Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis Immunothrombosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Focus of the Infection
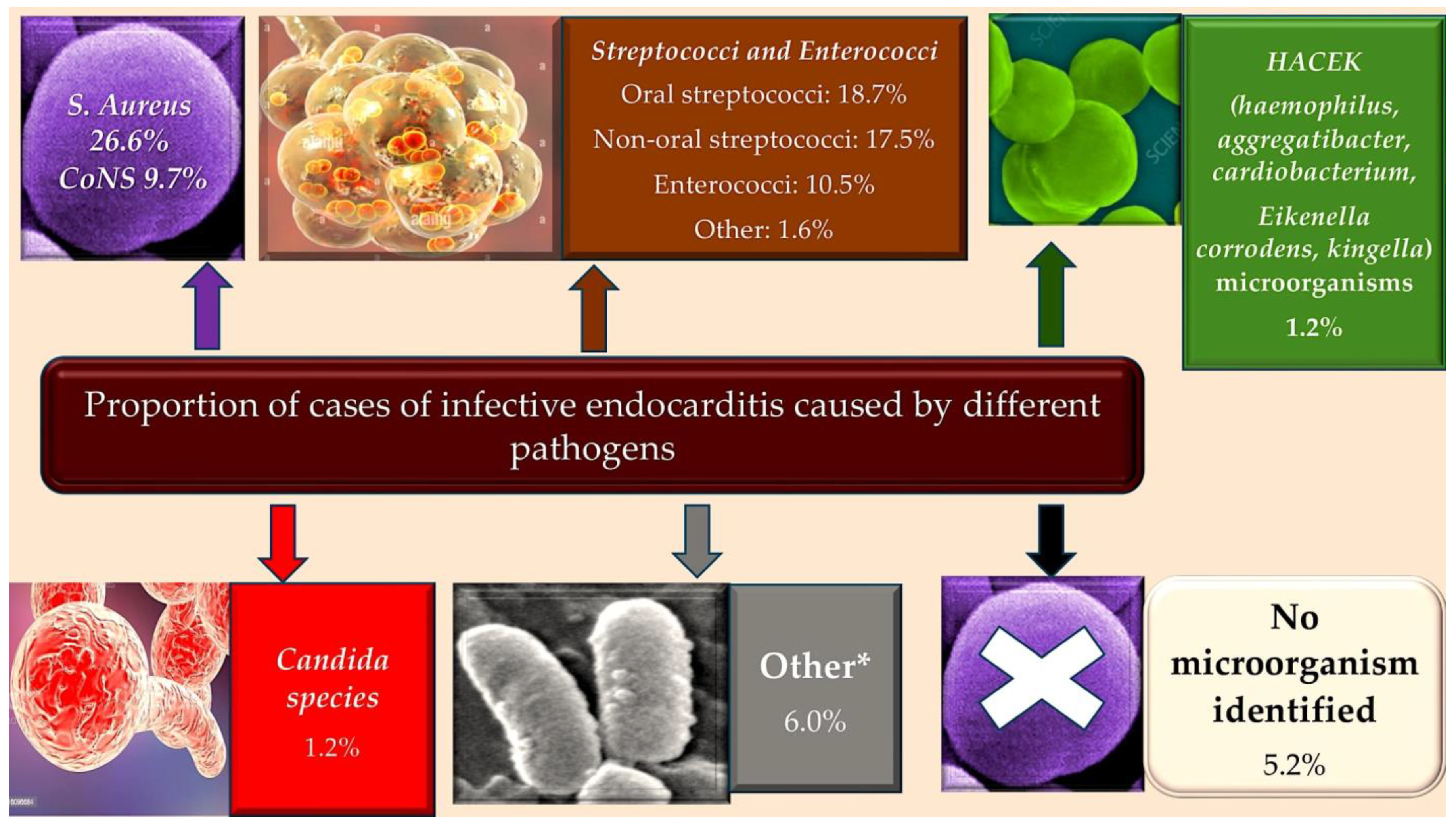
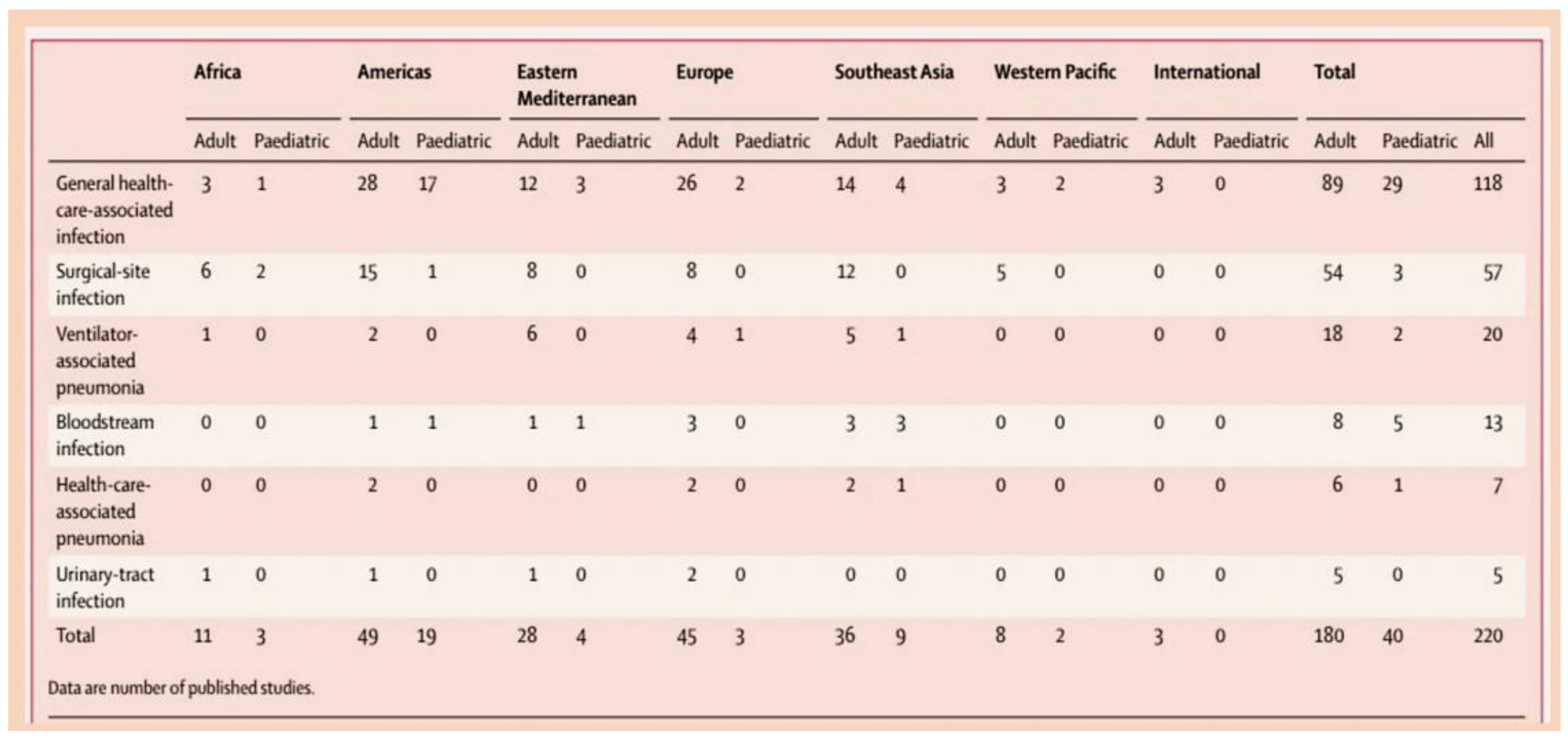
3.2. The Epidemiology of Infective Endocarditis and the Targeting of Vulnerable Populations to Staphylococcal Infection
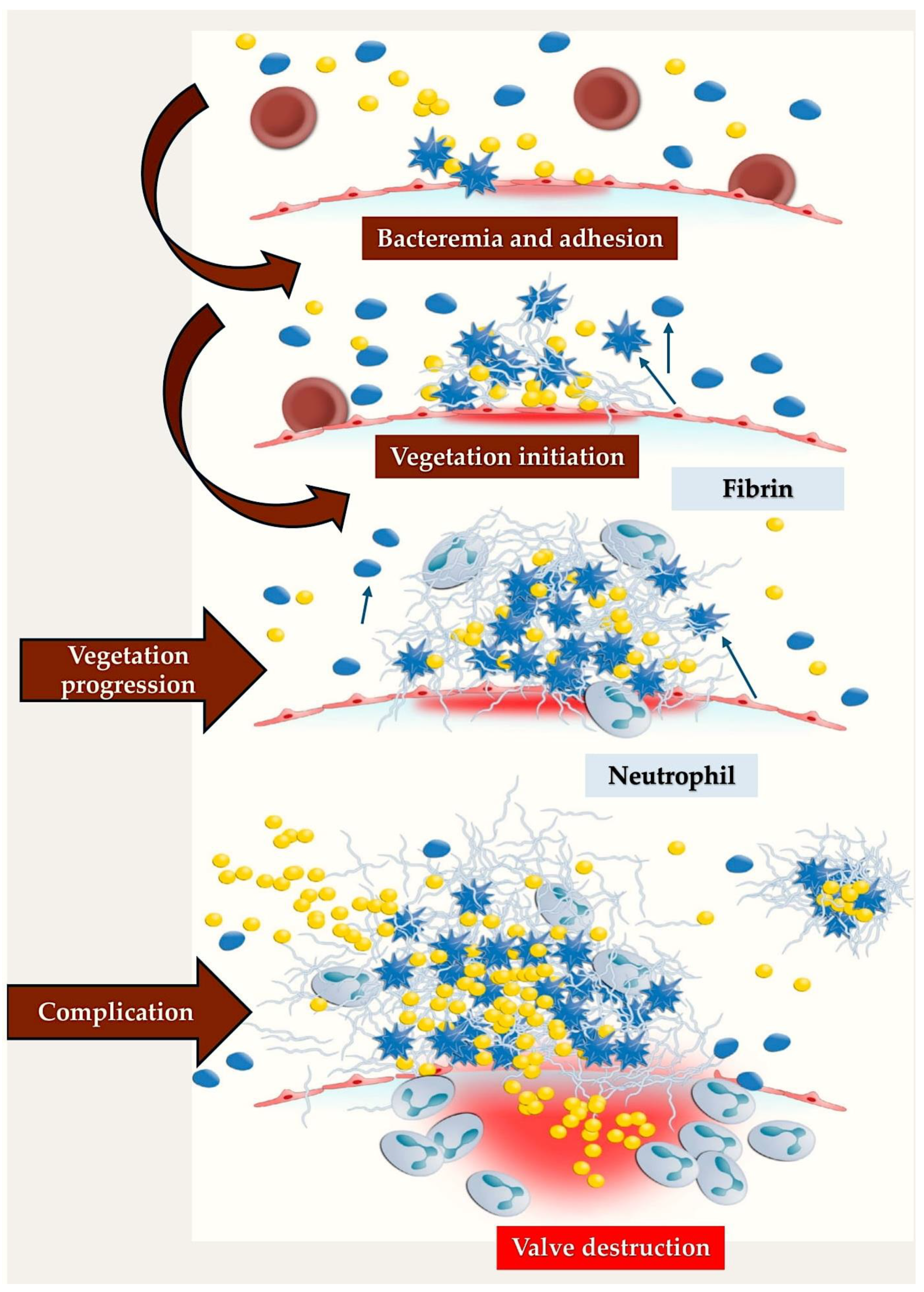
3.3. Infective Endocarditis: Could an Immunothrombosis Be the Underlying Cause?
3.4. Staphylococcus aureus’ Protective Barriers and Host Defence Responses: New Insights from Field Studies and the Role of Coagulases
3.5. Pathogen–Host Interplay in Establishing the Inflammatory Processes
- Surface molecules of Staphylococcus aureus
- The way the endothelial cell surface works.
3.6. Immunity to Staphylococcus aureus Infection
- Staphylo cytotoxins can change how the immune system works.
- Imbalance in how B cells and T cells work together.
