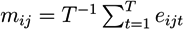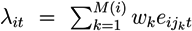Integrative Analysis of Longitudinal Metabolomics Data from a Personal Multi-Omics Profile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
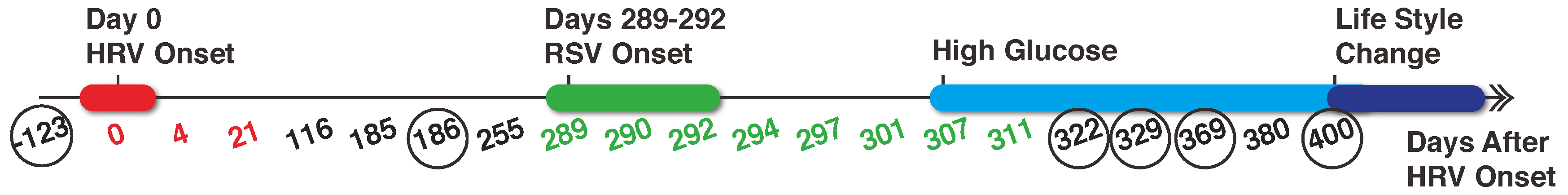
2.2. Metabolomics Data
2.3. Proteomics Data
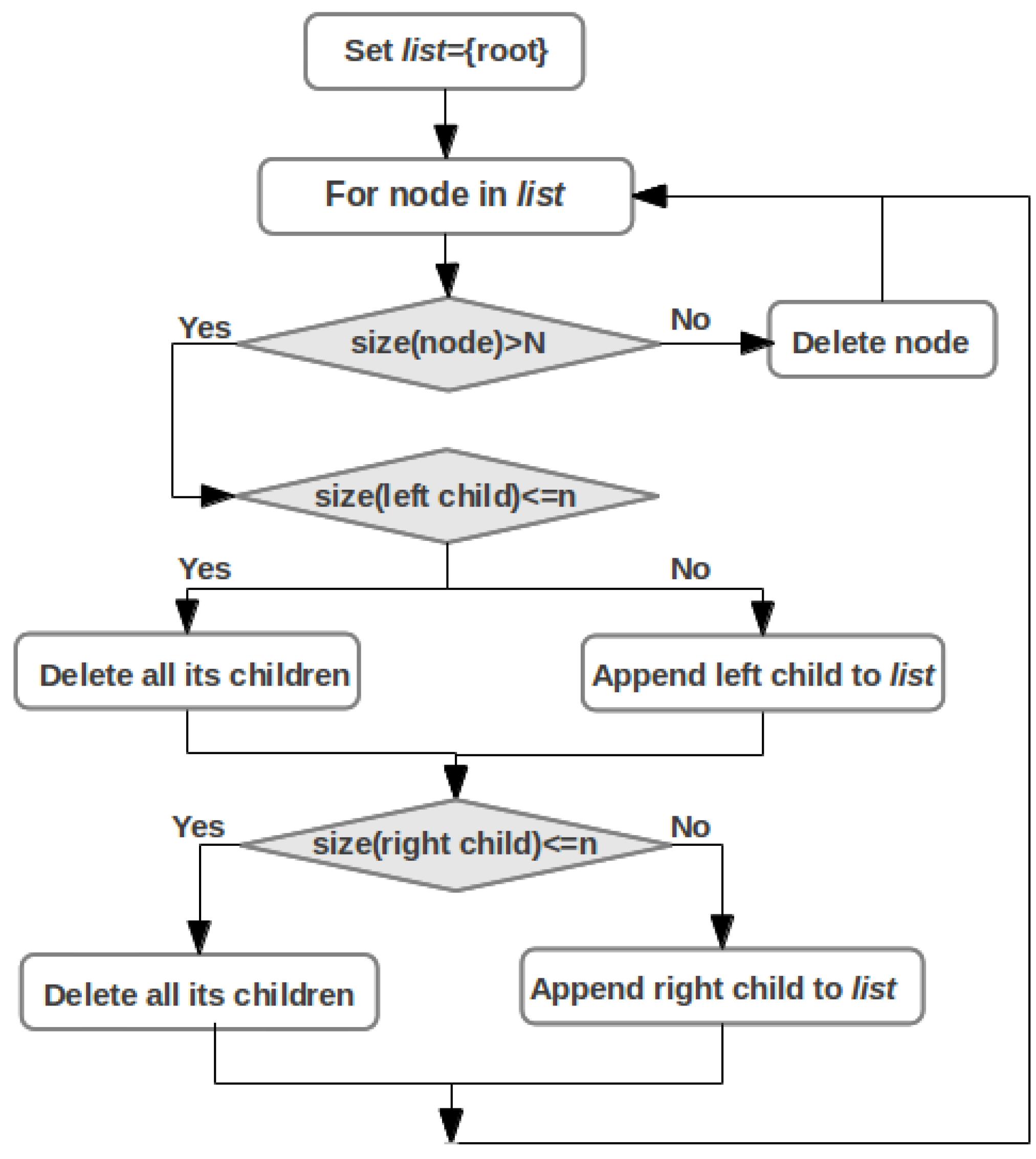
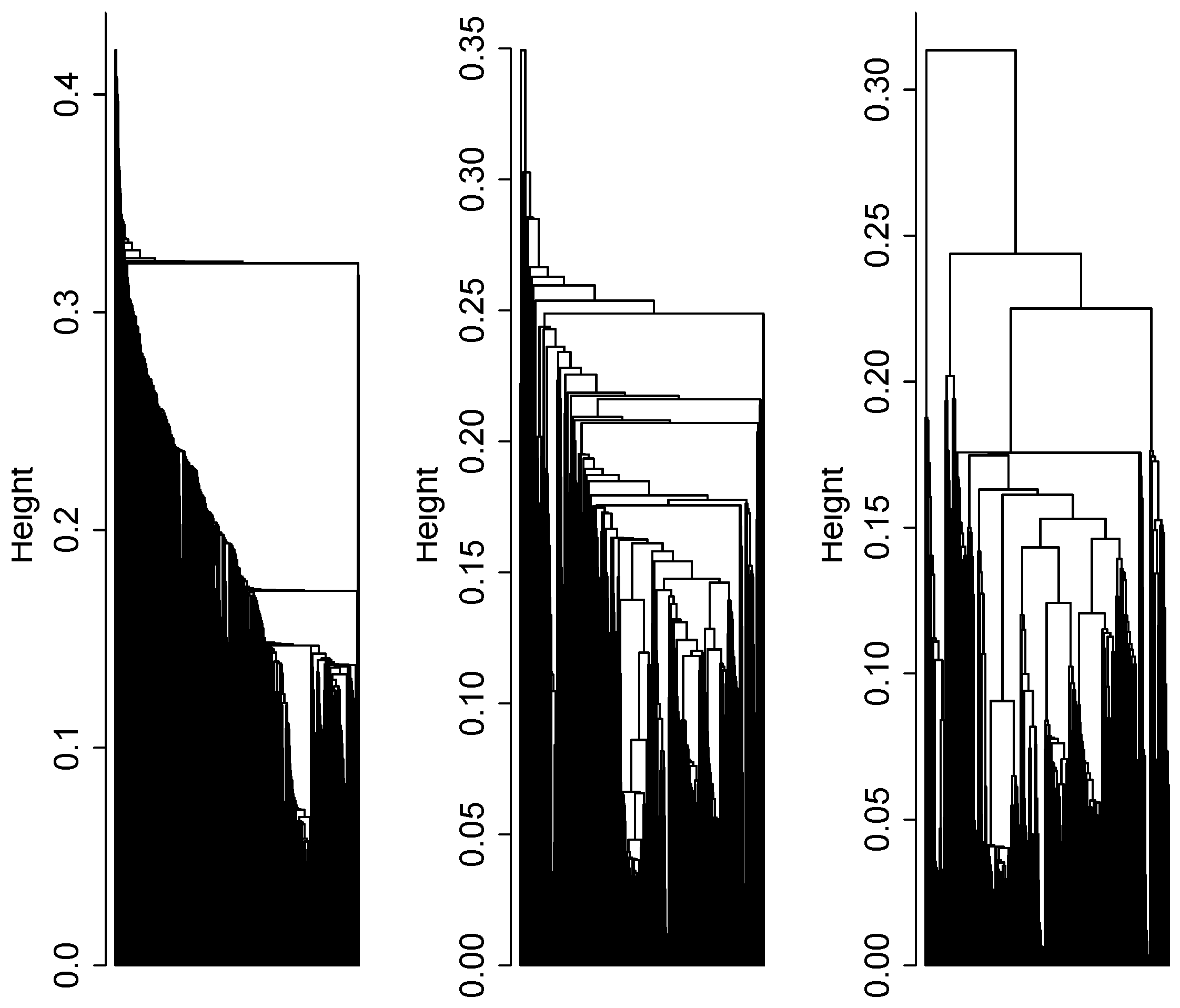
2.4. Cluster Analysis
2.5. Pathway Mapping
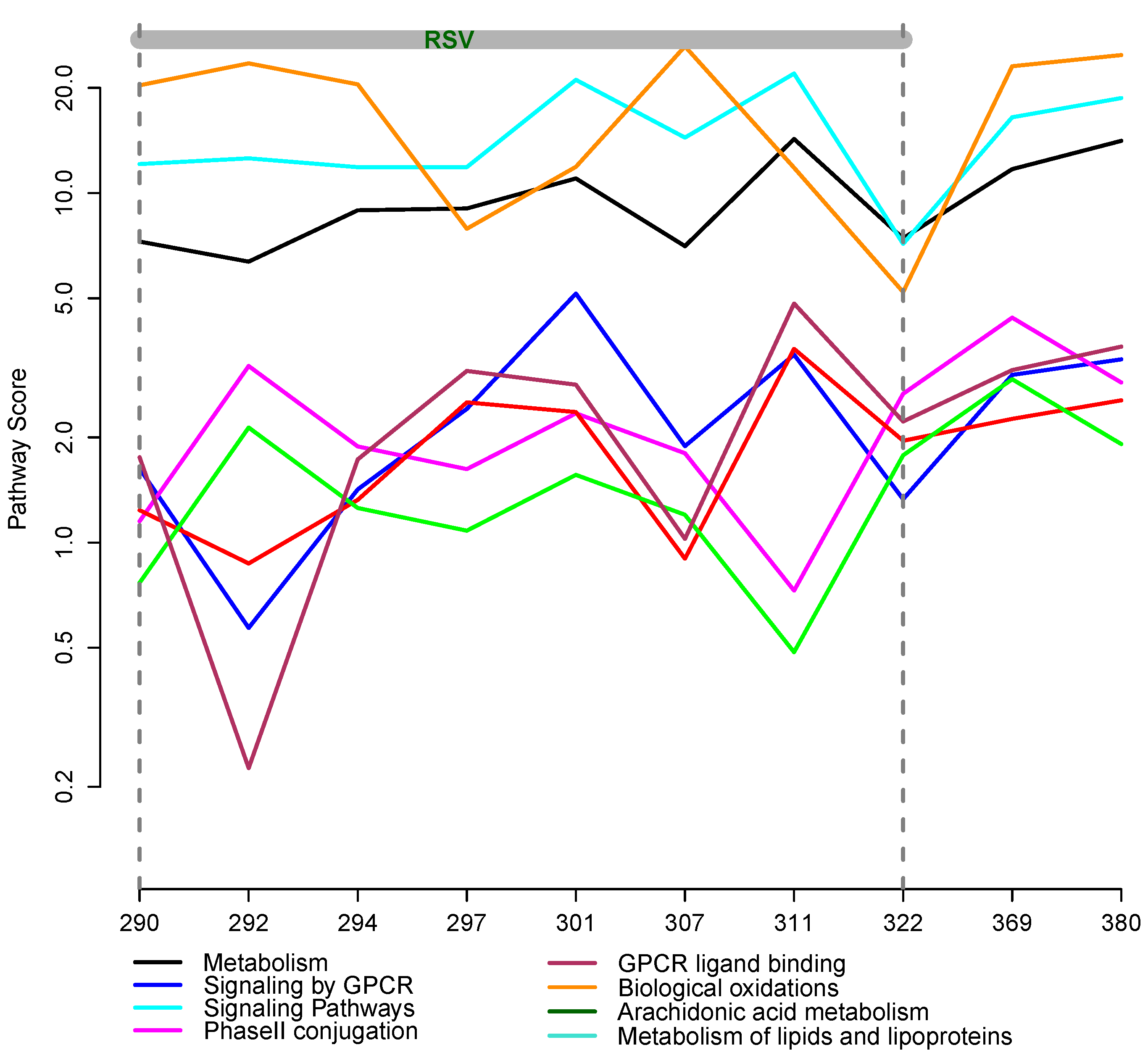
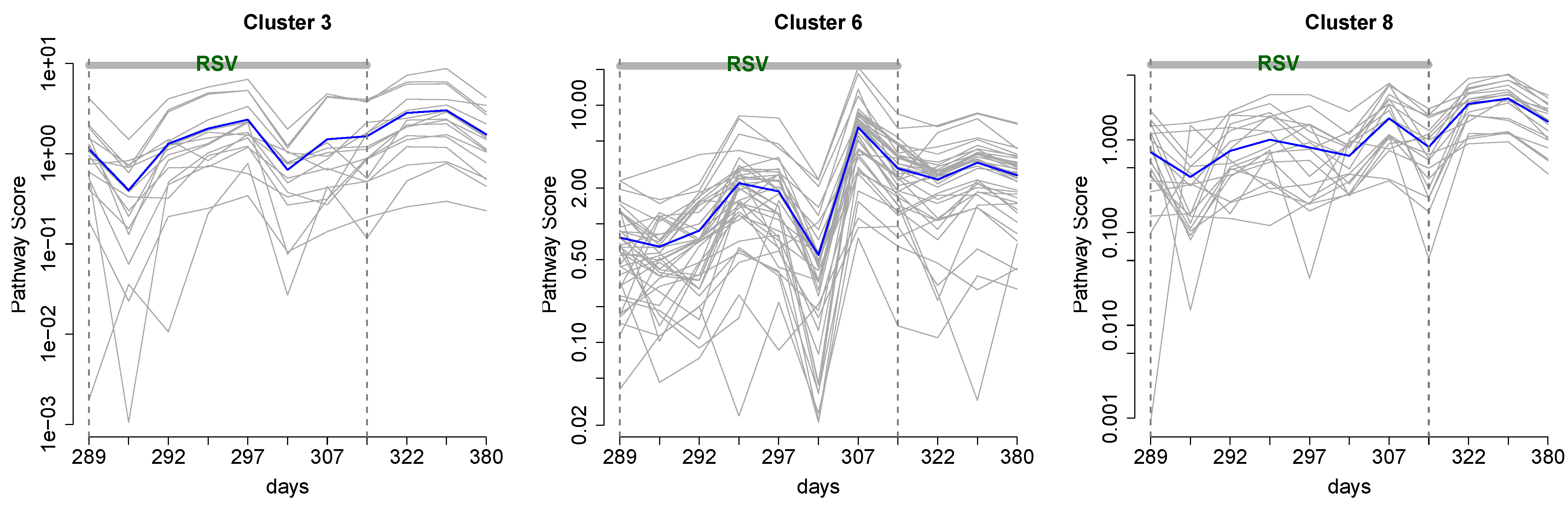
2.6. Integrative Pathway Analysis
- For each molecule, j, in pathway i, calculate the average log-relative expression, mij, across the time points:
.
- From mij, j = 1,..., Ni, use DEAP to identify the maximally scoring subpath and its constituting components: Si = {j1,..., jM(i)}.
- Given Si, at each time point, compute the score,
, where weights, wk, correspond to +1 and −1, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Cluster Analysis
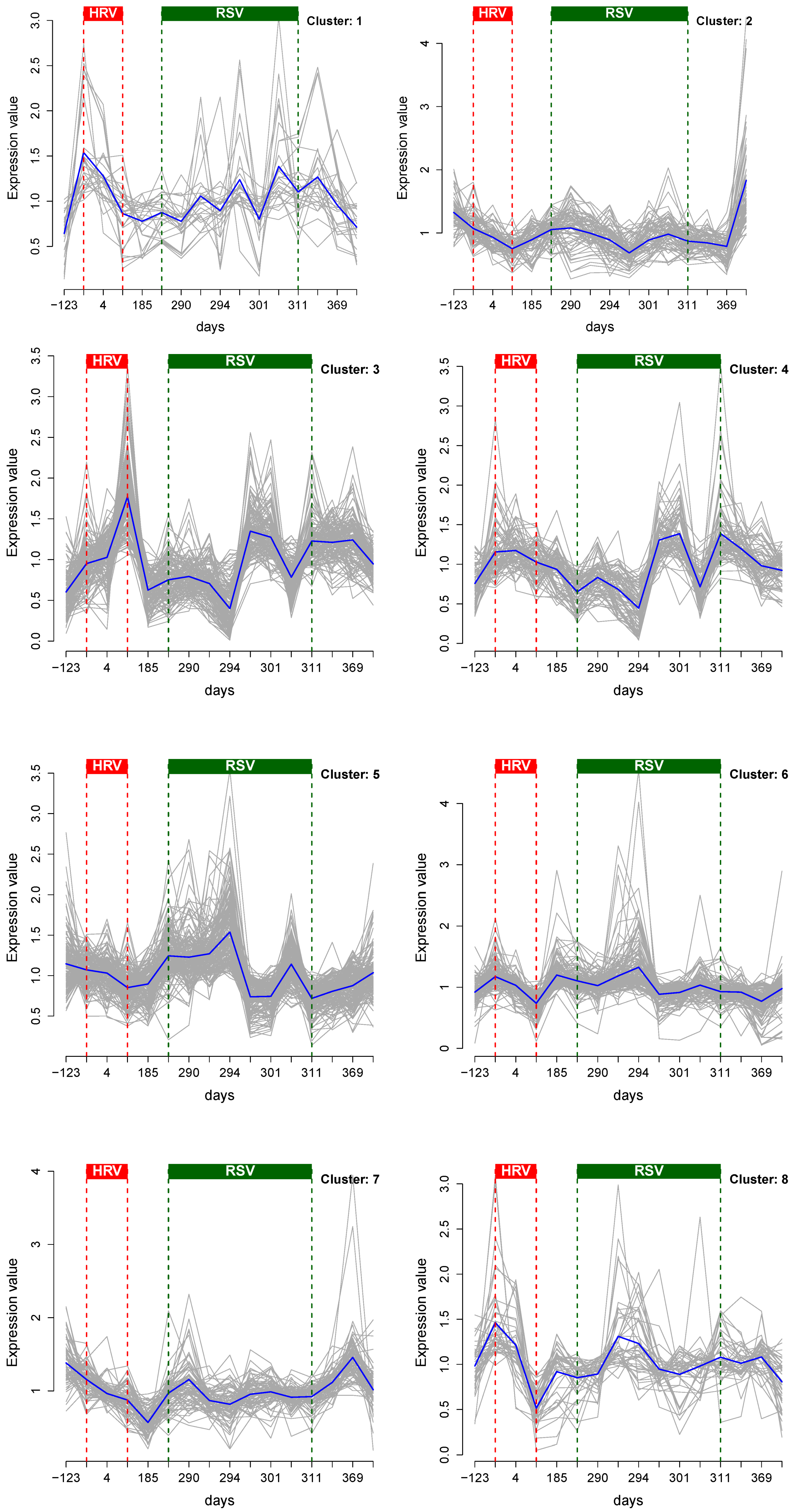
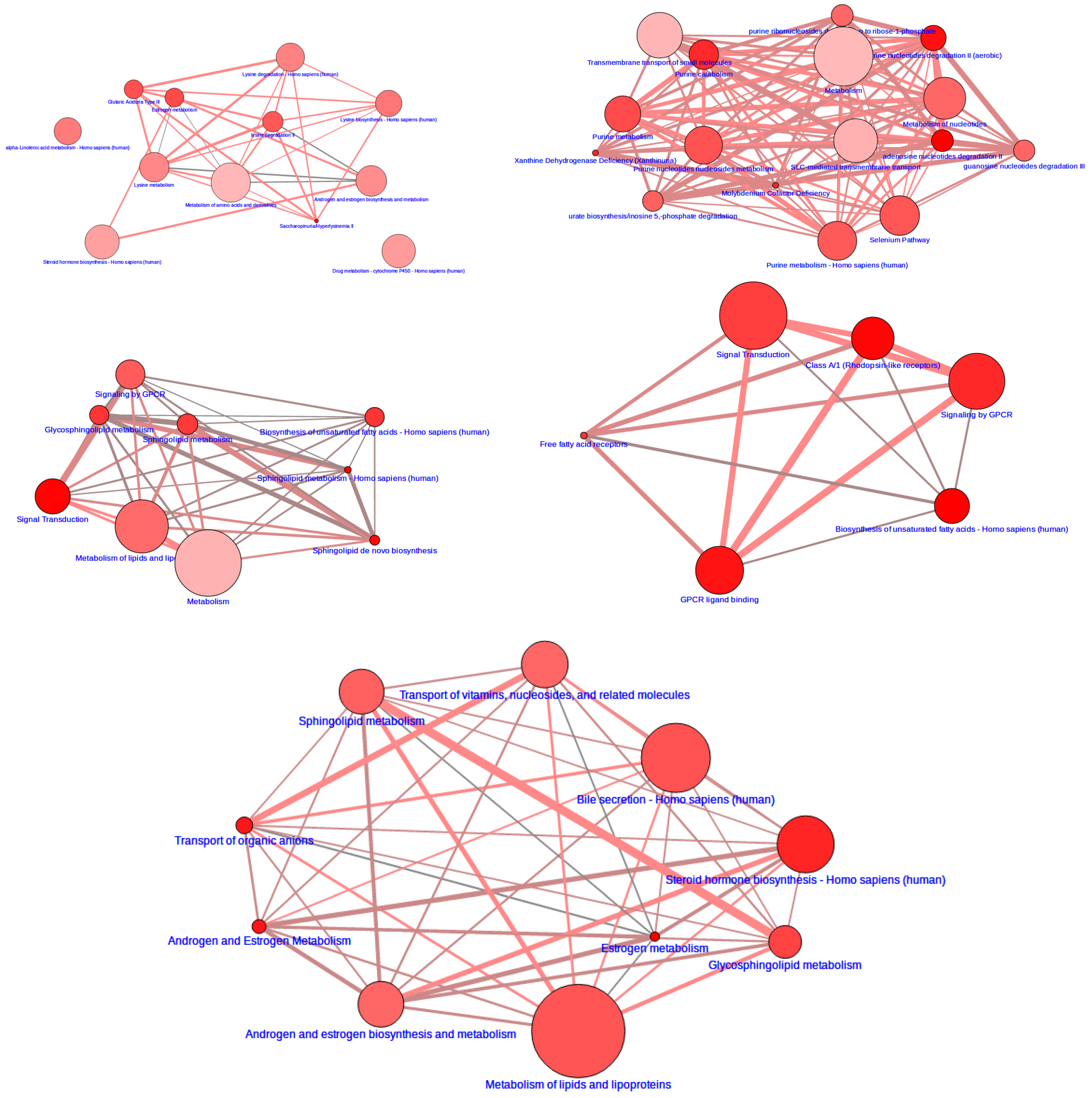
3.2. Integrative Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Data Dissemination
