Ceramide in Coronary Artery Disease: Troublesome or Helpful Future Tools in the Assessment of Risk Prediction and Therapy Effectiveness?
Abstract
1. Introduction
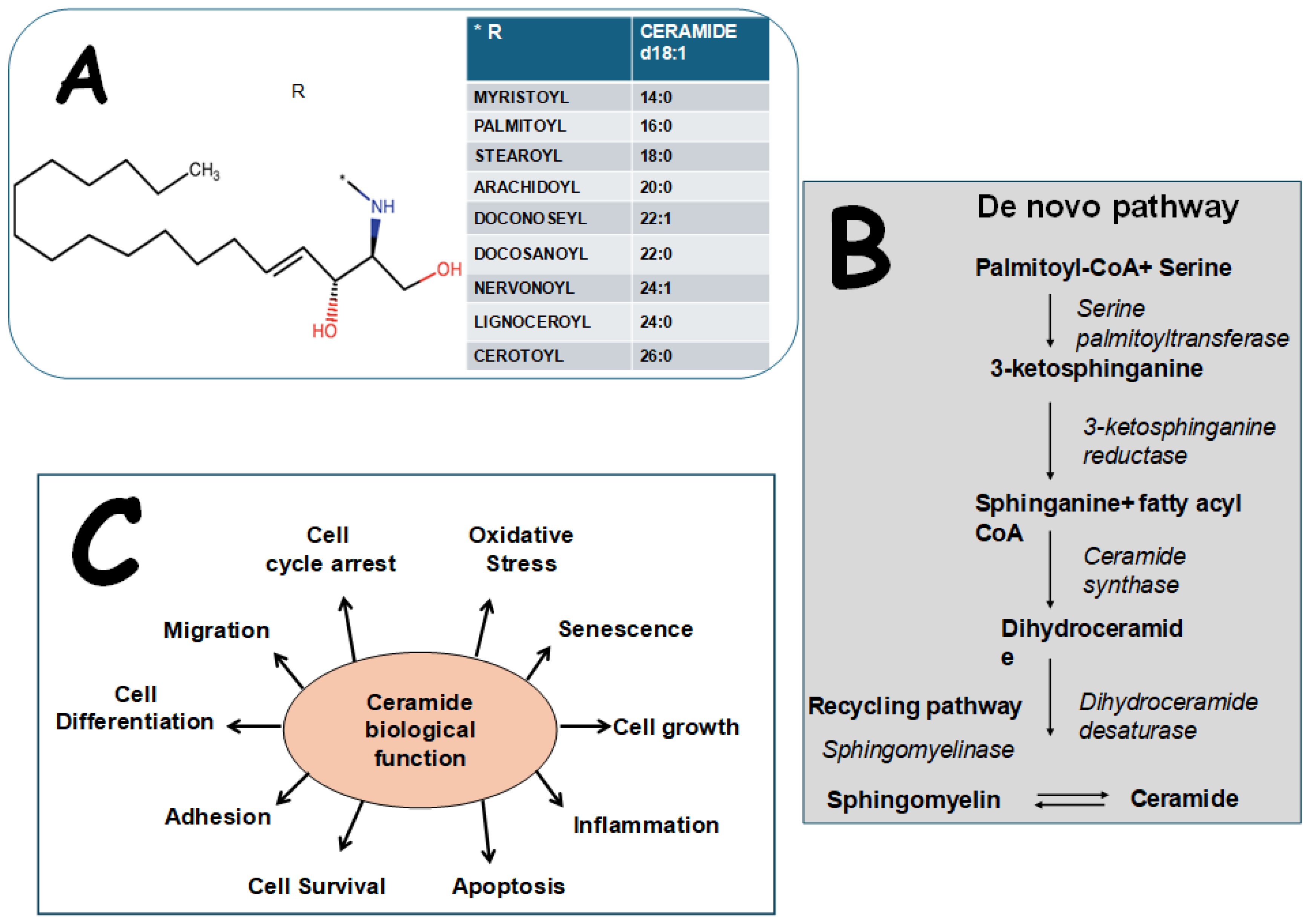
2. Biological Structure, Effects, and Measurement of Cers
3. Cersand Cardiometabolic Risk and Disease
3.1. CV Risk Factors
3.2. Atherosclerosis
3.3. CAD Severity and Plaque Characteristics
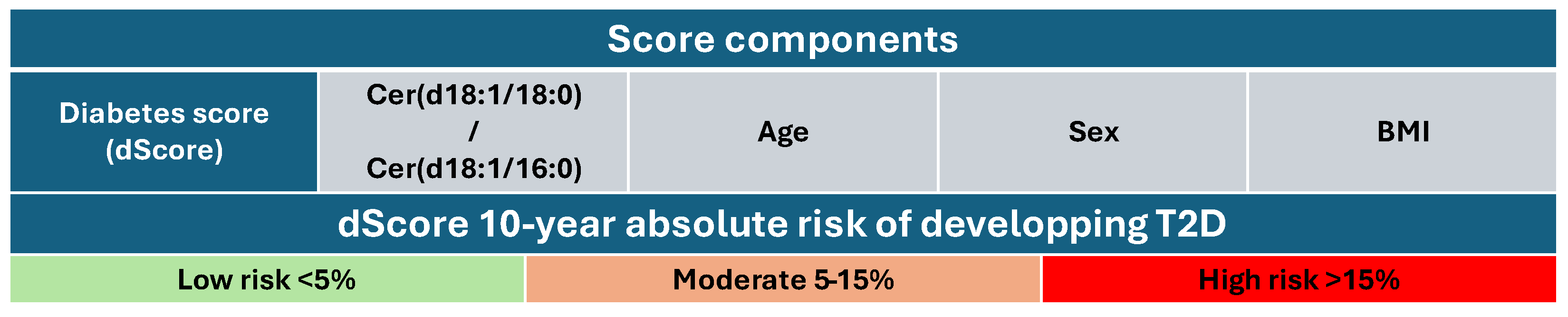
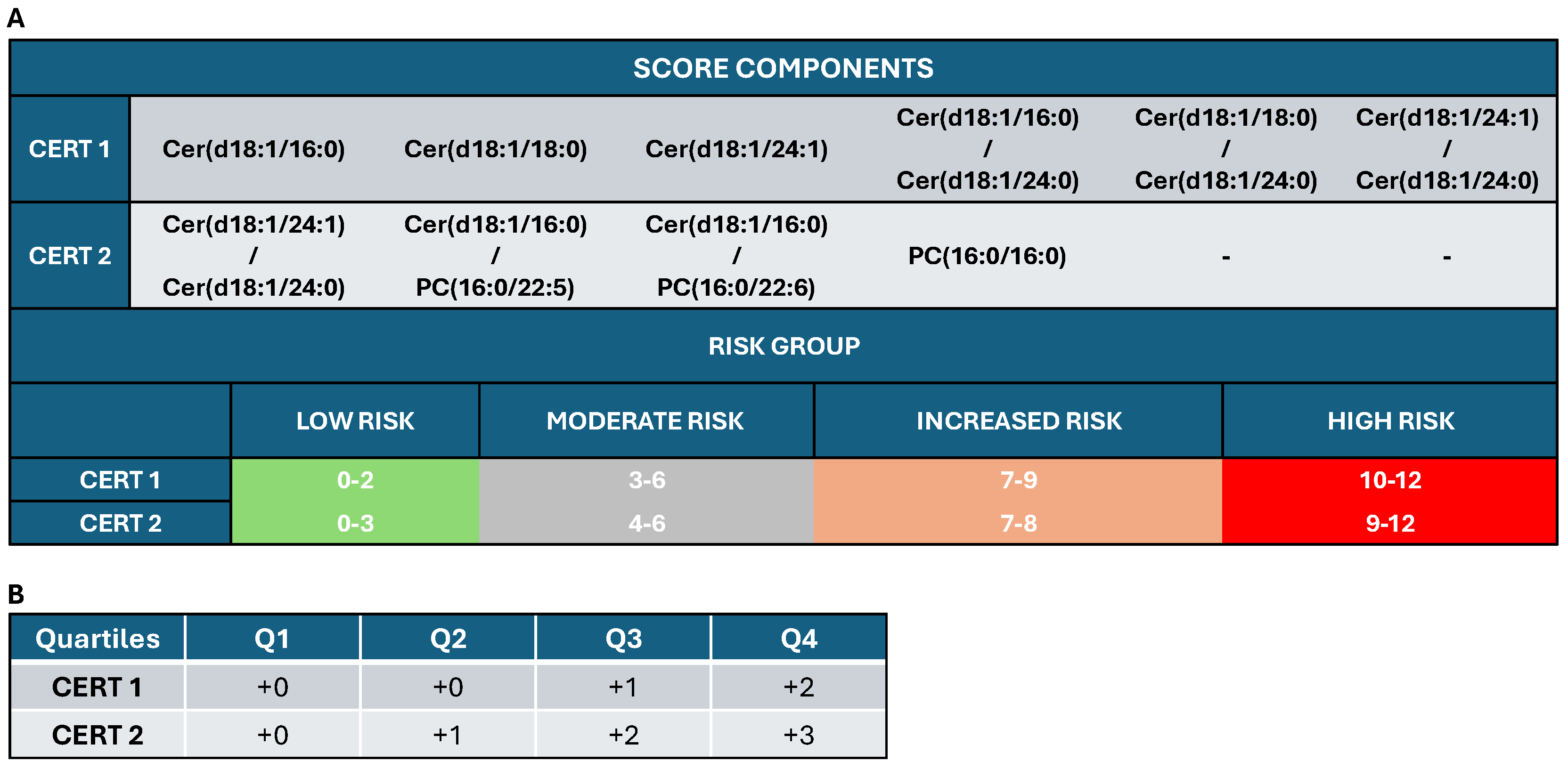
3.4. Outcome
3.5. Vitamin D
4. CerModulation
4.1. Dietary Effects
4.2. Exercise
4.3. Inactivity
4.4. Drugs
4.5. CerModulation in AMI and HF
5. Present and Future
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borén, J.; Chapman, M.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Packard, C.J.; Bentzon, J.F.; Binder, C.J.; Daemen, M.J.; Demer, L.L.; Hegele, R.A.; Nicholls, S.J.; et al. Low-Density Lipoproteins Cause Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Pathophysiological, Genetic, and Therapeutic Insights: A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2313–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggini, M.; Ndreu, R.; Michelucci, E.; Rocchiccioli, S.; Vassalle, C. Ceramides as Mediators of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Cardiometabolic Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Shirai, S.; Hiruta, N.; Shimoyama, E.; Tabata, T. Detection of Ceramide, a Risk Factor for Coronary Artery Disease, in Human Coronary Plaques by Fluorescent Angioscopy. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeusen, J.W.; Donato, L.J.; Jaffe, A.S. Lipid Biomarkers for Risk Assessment in Acute Coronary Syndromes. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2017, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelucci, E.; Rocchiccioli, S.; Gaggini, M.; Ndreu, R.; Berti, S.; Vassalle, C. Ceramides and Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Inflammatory Parameters and Left Ventricular Function in AMI Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Pingitore, A.; Vassalle, C. Plasma Ceramides Pathophysiology, Measurements, Challenges, and Opportunities. Metabolites 2021, 11, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Fenizia, S.; Vassalle, C. Sphingolipid Levels and Signaling via Resveratrol and Antioxidant Actions in Cardiometabolic Risk and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiherer, A.; Muendlein, A.; Saely, C.H.; Laaksonen, R.; Fraunberger, P.; Drexel, H. Ceramides Improve Cardiovascular Risk Prediction beyond Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. Eur. Heart J. Open 2024, 4, oeae001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Peng, Y.; Hang, W.; Li, N.; Zhou, N.; Wang, D.W. Emerging Roles of Ceramide in Cardiovascular Diseases. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skácel, J.; Slusher, B.S.; Tsukamoto, T. Small Molecule Inhibitors Targeting Biosynthesis of Ceramide, the Central Hub of the Sphingolipid Network. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Wegner, M.-S.; Wanger, R.A.; Ferreirós, N.; Schreiber, Y.; Lucks, J.; Schiffmann, S.; Geisslinger, G.; Grösch, S. The Equilibrium between Long and Very Long Chain Ceramides Is Important for the Fate of the Cell and Can Be Influenced by Co-Expression of CerS. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, B.; Talbot, C.L.; Summers, S.A. Adipocyte Ceramides—The Nexus of Inflammation and Metabolic Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 576347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-L.; Lin, C.-F.; Chang, W.-T.; Huang, W.-C.; Teng, C.-F.; Lin, Y.-S. Ceramide Induces P38 MAPK and JNK Activation through a Mechanism Involving a Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein-Mediated Pathway. Blood 2008, 111, 4365–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, S.A. Ceramides: Nutrient Signals That Drive Hepatosteatosis. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2020, 9, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadi Akbar Boojar, M.; Mashhadi Akbar Boojar, M.; Golmohammad, S. Ceramide Pathway: A Novel Approach to Cancer Chemotherapy. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Sabatino, L.; Vassalle, C. Conventional and Innovative Methods to Assess Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in the Clinical Cardiovascular Setting. BioTechniques 2020, 68, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaggiari, R.; Angelini, S.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Scaglione, G.; Morrone, S.; Finello, V.; Fagioli, S.; Castaldo, F.; Sanz, J.M.; Sergi, D.; et al. Ceramides as Emerging Players in Cardiovascular Disease: Focus on Their Pathogenetic Effects and Regulation by Diet. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Role of Ceramides in Diabetic Foot Ulcers (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 51, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilvo, M.; Salonurmi, T.; Havulinna, A.S.; Kauhanen, D.; Pedersen, E.R.; Tell, G.S.; Meyer, K.; Teeriniemi, A.-M.; Laatikainen, T.; Jousilahti, P.; et al. Ceramide Stearic to Palmitic Acid Ratio Predicts Incident Diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilvo, M.; Vasile, V.C.; Donato, L.J.; Hurme, R.; Laaksonen, R. Ceramides and Ceramide Scores: Clinical Applications for Cardiometabolic Risk Stratification. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 570628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilvo, M.; Wallentin, L.; Ghukasyan Lakic, T.; Held, C.; Kauhanen, D.; Jylhä, A.; Lindbäck, J.; Siegbahn, A.; Granger, C.B.; Koenig, W.; et al. Prediction of Residual Risk by Ceramide-Phospholipid Score in Patients With Stable Coronary Heart Disease on Optimal Medical Therapy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.P.; Marzuillo, P.; Guarino, S.; Scaglione, F.; Miraglia del Giudice, E.; Di Sessa, A. Omics Era in Type 2 Diabetes: From Childhood to Adulthood. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Michelucci, E.; Ndreu, R.; Rocchiccioli, S.; Chatzianagnostou, K.; Berti, S.; Vassalle, C. Lipidomic Analysis to Assess the Correlation between Ceramides, Stress Hyperglycemia, and HbA1c in Acute Myocardial Infarction. Molecules 2023, 28, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgil, M.D.; Sarkar, M.; Sands, C.; Lewis, M.R.; Herrington, D.M.; Kanaya, A.M. Associations of NAFLD with Circulating Ceramides and Impaired Glycemia. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 186, 109829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, R.N.; Yu, C.; Hoofnagle, A.; Hari, N.; Jensen, P.N.; Fretts, A.M.; Umans, J.G.; Howard, B.V.; Sitlani, C.M.; Siscovick, D.S.; et al. Circulating Sphingolipids, Insulin, HOMA-IR, and HOMA-B: The Strong Heart Family Study. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, N.; Grambergs, R.; Mondal, K.; Basu, S.K.; Tahia, F.; Dagogo-Jack, S. Role of Ceramides in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Salihovic, S.; Fall, T.; Hammar, U.; Ingelsson, E.; Ärnlöv, J.; Lind, L.; Sundström, J. Global Plasma Metabolomics to Identify Potential Biomarkers of Blood Pressure Progression. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, e227–e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spijkers, L.; Janssen, B.; Nelissen, J.; Meens, M.; Wijesinghe, D.; Chalfant, C.; Mey, J.D.; Alewijnse, A.; Peters, S. Antihypertensive Treatment Differentially Affects Vascular Sphingolipid Biology in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, J.K.; Beyer, A.M.; LoGiudice, J.A.; Hockenberry, J.C.; Gutterman, D.D. Ceramide Changes the Mediator of Flow-Induced Vasodilation from Nitric Oxide to Hydrogen Peroxide in the Human Microcirculation. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, L.; Junlin, Z.; Aimin, W.; Niansheng, L.; Benmei, C.; Minxiang, L. Inhibition of Ceramide Synthesis Reverses Endothelial Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, L.P.; Ruan, T.; Li, Y.; Ravindran, A.; Wan, X.; Nhan, J.K.; Walker, M.L.; Deeter, L.; Goodrich, R.; Johnson, E.; et al. Ceramide-Initiated Protein Phosphatase 2A Activation Contributes to Arterial Dysfunction In Vivo. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3914–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.P.; Mishra, B.H.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; Hilvo, M.; Juonala, M.; Kähönen, M.