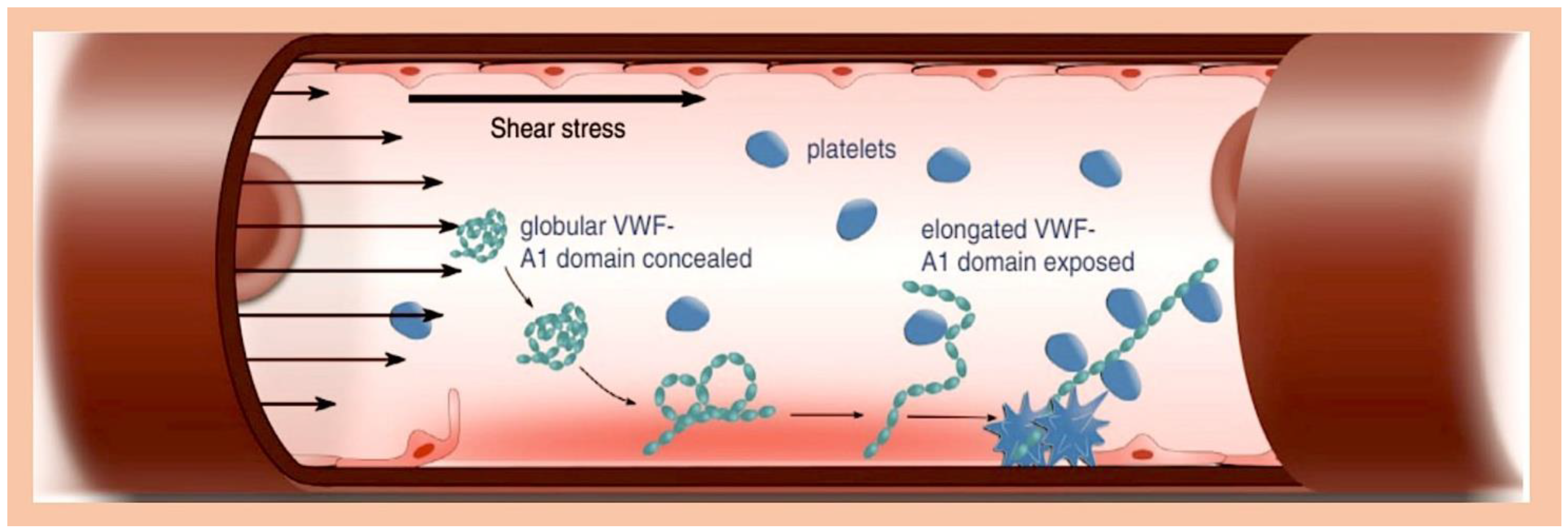
3.7. Infective Endocarditis, Platelet, and Antiaggregation
4. Perspective
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selton-Suty, C.; Célard, M.; Le Moing, V.; Doco-Lecompte, T.; Chirouze, C.; Iung, B.; Strady, C.; Revest, M.; Vandenesch, F.; Bouvet, A.; et al. Preeminence of Staphylococcus aureus in infective endocarditis: A 1-year population-based survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, D.R.; Corey, G.R.; Hoen, B.; Miró, J.M.; Fowler, V.G.; Bayer, A.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; Olaison, L.; Pappas, P.A.; Moreillon, P.; et al. Clinical presentation, etiology, and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century: The International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaqat, W.; Palaiodimos, L.; Li, W.; Karamanis, D.; Tahir, A.; Tzoumas, A.; Nagraj, S.; Tiwari, N.; Grushko, M.; Kokkinidis, D.; et al. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of infective endocarditis: A single-center retrospective study in the Bronx, New York. Infection 2022, 50, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; de Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Caselli, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, S.; Erba, P.A.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fowler, V.G.; Durack, D.T.; Selton-Suty, C.; Athan, E.; Bayer, A.S.; Chamis, A.L.; Dahl, A.; Di Bernardo, L.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Duval, X.; et al. The 2023 Duke-International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases Criteria for Infective Endocarditis: Updating the Modified Duke Criteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 77, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.E.; Herijgers, P.; Claus, P.; Vanderschueren, S.; Herregods, M.C.; Peetermans, W.E. Infective endocarditis: Changing epidemiology and predictors of 6-month mortality: A prospective cohort study. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, X.; Delahaye, F.; Alla, F.; Tattevin, P.; Obadia, J.F.; Le Moing, V.; Doco-Lecompte, T.; Celard, M.; Poyart, C.; Strady, C.; et al. The AEPEI Study Group;. Temporal trends in infective endocarditis in the context of prophylaxis guideline modifications: Threesuccessive population-based surveys. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoen, B.; Alla, F.; Selton-Suty, C.; Bouvet, A.; Briançon, S.; Casalta, J.P.; Danchin, N.; Delahaye, F.; Etienne, J.; Le Moing, V.; et al. Changing profile of infective endocarditis: Results of a 1-year survey in France. JAMA 2002, 288, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegranzi, B.; Nejad, S.B.; Combescure, C.; Graafmans, W.; Attar, H.; Donaldson, L.; Pittet, D. Burden of endemic health-careassociated infection in developing countries: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2011, 377, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, D.; Cullati, S.; Briot, P.; Righi, L.; Grauser, D.; Ourahmoune, A.; Chopard, P. How to improve hospital admission screening for patients at risk of multidrug-resistant organism carriage: A before-and-after interventional study and cost-effectiveness analysis. BMJ Open Qual. 2022, 11, e001699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J.V. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.L. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Science 2008, 321, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tao, C. Recent advances in metal-organic framework-based materials for anti-staphylococcus aureus infection. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6220–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F.; Martuscelli, G.; Bellomo, F.; Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Moon, M.R. Infective Endocarditis in High-Income Countries. Metabolites 2022, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.; Shalaby, A.; Saba, S. Rising rates of cardiac rhythm management device infections in the United States: 1996 through 2003. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 590–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traykov, V.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C. Antibiotic-Eluting Envelopes for the Prevention of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infections: Rationale, Efficacy, and Cost-Effectiveness. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 855233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, B.; Perl, L.; Hamdan, A.; Yahav, D.; Atamna, A.; Shaked, H.; Rubchevsky, V.; Sharony, R.; Bernstine, H.; Shapira, Y.; et al. The clinical value of the endocarditis team: Insights from before and after guidelines implementation strategy. Infection 2021, 50, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.C.; Hawkins, N.M.; Pearman, C.M.; Birnie, D.H.; Krahn, A.D. Epidemiology of cardiac implantable electronic device infections: Incidence and risk factors. Europace 2021, 23 (Suppl. 4), iv3–iv10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante-Mangoni, E.; Bradley, S.; Selton-Suty, C.; Tripodi, M.F.; Barsic, B.; Bouza, E.; Cabell, C.H.; Ramos, A.I.; Fowler, V., Jr.; Hoen, B.; et al. Results of the International Collaboration on Endocarditis Prospective Cohort Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampino, R.; Iossa, D.; Ursi, M.P.; Bertolino, L.; Karruli, A.; Molaro, R.; Esposito, G.; Vitrone, M.; D’Amico, F.; Albisinni, R.; et al. Clinical Significance and Prognostic Value of Hemostasis Parameters in 337 Patients with Acute Infective Endocarditis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F.; Spadaccio, C.; Dreyfus, J.; Attias, D.; Acar, C.; Bando, K. Mitral endocarditis: A new management framework. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 156, 1486–1495.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhan, J.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, Z. The Global, Regional, and National Burden and Trends of Infective Endocarditis from 1990 to 2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 774224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molton, J.S.; Tambyah, P.A.; Ang, B.S.P.; Ling, M.L.; Fisher, D.A. The global spread of healthcare-associated multidrug-resistant bacteria: A perspective from Asia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Çaglayan, Ç.; Barnes, S.L.; Pineles, L.L.; Harris, A.D.; Klein, E.Y. A Data-Driven Framework for Identifying Intensive Care Unit Admissions Colonized With Multidrug-Resistant Organisms. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 853757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Revilla, A.; Vilacosta, I.; Villacorta, E.; González-Juanatey, C.; Gómez, I.; Rollán, M.J.; Román, J.A.S. Definition, clinical profile, microbiological spectrum, and prognostic factors of early-onset prosthetic valve endocarditis. Eur. Hear. J. 2007, 28, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Valle, H.; Fariñas-Álvarez, C.; García-Palomo, J.D.; Bernal, J.M.; Martín-Durán, R.; Díez, J.F.G.; Revuelta, J.M.; Fariñas, M.C. Clinical course and predictors of death in prosthetic valve endocarditis over a 20-year period. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Tang, A.; Huang, D.; Pan, Q.; Fang, Z. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of MethicillinResistant Staphylococci Recovered from Public Shared Bicycles in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Prola, K.; Prévost, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Pathogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaca, A.O.; Lemos, J.A. Adaptation to Adversity: The Intermingling of Stress Tolerance and Pathogenesis in Enterococci. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2019, 83, e00008–e00019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, E.; Van Tyne, D.; Gilmore, M.S. Pathogenicity of Enterococci. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, H.M.S.; Yong, M.H.A.; Chong, K.K.L.; Kline, K.A. Model systems for the study of Enterococcal colonization and infection. Virulence 2017, 8, 1525–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Jitendra, V.; Fiore, A. Bridging Molecular and Clinical Sciences to Achieve the Best Treatment of Enterococcus faecalis Endocarditis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F. Current Knowledge of Enterococcal Endocarditis: A Disease Lurking in Plain Sight of Health Providers. Pathogens 2024, 13, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F. Native Infective Endocarditis: A State-of-the-Art-Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’ng, J.H.; Chong, K.K.L.; Lam, L.N.; Wong, J.J.; Kline, K.A. Biofilm-associated infection by enterococci. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Silva, V.; Dapkevicius, M.L.E.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Enterococci, from Harmless Bacteria to a Pathogen. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.L.; Baddour, L.M.; Bayer, A.S.; Hoen, B.; Miro, J.M.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Infective endocarditis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivito, S.; Lalande, S.; Nappi, F.; Hammoudi, N.; D’Alessandro, C.; Fouret, P.; Acar, C. Structural deterioration of the cryopreserved mitral homograft valve. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 144, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, M.; Hartke, A.; Huycke, M. The Physiology and Metabolism of Enterococci. In Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection; Gilmore, M.S., Clewell, D.B., Ike, Y., Shankar, N., Eds.; Massachusers Eye and Ear Infirmary: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton, F.; Willems, R.J.L.; Gilmore, M.S. Enterococcus Diversity, Origins in Nature, and Gut Colonization. In Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection; Gilmore, M.S., Clewell, D.B., Ike, Y., Shankar, N., Eds.; Massachusers Eye and Ear Infirmary: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, K.D.; Singh, K.V.; Nallapareddy, S.R.; Murray, B.E. Relative contributions of Enterococcus faecalis OG1RF sortase-encoding genes, srtA and bps (srtC), to biofilm formation and a murine model of urinary tract infection. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5399–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scor, J.R.; Zähner, D. Pili with strong arachments: Gram-positive bacteria do it differently. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, D.; Wirth, R.; Wanner, G. Identification of aggregation substances of Enterococcus faecalis cells after induction by sex pheromones. An immunological and ultrastructural investigation. Arch. Microbiol. 1989, 151, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmsted, S.B.; Kao, S.M.; van Pure, L.J.; Gallo, J.C.; Dunny, G.M. Role of the pheromone-inducible surface protein Asc10 in mating aggregate formation and conjugal transfer of the Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pCF10. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 7665–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, H.S.; Murdoch, D.R. Global trends in infective endocarditis epidemiology. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2012, 14, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapetis, J.R.; Steer, A.C.; Mulholland, E.K.; Weber, M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijon, E.; Ou, P.; Celermajer, D.S.; Ferreira, B.; Mocumbi, A.O.; Jani, D.; Paquet, C.; Jacob, S.; Sidi, D.; Jouven, X. Prevalence of Rheumatic Heart Disease Detected by Echocardiographic Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwebembera, J.; Nascimento, B.R.; Minja, N.W.; de Loizaga, S.; Aliku, T.; dos Santos, L.P.A.; Galdino, B.F.; Corte, L.S.; Silva, V.R.; Chang, A.Y.; et al. Recent Advances in the Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease Continuum. Pathogens 2022, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, B.D. The changing face of infective endocarditis. Heart 2006, 92, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Spadaccio, C.; Mihos, C. Infective endocarditis in the 21st century. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipczuk, L.; Codolosa, J.N.; Davila, C.D.; Romero-Corral, A.; Yun, J.; Pressman, G.S.; Figueredo, V.M. Infective Endocarditis Epidemiology Over Five Decades: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F.; Spadaccio, C.; Chello, M.; Acar, C. The Ross procedure: Underuse or under-comprehension? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, U.; Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Spadaccio, C.; Moon, M.R.; Nappi, F. A narrative review of the interpretationof guidelines for the treatment of infective endocarditis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, U.; Spadaccio, C.; Gentile, F.; Moon, M.R.; Nappi, F. A narrative review of early surgery versus conventional treatment for infective endocarditis: Do we have an answer? Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Spadaccio, C.; Moon, M.R. A management framework for left sided endocarditis: A narrative review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollari, F.; Ziegler, R.; Nappi, F.; Grossmann, I.; Steinmann, J.; Fischlein, T. Redo aortic valve replacement for prosthesis endocarditis in patients previously classified as high or prohibitive risk: A narrative review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Singh, S.S.A.; Spadaccio, C.; Acar, C. Revisiting the guidelines and choice the ideal substitute for aortic valve endocarditis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Nenna, A.; Petitti, T.; Spadaccio, C.; Gambardella, I.; Lusini, M.; Chello, M.; Acar, C. Long-term outcome of cryopreserved allograft for aortic valve replacement. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 156, 1357–1365.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F.; Spadaccio, C.; Acar, C. Use of allogeneic tissue to treat infective valvular disease: Has everything been said? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 153, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, P., Jr.; Fortes, C.Q.; do Nascimento, E.M.; Sousa, C.; Fortes, N.R.Q.; Thomaz, D.C.; de Bragança Pereira, B.; Pinto, F.J.; de Oliveira, G.M.M. In-hospital Outcomes of Infective Endocarditis from 1978 to 2015: Analysis through Machine-Learning Techniques. CJC Open 2021, 4, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Iervolino, A.; Singh, S.S.A. The New Challenge for Heart Endocarditis: From Conventional Prosthesis to New Devices and Platforms for the Treatment of Structural Heart Disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7302165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amat-Santos, I.J.; Messika-Zeitoun, D.