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Devescovi, V.; Chen, S.; Nardini, C. Multilevel omic data integration in cancer cell lines: Advanced annotation and emergent properties. BMC Syst. Biol. 2013, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Halvey, P.J.; Shyr, Y.; Slebos, R.J.C.; Liebler, D.C.; Zhang, B. Integrative omics analysis reveals the importance and scope of translational repression in microRNA-mediated regulation. Mol. Cell. Proteomics: MCP 2013, 12, 1900–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurland, I.J.; Accili, D.; Burant, C.; Fischer, S.M.; Kahn, B.B.; Newgard, C.B.; Ramagiri, S.; Ronnett, G.V.; Ryals, J.A.; Sanders, M.; et al. Application of combined omics platforms to accelerate biomedical discovery in diabesity. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1287, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchet, L.; Smolinska, A.; Attali, A.; Stoop, M.P.; Ampt, K.A.M.; van Aken, H.; Suidgeest, E.; Tuinstra, T.; Wijmenga, S.S.; et al. Fusion of metabolomics and proteomics data for biomarkers discovery: Case study on the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. BMC Bioinforma. 2011, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Olshen, A.B.; Ladanyi, M. Integrative clustering of multiple genomic data types using a joint latent variable model with application to breast and lung cancer subtype analysis. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaske, C.J.; Benz, S.C.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Earl, D.; Szeto, C.; Zhu, J.; Haussler, D.; Stuart, J.M. Inference of patient-specific pathway activities from multi-dimensional cancer genomics data using PARADIGM. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, i237–i245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignot, S.; Soria, J.C. Discrepancies between primary tumor and metastasis: Impact on personalized medicine. Bull. Cancer 2013, 100, 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Law, G.L.; Korth, M.J.; Benecke, A.G.; Katze, M.G. Systems virology: Host-directed approaches to viral pathogenesis and drug targeting. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanrıkulu, A.; Ağırbaşlı, M. Triple therapy (aspirin, clopidogrel and oral anticoagulant) after percutaneous coronary intervention: another call for personalized medicine. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2013, 13, 486–494. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, L.S.; Marciel, K.K.; Quittner, A.L. Utilization of patient-reported outcomes as a step towards collaborative medicine. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2013, 14, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyse, M.; Michiels, S. Omics-based clinical trial designs. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Mias, G.I.; Li-Pook-Than, J.; Jiang, L.; Lam, H.Y.K.; Chen, R.; Miriami, E.; Karczewski, K.J.; Hariharan, M.; Dewey, F.E.; et al. Personal omics profiling reveals dynamic molecular and medical phenotypes. Cell 2012, 148, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higdon, R.; Haynes, W.; Stanberry, L.; Stewart, E.; Yandl, G.; Howard, C.; Broomall, W.; Kolker, N.; Kolker, E. Unraveling the complexities of life sciences data. Big Data 2013, 1, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolker, E.; Stewart, E.; zdemir, V. DELSA global for “Big Data” and the Bioeconomy: Catalyzing Collective Innovation. Ind. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolker, E. Editorial: Special issue on data-intensive science. OMICS 2011, 15, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barga, R.; Howe, B.; Beck, D.; Bowers, S.; Dobyns, W.; Haynes, W.; Higdon, R.; Howard, C.; Roth, C.; Stewart, E.; et al. Bioinformatics and data-intensive scientific discovery in the beginning of the 21st century. Omics: A J. Integr. Biol. 2011, 15, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, L.; Gopinath, G.; Gillespie, M.; Caudy, M.; Croft, D.; de Bono, B.; Garapati, P.; Hemish, J.; Hermjakob, H.; Jassal, B.; et al. Reactome knowledgebase of human biological pathways and processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D619–D622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G.; Qiu, X.; Beason, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Ekanayake, J.; Gunarathne, T.; Rho, M.; Tang, H.; Devadasan, N.; Liu, G. Biomedical Case Studies in Data Intensive Computing. In Proceedings of the CloudCom ’09 Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Cloud Computing, Beijing, China, 1–4 December 2009; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 2–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, D.R.; Schroeder, M.; van Helden, J. Interactive visualization and exploration of relationships between biological objects. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.A.; Higdon, R.; Stanberry, L.; Collins, D.; Kolker, E. Differential expression analysis for pathways. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1002967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolker, E.; Higdon, R.; Welch, D.; Bauman, A.; Stewart, E.; Haynes, W.; Broomall, W.; Kolker, N. Corrigendum to “SPIRE: Systematic protein investigative research environment” [J. Proteomics 75 (1) (2011) 122–126]. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, V.; Pang, T.; Knoppers, B.M.; Avard, D.; Faraj, S.A.; Zawati, M.H.; Kolker, E. Vaccines of the 21st century and vaccinomics: Data-enabled science meets global health to spark collective action for vaccine innovation. OMICS: A J. Integr. Biol. 2011, 15, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.; Kolker, E. DELSA global workshop: Quantified human initiative. Big Data 2013, 3. in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, D.; Robards, K. Metabolomics: The greatest omics of them all? Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7954–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanberry, L.; Haynes, W.; Higdon, R.; Kolker, E. Pathway-centric analysis for multi-omics data. In preparation.
- Hastings, J.; de Matos, P.; Dekker, A.; Ennis, M.; Harsha, B.; Kale, N.; Muthukrishnan, V.; Owen, G.; Turner, S.; Williams, M.; et al. The ChEBI reference database and ontology for biologically relevant chemistry: Enhancements for 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D456–D463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R.; Wu, C.H.; Barker, W.C.; Boeckmann, B.; Ferro, S.; Gasteiger, E.; Huang, H.; Lopez, R.; Magrane, M.; et al. The universal protein resource (uniprot). Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D154–D159. [Google Scholar]
- Hartigan, J. Consistency of single linkage for high-density clusters. Am. Stat. 1981, 76, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hartigan, J. Distribution Problems in Clustering. In Classification and Clustering; Van Ryzin, J., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA; Harcourt Brace Jovanovich Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1977; Mathematics Research Center Publication, No. 37. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, V. Interpreting Multivariate Data; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1981; Wiley Series in Probability and Mathematical Statistics. [Google Scholar]
- Stanberry, L.; Nandy, R.; Cordes, D. Cluster analysis of fMRI data using dendrogram sharpening. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2003, 20, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murua, A.; Stanberry, L.; Stuetzle, W. On Potts model clustering, kernel K-means, and density estimation. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2008, 17, 629–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford Center for Biomedical Informatics Research (BMIR) at the Stanford University School of Medicine. Protege Project.
