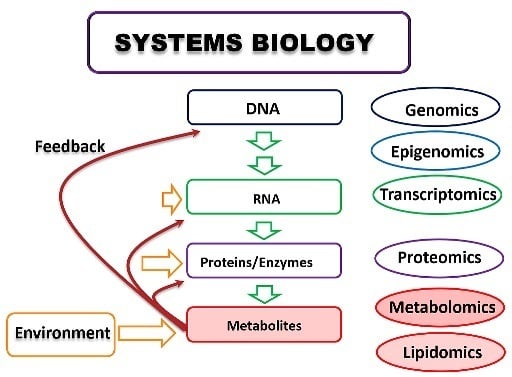
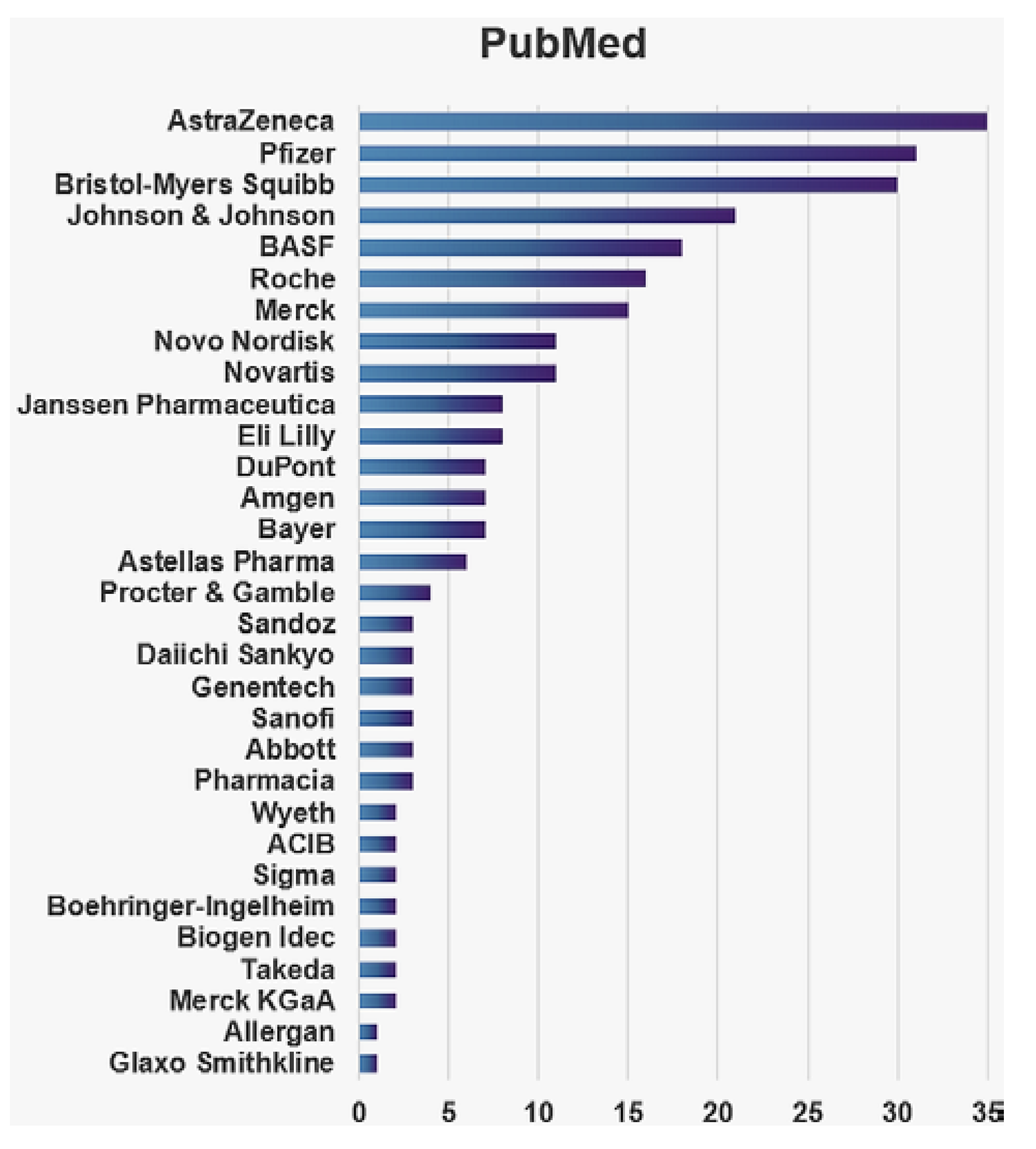
Metabolomics: Bridging the Gap between Pharmaceutical Development and Population Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analytical Considerations
3. Drug Discovery Applications
4. Clinical Applications
5. Future Developments
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hood, L.; Friend, S.H. Predictive, personalized, preventive, participatory (P4) cancer medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolan, N.V.; Parnas, M.L.; Baudhuin, L.M.; Cervinski, M.A.; Chan, A.S.; Holmes, D.T.; Horowitz, G.; Klee, E.W.; Kumar, R.B.; Master, S.R. “Big Data” in Laboratory Medicine. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffray, C.; Taniguchi, N.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Murray, H.; Visvikis-Siest, S.; Ansari, M.; Marc, J.; Jacobs, P.; Meyer, U.; Van Schaik, R.H.; et al. Systems medicine, personalized health and therapy. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar]
- Ress, A.L.; Wagle, R.; Pichler, M. Multi-omics in prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muellner, M.K.; Mair, B.; Ibrahim, Y.; Kerzendorfer, C.; Lechtermann, H.; Trefzer, C.; Klepsch, F.; Müller, A.C.; Leitner, E.; Macho-Maschler, S. Targeting a cell state common to triple-negative breast cancers. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2015, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, O.; Däbritz, J.H.; King, A.; Gottlieb, E.; Halsey, C. Research into cancer metabolomics: Towards a clinical metamorphosis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 43, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putluri, N.; Maity, S.; Kommagani, R.; Creighton, C.J.; Putluri, V.; Chen, F.; Nanda, S.; Bhowmik, S.K.; Terunuma, A.; Dorsey, T. Pathway-centric integrative analysis identifies RRM2 as a prognostic marker in breast cancer associated with poor survival and tamoxifen resistance. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciatore, S.; Loda, M. Innovation in metabolomics to improve personalized healthcare. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1346, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, A.; Armitage, E.G.; García, A.; Barbas, C. Metabolomics as a tool for drug discovery and personalized medicine. A review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Registry and results database. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 8 July 2016).
