Integrating Advanced Metabolomics and Machine Learning for Anti-Doping in Human Athletes
Abstract
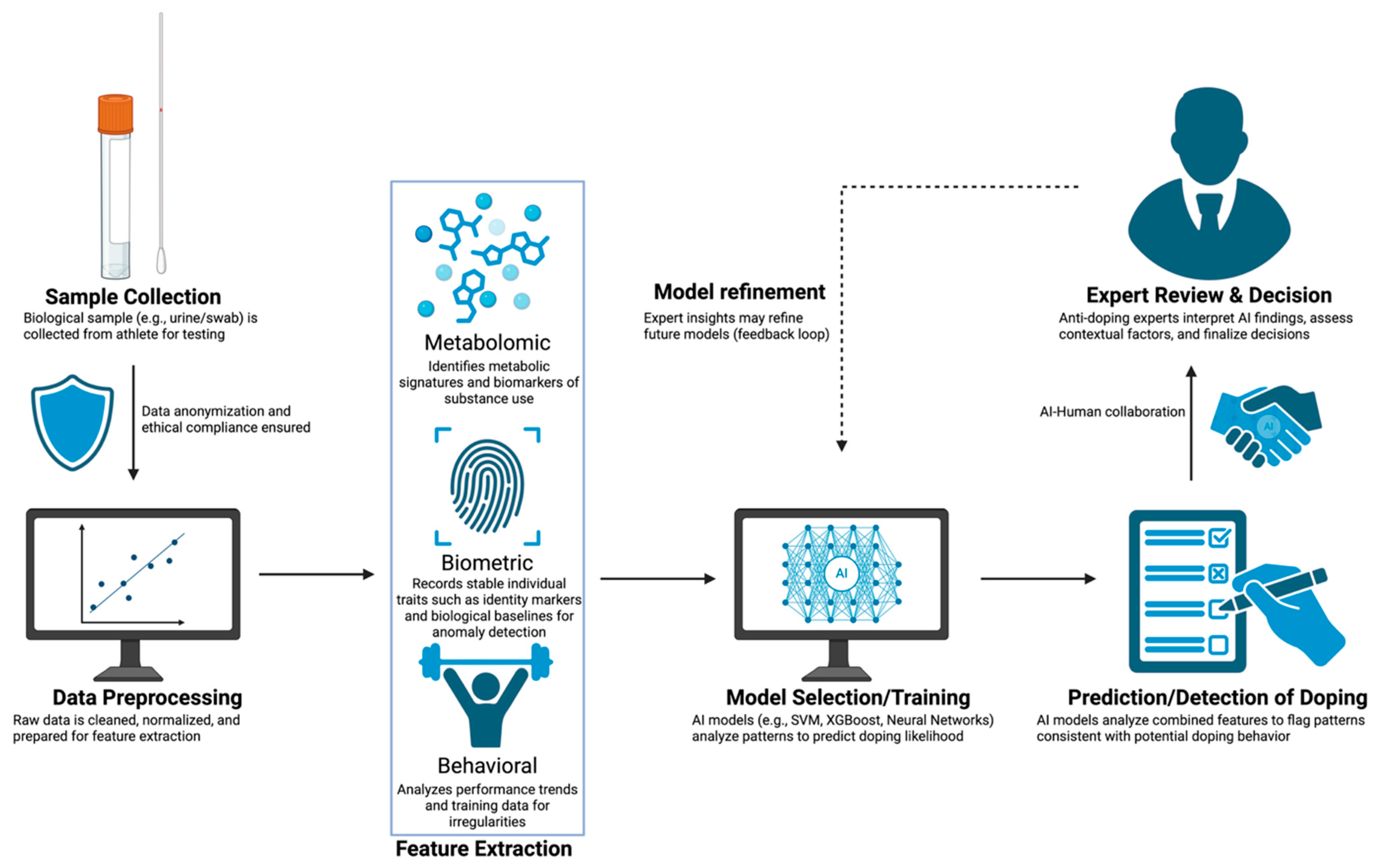
1. Introduction
2. Metabolomics in Anti-Doping
2.1. Workflow and Analytical Platforms
2.1.1. Workflow and Selection of Metabolites
2.1.2. Analytical Platforms and Statistical Analyses Used in Metabolomics
2.2. Case Studies
2.2.1. Salbutamol/Budesonide Abuse Detection
2.2.2. Detection of Testosterone-Induced Metabolome Alterations
3. AI/ML in Anti-Doping
3.1. Predictive Models
3.1.1. Supervised Learning
3.1.2. Unsupervised Learning
3.2. Multi-Omics Integration
3.3. Case Studies
4. WADA Technical Framework and Its Impact on Metabolomics and Machine Learning Approaches
5. Challenges and Future Directions
5.1. Metabolomics Limitations
5.2. AI/ML Barriers
5.3. Emerging Opportunities
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Q.; Xu, W.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q.; Niu, B. The Application of Machine Learning in Doping Detection. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2024, 64, 8673–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanovic, S.; Carlo, R.; Nikola, M.; Tamara, M.; Dajana, K.; Admir, K.; Vanja, M.; Mia, S.; Valerio, G.; Roberto, R.; et al. Doping in combat sports: A systematic review. Physician Sportsmed. 2025, 53, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, D.; Skinner, J.; Smith, A.C.; Lock, D.; Stanic, M. The challenges of harmonising anti-doping policy implementation. Sport Manag. Rev. 2024, 27, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoren, A.K.; Rulison, K.; Milroy, J.; Grist, P.; Fedoruk, M.; Lewis, L.; Wyrick, D. Doping Prevalence among U.S. Elite Athletes Subject to Drug Testing under the World Anti-Doping Code. Sports Med.-Open 2024, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.H.; Gerona, R.; Armenian, P.; French, D.; Petrie, M.; Lynch, K.L. Role of liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HR/MS) in clinical toxicology. Clin. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, B.; Cawley, A.; Reedy, B.; Fu, S. Metabolomics in clinical and forensic toxicology, sports anti-doping and veterinary residues. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botrè, F.; Georgakopoulos, C.; Elrayess, M.A. Metabolomics and doping analysis: Promises and pitfalls. Bioanalysis 2020, 12, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clish, C.B. Metabolomics: An emerging but powerful tool for precision medicine. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2015, 1, a000588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez de Souza, L.; Alseekh, S.; Scossa, F.; Fernie, A.R. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry variants for metabolomics research. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, H.; Cho, S.; Oh, T.; Kim, Y.; Suh, S.H. Identification of doping suspicions through artificial intelligence-powered analysis on athlete’s performance passport in female weightlifting. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1344340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottas, P.-E.; Saugy, M.; Saudan, C. Endogenous Steroid Profiling in the Athlete Biological Passport. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. 2010, 39, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, A.; Talal, M.; Moustafa, A. Applications of machine learning in metabolomics: Disease modeling and classification. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1017340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Liu, R.; Maass, W. Incorporating Metabolic Information into LLMs for Anomaly Detection in Clinical Time-Series. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.12830. [Google Scholar]
- Hullstein, I.R. Athlete Biological Passport and Longitudinal Steroid Profiles: New Metabolites, Confounding Factors and Sports Specific Variations; Norwegian Doping Control Laboratory: Oslo, Norway, 2019; Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/scientific-research/athlete-biological-passport-and-longitudinal-steroid-profiles-new?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Wasilewski, T.; Kamysz, W.; Gębicki, J. AI-Assisted Detection of Biomarkers by Sensors and Biosensors for Early Diagnosis and Monitoring. Biosensors 2024, 14, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, M.; S, D. Advantages of AI and ML over Other Doping Test Techniques. IJIRT 2025, 11, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar]
