An Efficient Single Phase Method for the Extraction of Plasma Lipids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Recovery of Lipids
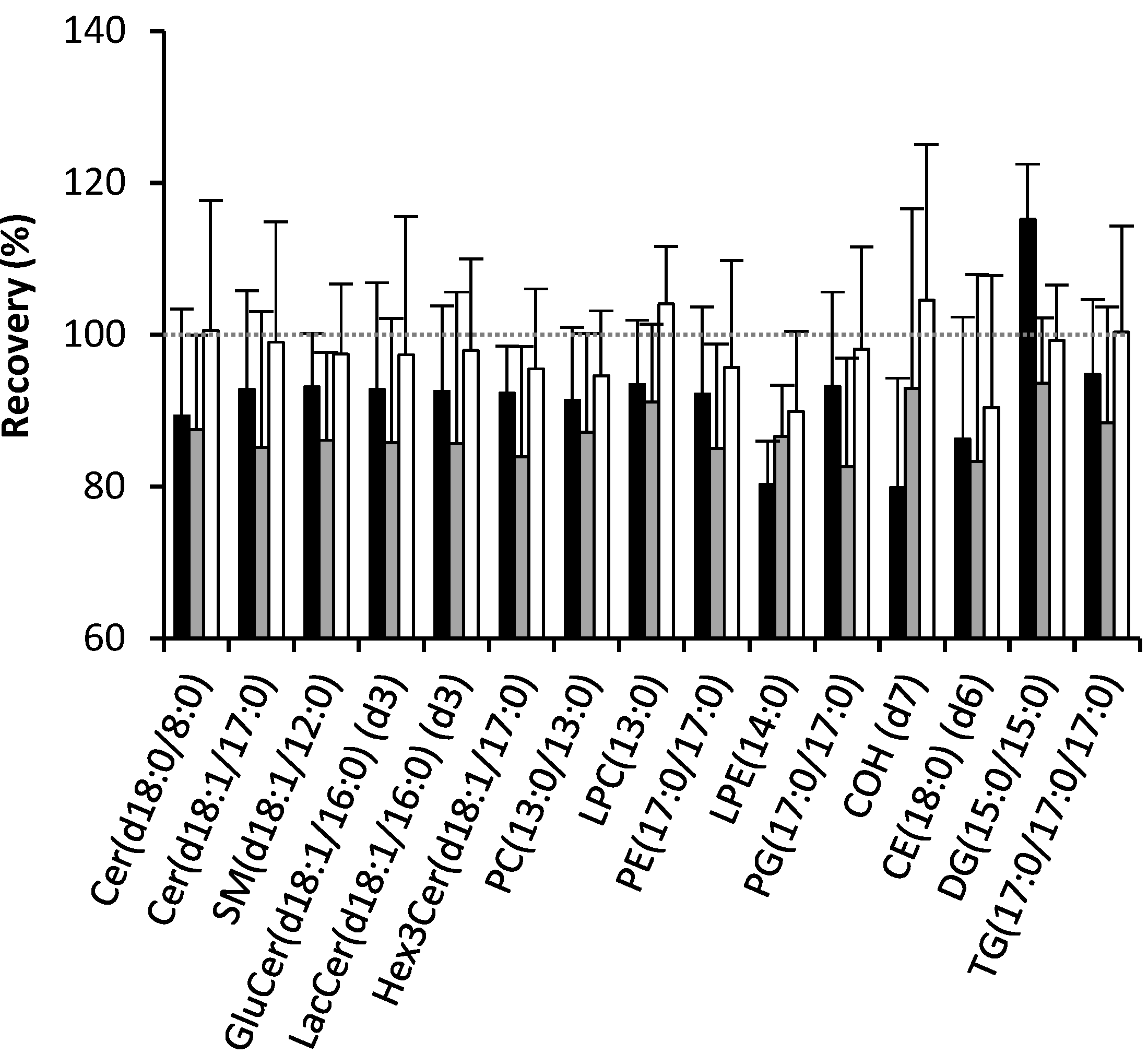
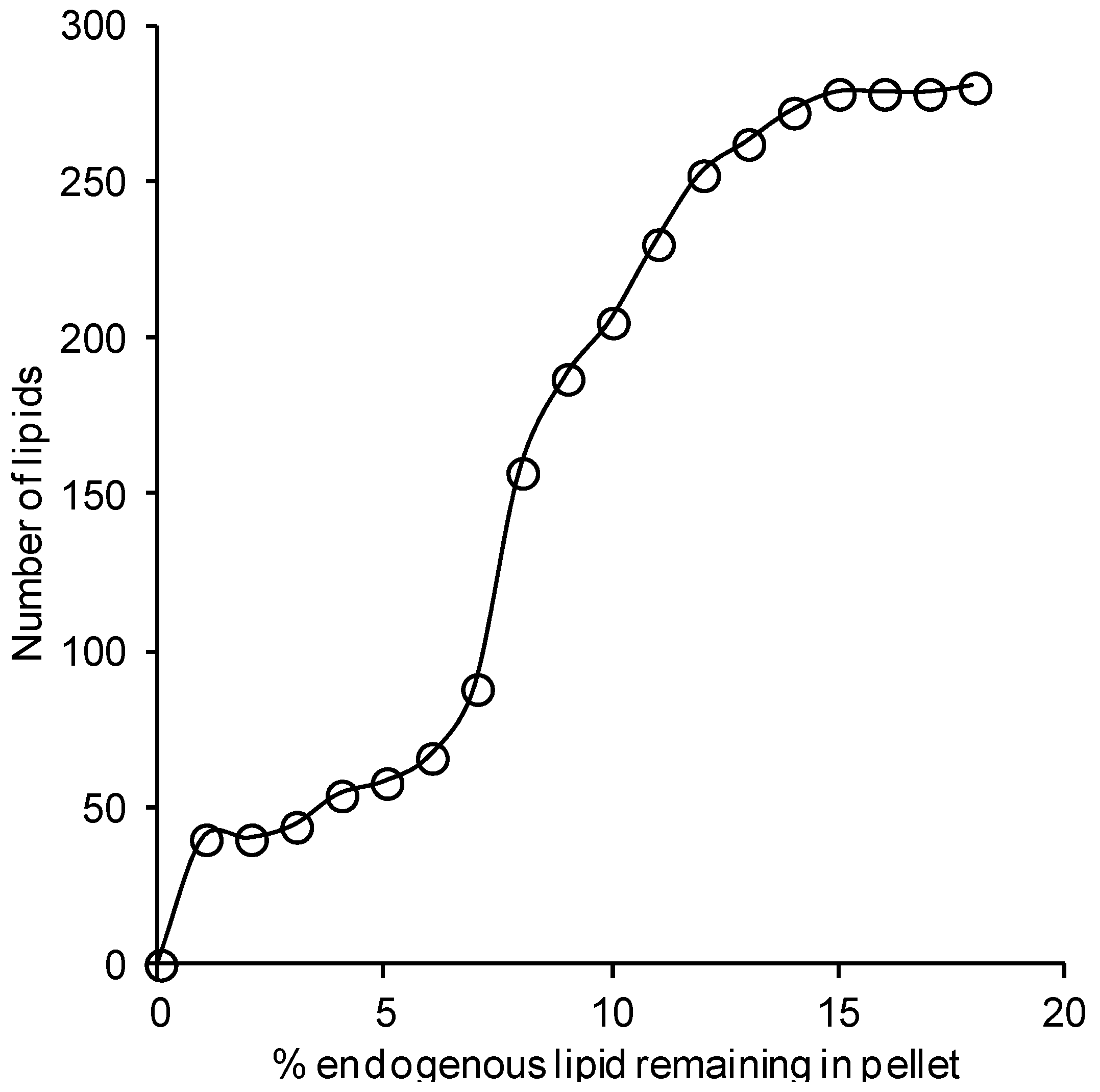
2.2. Effect of Solvents on Reverse-Phase Chromatography
2.3. Comparison of the Lipid Measurements with the 1-Butanol/Methanol (1:1 v/v) and Chloroform/Methanol Methods
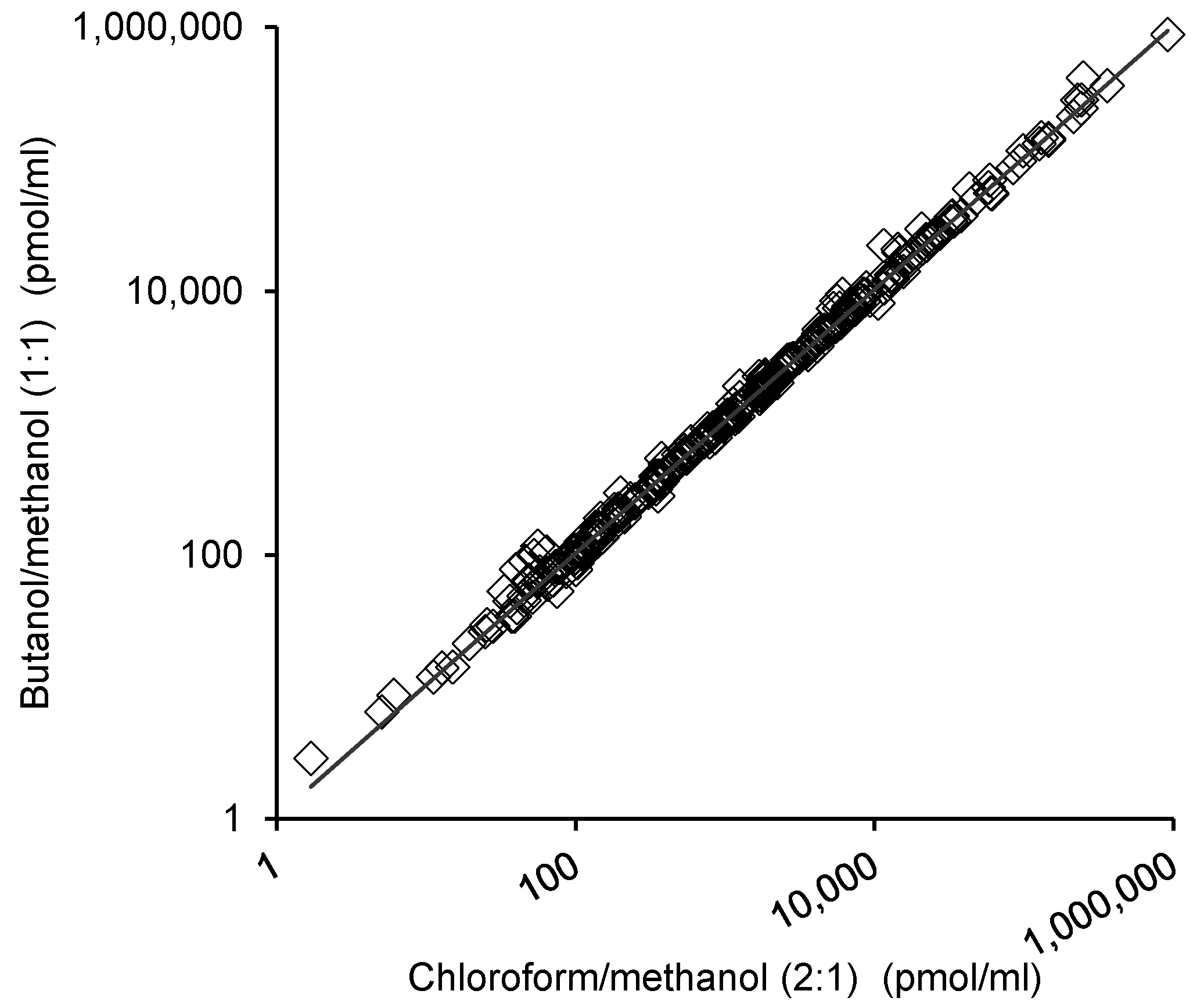
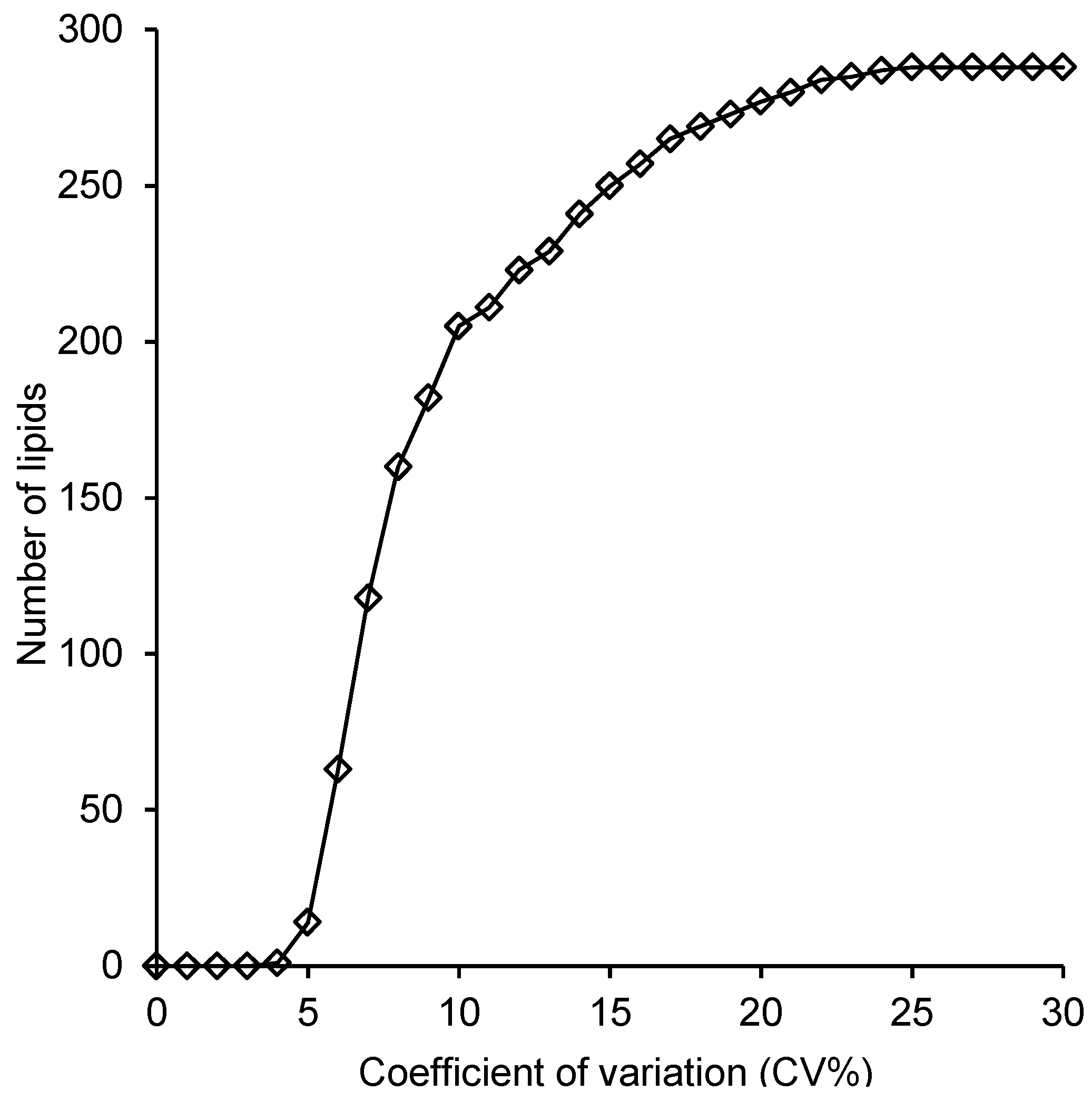
2.4. Reproducibility of the Lipid Measurements Following Extraction with Each Method
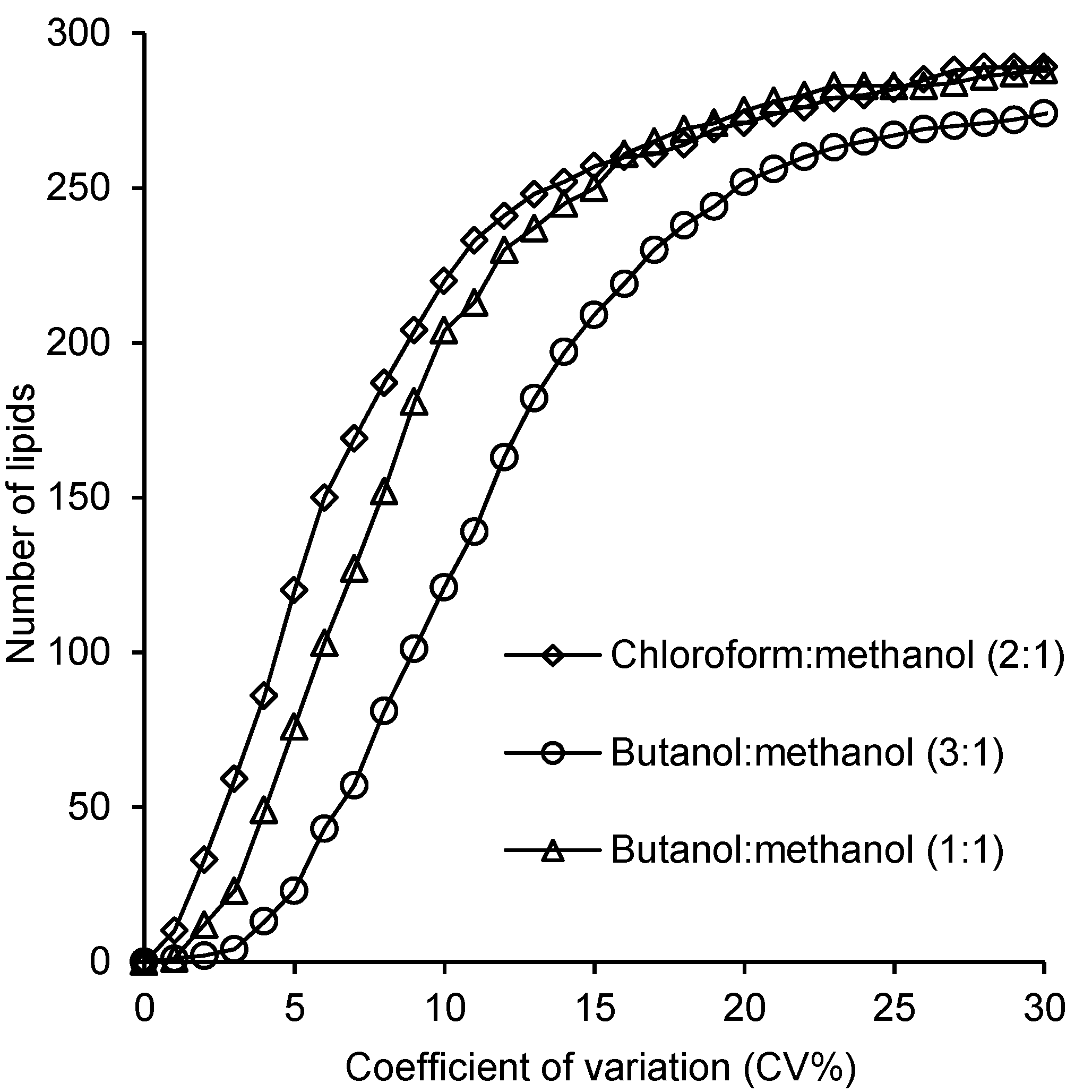
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Lipid Standards and Solvents
| Lipid Class | No. of species | Internal standard | Pmol 1 | Q1 (Parent ion) | Q3 (Product Ion) 2 | Voltage settings 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP | EP | CE | CXP | ||||||
| Dihydroceramide (dhCer) | 6 | Cer(d18:0/8:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | 284.3 | 90 | 30 | 28 | 10 |
| Ceramide (Cer) | 6 | Cer(d18:1/17:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | 264.3 | 50 | 10 | 35 | 12 |
| Monohexocylceramide (HexCer) | 6 | GluCer4(d18:1/16:0) (d3) | 50 | [M+H]+ | 264.3 | 77 | 10 | 50 | 12 |
| Dihexosylceramide (Hex2Cer) | 6 | LacCer4(d18:1/16:0) (d3) | 50 | [M+H]+ | 264.3 | 100 | 10 | 65 | 12 |
| Trihexosylceramide (Hex3Cer) | 6 | Hex3Cer(d18:1/17:0) | 50 | [M+H]+ | 264.3 | 130 | 10 | 73 | 12 |
| Sphingomyelin (SM) | 20 | SM(d18:1/12:0) | 200 | [M+H]+ | 184.1 | 65 | 10 | 35 | 12 |
| Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | 46 | PC(13:0/13:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | 184.1 | 100 | 10 | 45 | 11 |
| Alkylphosphatidylcholine (PC-O) | 19 | PC(13:0/13:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | 184.1 | 100 | 10 | 45 | 11 |
| Alkenylphosphatidylcholine (PC-P) | 14 | PC(13:0/13:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | 184.1 | 100 | 10 | 45 | 11 |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) | 22 | LPC(13:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | 184.1 | 90 | 10 | 38 | 12 |
| Lysoalkylphosphatidylcholine (LPC-O) | 10 | LPC(13:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | 104.1 | 90 | 10 | 42 | 5 |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) | 21 | PE(17:0/17:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | NL, 141 Da | 80 | 10 | 31 | 7 |
| Alkylphosphatidylethanolamine (PE-O) | 12 | PE(17:0/17:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | NL, 141 Da | 80 | 10 | 31 | 7 |
| Alkenylphosphatidylethanolamine (PE-P) | 11 | PE(17:0/17:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | NL, 141 Da | 80 | 10 | 31 | 7 |
| Lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) | 6 | LPE(14:0) | 100 | [M+H]+ | NL, 141 Da | 80 | 10 | 31 | 7 |
| Phosphatidylinositol (PI) | 16 | PE(17:0/17:0) | 100 | [M+NH4]+ | NL, 277 Da | 51 | 10 | 43 | 14 |
| Lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI) | 4 | LPE(14:0) | 100 | [M+ NH4]+ | NL, 277 Da | 80 | 10 | 31 | 7 |
| Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) | 3 | PG(17:0/17:0) | 100 | [M+ NH4]+ | NL, 189 Da | 60 | 10 | 25 | 12 |