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Kapadia, S.; Lerakis, S.; Cheema, A.N.; Gutiérrez-Ibañes, E.; Muñoz, A.; Pan, M.; Webb, J.G.; et al. Infective Endocarditis After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Results from a Large Multicenter Registry. Circulation 2015, 132, e372–e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangner, N.; Woitek, F.; Haussig, S.; Schlotter, F.; Stachel, G.; Höllriegel, R.; Wilde, J.; Lindner, A.; Holzhey, D.; Leontyev, S.; et al. Incidence, Predictors, and Outcome of Patients Developing Infective Endocarditis Following Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2907–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijck, I.; Budts, W.; Cools, B.; Eyskens, B.; Boshoff, D.E.; Heying, R.; Frerich, S.; Vanagt, W.Y.; Troost, E.; Gewillig, M. Infective endocarditis of a transcatheter pulmonary valve in comparison with surgical implants. Heart 2015, 101, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, L.R.; Calix, J.J.; Wildenthal, J.A.; Wallace, M.A.; Sawhney, S.S.; Ransom, E.M.; Durkin, M.J.; Henderson, J.P.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Dantas, G. Staphylococcus aureus injection drug use-associated bloodstream infections are propagated bycommunity outbreaks of diverse lineages. Commun. Med. 2021, 1, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyytikainen, O.; Ruotsalainen, E.; Jarvinen, A.; Valtonen, V.; Ruutu, P. Trends and outcome of nosocomial and communityacquired bloodstream infections due to Staphylococcus aureus in Finland, 1995–2001. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 24, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammerlaan, H.S.M.; Harbarth, S.; Buiting, A.G.M.; Crook, D.W.; Fitzpatrick, F.; Hanberger, H.; Herwaldt, L.A.; Van Keulen, P.H.J.; Kluytmans, J.A.J.W.; Kola, A.; et al. Secular Trends in Nosocomial Bloodstream Infections: Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Increase the Total Burden of Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 56, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsblom, E.; Kakriainen, A.; Ruotsalainen, E.; Järvinen, A. Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in aged patients: The importance of formal infectious specialist consultation. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, I.; Millon, B.; Meugnier, H.; Vandenesch, F.; Maurin, M.; Pavese, P.; Boisset, S. High prevalence of spa type t571 among methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus from bacteremic patients in a French University Hospital. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspon, A.J.; Patel, J.D.; Lau, E.; Ochoa, J.A.; Frisch, D.R.; Ho, R.T.; Pavri, B.B.; Kurtz, S.M. 16-year trends in the infection burden for pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator in the United States 1993 to 2008. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, P.B.; Brennan, M.T.; Sasser, H.C.; Fox, P.C.; Paster, B.J.; Bahrani-Mougeot, F.K. Bacteremia associated with toothbrushing and dental extraction. Circulation 2008, 117, 3118–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmer, E.; Que, Y.A.; Entenza, J.M.; Moreillon, P. New concepts in the pathophysiology of infective endocarditis. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2006, 8, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreillon, P.; Que, Y.A.; Bayer, A.S. Pathogenesis of streptococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 16, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, S.; Oechslin, F.; Menzi, C.; Que, Y.A.; Claes, J.; Heying, R.; Veloso, T.R.; Vanassche, T.; Missiakas, D.; Schneewind, O.; et al. Marginal role of von Willebrand factor-binding protein and coagulase in the initiation of endocarditis in rats with catheter-induced aortic vegetations. Virulence 2018, 9, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhamme, P.; Hoylaerts, M.F. Hemostasis and inflammation: Two of a kind? Thromb. J. 2009, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, K.N.; Teramura, Y.; Hamad, O.A.; Asif, S.; Duehrkop, C.; Fromell, K.; Gustafson, E.; Hong, J.; Kozarcanin, H.; Magnusson, P.U.; et al. Dangerous liaisons: Complement, coagulation, and kallikrein/kinin cross-talk act as a linchpin in the events leading to thromboinflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, I.-M.; Björck, L.; Herwald, H. The dual role of the contact system in bacterial infectious disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papareddy, P.; Rydengård, V.; Pasupuleti, M.; Walse, B.; Mörgelin, M.; Chalupka, A.; Malmsten, M.; Schmidtchen, A. Proteolysis of human thrombin generates novel host defense peptides. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesenborghs, L.; Verhamme, P.; Vanassche, T. Staphylococcus aureus, master manipulator of the human hemostatic system. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Bellomo, F.; Avtaar Singh, S.S. Insights into the Role of Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Causing Cardiovascular Complications in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Giacinto, O.; Ellouze, O.; Nenna, A.; Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Chello, M.; Bouzguenda, A.; Copie, X. Association between COVID-19 Diagnosis and Coronary Artery Thrombosis: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Nappi, P.; Gambardella, I.; Avtaar Singh, S.S. Thromboembolic Disease and Cardiac Thrombotic Complication in COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Metabolites 2022, 12, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAdow, M.; Missiakas, D.M.; Schneewind, O. Staphylococcus aureus secretes coagulase and von Willebrand factor binding protein to modify the coagulation cascade and establish host infections. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomer, L.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D. Multiple ligands of von Willebrand factor-binding protein (vWbp) promote Staphylococcus aureus clot formation in human plasma. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28283–28292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.P.; Kang, M.; Ganesh, V.K.; Ravirajan, D.; Li, B.; Höök, M. Coagulase and Efb of Staphylococcus aureus Have a Common Fibrinogen Binding Motif. mBio 2016, 7, e01885-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Liu, W.; Arora, S.; Ganesh, V.; Ko, Y.P.; Höök, M. The Complex Fibrinogen Interactions of the Staphylococcus aureus Coagulases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Arora, S.; Liu, W.; Churion, K.; Wu, Y.; Höök, M. vhp Is a Fibrinogen-Binding Protein Related to vWbp in Staphylococcus aureus. mBio 2021, 12, e0116721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrón, O.; Weggeman, M.; Grimbergen, J.; Clark, E.G.; Abrahams, S.; Hur, W.S.; Koopman, J.; Flick, M.J. Fibrinogen γ’ promotes host survival during Staphylococcus aureus septicemia in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 2277–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoglio, F.; Ko, Y.P.; Thomas, S.; Giordano, L.; Scommegna, F.R.; Meier, D.; Polten, S.; Becker, M.; Arora, S.; Hust, M.; et al. Antibodies to coagulase of Staphylococcus aureus crossreact to Efb and reveal different binding of shared fibrinogen binding repeats. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1221108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.; Töre, Y.; Hoesker, V.; Ameling, S.; Grün, K.; Völker, U.; Schulze, P.C.; Franz, M.; Faber, C.; Schaumburg, F.; et al. Host-pathogen interactions of clinical S. aureus isolates to induce infective endocarditis. Virulence 2021, 12, 2073–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.; Lox, M.; Kraisin, S.; Liesenborghs, L.; Martens, C.P.; Frederix, L.; Van Bruggen, S.; Crescente, M.; Missiakas, D.; Baatsen, P.; et al. Neutrophils Protect Against Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis Progression Independent of Extracellular Trap Release. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesenborghs, L.; Meyers, S.; Lox, M.; Criel, M.; Claes, J.; Peetermans, M.; Trenson, S.; Vande Velde, G.; Vanden Berghe, P.; Baatsen, P.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: Distinct mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to damaged and inflamed heart valves. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3248–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Y.-A.; Haefliger, J.-A.; Piroth, L.; Francois, P.; Widmer, E.; Entenza, J.M.; Sinha, B.N.M.; Herrmann, M.; Francioli, P.; Vaudaux, P.; et al. Fibrinogen and fibronectin binding cooperate for valve infection and invasion in Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.M.; Bowden, M.G.; Brown, E.L.; Laabei, M.; Massey, R.C. Staphylococcus aureus extracellular adherence protein triggers TNFα release, promoting attachment to endothelial cells via protein A. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.R.; Foster, T.J.; Cox, D. The interaction of bacterial pathogens with platelets. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veloso, T.R.; Chaouch, A.; Roger, T.; Giddey, M.; Vouillamoz, J.; Majcherczyk, P.; Que, Y.-A.; Rousson, V.; Moreillon, P.; Entenza, J.M. Use of a Human-Like Low-Grade Bacteremia Model of Experimental Endocarditis To Study the Role of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesins and Platelet Aggregation in Early Endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. The remarkably multifunctional fibronectin binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grønnemose, R.B.; Garde, C.; Wassmann, C.S.; Klitgaard, J.K.; Nielsen, R.; Mandrup, S.; Mattsson, A.H.; Andersen, T.E. Bacteria-host transcriptional response during endothelial invasion by Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumay, F.; Benchetrit, H.; Corvaglia, A.R.; van der Mee-Marquet, N.; François, P. The Staphylococcus aureus CC398 Lineage: An Evolution Driven by the Acquisition of Prophages and Other Mobile Genetic Elements. Genes 2021, 12, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, B.; Herrmann, M. Mechanism and consequences of invasion of endothelial cells by Staphylococcus aureus. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 266–277. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Haggar, A.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G.; Flock, J.-I.; Herrmann, M. Insertional Inactivation of eap in Staphylococcus aureus Strain Newman Confers Reduced Staphylococcal Binding to Fibroblasts. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2933–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palankar, R.; Binsker, U.; Haracska, B.; Wesche, J.; Greinacher, A.; Hammerschmidt, S. Interaction between the Staphylococcus aureus extracellular adherence protein Eap and its subdomains with platelets. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Haggar, A.; Peters, G.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Herrmann, M.; Flock, J.I.; Sinha, B. More than one tandem repeat domain of the extracellular adherence protein of Staphylococcus aureus is required for aggregation, adherence, and host cell invasion but not for leukocyte activation. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5615–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harraghy, N.; Hussain, M.; Haggar, A.; Chavakis, T.; Sinha, B.; Herrmann, M.; Flock, J.-I. The adhesive and immunomodulating properties of the multifunctional Staphylococcus aureus protein Eap. Microbiology 2003, 149, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavakis, T.; Wiechmann, K.; Preissner, K.T.; Herrmann, M. Staphylococcus aureus interactions with the endothelium: The role of bacterial “secretable expanded repertoire adhesive molecules” (SERAM) in disturbing host defense systems. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Scherr, T.D.; Lister, J.; Kielian, T.; Horswill, A.R. Extracellular adherence proteins reduce matrix porosity and enhance Staphylococcus aureus biofilm survival during prosthetic joint infection. Infect. Immun. 2025, 93, e0008625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heying, R.; van de Gevel, J.; Que, Y.A.; Moreillon, P.; Beekhuizen, H. Fibronectin-binding proteins and clumping factor A in Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis: FnBPA is sufficient to activate human endothelial cells. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroth, L.; Que, Y.-A.; Widmer, E.; Panchaud, A.; Piu, S.; Entenza, J.M.; Moreillon, P. The Fibrinogen- and Fibronectin-Binding Domains of Staphylococcus aureus Fibronectin-Binding Protein A Synergistically Promote Endothelial Invasion and Experimental Endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3824–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.; Vanassche, T.; Peetermans, M.; Liesenborghs, L.; Vandenbriele, C.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Missiakas, D.; Schneewind, O.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Heying, R.; et al. Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus to the vessel wall under flow is mediated by von Willebrand factor–binding protein. Blood 2014, 124, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappelbaum, K.I.; Gorzelanny, C.; Grässle, S.; Suckau, J.; Laschke, M.W.; Bischoff, M.; Bauer, C.; Schorpp-Kistner, M.; Weidenmaier, C.; Schneppenheim, R.; et al. Ultralarge von Willebrand Factor Fibers Mediate Luminal Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion to an Intact Endothelial Cell Layer Under Shear Stress. Circulation 2013, 128, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heying, R.; van de Gevel, J.; Que, Y.A.; Piroth, L.; Moreillon, P.; Beekhuizen, H. Contribution of (sub)domains of Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin-binding protein to the proinflammatory and procoagulant response of human vascular endothelial cells. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 101, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ythier, M.; Resch, G.; Waridel, P.; Panchaud, A.; Gfeller, A.; Majcherczyk, P.; Quadroni, M.; Moreillon, P. Proteomic and transcriptomic profiling of Staphylococcus aureus surface LPXTG-proteins: Correlation with agr genotypes and adherence phenotypes. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speziale, P.; Pietrocola, G. The Multivalent Role of Fibronectin-Binding Proteins A and B (FnBPA and FnBPB) of Staphylococcus aureus in Host Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.; Liesenborghs, L.; Peetermans, M.; Veloso, T.R.; Missiakas, D.; Schneewind, O.; Mancini, S.; Entenza, J.M.