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Raitakari, O.T.; Laaksonen, R.; et al. Assessment of Plasma Ceramides as Predictor for Subclinical Atherosclerosis. Atheroscler. Plus 2021, 45, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; Gao, X.; Liang, H.; Tan, D.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Zeng, Y. The Relationship between Ceramide Profile and Residual Inflammatory Risk in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from an Prospective Study. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2024, 18, e1015–e1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Xie, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Ni, W.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Zeng, Y. Association between Ceramides and Coronary Artery Stenosis in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basiak, M.; Kosowski, M.; Hachula, M.; Okopien, B. Plasma Concentrations of Cytokines in Patients with Combined Hyperlipidemia and Atherosclerotic Plaque before Treatment Initiation-A Pilot Study. Med. (Kaunas) 2022, 58, 624. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.M.; Suoniemi, M.; Kardys, I.; Vihervaara, T.; de Boer, S.P.M.; Akkerhuis, K.M.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Ekroos, K.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Oemrawsingh, R.M.; et al. Plasma Concentrations of Molecular Lipid Species in Relation to Coronary Plaque Characteristics and Cardiovascular Outcome: Results of the ATHEROREMO-IVUS Study. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousoulis, D. Novel Risk Factors in Coronary Artery Disease: Are They Clinically Relevant? Hell. J. Cardiol. 2019, 60, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haus, J.M.; Kashyap, S.R.; Kasumov, T.; Zhang, R.; Kelly, K.R.; Defronzo, R.A.; Kirwan, J.P. Plasma Ceramides Are Elevated in Obese Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes and Correlate with the Severity of Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2009, 58, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, B.R.; Canty, J.M. Ceramide Signaling in the Coronary Microcirculation: A Double-Edged Sword? Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hla, T.; Dannenberg, A.J. Sphingolipid Signaling in Metabolic Disorders. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaksonen, R.; Ekroos, K.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Hilvo, M.; Vihervaara, T.; Kauhanen, D.; Suoniemi, M.; Hurme, R.; März, W.; Scharnagl, H.; et al. Plasma Ceramides Predict Cardiovascular Death in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease and Acute Coronary Syndromes beyond LDL-Cholesterol. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Guo, B. Ceramides and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines for the Prediction of Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Multi-Marker Approach. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannidis, E.; Moysidis, D.V.; Papazoglou, A.S.; Panteris, E.; Deda, O.; Stalikas, N.; Sofidis, G.; Kartas, A.; Bekiaridou, A.; Giannakoulas, G.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Metabolomic Biomarkers in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Artery Disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panteris, E.; Deda, O.; Papazoglou, A.S.; Karagiannidis, E.; Liapikos, T.; Begou, O.; Meikopoulos, T.; Mouskeftara, T.; Sofidis, G.; Sianos, G.; et al. Machine Learning Algorithm to Predict Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from the CorLipid Trial. Metabolites 2022, 12, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Sun, M.; Wu, J.; Dong, H.; Liu, J.; Gao, R.; Fang, S.; Xing, L.; Hu, S.; Yu, B. Relationship between Elevated Plasma Ceramides and Plaque Rupture in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Atherosclerosis 2020, 302, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Dong, H.; Sun, R.; Zhao, L.; Sun, M.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.; et al. Plasma Ceramides in Relation to Coronary Plaque Characterization Determined by Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021, 14, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, L.P.; Tan, S.H.; Ow, G.-S.; Tang, Z.; Ching, J.; Kovalik, J.-P.; Poh, S.C.; Chin, C.