The Endogenous Inhibitor of CETP, apoC1, Remains Ineffective In Vivo after Correction of Hyperglycemia in People with Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
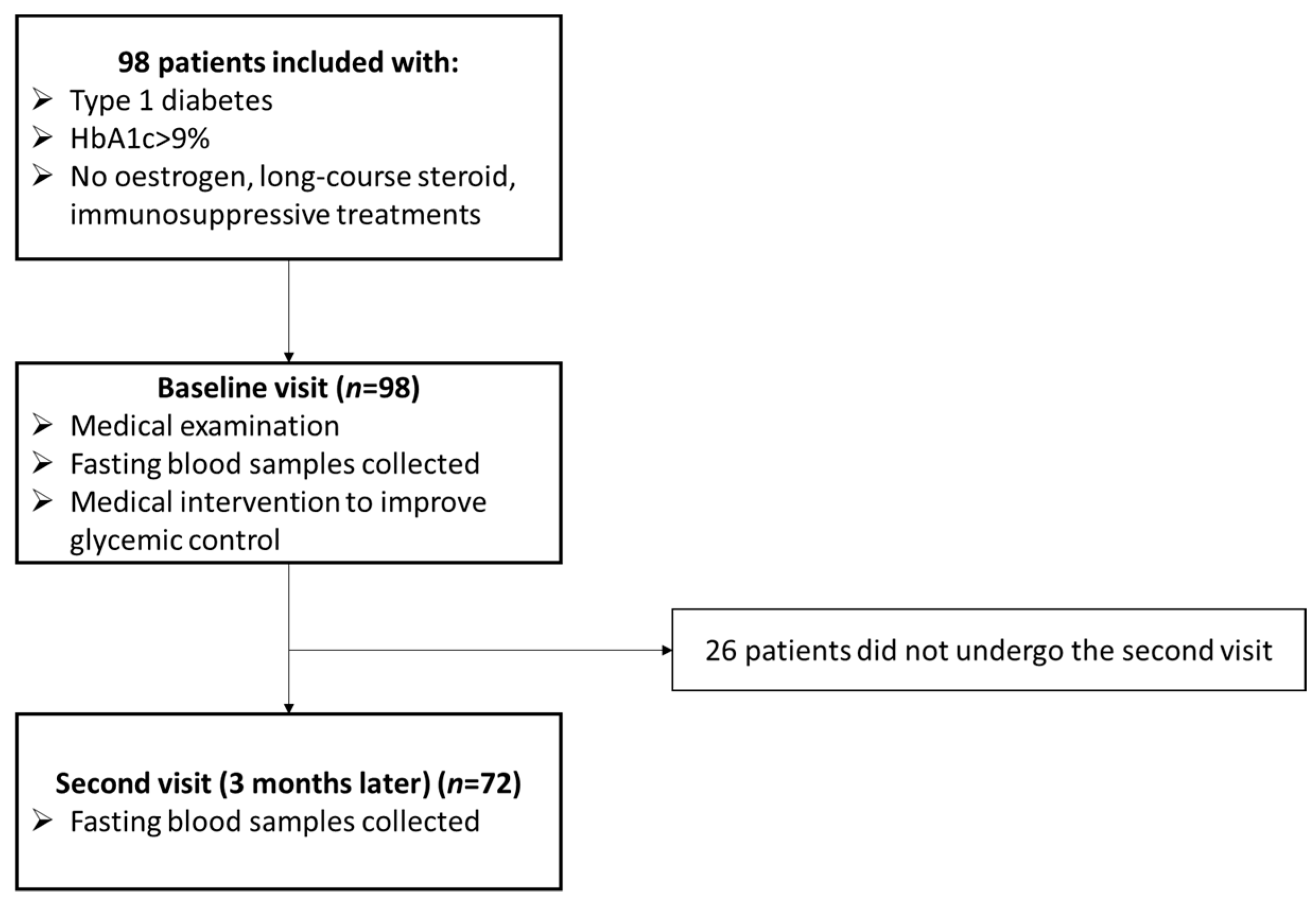
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Plasma Preparation
2.3. Routine Analytical Procedures
2.4. Measurement of apoC1 and CETP Concentration by Immunoassay
2.5. Measurement of CETP Activity Using a Radioactivity Method
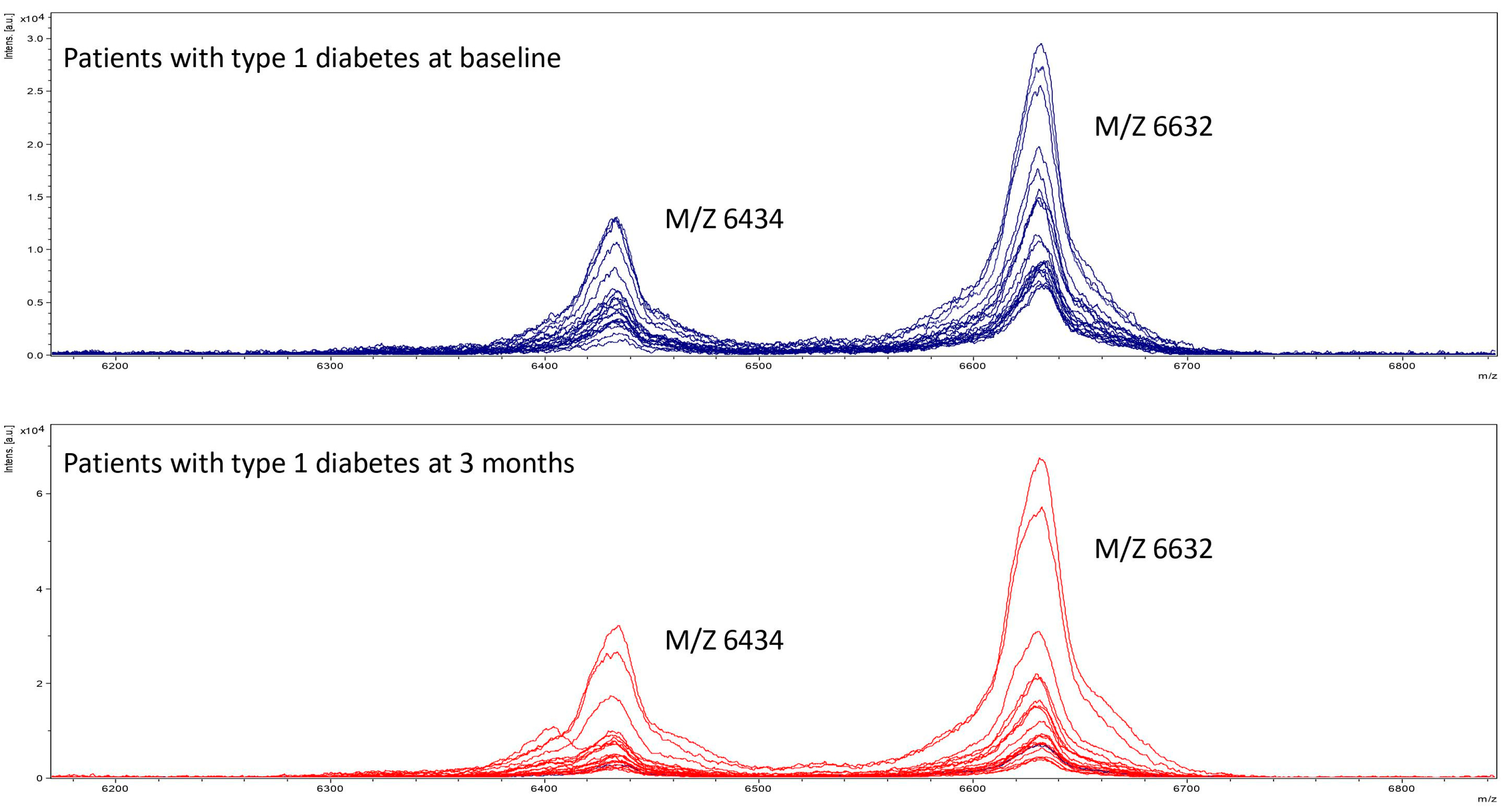
2.6. Detection of apoC1 in Mass Spectrometry
2.7. Measurement of Triglycerides in HDL
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Participants Characteristics
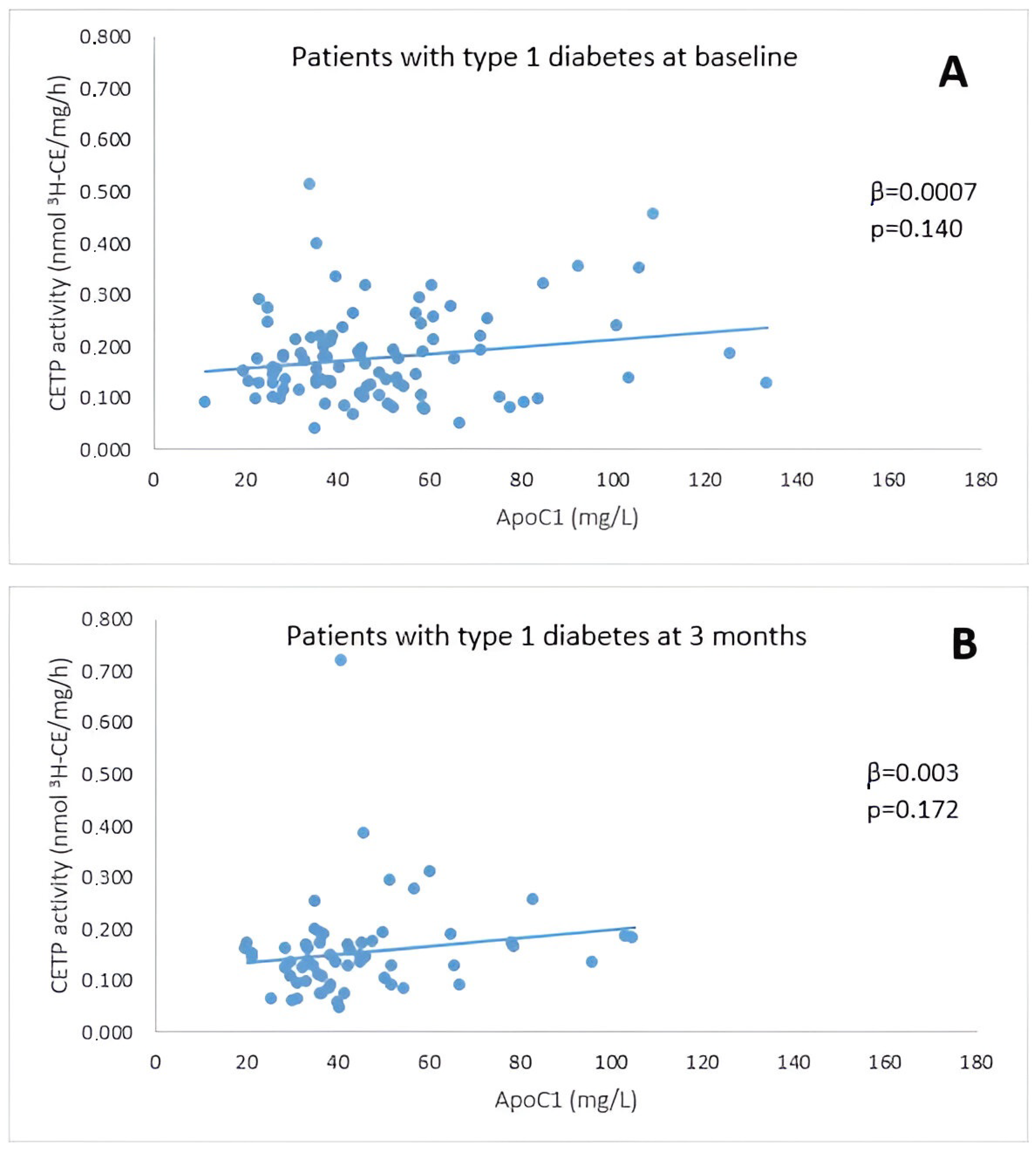
3.2. Association between CETP Activity and apoC1
3.3. Detection of apoC1 in Mass Spectrometry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.H.; Tanimura, M.; Luo, C.C.; Datta, S.; Chan, L. The apolipoprotein multigene family: Biosynthesis, structure, structure-function relationships, and evolution. J. Lipid Res. 1988, 29, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, J.S.; Tremblay, M.; Batal, R.; Jacques, H.; Veilleux, L.; Rodriguez, C.; Bernier, L.; Mamer, O.; Davignon, J. Plasma kinetics of VLDL and HDL apoC-I in normolipidemic and hypertriglyceridemic subjects. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmendier, C.L.; Lontie, J.F.; Grutman, G.A.; Delcroix, C. Metabolism of apolipoprotein C-I in normolipoproteinemic human subjects. Atherosclerosis 1986, 62, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouland, A.; Masson, D.; Lagrost, L.; Vergès, B.; Gautier, T.; Bouillet, B. Role of apolipoprotein C1 in lipoprotein metabolism, atherosclerosis and diabetes: A systematic review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gautier, T.; Masson, D.; de Barros, J.P.; Athias, A.; Gambert, P.; Aunis, D.; Metz-Boutigue, M.H.; Lagrost, L. Human apolipoprotein C-I accounts for the ability of plasma high density lipoproteins to inhibit the cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 37504–37509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chajek, T.; Fielding, C.J. Isolation and characterization of a human serum cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 3445–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, P.J.; Lally, J.I. The activity of an