Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease—The Role of Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiological Associations between Obesity and CKD
2.1. Obesity as a Risk Factor for the Development of Chronic Kidney Disease
2.2. Obesity as a Risk Factor for End Stage Kidney Disease
2.3. Obesity as a Risk Factor for the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease
3. Lipids in Renal Physiology
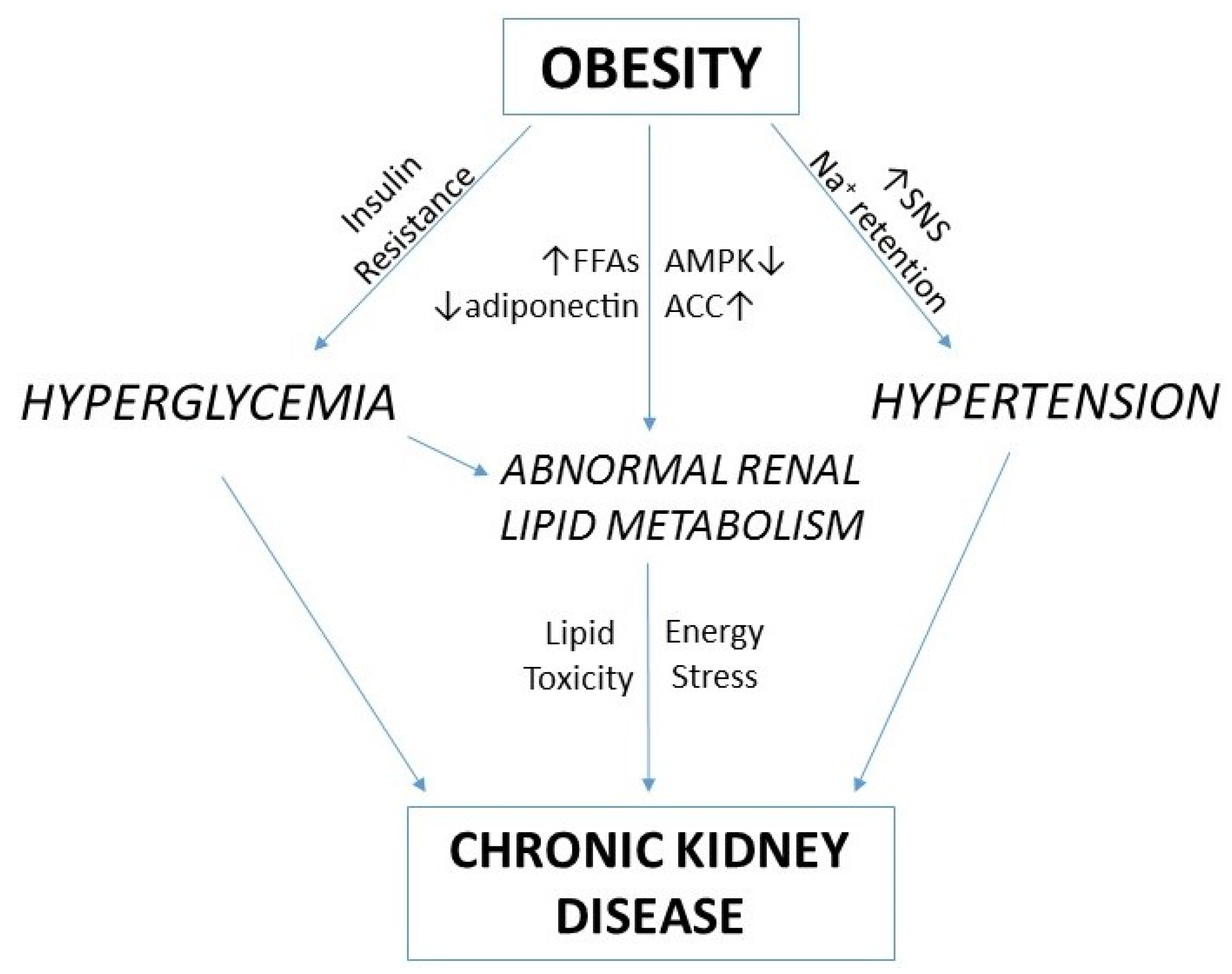
4. Renal Lipid Metabolism and Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease
5. AMPK and ACC in Energy and Lipid Metabolism
6. AMPK and ACC in Obesity-Related Kidney CKD
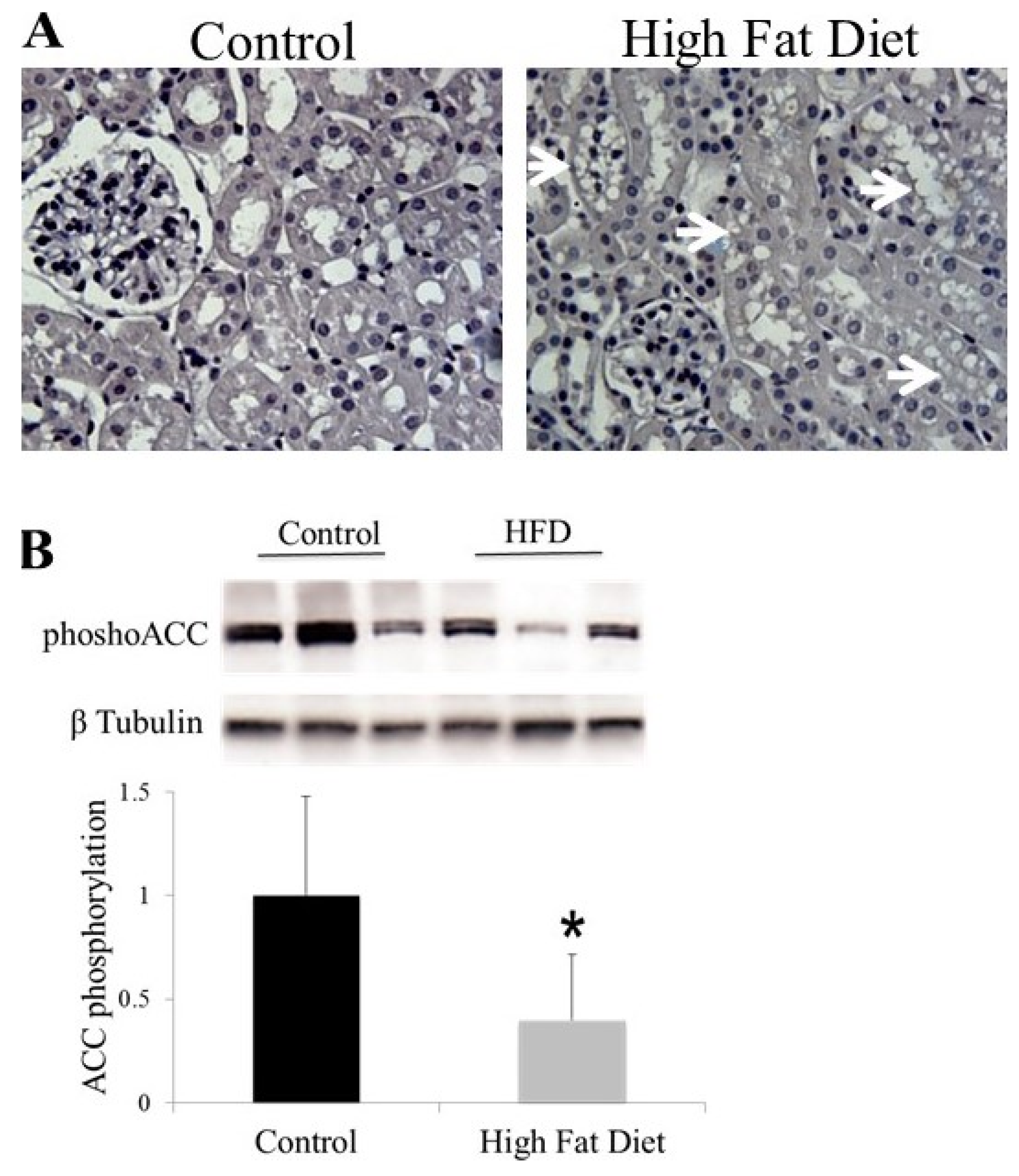
7. Lipid Accumulation and Toxicity in Proximal Tubular Cells
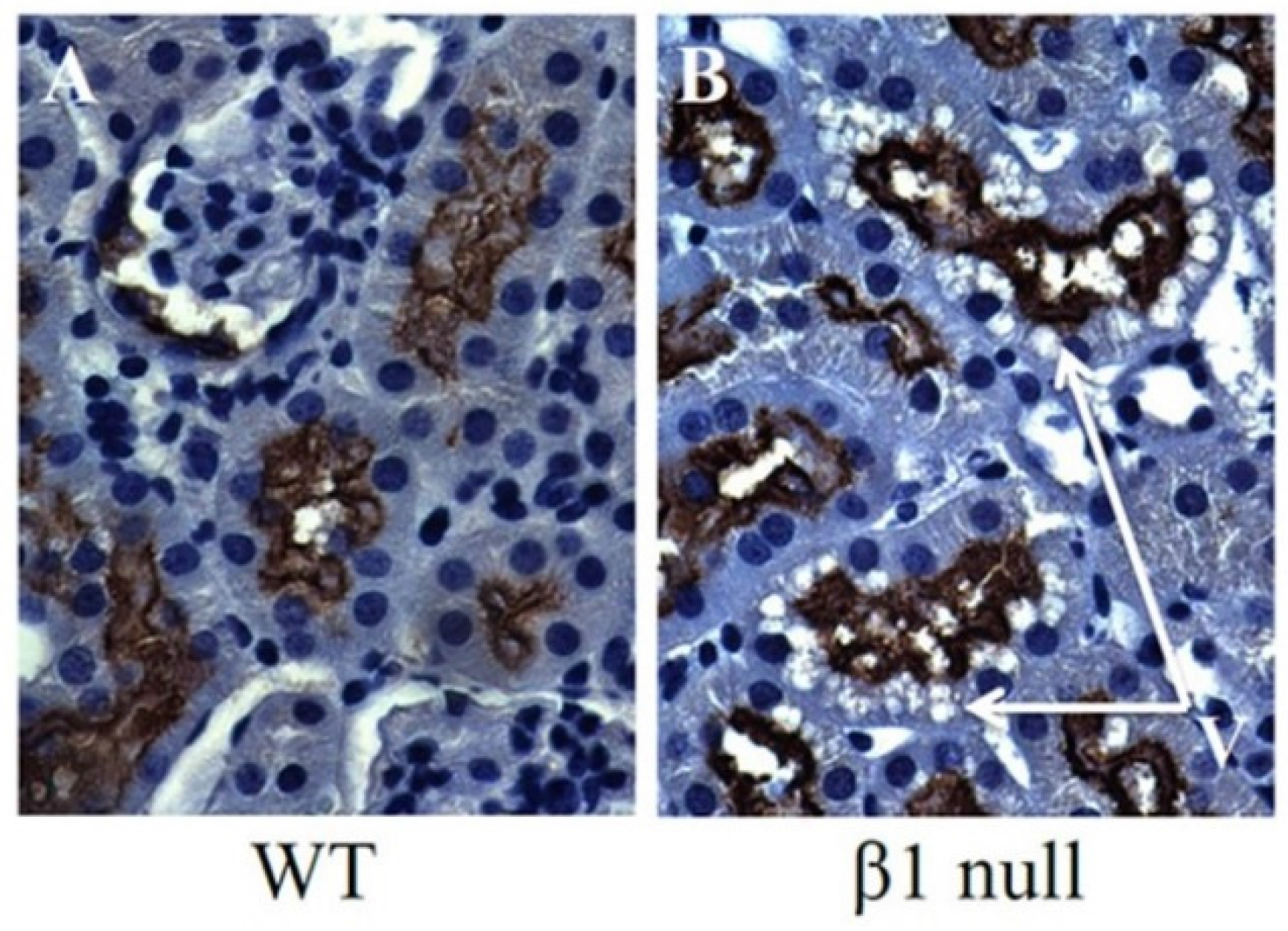
8. Lipid Accumulation and Toxicity in Podocytes
9. Lipid Accumulation and Toxicity in Mesangial Cells
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ting, S.M.; Nair, H.; Ching, I.; Taheri, S.; Dasgupta, I. Overweight, obesity and chronic kidney disease. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 112, c121–c127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chertow, G.M.; Hsu, C.Y.; Johansen, K.L. The enlarging body of evidence: Obesity and chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1501–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culleton, B.F.; Larson, M.G.; Evans, J.C.; Wilson, P.W.; Barrett, B.J.; Parfrey, P.S.; Levy, D. Prevalence and correlates of elevated serum creatinine levels: The framingham heart study. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, A.P.; Ruggenenti, P.; Ruan, X.Z.; Praga, M.; Cruzado, J.M.; Bajema, I.M.; D’Agati, V.D.; Lamb, H.J.; Barlovic, D.P.; Hojs, R.; et al. Fatty kidney: Emerging role of ectopic lipid in obesity-related renal disease. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Caballero, B.; Cheskin, L.J. Association between obesity and kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Juncos, L.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, J.E. Obesity, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambham, N.; Markowitz, G.S.; Valeri, A.M.; Lin, J.; D’Agati, V.D. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: An emerging epidemic. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobulescu, I.A. Renal lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2010, 19, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deji, N.; Kume, S.; Araki, S.; Soumura, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Isshiki, K.