-T.; Richards, A.M.; Martinez, E.C.; et al. Plasma Ceramides as Prognostic Biomarkers and Their Arterial and Myocardial Tissue Correlates in Acute Myocardial Infarction. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2018, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, D.; Yu, J.; Jia, Y.; Wen, J.; Li, W.; Tong, Y.; Wu, J.; Wan, Z.; Cao, Y.; et al. Association Between Plasma Ceramides and One-Year Mortality in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: Insight from the PEACP Study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2023, 18, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anroedh, S.; Hilvo, M.; Akkerhuis, K.M.; Kauhanen, D.; Koistinen, K.; Oemrawsingh, R.; Serruys, P.; van Geuns, R.-J.; Boersma, E.; Laaksonen, R.; et al. Plasma Concentrations of Molecular Lipid Species Predict Long-Term Clinical Outcome in Coronary Artery Disease Patients. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozhkina, N.G.; Gushchina, O.I.; Basov, N.V.; Gaisler, E.V.; Rogachev, A.D.; Sotnikova, Y.S.; Patrushev, Y.V.; Pokrovsky, A.G. Ceramides As Potential New Predictors of the Severity of Acute Coronary Syndrome in Conjunction with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Acta Naturae 2024, 16, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnan, C.; Le Stunff, H. Role of Hypothalamic de Novo Ceramides Synthesis in Obesity and Associated Metabolic Disorders. Mol. Metab. 2021, 53, 101298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.D.; Maceyka, M.; Cowart, L.A.; Spiegel, S. Sphingolipids in Metabolic Disease: The Good, the Bad, and the Unknown. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junqueira, D.L.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; Sallum, J.M.F.; Yasaki, E.; de Andrade Jesuíno, I.; Stach, A.; Negrelli, K.; de Oliveira Silva, L.; Lopes, M.A.; Caixeta, A.; et al. Plasma Ceramides as Biomarkers for Microvascular Disease and Clinical Outcomes in Diabetes and Myocardial Infarction. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, G.; Xie, Z.; Sun, N.; Wang, C.; Xiao, B.; et al. Ceramides and Metabolic Profiles of Patients with Acute Coronary Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1177765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Nera, G.; Sabatino, L.; Gaggini, M.; Gorini, F.; Vassalle, C. Vitamin D Determinants, Status, and Antioxidant/Anti-Inflammatory-Related Effects in Cardiovascular Risk and Disease: Not the Last Word in the Controversy. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Marchi, F.; Pylypiv, N.; Parlanti, A.; Storti, S.; Paradossi, U.; Berti, S.; Vassalle, C. Vitamin D and Ceramide Metabolomic Profile in Acute Myocardial Infarction. Metabolites 2024, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, S.; Da Eira, D.; Stefanovic, M.; Ceddia, R.B. The Ketogenic Diet Prevents Steatosis and Insulin Resistance by Reducing Lipogenesis, Diacylglycerol Accumulation and Protein Kinase C Activity in Male Rat Liver. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 4137–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilvi, T.-K.; Seppanen-Laakso, T.; Simolin, H.; Finckenberg, P.; Huotari, A.; Herzig, K.-H.; Korpela, R.; Oresic, M.; Mervaala, E.-M. Metabolomic Changes in Fatty Liver Can Be Modified by Dietary Protein and Calcium during Energy Restriction. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 4462–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghatrif, M.; Watts, V.L.; Niu, X.; Halushka, M.; Miller, K.L.; Vandegaer, K.; Bedja, D.; Fox-Talbot, K.; Bielawska, A.; Gabrielson, K.L.; et al. Beneficial Cardiac Effects of Caloric Restriction Are Lost with Age in a Murine Model of Obesity. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2013, 6, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, K.; Arias, E.B.; Kanzaki, M.; Cartee, G.D. Effects of Acute Exercise Combined With Calorie Restriction Initiated Late-in-Life on Insulin Signaling, Lipids, and Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle From Old Rats. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosqvist, F.; Kullberg, J.; Ståhlman, M.; Cedernaes, J.; Heurling, K.; Johansson, H.