esterified cholesterol transferring factor in human and rat serum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 531, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, P.J.; Hopkins, G.J.; Calvert, G.D. Transfers and exchanges of esterified cholesterol between plasma lipoproteins. Biochem. J. 1982, 208, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agellon, L.; Walsh, A.; Hayek, T.; Moulin, P.; Jiang, X.; Shelanski, S.; Breslow, J.; Tall, A. Reduced high density lipoprotein cholesterol in human cholesteryl ester transfer protein transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 10796–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiresan, S. Will cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibition succeed primarily by lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol? Insights from human genetics and clinical trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 2049–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Qi, Y. Circulating cholesteryl ester transfer protein and coronary heart disease: Mendelian randomization meta-analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dullaart, R.P.F.; Groener, J.E.M.; Dikkeschei, L.D.; Erkelens, D.W.; Doorenbos, H. Increased cholesterylester transfer activity in complicated Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus—Its relationship with serum lipids. Diabetologia 1989, 32, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, L.; Gautier, T.; de Barros, J.P.P.; Laplanche, H.; Blache, D.; Ducoroy, P.; Fruchart, J.; Fruchart, J.C.; Gambert, P.; Masson, D.; et al. Molecular mechanism of the blockade of plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein by its physiological inhibitor apolipoprotein CI. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38108–38116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, J.-P.P.; Boualam, A.; Gautier, T.; Dumont, L.; Vergès, B.; Masson, D.; Lagrost, L. Apolipoprotein CI is a physiological regulator of cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity in human plasma but not in rabbit plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillois, X.; Gautier, T.; Bouillet, B.; de Barros, J.-P.P.; Jeannin, A.; Vergès, B.; Bonnet, J.; Lagrost, L. Constitutive inhibition of plasma CETP by apolipoprotein C1 is blunted in dyslipidemic patients with coronary artery disease. