Microbiome-Metabolome Analysis Insight into the Effects of the Extract of Phyllanthus emblica L. on High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. The Components Analysis of FEPE
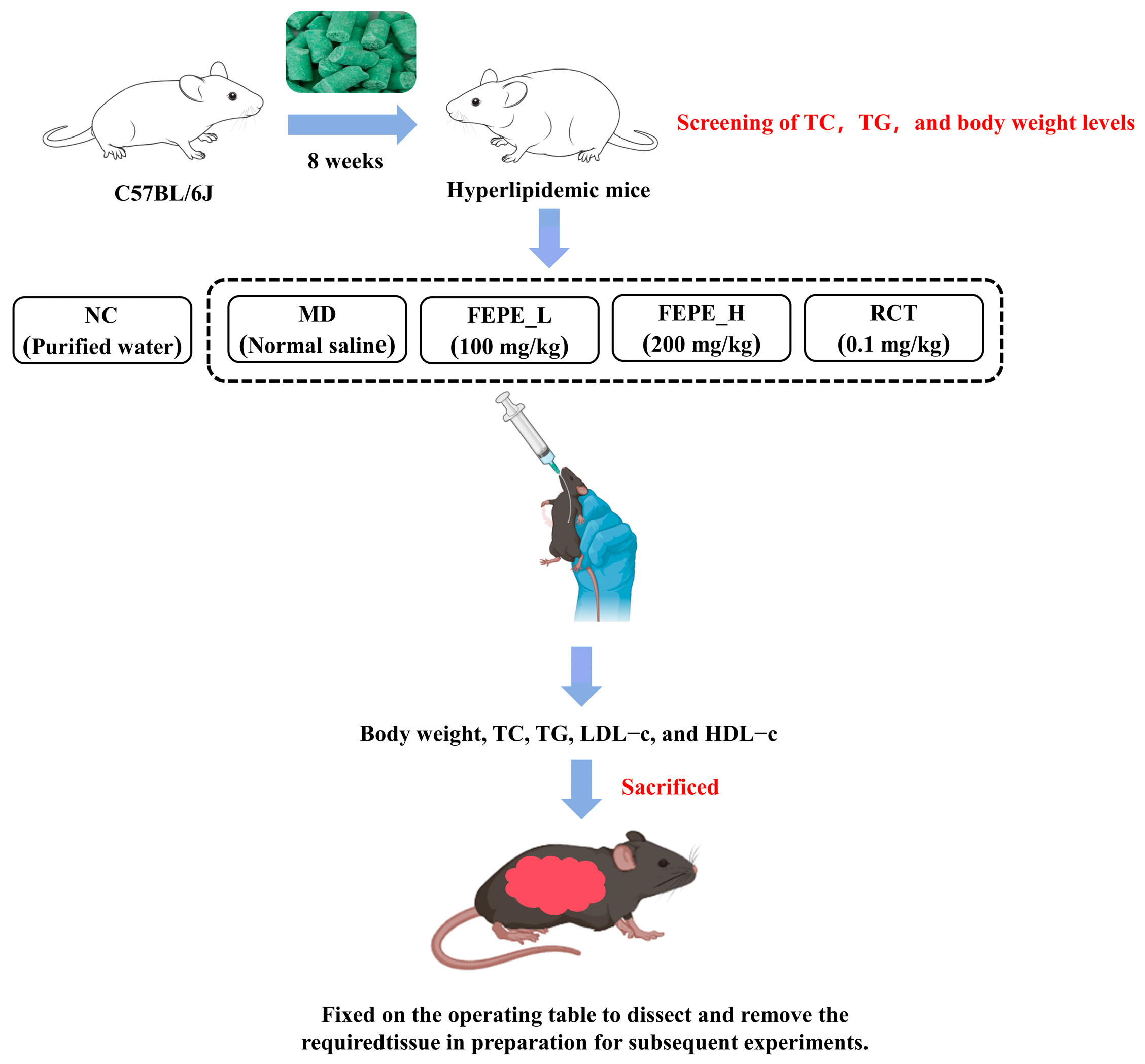
2.3. Animals and Treatment
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Histopathological Analysis
2.6. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.7. SCFAs Analysis in Feces
2.8. Liver Metabonomics Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Main Polyphenolic Component Analysis in FEPE Material
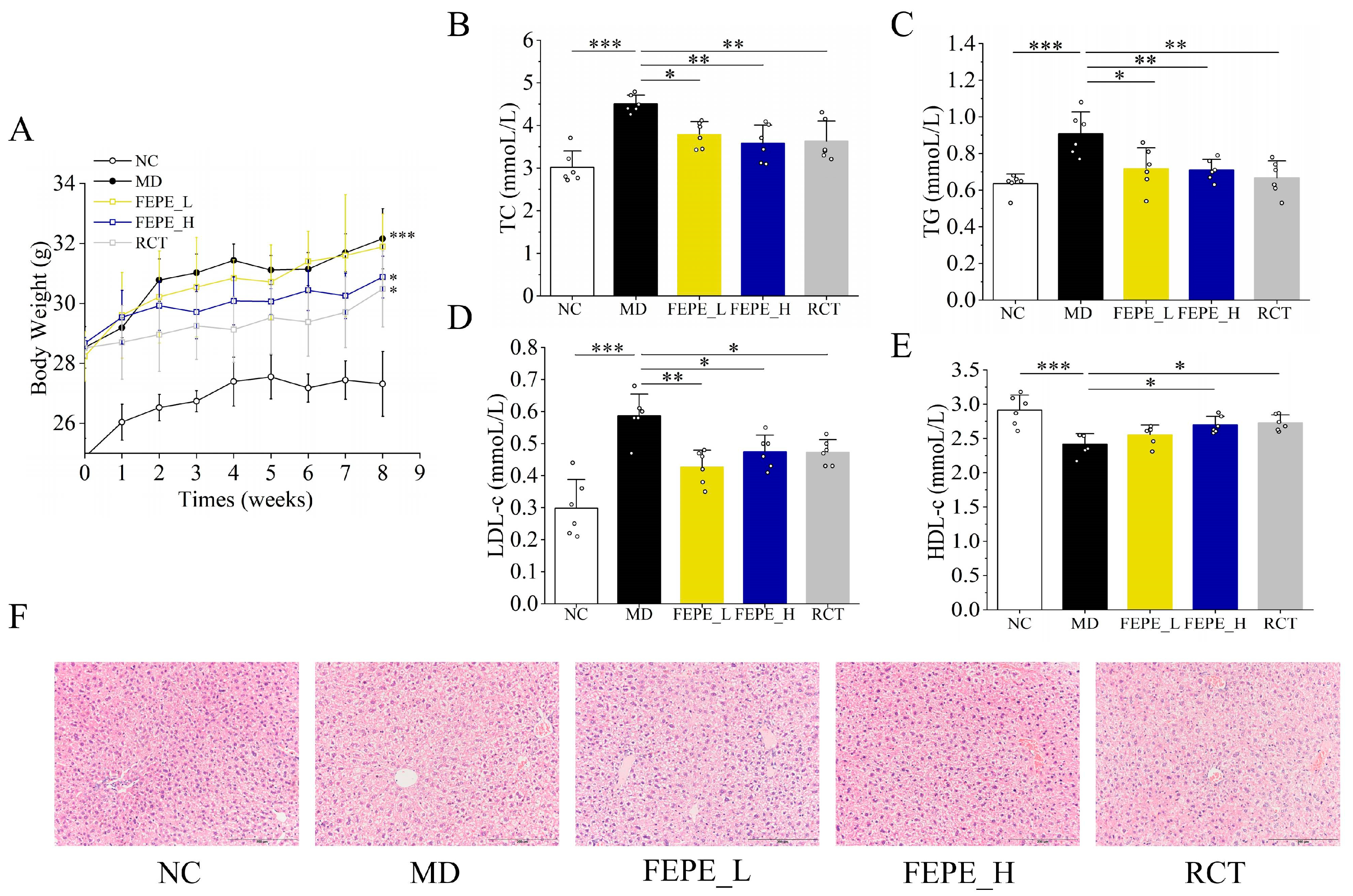
3.2. Effect of FEPE on HFD-Induced Hyperlipidemia in Mice
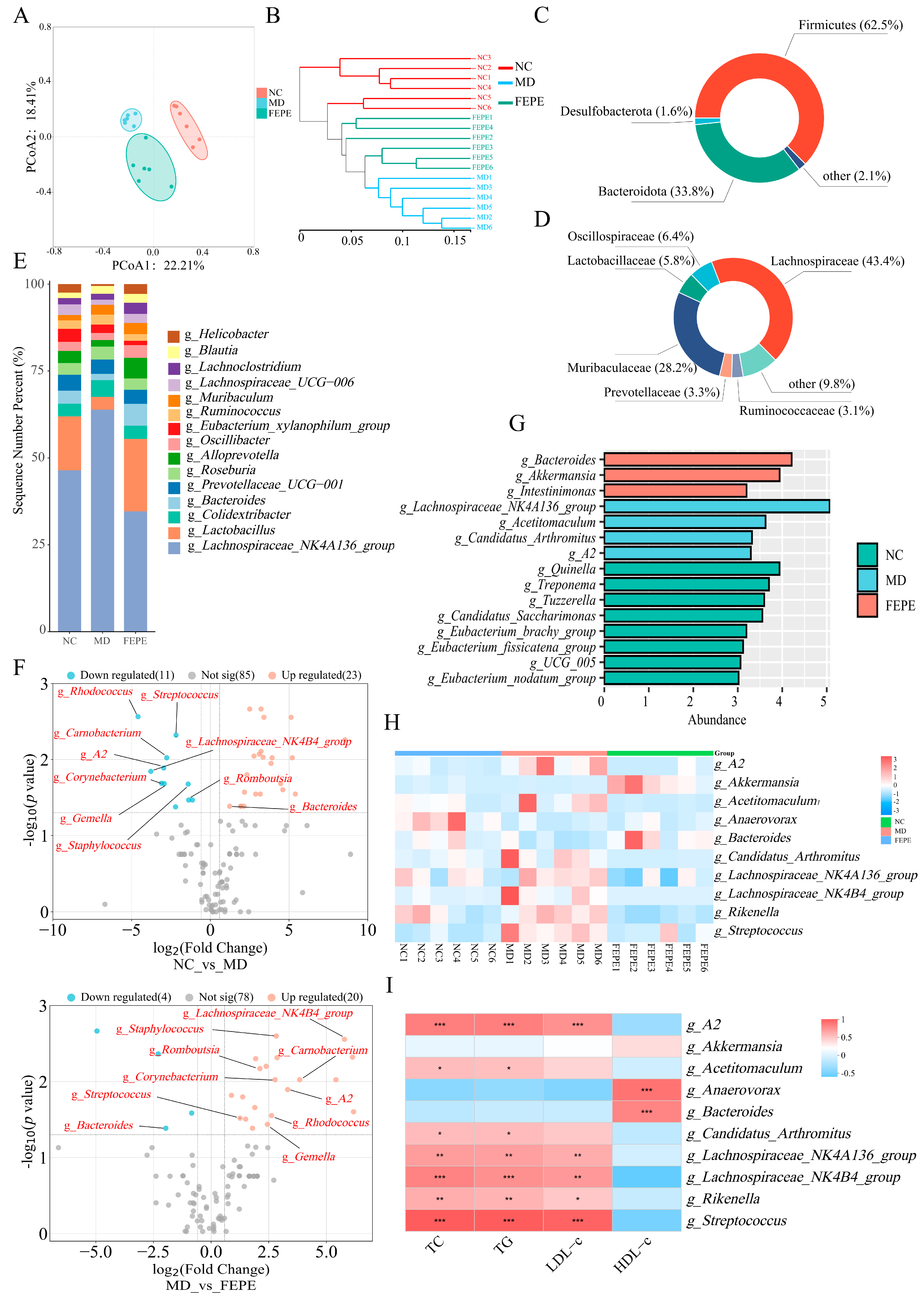
3.3. Effects of FEPE on Gut Microbiota in Mice
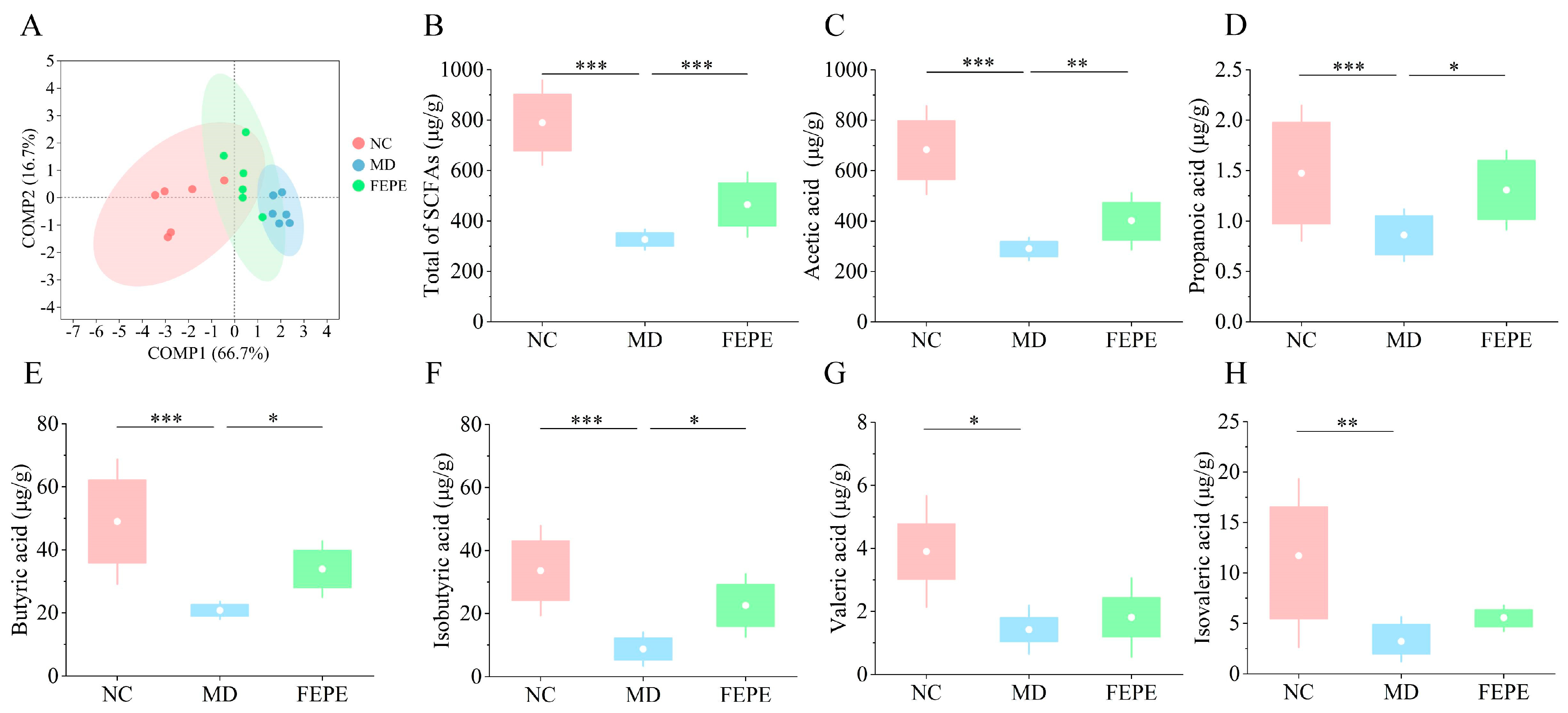
3.4. The FEPE Intervention Ameliorated the Dramatic Reduction in Levels of SCFAs Caused by the Chronic HFD
3.5. Metabolomics Analysis
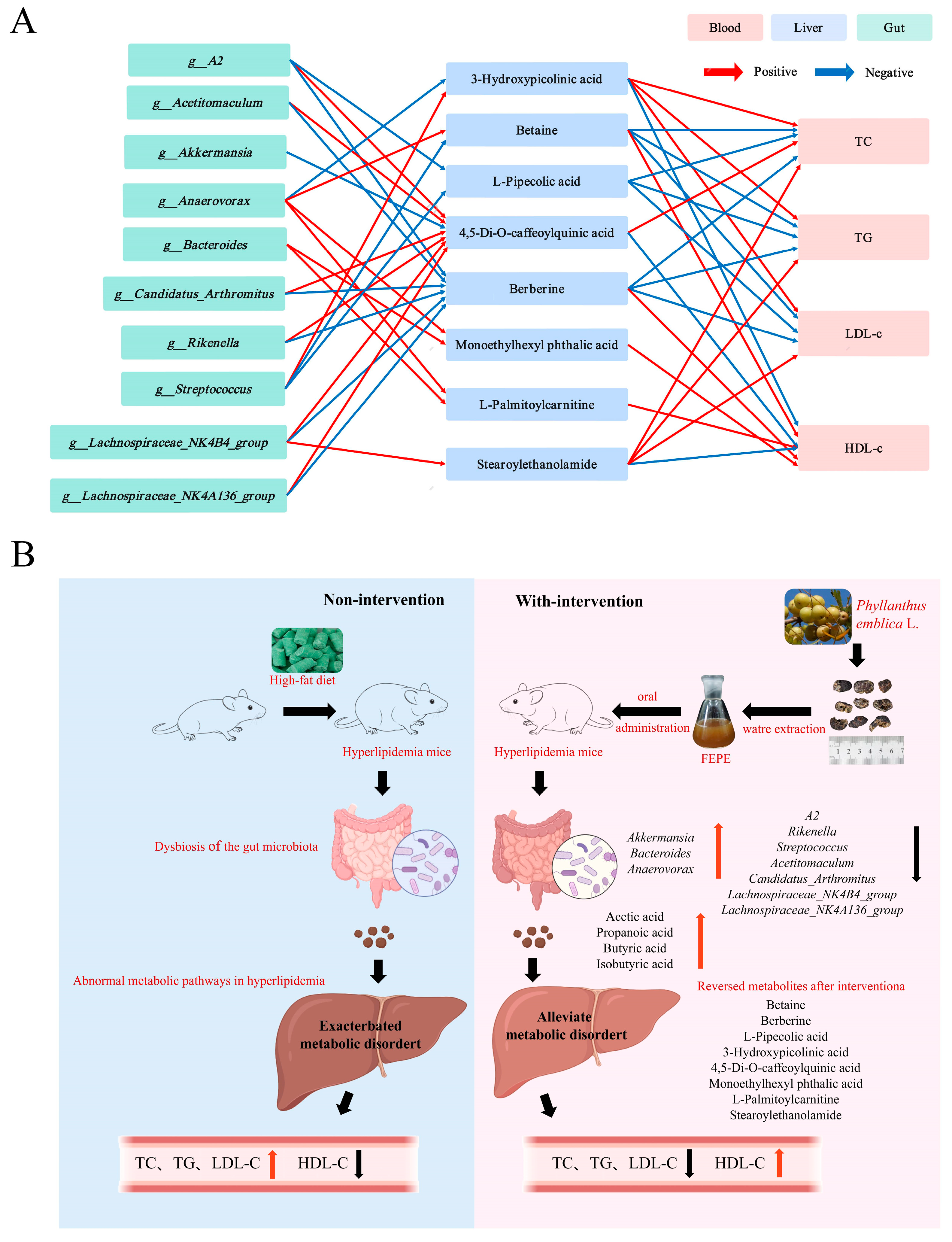
3.6. Correlation Analysis of Lipid Levels, Key Gut Bacteria, and Key Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, S.; He, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H. Effect of lotus seed resistant starch on small intestinal flora and bile acids in hyperlipidemic rats. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.-S.; Li, L.; Rui, J.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Cui, D.; Xu, B. Tomato seed oil attenuates hyperlipidemia and modulates gut microbiota in C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4275–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, P.; Conarello, S.; Wyche, T.P.; Zhang, N.R.; Chng, K.; Kang, J.; Sana, T.R. Metabolomics and Lipidomics Analyses Aid Model Classification of Type 2 Diabetes in Non-Human Primates. Metabolites 2024, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascal, S.; Jacques, M.; Alain, L. New insights into mechanisms of statin-associated myotoxicity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewski, M.; Stępień, K.M.; Tomaszewska, J.; Czuczwar, S.J. Statin-induced myopathies. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, N.C.; Watts, G.F.; Eckel, R.H. Statin Toxicity. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 328–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, M.; Liu, Z.-W.; Iahtisham Ul, H.; Rabail, R.; Faheem, F.; Walayat, N.; Nawaz, A.; Shabbir, M.A.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; et al. Functional and Nutraceutical Significance of Amla (Phyllanthus emblica L.): A Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaveni, M.; Mirunalini, S. Therapeutic potential of Phyllanthus emblica (amla): The ayurvedic wonder. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 21, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Sharma, N.; Oladeji, O.S.; Sourirajan, A.; Dev, K.; Zengin, G.; El-Shazly, M.; Kumar, V. Traditional uses, bioactive composition, pharmacology, and toxicology of Phyllanthus emblica fruits: A comprehensive review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.-J.; Li, M.-Z.; Chen, C.-H.; Hong, T.; Yang, J.-R.; Huang, X.-J.; Geng, F.; Hu, J.-L.; Nie, S.-P. Tea polyphenol and epigallocatechin gallate ameliorate hyperlipidemia via regulating liver metabolism and remodeling gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Tian, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Guo, P. The pandanus tectorius fruit extract (PTF) modulates the gut microbiota and exerts anti-hyperlipidaemic effects. Phytomedicine 2019, 58, 152863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, C.; Mei, X.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, C. Effect of the polyphenol-rich extract from Allium cepa on hyperlipidemic sprague-dawley rats. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzepecka-Stojko, A.; Stojko, J.; Jasik, K.; Buszman, E. Anti-Atherogenic Activity of Polyphenol-Rich Extract from Bee Pollen. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.; Whon, T.; Lee, M.; Bae, J. An increase in the Akkermansia spp. population induced by metformin treatment improves glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obese mice. Gut 2014, 63, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Tian, H.; Xue, Y.