- Han, X.; Gross, R.W. Global analyses of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples by ESI mass spectrometry: A bridge to lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, E.A. Lipidomics joins the omics evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2089–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Raftery, D. Can NMR solve some significant challenges in metabolomics? J. Magn. Reson. 2015, 260, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinaixaa, M.; Schymanskid, E.L.; Neumann, S.; Navarro, M.; Salek, R.M.; Yanes, O. Mass spectral databases for LC/MS- and GC/MS-based metabolomics: State of the field and future prospects. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 78, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.C.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B. The human serum metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouatra, S.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.R.; Knox, C.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Saleem, F.; Liu, P. The human urine metabolome. PLoS One 2013, 8, e73076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Chaudhary, K.K.; Liu, P.; Yallou, F.S.; Dong, E.; Aziat, F.; Wishart, D.S. Multi-platform characterization of the human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome: A comprehensive and quantitative update. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, K.F.; Aggio, R.B.M.; Van Houtte, J.R.; Villas-Bôas, S.G. Analytical platform for metabolome analysis of microbial cells using methyl chloroformate derivatization followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1709–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstikov, V.; Nikolayev, A.; Dong, S.; Zhao, G.; Kuo, M.S. Metabolomics analysis of metabolic effects of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) inhibition on human cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; She, J.; Tolstikov, V.V. A comprehensive workflow of mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics in cancer metabolic biomarker discovery using human plasma and urine. Metabolites 2013, 3, 787–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallik, A.K.; Qiu, H.; Kuwahara, Y.; Takafuji, M.; Ihara, H. A remarkable enhancement of selectivity towards versatile analytes by a strategically integrated H-bonding site containing phase. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14243–14246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creek, D.J.; Jankevics, A.; Burgess, K.E.; Breitling, R.; Barrett, M.P. IDEOM: An Excel interface for analysis of LC-MS-based metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1048–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoulaki, I.; Ebbels, T.M.; Valdes, A.; Elliott, P.; Ioannidis, J.P. Design and analysis of metabolomics studies in epidemiologic research: A primer on -omic technologies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Wilson, I.D.; Nicholls, A.W.; Broadhurst, D. The importance of experimental design and QC samples in large-scale and MS-driven untargeted metabolomic studies of humans. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 2249–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.C.Y.; Pasikanti, K.K.; Nicholson, J.K. Global urinary metabolic profiling procedures using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1483–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N. Procedures for largescale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Breitkopf, S.B.; Yang, X.; Asara, J.M. A positive/negative ion-switching, targeted mass spectrometry-based metabolomics platform for bodily fluids, cells, and fresh and fixed tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Want, E.J.; Wilson, I.D.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling procedures for urine using UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Kastenmüller, G.; He, Y. Differences between Human Plasma and Serum Metabolite Profiles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breier, M.; Wahl, S.; Prehn, C.; Fugmann, M.; Ferrari, U.; Weise, M.; Banning, F.; Seissler, J.; Grallert, H.; Adamski, J. Targeted Metabolomics Identifies Reliable and Stable Metabolites in Human Serum and Plasma Samples. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89728. [Google Scholar]
- Thijssen, M.A.; Swinkels, D.W.; Ruers, T.J.; de Kok, J.B. Difference between free circulating plasma and serum DNA in patients with colorectal liver metastases. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamlage, B.; Maldonado, S.G.; Bethan, B.; Peter, E.; Schmitz, O.; Liebenberg, V.; Schatz, P. Quality markers addressing preanalytical variations of blood and plasma processing identified by broad and targeted metabolite profiling. Clin. Chem. 2014, 60, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MxP® Quality Control Plasma. Available online: http://www.metanomics-health.com/en/mxp-quality-control.html (accessed on 8 July 2016).
- Xia, J.; Sinelnikov, I.; Han, B.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst 3.0—Making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucl. Acids Res. 2015, 43, W251–W257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, M.C. Statistical principles for omics-based clinical trials. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tolstikov, V.; Nikolayev, A.; Laska, A.D.; Kuo, M.S.; Duffin, K.L. Metabolomics input in a search for chronic kidney disease targets utilizing clinical cross-platform omics data integration. In Proceedings of the 61th ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9–13 June 2013.