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillet, B.; Gautier, T.; Blache, D.; de Barros, J.P.P.; Duvillard, L.; Petit, J.M.; Lagrost, L.; Vergès, B. Glycation of apolipoprotein C1 impairs its CETP inhibitory property: Pathophysiological relevance in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergès, B. Dyslipidemia in Type 1 Diabetes: AMaskedDanger. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrost, L.; Perségol, L.; Lallemant, C.; Gambert, P. Influence of apolipoprotein composition of high density lipoprotein particles on cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity. Particles containing various proportions of apolipoproteins AI and AII. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 3189–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrost, L.; Barter, P.J. Effects of various non esterified fatty acids on the transfer of cholesteryl esters from HDL to LDL induced by the cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1085, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.T.; Liao, H.Y.; Chang, C.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Tsai, F.J.; Chen, C.J. Oxidized ApoC1 on MALDI-TOF and glycated-ApoA1 band on gradient gel as potential diagnostic tools for atherosclerotic vascular disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 420, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassenius, M.I.; Mäkinen, V.P.; Fogarty, C.L.; Peräneva, L.; Jauhiainen, M.; Pussinen, P.J.; Taskinen, M.R.; Kirveskari, J.; Vaarala, O.; Nieminen, J.K.; et al. Patients with type 1 diabetes show signs of vascular dysfunction in response to multiple high-fat meals. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Kahri, J.; Groop, P.H.; Elliott, T.; Viberti, G.; Taskinen, M.R. Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein and its relationship to plasma lipoproteins and apolipoprotein A-I-containing lipoproteins in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria and clinical nephropathy. Diabetes Care 1994, 17, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjali, S.