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Koya, D.; Haneda, M.; et al. Structural and functional changes in the kidneys of high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 296, F118–F126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, S.; Uzu, T.; Araki, S.; Sugimoto, T.; Isshiki, K.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Kubota, N.; Terauchi, Y.; Kadowaki, T.; et al. Role of altered renal lipid metabolism in the development of renal injury induced by a high-fat diet. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.; Proctor, G.; Moskowitz, S.; Liebman, S.E.; Rogers, T.; Lucia, M.S.; Li, J.; Levi, M. Diet-induced obesity in c57bl/6j mice causes increased renal lipid accumulation and glomerulosclerosis via a sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 32317–32325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.M.; Ahn, S.H.; Choi, P.; Ko, Y.A.; Han, S.H.; Chinga, F.; Park, A.S.; Tao, J.; Sharma, K.; Pullman, J.; et al. Defective fatty acid oxidation in renal tubular epithelial cells has a key role in kidney fibrosis development. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, R.M.; Brown, T.M.; Muntner, P. Epidemiology of obesity, the metabolic syndrome, and chronic kidney disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2012, 14, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverwood, R.J.; Pierce, M.; Thomas, C.; Hardy, R.; Ferro, C.; Sattar, N.; Whincup, P.; Savage, C.; Kuh, D.; Nitsch, D.; et al. Association between younger age when first overweight and increased risk for ckd. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverwood, R.J.; Pierce, M.; Hardy, R.; Thomas, C.; Ferro, C.; Savage, C.; Sattar, N.; Kuh, D.; Nitsch, D.; National Survey of Health and Development Scientific and Data Collection Teams. Early-life overweight trajectory and ckd in the 1946 british birth cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, I.H.; Katz, R.; Fried, L.F.; Ix, J.H.; Luchsinger, J.; Sarnak, M.J.; Shlipak, M.G.; Siscovick, D.S.; Kestenbaum, B. Obesity and change in estimated gfr among older adults. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Iribarren, C.; McCulloch, C.E.; Darbinian, J.; Go, A.S. Risk factors for end-stage renal disease: 25-year follow-up. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkhaugen, J.; Lydersen, S.; Wideroe, T.E.; Hallan, S. Prehypertension, obesity, and risk of kidney disease: 20-year follow-up of the hunt i study in norway. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, F.; Deprele, C.; Sassolas, A.; Moulin, P.; Alamartine, E.; Berthezene, F.; Berthoux, F. Excessive body weight as a new independent risk factor for clinical and pathological progression in primary iga nephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoux, F.; Mariat, C.; Maillard, N. Overweight/obesity revisited as a predictive risk factor in primary iga nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, H.; Ohara, M.; Shibui, K.; Sato, M.; Suzuki, T.; Amemiya, N.; Watanabe, Y.; Honda, K.; Mochizuki, T.; Nitta, K. Overweight and obesity accelerate the progression of iga nephropathy: Prognostic utility of a combination of bmi and histopathological parameters. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2012, 16, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, M.; Kawar, B.; El Nahas, A.M. Influence of obesity on progression of non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: A retrospective cohort study. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 113, c16–c23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.N.K.L.; Mohsen, A.; Green, D.; Hoefield, R.A.; Summers, L.K.M.; Middleton, R.J.; O’Donoghue, D.J.; Kalra, P.A.; New, D.I. Body mass index has no effect on rate of progression of chronic kidney disease in non-diabetic subjects. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2776–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagnac, A.; Weinstein, T.; Herman, M.; Hirsh, J.; Gafter, U.; Ori, Y. The effects of weight loss on renal function in patients with severe obesity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praga, M.; Hernandez, E.; Herrero, J.C.; Morales, E.; Revilla, Y.; Diaz-Gonzalez, R.; Rodicio, J.L. Influence of obesity on the appearance of proteinuria and renal insufficiency after unilateral nephrectomy. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneethan, S.D.; Yehnert, H.; Moustarah, F.; Schreiber, M.J.; Schauer, P.R.; Beddhu, S. Weight loss interventions in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolignano, D.; Zoccali, C. Effects of weight loss on renal function in obese ckd patients: A systematic review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, iv82–iv98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druilhet, R.E.; Overturf, M.L.; Kirkendall, W.M. Cortical and medullary lipids of normal and nephrosclerotic human kidney. Int. J. Biochem. 