- Cao, H.; Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Kong, L.; Wang, X. Metabolomics-proteomics profiles delineate metabolic changes in kidney fibrosis disease. Proteomics 2015, 15, 3699–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, L.; Zurich, M.G.; Culot, M.; Costa, A.; Landry, C.; Bellwon, P.; Kristl, T.; Hörmann, K.; Ruzek, S.; Aiche, S. Evaluation of drug-induced neurotoxicity based on metabolomics, proteomics and electrical activity measurements in complementary CNS in vitro models. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 30, 139–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavill, R.; Jennen, D.; Kleinjans, J.; Briedé, J.J. Transcriptomic and metabolomic data integration. Brief. Bioinform. 2015. pii: bbv090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, K.; Metallo, C.M.; Kelleher, J.K.; Stephanopoulos, G. Nontargeted elucidation of metabolic pathways using stable-isotope tracers and mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6621–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, P.M.; Johnson-Farley, N.; Lin, H.; Shelton, L.M.; Ooga, T.; Mackay, G.; Broek, N.V.; Bertino, J.R.; Vazquez, A. Quantification of folate metabolism using transient metabolic flux analysis. Cancer Metab. 2015, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.K.; Huang, S.C.; Sergushichev, A.; Lampropoulou, V.; Ivanova, Y.; Loginicheva, E.; Chmielewski, K.; Stewart, K.M.; Ashall, J.; Everts, B. Network integration of parallel metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that regulate macrophage polarization. Immunity 2015, 42, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaitheesvaran, B.; Xu, J.; Yee, J.; Lu, Q.Y.; Go, V.L.; Xiao, G.G.; Lee, W.N. The Warburg effect: A balance of flux analysis. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, A.D.; Hood, L. Systems biology, proteomics, and the future of health care: Toward predictive, preventative, and personalized medicine. J. Proteome Res. 2004, 3, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, G.M.; Zheng, L.; van den Broek, N.J.; Gottlieb, E. Analysis of Cell Metabolism Using LC-MS and Isotope Tracers. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 561, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cluntun, A.A.; Huang, H.; Dai, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Locasale, J.W. The rate of glycolysis quantitatively mediates specific histone acetylation sites. Cancer Metab. 2015, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buescher, J.M.; Antoniewicz, M.R.; Boros, L.G.; Burgess, S.C.; Brunengraber, H.; Clish, C.B.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Feron, O.; Frezza, C.; Ghesquiere, B. A roadmap for interpreting 13C metabolite labeling pattern from cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 34, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Hasan, M.R. Cancer Metabolism and Drug Resistance. Metabolites 2015, 5, 571–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluger, B.; Bueschl, C.; Neumann, N.; Stückler, R.; Doppler†, M.; Chassy, A.W.; Waterhouse, A.L.; Rechthaler, J.; Kampleitner, N.; Thallinger, G.G. Untargeted profiling of tracer-derived metabolites using stable isotopic labeling and fast polarity-switching LC-ESI-HRMS. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11533–11537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Moir, R.; Willis, I.; Beecher, C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Garrett, T.J.; Yost, R.A.; Kurland, I.J. Isotopic Ratio Outlier Analysis of the S. cerevisiae Metabolome Using Accurate Mass Gas Chromatography/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry: A New Method for Discovery. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Q.; Ye, J.; Denduluri, S.K.; Wang, X.; Mohammed, M.K.; Luu, H.H.; Haydon, R.C.; He, T.C. Insider information: Testing cancer drug sensitivity for personalized therapy. Genes Dis. 2015, 2, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyass, A.; Turcotte, M.; Meyre, D. From big data analysis to personalized medicine for all: Challenges and opportunities. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, B. Phenotypic Characterization Analysis of Human Hepatocarcinoma by Urine Metabolomics Approach. Sci. Rep. 2016, 25, 19763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, P.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Metabolomics in diagnosis and biomarker discovery of colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, R. The Current State of Drug Discovery and a Potential Role for NMR Metabolomics. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5860–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnike, J.H.; Li, Z.; Wright, F.A.; Macdonald, J.M.; O’Connell, T.M.; Watkins, P.B. Use of pharmaco-metabonomics for early prediction of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 88, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, G.A.; Strauss, V.; Fabian, E.; Kamp, H.; Mellert, W.; Walk, T.; Looser, R.; Herold, M.; Krennrich, G.; Peter, E. Mechanistic analysis of metabolomics patterns in rat plasma during administration of direct thyroid hormone synthesis inhibitors or compounds increasing thyroid hormone clearance. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 225, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimi, N.; Futamura, T.; Bergen, S.E.; Iwayama, Y.; Ishima, T.; Sellgren, C.; Ekman, C.J.; Jakobsson, J.; Pålsson, E.; Kakumoto, K. Cerebrospinal fluid metabolomics identifies a key role of isocitrate dehydrogenase in bipolar disorder: Evidence in support of mitochondrial dysfunction hypothesis. Mol. Psychiatry 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reily, M.D.; Tymiak, A.A. Metabolomics in the pharmaceutical industry. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2015, 13, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Ahmed, S. Emerging Field of Metabolomics: Big Promise for Cancer Biomarker Identification and Drug Discovery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Tao, J.; Qin, C.; Wei, J.; Lu, Q. Metabolomics in bladder cancer: A systematic review. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 11052–11063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medina, S.; Domínguez-Perles, R.; Gil, J.I.; Ferreres, F.; Gil-Izquierdo, A. Metabolomics and the Diagnosis of Human Diseases—A Guide to the Markers and Pathophysiological Pathways Affected. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 823–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.K.; Liu, R.H.; Jin, H.Z.; Liu, X.R.; Ye, J.; Shan, L.; Zhang, W.D. “Omics” in pharmaceutical research: Overview, applications, challenges, and future perspectives. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hong, H.; Mendrick, D.L.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, F. Biomarker-based drug safety assessment in the age of systems pharmacology: From foundational to regulatory science. Biomark. Med. 2015, 9, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, S.; Brietzke, E. Omics-Based Biomarkers: Application of Metabolomics in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, E. Personalized medicine in diabetes: The role of ‘omics’ and biomarkers. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Nowak, G.; Caso, J.R.; Leza, J.C.; Song, C.; Kubera, M.; Klein, H.; Galecki, P.; Noto, C.; Glaab, E. Toward Omics-Based, Systems Biomedicine, and Path and Drug Discovery Methodologies for Depression-Inflammation Research. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2927–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisek, K.; Krochmal, M.; Klein, J.; Mischak, H. The application of multi-omics and systems biology to identify therapeutic targets in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015. pii: gfv364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajahan-Haq, A.N.; Cheema, M.S.; Clarke, R. Application of metabolomics in drug resistant breast cancer research. Metabolites 2015, 5, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beebe, K.; Kennedy, A.D. Sharpening Precision Medicine by a thorough interrogation of Metabolic Individuality. CSBJ 2016, 14, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettunen, J.; Tukiainen, T.; Sarin, A.P.; Ortega-Alonso, A.; Tikkanen, E.; Lyytikäinen, L.P.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Würtz, P.; Silander, K. Genome-wide association study identifies multiple loci influencing human serum metabolite levels. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueedi, R.; Ledda, M.; Nicholls, A.W.; Salek, R.M.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Morya, E.; Sameshima, K.; Montoliu, I.; Silva, L.D.; Collino, S. Genome-wide association study of metabolic traits reveals novel gene-metabolite-disease links. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, K.; Fox, M.P.; Bousamra, M.; Slone, S.P.; Higashi, R.M.; Miller, D.M.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Yuneva, M.O.; Deshpande, R. Pyruvate carboxylase is critical for non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngblood, V.M.; Kim, L.C.; Edwards, D.N.; Hwang, Y.; Santapuram, P.R.; Stirdivant, S.M.; Lu, P.; Ye, F.; Brantley-Sieders, D.M.; Chen, J. The ephrin-A1/EPHA2 signaling axis regulates glutamine metabolism in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, J.C.; Siegelin, M.D.; Vaira, V.; Faversani, A.; Tavecchio, M.; Chae, Y.C.; Lisanti, S.; Rampini, P.; Giroda, M.; Caino, M.C. Adaptive mitochondrial reprogramming and resistance to PI3K therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, dju502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaught, J. Biobanking Comes of Age: The Transition to Biospecimen Science. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Milburn, M.V.; Ryals, J.A.; Lonergan, S.C.; Mitchell, M.W.; Wulff, J.E.; Alexander, D.C.; Evans, A.M.; Bridgewater, B.; Miller, L. Plasma metabolomic profiles enhance precision medicine for volunteers of normal health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4901–E4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köttgen, A.; Albrecht, E.; Teumer, A.; Vitart, V.; Krumsiek, J.; Hundertmark, C.; Pistis, G.; Ruggiero, D.; O'Seaghdha, C.M.; Haller, T. Genome-wide association analyses identify 18 new loci associated with serum urate concentrations. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aw, W.; Fukuda, S. Toward the comprehensive understanding of the gut ecosystem via metabolomics-based integrated omics approach. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Morris, A.; Ghedin, E. The human mycobiome in health and disease. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seed, P.C. The human mycobiome. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 5, a019810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Aranda, V.; Bardelli, A.; Blanpain, C.; Bock, C.; Borowski, C.; Caldas, C.; Califano, A.; Doherty, M.; Elsner, M. Toward understanding and exploiting tumor heterogeneity. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentzmik, F.; Stephan, C.; Lein, M.; Millera, K.; Kamlagec, B.; Bethanc, B.; Kristiansend, G.; Jung, K. Sarcosine in prostate cancer tissue is not a differential metabolite for prostate cancer aggressiveness and biochemical progression. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankerst, D.P.; Liss, M.; Zapata, D.; Hoefler, J.; Thompson, I.M.; Leach, R.J. A case control study of sarcosine as an early prostate cancer detection biomarker. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priolo, C.; Pyne, S.; Rose, J.; Regan, E.R.; Zadra, G.; Photopoulos, C.; Cacciatore, S.; Schultz, D.; Scaglia, N.; McDunn, J. AKT1 and MYC induce distinctive metabolic fingerprints in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7198–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, J.R. Pharmacometabonomics in Humans: A new Tool for Personalized Medicine. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsila, T.; Konstantinou, E.; Lavda, I.; Malakis, H.; Papantoni, I.; Skondra, L.; Patrinos, G.P. Pharmacometabolomics-aided Pharmacogenomics in Autoimmune Disease. EBioMedicine 2016, 5, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, T.A.; Lindon, J.C.; Cloarec, O.; Antti, H.; Charuel, C.; Hanton, G.; Provost, J.P.; Net, J.L.; Baker, D.; Walley, R.J. Pharmaco-metabonomic phenotyping and personalized drug treatment. Nature 2006, 440, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellero-Simatos, S.; Beitelshees, A.L.; Lewis, J.P.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Georgiades, A.; Dane, A.; Harms, A.C.; Strassburg, K.; Guled, F.; Hendriks, M.M. Oxylipid Profile of Low-Dose Aspirin Exposure: A Pharmacometabolomics Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouden, H.; Pellis, L.; Rutten, G.; Vonderen, I.K.; Rubingh, C.M.; Ommen, B.V.; Erk, M.J.; Beulens, J.W. Metabolomic biomarkers for personalised glucose lowering drugs treatment in type 2 diabetes. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Neavin, D.; Liu, D.; Biernacka, J.; Hall-Flavin, D.; Bobo, W.V.; Frye, M.A.; Skime, M.; Jenkins, G.D.; Batzler, A. TSPAN5, ERICH3 and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in major depressive disorder: Pharmacometabolomics-informed pharmacogenomics. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tolstikov, V. Metabolomics: Bridging the Gap between Pharmaceutical Development and Population Health. Metabolites 2016, 6, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6030020
Tolstikov V. Metabolomics: Bridging the Gap between Pharmaceutical Development and Population Health. Metabolites. 2016; 6(3):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleTolstikov, Vladimir. 2016. "Metabolomics: Bridging the Gap between Pharmaceutical Development and Population Health" Metabolites 6, no. 3: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6030020
APA StyleTolstikov, V. (2016). Metabolomics: Bridging the Gap between Pharmaceutical Development and Population Health. Metabolites, 6(3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6030020