- WADA. Athlete Biological Passport (ABP) Operating Guidelines. July 2023; Version 9.0. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/2023-07/guidelines_abp_v9_2023_final_eng_1.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Piper, T.; Geyer, H.; Haenelt, N.; Huelsemann, F.; Schaenzer, W.; Thevis, M. Current Insights into the Steroidal Module of the Athlete Biological Passport. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragčević, D.; Pandžić Jakšić, V.; Jakšić, O. Athlete biological passport: Longitudinal biomarkers and statistics in the fight against doping. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2024, 75, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WADA. Measurement and Reporting of Endogenous Anabolic Androgenic Steroid (EAAS) Markers of the Urinary Steroid Profile. May 2021; Version 2.0. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/td2021eaas_final_eng_v_2.0.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- WADA. Laboratory Guidelines: Human Growth Hormone (hGH) Biomarkers Test. January 2021; Version 3.0. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/wada_guidelines_hgh_biomarkers_test_v3_jan_2021_eng.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- de Figueiredo, M.; Marchand, A.; Rhumorbarbe, D.; Mann, R.; Saugy, J.; Robinson, N.; Lobigs, L.M.; Ericsson, M. Evaluating the Early Operational Performance of the Endocrine Module in the Athlete Biological Passport. Drug Test. Anal. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajnajafi, K.; Iqbal, M.A. Mass-spectrometry based metabolomics: An overview of workflows, strategies, data analysis and applications. Proteome Sci. 2025, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, F.; Zhu, J. Bridging Targeted and Untargeted Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics via Hybrid Approaches. Metabolites 2020, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.D.; Souza, A.L.; Gerszten, R.E.; Clish, C.B. Targeted metabolomics. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2012, 98, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevis, M.; Walpurgis, K.; Thomas, A. Analytical Approaches in Human Sports Drug Testing: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Solutions. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narduzzi, L.; Dervilly, G.; Audran, M.; Le Bizec, B.; Buisson, C. A role for metabolomics in the antidoping toolbox? Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, B.; Cawley, A.; Fouracre, C.; Pyke, J.; Fu, S. Towards an untargeted mass spectrometric approach for improved screening in equine antidoping. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.-Q.; Tang, H.-M.; Yu, Y.-D.; Fu, L.-Z.; Li, S.-J.; Zhu, M.-X. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomic as a powerful tool to unravel the component and mechanism in TCM. Chin. Med. 2025, 20, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoud, F.; Boccard, J.; Schweizer, C.; Pralong, F.; Saugy, M.; Baume, N. Profiling of steroid metabolites after transdermal and oral administration of testosterone by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 138, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raro, M.; Ibáñez, M.; Gil, R.; Fabregat, A.; Tudela, E.; Deventer, K.; Ventura, R.; Segura, J.; Marcos, J.; Kotronoulas, A.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomics in Doping Control: Detection of New Markers of Testosterone Misuse by Ultrahigh Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8373–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, B.; Deshpande, R.R.; Bird, S.S. Simultaneous Quantitation and Discovery (SQUAD) Analysis: Combining the Best of Targeted and Untargeted Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites 2023, 13, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timperio, A.M.; Lelli, V.; Belardo, A. From Targeted Quantification to Untargeted Metabolomics. In Metabolomics—Methodology and Applications in Medical Sciences and Life Sciences; Zhan, X., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, Á.; Ángeles, L.-G.; Clive, B.-T.T.; Barbas, C. A review of validated biomarkers obtained through metabolomics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 18, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.; Gu, H.; Baniasadi, H.; Raftery, D. Statistical Analysis and Modeling of Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Data. In Mass Spectrometry in Metabolomics: Methods and Protocols; Raftery, D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 333–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwardeen, N.R.; Diboun, I.; Mokrab, Y.; Althani, A.A.; Elrayess, M.A. Statistical methods and resources for biomarker discovery using metabolomics. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Padilla, M.; Marco, S. The Need of External Validation for Metabolomics Predictive Models. In Volatile Organic Compound Analysis in Biomedical Diagnosis Applications; Apple Academic Press: Waretown, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikin, R.; Norbert, B.; Tristan, E.; Rabin, O. Biomarkers of Doping: Uses, Discovery and Validation. Bioanalysis 2020, 12, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhieu, S.Y.; Urbas, A.A.; Lippa, K.A.; Reipa, V. Quantitative measurements of glutathione in yeast cell lysate using 1H NMR. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4963–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.L.; Kleinsorge, N.G.; Zhang, L.; Kleintop, B. Advancing stereoisomeric separation of an atropisomeric Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor by using sub-2 µm immobilized polysaccharide-based chiral columns in supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1626, 461320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.L.; Engeser, M. Gas-phase fragmentations of N-methylimidazolidin-4-one organocatalysts. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 52, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, J.E.; Thörngren, J.-O.; Schulze, J.J.; Ericsson, M.; Gårevik, N.; Lehtihet, M.; Ekström, L. Urinary steroid profile in females—the impact of menstrual cycle and emergency contraceptives. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Byun, J.; Pennathur, S. Analytical approaches to metabolomics and applications to systems biology. Semin. Nephrol. 2010, 30, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, B.D.; Starcevic, B.; Butch, A.W. Detection of Prohibited Substances by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Sports Doping Control. In LC-MS in Drug Analysis: Methods and Protocols; Langman, L.J., Snozek, C.L.H., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevis, M.; Kuuranne, T.; Geyer, H. Annual banned-substance review—Analytical approaches in human sports drug testing 2021/2022–. Drug Test. Anal. 2023, 15, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Anti-Doping Agency. Detection of Synthetic Forms of Prohibited Substances by GC/C/IRMS (TD2022IRMS); World Anti-Doping Agency: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2022; Volume 2022. [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre, X.; Jardines, D.; Curcio, D.; Colamonici, C.; Botrè, F. Isotope ratio mass spectrometry in antidoping analysis: The use of endogenous reference compounds. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 33, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Anti-Doping Agency. Minimum Required Performance Levels and Applicable Minimum Reporting Levels for Non-Threshold Substances Analyzed by Chromatographic–Mass Spectrometric Analytical Methods (TD2022MRPL); World Anti-Doping Agency: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2022; Volume 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Combined Targeted and Untargeted Profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30.34.31–30.34.32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stettin, D.; Poulin, R.X.; Pohnert, G. Metabolomics Benefits from Orbitrap GC-MS-Comparison of Low- and High-Resolution GC-MS. Metabolites 2020, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakalof, A.; Sysoev, A.A.; Vyatkina, K.V.; Eganov, A.A.; Eroshchenko, N.N.; Kiryushin, A.N.; Adamov, A.Y.; Danilova, E.Y.; Nosyrev, A.E. Current Role and Potential of Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry in Biomedical Research and Clinical Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espina, R.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Tong, Z.; Vashishtha, S.; Talaat, R.; Scatina, J.; Mutlib, A. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy as a Quantitative Tool To Determine the Concentrations of Biologically Produced Metabolites: Implications in Metabolites in Safety Testing. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letertre, M.P.M.; Dervilly, G.; Giraudeau, P. Combined Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Approaches for Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 500–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardela, V.F.; Martucci, M.E.P.; de Araújo, A.L.D.; Leal, E.C.; Oliveira, D.S.; Carneiro, G.R.A.; Deventer, K.; Van Eenoo, P.; Pereira, H.M.G.; Aquino Neto, F.R. Comprehensive analysis by liquid chromatography Q-Orbitrap mass spectrometry: Fast screening of peptides and organic molecules. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 53, 476–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abushareeda, W.; Tienstra, M.; Lommen, A.; Blokland, M.; Sterk, S.; Kraiem, S.; Horvatovich, P.; Nielen, M.; Al-Maadheed, M.; Georgakopoulos, C. Comparison of gas chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight and quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometry in anti-doping analysis: I. Detection of anabolic-androgenic steroids. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevis, M.; Volmer, D.A. Recent instrumental progress in mass spectrometry: Advancing resolution, accuracy, and speed of drug detection. Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojanperä, I.; Kolmonen, M.; Pelander, A. Current use of high-resolution mass spectrometry in drug screening relevant to clinical and forensic toxicology and doping control. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1203–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, D.; Mortimer, K.; Harrison, T. Budesonide/formoterol in the treatment of asthma. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2010, 4, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, Q. Effects of budesonide combined with salbutamol on pulmonary function and peripheral blood eosinophiles and IgE in patients with acute attack of bronchial asthma. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, S.; Monfort, N.; Matabosch, X.; Papakonstantinou, K.; Pérez-Mañá, C.; Mateus, J.A.; Ventura, R. Budesonide use and misuse in sports: Elimination profiles of budesonide and metabolites after intranasal, high-dose inhaled and oral administrations. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helge, T.; Godhe, M.; Berglund, B.; Ekblom, B. Inhaling salbutamol may decrease time to exhaustion in some contexts of heavy endurance performances. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2023, 23, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalska, M.; Witkowska-Piłaszewicz, O. Gene doping in horse racing and equine sports: Current landscape and future perspectives. Equine Vet. J. 2025, 57, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deventer, K.; Mikulcíková, P.; Van Hoecke, H.; Van Eenoo, P.; Delbeke, F.T. Detection of budesonide in human urine after inhalation by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 42, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harps, L.C.; Bizjak, D.A.; Girreser, U.; Zügel, M.; Steinacker, J.M.; Diel, P.; Parr, M.K. Quantitation of Formoterol, Salbutamol, and Salbutamol-4′-O-Sulfate in Human Urine and Serum via UHPLC-MS/MS. Separations 2023, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, A.; Lucio, M.; Fildier, A.; Buisson, C.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Cren-Olivé, C. Doping control using high and ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry based non-targeted metabolomics-a case study of salbutamol and budesonide abuse. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamy, E.; Mahjoubi, A.; Salvator, H.; Lambinet, F.; Devillier, P.; Grassin-Delyle, S. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the quantification of corticosteroids, β(2)-adrenoreceptor agonists and anticholinergics in human hair. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 190, 113530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, J.; Moir, H.J.; Petróczi, A. Chapter 48—The Use and Misuse of Testosterone in Sport: The Challenges and Opportunities in Doping Control. In Nutrition and Enhanced Sports Performance, 2nd ed.; Bagchi, D., Nair, S., Sen, C.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, F.; Ascione, A. Anabolic androgenic steroids and doping in sport. Med. Sport. J. Rom. Sports Med. Soc. 2013, 9, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, M.K.; Flenker, U.; Schänzer, W. Sports-Related Issues and Biochemistry of Natural and Synthetic Anabolic Substances. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manocha, A.; Kankra, M.; Singla, P.; Sharma, A.; Ahirwar, A.K.; Bhargava, S. Clinical significance of reproductive hormones. Curr. Med. Res. Pract. 2018, 8, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Basit, A.; Gupta, A.; Gáborik, Z.; Kis, E.; Prasad, B. Major glucuronide metabolites of testosterone are primarily transported by MRP2 and MRP3 in human liver, intestine and kidney. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 191, 105350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítků, J.; Hampl, R. Steroid Conjugates and Their Physiological Role. Physiol. Res. 2023, 72, S317–S322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.L.; Meredith, W.; Snape, C.E.; Sephton, M.A. Analysis of conjugated steroid androgens: Deconjugation, derivatisation and associated issues. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hartmann, M.F.; Wudy, S.A. Targeted LC-MS/MS analysis of steroid glucuronides in human urine. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 205, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudan, C.; Baume, N.; Robinson, N.; Avois, L.; Mangin, P.; Saugy, M. Testosterone and doping control. Br. J. Sports Med. 2006, 40, i21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, A.; Botrè, F.; de la Torre, X.; Zamboni, N. Non-targeted LC-MS based metabolomics analysis of the urinary steroidal profile. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 964, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Girolamo, F.G.; Biasinutto, C.; Mangogna, A.; Fiotti, N.; Vinci, P.; Pisot, R.; Mearelli, F.; Simunic, B.; Roni, C.; Biolo, G. Metabolic Consequences of Anabolic Steroids, Insulin, and Growth Hormone Abuse in Recreational Bodybuilders: Implications for the World Anti-Doping Agency Passport. Sports Med. Open 2024, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Liao, L.; Ge, Y.; Liu, M.; Fang, X.; Sun, H.; Zheng, S.; Deng, X. Screening anabolic androgenic steroids in human urine: An application of the state-of-the-art gas chromatography-Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 3223–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khelaifi, F.; Diboun, I.; Donati, F.; Botrè, F.; Alsayrafi, M.; Georgakopoulos, C.; Suhre, K.; Yousri, N.A.; Elrayess, M.A. A pilot study comparing the metabolic profiles of elite-level athletes from different sporting disciplines. Sports Med.-Open 2018, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, T.; Haenelt, N.; Fusshöller, G.; Geyer, H.; Thevis, M. Sensitive detection of testosterone and testosterone prohormone administrations based on urinary concentrations and carbon isotope ratios of androsterone and etiocholanolone. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1835–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzetto, F.; Boccard, J.; Nicoli, R.; Kuuranne, T.; Saugy, M.; Rudaz, S. Steroidomics for Highlighting Novel Serum Biomarkers of Testosterone Doping. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccard, J.; Badoud, F.; Jan, N.; Nicoli, R.; Schweizer, C.; Pralong, F.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Baume, N.; Rudaz, S.; Saugy, M. Untargeted Profiling of Urinary Steroid Metabolites After Testosterone Ingestion: Opening New Perspectives for Antidoping Testing. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 2523–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloteau, C.; Dervilly, G.; Kaabia, Z.; Bagilet, F.; Delcourt, V.; Loup, B.; Guitton, Y.; Royer, A.-L.; Monteau, F.; Garcia, P.; et al. From a non-targeted metabolomics approach to a targeted biomarkers strategy to highlight testosterone abuse in equine. Illustration of a methodological transfer between platforms and laboratories. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yan, J.; Ou, G.; Fu, L. A Review of Recent Progress in Drug Doping and Gene Doping Control Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Bhattacharya, M.; Pal, S.; Lee, S.-S. From machine learning to deep learning: Advances of the recent data-driven paradigm shift in medicine and healthcare. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2024, 7, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Alsmadi, M.k.; Omar, K.B.; Noah, S.A.; Almarashdah, I. Performance Comparison of Multi-layer Perceptron (Back Propagation, Delta Rule and Perceptron) algorithms in Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference, Patiala, India, 6–7 March 2009; pp. 296–299. [Google Scholar]