1978, 9, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, R.S.; Mandel, L.J. Metabolic substrate utilization by rabbit proximal tubule. An nadh fluorescence study. Am. J. Physiol. 1988, 254, F407–F416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nieth, H.; Schollmeyer, P. Substrate-utilization of the human kidney. Nature 1966, 209, 1244–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickards, E. Remarks on the fatty transformation of the kidney. Br. Med. J. 1883, 2, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorhead, J.F.; Chan, M.K.; El-Nahas, M.; Varghese, Z. Lipid nephrotoxicity in chronic progressive glomerular and tubulo-interstitial disease. Lancet 1982, 2, 1309–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, S.; Trompier, D.; Andreoletti, P.; Le Borgne, F.; Demarquoy, J.; Lizard, G. Fatty acids—Induced lipotoxicity and inflammation. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decleves, A.E.; Mathew, A.V.; Cunard, R.; Sharma, K. Ampk mediates the initiation of kidney disease induced by a high-fat diet. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallows, K.R.; Mount, P.F.; Pastor-Soler, N.M.; Power, D.A. Role of the energy sensor amp-activated protein kinase in renal physiology and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullerton, M.D.; Galic, S.; Marcinko, K.; Sikkema, S.; Pulinilkunnil, T.; Chen, Z.P.; O’Neill, H.M.; Ford, R.J.; Palanivel, R.; O’Brien, M.; et al. Single phosphorylation sites in acc1 and acc2 regulate lipid homeostasis and the insulin-sensitizing effects of metformin. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, S.A.; Choy, S.W.; Pastor-Soler, N.M.; Li, H.; Davies, M.R.; Cook, N.; Katerelos, M.; Mount, P.F.; Gleich, K.; McRae, J.L.; et al. Ampk couples plasma renin to cellular metabolism by phosphorylation of acc1. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 305, F679–F690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Kobayashi, M.A.; Araki, S.; Babazono, T.; Freedman, B.I.; Bostrom, M.A.; Cooke, J.N.; Toyoda, M.; Umezono, T.; Tarnow, L.; et al. A single nucleotide polymorphism within the acetyl-coenzyme a carboxylase beta gene is associated with proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Ramachandrarao, S.; Qiu, G.; Usui, H.K.; Zhu, Y.; Dunn, S.R.; Ouedraogo, R.; Hough, K.; McCue, P.; Chan, L.; et al. Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammisotto, P.G.; Londono, I.; Gingras, D.; Bendayan, M. Control of glycogen synthase through adipor1-ampk pathway in renal distal tubules of normal and diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2008, 294, F881–F889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decleves, A.E.; Zolkipli, Z.; Satriano, J.; Wang, L.; Nakayama, T.; Rogac, M.; Le, T.P.; Nortier, J.L.; Farquhar, M.G.; Naviaux, R.K.; et al. Regulation of lipid accumulation by amk-activated kinase in high fat diet-induced kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.E.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, A.S.; Lee, S.; Park, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, B.H.; Kim, W.; Kang, K.P. Metformin decreases high-fat diet-induced renal injury by regulating the expression of adipokines and the renal amp-activated protein kinase/acetyl-coa carboxylase pathway in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Lim, J.H.; Youn, H.H.; Hong, Y.A.; Yang, K.S.; Park, H.S.; Chung, S.; Koh, S.H.; Shin, S.J.; Choi, B.S.; et al. Resveratrol prevents renal lipotoxicity and inhibits mesangial cell glucotoxicity in a manner dependent on the AMPK-SIRT1-PGC1alpha axis in db/db mice. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampe, K.; Sieber, J.; Orellana, J.M.; Mundel, P.; Jehle, A.W. Susceptibility of podocytes to palmitic acid is regulated by fatty acid oxidation and inversely depends on acetyl-coa carboxylases 1 and 2. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 306, F401–F409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Abu Jawdeh, B.G.; Goel, M.; Schilling, W.P.; Parker, M.D.; Puchowicz, M.A.; Yadav, S.P.; Harris, R.C.; El-Meanawy, A.; Hoshi, M.; et al. Lipotoxic disruption of nhe1 interaction with pi(4,5)p2 expedites proximal tubule apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kume, S.; Araki, S.; Isshiki, K.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Koya, D.; Haneda, M.; Kashiwagi, A.; et al. Fenofibrate, a pparalpha agonist, has renoprotective effects in mice by enhancing renal lipolysis. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camici, M.; Galetta, F.; Abraham, N.; Carpi, A. Obesity-related glomerulopathy and podocyte injury: A mini review. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornoni, A.; Merscher, S.; Kopp, J.B. Lipid biology of the podocyte—New perspectives offer new opportunities. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlondorff, D.; Banas, B. The mesangial cell revisited: No cell is an island. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.Z.; Varghese, Z.; Powis, S.H.; Moorhead, J.F. Human mesangial cells express inducible macrophage scavenger receptor. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Wen, Y.; Li, X. Very-low-density lipoprotein-induced triglyceride accumulation in human mesangial cells is mainly mediated by lipoprotein lipase. Nephron Physiol. 2008, 110, p1–p10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.Z.; Varghese, Z.; Powis, S.H.; Moorhead, J.F. Dysregulation of ldl receptor under the influence of inflammatory cytokines: A new pathway for foam cell formation1. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berfield, A.K.; Andress, D.L.; Abrass, C.K. Igf-1-induced lipid accumulation impairs mesangial cell migration and contractile function. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.A.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, Y.; Yang, K.S.; Park, H.S.; Choi, S.R.; Chung, S.; Kim, H.W.; et al. Fenofibrate improves renal lipotoxicity through activation of ampk-pgc-1alpha in db/db mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mount, P.; Davies, M.; Choy, S.-W.; Cook, N.; Power, D. Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease—The Role of Lipid Metabolism. Metabolites 2015, 5, 720-732. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5040720
Mount P, Davies M, Choy S-W, Cook N, Power D. Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease—The Role of Lipid Metabolism. Metabolites. 2015; 5(4):720-732. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5040720
Chicago/Turabian StyleMount, Peter, Matthew Davies, Suet-Wan Choy, Natasha Cook, and David Power. 2015. "Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease—The Role of Lipid Metabolism" Metabolites 5, no. 4: 720-732. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5040720
APA StyleMount, P., Davies, M., Choy, S.-W., Cook, N., & Power, D. (2015). Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease—The Role of Lipid Metabolism. Metabolites, 5(4), 720-732. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5040720




