Urine Metabolomics of Gout Reveals the Dynamic Reprogramming and Non-Invasive Biomarkers of Disease Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Sample Treatment
2.3. UHPLC-MS/MS
2.4. Data Preprocessing and Metabolite Identification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Participants
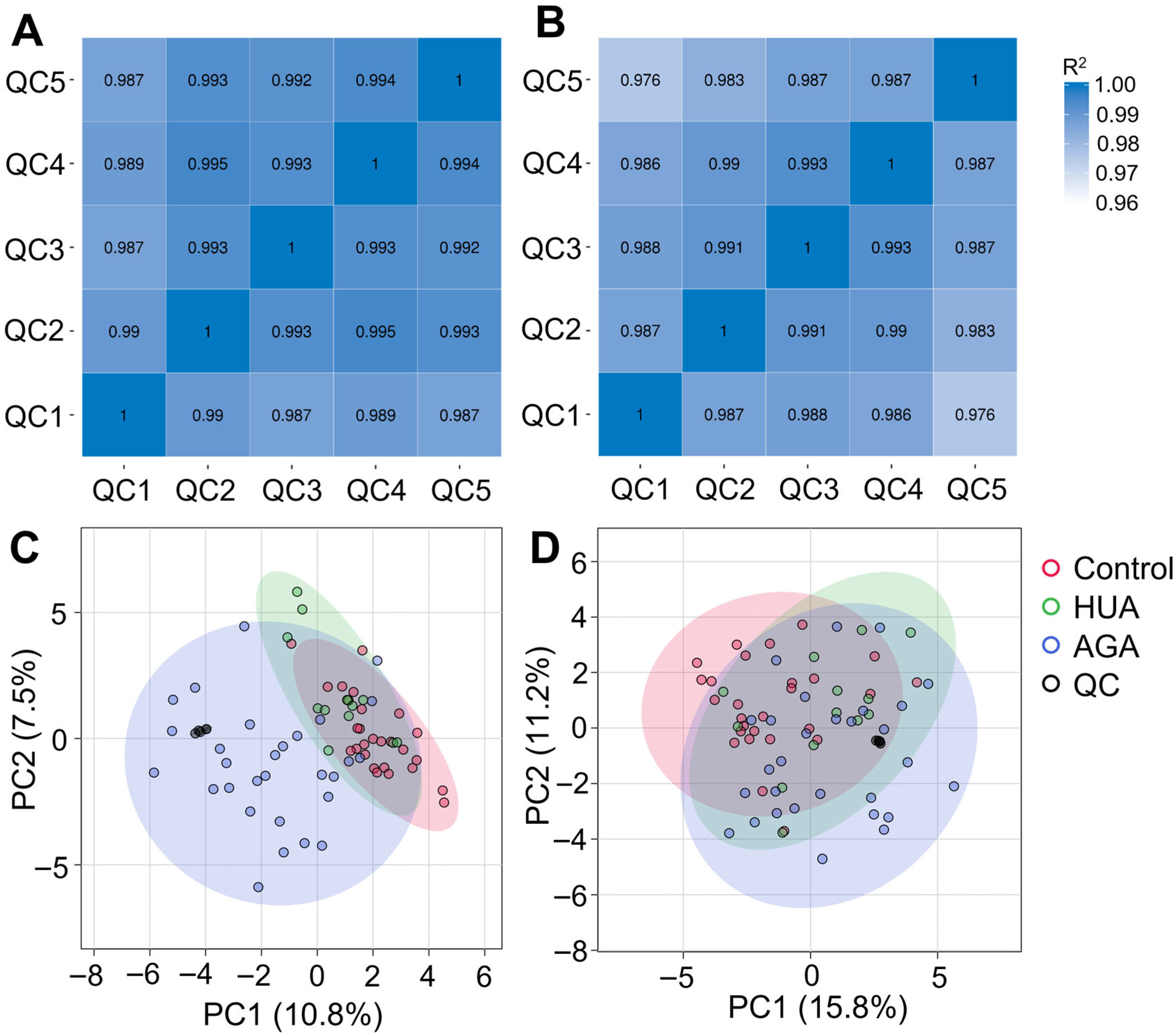
3.2. Quality Control of Metabolomics Data Using UHPLC-MS/MS
3.3. Metabolite Analysis
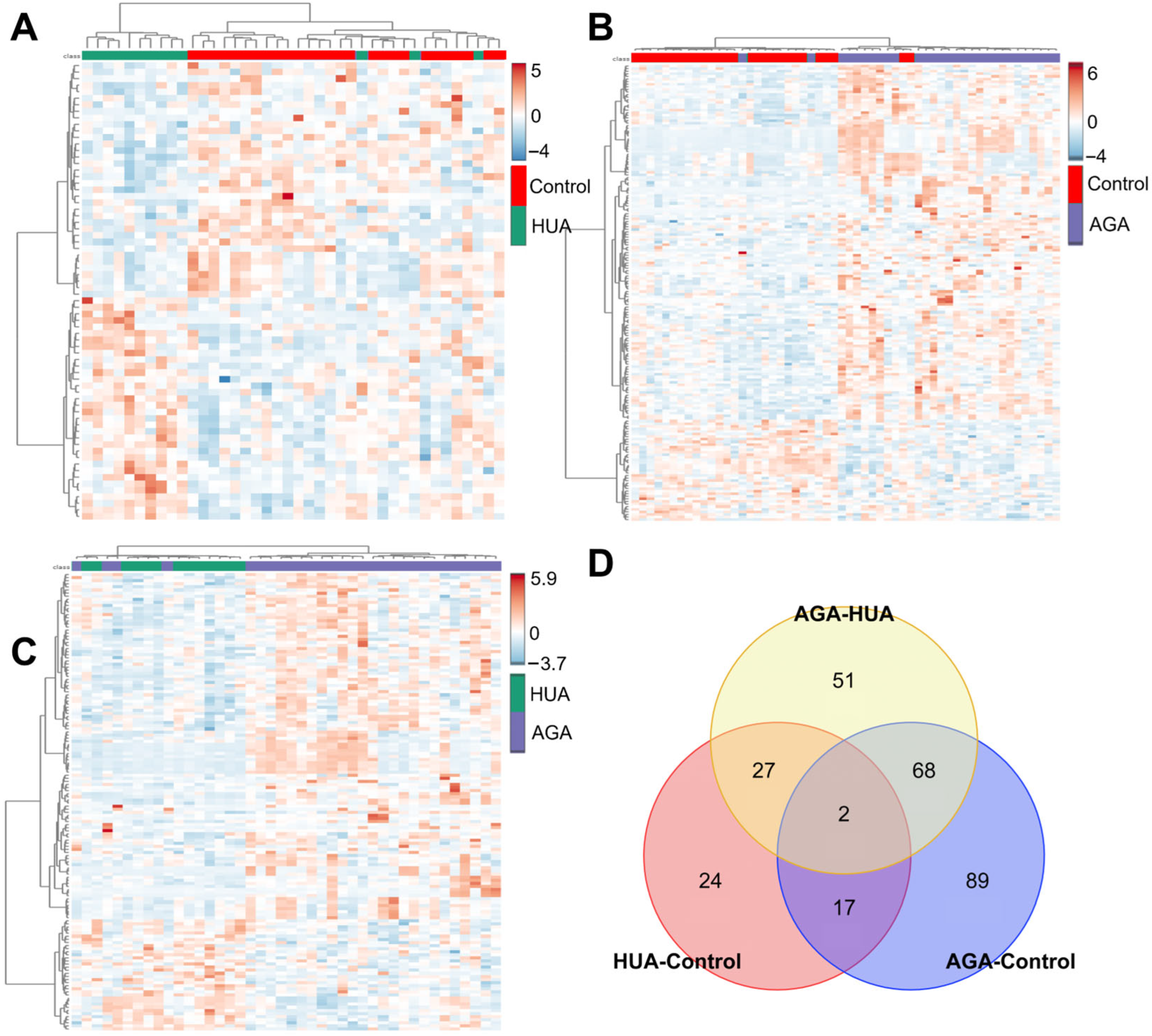
3.4. Screening of Differential Metabolites
3.5. Differential Metabolite Analysis
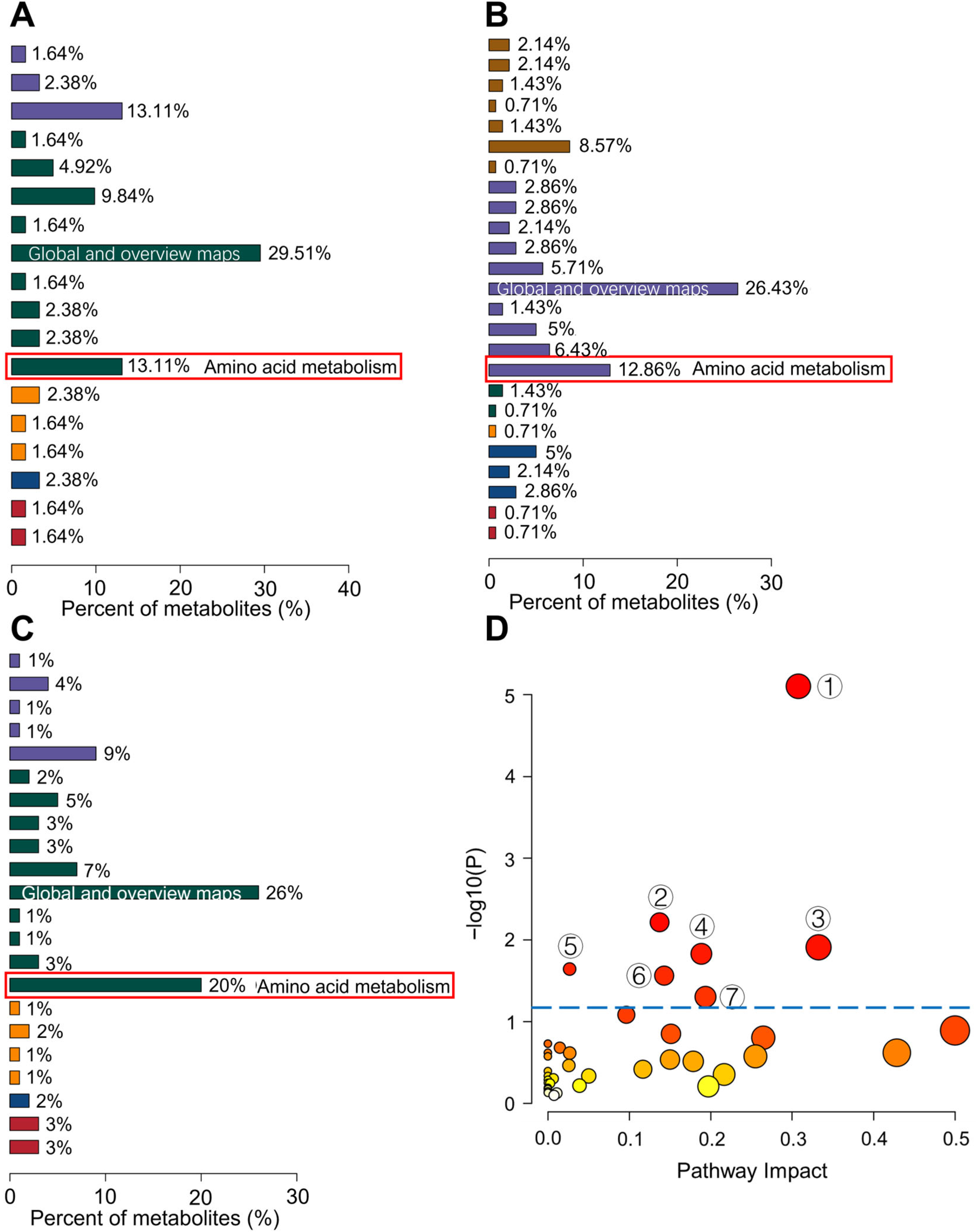
3.6. KEGG Analysis of Differential Metabolites
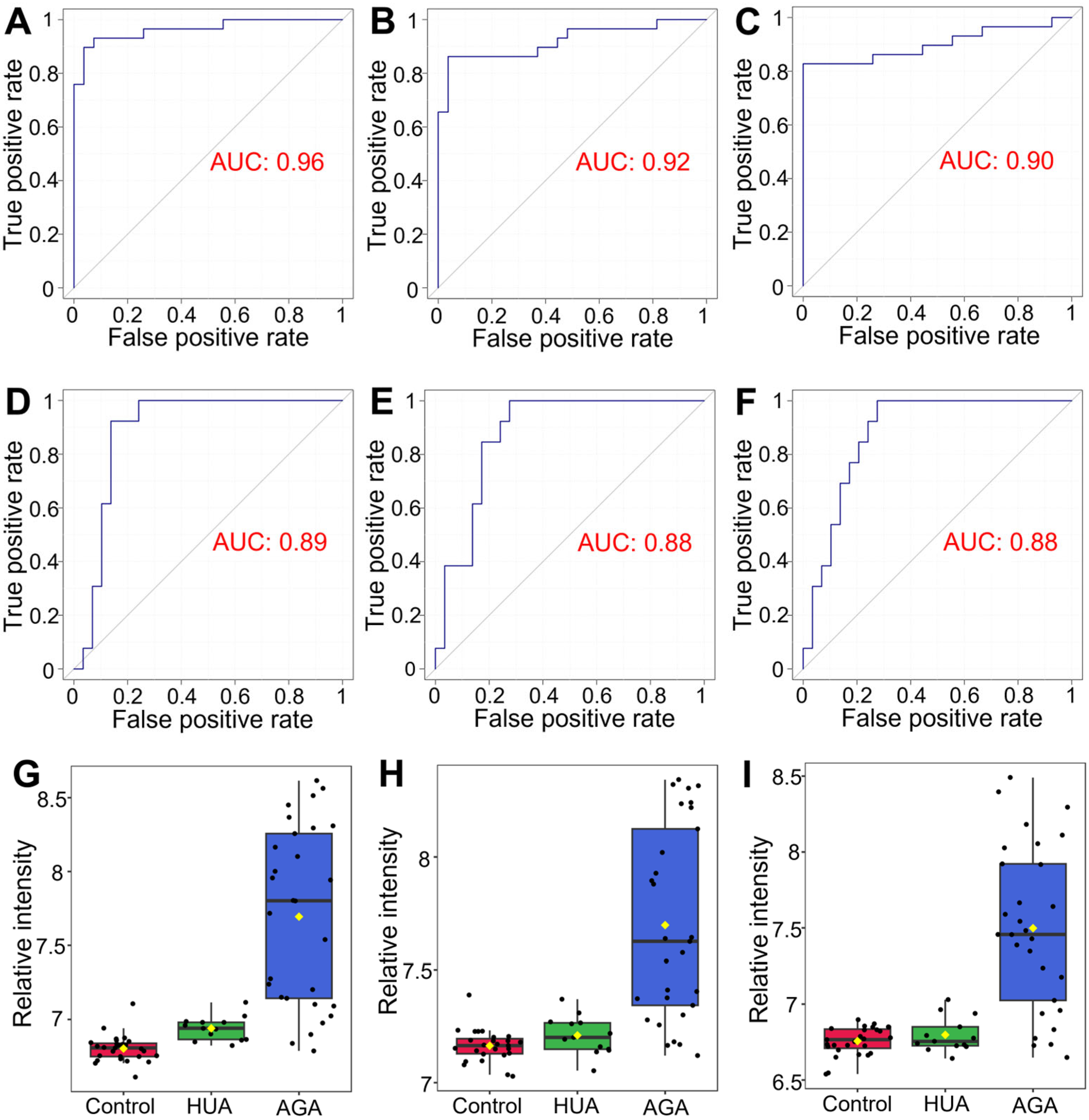
3.7. Early Warning Biomarkers of Gout
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HUA | Hyperuricemia |
| AGA | Acute gouty arthritis |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| UHPLC-MS | Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| FC | Fold change |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| VIP | Variable importance in projection |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| GLU | Glucose |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TCH | Total cholesterol |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| CR | Creatinine |
| SUA | Serum urate acid |
| QC | Quality control |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| NAD+ | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NADP+ | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
References
- Asghari, K.M.; Zahmatyar, M.; Seyedi, F.; Motamedi, A.; Zolfi, M.; Alamdary, S.J.; Fazlollahi, A.; Shamekh, A.; Mousavi, S.E.; Nejadghaderi, S.A. Gout: Global epidemiology, risk factors, comorbidities and complications: A narrative review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehlin, M.; Jacobsson, L.; Roddy, E. Global epidemiology of gout: Prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Chen, W.; Qiu, X.; Wang, W. Epidemiology of gout-global burden of disease research from 1990 to 2019 and future trend predictions. