one may note that the HBT radii are also connected to the lifetime of the quark medium [46], which is also influenced by the equation of state of the medium. Hence, the collision energy dependence of HBT radii serves as an important tool to investigate the QCD phase diagram.
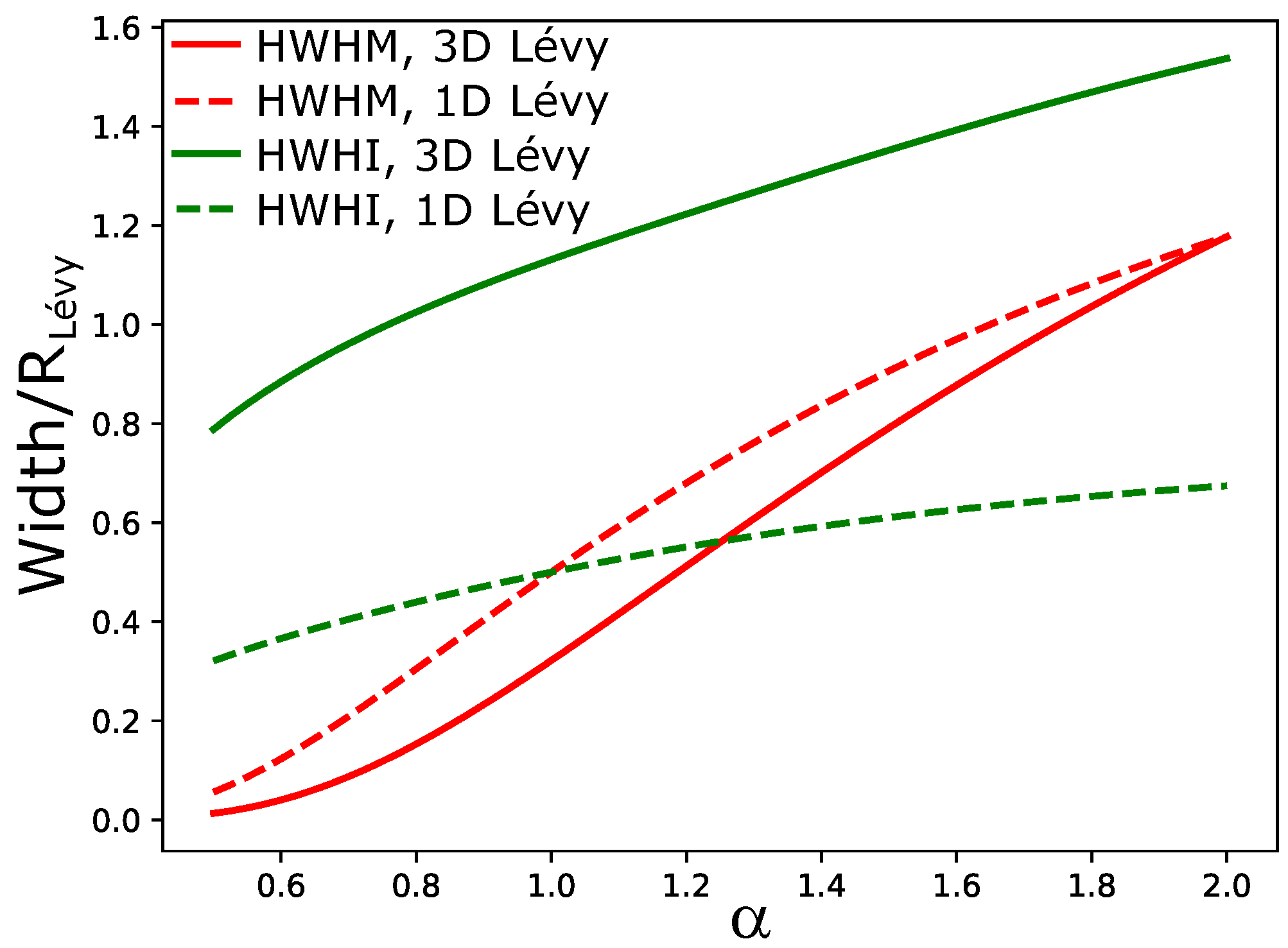
Let us now suppose a scenario where the Lévy scale exhibits a maximum near GeV, while the Lévy exponent has a minimum at the same location, as shown in Figure 3. The values depicted on this plot are purely hypothetical, assumed to take the value shown on the figure for illustration purposes. Let us then generate correlation functions with a toy model where the supposed Lévy parameters are generated with realistic statistical uncertainties (following those from experimental data, such as the one in Ref. [6]). We investigate three different size measures (besides , which is an input, but it was confirmed that from a Lévy fit it can be retained):
Figure 2 shows the results, and the observation is that , contrary to the input , shows an approximately monotonic increase with . On the other hand, there is a minimum in HWHM, and HWHI exhibits a trend change.
