Implementation of FAIR Practices in Computational Metabolomics Workflows—A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods: Demonstration on Making Metabolome Annotation Workflow (MAW) FAIR
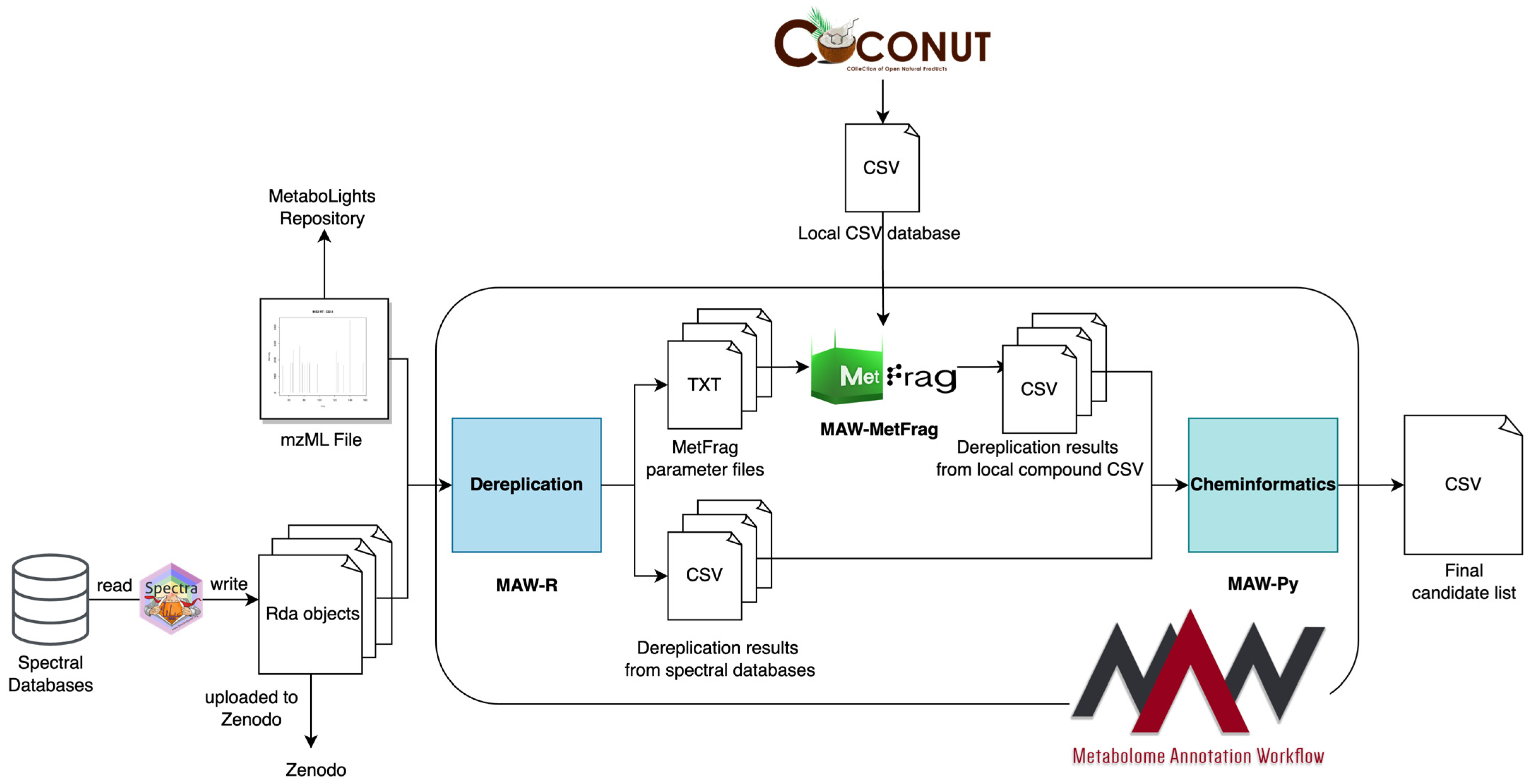
2.1. Use Case: Metabolome Annotation Workflow (MAW)
2.2. FAIRification of MAW
2.2.1. Findability
Assigning a Persistent Identifier to the Workflow (F1)
Use Descriptive Metadata (F2)
Associate Workflow with Metadata Using Identifiers (F3)
Registering to Searchable Repositories (F4)
2.2.2. Accessibility
The Workflow and Metadata Are Retrievable by Their Identifier Using a Standardised Communication Protocol (A1)
Metadata Should Be Accessible Even When the Workflow Is No Longer Available (A2)
2.2.3. Interoperability
Workflow Uses a Standardised and Interoperable Language for Representation (I1)
Use of FAIR Vocabularies (I2)
Linking Qualified References among Metadata (I3)
2.2.4. Reusability
Metadata Are Richly Described with a Plurality of Accurate and Relevant Attributes (R1)
3. Results and Discussion: Towards Reproducibility in FAIR Metabolomics Data, Software, and Workflows
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| API | Application programming interface |
| BSD | Berkeley Source Distribution |
| CLI | Command line interface |
| CSV | Comma-Separated Values |
| CWL | Common Workflow Language |
| DOI | Digital Object Identifier |
| FAIR | Findable, accessible, interoperable, reusable |
| GPL | GNU General Public License |
| GUI | Graphical user interface |
| HTTPS | Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| JSON-LD | JSON for Linked Data |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| LC-MS2 | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| MAW | Metabolome Annotation Workflow |
| MAW-Py | Metabolome Annotation Workflow—Python Segment |
| MAW-R | Metabolome Annotation Workflow—R Segment |
| OWL | Web Ontology Language |
| PID | Persistent identifier |
| RDF | Resource Description Framework |
| WfMS | Workflow management system |
| TXT | Text |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| YAML | Yet Another Markup Language or YAML ain’t markup language |
References
- Wratten, L.; Wilm, A.; Göke, J. Reproducible, scalable, and shareable analysis pipelines with bioinformatics workflow managers. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, P. Automation of in-silico data analysis processes through workflow management systems. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Boulakia, S.; Belhajjame, K.; Collin, O.; Chopard, J.; Froidevaux, C.; Gaignard, A.; Hinsen, K.; Larmande, P.; Le Bras, Y.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Scientific workflows for computational reproducibility in the life sciences: Status, challenges and opportunities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 75, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, P.; Mikheev, M.; Crusoe, M.R.; Tijanić, N.; Lampa, S. Existing Workflow Systems. Common Workflow Language wiki, GitHub. In: GitHub. Available online: https://s.apache.org/existing-workflow-systems (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Kanwal, S.; Khan, F.Z.; Lonie, A.; Sinnott, R.O. Investigating reproducibility and tracking provenance—A genomic workflow case study. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.-W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GO FAIR. FAIR Principles. Available online: https://www.go-fair.org/fair-principles/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Goble, C.; Cohen-Boulakia, S.; Soiland-Reyes, S.; Garijo, D.; Gil, Y.; Crusoe, M.R.; Peters, K.; Schober, D. FAIR Computational Workflows. Data Intell. 2020, 2, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Logan, J.; Mehta, K.; Jacobson, D.; Cashman, M.; Walker, A.M.; Eisenhauer, G.; Widener, P.; Cliff, A. Reusability First: Toward FAIR Workflows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing (CLUSTER), Portland, OR, USA, 7–10 September 2021; pp. 444–455. [Google Scholar]
