Universal Properties of the Evolution of the Universe in Modified Loop Quantum Cosmology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Effective Dynamics of Modified Loop Quantum Cosmology
3. Numerical Solutions of the Evolution of the Universe
- The first-order Hubble rate and potential slow-roll parametersThese sets of slow-roll parameters are typically used for different purposes [75]. In particular, the slow-roll parameters with the subscript “V” can be used to determine which part of the potential can successfully drive inflation. On the other hand, slow-roll parameters with subscript “H” are used for numerical simulations to define when slow-roll inflation begins and ends. In the classical regime, the scale factor acceleration equation satisfies the following relation:The Universe experiences an accelerated expansion when , whereas slow-roll inflation occurs only when and [75]. For the sake of concreteness, we define the onset of inflation as the time when for the first time in the transition phase. The end of the slow-roll inflation is defined at the time when for the first time after .
- The e-fold N during the inflationary phase: This number is usually defined as follows:To have a successful slow-roll inflation, the inflation potential has to be very flat, so that the Universe can expand large enough [75]. All the cosmological problems can be resolved if the Universe expands about 60 e-fold during the inflationary phase, although its exact value depends on the inflationary models [2]. Therefore, in the following one will see that the minimal e-fold will be different in different models.
3.1. Chaotic Potential
3.2. Starobinsky Potential
3.3. -Attractor Potentials
3.3.1. Generalized Starobinsky Potentials
3.3.2. Polynomial of the First Kind
3.3.3. Polynomial of the Second Kind
3.3.4. Generalized T-Models
3.4. Natural Inflation
3.4.1.
3.4.2.
4. Analytical Solutions for the Evolution of the Universe
5. Conclusions and Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The concept of a bouncing universe was inspired by string theory, first proposed in Ref. [20], and later studied intensively by various authors, see, for example Refs. [21,22,23,24,25] and references therein. Other bouncing models have been also studied extensively [26,27,28,29,30,31]. In this paper, we focus specifically on the quantum bounce from LQG, driven purely by quantum geometric effects. |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
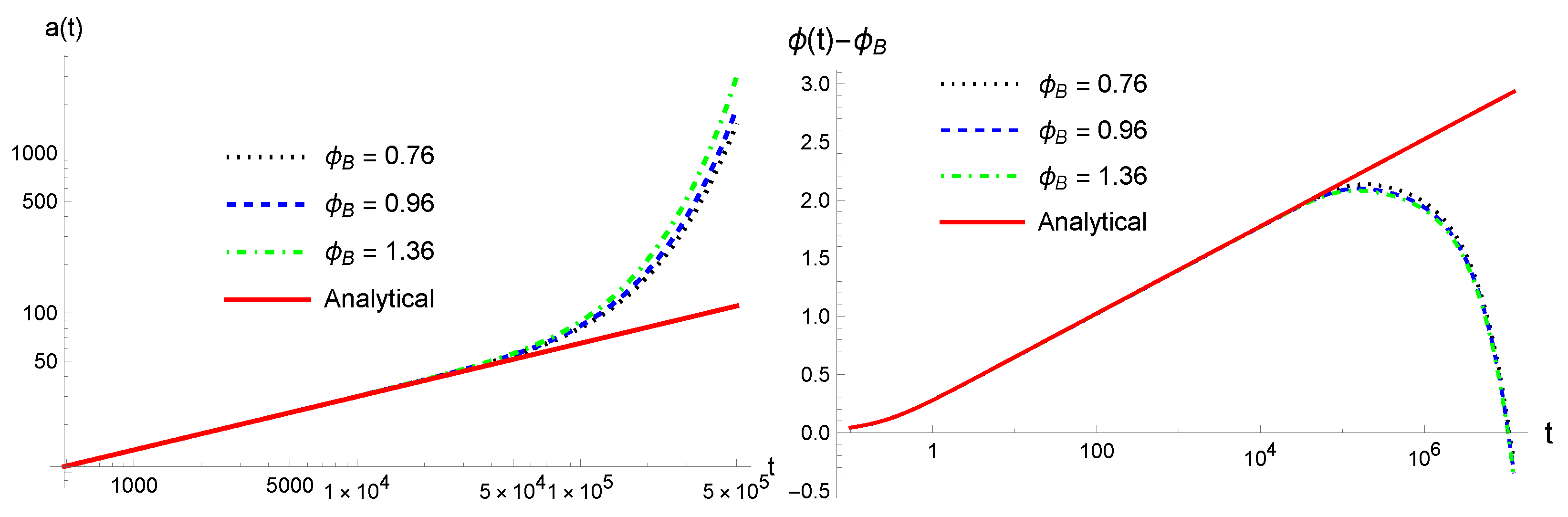
| 4 | It is found that numerically it is more convenient to solve the dynamical Equations (7)–(10) than the ones of Equations (11), (12), (18) and (19), although they should give the same results. However, in the latter, the integration needs to be carried out in the pre- and post-bounce separately, and then connect them smoothly across the bounce. |
References
- Guth, A.H. Inflationary universe: A possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems. Phys. Rev. 1981, 23, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, Y.; Arroja, F.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; et al. Planck 2018 results. X. Constraints on inflation. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borde, A.; Guth, A.H.; Vilenkin, A. Inflationary space-times are incompletein past directions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 151301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.B.; Schwarz, J.H.; Witten, E. Superstring Theory: 25th Anniversary Edition; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, K.; Becker, M.; Schwarz, J.H. String Theory and M-Theory: A Modern Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Lewandowski, J. Background independent quantum gravity: A Status report. Class. Quant. Grav. 2004, 21, R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, T. Modern Canonical Quantum General Relativity; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bojowald, M. Canonical Gravity and Applications: Cosmology, Black Holes, and Quantum Gravity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gambini, R.; Pullin, J. A First Course in Loop Quantum Gravity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rovelli, C.; Vidotto, F. Covariant Loop Quantum Gravity: An Elementary Introduction to Quantum Gravity and Spinfoam Theory; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bojowald, M. Loop quantum cosmology. Living Rev. Rel. 2005, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashtekar, A.; Singh, P. Loop Quantum Cosmology: A Status Report. Class. Quant. Grav. 2011, 28, 213001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Barrau, A. Loop quantum cosmology: From pre-inflationary dynamics to observations. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 234001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agullo, I.; Singh, P. Loop Quantum Cosmology. In Loop Quantum Gravity: The First 30 Years; Ashtekar, A., Pullin, J., Eds.; WSP: London, UK, 2017; pp. 183–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Ewing, E. Testing loop quantum cosmology. Comptes Rendus Physique 2017, 18, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizaga Navascués, B.; Marugán, G.A.M. Hybrid Loop Quantum Cosmology: An Overview. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2021, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Bianchi, E. A short review of loop quantum gravity. Rept. Prog. Phys. 2021, 84, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Singh, P. Loop Quantum Cosmology: Physics of Singularity Resolution and its Implications. In Handbook of Quantum Gravity; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Agulló, I.; Wang, A.; Wilson-Ewing, E. Loop quantum cosmology: Relation between theory and observations. In Handbook of Quantum Gravity; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gasperini, M.; Veneziano, G. Pre-big-bang in string cosmology. Astropart. Phys. 1993, 1, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, M.; Maggiore, M.; Veneziano, G. Towards a nonsingular pre-big bang cosmology. Nucl. Phys. B 1997, 494, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, M.; Veneziano, G. The Pre-big bang scenario in string cosmology. Phys. Rept. 2003, 373, 1–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, J. Cosmological perturbations in teleparallel Loop Quantum Cosmology. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 11, 068, Erratum in J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 5, E01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Serrano, A.; Liška, M.; Vicente-Becceril, A. Friedmann equations and cosmic bounce in a modified cosmological scenario. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 839, 137827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzinu, P.; Fanizza, G.; Gasperini, M.; Pavone, E.; Tedesco, L.; Veneziano, G. From the string vacuum to FLRW or de Sitter via α’ corrections. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 12, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.; Ovrut, B.A.; Steinhardt, P.J.; Turok, N. The Ekpyrotic universe: Colliding branes and the origin of the hot big bang. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 123522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.G.; Freese, K.; Kinney, W.H. The Phantom bounce: A New oscillating cosmology. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 3, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battefeld, D.; Peter, P. A Critical Review of Classical Bouncing Cosmologies. Phys. Rept. 2015, 571, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, R.; Peter, P. Bouncing Cosmologies: Progress and Problems. Found. Phys. 2017, 47, 797–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijjas, A.; Steinhardt, P.J. Bouncing Cosmology made simple. Class. Quant. Grav. 2018, 35, 135004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, S.M.; Shankaranarayanan, S. Distinguishing bounce and inflation via quantum signatures from cosmic microwave background. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.08543. [Google Scholar]
- Taveras, V. Corrections to the Friedmann Equations from LQG for a Universe with a Free Scalar Field. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 064072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P. Glimpses of Space-Time Beyond the Singularities Using Supercomputers. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2018, 20, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corichi, A.; Singh, P. Quantum bounce and cosmic recall. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 161302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, W.; Kolanowski, M.; Lewandowski, J. Dressed metric predictions revisited. Class. Quant. Grav. 2020, 37, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetle, C.; Engle, J.S.; Hogan, M.E.; Mendonça, P. Diffeomorphism invariant cosmological sector in loop quantum gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2017, 34, 225009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojowald, M. Space–Time Physics in Background-Independent Theories of Quantum Gravity. Universe 2021, 7, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Singh, P.; Wang, A. Phenomenological implications of modified loop cosmologies: An overview. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2021, 8, 701417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ding, Y.; Ma, Y. Alternative quantization of the Hamiltonian in loop quantum cosmology II: Including the Lorentz term. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 682, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, T. Quantum spin dynamics (qsd). 2. Class. Quant. Grav. 1998, 15, 875–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, T. Quantum spin dynamics (QSD). Class. Quant. Grav. 1998, 15, 839–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assanioussi, M.; Dapor, A.; Liegener, K.; Pawłowski, T. Emergent de Sitter Epoch of the Quantum Cosmos from Loop Quantum Cosmology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 081303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assanioussi, M.; Dapor, A.; Liegener, K.; Pawłowski, T. Emergent de Sitter epoch of the Loop Quantum Cosmos: A detailed analysis. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 084003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Singh, P.; Wang, A. Towards Cosmological Dynamics from Loop Quantum Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 084029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Singh, P.; Wang, A. Qualitative dynamics and inflationary attractors in loop cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 066016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Singh, P.; Wang, A. Genericness of pre-inflationary dynamics and probability of the desired slow-roll inflation in modified loop quantum cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 063513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapor, A.; Liegener, K. Cosmological Effective Hamiltonian from full Loop Quantum Gravity Dynamics. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 785, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapor, A.; Liegener, K. Cosmological coherent state expectation values in loop quantum gravity I. Isotropic kinematics. Class. Quant. Grav. 2018, 35, 135011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Liu, H. Loop quantum gravity on dynamical lattice and improved cosmological effective dynamics with inflaton. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 024011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haro, J. The Dapor–Liegener model of loop quantum cosmology: A dynamical analysis. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Singh, P. Generic absence of strong singularities and geodesic completeness in modified loop quantum cosmologies. Class. Quant. Grav. 2019, 36, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Singh, P. Von Neumann stability of modified loop quantum cosmologies. Class. Quant. Grav. 2019, 36, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Singh, P. Loop quantum gravity effects might restrict a cyclic evolution. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 046013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonga, B.; Gupt, B. Phenomenological investigation of a quantum gravity extension of inflation with the Starobinsky potential. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 063513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, A.; Kirsten, K.; Cleaver, G.; Sheng, Q. Universal features of quantum bounce in loop quantum cosmology. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 773, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, A.; Cleaver, G.; Kirsten, K.; Sheng, Q. Pre-inflationary universe in loop quantum cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 083520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahalam, M.; Sharma, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, A. Preinflationary dynamics in loop quantum cosmology: Power-law potentials. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 123533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahalam, M.; Sami, M.; Wang, A. Preinflationary dynamics of α-attractor in loop quantum cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 043524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Shahalam, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, A. Preinflationary dynamics in loop quantum cosmology: Monodromy Potential. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 11, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Zhu, T.; Wang, A. Background dynamics of pre-inflationary scenario in Brans-Dicke loop quantum cosmology. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2019, 71, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahalam, M.; Al Ajmi, M.; Myrzakulov, R.; Wang, A. Revisiting pre-inflationary Universe of family of α-attractor in loop quantum cosmology. Class. Quant. Grav. 2020, 37, 195026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, A.; Kirsten, K.; Cleaver, G.; Sheng, Q. High-order Primordial Perturbations with Quantum Gravitational Effects. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 123525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.L.L.W.; Ramos, R.O. α-attractor potentials in loop quantum cosmology. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10149. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.F.; Singh, P.; Wang, A. Primordial power spectrum from the dressed metric approach in loop cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 086004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Olmedo, J.; Singh, P.; Wang, A. Primordial scalar power spectrum from the hybrid approach in loop cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 126025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Motaharfar, M.; Singh, P. Constraining regularization ambiguities in Loop Quantum Cosmology via CMB. Phys. Rev. 2024, 110, 066005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Singh, P. Close relationship between the dressed metric and the hybrid approach to perturbations in effective loop quantum cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 086015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, K.A. Black hole entropy in loop quantum gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2004, 21, 5245–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C.; Smolin, L. Discreteness of area and volume in quantum gravity. Nucl. Phys. B 1995, 442, 593–622, Erratum in Nucl. Phys. B 1995, 456, 753–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Lewandowski, J. Quantum theory of geometry. 1: Area operators. Class. Quant. Grav. 1997, 14, A55–A82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Sloan, D. Probability of Inflation in Loop Quantum Cosmology. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2011, 43, 3619–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Sloan, D. Loop quantum cosmology and slow roll inflation. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 694, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallosh, R.; Linde, A. Polynomial α-attractors. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 4, 017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Zhu, T.; Wang, A.; Kirsten, K.; Cleaver, G.; Sheng, Q. Preinflationary perturbations from the closed algebra approach in loop quantum cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 103536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, D. Inflation. In Proceedings of the Theoretical Advanced Study Institute in Elementary Particle Physics: Physics of the Large and the Small; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011; pp. 523–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A.D. Chaotic Inflation. Phys. Lett. B 1983, 129, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starobinskii, A. Spectrum of relict gravitational radiation and the early state of the universe. JETP Lett. 1979, 30, 682–685. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K.i. Inflation as a transient attractor in R2 cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, S.; Kallosh, R.; Linde, A.; Porrati, M. Minimal Supergravity Models of Inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 085038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Dutta, K.; Gangopadhyay, M.R.; Maharana, A. α-attractor inflation: Models and predictions. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 103530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallosh, R.; Linde, A.; Roest, D. Superconformal Inflationary α-Attractors. J. High Energy Phys. 2013, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, F.C.; Bond, J.R.; Freese, K.; Frieman, J.A.; Olinto, A.V. Natural inflation: Particle physics models, power law spectra for large scale structure, and constraints from COBE. Phys. Rev. D 1993, 47, 426–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




























Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saeed, J.; Pan, R.; Brown, C.; Cleaver, G.; Wang, A. Universal Properties of the Evolution of the Universe in Modified Loop Quantum Cosmology. Universe 2024, 10, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10100397
Saeed J, Pan R, Brown C, Cleaver G, Wang A. Universal Properties of the Evolution of the Universe in Modified Loop Quantum Cosmology. Universe. 2024; 10(10):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10100397
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaeed, Jamal, Rui Pan, Christian Brown, Gerald Cleaver, and Anzhong Wang. 2024. "Universal Properties of the Evolution of the Universe in Modified Loop Quantum Cosmology" Universe 10, no. 10: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10100397
APA StyleSaeed, J., Pan, R., Brown, C., Cleaver, G., & Wang, A. (2024). Universal Properties of the Evolution of the Universe in Modified Loop Quantum Cosmology. Universe, 10(10), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10100397







