Soluble Siglec-9 Improves Intestinal Barrier Function in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of SHED-CM
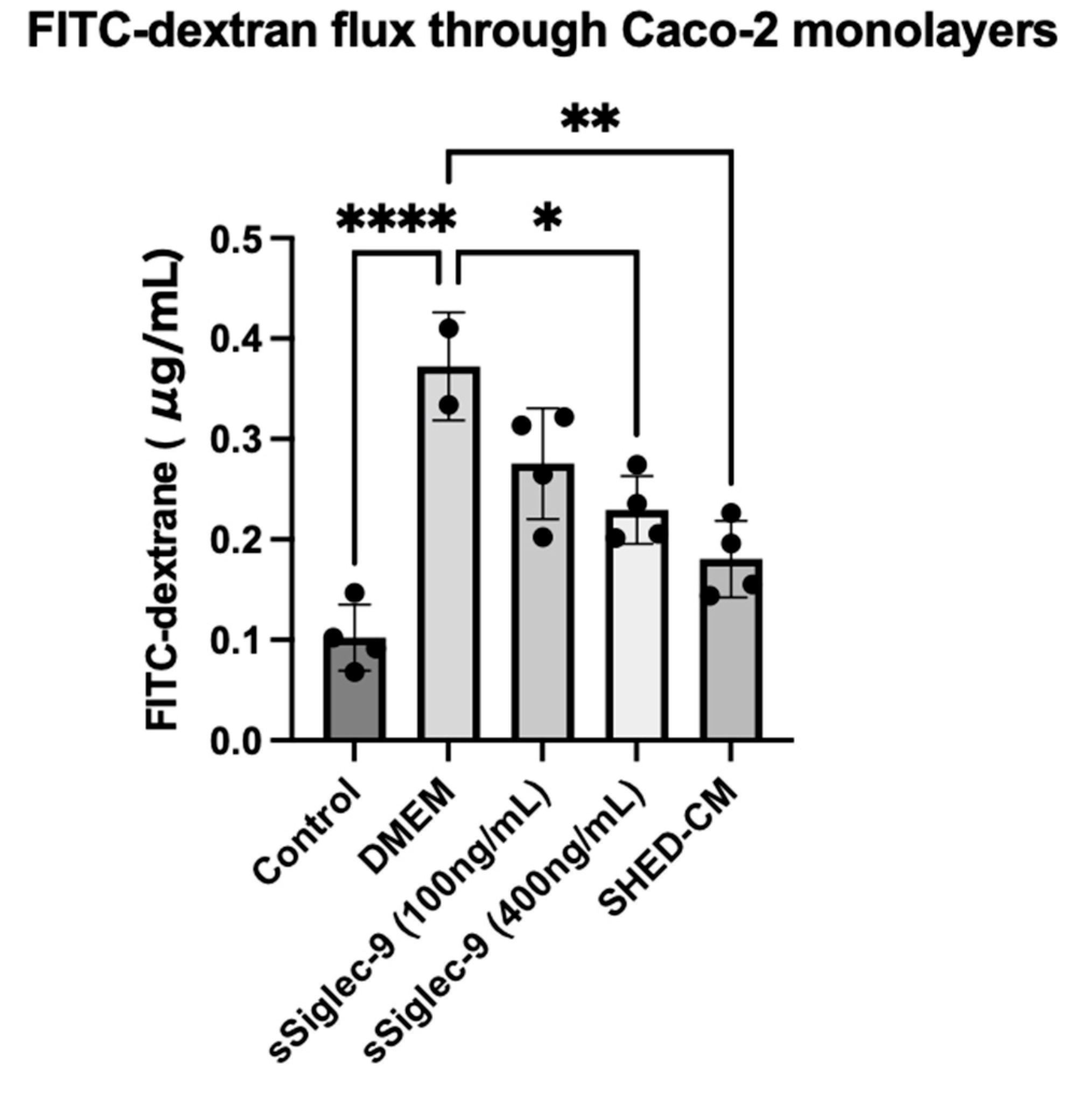
2.2. Caco-2 Monolayer Assay
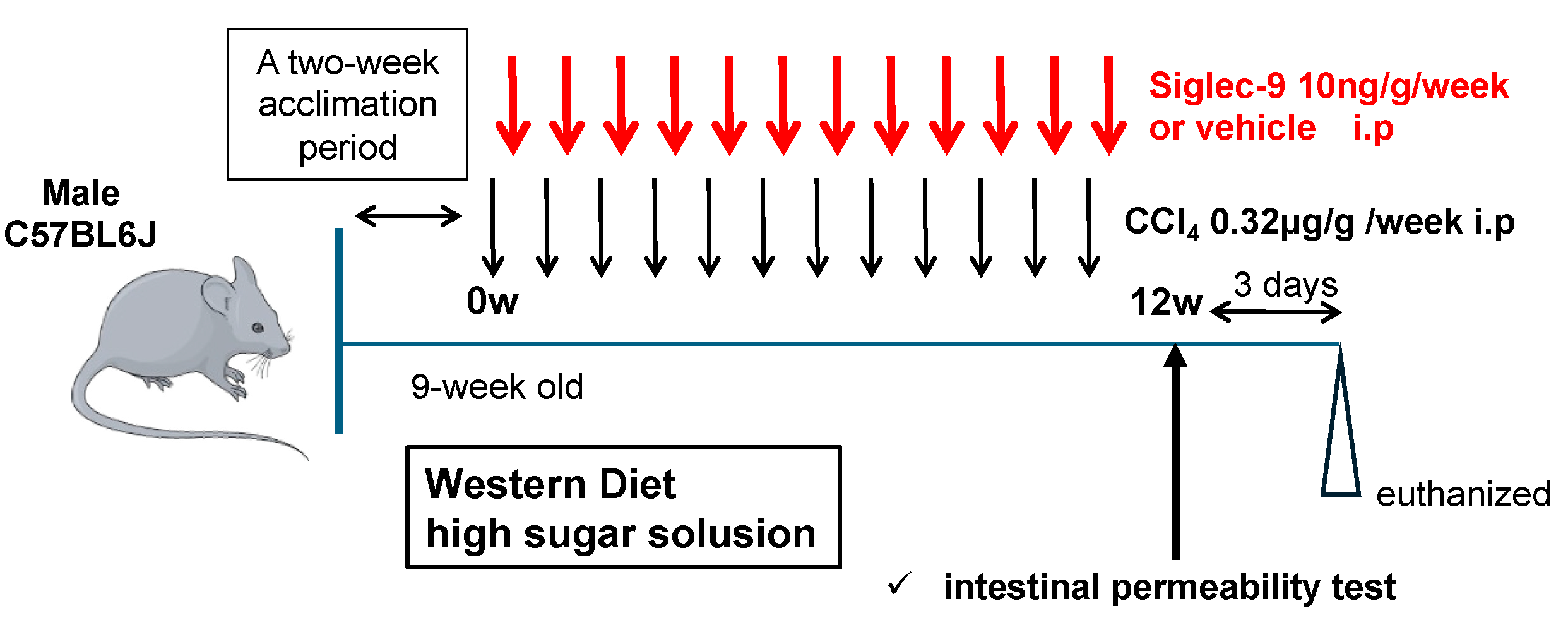
2.3. Murine MASH Model and Treatment with sSiglec-9
2.4. Intestinal Permeability
2.5. Histological Analyses
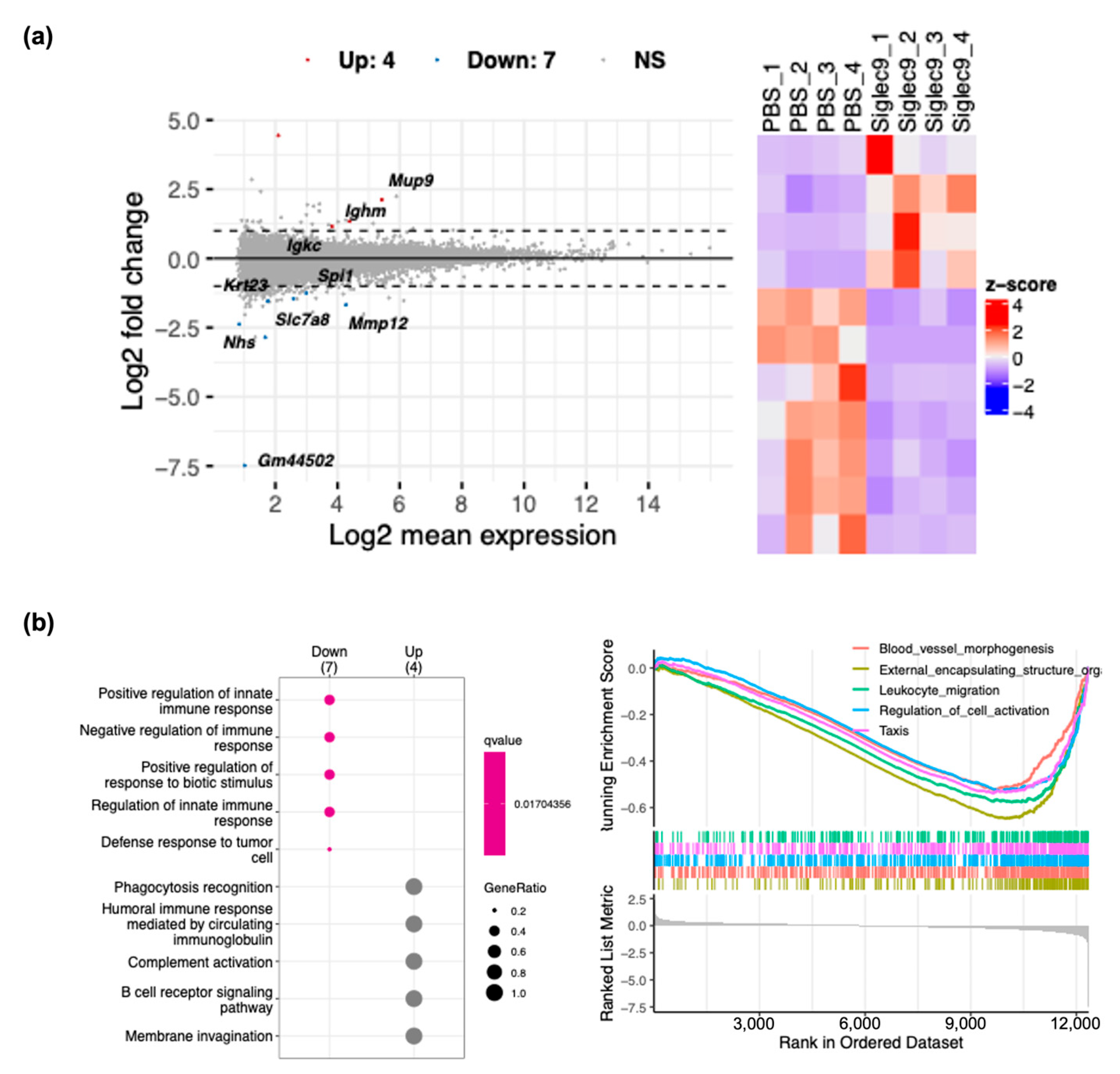
2.6. RNA Sequencing Analysis
2.7. Analysis of Gut Microbiota
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. sSiglec-9 Restores Caco-2 Monolayer Dysfunction In Vitro
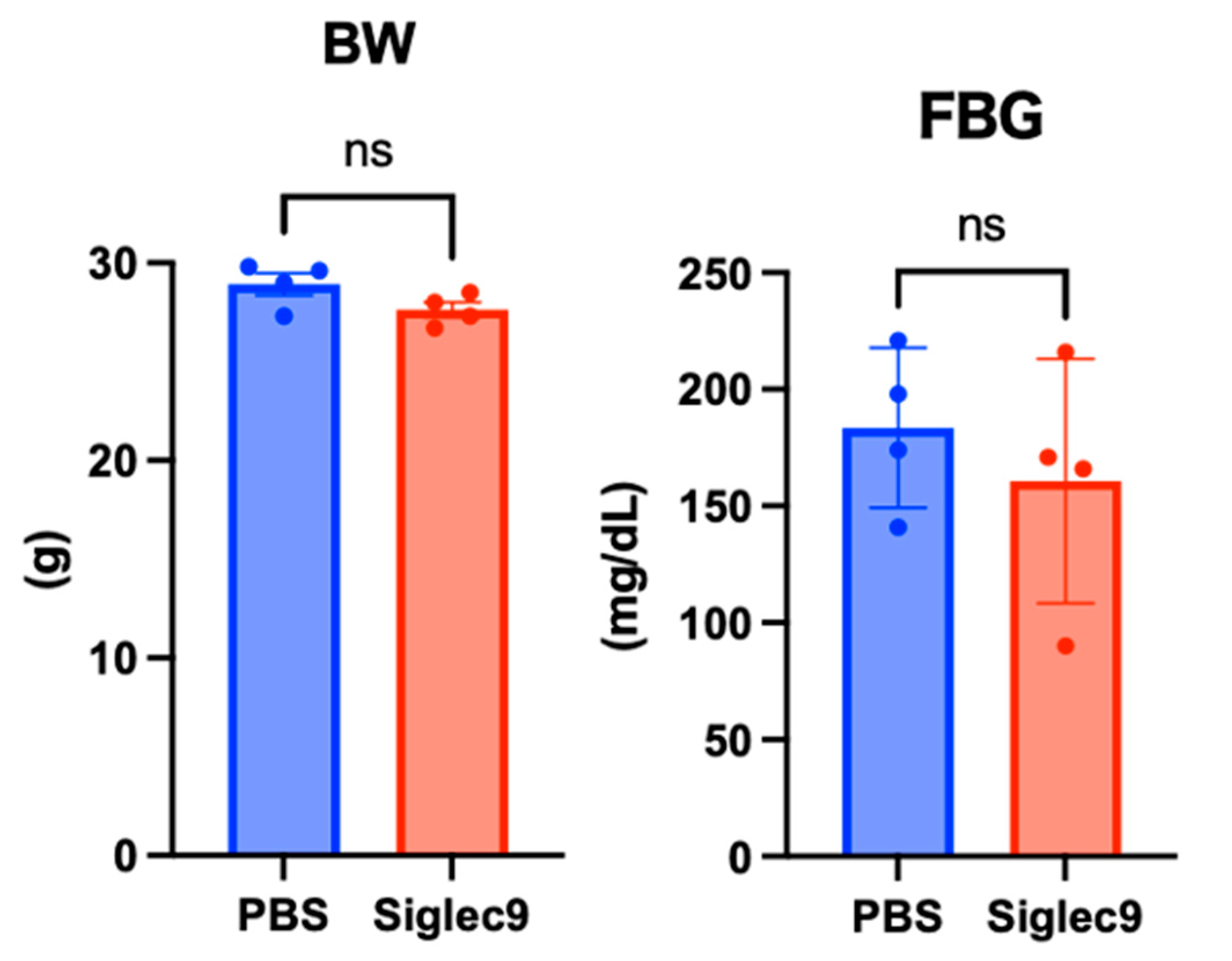
3.2. Establishment of the Murine MASH Model
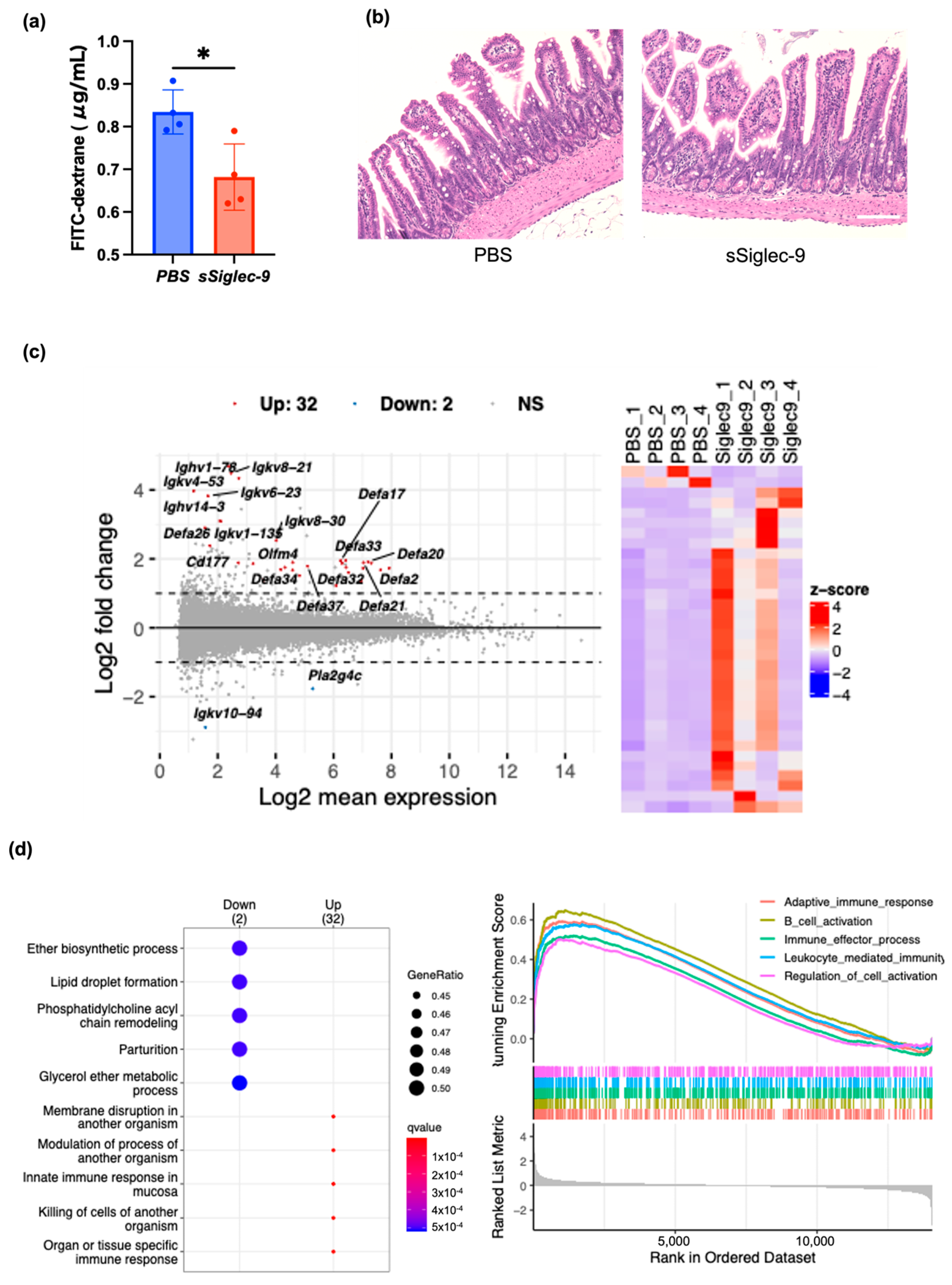
3.3. sSiglec-9 Protects the Intestinal Barrier in the MASH Mouse Model
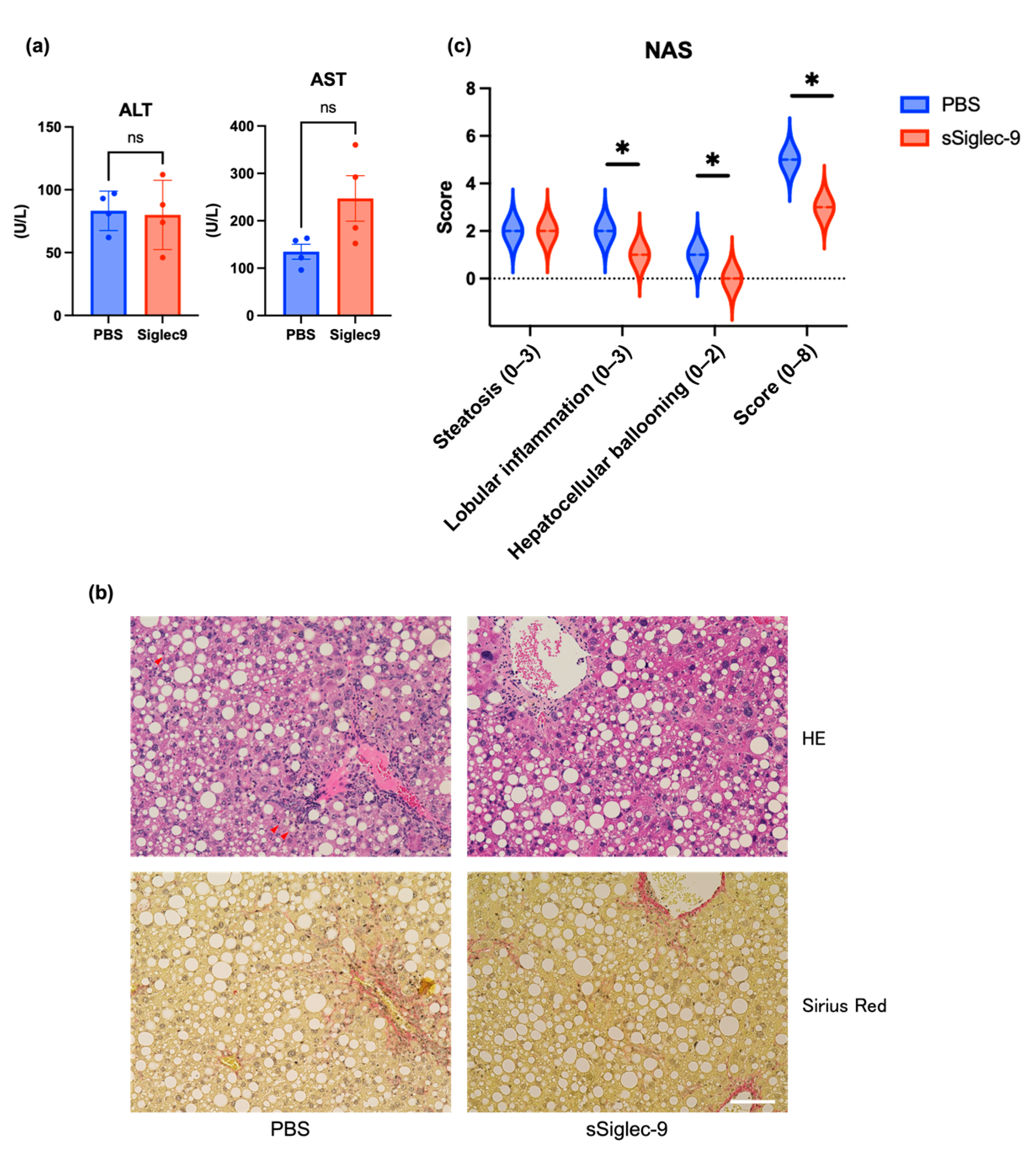
3.4. sSiglec-9 Attenuates Liver Inflammation in the MASH Mouse Model
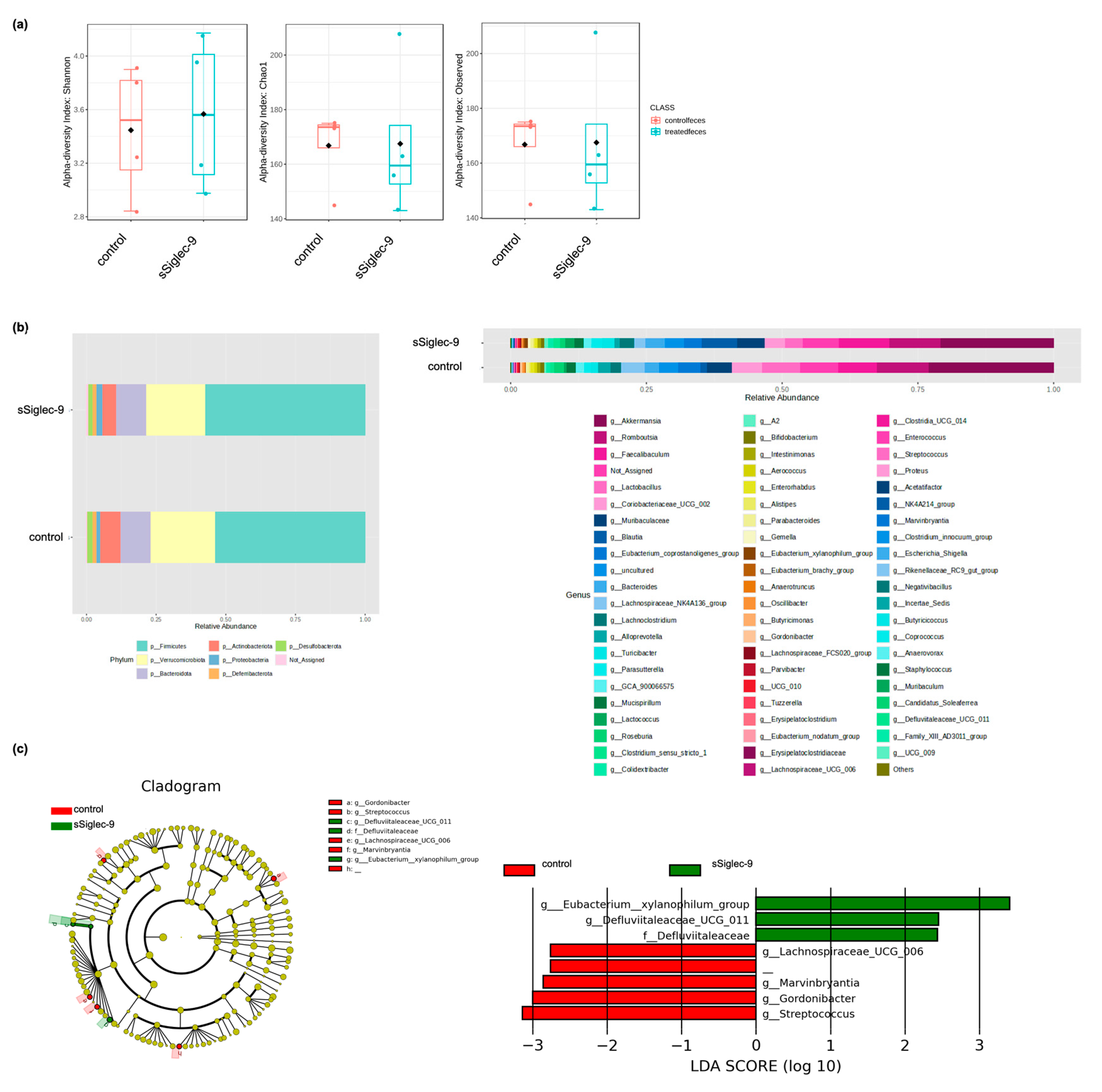
3.5. sSiglec-9 Treatment Does Not Alter Diversity of the Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BW | body weight |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| DEG | differentially expressed gene |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| FBG | fasting blood glucose |
| FITC | fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| GSEA | gene set enrichment analysis |
| H&E | hematoxylin–eosin |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| LEfSe | linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| MASH | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NAS | NAFLD activity score |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| SCFA | short-chain fatty acids |
| SHED | stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth |
| SHED-CM | stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth-conditioned media |