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Lan, R.; Qiao, L.; Lin, X.; Hu, D.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Ren, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Bacteroides vulgatus Ameliorates Lipid Metabolic Disorders and Modulates Gut Microbial Composition in Hyperlipidemic Rats. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0251722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havel, R.J. Role of the Liver in Hyperlipidemia. Semin. Liver Dis. 1992, 12, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esen, A.; Nuriye Nuray, U.; Füsun, T.; Göksun, A.; Ferit, T.; Müjde, A.; Metin, A.; Cimen, K. Effects of rosiglitazone treatment on the pentose phosphate pathway and glutathione-dependent enzymes in liver and kidney of rats fed a high-fat diet. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2004, 65, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarinyaporn, N.; Supaporn, W.; Patchareewan, P. Vernonia cinerea water extract improves insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutr. Res. 2018, 56, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Zhong, F.; Chen, Y.; Mao, S.; Yan, Z.; Ma, Y. An integrated spectroscopic strategy to trace the geographical origins of emblic medicines: Application for the quality assessment of natural medicines. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchabhai, T.; Ambarkhane, S.; Joshi, A.; Samant, B.; Rege, N. Protective effect of Tinospora cordifolia, Phyllanthus emblica and their combination against antitubercular drugs induced hepatic damage: An experimental study. Phytother. Res. PTR 2008, 22, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Cao, J.; Shen, X.; Li, C. Holothuria Leucospilota Polysaccharides Ameliorate Hyperlipidemia in High-Fat Diet-Induced Rats via Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production and Lipid Metabolism Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, S.; Huo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wan, C. Huangjinya Black Tea Alleviates Obesity and Insulin Resistance via Modulating Fecal Metabolome in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 2000353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Shiyan, J.; Dan, G.; Chaoyu, W.; Zhongquan, X.; Limeng, Z.; Tao, K.; Jiawei, W.; Yulong, Y.; Baichuan, D. Fecal microbiota, and metabolomics revealed the effect of long-term consumption of gallic acid on canine lipid metabolism and gut health. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fang, Q.; Nie, Q.; Hu, J.; Yang, C.; Huang, T.; Li, H.; Nie, S. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Mechanism of Tea Polysaccharides on Type 2 Diabetic Rats via Gut Microbiota and Metabolism Alteration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 10015–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liang, L.; Yu, G.; Li, Q. Pumpkin polysaccharide modifies the gut microbiota during alleviation of type 2 diabetes in rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Araki, Y.; Hanzawa, F.; Umeki, M.; Kojima, T.; Nishimura, N.; Ikeda, S.; Mochizuki, S.; Oda, H. High sucrose diet-induced dysbiosis of gut microbiota promotes fatty liver and hyperlipidemia in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 93, 108621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y. Effects of Astragaloside IV on Hearing, Inflammatory Factors, and Intestinal Flora in Mice Exposed to Noise. Metabolites 2024, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Zheng, H. Dietary Polyphenol, Gut Microbiota, and Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Daza, M.; Pulido-Mateos, E.; Lupien-Meilleur, J.; Guyonnet, D.; Desjardins, Y.; Roy, D. Polyphenol-Mediated Gut Microbiota Modulation: Toward Prebiotics and Further. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 689456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, S.; Avagliano, C.; Calignano, A.; Berni Canani, R. The Protective Role of Butyrate against Obesity and Obesity-Related Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Liang, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, A.; Tang, P.; et al. Gut microbiota induces DNA methylation via SCFAs predisposing obesity-prone individuals to diabetes. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Shen, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhuang, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Dong, Z.; Wan, X. Sodium butyrate alleviates cholesterol gallstones by regulating bile acid metabolism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 908, 174341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Pan, Q.; Xin, F.-Z.; Zhang, R.-N.; He, C.-X.; Chen, G.-Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Fan, J.-G. Sodium butyrate attenuates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice by improving gut microbiota and gastrointestinal barrier. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Feng, M.; Chu, Y.; Wang, S.; Shete, V.; Tuohy, K.M.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Kamil, A.; Pan, D. The prebiotic effects of oats on blood lipids, gut microbiota, and short-chain fatty acids in mildly hypercholesterolemic subjects compared with rice: A randomized, controlled trial. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 787797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Qiu, M.; Lin, J.; Li, M.; Ma, X.; Ran, F.; Luo, C.; Wei, X.; Xu, R.; Tan, P.; et al. Potential effect of tropical fruits Phyllanthus emblica L. for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetic complications: A systematic review of recent advances. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 3525–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Lin, Y.; Xie, H.; Farag, M.; Feng, S.; Li, J.; Shao, P. Dendrobium officinale leaf polysaccharides ameliorated hyperglycemia and promoted gut bacterial associated SCFAs to alleviate type 2 diabetes in adult mice. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossipov, V.; Khazieva, F.; Baleev, D.; Salminen, J.-P.; Sidelnikov, N. Comparative Metabolomics of Ligulate and Tubular Flowers of Two Cultivars of Calendula officinalis L. Metabolites 2024, 14, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, H.; Fuhan, F.; Na, X.; Yi, Z.; Xiaobo, W.; Xianli, M. Rhodiola crenulata alleviates hypobaric hypoxia-induced brain injury by maintaining BBB integrity and balancing energy metabolism dysfunction. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Shen, L.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Gan, M.; Yang, Q.; Ma, J.; Jiang, A.a.; et al. Betaine Supplementation Enhances Lipid Metabolism and Improves Insulin Resistance in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, W.; Feng, Y.; Wu, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, R. Betaine Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Disruptionof Hepatic Lipid and Iron Homeostasis in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, C. Non-Histone Lysine Crotonylation Is Involved in the Regulation of White Fat Browning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekala, J.; Patkowska-Sokoła, B.; Bodkowski, R.; Jamroz, D.; Nowakowski, P.; Lochyński, S.; Librowski, T. L-carnitine-metabolic functions and meaning in humans life. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Gao, X. Lysine Enhances the Stimulation of Fatty Acids on Milk Fat Synthesis via the GPRC6A-PI3K-FABP5 Signaling in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7005–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Wang, Q.; Ji, S.; Sun, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Yan, S.; Jin, H. ShanmeiMetabolomic and Microbial Remodeling by Capsule Improves Hyperlipidemia in High Fat Food-Induced Mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 729940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Zou, Y.; Han, X.; Bae, J.; Jeon, C. Gut microbiome-mediated mechanisms for reducing cholesterol levels: Implications for ameliorating cardiovascular disease. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.; Depommier, C.; Derrien, M.; Everard, A.; de Vos, W. Akkermansia muciniphila: Paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Cheng, L.; Buch, H.; Zhang, F. Akkermansia muciniphila is a promising probiotic. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1109–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vourakis, M.; Mayer, G.; Rousseau, G. The Role of Gut Microbiota on Cholesterol Metabolism in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Wu, S. Impact of gut microbiota and microbiota-related metabolites on hyperlipidemia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 634780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Guan, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, J.A.; Shen, M. Flavonoids from whole-grain oat alleviated high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia via regulating bile acid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7629–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, Y.-H.; Lee, D.-B.; Lee, Y.-W.; Yoon, S.-M.; Lee, A.-R. Hypoglycemic and hypolipogenic action of acetic acid and Monascus-fermented grain vinegar: A comparative study. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Liao, C.; Su, D.; Mula, T.; Gegen, Z.; Li, Z.; Tu, Y. Wuwei Qingzhuo San Ameliorates Hyperlipidemia in Mice Fed With HFD by Regulating Metabolomics and Intestinal Flora Composition. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 842671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.; Elias-Oliveira, J.; Pereira, Í.; Pereira, J.; Barbosa, S.; Machado, M.; Carlos, D. Akkermansia muciniphila and Gut Immune System: A Good Friendship That Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Obesity, and Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Betaine in Inflammation: Mechanistic Aspects and Applications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punithavathi, V.; Stanely Mainzen Prince, P.; Kumar, M.; Selvakumari, C. Protective effects of gallic acid on hepatic lipid peroxide metabolism, glycoprotein components and lipids in streptozotocin-induced type II diabetic Wistar rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2011, 25, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, S.; Park, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, M.; Jeon, S.; Jeong, T.; Choi, M. Quercetin dihydrate and gallate supplements lower plasma and hepatic lipids and change activities of hepatic antioxidant enzymes in high cholesterol-fed rats. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. Int. Z. Vitam.