These findings again underline the importance of quantifying the shape and the scale (size) of the source at the same time, as these two are entangled in source size measures such as HWHI, HWHM, or Gaussian radius.
Figure 3.
Various source geometry characteristics versus collision energy () in a hypothetical scenario where (red crosses, right vertical axis) has a minimum and a maximum near GeV. The following calculated source measures were calculated and are shown: half width at half integral (, orange downward-facing triangles), half width at half maximum (, green upward-facing triangles), and a radius from a forced Gaussian fit (, purple squares).
Figure 3.
Various source geometry characteristics versus collision energy () in a hypothetical scenario where (red crosses, right vertical axis) has a minimum and a maximum near GeV. The following calculated source measures were calculated and are shown: half width at half integral (, orange downward-facing triangles), half width at half maximum (, green upward-facing triangles), and a radius from a forced Gaussian fit (, purple squares).
5. Experimental Results from SPS through RHIC to LHC
After the above phenomenological considerations, let us discuss recent experimental results as well. These can be compared to the first thorough two-pion Lévy HBT analysis in heavy-ion collisions, as detailed in Ref. [6]. In this paper, GeV Au+Au collisions with 0–30% centrality were analyzed, and values around 1.2 were found, with a close to negligible dependence on . These were later confirmed in a preliminary 3D analysis [42]. In both analyses [6,42], a decreasing trend of the Lévy HBT scale R was found with , a feature usually attributed to the expansion of the fireball, as this leads to smaller sources for particles with larger momenta [46,47,48]. This, however, was calculated and predicted for Gaussian HBT radii. Hence, it is an open question why this feature of holds for Lévy HBT radii as well. In the mentioned analysis of Ref. [6], an interesting behavior of the correlation strength parameter was found: it exhibits a “hole” (i.e., a strong decrease) in the small- region, attributed to an in-medium mass decrease of the meson (see Ref. [6] for details). These are the features of the Lévy HBT parameters (, R, ) that shall be investigated in recent results as well.