| Siglecs | sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins |
| sSiglec-9 | soluble Siglec-9 |
References
- Tateishi, R.; Uchino, K.; Fujiwara, N.; Takehara, T.; Okanoue, T.; Seike, M.; Yoshiji, H.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Shimizu, M.; Torimura, T.; et al. A nationwide survey on non-B, non-C hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: 2011–2015 update. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, H.; Akuta, N.; Hikita, H.; Suda, G.; Inoue, J.; Tamaki, N.; Ito, K.; Akahane, T.; Kawaoka, T.; Morishita, A.; et al. Etiological changes of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma-complicated liver cirrhosis in Japan: Updated nationwide survey from 2018 to 2021. Hepatol. Res. 2024, 54, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.K.; Chuah, K.H.; Rajaram, R.B.; Lim, L.L.; Ratnasingam, J.; Vethakkan, S.R. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): A state-of-the-art review. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Shen, J.; Sun, T.T.; Zhang, X.; Wong, N. Obesity, insulin resistance, NASH and hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A phase 3, randomized, controlled trial of resmetirom in NASH with liver fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Heterogeneous pathomechanisms and effectiveness of metabolism-based treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouries, J.; Brescia, P.; Silvestri, A.; Spadoni, I.; Sorribas, M.; Wiest, R.; Mileti, E.; Galbiati, M.; Invernizzi, P.; Adorini, L.; et al. Microbiota-driven gut vascular barrier disruption is a prerequisite for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis development. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, H.; Ito, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Imai, N.; Ishizu, Y.; Maeda, K.; Honda, T.