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Banach, M.; Pirro, M.; Sahebkar, A. HDL functionality in type 1 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2017, 267, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, N.L.; Wang, L.; Small, D.M. Apolipoprotein C-I binds more strongly to phospholipid/triolein/water than triolein/water interfaces: A possible model for inhibiting cholesterol ester transfer protein activity and triacylglycerol-rich lipoprotein uptake. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- James, P.F.; Dogovski, C.; Dobson, R.C.; Bailey, M.F.; Goldie, K.N.; Karas, J.A.; Scanlon, D.B.; O’hair, R.A.; Perugini, M.A. Aromatic residues in the C-terminal helix of human apoC-I mediate phospholipid interactions and particle morphology. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mendoza-Espinosa, P.; Moreno, A.; Castillo, R.; Mas-Oliva, J. Lipid dependant disorder-to-order conformational transitions in apolipoprotein CI derived peptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 365, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, A.; Larson, S.B. The structure of human apolipoprotein C-1 in four different crystal forms. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Perségol, L.; Foissac, M.; Lagrost, L.; Athias, A.; Gambert, P.; Vergès, B.; Duvillard, L. HDL particles from type 1 diabetic patients are unable to reverse the inhibitory effect of oxidised LDL on endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2384–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjunatha, S.; Distelmaier, K.; Dasari, S.; Carter, R.E.; Kudva, Y.C.; Nair, K.S. Functional and proteomic alterations of plasma high density lipoproteins in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourgari, E.; Playford, M.P.; Campia, U.; Dey, A.K.; Cogen, F.; Gubb-Weiser, S.; Mete, M.; Desale, S.; Sampson, M.; Taylor, A.; et al. Low cholesterol efflux capacity and abnormal lipoprotein particles in youth with type 1 diabetes: A case control study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dautin, G.; Soltani, Z.; Ducloux, D.; Gautier, T.; de Barros, J.P.; Gambert, P.; Lagrost, L.; Masson, D. Hemodialysis reduces plasma apolipoprotein C-I concentration making VLDL a better substrate for lipoprotein lipase. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawshani, A.; Rawshani, A.; Franzén, S.; Eliasson, B.; Svensson, A.M.; Miftaraj, M.; McGuire, D.K.; Sattar, N.; Rosengren, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S. Range of Risk Factor Levels: Control, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2017, 135, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lind, M.; Svensson, A.