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 15, 20420188241227295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Manley, N.; Mikuls, T.R. Gout flare burden, diagnosis, and management: Navigating care in older patients with comorbidity. Drugs Aging 2021, 38, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towiwat, P.; Chhana, A.; Dalbeth, N. The anatomical pathology of gout: A systematic literature review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwah, R.K. Comorbidities in gouty arthritis. J. Invest. Med. 2011, 59, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; You, C. The biomarkers discovery of hyperuricemia and gout: Proteomics and metabolomics. PeerJ 2022, 11, e14554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Ge, D.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Xia, T. Monosodium urate crystal-induced pyroptotic cell death in neutrophil and macrophage facilitates the pathological progress of gout. Small 2024, 20, 2308749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galozzi, P.; Bindoli, S.; Luisetto, R.; Sfriso, P.; Ramonda, R.; Scanu, A.; Oliviero, F. Regulation of crystal induced inflammation: Current understandings and clinical implications. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Xiong, Q.; Xu, S.; Kang, D.; He, Z.; Yao, C.; Jian, G. Advancements in the study of IL-6 and its receptors in the pathogenesis of gout. Cytokine 2024, 182, 156705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweyer, S.; Hemmerlein, B.; Radzun, H.; Fayyazi, A. Continuous recruitment, co-expression of tumour necrosis factor-α and matrix metalloproteinases, and apoptosis of macrophages in gout tophi. Virchows Arch. 2000, 437, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-Z. Why does hyperuricemia not necessarily induce gout? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Dong, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhai, G.; Zhang, K. Identification of abnormal proteins in plasma from gout patients by LC-MS/MS. Separations 2021, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Yu, H.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Bao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. The development from hyperuricemia to gout: Key mechanisms and natural products for treatment. Acupunct. Herb. Med. 2022, 2, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, B.; Just, J.; Bleckwenn, M.; Weckbecker, K. Treatment Options for Gout. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2017, 114, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascart, T.; Lioté, F. Gout: State of the art after a decade of developments. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, N. Diagnosis of gout: Clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings. Am. J. Manag. Care 2005, 11 (Suppl. S15), S443–S450. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Ruiz, F.; Castillo, E.; Chinchilla, S.P.; Herrero-Beites, A.M. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of gout. Rheum. Dis. Clin. 2014, 40, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Salcedo, M.; Manzano, J.I.; Yuste, S.; Iñiguez, M.; Pérez-Matute, P.; Motilva, M.-J. Exploring biomarkers of regular wine consumption in human urine: Targeted and untargeted metabolomics approaches. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Chao, Z.; Liu, J. Untargeted metabolomics analysis of the urinary metabolic signature of acute and chronic gout. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 565, 119968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, Y.; Ooyama, H.; Makinoshima, H.; Takada, T.; Matsuo, H.; Ichida, K. Plasma and urinary metabolomic analysis of gout and asymptomatic hyperuricemia and profiling of potential biomarkers: A pilot study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xie, R.; Dai, Q.; Fang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, B. Exploring the mechanism underlying hyperuricemia using comprehensive research on multi-omics. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouatra, S.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.R.; Knox, C.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Saleem, F.; Liu, P. The human urine metabolome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Wang, L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, D.; Law, P.J.; Larsson, S.C. Systematic investigation of genetically determined plasma and urinary metabolites to discover potential interventional targets for colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2024, 116, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Ren, J.