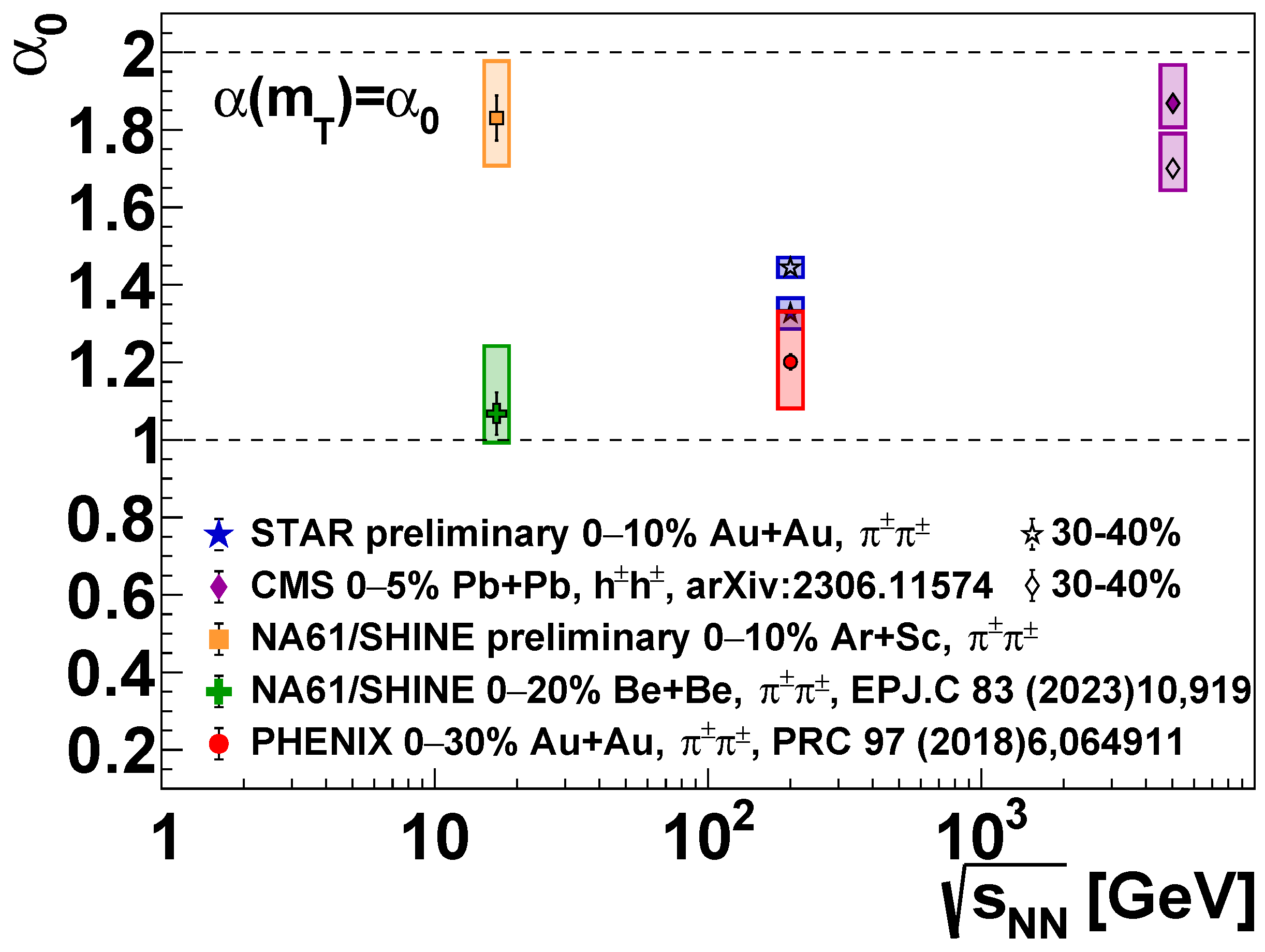
The detailed centrality and average transverse mass dependence of these two-pion Lévy HBT parameters have been measured in Au+Au collisions with STAR at GeV and reported recently by D. Kincses at the 52nd International Symposium on Multiparticle Dynamics and the XVI. Workshop of Particle Correlations and Femtoscopy, and in Ref. [49]. These results are summarized in the same Special Issue as this paper. We note here that a similar value was found as in Ref. [6], as shown in the summary plot of Figure 4, and similar features for the -dependence of R and parameters were found as in Ref. [6].
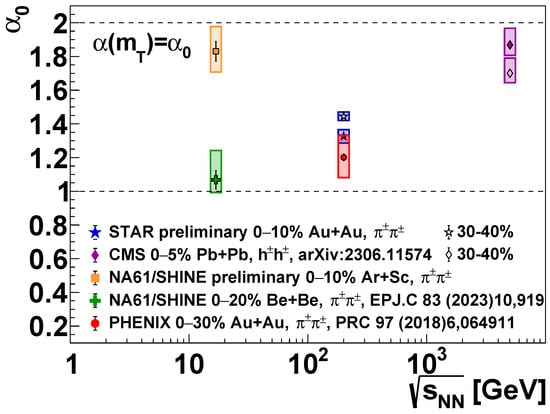
Figure 4.
Experimental results on the mean (-averaged) value (denoted here as ), as a function of collision energy (). The STAR preliminary results are from [49]. The CMS TeV Pb+Pb results are from Ref. [50]. The PHENIX GeV 0–30% Au+Au result is from Ref. [6]. The 150A GeV () Ar+Sc results are from Ref. [51], while the 150A GeV Be+Be results are from Ref. [52].
A similar analysis in the CMS experiment in TeV Pb+Pb collisions was also performed (albeit without particle identification, under the assumption that most detected particles are pions), as reported in Ref. [50]. Here, it was found that the Lévy scale R follows a similar trend versus as present in the RHIC results discussed above. It was also found that the exponent is closer to the Gaussian case but clearly not equal to it. Furthermore, values were found to be larger (closer to 2) for central collisions; this behavior is distinctly different from what was found in STAR. Figure 4 also shows a central and a peripheral measurement for both STAR and CMS, where the opposite trend is apparent.