-M.; Kosiborod, M.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Pivodic, A.; Wedel, H.; Dahlqvist, S.; Clements, M.; Rosengren, A. Glycemic control and excess mortality in type 1 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergès, B. Cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes, an underestimated danger: Epidemiological and pathophysiological data. Atherosclerosis 2024, 394, 117158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Normal Range of Laboratory | T1D Patients at Baseline (n = 98) | T1D Patients 3 Months Later (n = 72) | p-Value (Baseline vs. 3 Months Later) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 32.8 ± 12.2 | 33.8 ± 12.5 | N/A | |
| Male sex (n(%)) | 53 (54) | 35 (48.6) | N/A | |
| Weight (kg) | 71.5 ± 15.8 | 72.5 ± 14.9 | p = 0.0002 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 5.3 | 25.2 ± 4.8 | p = 0.0001 | |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 13.3 ± 12 | 14.1 ± 12.6 | N/A | |
| Diabetes complications: | ||||
| Retinopathy (n(%)) | 27 (27.6) | 19 (26.4) | N/A | |
| Nephropathy (n(%)) | 21 (21.4) | 19 (26.4) | N/A | |
| Neuropathy (n(%)) | 17 (17.3) | 10 (14.5) | N/A | |
| HbA1c (%, mmol/mol) | 10.8 ± 2 | 8.7 ± 1.7 | p < 0.0001 | |
| Smoking status: Smokers (n(%)) | 43 (43.9) | 24 (33.3) | ||
| Use of statins (n(%)) | 15 (15.3) | 11 (15.3) | N/A | |
| Fasting glycemia (mmol/L) | 4.3–5.9 | 9.6 ± 4.6 | ||
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 59–104 | 63.6 ± 16 | 64.6 ± 16.2 | p = 0.32 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 3.1–5.7 | 4.7 ± 1 | 4.6 ± 0.8 | p = 0.80 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.04–1.55 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | p < 0.0001 |
| LDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.7 ± 0.9 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | p = 0.22 | |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 0.50–1.70 | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 1 ± 0.5 | p = 0.0002 |
| ApoC1 (mg/L) | 49.2 ± 23.2 | 45.6 ± 19.2 | p = 0.85 | |
| CETP mass (mg/L) | 4.9 ± 1.4 | 5.6 ± 2.7 | p = 0.218 | |
| CETP activity (nmol 3H-CE/mg/h) | 0.176 ± 0.087 | 0.167 ± 0.170 | p = 0.057 |