- Making Computational Workflows FAIR. Available online: https://fairplus.github.io/the-fair-cookbook/content/recipes/applied-examples/fair-workflows.html (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Weigel, T.; Schwardmann, U.; Klump, J.; Bendoukha, S.; Quick, R. Making Data and Workflows Findable for Machines. Data Intell. 2020, 2, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusoe, M.; Abeln, S.; Iosup, A.; Amstutz, P.; Chilton, J.; Tijanić, N.; Ménager, H.; Soiland-Reyes, S.; Gavrilović, B.; Goble, C.; et al. Methods Included: Standardizing Computational Reuse and Portability with the Common Workflow Language. Commun. ACM 2022, 65, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.; Eisenhauer, G.; Kapadia, A.; Knight, K.; Logan, J.; Widener, P.; Wolf, M. F*** workflows: When parts of FAIR are missing. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Science (e-Science), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 11–14 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goble, C.; Soiland-Reyes, S.; Bacall, F.; Owen, S.; Williams, A.; Eguinoa, I.; Droesbeke, B.; Leo, S.; Pireddu, L.; Rodríguez-Navas, L.; et al. Implementing FAIR Digital Objects in the EOSC-Life Workflow Collaboratory. Zenodo, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soiland-Reyes, S.; Sefton, P.; Crosas, M.; Castro, L.J. Packaging research artefacts with RO-Crate. Data Sci. 2022, 5, 97–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Philtron, D.; Zhang, W.; Kechris, K.; Ghosh, D. Reproducibility of mass spectrometry based metabolomics data. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Caldwell, G.W.; Li, Y.; Lang, W.; Masucci, J. Inter-laboratory reproducibility of an untargeted metabolomics GC–MS assay for analysis of human plasma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.A.; Peltzer, A.; Fillinger, S.; Patel, H.; Alneberg, J.; Wilm, A.; Garcia, M.U.; Di Tommaso, P.; Nahnsen, S. The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M.; Gadelha, L.; Steinbeck, C.; Sorokina, M.; Peters, K. MAW: The reproducible Metabolome Annotation Workflow for untargeted tandem mass spectrometry. J. Cheminformatics 2023, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Shen, L. Advances and Trends in Omics Technology Development. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 911861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Metabolomics. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Brown, J.B.; Huang, H.; Bickel, P.J. Measuring reproducibility of high-throughput experiments. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2011, 5, 1752–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadelha, L.; Hohmuth, M.; Zulfiqar, M.; Schöne, D.; Samuel, S.; Sorokina, M.; Steinbeck, C.; König-Ries, B. Toward a Framework for Integrative, FAIR, and Reproducible Management of Data on the Dynamic Balance of Microbial Communities. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Science (e-Science), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 11–14 October 2022; pp. 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, L.; Chambers, M.; Sturm, M.; Kessner, D.; Levander, F.; Shofstahl, J.; Tang, W.H.; Römpp, A.; Neumanna, S.; Pizarro, A.D.; et al. mzML—A Community Standard for Mass Spectrometry Data. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2011, 10, R110.000133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, N.S.; Haug, K.; Conesa, P.; Jayseelan, K.; Moreno, P.; Rocca-Serra, P.; Nainala, V.C.; Spicer, R.A.; Williams, M.; Li, X.; et al. MetaboLights: An Open-Access Database Repository for Metabolomics Data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma 2016, 53, 14.13.1–14.13.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K.; et al. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainer, J.; Vicini, A.; Salzer, L.; Stanstrup, J.; Badia, J.M.; Neumann, S.; Stravs, M.A.; Hernandes, V.V.; Gatto, L.; Gibb, S.; et al. A Modular and Expandable Ecosystem for Metabolomics Data Annotation in R. Metabolites 2022, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruttkies, C.; Schymanski, E.L.; Wolf, S.; Hollender, J.; Neumann, S. MetFrag relaunched: Incorporating strategies beyond in silico fragmentation. J. Cheminformatics 2016, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokina, M.; Merseburger, P.; Rajan, K.; Yirik, M.A.; Steinbeck, C. COCONUT online: Collection of Open Natural Products database. J. Cheminformatics 2021, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dührkop, K.; Fleischauer, M.; Ludwig, M.; Aksenov, A.A.; Melnik, A.V.; Meusel, M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rousu, J.; Böcker, S. SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivian, J.; Rao, A.A.; Nothaft, F.A.; Ketchum, C.; Armstrong, J.; Novak, A.; Pfeil, J.; Narkizian, J.; Deran, A.D.; Musselman-Brown, A.; et al. Toil enables reproducible, open source, big biomedical data analyses. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonnelli, I.; Cantalupo, B.; Merelli, I.; Aldinucci, M. StreamFlow: Cross-Breeding Cloud with HPC. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2021, 9, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.; Lamothe, L.; Eldakroury, H.; Kierkegaard, M.; Priya, A.; Machinda, A.; Singh Khanduja, U.; Patoliya, D.; Rathi, R.; Che, N.; et al. EDAM: The bioscientific data analysis ontology (update 2021). F1000 Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.J.G.; Goble, C.; Jimenez, R.C. Bioschemas: From Potato Salad to Protein Annotation. In Proceedings of the ISWC 2017 Posters & Demonstrations and Industry Tracks Co-Located with 16th International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC 2017), Vienna, Austria, 23–25 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bioschemas—Bioschemas. Available online: https://bioschemas.org/ (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Zulfiqar, M.; Gadelha, L.; Steinbeck, C.; Sorokina, M.; Peters, K. Metabolome Annotation Workflow (MAW). Zenodo, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Source Initiat. The MIT License. 2006. Available online: https://opensource.org/license/mit/ (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- cwltool: The Reference Implementation of the Common Workflow Language Standards. 2023. Available online: https://cwltool.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Dearle, A. Software Deployment, Past, Present and Future. In Future Software Engineering FOSE 07; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, C.; Lu, S.; Chebotko, A.; Fotouhi, F. Prospective and Retrospective Provenance Collection in Scientific Workflow Environments. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Services Computing, Miami, FL, USA, 5–10 July 2010; pp. 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Labastida, I.; Margoni, T. Licensing FAIR Data for Reuse. Data Intell. 2020, 2, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-Y.; Colby, S.M.; Du, X.; Gomez, J.D.; Helf, M.J.; Kechris, K.; Kirkpatrick, C.R.; Li, S.; Patti, G.J.; Renslow, R.S.; et al. A Practical Guide to Metabolomics Software Development. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, C.D.; Moseley, H.N.B. The Metabolomics Workbench File Status Website: A Metadata Repository Promoting FAIR Principles of Metabolomics Data. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Huan, T. Computational Variation: An Underinvestigated Quantitative Variability Caused by Automated Data Processing in Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal Chem. 2021. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Garrett, T.J.; Brochhausen, M.; Hogan, W.R.; Lemas, D.J. A Checklist for Reproducible Computational Analysis in Clinical Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2022, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dührkop, K.; Shen, H.; Meusel, M.; Rousu, J.; Böcker, S. Searching molecular structure databases with tandem mass spectra using, CSI:FingerID. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12580–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, F.; Pon, A.; Wilson, M.; Greiner, R.; Wishart, D. CFM-ID: A web server for annotation, spectrum prediction and metabolite identification from tandem mass spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W94–W99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.; Bradbury, J.; Bergmann, S.; Capuccini, M.; Cascante, M.; de Atauri, P.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Foguet, C.; Glen, R.; Gonzalez-Beltran, A.; et al. PhenoMeNal: Processing and analysis of metabolomics data in the cloud. GigaScience 2019, 8, giy149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Johnson, C.H.; Kurczy, M.E.; Benton, H.P.; Rinehart, D.; Nguyen, T.; Ray, J.; Kuehl, J.; Arevalo, B. Interactive XCMS Online: Simplifying advanced metabolomic data processing and subsequent statistical analyses. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6931–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epskamp, S. Reproducibility and Replicability in a Fast-Paced Methodological World. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 2, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.Z.; Soiland-Reyes, S.; Sinnott, R.O.; Lonie, A.; Goble, C.; Crusoe, M.R. Sharing interoperable workflow provenance: A review of best practices and their practical application in CWLProv. GigaScience 2019, 8, giz095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M. GitHub Repository for Metabolome Annotation Workflow (MAW). 2022. Available online: www.github.com/zmahnoor14/MAW (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Zulfiqar, M. COCONUT Database January 2022 Version CSV. Zenodo, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M. Spectral Databases (GNPS, HMDB, MassBank). Zenodo, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M. MAW/Cwl/Usage_Example.Md at Main Zmahnoor14/MAW. Available online: https://github.com/zmahnoor14/MAW/blob/main/cwl/Usage_Example.md (accessed on 24 January 2024).


| FAIR Components | Docker | CWL | Bioschemas | RO-Crate | WorkflowHub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Findable | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Accessible | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Interoperable | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Reusable | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zulfiqar, M.; Crusoe, M.R.; König-Ries, B.; Steinbeck, C.; Peters, K.; Gadelha, L. Implementation of FAIR Practices in Computational Metabolomics Workflows—A Case Study. Metabolites 2024, 14, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020118
Zulfiqar M, Crusoe MR, König-Ries B, Steinbeck C, Peters K, Gadelha L. Implementation of FAIR Practices in Computational Metabolomics Workflows—A Case Study. Metabolites. 2024; 14(2):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020118
Chicago/Turabian StyleZulfiqar, Mahnoor, Michael R. Crusoe, Birgitta König-Ries, Christoph Steinbeck, Kristian Peters, and Luiz Gadelha. 2024. "Implementation of FAIR Practices in Computational Metabolomics Workflows—A Case Study" Metabolites 14, no. 2: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020118
APA StyleZulfiqar, M., Crusoe, M. R., König-Ries, B., Steinbeck, C., Peters, K., & Gadelha, L. (2024). Implementation of FAIR Practices in Computational Metabolomics Workflows—A Case Study. Metabolites, 14(2), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020118