-E.; Iggman, D.; Wilking, H.; Larsson, A.; Eriksson, O.; et al. Overeating Saturated Fat Promotes Fatty Liver and Ceramides Compared With Polyunsaturated Fat: A Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 6207–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prisco, S.Z.; Eklund, M.; Moutsoglou, D.M.; Prisco, A.R.; Khoruts, A.; Weir, E.K.; Thenappan, T.; Prins, K.W. Intermittent Fasting Enhances Right Ventricular Function in Preclinical Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e022722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkour, M.I.; Islam, M.T.; Tippetts, T.S.; Chowdhury, K.H.; Lesniewski, L.A.; Summers, S.A.; Zeb, F.; Abdelrahim, D.N.; AlKurd, R.; Khraiwesh, H.M.; et al. Ramadan Intermittent Fasting Is Associated with Ameliorated Inflammatory Markers and Improved Plasma Sphingolipids/Ceramides in Subjects with Obesity: Lipidomics Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.C.; Lai, K.; Muirhead, R.P.; Chung, L.H.; Huang, Y.; James, E.; Liu, X.T.; Wu, J.; Atkinson, F.S.; Yan, S.; et al. Deep Serum Lipidomics Identifies Evaluative and Predictive Biomarkers for Individualized Glycemic Responses Following Low-Energy Diet-Induced Weight Loss: A PREVention of Diabetes through Lifestyle Intervention and Population Studies in Europe and around the World (PREVIEW) Substudy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 120, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankinen, M.; Schwab, U.; Kolehmainen, M.; Paananen, J.; Nygren, H.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Poutanen, K.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Risérus, U.; Savolainen, M.J.; et al. A Healthy Nordic Diet Alters the Plasma Lipidomic Profile in Adults with Features of Metabolic Syndrome in a Multicenter Randomized Dietary Intervention123. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.A.; Summers, S.A. Characterizing the Effects of Saturated Fatty Acids on Insulin Signaling and Ceramide and Diacylglycerol Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and C2C12 Myotubes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 419, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.-H.; Mu, Y.-M.; Wang, B.-A.; Li, X.-L.; Lu, J.-M.; Li, J.-Y.; Pan, C.-Y.; Yanase, T.; Nawata, H. Saturated Free Fatty Acids, Palmitic Acid and Stearic Acid, Induce Apoptosis by Stimulation of Ceramide Generation in Rat Testicular Leydig Cell. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 303, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Sädevirta, S.; Zhou, Y.; Kayser, B.; Ali, A.; Ahonen, L.; Lallukka, S.; Pelloux, V.; Gaggini, M.; Jian, C.; et al. Saturated Fat Is More Metabolically Harmful for the Human Liver Than Unsaturated Fat or Simple Sugars. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, B.N.; Van Guilder, G.P.; Aly, M.; Spence, L.A.; Diaz-Rubio, M.E.; Le, H.H.; Johnson, E.L.; McFadden, J.W.; Perry, C.A. Changes in Choline Metabolites and Ceramides in Response to a DASH-Style Diet in Older Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Simonetta, I.; Daidone, M.; Mogavero, A.; Ortello, A.; Pinto, A. Metabolic and Vascular Effect of the Mediterranean Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzianagnostou, K.; Del Turco, S.; Pingitore, A.; Sabatino, L.; Vassalle, C. The Mediterranean Lifestyle as a Non-Pharmacological and Natural Antioxidant for Healthy Aging. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 719–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Toledo, E.; Hruby, A.; Rosner, B.A.; Willett, W.C.; Sun, Q.; Razquin, C.; Zheng, Y.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; et al. Plasma Ceramides, Mediterranean Diet, and Incident Cardiovascular Disease in the PREDIMED Trial (Prevención Con Dieta Mediterránea). Circulation 2017, 135, 2028–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccinardi, D.; Di Mauro, A.; Lattanzi, G.; Rossini, G.; Monte, L.; Beato, I.; Spiezia, C.; Bravo, M.; Watanabe, M.; Soare, A.; et al. An Extra Virgin Olive Oil-Enriched Chocolate Spread Positively Modulates Insulin-Resistance Markers Compared with a Palm Oil-Enriched One in Healthy Young Adults: A Double-Blind, Cross-over, Randomised Controlled Trial. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2022, 38, e3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Taeb, S.; Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Afrashi, S.; Moloudi, K.; Musa, A.E.; Najafi, M.; Farhood, B. Resveratrol as an Enhancer of Apoptosis in Cancer: A Mechanistic Review. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charytoniuk, T.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Polak, A.; Drygalski, K.; Berk, K.; Chabowski, A.; Konstantynowicz-Nowicka, K. Influence of Resveratrol on Sphingolipid Metabolism in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells in Lipid Overload State. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersöz, N.Ş.; Adan, A. Resveratrol Triggers Anti-Proliferative and Apoptotic Effects in FLT3-ITD-Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via Inhibiting Ceramide Catabolism Enzymes. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, M.F.; Rutters, F.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Davids, M.; van Valkengoed, I.; Galenkamp, H.; van den Born, B.-J.; Beulens, J.W.J.; Muilwijk, M. Plasma Sphingolipids Mediate the Association between Gut Microbiome Composition and Type 2 Diabetes Risk in the HELIUS Cohort: A Case-Cohort Study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2024, 12, e004180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Astbury, S.; Panayiotis, L.; Marques, F.Z.; Spector, T.D.; Menni, C.; Valdes, A.M. Dietary Interventions Reduce Traditional and Novel Cardiovascular Risk Markers by Altering the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 691564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenizia, S.; Gaggini, M.; Vassalle, C. Interplay between Vitamin D and Sphingolipids in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gil, M.; Pierucci, F.; Vestri, A.; Meacci, E. Crosstalk between Sphingolipids and Vitamin D3: Potential Role in the Nervous System. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrard, J.; Guerini, C.; Appenzeller-Herzog, C.; Infanger, D.; Königstein, K.; Streese, L.; Hinrichs, T.; Hanssen, H.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Ivanisevic, J.; et al. The Metabolic Signature of Cardiorespiratory Fitness: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, M.Y.; Gajjar, P.; Walker, M.E.; Miller, P.; Xanthakis, V.; Murthy, V.L.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Shah, R.V.; Lewis, G.D.; et al. Association of Healthy Dietary Patterns and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in the Community. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatloukal, J.; Zylla, S.; Markus, M.R.P.; Ewert, R.; Gläser, S.; Völzke, H.; Albrecht, D.; Friedrich, N.; Nauck, M.; Peterson, L.R.; et al. The Association Between C24:0/C16:0 Ceramide Ratio and Cardiorespiratory Fitness Is Robust to Effect Modifications by Age and Sex. Adv. Biosyst. 2024, 8, 2300633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipryan, L.; Kosek, V.; García, C.J.; Dostal, T.; Bechynska, K.; Hajslova, J.; Hofmann, P. A Lipidomic and Metabolomic Signature of a Very Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet and High-Intensity Interval Training: An Additional Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Metabolomics 2023, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Herrmann, N.; Dinoff, A.; Marzolini, S.; Mielke, M.M.; Andreazza, A.; Oh, P.I.; Vattem Venkata, S.L.; Haughey, N.J.; Lanctôt, K.L. Association Between Sphingolipids and Cardiopulmonary Fitness in Coronary Artery Disease Patients Undertaking Cardiac Rehabilitation. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Vassalle, C.; Carli, F.; Maltinti, M.; Sabatino, L.; Buzzigoli, E.; Mastorci, F.; Sbrana, F.; Gastaldelli, A.; Pingitore, A. Changes in Plasma Bioactive Lipids and Inflammatory Markers during a Half-Marathon in Trained Athletes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, B.C.; Brozinick, J.T.; Strauss, A.; Bacon, S.; Kerege, A.; Bui, H.H.; Sanders, P.; Siddall, P.; Kuo, M.S.; Perreault, L. Serum Sphingolipids: Relationships to Insulin Sensitivity and Changes with Exercise in Humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E398–E408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Tanner, R.E.; Barrows, K.M.; Runtsch, M.; Symons, J.D.; Jalili, T.; Bikman, B.T.; McClain, D.A.; O’Connell, R.M.; Drummond, M.J. MyD88 Regulates Physical Inactivity-Induced Skeletal Muscle Inflammation, Ceramide Biosynthesis Signaling, and Glucose Intolerance. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E11–E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrocelli, J.J.; McKenzie, A.I.; Mahmassani, Z.S.; Reidy, P.T.; Stoddard, G.J.; Poss, A.M.; Holland, W.L.; Summers, S.A.; Drummond, M.J. Ceramide Biomarkers Predictive of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Increase in Healthy Older Adults After Bed Rest. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, K.; Ekroos, K.; Suoniemi, M.; Kauhanen, D.; Sylvänne, T.; Hurme, R.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Berthold, H.K.; Kleber, M.E.; Laaksonen, R.; et al. Molecular Lipids Identify Cardiovascular Risk and Are Efficiently Lowered by Simvastatin and PCSK9 Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E45–E52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.W.K.; Ooi, E.M.M.; Watts, G.F.; Chan, D.C.; Weir, J.M.; Meikle, P.J.; Barrett, P.H.R. Dose-Dependent Effects of Rosuvastatin on the Plasma Sphingolipidome and Phospholipidome in the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2335–E2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilvo, M.; Simolin, H.; Metso, J.; Ruuth, M.; Öörni, K.; Jauhiainen, M.; Laaksonen, R.; Baruch, A. PCSK9 Inhibition Alters the Lipidome of Plasma and Lipoprotein Fractions. Atherosclerosis 2018, 269, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zobel, E.H.; Wretlind, A.; Ripa, R.S.; Rotbain Curovic, V.; von Scholten, B.J.; Suvitaival, T.; Hansen, T.W.; Kjær, A.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Rossing, P. Ceramides and Phospholipids Are Downregulated with Liraglutide Treatment: Results from the LiraFlame Randomized Controlled Trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, M.; Lisowska, A.; Knapp, P.; Baranowski, M. Dose-Dependent Effect of Aspirin on the Level of Sphingolipids in Human Blood. Adv. Med. Sci. 2013, 58, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Peng, Q.; Huang, Y. Potential Therapeutic Targets for Atherosclerosis in Sphingolipid Metabolism. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2019, 133, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekry, B.; Esmaeilniakooshkghazi, A.; Krupenko, S.A.; Krupenko, N.I. Ceramide Synthase 6 Is a Novel Target of Methotrexate Mediating Its Antiproliferative Effect in a P53-Dependent Manner. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-D.; Wang, J.-W. Ceramide de Novo Synthesis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 202, 115157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.-S.; Hu, Y.; Noh, H.-L.; Drosatos, K.; Okajima, K.; Buchanan, J.; Tuinei, J.; Homma, S.; Jiang, X.-C.; Abel, E.D.; et al. Ceramide Is a Cardiotoxin in Lipotoxic Cardiomyopathy. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 2101–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Akashi, H.; Drosatos, K.; Liao, X.; Jiang, H.; Kennel, P.J.; Brunjes, D.L.; Castillero, E.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L.Y.; et al. Increased de Novo Ceramide Synthesis and Accumulation in Failing Myocardium. JCI Insight 2017, 2, 96203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reforgiato, M.R.; Milano, G.; Fabriàs, G.; Casas, J.; Gasco, P.; Paroni, R.; Samaja, M.; Ghidoni, R.; Caretti, A.; Signorelli, P. Inhibition of Ceramide de Novo Synthesis as a Postischemic Strategy to Reduce Myocardial Reperfusion Injury. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2016, 111, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.; Palioura, D.; Kyriazis, I.D.; Cimini, M.; Badolia, R.; Rajan, S.; Gao, E.; Nikolaidis, N.; Schulze, P.C.; Goldberg, I.J.; et al. Cardiomyocyte Krüppel-Like Factor 5 Promotes De Novo Ceramide Biosynthesis and Contributes to Eccentric Remodeling in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2021, 143, 1139–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadas, Y.; Vincek, A.S.; Youssef, E.; Żak, M.M.; Chepurko, E.; Sultana, N.; Sharkar, M.T.K.; Guo, N.; Komargodski, R.; Kurian, A.A.; et al. Altering Sphingolipid Metabolism Attenuates Cell Death and Inflammatory Response After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2020, 141, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandhuvula, P.; Honbo, N.; Wang, G.