-Ernahrungsforsch. J. Int. Vitaminol. Nutr. 2002, 72, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki Hoon, L.; Eui-Seon, J.; Goeun, J.; Ju-Ryun, N.; Soyi, P.; Wan Seok, K.; Eun, K.; Hakjoon, C.; Jin Seok, K.; Sunoh, K. Unripe Rubus coreanus Miquel Extract Containing Ellagic Acid Regulates AMPK, SREBP-2, HMGCR, and INSIG-1 Signaling and Cholesterol Metabolism In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients 2020, 12, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishwarya, V.; Anand, T.; Vairamuthu, S.; Solaipriya, S.; Sangaran, A.; Satish, R.; Sivaramakrishnan, V. Ameliorative role of ellagic acid against acute liver steatosis in adult zebrafish experimental model. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 247, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Zhong, F.; Wu, S.; An, G.; Liao, W.; Qi, L.; Ma, Y. Microbiome-Metabolome Analysis Insight into the Effects of the Extract of Phyllanthus emblica L. on High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia. Metabolites 2024, 14, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14050257
Wang J, Dong J, Zhong F, Wu S, An G, Liao W, Qi L, Ma Y. Microbiome-Metabolome Analysis Insight into the Effects of the Extract of Phyllanthus emblica L. on High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia. Metabolites. 2024; 14(5):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14050257
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiahao, Jijing Dong, Furong Zhong, Sha Wu, Guangqin An, Wan Liao, Luming Qi, and Yuntong Ma. 2024. "Microbiome-Metabolome Analysis Insight into the Effects of the Extract of Phyllanthus emblica L. on High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia" Metabolites 14, no. 5: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14050257
APA StyleWang, J., Dong, J., Zhong, F., Wu, S., An, G., Liao, W., Qi, L., & Ma, Y. (2024). Microbiome-Metabolome Analysis Insight into the Effects of the Extract of Phyllanthus emblica L. on High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia. Metabolites, 14(5), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14050257