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Conditioned medium from stem cells derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorates NASH via the Gut-Liver axis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Matsushita, Y.; Sakai, K.; Kano, F.; Kondo, M.; Noda, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Imagama, S.; Ishiguro, N.; Suzumura, A.; et al. Secreted ectodomain of sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin-9 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 promote recovery after rat spinal cord injury by altering macrophage polarity. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 2452–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Ishigami, M.; Matsushita, Y.; Hirata, M.; Matsubara, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Hibi, H.; Ueda, M.; Hirooka, Y.; Goto, H.; et al. Secreted ectodomain of SIGLEC-9 and MCP-1 synergistically improve acute liver failure in rats by altering macrophage polarity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.A.; Soh, H.; Park, S.; Lee, H.J.; Im, J.P.; Kim, J.S. Soluble Siglec-9 alleviates intestinal inflammation through inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 86, 106695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C.; Varki, A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.; Netravali, I.A.; Cariappa, A.; Mattoo, H. Siglecs and immune regulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukan, E.N.; Fabiano, G.L.; Cobb, B.A. Siglecs as modulators of macrophage phenotype and function. Semin. Immunol. 2024, 73, 101887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.S.; Jiang, N.; Jain, A.; Lim, J. Development of effective Siglec-9 antibodies against cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, Z.; Liu, S. Siglec-9, a putative immune checkpoint marker for cancer progression across multiple cancer types. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 743515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Matsubara, K.; Nakamura, S.; Naruse, M.; Yamagata, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Tauchi, R.; Wakao, N.; Imagama, S.; et al. Human dental pulp-derived stem cells promote locomotor recovery after complete transection of the rat spinal cord by multiple neuro-regenerative mechanisms. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, M.; Kamzolas, I.; Harder, L.M.; Oakley, F.; Trautwein, C.; Hatting, M.; Ross, T.; Bernardo, B.; Oldenburger, A.; Hjuler, S.T.; et al. An unbiased ranking of murine dietary models based on their proximity to human metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 1178–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Lee, Y.A.; Fujiwara, N.; Ybanez, M.; Allen, B.; Martins, S.; Fiel, M.I.; Goossens, N.; Chou, H.-I.; Hoshida, Y.; et al. A simple diet-and chemical-induced murine NASH model with rapid progression of steatohepatitis, fibrosis and liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Shih, D.Q.; Zhang, X. Protective role of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 in the mucosal injury and epithelial barrier disruption in DSS-induced acute colitis in mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Barrios, D. RaNA-Seq: Interactive RNA-Seq analysis from FASTQ files to functional analysis. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1955–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etoh, K.; Nakao, M. A web-based integrative transcriptome analysis, RNAseqChef, uncovers the cell/tissue type-dependent action of sulforaphane. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Maeda, K.; Ohashi, A.; Urano, T.; Nariai, Y.; Kamino, H.; Nakamura, M.; Yamamura, T.; Sawada, T.; Ishikawa, E.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies against mature interleukin-18 ameliorate colitis and repair goblet cell function. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2024, 69, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Ewald, J.; Pang, Z.; Shiri, T.; Xia, J. MicrobiomeAnalyst 2.0: Comprehensive statistical, functional and integrative analysis of microbiome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W310–W318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Ishigami, M.; Zou, B.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kurosaki, M.; Maeda, M.; Thin, K.N.; Tanaka, K.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. The epidemiology of NAFLD and lean NAFLD in Japan: A meta-analysis with individual and forecasting analysis, 1995–2040. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tincopa, M.A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Loomba, R. New and emerging treatments for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 912–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergheim, I.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M. The relevance of intestinal barrier dysfunction, antimicrobial proteins and bacterial endotoxin in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2024, 54, e14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, L.I.; Rodrigues, C.S.; Bakshani, C.R.; Tavares-Gomes, L.; Gaifem, J.; Pinho, S.S. The role of glycans in health and disease: Regulators of the interaction between gut microbiota and host immune system. Semin. Immunol. 2024, 73, 101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avril, T.; Floyd, H.; Lopez, F.; Vivier, E.; Crocker, P.R. The membrane-proximal immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif is critical for the inhibitory signaling mediated by Siglecs-7 and-9, CD33-related Siglecs expressed on human monocytes and NK cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6841–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, B. Regulation of neutrophil functions through inhibitory receptors: An emerging paradigm in health and disease. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 273, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zong, X.; Jin, M.; Min, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Mechanisms and regulation of defensins in host defense. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Nakamura, K.; Yokoi, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Ohira, S.; Hagiwara, M.; Song, Z.; Gan, L.; Aizawa, T.; Hashimoto, D.; et al. Decreased Paneth cell α-defensins promote fibrosis in a choline-deficient L-amino acid-defined high-fat diet-induced mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via disrupting intestinal microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms, L.A.; Doecke, J.D.; Walsh, M.D.; Huang, N.; Fowler, E.V.; Radford-Smith, G.L. Reduced α-defensin expression is associated with inflammation and not NOD2 mutation status in ileal Crohn’s disease. Gut 2008, 57, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörbe, U.M.; Jørgensen, P.B.; Fenton, T.M.; von Burg, N.; Riis, L.B.; Spencer, J.; Agace, W.W. Human gut-associated lymphoid tissues (GALT); diversity, structure, and function. Mucosal Immunol. 