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Heying, R.; et al. Clumping factor A, von Willebrand factor-binding protein and von Willebrand factor anchor Staphylococcus aureus to the vessel wall. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, J.; Ditkowski, B.; Liesenborghs, L.; Veloso, T.R.; Entenza, J.M.; Moreillon, P.; Vanassche, T.; Verhamme, P.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Heying, R. Assessment of the Dual Role of Clumping Factor A in S. aureus Adhesion to Endothelium in Absence and Presence of Plasma. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, M.; Hu, Z.; Mohammad, M.; Stroparo, M.D.N.; Ali, A.; Fei, Y.; Jarneborn, A.; Verhamme, P.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D.; et al. The Expression of von Willebrand Factor-Binding Protein Determines Joint-Invading Capacity of Staphylococcus aureus, a Core Mechanism of Septic Arthritis. mBio 2020, 11, e02472-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.C.S.; Khamas, A.B.; Payne-Dwyer, A.; Wollman, A.J.M.; Rasmussen, K.S.; Klitgaard, J.K.; Kallipolitis, B.; Leake, M.C.; Meyer, R.L. Cooperation between coagulase and von willebrand factor binding protein in Staphylococcus aureus fibrin pseudocapsule formation. Biofilm 2024, 8, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scialla, S.; Martuscelli, G.; Nappi, F.; Singh, S.S.A.; Iervolino, A.; Larobina, D.; Ambrosio, L.; Raucci, M.G. Trends in Managing Cardiac and Orthopaedic Device-Associated Infections by Using Therapeutic Biomaterials. Polymers 2021, 13, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Meghji, S.; Williams, R.J.; Henderson, B.; Brock, J.H.; Nair, S.P. Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin binding proteins are essential for internalization by osteoblasts but do not account for differences in intracellular levels of bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 2872–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, R.C.; Kantzanou, M.N.; Fowler, T.; Day, N.P.J.; Schofield, K.; Wann, E.R.; Berendt, A.R.; Hook, M.; Peacock, S.J. Fibronectinbinding protein A of Staphylococcus aureus has multiple, substituting, binding regions that mediate adherence to fibronectin and invasion of endothelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, R.A.; Douglas, I.; Whawell, S.A. Differential adhesion and invasion by Staphylococcus aureus of epithelial cells derived from different anatomical sites. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61 Pt 12, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, S.; Nguyen, M.-T.; Eble, J.A.; Chasan, A.I.; Mrakovcic, M.; Böttcher, R.T.; Preissner, K.T.; Roßlenbroich, S.; Peters, G.; Herrmann, M. More Is Not Always Better—The Double-Headed Role of Fibronectin in Staphylococcus aureus Host Cell Invasion. mBio 2021, 12, e0106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, A.W.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Yongsunthon, R.; Liu, J.; DiBartola, A.C.; Que, Y.A.; Moreillon, P.; Lower, S.K. Bonds between fibronectin and fibronectin-binding proteins on Staphylococcus aureus and Lactococcus lactis. Langmuir 2010, 26, 10764–10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, B.E. The role of fibronectin binding proteins in the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 16, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, B.; Francois, P.; Que, Y.A.; Hussain, M.; Heilmann, C.; Moreillon, P.; Lew, D.; Krause, K.H.; Peters, G.; Herrmann, M. Heterologously expressed Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin-binding proteins are sufficient for invasion of host cells. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6871–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrocola, G.; Pellegrini, A.; Alfeo, M.J.; Marchese, L.; Foster, T.J.; Speziale, P. The iron-regulated surface determinant B (IsdB) protein from Staphylococcus aureus acts as a receptor for the host protein vitronectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 10008–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfeo, M.J.; Pagotto, A.; Barbieri, G.; Foster, T.J.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; De Filippis, V.; Speziale, P.; Pietrocola, G. Staphylococcus aureus iron-regulated surface determinant B (IsdB) protein interacts with von Willebrand factor and promotes adherence to endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manukumar, H.M.; Umesha, S. MALDI-TOF-MS based identification and molecular characterization of food associated methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mempel, M.; Schnopp, C.; Hojka, M.; Fesq, H.; Weidinger, S.; Schaller, M.; Korting, H.; Ring, J.; Abeck, D. Invasion of human keratinocytes by Staphylococcus aureus and intracellular bacterial persistence represent haemolysin-independent virulence mechanisms that are followed by features of necrotic and apoptotic keratinocyte cell death. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 146, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Katayama, Y.; Oguma, R.; Wakabayashi, S.; Nygaard, T.; Saijo, S.; Inohara, N.; Otto, M.; Matsue, H.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Virulent PSMα Peptides Induce Keratinocyte Alarmin Release to Orchestrate IL-17-Dependent Skin Inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 667–677.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, B.; Philpott, D.J. Recognition of Staphylococcus aureus by the innate immune system. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawa, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupper, T.S.; Fuhlbrigge, R.C. Immune surveillance in the skin: Mechanisms and clinical consequences. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestle, F.O.; Di, M.P.; Qin, J.Z.; Nickoloff, B.J. Skin immune sentinels in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Ton-That, H.; Su, K.; Schneewind, O. An iron-regulated sortase anchors a class of surface protein during Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2293–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigg, J.C.; Vermeiren, C.L.; Heinrichs, D.E.; Murphy, M.E. Haem recognition by a Staphylococcus aureus NEAT domain. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 63, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.R.; Mohamed, R.; Bian, L.; Routh, A.F.; Kokai-Kun, J.F.; Mond, J.J.; Tarkowski, A.; Foster, S.J. The Staphylococcus aureus surface protein IsdA mediates resistance to innate defenses of human skin. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 1, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauber, J.; Dorschner, R.A.; Coda, A.B.; Büchau, A.S.; Liu, P.T.; Kiken, D.; Helfrich, Y.R.; Kang, S.; Elalieh, H.Z.; Steinmeyer, A.; et al. Injury enhances TLR2 function and antimicrobial peptide expression through a vitamin D-dependent mechanism. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgel, P.; Crozat, K.; Lauth, X.; Makrantonaki, E.; Seltmann, H.; Sovath, S.; Hoebe, K.; Du, X.; Rutschmann, S.; Jiang, Z.; et al. A toll-like receptor 2-responsive lipid effector pathway protects mammals against skin infections with gram-positive bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 4512–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizet, V.; Ohtake, T.; Lauth, X.; Trowbridge, J.; Rudisill, J.; Dorschner, R.A.; Pestonjamasp, V.; Piraino, J.; Huttner, K.; Gallo, R.L. Innate antimicrobial peptide protects the skin from invasive bacterial infection. Nature 2001, 414, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takigawa, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Kuzukawa, M.; Mori, H.; Imokawa, G. Deficient production of hexadecenoic acid in the skin is associated in part with the vulnerability of atopic dermatitis patients to colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. Dermatology 2005, 211, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, P.Y.; Ohtake, T.; Brandt, C.; Strickland, I.; Boguniewicz, M.; Ganz, T.; Gallo, R.L.; Leung, D.Y. Endogenous antimicrobial peptides and skin infections in atopic dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malachowa, N.; Whitney, A.R.; Kobayashi, S.D.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Kennedy, A.D.; Braughton, K.R.; Shabb, D.W.; Diep, B.A.; Chambers, H.F.; Otto, M.; et al. Global Changes in Staphylococcus aureus Gene Expression in Human Blood. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonzo, F., 3rd; Kozhaya, L.; Rawlings, S.A.; Reyes-Robles, T.; DuMont, A.L.; Myszka, D.G.; Landau, N.R.; Unutmaz, D.; Torres, V.J. CCR5 is a receptor for Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin ED. Nature 2013, 493, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, F., 3rd; Torres, V.J. Bacterial survival amidst an immune onslaught: The contribution of the Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxins. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Joo, H.-S.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Otto, M. Phenol-soluble modulins—Critical determinants of staphylococcal virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 698–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berube, B.J.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin: Nearly a century of intrigue. Toxins 2013, 5, 1140–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Immune evasion by staphylococci. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, G.J.; Goodyear, C.S. Confounding B-cell defences: Lessons from a staphylococcal superantigen. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Cheng, A.G.; Kim, H.Y.; Missiakas, D.M.; Schneewind, O. Nontoxigenic protein A vaccine for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Frankel, M.B.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D. Release of protein A from the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1574–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Avtaar Singh, S.S. Endothelial Dysfunction in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Fiore, A.; Masiglat, J.; Cavuoti, T.; Romandini, M.; Nappi, P.; Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Couetil, J.P. Endothelium-Derived Relaxing Factors and Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeten, K.; Jacques, N.; Lancellotti, P.; Oury, C. Aspirin or Ticagrelor in Staphylococcus aureus Infective Endocarditis: Where Do We Stand? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 716302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditkowski, B.; Bezulska-Ditkowska, M.; Jashari, R.; Baatsen, P.; Moreillon, P.; Rega, F.; Veloso, T.R.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Heying, R. Congenital Cardiology Cardiac Surgery Group Antiplatelet therapy abrogates platelet-assisted Staphylococcus aureus infectivity of biological heart valve conduits. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 161, e457–e472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannachi, N.; Habib, G.; Camoin-Jau, L. Aspirin Effect on Staphylococcus aureus-Platelet Interactions During Infectious Endocarditis. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancellotti, P.; Musumeci, L.; Jacques, N.; Servais, L.; Goffin, E.; Pirotte, B.; Oury, C. Antibacterial activity of ticagrelor in conventional antiplatelet dosages against antibiotic-resistant gram-positive bacteria. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Reinhart, K.; Opal, S.; Demeyer, I.; Doig, C.; Rodriguez, A.L.; Beale, R.; Svoboda, P.; Laterre, P.F.; Simon, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tifacogin (recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor) in severe sepsis: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2003, 290, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, T.R.; Que, Y.A.; Chaouch, A.; Giddey, M.; Vouillamoz, J.; Rousson, V.; Moreillon, P.; Entenza, J.M. Prophylaxis of experimental endocarditis with antiplatelet and antithrombin agents: A role for long-term prevention of infective endocarditis in humans? J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, T.R.; Oechslin, F.; Que, Y.A.; Moreillon, P.; Entenza, J.M.; Mancini, S. Aspirin plus ticlopidine prevented experimental endocarditis due to Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus gallolyticus. Pathog. Dis. 2015, 73, ftv060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.L.; Dumesnil, J.G.; Cujec, B.; Sanfilippo, A.J.; Jue, J.; Turek, M.A.; Robinson, T.I.; Moher, D.; Investigators of the Multicenter Aspirin Study in Infective Endocarditis. A randomized trial of aspirin on the risk of embolic events in patients with infective endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, G.; Lancellotti, P.; Antunes, M.J.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Casalta, J.P.; Del Zotti, F.; Dulgheru, R.; El Khoury, G.; Erba, P.A.; Iung, B.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3075–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baddour, L.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Bayer, A.S.; Fowler Jr, V.G.; Tleyjeh, I.M.; Rybak, M.J.; Barsic, B.; Lockhart, P.B.; Gewitz, M.H.; Levison, M.E.; et al. Infective endocarditis in adults: Diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 132, 1435–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, S.; Cox, B.; Williams, M.J. Lack of progress in valvular heart disease in the pre-transcatheter aortic valve replacement era: Increasing deaths and minimal change in mortality rate over the past three decades. Am. Heart J. 2014, 167, 562–567.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, X.; Iung, B.; Klein, I.; Brochet, E.; Thabut, G.; Arnoult, F.; Lepage, L.; Laissy, J.P.; Wolff, M.; Leport, C.; et al. Effect of early cerebral magnetic resonance imaging on clinical decisions in infective endocarditis: A prospective study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 152, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Coagulation and sepsis. Thromb. Res. 2017, 149, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nappi, F. Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis Immunothrombosis. Metabolites 2025, 15, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050328
Nappi F. Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis Immunothrombosis. Metabolites. 2025; 15(5):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050328
Chicago/Turabian StyleNappi, Francesco. 2025. "Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis Immunothrombosis" Metabolites 15, no. 5: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050328
APA StyleNappi, F. (2025). Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis Immunothrombosis. Metabolites, 15(5), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050328