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X. Using metabolomics and proteomics to identify the potential urine biomarkers for prediction and diagnosis of gestational diabetes. Ebiomedicine 2024, 101, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Kanno, T.; Slater, R.; Rossi, M.; Irving, P.M.; Lomer, M.C.; Probert, C.; Mason, A.J.; Whelan, K. Faecal and urine metabolites, but not gut microbiota, may predict response to low FODMAP diet in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 58, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengual, L.; Lozano, J.J.; Ingelmo-Torres, M.; Gazquez, C.; Ribal, M.J.; Alcaraz, A. Using microRNA profiling in urine samples to develop a non-invasive test for bladder cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, C.; Allen, B.; Luies, L. Optimising a urinary extraction method for non-targeted GC–MS metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, L.; Li, C.; Liu, M. NMR spectroscopy for metabolomics in the living system: Recent progress and future challenges. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 2319–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruya, T.; Goga, H.; Yanagida, M. Aging markers in human urine: A comprehensive, non-targeted LC-MS study. FASEB BioAdvances 2020, 2, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, C.; Liang, N.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.J.; Merriman, T.R.; Dalbeth, N.; Terkeltaub, R.; Li, C.; et al. Serum metabolomics identifies dysregulated pathways and potential metabolic biomarkers for hyperuricemia and gout. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, M.-J.; Lu, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, W.; Ke, M.; Zhou, G.; et al. Serum lipidomics reveals distinct metabolic profiles for asymptomatic hyperuricemic and gout patients. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, R.; Qi, H.; Pang, L.; Cui, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, R.; Hu, S.; Liang, N.; et al. Metabolomics and machine learning identify metabolic differences and potential biomarkers for frequent versus Infrequent Gout Flares. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 2252–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhou, L.; Fan, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, F.; Gai, X.; Chang, C.; Xiong, J.; Rao, Y. Infection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis promotes both M1/M2 polarization and MMP production in cigarette smoke-exposed macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAdams-DeMarco, M.A.; Law, A.; Maynard, J.W.; Coresh, J.; Baer, A.N. Risk factors for incident hyperuricemia during mid-adulthood in African American and white men and women enrolled in the ARIC cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Che, D.; Qin, G.; Farouk, M.H.; Hailong, J.; Rui, H. Novel biosynthesis, metabolism and physiological functions of L-homoarginine. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Rao, Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, S.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Ke, S.; OuYang, H.; He, M.; Feng, Y. Metabolomics analysis reveals four biomarkers associated with the gouty arthritis progression in patients with sequential stages. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 55, 152022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylona, E.E.; Mouktaroudi, M.; Crisan, T.O.; Makri, S.; Pistiki, A.; Georgitsi, M.; Savva, A.; Netea, M.G.; van der Meer, J.W.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; et al. Enhanced interleukin-1β production of PBMCs from patients with gout after stimulation with Toll-like receptor-2 ligands and urate crystals. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangam, E.B.; Jemima, E.A.; Singh, H.; Baig, M.S.; Khan, M.; Mathias, C.B.; Church, M.K.; Saluja, R. The role of histamine and histamine receptors in mast cell-mediated allergy and inflammation: The hunt for new therapeutic targets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Chen, M.; Bucsek, M.J.; Repasky, E.A.; Hylander, B.L. Adrenergic signaling: A targetable checkpoint limiting development of the antitumor immune response. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Tao, J. Trace amine-associated receptor 1 regulation of Kv1. 