2021, 14, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Hirohata, S. The role of IL-10 in human B cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 4341–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, G.; Khare, V.; Gasche, C. Inflamed gut mucosa: Downstream of interleukin-10. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 42, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lordan, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Gut microbes from the phylogenetically diverse genus Eubacterium and their various contributions to gut health. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1802866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.S.; Lin, Y.E.; Panyod, S.; Chen, R.A.; Lin, Y.C.; Chai, L.M.X.; Hsu, C.C.; Wu, W.K.; Lu, K.H.; Huang, Y.J.; et al. Anti-depressive-like and cognitive impairment alleviation effects of Gastrodia elata Blume water extract is related to gut microbiome remodeling in ApoE−/− mice exposed to unpredictable chronic mild stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 302, 115872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, S. Gut microbiota and immune mediation: A Mendelian randomization study on granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1296016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Li, S.; Ye, H.; Yang, Y.; Jia, X.; Lin, M.; Chu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Z.; et al. Gut microbiome and frailty: Insight from genetic correlation and mendelian randomization. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2282795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Ishigami, M.; Honda, T.; Takeyama, T.; Ito, T.; Ishizu, Y.; Kuzuya, T.; Hayashi, K.; Goto, H.; Hirooka, Y. Influence of proton pump inhibitors on microbiota in chronic liver disease patients. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Lei, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, L. Characterization of fecal microbial communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Ishigami, M.; Matsushita, Y.; Ito, T.; Hattori, H.; Hibi, H.; Goto, H.; Ueda, M.; Yamamoto, A. Multifaceted therapeutic benefits of factors derived from dental pulp stem cells for mouse liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muto, H.; Mizuno, F.; Honda, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ito, T.; Imai, N.; Ishizu, Y.; Sakai, K.; et al. Soluble Siglec-9 Improves Intestinal Barrier Function in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Metabolites 2025, 15, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060366
Muto H, Mizuno F, Honda T, Yokoyama S, Tanaka T, Yamamoto K, Ito T, Imai N, Ishizu Y, Sakai K, et al. Soluble Siglec-9 Improves Intestinal Barrier Function in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Metabolites. 2025; 15(6):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060366
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuto, Hisanori, Fumitaka Mizuno, Takashi Honda, Shinya Yokoyama, Taku Tanaka, Kenta Yamamoto, Takanori Ito, Norihiro Imai, Yoji Ishizu, Kiyoshi Sakai, and et al. 2025. "Soluble Siglec-9 Improves Intestinal Barrier Function in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis" Metabolites 15, no. 6: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060366
APA StyleMuto, H., Mizuno, F., Honda, T., Yokoyama, S., Tanaka, T., Yamamoto, K., Ito, T., Imai, N., Ishizu, Y., Sakai, K., Hibi, H., Ishigami, M., & Kawashima, H. (2025). Soluble Siglec-9 Improves Intestinal Barrier Function in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Metabolites, 15(6), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060366