| At Baseline | At 3 Months | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CETP Activity | CETP Activity | |||
| β | p | β | p | |
| ApoC1 | 0.0007 | 0.140 | 0.003 | 0.172 |
| Age | 0.001 | 0.132 | 0.0004 | 0.733 |
| Sex | −0.0002 | 0.991 | −0.035 | 0.394 |
| Smoking status | 0.001 | 0.938 | 0.022 | 0.681 |
| BMI | 0.001 | 0.566 | 0.008 | 0.234 |
| Creatinine | 0.0002 | 0.697 | −0.0005 | 0.637 |
| Triglycerides | 0.043 | 0.001 | 0.167 | 0.125 |
| HDL cholesterol | −0.029 | 0.150 | −0.077 | 0.256 |
| LDL cholesterol | 0.027 | 0.021 | 0.122 | 0.095 |
| Total cholesterol | 0.026 | 0.007 | 0.086 | 0.162 |
| Retinopathy | 0.027 | 0.134 | 0.004 | 0.902 |
| Nephropathy | 0.028 | 0.130 | 0.011 | 0.752 |
| Neuropathy | 0.037 | 0.137 | 0.027 | 0.381 |
| Diabetes duration | 0.001 | 0.008 | −0.0004 | 0.830 |
| Statin treatment | 0.02 | 0.163 | 0.0047 | 0.898 |
| HbA1c | 0.002 | 0.450 | 0.018 | 0.335 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rouland, A.; Gautier, T.; Denimal, D.; Duvillard, L.; Simoneau, I.; Rageot, D.; Vergès, B.; Bouillet, B. The Endogenous Inhibitor of CETP, apoC1, Remains Ineffective In Vivo after Correction of Hyperglycemia in People with Type 1 Diabetes. Metabolites 2024, 14, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090487
Rouland A, Gautier T, Denimal D, Duvillard L, Simoneau I, Rageot D, Vergès B, Bouillet B. The Endogenous Inhibitor of CETP, apoC1, Remains Ineffective In Vivo after Correction of Hyperglycemia in People with Type 1 Diabetes. Metabolites. 2024; 14(9):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090487
Chicago/Turabian StyleRouland, Alexia, Thomas Gautier, Damien Denimal, Laurence Duvillard, Isabelle Simoneau, David Rageot, Bruno Vergès, and Benjamin Bouillet. 2024. "The Endogenous Inhibitor of CETP, apoC1, Remains Ineffective In Vivo after Correction of Hyperglycemia in People with Type 1 Diabetes" Metabolites 14, no. 9: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090487
APA StyleRouland, A., Gautier, T., Denimal, D., Duvillard, L., Simoneau, I., Rageot, D., Vergès, B., & Bouillet, B. (2024). The Endogenous Inhibitor of CETP, apoC1, Remains Ineffective In Vivo after Correction of Hyperglycemia in People with Type 1 Diabetes. Metabolites, 14(9), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090487