4 channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons contributes to nociceptive behaviors. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiske, L.; Schmucker, S.; Pfaffinger, B.; Weiler, U.; Steuber, J.; Stefanski, V. Intravenous infusion of cortisol, adrenaline, or noradrenaline alters porcine immune cell numbers and promotes innate over adaptive immune functionality. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 3205–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Cheng, W. Tyramine’s modulation of immune resistance functions in Litopenaeus vannamei and its signal pathway. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 95, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, R.-S.; Handy, D.E.; Loscalzo, J. NAD (H) and NADP (H) redox couples and cellular energy metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Deng, M.; Ren, L.; Fan, Z.; Yang, S.; Liu, S.; Ren, X.; Gao, J.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J. Pyroptosis of oral keratinocyte contributes to energy metabolic reprogramming of T cells in oral lichen planus via OPA1-mediated mitochondrial fusion. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kou, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Wei, M. A metabonomic study to explore potential markers of asymptomatic hyperuricemia and acute gouty arthritis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Normal Controls (n = 28) | Patients with HUA (n = 13) | Patients with AGA (n = 29) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 26 (24–28) | 26 (24–27) | 32 (22–51) †,‡ |
| BMI, kg/m2, median (IQR) | 23.4 (19.6–28.4) | 26.3 (22.0–29.3) † | 26.5 (17.0–32.0) † |
| Smoking, n (%) a | 2 (11.1) | 1 (10.0) | 19 (67.9) †,‡ |
| Drinking, n (%) b | 0 (0) | 1 (10.0) | 7 (25.0) † |
| Beverage, n (%) c | 8 (44.4) | 3 (30.0) | 9 (32.1) |
| Sleep time, hours/day, median (IQR) | 7 (6–8) | 7 (4–8) | 7 (5.5–8) † |
| ALT, units/liter, median (IQR) | 25.1 (7.7–70.8) | 29.2 (19.8–65.2) | 35.9 (16.9–91.6) † |
| AST, units/liter, median (IQR) | 20.8 (8.9–67.6) | 24.2 (12–30.6) | 25.1 (10.4–54) |
| GLU, mmoles/liter, median (IQR) | 4.7 (3.5–5.6) | 4.9 (4.3–5.1) | 5.0 (3.8–6.8) † |
