Metabolic Signatures in Lean MASLD: Current Insights and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics, and Diagnostic Implications
3. Mechanistic Insights into Lean MASLD
4. Metabolic Signatures in Lean MASLD
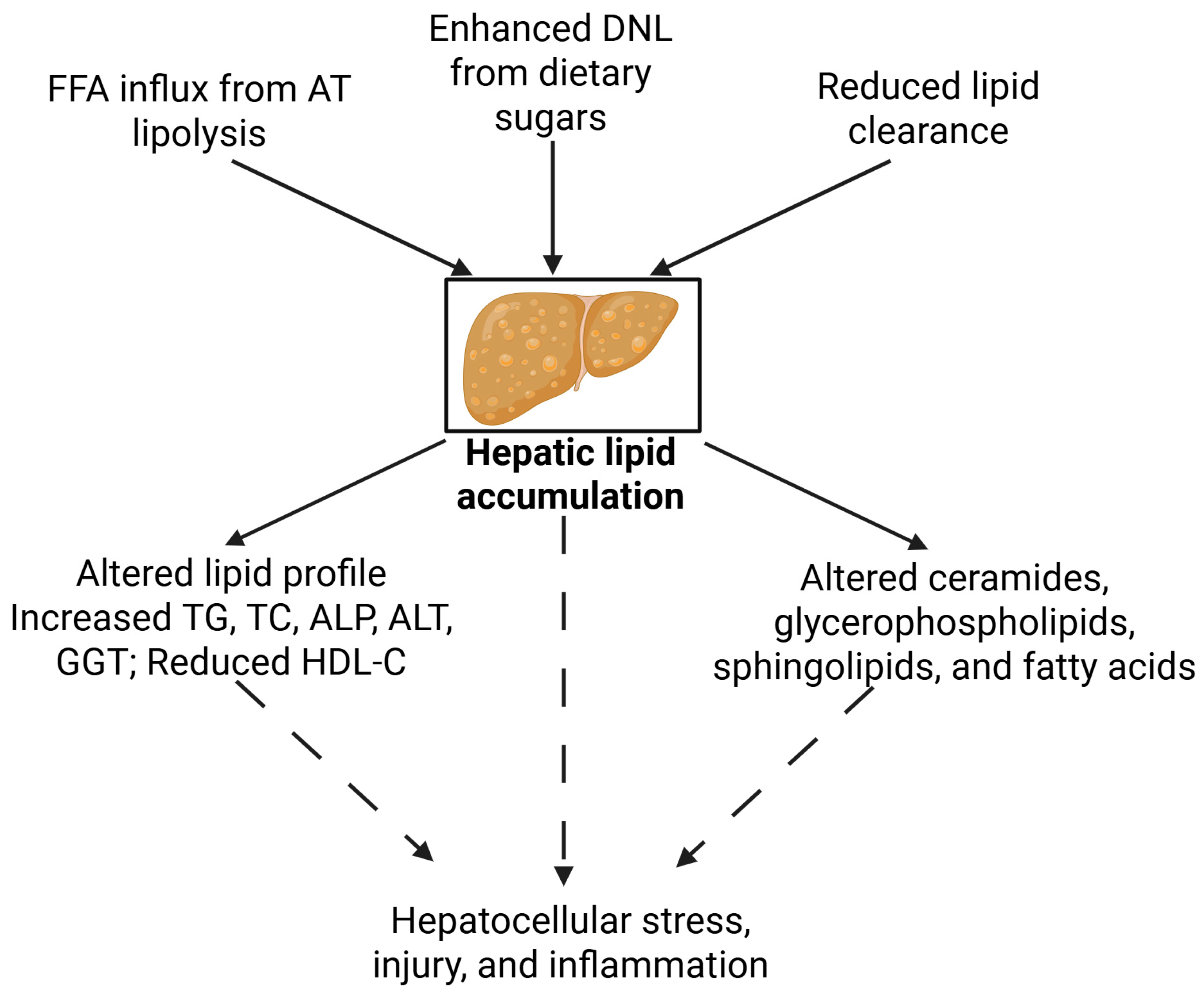
4.1. Lipid Metabolism
4.2. Amino Acid Metabolism
| Category | Alteration | Key Metabolite/Mechanism | Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid Metabolism | ↑ De novo lipogenesis ↓ APOA1↑ Triglycerides ↑ Total cholesterol, ALP | - Elevated fatty acids - Increased ceramides - Increased glycerophospholipids (e.g., LPC 18:0, PC 36:3) | Lipotoxicity, ER stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, hepatocellular damage | [23,28,32] |
| Amino Acid Metabolism | ↑ BCAAs (Leu, Ile, Val) ↑ Aromatic AAs (e.g., tyrosine) ↑ SAM, SAH ↓ Glutamine/glutamate ratio | - Impaired BCAA oxidation, mTOR activation - One-carbon cycle dysfunction - Elevated GSG index - Kynurenine pathway activation (↑ Kyn/Trp) | Insulin resistance, oxidative stress, hepatic inflammation, early fibrosis | [37,41,42] |
| Bile Acid and Gut Microbial Metabolites | ↑ Secondary BAs↑ FGF19 ↑ SCFAs (isobutyrate, propionate) ↓ 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one | - Increased thermogenic BAs (e.g., cholic acid) - SCFA-specific changes in lean MASLD | Gut–liver axis dysregulation, altered energy metabolism, hepatic inflammation | [45,46] |
| Genetic Modifiers | ↑ PNPLA3 (GG), TM6SF2 (TT)PEMT (Val175Met variant) | - Reduced lipid export, phospholipid imbalance - Epigenetic risk via DNA methylation | Genetic predisposition in lean phenotypes | [25] |
| Epigenetics and miRNAs | ↓ Histone variants (macroH2A1.1, 1.2) ↑ miR-4488 | - Gene silencing of protective regulators | [47,48] |
4.3. Bile Acids and Gut Microbial Metabolites
4.4. Other Metabolites
5. Genetic and Epigenetic Modifiers
6. Future Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| MASLD | Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BA | Bile acid |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 Index |
| NFS | NAFLD Fibrosis Score |
| MRE | Magnetic resonance elastography |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
| DNL | De-novo lipogenesis |
| VLDL | Very low-density lipoprotein |
| PA | Palmitic acid |
| OA | Oleic acid |
| LA | Linoleic acid |
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
| LPC | Lysophosphatidylcholine |
| BCAA | Branched-chain amino acid |
| AAA | Aromatic amino acid |
| SAM | S-adenosylmethionine |
| SAH | S-adenosylhomocysteine |
| GSG | Glutamate–serine–glycine |
| IDO1 | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| SCFA | Short-chain fatty acid |
| FGF19 | Fibroblast growth factor 19 |
| TriHOME | 9,12,13-trihydroxyoctadecenoic acid |
References
- Boldys, A.; Buldak, L. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Navigating terminological evolution, diagnostic frontiers and therapeutic horizon-an editorial exploration. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, A.; Negrea, M.O.; Cipăian, C.R.; Boicean, A.; Mihaila, R.; Rezi, C.; Cristinescu, B.A.; Berghea-Neamtu, C.S.; Popa, M.L.; Teodoru, M.; et al. Interactions between Metabolic Syndrome, MASLD, and Arterial Stiffening: A Single-Center Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotaru, A.; Stafie, R.; Stratina, E.; Zenovia, S.; Nastasa, R.; Minea, H.; Huiban, L.; Cuciureanu, T.; Muzica, C.; Chiriac, S.; et al. Lean MASLD and IBD: Exploring the Intersection of Metabolic Dysfunction and the Gut–Liver Axis. Life 2025, 15, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Martínez-Montoro, J.I.; Choudhary, N.S.; Fernández-García, J.C.; Ramos-Molina, B. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean and Non-Obese Individuals: Current and Future Challenges. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Negro, F.; Hallaji, S.; Younossi, Y.; Lam, B.; Srishord, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals in the United States. Medicine 2012, 91, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.Y.; Muthiah, M.D.; Sanyal, A.J. Metabolomics at the cutting edge of risk prediction of MASLD. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ren, J.; Zhou, W.; Huang, J.; Wu, G.; Yang, F.; Yuan, S.; Fang, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. Lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (Lean-NAFLD) and the development of metabolic syndrome: A retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albhaisi, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Sanyal, A.J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.B.; Zheng, K.I.; Rios, R.S.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Zheng, M.H. Global epidemiology of lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Das, K.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, S.; Mridha, A.R.; Dhibar, T.; Bhattacharya, B.; Bhattacharya, D.; Manna, B.; et al. Nonobese population in a developing country has a high prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver and significant liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Feng, J.; Befroy, D.; Dziura, J.; Dalla Man, C.; Cobelli, C.; Shulman, G.I. Increased prevalence of insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Asian-Indian men. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18273–18277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellentani, S.; Saccoccio, G.; Masutti, F.; Crocè, L.S.; Brandi, G.; Sasso, F.; Cristanini, G.; Tiribelli, C. Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatic steatosis in northern Italy. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 132, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Danpanichkul, P.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Cholankeril, G.; Loomba, R.; Ahmed, A. Current Burden of Lean Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Among US Adults, 2017–2023. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 61, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato-Espinoza, K.; Chotiprasidhi, P.; Huaman, M.R.; Díaz-Ferrer, J. Update in lean metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frączek, J.; Sowa, A.; Agopsowicz, P.; Migacz, M.; Dylińska-Kala, K.; Holecki, M. Non-Invasive Tests as a Replacement for Liver Biopsy in the Assessment of MASLD. Medicina 2025, 61, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrellas, N.; Alemany, M.; Urquizu, M.; Bartres, C.; Pera, G.; Juvé, E.; Rodríguez, L.; Torán, P.; Caballería, L. Using transient elastography to detect chronic liver diseases in a primary care nurse consultancy. Nurs. Res. 2013, 62, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sánchez Antolin, G.; Garcia Pajares, F.; Vallecillo, M.A.; Fernandez Orcajo, P.; Gómez de la Cuesta, S.; Alcaide, N.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Velicia, R.; Caro-Patón, A. FibroScan Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis in Liver Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mohan, S. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean Subjects: Characteristics and Implications. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooli, R.G.R.; Mukhi, D.; Ramakrishnan, S.K. Oxidative Stress and Redox Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases. Compr. Physiol. 2022, 12, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, S.; Rajak, S.; Yen, P.M.; Sinha, R.A. Autophagy and hepatic lipid metabolism: Mechanistic insight and therapeutic potential for MASLD. npj Metab. Heal. Dis. 2024, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.; Eder, S.K.; Felder, T.K.; Kedenko, L.; Paulweber, B.; Stadlmayr, A.; Huber-Schönauer, U.; Niederseer, D.; Stickel, F.; Auer, S.; et al. Clinical and Metabolic Characterization of Lean Caucasian Subjects with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Z.; Si, Q.; Hu, X.; Yang, L.; Gu, X.; Du, L.; Wang, L.; Pan, L.; Li, Y.; et al. The Association of Sarcopenia and Visceral Obesity with Lean Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 2229139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wong, G.L.H.; Whatling, C.; Chan, A.W.H.; Leung, H.H.W.; Tse, C.H.; Shu, S.S.T.; Chim, A.M.L.; Lai, J.C.T.; Yip, T.C.F.; et al. Association of genetic variations with NAFLD in lean individuals. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogelson, K.A.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Zarrinpar, A.; Knight, R. The Gut Microbial Bile Acid Modulation and Its Relevance to Digestive Health and Diseases. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovics, N.; Heering, G.; Frishman, W.H.; Lebovics, E. Lean MASLD and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. Cardiol. Rev. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.Q.; Yuan, Y.F.; Cao, Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Dong, W.M.; Guo, L.L. Targeted metabolomics study of fatty-acid metabolism in lean metabolic-associated fatty liver disease patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 3290–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjunath, C.N.; Rawal, J.R.; Irani, P.M.; Madhu, K. Atherogenic dyslipidemia. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, O.; Sarac, G.A.; Rota, D.D.; Aksoy, H. Evaluation of pro-atherogenic lipid profile and high atherohenic indexes in patients with Behçet’s disease: A case–control study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolis, A.A.; Manolis, T.A.; Vouliotis, A.; Manolis, A.S. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and the cardiovascular system. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 35, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. C 2018, 75, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcová, A.; Červinková, Z.; Kučera, O.; Mezera, V.; Rychtrmoc, D.; Lotková, H. The effect of oleic and palmitic acid on induction of steatosis and cytotoxicity on rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, S627–S636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Su, W.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Ji, X.F.; Wang, J.W.; Wang, K. Identification and verification of biomarkers associated with arachidonic acid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, D.; Ossowski, P.; Drozd, A.; Ryterska, K.; Jamioł-Milc, D.; Banaszczak, M.; Kaczorowska, M.; Sabinicz, A.; Raszeja-Wyszomirska, J.; Stachowska, E. Metabolites of arachidonic acid and linoleic acid in early stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A pilot study. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015, 121, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamatsu, H.; Ohnishi, S.; Sakai, S.; Yuyama, K.; Mitsutake, S.; Takeda, H.; Hashino, S.; Igarashi, Y. Altered levels of serum sphingomyelin and ceramide containing distinct acyl chains in young obese adults. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Q.; Li, L. Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Liver Diseases: Complexity and Controversy. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, C.J.; Adams, S.H. Branched-chain amino acids in metabolic signalling and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyyarikkandy, M.S.; McLeod, M.; Maguire, M.; Mahar, R.; Kattapuram, N.; Zhang, C.; Surugihalli, C.; Muralidaran, V.; Vavilikolanu, K.; Mathews, C.E.; et al. Branched chain amino acids and carbohydrate restriction exacerbate ketogenesis and hepatic mitochondrial oxidative dysfunction during NAFLD. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 14832–14849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.; Eder, S.K.; Felder, T.K.; Paulweber, B.; Zandanell, S.; Stechemesser, L.; Schranz, M.; Strebinger, G.; Huber-Schönauer, U.; Niederseer, D.; et al. Clinical and metabolic characterization of obese subjects without non-alcoholic fatty liver: A targeted metabolomics approach. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, N.F.; Hamid, M.; Khayat, M.E. Amino Acid-Induced Impairment of Insulin Signaling and Involvement of G-Protein Coupling Receptor. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.J.; Cutler, P.; Melnyk, S.; Jernigan, S.; Janak, L.; Gaylor, D.W.; Neubrander, J.A. Metabolic biomarkers of increased oxidative stress and impaired methylation capacity in children with autism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, T.; Mu, G.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, B.; Zhu, J.; Shen, Z. Dysregulated homocysteine metabolism and cardiovascular disease and clinical treatments. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2025, 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorbagy, A.K.; Nijpels, G.; Valdivia-Garcia, M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Ocke, M.; Refsum, H.; Dekker, J.M. S-Adenosylmethionine Is Associated with Fat Mass and Truncal Adiposity in Older Adults. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Esmaili, S.; Rogers, G.B.; Bugianesi, E.; Petta, S.; Marchesini, G.; Bayoumi, A.; Metwally, M.; Azardaryany, M.K.; Coulter, S.; et al. Lean NAFLD: A Distinct Entity Shaped by Differential Metabolic Adaptation. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haag, M.; Winter, S.; Kemas, A.M.; Tevini, J.; Feldman, A.; Eder, S.K.; Felder, T.K.; Datz, C.; Paulweber, B.; Liebisch, G.; et al. Circulating metabolite signatures indicate differential gut-liver crosstalk in lean and obese MASLD. JCI Insight 2025, 10, e180943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzova, D.; Maugeri, A.; Liguori, A.; Napodano, C.; Lo Re, O.; Oben, J.; Alisi, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Grieco, A.; Cerveny, J.; et al. Circulating histone signature of human lean metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Tang, L.; Qian, Y.; Pan, J.; Pan, J.; Miao, H.; Zhang, H.; Fang, H.; Yu, X.; Xing, L. Serum miR-4488 as a potential biomarker of lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2023, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njei, B.; Al-Ajlouni, Y.A.; Ameyaw, P.; Njei, L.P.; Boateng, S. Role of ammonia and glutamine in the pathogenesis and progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A systematic review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 1788–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Rosso, C.; Buzzigoli, E.; Marietti, M.; Della Latta, V.; Ciociaro, D.; Abate, M.L.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M.; et al. Altered amino acid concentrations in NAFLD: Impact of obesity and insulin resistance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Chitneni, S.K.; Suzuki, A.; Wang, Y.; Henao, R.; Hyun, J.; Premont, R.T.; Naggie, S.; Moylan, C.A.; Bashir, M.R.; et al. Increased Glutaminolysis Marks Active Scarring in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Progression. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Yoshikawa, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Morikawa, S.; Nakashima, M.; Asai, T.; Matsuda, S. The Tryptophan and Kynurenine Pathway Involved in the Development of Immune-Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolowczuk, I.; Hennart, B.; Leloire, A.; Bessede, A.; Soichot, M.; Taront, S.; Caiazzo, R.; Raverdy, V.; Pigeyre, M.; Guillemin, G.J.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism activation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in adipose tissue of obese women: An attempt to maintain immune homeostasis and vascular tone. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 303, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunis, C.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Hanssen, N. Interactions between Tryptophan Metabolism, the Gut Microbiome and the Immune System as Potential Drivers of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Metabolic Diseases. Metabolites 2022, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Horai, Y.; Houten, S.M.; Morimoto, K.; Sugizaki, T.; Arita, E.; Mataki, C.; Sato, H.; Tanigawara, Y.; Schoonjans, K.; et al. Lowering bile acid pool size with a synthetic farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist induces obesity and diabetes through reduced energy expenditure. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26913–26920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Houten, S.M.; Mataki, C.; Christoffolete, M.A.; Kim, B.W.; Sato, H.; Messaddeq, N.; Harney, J.W.; Ezaki, O.; Kodama, T.; et al. Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting intracellular thyroid hormone activation. Nature 2006, 439, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeders, E.P.M.; Nascimento, E.B.M.; Havekes, B.; Brans, B.; Roumans, K.H.M.; Tailleux, A.; Schaart, G.; Kouach, M.; Charton, J.; Deprez, B.; et al. The bile acid chenodeoxycholic acid increases human brown adipose tissue activity. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowska, A.; Poniedziałek-Czajkowska, E.; Mierzyński, R. The Role of the FGF19 Family in the Pathogenesis of Gestational Diabetes: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.I.; Shankaran, M.; Yoshino, M.; Schweitzer, G.G.; Chondronikola, M.; Beals, J.W.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; Nyangau, E.; Field, T.; et al. Insulin resistance drives hepatic de novo lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, W.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhang, W. New aspects characterizing non-obese NAFLD by the analysis of the intestinal flora and metabolites using a mouse model. mSystems 2024, 9, e01027-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprince, A.; Haas, J.T.; Staels, B. Dysregulated lipid metabolism links NAFLD to cardiovascular disease. Mol. Metab. 2020, 42, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinkauf, H. The role of 4′-phosphopantetheine in the biosynthesis of fatty acids, polyketides and peptides. BioFactors 2000, 11, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Pan, J.; Zhou, W.; Ji, G.; Dang, Y. Recent advances in lean NAFLD. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Hirose, A.; Nozaki, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Ono, M.; Akisawa, N.; Iwasaki, S.; Saibara, T.; et al. The phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene V175M single nucleotide polymorphism confers the susceptibility to NASH in Japanese population. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, R.A.; Vickers, K.C. Intercellular transport of MicroRNAs. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Bravo Vázquez, L.A.; Uribe, S.P.; Manzanero Cárdenas, L.A.; Ruíz Aguilar, M.F.; Chakraborty, S.; Sharma, A. Roles of microRNAs in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism disorders and their therapeutic potential. Biochimie 2021, 187, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojima, M.; Kimura, T.; Aoki, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Hayashi, K.; Ohtake, J.; Kimura-Asami, M.; Suzuki, K.; Urayama, K.; Matsuura, M.; et al. A Metabolomics-Based Approach for Diagnosing NAFLD and Identifying Its Pre-Condition Along the Potential Disease Spectrum. Livers 2025, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babu, A.F. Metabolic Signatures in Lean MASLD: Current Insights and Future Directions. Metabolites 2025, 15, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090583
Babu AF. Metabolic Signatures in Lean MASLD: Current Insights and Future Directions. Metabolites. 2025; 15(9):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090583
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabu, Ambrin Farizah. 2025. "Metabolic Signatures in Lean MASLD: Current Insights and Future Directions" Metabolites 15, no. 9: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090583
APA StyleBabu, A. F. (2025). Metabolic Signatures in Lean MASLD: Current Insights and Future Directions. Metabolites, 15(9), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090583