A two-pion HBT measurement was reported by the NA61/SHINE experiment in Refs. [51,52] in 150A GeV ( GeV) Be+Be and Ar+Sc collisions. For the Lévy index , a significant difference between the two systems was found, a result yet to be understood. Average values for both systems are shown in Figure 4. For the Lévy scale R, the difference between the two systems is close to the initial size ratio of roughly 1.6 (based on nuclear sizes), and it decreases with , similarly to the case of RHIC and LHC. Interestingly, however, the parameter does not show the “hole” mentioned above for the RHIC case, which may be a signal of the in-medium mass modification effect being turned off at SPS energies.
As mentioned, Figure 4 compares the mean values at several collision energies from SPS through RHIC to LHC. Interestingly, the 5.02 TeV Pb+Pb results and the 16.82 GeV Ar+Sc results yield the largest values, while those for 200 GeV Au+Au and 16.82 GeV Be+Be collisions are significantly smaller. It is important to note, however, that the kinematic range of these experiments is also quite different: While there is essentially no low-momentum cut in NA61/SHINE (as in the fixed-target setup, small momentum particles can also be detected), there is one of about 0.2 GeV (in transverse momentum) in the RHIC experiments, while in case of CMS, particles with transverse momenta smaller than 0.5 GeV are discarded. This may also strongly influence the results of Figure 4.
Besides the pion parameters, kaon analyses have been performed both with PHENIX [53] and with STAR [54] in central GeV Au+Au collisions. Contrary to the anomalous diffusion expectation of , as detailed in Section 2, it was found that the parameter for kaons is close to or slightly above to the one for pions. It was also found that the Lévy radii (R) for kaons and pions are compatible at the same . These results indicate that it is not just hadronic anomalous diffusion that is responsible for the apparent Lévy source distributions, and that further modeling is required to understand the processes shaping the source.
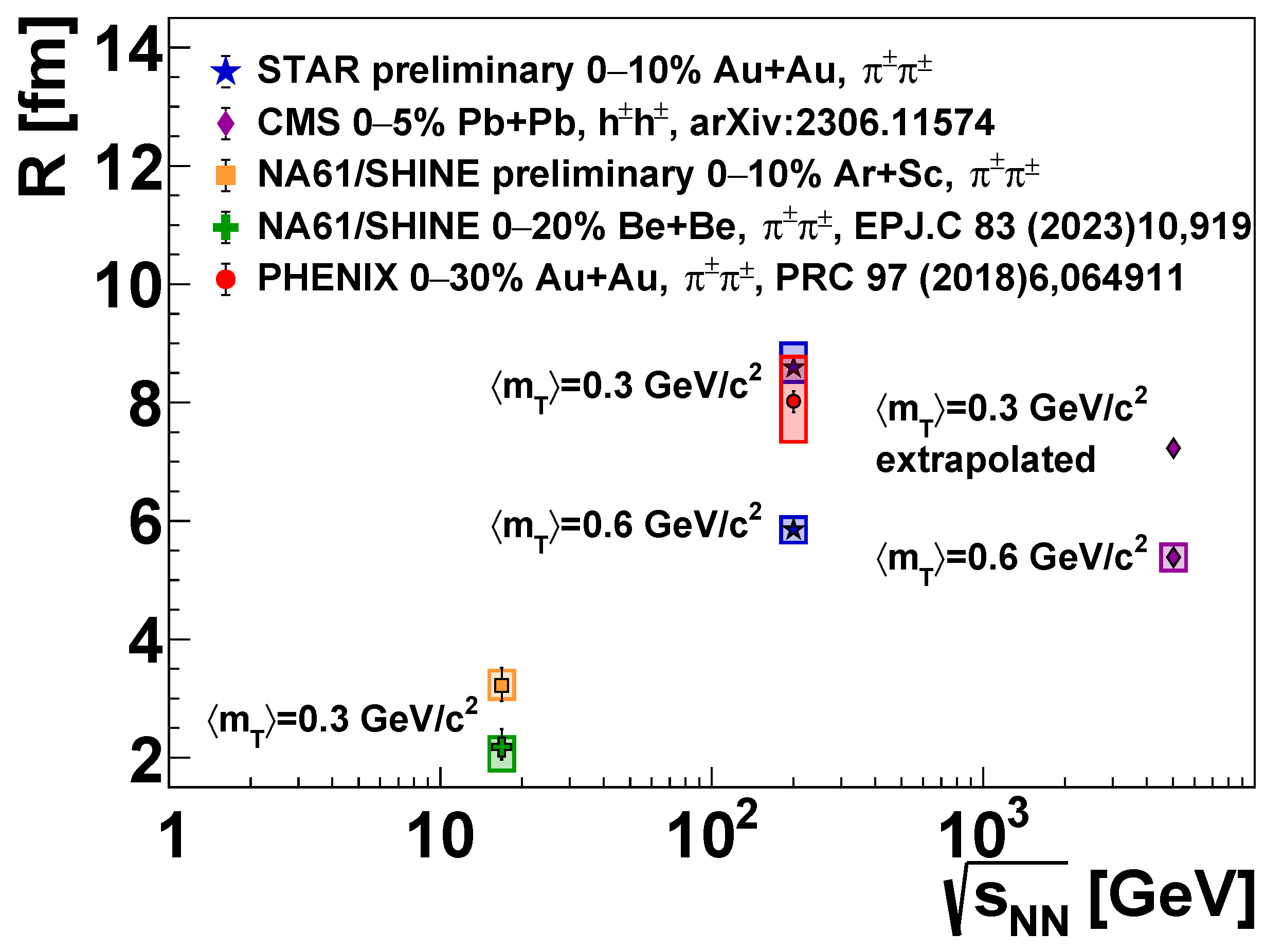