-Y.; Jin, Z.-Q.; Fyrst, H.; Zhang, M.; Borowsky, A.D.; Dillard, L.; Karliner, J.S.; Saba, J.D. S1P Lyase: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of the Heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H1753–H1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyachkin, Y.M.; Nagareddy, P.R.; Ye, S.; Wysoczynski, M.; Asfour, A.; Gao, E.; Sunkara, M.; Brandon, J.A.; Annabathula, R.; Ponnapureddy, R.; et al. Pharmacological Elevation of Circulating Bioactive Phosphosphingolipids Enhances Myocardial Recovery After Acute Infarction. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klevstig, M.; Ståhlman, M.; Lundqvist, A.; Scharin Täng, M.; Fogelstrand, P.; Adiels, M.; Andersson, L.; Kolesnick, R.; Jeppsson, A.; Borén, J.; et al. Targeting Acid Sphingomyelinase Reduces Cardiac Ceramide Accumulation in the Post-Ischemic Heart. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2016, 93, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, M.R.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Langsted, A.; Chapman, M.J.; Aakre, K.M.; Baum, H.; Borén, J.; Bruckert, E.; Catapano, A.; Cobbaert, C.; et al. Quantifying Atherogenic Lipoproteins for Lipid-Lowering Strategies: Consensus-Based Recommendations from EAS and EFLM. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 496–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, J.W.; Donato, L.J.; Kopecky, S.L.; Vasile, V.C.; Jaffe, A.S.; Laaksonen, R. Ceramides Improve Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment beyond Standard Risk Factors. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 511, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilvo, M.; Meikle, P.J.; Pedersen, E.R.; Tell, G.S.; Dhar, I.; Brenner, H.; Schöttker, B.; Lääperi, M.; Kauhanen, D.; Koistinen, K.M.; et al. Development and Validation of a Ceramide- and Phospholipid-Based Cardiovascular Risk Estimation Score for Coronary Artery Disease Patients. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, V.C.; Meeusen, J.W.; Medina Inojosa, J.R.; Donato, L.J.; Scott, C.G.; Hyun, M.S.; Vinciguerra, M.; Rodeheffer, R.R.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Jaffe, A.S. Ceramide Scores Predict Cardiovascular Risk in the Community. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Zusi, C.; Lunardi, G.; Bonapace, S.; Lippi, G.; Maffeis, C.; Targher, G. Association between KLF6 Rs3750861 Polymorphism and Plasma Ceramide Concentrations in Post-Menopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, J.-P.; Mononen, N.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Lehtimäki, M.; Hilvo, M.; Kauhanen, D.; Juonala, M.; Viikari, J.; Kähönen, M.; Raitakari, O.; et al. New Evidence from Plasma Ceramides Links apoE Polymorphism to Greater Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Finnish Adults. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaggini, M.; Suman, A.F.; Vassalle, C. Ceramide in Coronary Artery Disease: Troublesome or Helpful Future Tools in the Assessment of Risk Prediction and Therapy Effectiveness? Metabolites 2025, 15, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030168
Gaggini M, Suman AF, Vassalle C. Ceramide in Coronary Artery Disease: Troublesome or Helpful Future Tools in the Assessment of Risk Prediction and Therapy Effectiveness? Metabolites. 2025; 15(3):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030168
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaggini, Melania, Adrian Florentin Suman, and Cristina Vassalle. 2025. "Ceramide in Coronary Artery Disease: Troublesome or Helpful Future Tools in the Assessment of Risk Prediction and Therapy Effectiveness?" Metabolites 15, no. 3: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030168
APA StyleGaggini, M., Suman, A. F., & Vassalle, C. (2025). Ceramide in Coronary Artery Disease: Troublesome or Helpful Future Tools in the Assessment of Risk Prediction and Therapy Effectiveness? Metabolites, 15(3), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030168






