Daily Injection of the β2 Adrenergic Agonist Clenbuterol Improved Muscle Glucose Metabolism, Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion, and Hyperlipidemia in Juvenile Lambs Following Heat-Stress-Induced Intrauterine Growth Restriction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Surgical Catheterization
2.3. In Vivo Metabolic Analyses
2.3.1. Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion
2.3.2. Hindlimb Glucose Metabolism
2.4. Blood Hormones and Metabolites
2.5. Whole-Body Oxidative Metabolism
2.6. Ex Vivo Skeletal Muscle Glucose Metabolism
2.7. Pancreatic Islet Morphometrics
2.8. Skeletal Muscle Protein Expression
2.9. Muscle Glycogen Content
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Parameters
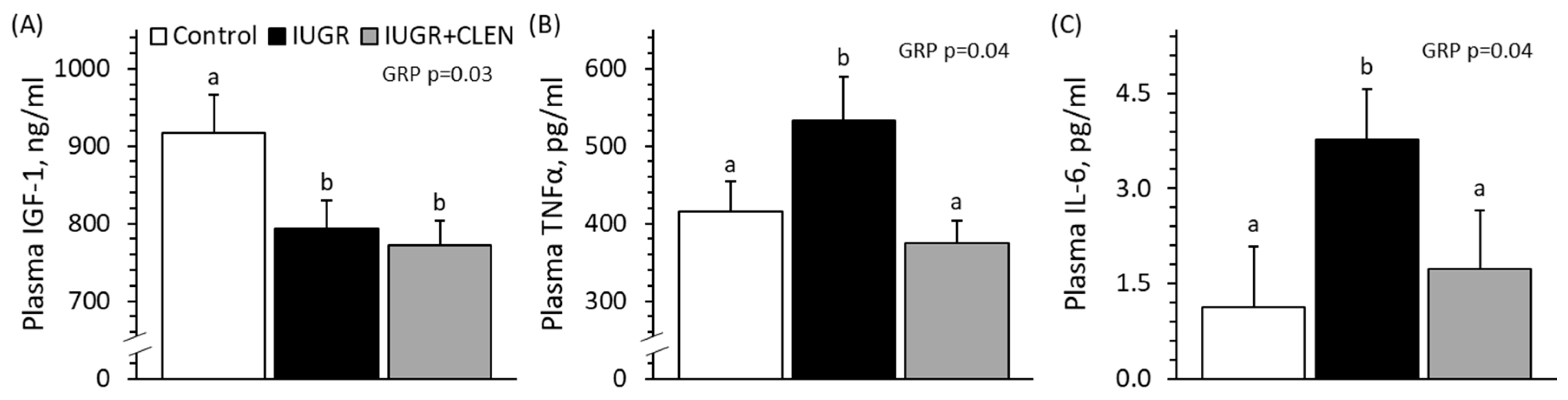
3.2. Daily Blood Hormone Concentrations
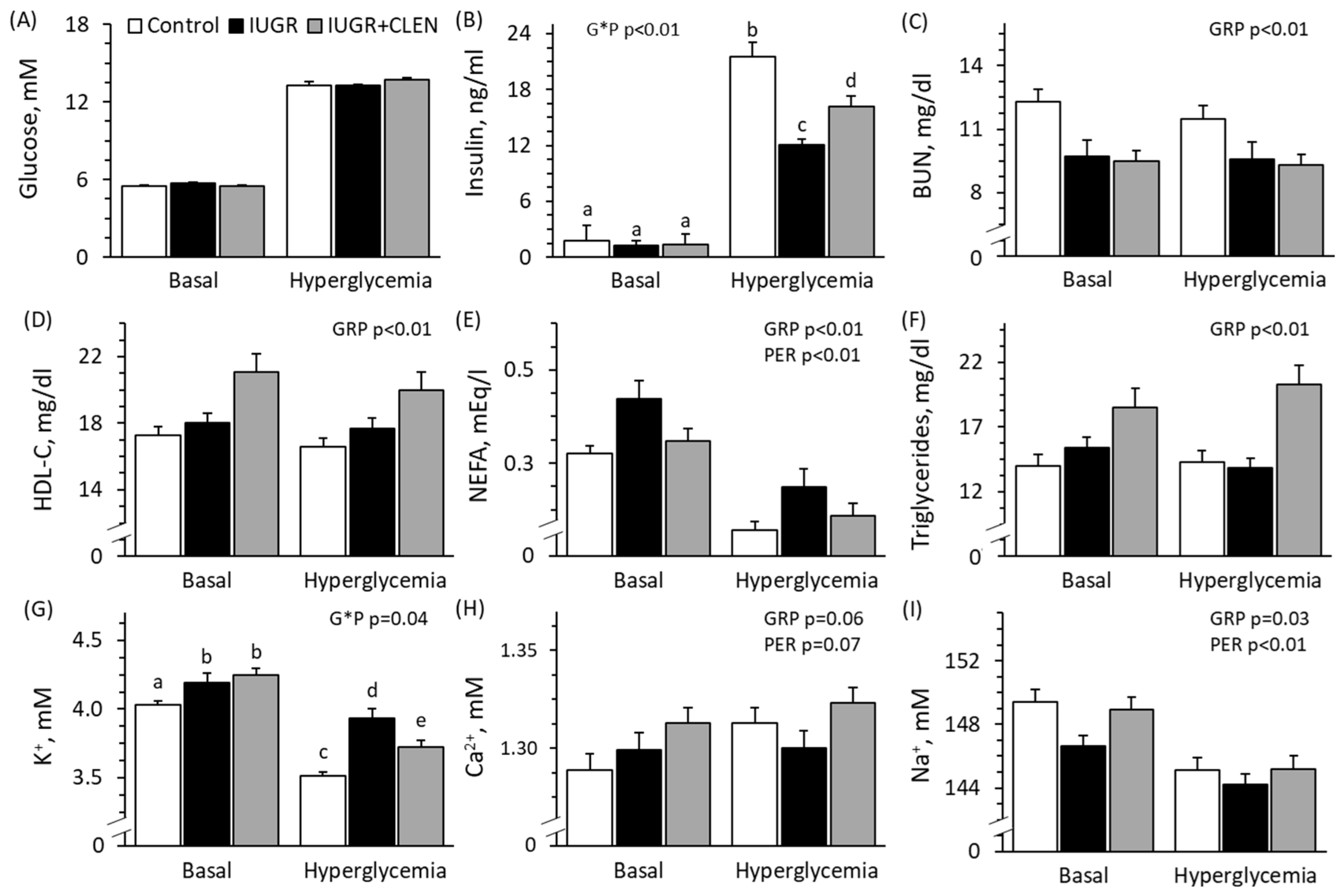
3.3. Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion
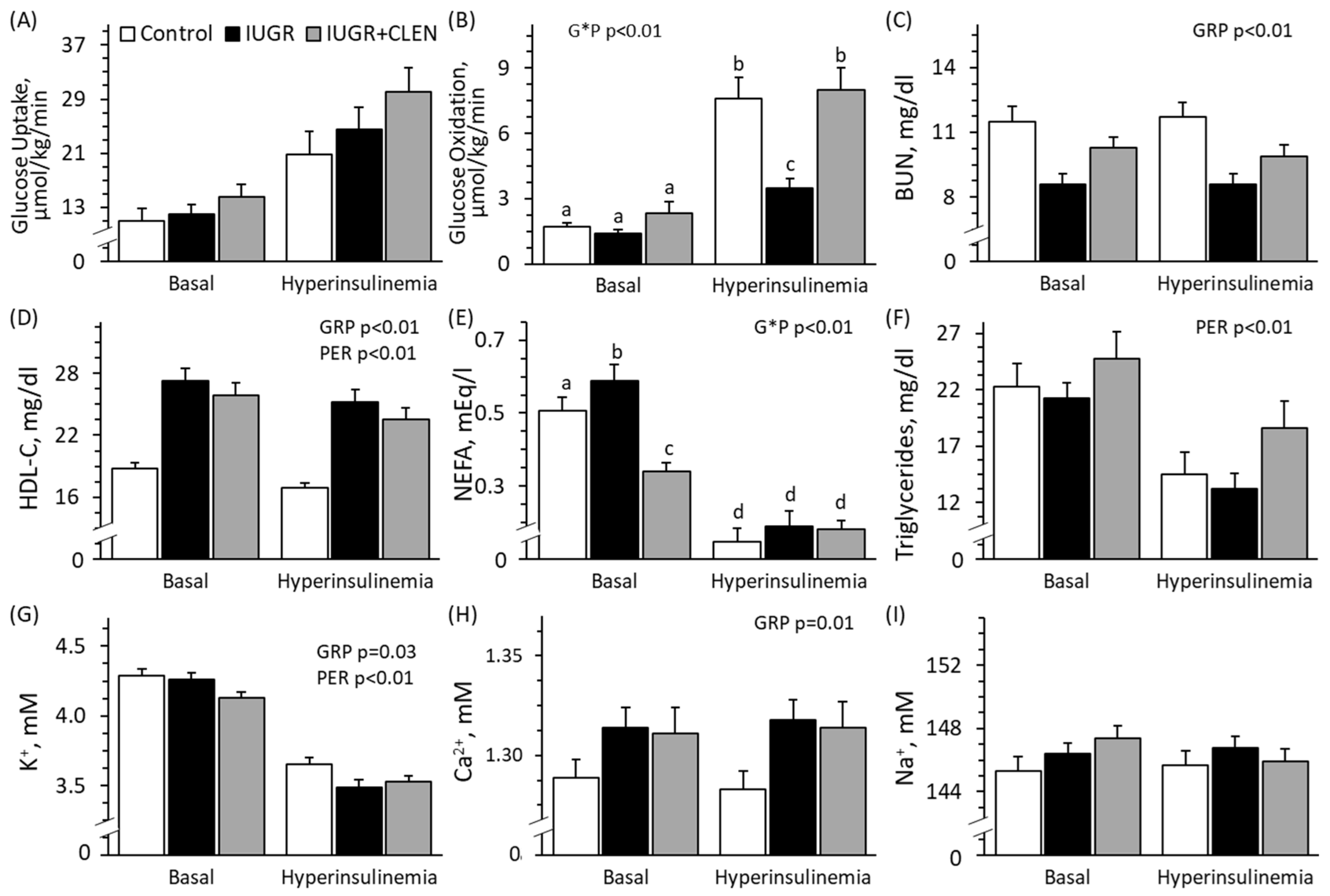
3.4. Insulin-Stimulated Hindlimb Metabolism
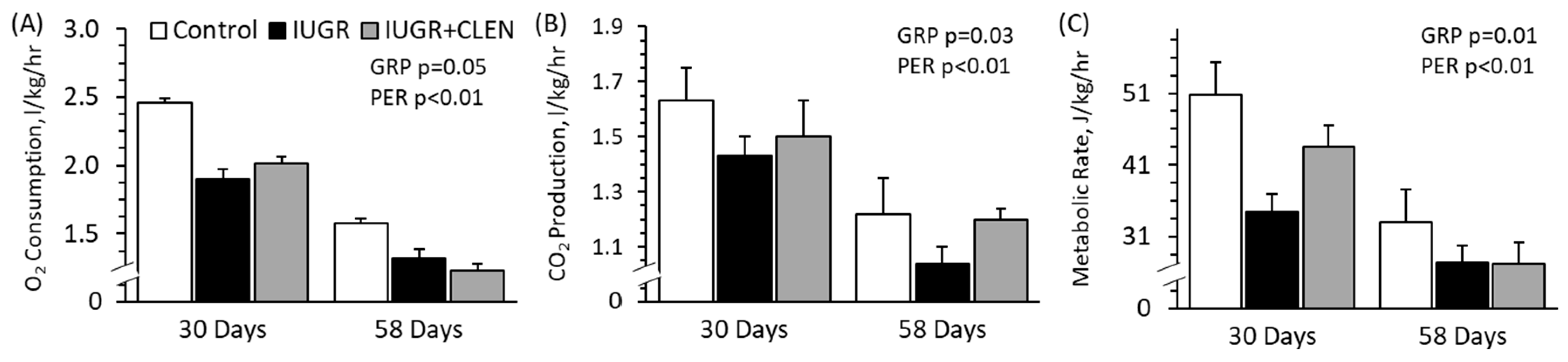
3.5. Whole-Body Oxidative Metabolism
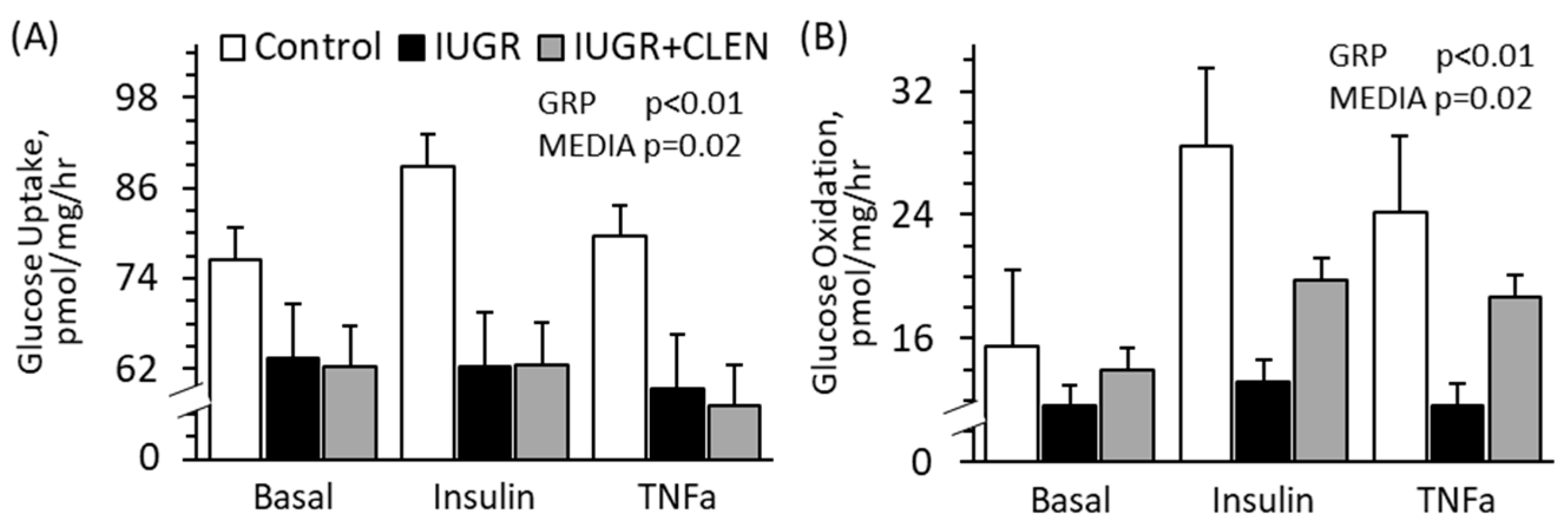
3.6. Ex Vivo Skeletal Muscle Glucose Metabolism
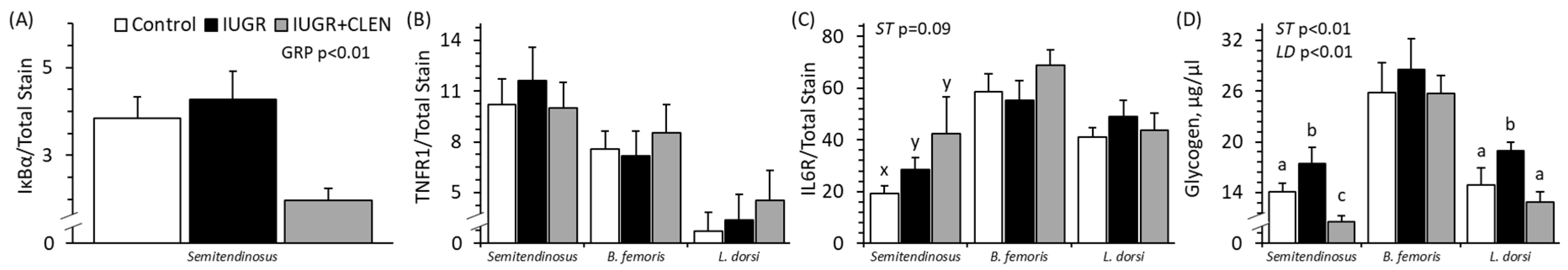
3.7. Muscle Protein and Glycogen Content
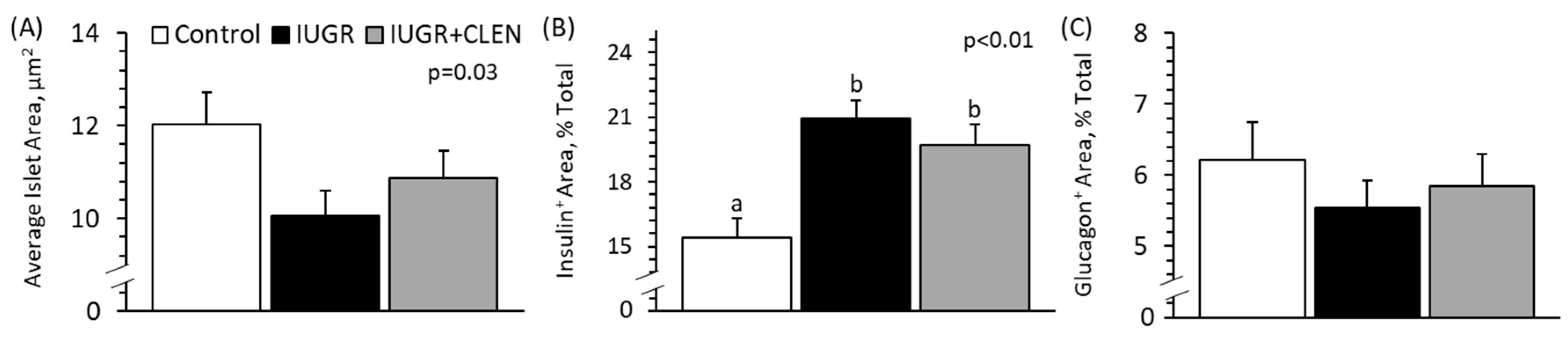
3.8. Pancreatic Islet Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, L.D. Endocrine regulation of fetal skeletal muscle growth: Impact on future metabolic health. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 221, R13–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, R.L.; Yates, D.T. The Price of Surviving on Adrenaline: Developmental Programming Responses to Chronic Fetal Hypercatecholaminemia Contribute to Poor Muscle Growth Capacity and Metabolic Dysfunction in IUGR-Born Offspring. Front. Anim. Sci. 2021, 2, 769334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.D.; Rozance, P.J.; Bruce, J.L.; Friedman, J.E.; Hay, W.W., Jr.; Wesolowski, S.R. Limited capacity for glucose oxidation in fetal sheep with intrauterine growth restriction. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R920–R928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadaret, C.N.; Merrick, E.M.; Barnes, T.L.; Beede, K.A.; Posont, R.J.; Petersen, J.L.; Yates, D.T. Sustained maternal inflammation during the early third-trimester yields intrauterine growth restriction, impaired skeletal muscle glucose metabolism, and diminished beta-cell function in fetal sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 4822–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.N.; Barker, D.J. Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: The thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Diabetologia 1992, 35, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, P.L.; Bell, A.W. Developmental Programming and Growth of Livestock Tissues for Meat Production. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2019, 35, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Jauniaux, E. Pathophysiology of placental-derived fetal growth restriction. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, S745–S761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posont, R.J.; Yates, D.T. Postnatal Nutrient Repartitioning due to Adaptive Developmental Programming. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2019, 35, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.A.; Camacho, L.E.; Pendleton, A.L.; Antolic, A.T.; Luna-Ramirez, R.I.; Kelly, A.C.; Steffens, N.R.; Anderson, M.J.; Limesand, S.W. Augmented glucose production is not contingent on high catecholamines in fetal sheep with IUGR. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 249, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.A.; Macko, A.R.; Steyn, L.V.; Anderson, M.J.; Limesand, S.W. Fetal adrenal demedullation lowers circulating norepinephrine and attenuates growth restriction but not reduction of endocrine cell mass in an ovine model of intrauterine growth restriction. Nutrients 2015, 7, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozance, P.J.; Zastoupil, L.; Wesolowski, S.R.; Goldstrohm, D.A.; Strahan, B.; Cree-Green, M.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Meschia, G.; Hay, W.W., Jr.; Wilkening, R.B.; et al. Skeletal muscle protein accretion rates and hindlimb growth are reduced in late gestation intrauterine growth-restricted fetal sheep. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Fahy, A.L.; Green, A.S.; Anderson, M.J.; Rhoads, R.P.; Limesand, S.W. β2-Adrenergic receptor desensitization in perirenal adipose tissue in fetuses and lambs with placental insufficiency-induced intrauterine growth restriction. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 3539–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, D.T.; Camacho, L.E.; Kelly, A.C.; Steyn, L.V.; Davis, M.A.; Antolic, A.T.; Anderson, M.J.; Goyal, R.; Allen, R.E.; Papas, K.K.; et al. Postnatal beta2 adrenergic treatment improves insulin sensitivity in lambs with IUGR but not persistent defects in pancreatic islets or skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 5835–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadaret, C.N.; Posont, R.J.; Swanson, R.M.; Beard, J.K.; Gibbs, R.L.; Barnes, T.L.; Marks-Nelson, E.S.; Petersen, J.L.; Yates, D.T. Intermittent maternofetal oxygenation during late gestation improved birthweight, neonatal growth, body symmetry, and muscle metabolism in intrauterine growth-restricted lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skab358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.; Brørs, O.; Dahl, H.A. Different beta-adrenergic receptor density in different rat skeletal muscle fibre types. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 76, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Sainz, R.D.; Molenaar, P.; Summers, R.J. Characterization of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in rat skeletal muscles. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 42, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.L.; Swanson, R.M.; Beard, J.K.; Hicks, Z.M.; Most, M.S.; Beer, H.N.; Grijalva, P.C.; Clement, S.M.; Marks-Nelson, E.S.; Schmidt, T.B.; et al. Daily injection of the β2 adrenergic agonist clenbuterol improved poor muscle growth and body composition in lambs following heat stress-induced intrauterine growth restriction. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1252508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leos, R.A.; Anderson, M.J.; Chen, X.; Pugmire, J.; Anderson, K.A.; Limesand, S.W. Chronic exposure to elevated norepinephrine suppresses insulin secretion in fetal sheep with placental insufficiency and intrauterine growth restriction. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E770–E778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macko, A.R.; Yates, D.T.; Chen, X.; Green, A.S.; Kelly, A.C.; Brown, L.D.; Limesand, S.W. Elevated plasma norepinephrine inhibits insulin secretion, but adrenergic blockade reveals enhanced beta-cell responsiveness in an ovine model of placental insufficiency at 0.7 of gestation. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2013, 4, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Green, A.S.; Macko, A.R.; Yates, D.T.; Kelly, A.C.; Limesand, S.W. Enhanced insulin secretion responsiveness and islet adrenergic desensitization after chronic norepinephrine suppression is discontinued in fetal sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E58–E64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beermann, D.H. Beta-Adrenergic receptor agonist modulation of skeletal muscle growth. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, E18–E23. [Google Scholar]
- van Beek, S.M.M.; Bruls, Y.M.H.; Vanweert, F.; Fealy, C.E.; Connell, N.J.; Schaart, G.; Moonen-Kornips, E.; Jorgensen, J.A.; Vaz, F.M.; Smeets, E.; et al. Effect of beta2-agonist treatment on insulin-stimulated peripheral glucose disposal in healthy men in a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholpa, N.E.; Simmons, E.C.; Crossman, J.D.; Schnellmann, R.G. Time-to-treatment window and cross-sex potential of β(2)-adrenergic receptor-induced mitochondrial biogenesis-mediated recovery after spinal cord injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 411, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, J.; Bone, D.B.J.; Knudsen, J.R.; Barella, L.F.; Liu, L.; Lee, R.; Gavrilova, O.; Chen, M.; Weinstein, L.S.; Kleinert, M.; et al. In vivo metabolic effects after acute activation of skeletal muscle G(s) signaling. Mol. Metab. 2022, 55, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.; Silva Junior, S.D.; de Carvalho, M.H.; Akamine, E.H.; Michelini, L.C.; Franco, M.C. Intrauterine growth restriction increases circulating mitochondrial DNA and Toll-like receptor 9 expression in adult offspring: Could aerobic training counteract these adaptations? J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, R.; Luo, N.; Lou, P.; Limesand, S.W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X. Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Dysregulation Associate with Enhanced Reactive Oxygen Species and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine in Low-Birth-Weight Goats. Animals 2022, 12, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posont, R.J.; Cadaret, C.N.; Beard, J.K.; Swanson, R.M.; Gibbs, R.L.; Marks-Nelson, E.S.; Petersen, J.L.; Yates, D.T. Maternofetal inflammation induced for two weeks in late gestation reduced birthweight and impaired neonatal growth and skeletal muscle glucose metabolism in lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, H.W.; Wilson, J.A.; Beever, E.A. Facing a Changing World: Thermal Physiology of American Pikas (Ochotona princeps). West. N. Am. Nat. 2015, 75, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ciurej, A.K.; Oblander, A.; Swift, A.W.; Wilson, J.A. Melanism as a potential thermal benefit in eastern fox squirrels (Sciurus niger). Eur. J. Ecol. 2019, 5, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limesand, S.W.; Jensen, J.; Hutton, J.C.; Hay, W.W., Jr. Diminished beta-cell replication contributes to reduced beta-cell mass in fetal sheep with intrauterine growth restriction. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, R1297–R1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.T.; Cadaret, C.N.; Beede, K.A.; Riley, H.E.; Macko, A.R.; Anderson, M.J.; Camacho, L.E.; Limesand, S.W. Intrauterine growth-restricted sheep fetuses exhibit smaller hindlimb muscle fibers and lower proportions of insulin-sensitive Type I fibers near term. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R1020–R1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dain, A. The incidence of freemartinism in sheep. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1971, 24, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Garcia, D.; Coleman, M.; Ekeren, P.; Lunt, D.; Wagner, K.; Procknor, M.; Welsh, T., Jr.; Smith, S. Adipose tissue, longissimus muscle and anterior pituitary growth and function in clenbuterol-fed heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 1988, 66, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.K.; Ozanne, S.E. Pathways linking the early environment to long-term health and lifespan. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 106, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, S.R.; Rozance, P.J.; Brown, L.D.; Hay, W.W. The Intrauterine Growth Restriction Phenotype: Fetal Adaptations and Potential Implications for Later Life Insulin Resistance and Diabetes. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2011, 29, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, Z.M.; Yates, D.T. Going Up Inflame: Reviewing the Underexplored Role of Inflammatory Programming in Stress-Induced Intrauterine Growth Restricted Livestock. Front. Anim. Sci. 2021, 2, 761421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadaret, C.N.; Beede, K.A.; Riley, H.E.; Yates, D.T. Acute exposure of primary rat soleus muscle to zilpaterol HCl (β2 adrenergic agonist), TNFa, or IL-6 in culture increases glucose oxidation rates independent of the impact on insulin signaling or glucose uptake. Cytokine 2017, 96, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieck, R.L.; Treffer, L.K.; Fuller, A.M.; Ponte Viana, M.; Khalimonchuk, O.; Schmidt, T.B.; Yates, D.T.; Petersen, J.L. Short Communication: Beta-adrenergic agonists alter oxidative phosphorylation in primary myoblasts. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stremming, J.; Chang, E.I.; Knaub, L.A.; Armstrong, M.L.; Baker, P.R., 2nd; Wesolowski, S.R.; Reisdorph, N.; Reusch, J.E.B.; Brown, L.D. Lower citrate synthase activity, mitochondrial complex expression, and fewer oxidative myofibers characterize skeletal muscle from growth-restricted fetal sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 322, R228–R240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendleton, A.L.; Antolic, A.T.; Kelly, A.C.; Davis, M.A.; Camacho, L.E.; Doubleday, K.; Anderson, M.J.; Langlais, P.R.; Lynch, R.M.; Limesand, S.W. Lower oxygen consumption and Complex I activity in mitochondria isolated from skeletal muscle of fetal sheep with intrauterine growth restriction. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E67–E80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsen, A.; Hostrup, M.; Backer, V.; Bangsbo, J. Effect of formoterol, a long-acting β2-adrenergic agonist, on muscle strength and power output, metabolism, and fatigue during maximal sprinting in men. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R1312–R1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, D.; Petersen, K.F.; Russell, R.R.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I. Effect of epinephrine on muscle glycogenolysis and insulin-stimulated muscle glycogen synthesis in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, E130–E138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.; Aslesen, R.; Jebens, E.; Skrondal, A. Adrenaline-mediated glycogen phosphorylase activation is enhanced in rat soleus muscle with increased glycogen content. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1472, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConville, P.; Lakatta, E.G.; Spencer, R.G. Greater glycogen utilization during 1- than 2-adrenergic receptor stimulation in the isolated perfused rat heart. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1828–E1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinovich, A.; Dehvari, N.; Aslund, A.; van Beek, S.; Halleskog, C.; Olsen, J.; Forsberg, E.; Zacharewicz, E.; Schaart, G.; Rinde, M.; et al. Treatment with a beta-2-adrenoceptor agonist stimulates glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and improves glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in mice with diet-induced obesity. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1603–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onslev, J.; Thomassen, M.; Wojtaszewski, J.; Bangsbo, J.; Hostrup, M. Salbutamol Increases Leg Glucose Uptake and Metabolic Rate but not Muscle Glycogen Resynthesis in Recovery from Exercise. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e1193–e1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.R.; Yates, D.T. Dousing the flame: Reviewing the mechanisms of inflammatory programming during stress-induced intrauterine growth restriction and the potential for ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intervention. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1250134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posont, R.J.; Most, M.S.; Cadaret, C.N.; Marks-Nelson, E.S.; Beede, K.A.; Limesand, S.W.; Schmidt, T.B.; Petersen, J.L.; Yates, D.T. Primary myoblasts from intrauterine growth-restricted fetal sheep exhibit intrinsic dysfunction of proliferation and differentiation that coincides with enrichment of inflammatory cytokine signaling pathways. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Fang, Y.; Sun, X.; Jiang, Q.; Song, C.; Chen, M.; Ding, J.; Lu, M.; Hu, G. Salmeterol, agonist of β2-aderenergic receptor, prevents systemic inflammation via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 150, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudmore, L.A.; Muurlink, T.; Whittem, T.; Bailey, S.R. Effects of oral clenbuterol on the clinical and inflammatory response to endotoxaemia in the horse. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 94, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, R.M.; Tait, R.G.; Galles, B.M.; Duffy, E.M.; Schmidt, T.B.; Petersen, J.L.; Yates, D.T. Heat stress-induced deficits in growth, metabolic efficiency, and cardiovascular function coincided with chronic systemic inflammation and hypercatecholaminemia in ractopamine-supplemented feedlot lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.H.; Nystrom, G.; Frost, R.A. Beta-adrenergic blockade exacerbates sepsis-induced changes in tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in skeletal muscle and is associated with impaired translation initiation. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2008, 64, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, E.; Yssel, J.D.; McNamara, C.; Harkin, A. Pharmacological targeting of β(2) -adrenoceptors is neuroprotective in the LPS inflammatory rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorotea, D.; Ha, H. Activation of β(2) adrenergic receptor signaling modulates inflammation: A target limiting the progression of kidney diseases. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2021, 44, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.J.; Griffin, É.; Yssel, J.D.; Ryan, K.M.; McNamee, E.N.; Harkin, A.; Connor, T.J. Stimulation of central β2-adrenoceptors suppresses NFκB activity in rat brain: A role for IκB. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, L.C.; Ryan, K.J.; Griffin, E.W.; Connor, T.J.; Harkin, A. The β2-adrenoceptor agonist clenbuterol elicits neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory and neurotrophic actions in the kainic acid model of excitotoxicity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovska, V.; Sharma, N.; Dijkstra, D.J.; Scherjon, S.A.; Jäger, A.; Schorle, H.; Plösch, T. Placental insufficiency contributes to fatty acid metabolism alterations in aged female mouse offspring. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R1107–R1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.M.; Milne, J.S.; Aitken, R.P.; Adam, C.L. Influence of birth weight and gender on lipid status and adipose tissue gene expression in lambs. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 53, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, J.M.; Hanson, C. Catecholamines inhibit growth in fetal sheep in the absence of hypoxemia. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, R1536–R1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, J.M.; Weeding, C.M.; Hanson, C. Desensitization of beta-receptor mediated responses to epinephrine in fetal lambs by prolonged ritodrine administration. Pediatr. Res. 1990, 28, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Liu, M.; Tai, W.; Yu, H.; Hao, X.; Loor, J.J.; Jiang, Q.; Fang, Z.; Gao, X.; Fan, M.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes lipolysis and reduces insulin sensitivity by activating nuclear factor kappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase in primary bovine adipocytes. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 8426–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterla, T.A.; Scanes, C.G. Effect of beta-adrenergic agonists on lipolysis and lipogenesis by porcine adipose tissue in vitro. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 68, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; She, Y.; Mangat, R.; Makarowski, A.; Roy, B.C.; Bruce, H.L.; Dyck, M.K.; Richard, C.; Proctor, S.D. Preferential deposition of dairy derived fatty acids in muscle tissue is partially due to the upregulation of CD36 in a low-birth-weight swine model. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 101, skad113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Kelly, A.C.; Luna-Ramirez, R.I.; Bidwell, C.A.; Anderson, M.J.; Limesand, S.W. Decreased Pyruvate but Not Fatty Acid Driven Mitochondrial Respiration in Skeletal Muscle of Growth Restricted Fetal Sheep. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, R.R.; Louey, S.; Thornburg, K.L. Intrauterine growth restriction elevates circulating acylcarnitines and suppresses fatty acid metabolism genes in the fetal sheep heart. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlop, K.; Cedrone, M.; Staples, J.F.; Regnault, T.R. Altered fetal skeletal muscle nutrient metabolism following an adverse in utero environment and the modulation of later life insulin sensitivity. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, M.; Gerich, J.E. Adrenergic modulation of pancreatic somatostatin, insulin, and glucagon secretion: Evidence for differential sensitivity of islet A, B, and D cells. Metabolism 1982, 31, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleson, B.; McGraw, J.; Broniowska, K.; Annamalai, M.; Chen, J.; Bushkofsky, J.; Davis, D.; Corbett, J.; Mathews, C. Distinct differences in the responses of the human pancreatic β-cell line EndoC-βH1 and human islets to proinflammatory cytokines. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R525–R534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limesand, S.W.; Rozance, P.J.; Zerbe, G.O.; Hutton, J.C.; Hay, W.W., Jr. Attenuated insulin release and storage in fetal sheep pancreatic islets with intrauterine growth restriction. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozance, P.J.; Limesand, S.W.; Zerbe, G.O.; Hay, W.W., Jr. Chronic fetal hypoglycemia inhibits the later steps of stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic beta-cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E1256–E1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kelly, A.C.; Bidwell, C.A.; Chen, X.; Macko, A.R.; Anderson, M.J.; Limesand, S.W. Chronic Adrenergic Signaling Causes Abnormal RNA Expression of Proliferative Genes in Fetal Sheep Islets. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 3565–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, R.A. Developmental origins of beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: The role of epigenetic mechanisms. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 61, 64r–67r. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, P.; Houtz, J.; Leach, S.D.; Kuruvilla, R. Sympathetic innervation during development is necessary for pancreatic islet architecture and functional maturation. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceasrine, A.M.; Lin, E.E.; Lumelsky, D.N.; Iyer, R.; Kuruvilla, R. Adrb2 controls glucose homeostasis by developmental regulation of pancreatic islet vasculature. eLife 2018, 7, e39689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, C.M.; Yang, Y.; Fu, Q.; Brown, A.S.; Yu, B.; Callaway, C.W.; Li, J.; Lane, R.H.; McKnight, R.A. IUGR prevents IGF-1 upregulation in juvenile male mice by perturbing postnatal IGF-1 chromatin remodeling. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fu, Q.; Yu, X.; Callaway, C.W.; Lane, R.H.; McKnight, R.A. Epigenetics: Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) modifies the histone code along the rat hepatic IGF-1 gene. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2438–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, S.S.; Kamna, D.; Loturco, D.; Kailey, J.; Brown, L.D. IUGR impairs cardiomyocyte growth and maturation in fetal sheep. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 239, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, F.H.; Bauer, M.K.; van Zijl, P.L.; Gluckman, P.D.; Harding, J.E. Amniotic IGF-I supplements improve gut growth but reduce circulating IGF-I in growth-restricted fetal sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E259–E269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Awede, B.L.; Thissen, J.P.; Lebacq, J. Role of IGF-I and IGFBPs in the changes of mass and phenotype induced in rat soleus muscle by clenbuterol. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E31–E37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibbs, R.L.; Wilson, J.A.; Swanson, R.M.; Beard, J.K.; Hicks, Z.M.; Beer, H.N.; Marks-Nelson, E.S.; Schmidt, T.B.; Petersen, J.L.; Yates, D.T. Daily Injection of the β2 Adrenergic Agonist Clenbuterol Improved Muscle Glucose Metabolism, Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion, and Hyperlipidemia in Juvenile Lambs Following Heat-Stress-Induced Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Metabolites 2024, 14, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030156
Gibbs RL, Wilson JA, Swanson RM, Beard JK, Hicks ZM, Beer HN, Marks-Nelson ES, Schmidt TB, Petersen JL, Yates DT. Daily Injection of the β2 Adrenergic Agonist Clenbuterol Improved Muscle Glucose Metabolism, Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion, and Hyperlipidemia in Juvenile Lambs Following Heat-Stress-Induced Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Metabolites. 2024; 14(3):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030156
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibbs, Rachel L., James A. Wilson, Rebecca M. Swanson, Joslyn K. Beard, Zena M. Hicks, Haley N. Beer, Eileen S. Marks-Nelson, Ty B. Schmidt, Jessica L. Petersen, and Dustin T. Yates. 2024. "Daily Injection of the β2 Adrenergic Agonist Clenbuterol Improved Muscle Glucose Metabolism, Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion, and Hyperlipidemia in Juvenile Lambs Following Heat-Stress-Induced Intrauterine Growth Restriction" Metabolites 14, no. 3: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030156
APA StyleGibbs, R. L., Wilson, J. A., Swanson, R. M., Beard, J. K., Hicks, Z. M., Beer, H. N., Marks-Nelson, E. S., Schmidt, T. B., Petersen, J. L., & Yates, D. T. (2024). Daily Injection of the β2 Adrenergic Agonist Clenbuterol Improved Muscle Glucose Metabolism, Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion, and Hyperlipidemia in Juvenile Lambs Following Heat-Stress-Induced Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Metabolites, 14(3), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030156