The R parameter obtained in the above-mentioned experimental analyses exhibits a typical and characteristic dependence on : it decreases significantly as increases, due to the non-static nature of the source and the fact that R is not a geometric size but a kind of measure of homogeneity, as mentioned in the introduction. Hence, -averaging would not be meaningful. To facilitate a comparison, in Figure 5, we show R values from SPS [51,52] and RHIC [6,49] at GeV/, along with an extrapolation of the CMS data [50] to this value, using the formula for utilized in Ref. [49]. We furthermore compare RHIC and LHC results at GeV/ (extrapolation of the SPS data to 0.6 GeV/ is less feasible due to the larger uncertainties there). It is clear that R decreases with , as detailed in the above-cited experimental papers as well. It is also clear that the Lévy scale depends on the initial system size; in particular, R for Be+Be is smaller than for Ar+Sc at the same energy. There is also an increase from SPS to RHIC, partly probably due to the system size change but also due to the increased energy. Rather surprisingly, however, Lévy scales at the LHC are not larger than those at RHIC but slightly smaller. This may be connected to the larger measured at LHC and the anti-correlation of R and , as demonstrated by Figure 7c of Ref. [6], Figure 5 of Ref. [36], and Figures 4 and 5 of Ref. [9].
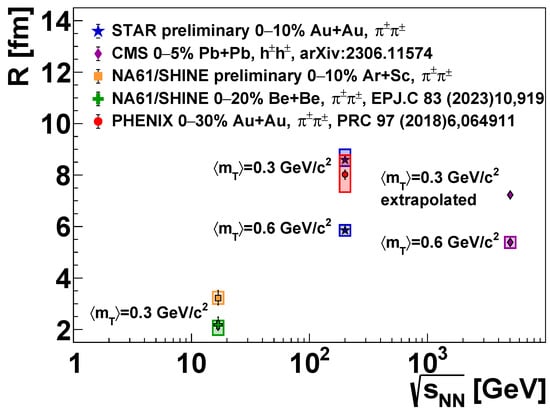
Figure 5.
Experimental results on the R value (at a mean of 0.3 and 0.6 GeV/), as a function of collision energy (). The source of the data is the same as for Figure 4. The CMS data point for GeV/ was obtained via an extrapolation, as noted in the text.
The third important physical parameter of HBT correlation functions is the correlation strength parameter , as introduced in the first section. It was observed at RHIC [6] that there is a decrease of at small values. The core–halo model interpretation utilized in Ref. [6] suggests that this may indirectly connect to an in-medium mass modification of the meson. It is, hence, quite interesting that this behavior is absent at SPS, as if this effect could be “turned off” when decreasing the collision energy from RHIC to SPS. Investigating this (the -dependence of ) at various energies also in data from the RHIC beam energy scan will be important and interesting. Note that no particle identification was employed in the CMS analysis of Ref. [50]. Hence, cannot be interpreted in terms of the core–halo model only. In Ref. [50], an attempt was made to correct for the lack of particle identification, and a new parameter was shown. However, the accessible -range of CMS does not allow for investigating the phenomenon mentioned above (i.e., the decrease of at small ).