| Cholesteryl ester (CE) | 26 | CE(18:0) (d6) | 1000 | [M+ NH4]+ | 369.3 | 30 | 10 | 20 | 12 |
| Free cholesterol (COH) | 1 | Cholesterol (d7) | 1000 | [M+ NH4]+ | 369.3 | 55 | 10 | 17 | 12 |
| Diacylglycerol (DG) | 24 | DG(15:0/15:0) | 200 | [M+ NH4]+ | NL, NH3 + fatty acid | 55 | 10 | 30 | 22 |
| Triacylglycerol (TG) | 25 | TG(17:0/17:0/17:0) | 100 | [M+ NH4]+ | NL, NH3 + fatty acid | 95 | 10 | 30 | 12 |
4.2. Human Plasma
4.3. Lipid Extraction Methods
4.3.1. 1-Butanol/Methanol (1:1 v/v) Method
4.3.2. Chloroform/Methanol Extraction
4.3.3. 1-Butanol/Methanol (3:1, v/v) Extraction
4.4. Lipid Analysis
4.5. Extraction Performance
4.5.1. Recovery
4.5.2. Reproducibility
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavusoglu, E.; Chhabra, S.; Jiang, X.C.; Hojjati, M.R.; Chopra, V.; Eng, C.; Gupta, A.; Yanamadala, S.; Pinsky, D.J.; Marmur, J.D. Relation of baseline plasma phospholipid levels to cardiovascular outcomes at two years in men with acute coronary syndrome referred for coronary angiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2007, 100, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, R.; Mori, C.; Kitazato, K.; Arata, S.; Obama, T.; Mori, M.; Takahashi, K.; Aiuchi, T.; Takano, T.; Itabe, H. Transient increase in plasma oxidized ldl during the progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e knockout mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voight, B.F.; Peloso, G.M.; Orho-Melander, M.