- Kamburov, A.; Pentchev, K.; Galicka, H.; Wierling, C.; Lehrach, H.; Herwig, R. ConsensusPathDB: Toward a more complete picture of cell biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D712–D717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukreyev, A.; Whitehead, S.S.; Prussin, C.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L. Effect of coexpression of interleukin-2 by recombinant respiratory syncytial virus on virus replication, immunogenicity, and production of other cytokines. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 7151–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, L.M.; Moore, D.D.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Finberg, R.W.; Anderson, L.J.; Tripp, R.A. Involvement of toll-like receptor 4 in innate immunity to respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 10730–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallabhandi, P.; Phillips, R.L.; Boukhvalova, M.S.; Pletneva, L.M.; Shirey, K.A.; Gioannini, T.L.; Weiss, J.P.; Chow, J.C.; Hawkins, L.D.; Vogel, S.N.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein-induced toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling is inhibited by the TLR4 antagonists Rhodobacter sphaeroides lipopolysaccharide and eritoran (E5564) and requires direct interaction with MD-2. mBio 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgel, P.; Nadel, J. Roles of epidermal growth factor receptor activation in epithelial cell repair and mucin production in airway epithelium. Thorax 2004, 59, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. Fibroblast growth factors. Genome biology 2001, 2, REVIEWS3005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monick, M.M.; Cameron, K.; Staber, J.; Powers, L.S.; Yarovinsky, T.O.; Koland, J.G.; Hunninghake, G.W. Activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by respiratory syncytial virus results in increased inflammation and delayed apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3589–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFrancesco, L. Omics gets personal. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 332–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Pook-Than, J.; Snyder, M. iPOP goes the world: Integrated personalized omics profiling and the road toward improved health care. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenberg, M. SKINOMICS: Transcriptional profiling in dermatology and skin biology. Curr. Genomics 2012, 13, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez de Castro, D.; Clarke, P.A.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Workman, P. Personalized cancer medicine: Molecular diagnostics, predictive biomarkers, and drug resistance. Clin. Pharmacol. Therapeutics 2013, 93, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, F.; Pathan, S.; Schena, F.P. From -omics to personalized medicine in nephrology: Integration is the key. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.-Eur. Renal Assoc. 2013, 28, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rojo Venegas, K.; Aguilera Gmez, M.; Caada Garre, M.; Snchez, A.G.; Contreras-Ortega, C.; Calleja Hernndez, M.A. Pharmacogenetics of osteoporosis: Towards novel theranostics for personalized medicine? Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Snyder, M. Promise of personalized omics to precision medicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2013, 5, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mias, G.I.; Snyder, M. Personal genomes, quantitative dynamic omics and personalized medicine. Quant. Biol. 2013, 1, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaas, A.K.; Chen, M.; Varkey, J.; Veldman, T.; Hero, A.O.; Lucas, J.; Huang, Y.; Turner, R.; Gilbert, A.; Lambkin-Williams, R.; et al. Gene expression signatures diagnose influenza and other symptomatic respiratory viral infection in humans. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, C.M.; Podyminogin, R.L.; Navarro, G.; Zhao, G.W.; Askovich, P.S.; Weiss, M.J.; Aderem, A. miR-451 regulates dendritic cell cytokine responses to influenza infection. J. Immunol. (Baltimore, Md.: 1950) 2012, 189, 5965–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, M. The quantified self: Fundamental disruption in big data science and biological discovery. Big Data 2013, 1, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Ferracin, M.; Gaf, R.; Veronese, A.; Spizzo, R.; Pichiorri, F.; Liu, C.g.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M.; Negrini, M. mRNA/microRNA gene expression profile in microsatellite unstable colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panguluri, S.K.; Bhatnagar, S.; Kumar, A.; McCarthy, J.J.; Srivastava, A.K.; Cooper, N.G.; Lundy, R.F.; Kumar, A. Genomic profiling of messenger RNAs and microRNAs reveals potential mechanisms of TWEAK-induced skeletal muscle wasting in mice. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrydziuszko, O.; Viant, M.R. Missing values in mass spectrometry based metabolomics: An undervalued step in the data processing pipeline. Metabolomics 2011, 8, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb-Robertson, B.J.M.; Matzke, M.M.; Metz, T.O.; McDermott, J.E.; Walker, H.; Rodland, K.D.; Pounds, J.G.; Waters, K.M. Sequential projection pursuit principal component analysis-dealing with missing data associated with new -omics technologies. BioTechniques 2013, 54, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Weckwerth, W. Metabolomics: Methods and Protocols. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; No. 358. [Google Scholar]
- Kolker, E.; Higdon, R.; Haynes, W.; Welch, D.; Broomall, W.; Lancet, D.; Stanberry, L.; Kolker, N. MOPED: Model organism protein expression database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1093–D1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Materials
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanberry, L.; Mias, G.I.; Haynes, W.; Higdon, R.; Snyder, M.; Kolker, E. Integrative Analysis of Longitudinal Metabolomics Data from a Personal Multi-Omics Profile. Metabolites 2013, 3, 741-760. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030741
Stanberry L, Mias GI, Haynes W, Higdon R, Snyder M, Kolker E. Integrative Analysis of Longitudinal Metabolomics Data from a Personal Multi-Omics Profile. Metabolites. 2013; 3(3):741-760. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030741
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanberry, Larissa, George I. Mias, Winston Haynes, Roger Higdon, Michael Snyder, and Eugene Kolker. 2013. "Integrative Analysis of Longitudinal Metabolomics Data from a Personal Multi-Omics Profile" Metabolites 3, no. 3: 741-760. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030741
APA StyleStanberry, L., Mias, G. I., Haynes, W., Higdon, R., Snyder, M., & Kolker, E. (2013). Integrative Analysis of Longitudinal Metabolomics Data from a Personal Multi-Omics Profile. Metabolites, 3(3), 741-760. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030741