6. Discussion and Conclusions
We have detailed several phenomenological and experimental results related to femtoscopy with Lévy sources. In light of these, the natural question arises: is it advantageous to utilize Lévy distributed sources in describing momentum correlations? We have shown above that the appearing extra parameter, the Lévy exponent has a physical meaning for each of the possible physical reasons for its appearance (jet fragmentation, critical phenomena, anomalous diffusion, resonance decays). In order to interpret it, one needs to disentangle the above effects. Equally importantly, when measuring source size (R) or strength () parameters with a Gaussian assumption, the actual size and shape information are entangled, and the more general Lévy assumption leads to refined results. One shall also note that the source, of course, does not necessarily exhibit an exact Lévy shape—deviations from it can be investigated via the method of Lévy expansion [55], and in Ref. [6] all expansion terms turned out to be zero, i.e., no deviation from the Lévy shape was found. This is not necessarily true, however, for all other experiments, and a similar expansion analysis can be performed in those cases as well.
One may also note that there are a few complications when fitting correlation functions based on Lévy sources. First of all, the extra parameter () is significantly correlated with the other physical parameters (R and ). Hence, fit range stability and statistical uncertainties need a careful approach. Furthermore, the Coulomb correction is more complicated to determine in this case; but as noted above, a novel method exits [8] with which this can be treated in a self-consistent and accurate calculation.
It is furthermore an important question whether utilizing the imaging technique mentioned above and detailed in Ref. [43] or the related technique of spherical decomposition [56] makes the Lévy source assumption superfluous. Indeed, these methods help us map out the particle emitting source. In order to quantify the collision energy or centrality evolution of the source (for example, its size), one then would proceed to determine source measures such as HWHI and HWHM (or even a root-mean-square)—or fit the imaged sources with a suitable shape, such as a Gaussian or a Lévy distribution. If this shape indeed describes the data, then it is equivalent to fitting the source or the correlation function. However, in the case of the correlation function, the uncertainties are more clear; hence, even in that case, it is advantageous to fit this experimental object. Therefore, the utilization of the Lévy sources (possibly with the Lévy expansion technique) has no real disadvantage compared to imaging as well.
In summary, Lévy sources have been observed from SPS through RHIC to LHC. The possible reasons for the appearance of Lévy sources in high-energy physics include, depending on system size and collision energy, jet fragmentation, critical phenomena, resonance decays, and anomalous diffusion, which need to be disentangled. In measurements, Lévy exponent values between 1 and 2 were found, with a nontrivial collision energy and system size dependence, suggesting that multiple phenomena contribute to the observed . The particle type dependence was also found to be nontrivial, not following the simplest predictions based on anomalous diffusion in the hadronic stage. The Lévy scale (or HBT radius) R was found to exhibit an -dependence that was predicted for Gaussian radii: a feature yet to be understood via model calculations. Finally, femtoscopy with Lévy sources provides a method to measure the correlation strength accurately, and differences were found in the low- behavior between RHIC and SPS, possibly hinting at an effect being absent at SPS energies. These results underline the importance of considering Lévy shapes when describing momentum correlation functions in high-energy physics and the need for more detailed phenomenological studies to explore all factors contributing to the shape of the particle emitting source.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C. and D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C.; writing—review and editing, D.K.; visualization, M.C. and D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the NKFIH grants K-138136, TKP2021-NKTA-64, PD-146589 and K-146913.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Nagy for their insightful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HBT | Hanbury Brown and Twiss |
| QCD | Quantum Chromodynamics |
| LCMS | Longitudinally Comoving System |
| SPS | Super Proton Synchrotron |
| RHIC | Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider |
| LHC | Large Hadron Collider |
| HWHM | Half width at half maximum |
| HWHI | Half width at half integral |
References