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Barbalic, M.; Jensen, M.K.; Hindy, G.; Holm, H.; Ding, E.L.; Johnson, T.; et al. Plasma hdl cholesterol and risk of myocardial infarction: A mendelian randomisation study. Lancet 2012, 380, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, R.; Pruneta-Deloche, V.; Guichardant, M.; Luquain-Costaz, C.; Cugnet-Anceau, C.; Moret, M.; Vidal, H.; Moulin, P.; Lagarde, M.; Calzada, C. Increased lipid peroxidation in ldl from type-2 diabetic patients. Lipids 2010, 45, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.L. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis. Model. Mech. 2009, 2, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, P.J.; Wong, G.; Tsorotes, D.; Barlow, C.K.; Weir, J.M.; Christopher, M.J.; MacIntosh, G.L.; Goudey, B.; Stern, L.; Kowalczyk, A.; et al. Plasma lipidomic analysis of stable and unstable coronary artery disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2723–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, J.M.; Wong, G.; Barlow, C.K.; Greeve, M.A.; Kowalczyk, A.; Almasy, L.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Mahaney, M.C.; Jowett, J.B.; Shaw, J.; et al. Plasma lipid profiling in a large population-based cohort. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2898–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, P.J.; Wong, G.; Barlow, C.K.; Kingwell, B.A. Lipidomics: Potential role in risk prediction and therapeutic monitoring for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiukka, A.; Stahlman, M.; Pettersson, C.; Levin, M.; Adiels, M.; Teneberg, S.; Leinonen, E.S.; Hulten, L.M.; Wiklund, O.; Oresic, M.; et al. Apociii-enriched ldl in type 2 diabetes displays altered lipid composition, increased susceptibility for sphingomyelinase, and increased binding to biglycan. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Kong, H.; Qu, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Gao, P.; Peng, S.; Xu, G. Application of plasma lipidomics in studying the response of patients with essential hypertension to antihypertensive drug therapy. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorente, A.; Skotland, T.; Sylvanne, T.; Kauhanen, D.; Rog, T.; Orlowski, A.; Vattulainen, I.; Ekroos, K.; Sandvig, K. Molecular lipidomics of exosomes released by pc-3 prostate cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbenoit, N.; Saussereau, E.; Bich, C.; Bourderioux, M.; Fritsch, J.; Edelman, A.; Brunelle, A.; Ollero, M. Localized lipidomics in cystic fibrosis: Tof-sims imaging of lungs from pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected mice. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 52, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang-Sattler, R.; Yu, Y.; Mittelstrass, K.; Lattka, E.; Altmaier, E.; Gieger, C.; Ladwig, K.H.; Dahmen, N.; Weinberger, K.M.; Hao, P.; et al. Metabolic profiling reveals distinct variations linked to nicotine consumption in humans––First results from the kora study. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laaksonen, R.; Katajamaa, M.; Paiva, H.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Saarinen, L.; Junni, P.; Lutjohann, D.; Smet, J.; Van Coster, R.; Seppanen-Laakso, T.; et al. A systems biology strategy reveals biological pathways and plasma biomarker candidates for potentially toxic statin-induced changes in muscle. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekroos, K.; Janis, M.; Tarasov, K.; Hurme, R.; Laaksonen, R. Lipidomics: A tool for studies of atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2010, 12, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; McEvoy, J.; Baillie, R.A.; Lee, D.; Yao, J.K.; Doraiswamy, P.M.; Krishnan, K.R.R. Metabolomic mapping of atypical antipsychotic effects in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, P.J.; Christopher, M.J. Lipidomics is providing new insight into the metabolic syndrome and its sequelae. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2011, 22, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahlman, M.; Ejsing, C.S.; Tarasov, K.; Perman, J.; Boren, J.; Ekroos, K. High-throughput shotgun lipidomics by quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 2664–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, A.E.; Pagano, R.E. An improved synthesis of 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole analogs of cdp-diacylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1991, 60, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid extraction by methyl-tert-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofgren, L.; Stahlman, M.; Forsberg, G.B.; Saarinen, S.; Nilsson, R.; Hansson, G.I. The bume method: A novel automated chloroform-free 