- Neijzen, D.; Lunter, G. Unsupervised learning for medical data: A review of probabilistic factorization methods. Stat. Med. 2023, 42, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, R.; Grampp, G.; Kang, H.N.; Knezevic, I. Quality assessment and its impact on clinical performance of a biosimilar erythropoietin: A simulated case study. Biologicals 2019, 62, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Pan, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, G.P. Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases. MedComm 2023, 4, e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, A.; Ono, K.; Nozawa, K.; Sato, M.; Onuki, M.; Sese, J.; Yumoto, Y.; Matsushita, S.; Matsumoto, T. Wearable Sensor and Mobile App-Based mHealth Approach for Investigating Substance Use and Related Factors in Daily Life: Protocol for an Ecological Momentary Assessment Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2023, 12, e44275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fan, C.; Kargarandehkordi, A.; Sun, Y.; Slade, C.; Jaiswal, A.; Benzo, R.M.; Phillips, K.T.; Washington, P. Monitoring Substance Use with Fitbit Biosignals: A Case Study on Training Deep Learning Models Using Ecological Momentary Assessments and Passive Sensing. AI 2024, 5, 2725–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Khaliq, L.A.; Piper, T.; Geyer, H.; Equey, T.; Baume, N.; Aikin, R.; Maass, W. SACNN: Self Attention-based Convolutional Neural Network for Fraudulent Behaviour Detection in Sports. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 3–9 August 2024; pp. 6017–6025. [Google Scholar]
- Parisotto, R.; Wu, M.; Ashenden, M.J.; Emslie, K.R.; Gore, C.J.; Howe, C.; Kazlauskas, R.; Sharpe, K.; Trout, G.J.; Xie, M. Detection of recombinant human erythropoietin abuse in athletes utilizing markers of altered erythropoiesis. Haematologica 2001, 86, 128–137. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.R.; Bejder, J.; Bonne, T.C.; Andersen, A.B.; Huertas, J.R.; Aikin, R.; Nordsborg, N.B.; Maaß, W. AI-based approach for improving the detection of blood doping in sports. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.00001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Anti-Doping Agency. Laboratory Documentation Package (TD2023LDOC); World Anti-Doping Agency: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2023; Volume 2023. [Google Scholar]
- World Anti-Doping Agency. Decision Limits for the Confirmatory Quantification of Exogenous Threshold Substances by Chromatography-Based Analytical Methods (TD2022DL); World Anti-Doping Agency: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2022; Volume 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wahi, A.; Nagpal, R.; Verma, S.; Narula, A.; Kumar Tonk, R.; Kumar, S. A comprehensive review on current analytical approaches used for the control of drug abuse in sports. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas-Bôas, S.G.; Koulman, A.; Lane, G.A. Analytical methods from the perspective of method standardization. In Metabolomics: A Powerful Tool in Systems Biology; Nielsen, J., Jewett, M.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 11–52. [Google Scholar]
- Scalbert, A.; Brennan, L.; Fiehn, O.; Hankemeier, T.; Kristal, B.S.; van Ommen, B.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Verheij, E.; Wishart, D.; Wopereis, S. Mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics: Limitations and recommendations for future progress with particular focus on nutrition research. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, B.; Wikoff, W.R.; Patti, G.J.; Woo, H.-K.; Kalisiak, E.; Heideker, J.; Siuzdak, G. Variability Analysis of Human Plasma and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Reveals Statistical Significance of Changes in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8538–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, D.M.; Paschos, G.K.; Sehgal, A.; Weljie, A.M. Circadian and Sleep Metabolomics Across Species. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 3578–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Vallejo, M.; García, A.; Barbas, C. Method validation strategies involved in non-targeted metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1353, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiehn, O.; Kristal, B.; Ommen, B.V.; Sumner, L.W.; Sansone, S.-A.; Taylor, C.; Hardy, N.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R. Establishing Reporting Standards for Metabolomic and Metabonomic Studies: A Call for Participation. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2006, 10, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattias, E.; Stefan, R.; Johan, T. From Data Processing to Multivariate Validation—Essential Steps in Extracting Interpretable Information from Metabolomics Data. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gika, H.G.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.A. LC–MS-based holistic metabolic profiling. Problems, limitations, advantages, and future perspectives. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 966, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courant, F.; Antignac, J.