| TG, mmoles/liter, median (IQR) | 0.9 (0.5–2.2) | 1.3 (0.7–1.9) | 1.4 (0.7–4.2) † |
| TCH, mmoles/liter, median (IQR) | 4.7 (3.4–6.1) | 5.0 (3.8–6.3) | 4.6 (1.8–6.9) |
| BUN, mmoles/liter, median (IQR) | 5.5 (3.7–8.4) | 4.8 (3.7–5.8) † | 5.1 (3.9–7.7) |
| CR, mmoles/liter, median (IQR) | 78.0 (62.0–93.0) | 86.0 (67.0–96.0) | 81.1 (65.0–106.0) |
| SUA, µmoles/liter, median (IQR) | 342.0 (231.6–427.3) | 477.1 (431.8–567.9) † | 465.0 (336.0–696.0) † |
| Cotinine | L-Homocitrulline | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | log2FC | p Value | VIP | FC | log2FC | p Value | VIP | |
| HUA vs. control | 1.71 | 0.77 | 5.24 × 10−7 | 1.10 | 1.61 | 0.69 | 6.87 × 10−3 | 1.92 |
| AGA vs. control | 10.24 | 3.36 | 1.80 × 10−9 | 2.99 | 0.61 | −0.72 | 3.84 × 10−4 | 1.67 |
| AGA vs. HUA | 5.98 | 2.58 | 1.88 × 10−6 | 2.01 | 0.38 | −1.41 | 2.79 × 10−6 | 3.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, G.; Luo, Y.; Su, N.; Zheng, X.; Mei, Z.; Ye, Q.; Peng, J.; An, P.; Song, Y.; Luo, W.; et al. Urine Metabolomics of Gout Reveals the Dynamic Reprogramming and Non-Invasive Biomarkers of Disease Progression. Metabolites 2025, 15, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090580
Zhu G, Luo Y, Su N, Zheng X, Mei Z, Ye Q, Peng J, An P, Song Y, Luo W, et al. Urine Metabolomics of Gout Reveals the Dynamic Reprogramming and Non-Invasive Biomarkers of Disease Progression. Metabolites. 2025; 15(9):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090580
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Guizhen, Yuan Luo, Nan Su, Xiangyi Zheng, Zhusong Mei, Qiao Ye, Jie Peng, Peiyu An, Yangqian Song, Weina Luo, and et al. 2025. "Urine Metabolomics of Gout Reveals the Dynamic Reprogramming and Non-Invasive Biomarkers of Disease Progression" Metabolites 15, no. 9: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090580
APA StyleZhu, G., Luo, Y., Su, N., Zheng, X., Mei, Z., Ye, Q., Peng, J., An, P., Song, Y., Luo, W., Li, H., Wang, G., & Zhang, H. (2025). Urine Metabolomics of Gout Reveals the Dynamic Reprogramming and Non-Invasive Biomarkers of Disease Progression. Metabolites, 15(9), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090580