- Lednicky, R. Femtoscopy with unlike particles. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Physics of the Quark Gluon Plasma, Palaiseau, France, 4–7 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lisa, M.A.; Pratt, S.; Soltz, R.; Wiedemann, U. Femtoscopy in relativistic heavy ion collisions. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2005, 55, 357–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbury Brown, R.; Jennison, R.C.; Das Gupta, M.K. Apparent Angular Sizes of Discrete Radio Sources: Observations at Jodrell Bank, Manchester. Nature 1952, 170, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber, G.; Goldhaber, S.; Lee, W.Y.; Pais, A. Influence of Bose-Einstein statistics on the antiproton proton annihilation process. Phys. Rev. 1960, 120, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csanád, M. Two- and three-pion Lévy femtoscopy with PHENIX. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1070, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adare, A. et al. [PHENIX Collaboration] Lévy-stable two-pion Bose-Einstein correlations in = 200 GeV Au+Au collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 97, 064911, Erratum in Phys. Rev. C 2023, 108, 049905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurgyis, B.; Kincses, D.; Nagy, M.; Csanád, M. Coulomb Corrections for Bose–Einstein Correlations from One- and Three-Dimensional Lévy-Type Source Functions. Universe 2023, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, M.; Purzsa, A.; Csanád, M.; Kincses, D. A novel method for calculating Bose–Einstein correlation functions with Coulomb final-state interaction. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kórodi, B.; Kincses, D.; Csanád, M. Event-by-event investigation of the two-particle source function in sNN = 2.76 TeV PbPb collisions with EPOS. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 847, 138295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csörgő, T.; Lörstad, B.; Zimányi, J. Bose-Einstein correlations for systems with large halo. Z. Phys. C 1996, 71, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csörgő, T. Particle interferometry from 40-MeV to 40-TeV. Acta Phys. Hung. A 2002, 15, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csanad, M.; Jakovac, A.; Lokos, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Tripathy, S.K. Multi-particle quantum-statistical correlation functions in a Hubble-expanding hadron gas. In Gribov-90 Memorial Volume; World Scientific: Singapore, 2020; pp. 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J. et al. [STAR Collaboration] Flow and interferometry results from Au+Au collisions at = 4.5 GeV. Phys. Rev. C 2021, 103, 034908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, R.A. Indications for a Critical End Point in the Phase Diagram for Hot and Dense Nuclear Matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 142301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, L. et al. [STAR Collaboration] Beam-energy-dependent two-pion interferometry and the freeze-out eccentricity of pions measured in heavy ion collisions at the STAR detector. Phys. Rev. C 2015, 92, 014904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adare, A. et al. [PHENIX Collaboration] Azimuthal-angle dependence of charged-pion-interferometry measurements with respect to second- and third-order event planes in Au+Au collisions at = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 222301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lökös, S.; Csanád, M.; Tomášik, B.; Csörgő, T. Higher order anisotropies in the Buda-Lund model: Disentangling flow and density field anisotropies. Eur. Phys. J. A 2016, 52, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimerman, J.; Tomasik, B.; Csanad, M.; Lokos, S. Higher-order anisotropies in the Blast-Wave Model—Disentangling flow and density field anisotropies. Eur. Phys. J. A 2017, 53, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincses, D.; Nagy, M.I.; Csanád, M. Coulomb and strong interactions in the final state of Hanbury-Brown–Twiss correlations for Lévy-type source functions. Phys. Rev. C 2020, 102, 064912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbietti, L.; Mantovani Sarti, V.; Vazquez Doce, O. Study of the Strong Interaction Among Hadrons with Correlations at the LHC. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2021, 71, 377–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisiel, A.; Zbroszczyk, H.; Szymański, M. Extracting baryon-antibaryon strong interaction potentials from femtoscopic correlation functions. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 89, 054916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasiev, S. et al. [PHENIX Collaboration] Source breakup dynamics in Au+Au Collisions at s(NN)**(1/2) = 200-GeV via three-dimensional two-pion source imaging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 232301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.S. et al. [PHENIX Collaboration] Evidence for a long-range component in the pion emission source in Au+Au collisions at s(NN)**(1/2) = 200-GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 132301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csörgő, T.; Hegyi, S.; Zajc, W.A. Bose-Einstein correlations for Levy stable source distributions. Eur. Phys. J. C 2004, 36, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnedenko, B.V.; Kolmogorov, A.N.; Chung, K.L. Limit Distributions for Sums of Independent Random Variables; Addisson-Wesley: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Nolan, J.P. Univariate Stable Distributions; Springer Series in Operations Research and Financial Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, R.; Barkai, E.; Klafter, J. Anomalous Diffusion and Relaxation Close to Thermal Equilibrium: A Fractional Fokker-Planck Equation Approach. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 3563–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csanád, M.; Csörgő, T.; Nagy, M. Anomalous diffusion of pions at RHIC. Braz. J. Phys. 2007, 37, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csörgő, T.; Hegyi, S.; Novak, T.; Zajc, W.A. Bose-Einstein or HBT correlations and the anomalous dimension of QCD. Acta Phys. Polon. B 2005, 36, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Achard, P. et al. [L3 Collaboration] Test of the τ-Model of Bose-Einstein Correlations and Reconstruction of the Source Function in Hadronic Z-boson Decay at LEP. Eur. Phys. J. C 2011, 71, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csörgő, T.; Hegyi, S.; Novák, T.; Zajc, W.A. Bose-Einstein or HBT correlation signature of a second order QCD phase transition. AIP Conf. Proc. 2006, 828, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Showk, S.; Paulos, M.F.; Poland, D.; Rychkov, S.; Simmons-Duffin, D.; Vichi, A. Solving the 3d Ising Model with the Conformal Bootstrap II. c-Minimization and Precise Critical Exponents. J. Stat. Phys. 2014, 157, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, H. Critical behavior of the three-dimensional random-field Ising model: Two-exponent scaling and discontinuous transition. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 6659–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasz, A.M.; Jackson, A.D.; Shrock, R.E.; Stephanov, M.A.; Verbaarschot, J.J.M. On the phase diagram of QCD. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 096007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanov, M.A.; Rajagopal, K.; Shuryak, E.V. Signatures of the tricritical point in QCD. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 4816–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincses, D.; Stefaniak, M.; Csanád, M. Event-by-Event Investigation of the Two-Particle Source Function in Heavy-Ion Collisions with EPOS. Entropy 2022, 24, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, J. Development of geological disposal systems for spent fuels and high-level radioactive wastes in korea. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2013, 45, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomášik, B.; Cimerman, J.; Plumberg, C. Averaging and the Shape of the Correlation Function. Universe 2019, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimerman, J.; Tomášik, B.; Plumberg, C. The Shape of the Correlation Function. Phys. Part. Nucl. 2020, 51, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, S. Pion Interferometry of Quark-Gluon Plasma. Phys. Rev. D 1986, 33, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, G.F. Pion Interferometry as a Probe of the Plasma. Nucl. Phys. A 1989, 498, 173C–180C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurgyis, B. Three dimensional Lévy HBT results from PHENIX. In Proceedings of the 13th Workshop on Particle Correlations and Femtoscopy, Krakow, Poland, 22–26 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.A.; Danielewicz, P. Imaging of sources in heavy ion reactions. Phys. Lett. B 1997, 398, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, H.G.; Fernandez, L.A.; Martin-Mayor, V.; Munoz Sudupe, A. Finite size effects on measures of critical exponents in d = 3 O(N) models. Phys. Lett. B 1996, 387, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytas, N.G.; Martín-Mayor, V.; Parisi, G.; Picco, M.; Sourlas, N. Finite-size scaling of the random-field Ising model above the upper critical dimension. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 108, 044146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlin, A.N.; Sinyukov, Y.M. Hydrodynamics of Hadron Matter Under Pion Interferometric Microscope. Z. Phys. C 1988, 39, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csörgő, T.; Lörstad, B. Bose-Einstein correlations for three-dimensionally expanding, cylindrically symmetric, finite systems. Phys. Rev. C 1996, 54, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisa, M.A.; Pratt, S. Femtoscopically Probing the Freeze-out Configuration in Heavy Ion Collisions. In Landolt-Börnstein—Group I Elementary Particles, Nuclei and Atoms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Chapter 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincses, D. Pion interferometry with Levy sources in = 200 GeV Au+Au Collisions at STAR. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.11169. [Google Scholar]
- Tumasyan, A. et al. [CMS Collaboration] Two-particle Bose-Einstein correlations and their Lévy parameters in PbPb collisions at = 5.02 TeV. Phys. Rev. C, 2024; accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Porfy, B. Femtoscopic Correlation Measurement with Symmetric Lévy-Type Source at NA61/SHINE. Universe 2023, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, H. et al. [NA61/SHINE Collaboration] Two-pion femtoscopic correlations in Be+Be collisions at = 16.84 GeV measured by the NA61/SHINE at CERN. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, L. Charged Kaon Femtoscopy with Lévy Sources in = 200 GeV Au+Au Collisions at PHENIX. Universe 2023, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A. Kaon femtoscopy with Lévy-stable sources from = 200 GeV Au+Au collisions at RHIC. Universe 2023, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, T.; Csörgő, T.; Eggers, H.C.; de Kock, M. Model independent analysis of nearly Lévy correlations. Acta Phys. Pol. Suppl. 2016, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisiel, A.; Brown, D.A. Efficient and robust calculation of femtoscopic correlation functions in spherical harmonics directly from the raw pairs measured in heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2009, 80, 064911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).