-P.; Dervilly-Pinel, G.; Le Bizec, B. Basics of mass spectrometry based metabolomics. Proteomics 2014, 14, 2369–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, P.; Jardines, D.; Martinez-Brito, D.; Domenici, E.; de la Torre, X.; Parr, M.K.; Botrè, F. Metabolomics workflow as a driven tool for rapid detection of metabolites in doping analysis. Development and validation. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Li, L. Evaluating and minimizing batch effects in metabolomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2022, 41, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märtens, A.; Holle, J.; Mollenhauer, B.; Wegner, A.; Kirwan, J.; Hiller, K. Instrumental Drift in Untargeted Metabolomics: Optimizing Data Quality with Intrastudy QC Samples. Metabolites 2023, 13, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrens, R.; Hageman, J.A.; van Eeuwijk, F.; Kooke, R.; Flood, P.J.; Wijnker, E.; Keurentjes, J.J.; Lommen, A.; van Eekelen, H.D.; Hall, R.D.; et al. Improved batch correction in untargeted MS-based metabolomics. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Lin, G.; Dong, L.; Cheng, K.K.; Deng, L.; Xu, X.; Raftery, D.; Dong, J. Concordance-Based Batch Effect Correction for Large-Scale Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 7220–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanichthanarak, K.; Jeamsripong, S.; Pornputtapong, N.; Khoomrung, S. Accounting for biological variation with linear mixed-effects modelling improves the quality of clinical metabolomics data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and considerations for the use of system suitability and quality control samples in mass spectrometry assays applied in untargeted clinical metabolomic studies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, R.D.; Dunn, W.B.; Bandukwala, A.; Bethan, B.; Broadhurst, D.; Clish, C.B.; Dasari, S.; Derr, L.; Evans, A.; Fischer, S.; et al. Towards quality assurance and quality control in untargeted metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza-Yates, R. The Limitations of Data, Machine Learning and Us. In Proceedings of Companion of the 2024 International Conference on Management of Data, Santiago, Chile, 9–15 June 2024; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, P. Artificial Intelligence and the Limitations of Information. Information 2018, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Mehta, R. Use of Artificial Intelligence in the fight against doping. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Smart Devices (ICSD), Dehradun, India, 2–3 May 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, T.S.; Holmen, S.J.; Ryberg, J. AI, doping and ethics: On why increasing the effectiveness of detecting doping fraud in sport may be morally wrong. J. Med. Ethics 2025, 51, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.R. AI and accessibility. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Youn, B.-Y. Ethical implications of artificial intelligence in sport: A systematic scoping review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2025, 14, 101047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. Role of AI in Enhancing Accessibility for People with Disabilities. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. (JAIGS) 2024, 3, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Mehta, R. Unmasking the Hidden Threat: How AI Can Expose Doping Drug Dealers on the Dark Web. Int. J. Sci. Technol. (IJSAT) 2025, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.; Beharry, A.; Fedoruk, M.N. Applying Machine Learning Techniques to Advance Anti-Doping. Eur. J. Sports Exerc. Sci. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Holz, M.; Robertson, J. How to Develop Intelligence Gathering in Efficient and Practical Anti-Doping Activities. In Acute Topics in Anti-Doping; S.Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://karger.com/books/book/318/chapter-abstract/5507553/How-to-Develop-Intelligence-Gathering-in-Efficient?redirectedFrom=fulltext (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Novatchkov, H.; Baca, A. Artificial intelligence in sports on the example of weight training. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2013, 12, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks, P.I.; Dalgleish, J.K.; Shelley, J.T.; Kirleis, M.A.; McNicholas, M.T.; Li, L.; Chen, T.