96-well total lipid extraction method for blood plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Blackburn, G.J.; Mohd Fauzi, N.; Pitt, A.R.; Spickett, C.M. A comparison of five lipid extraction solvent systems for lipidomic studies of human ldl. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lydic, T.A.; Busik, J.V.; Reid, G.E. A monophasic extraction strategy for the simultaneous lipidome analysis of polar and nonpolar retina lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshehry, Z.H.; Barlow, C.K.; Weir, J.M.; Zhou, Y.; McConville, M.J.; Meikle, P.J. An Efficient Single Phase Method for the Extraction of Plasma Lipids. Metabolites 2015, 5, 389-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5020389
Alshehry ZH, Barlow CK, Weir JM, Zhou Y, McConville MJ, Meikle PJ. An Efficient Single Phase Method for the Extraction of Plasma Lipids. Metabolites. 2015; 5(2):389-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5020389
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshehry, Zahir H., Christopher K. Barlow, Jacquelyn M. Weir, Youping Zhou, Malcolm J. McConville, and Peter J. Meikle. 2015. "An Efficient Single Phase Method for the Extraction of Plasma Lipids" Metabolites 5, no. 2: 389-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5020389
APA StyleAlshehry, Z. H., Barlow, C. K., Weir, J. M., Zhou, Y., McConville, M. J., & Meikle, P. J. (2015). An Efficient Single Phase Method for the Extraction of Plasma Lipids. Metabolites, 5(2), 389-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5020389