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Duncan, J.S.; Boudreau, F.; et al. Autonomous in Situ Analysis and Real-Time Chemical Detection Using a Backpack Miniature Mass Spectrometer: Concept, Instrumentation Development, and Performance. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2900–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.M.; Roth, M.J.; Keil, A.D.; Grossenbacher, J.W.; Justes, D.R.; Patterson, G.E.; Barket, D.J. Implementation of DART and DESI ionization on a fieldable mass spectrometer. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 19, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaney, L.M.; Ruszkiewicz, D.M.; Arthur, K.L.; Hadjithekli, A.; Aldcroft, C.; Lindley, M.R.; Thomas, C.L.P.; Turner, M.A.; Reynolds, J.C. Real-Time Monitoring of Exhaled Volatiles Using Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization on A Compact Mass Spectrometer. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Analytical Platform | Key Features | Advantages | Limitations | Targeted/Untargeted | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry) | Most frequently used in doping screening | - High sensitivity, precision, and reproducibility - Effective for quantifying low-abundance metabolites - Discriminates structurally similar metabolites (improved specificity) | Context-dependent sample preparation *: for many matrices/targets, simple dilute-and-shoot or protein precipitation is sufficient; escalation to SPE/LLE or additional cleanup is used for complex matrices, isobaric interferences, or very low-abundance analytes | Primarily targeted (with semi-untargeted applications) | [26,40] |
| NMR Spectroscopy (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) | Non-destructive, highly reproducible; excellent for structural elucidation | - Quantitative, non-destructive, highly reproducible - Excellent for structural elucidation - Suitable for detecting broad metabolic shifts | - Lower sensitivity than MS platforms - Less effective for low-abundance metabolites | Primarily untargeted | [48,49] |
| High-Resolution MS Techniques (e.g., Orbitrap, FT-ICR/MS, QTOF-MS) | Used in untargeted metabolomics and biomarker discovery | - High accuracy and resolution - Enables detection of novel or unknown metabolites - Differentiates physiological vs. doping-induced changes | - Higher cost - Complex data analysis | Both targeted and untargeted | [7,50,51,52,53] |
| GC-MS/MS | Gas chromatography with triple-quadrupole MS/MS; often preceded by enzymatic hydrolysis, LLE/SPE, and derivatization (e.g., TMS) | High selectivity/sensitivity for volatile/derivatized analytes; extensive method maturity in WADA labs; aligns with MRPL guidance for many classes | Requires derivatization for many steroids; less suitable for very polar/thermolabile metabolites; matrix-dependent prep | Targeted (primary); limited untargeted | [26,45] |
| GC-C-IRMS (Isotope-Ratio MS) | GC separation coupled to on-line combustion and IRMS for δ13C of target steroids vs. endogenous references | Distinguishes synthetic from endogenous steroid origin; mandated confirmatory tool after suspicious steroid profiles; strong legal defensibility | Specialized instrumentation; higher sample/analysis time per target; requires sufficient analyte abundance and clean chromatographic resolution | Targeted confirmatory | [42,43,44] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AbuHaweeleh, M.N.; Hamdan, A.; Al-Essa, J.; Aljaal, S.; Al Saad, N.; Georgakopoulos, C.; Botre, F.; Elrayess, M.A. Integrating Advanced Metabolomics and Machine Learning for Anti-Doping in Human Athletes. Metabolites 2025, 15, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110696
AbuHaweeleh MN, Hamdan A, Al-Essa J, Aljaal S, Al Saad N, Georgakopoulos C, Botre F, Elrayess MA. Integrating Advanced Metabolomics and Machine Learning for Anti-Doping in Human Athletes. Metabolites. 2025; 15(11):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110696
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbuHaweeleh, Mohannad N., Ahmad Hamdan, Jawaher Al-Essa, Shaikha Aljaal, Nasser Al Saad, Costas Georgakopoulos, Francesco Botre, and Mohamed A. Elrayess. 2025. "Integrating Advanced Metabolomics and Machine Learning for Anti-Doping in Human Athletes" Metabolites 15, no. 11: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110696
APA StyleAbuHaweeleh, M. N., Hamdan, A., Al-Essa, J., Aljaal, S., Al Saad, N., Georgakopoulos, C., Botre, F., & Elrayess, M. A. (2025). Integrating Advanced Metabolomics and Machine Learning for Anti-Doping in Human Athletes. Metabolites, 15(11), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110696









