Prediction of Clinical Remission with Adalimumab Therapy in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis by Fourier Transform–Infrared Spectroscopy Coupled with Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
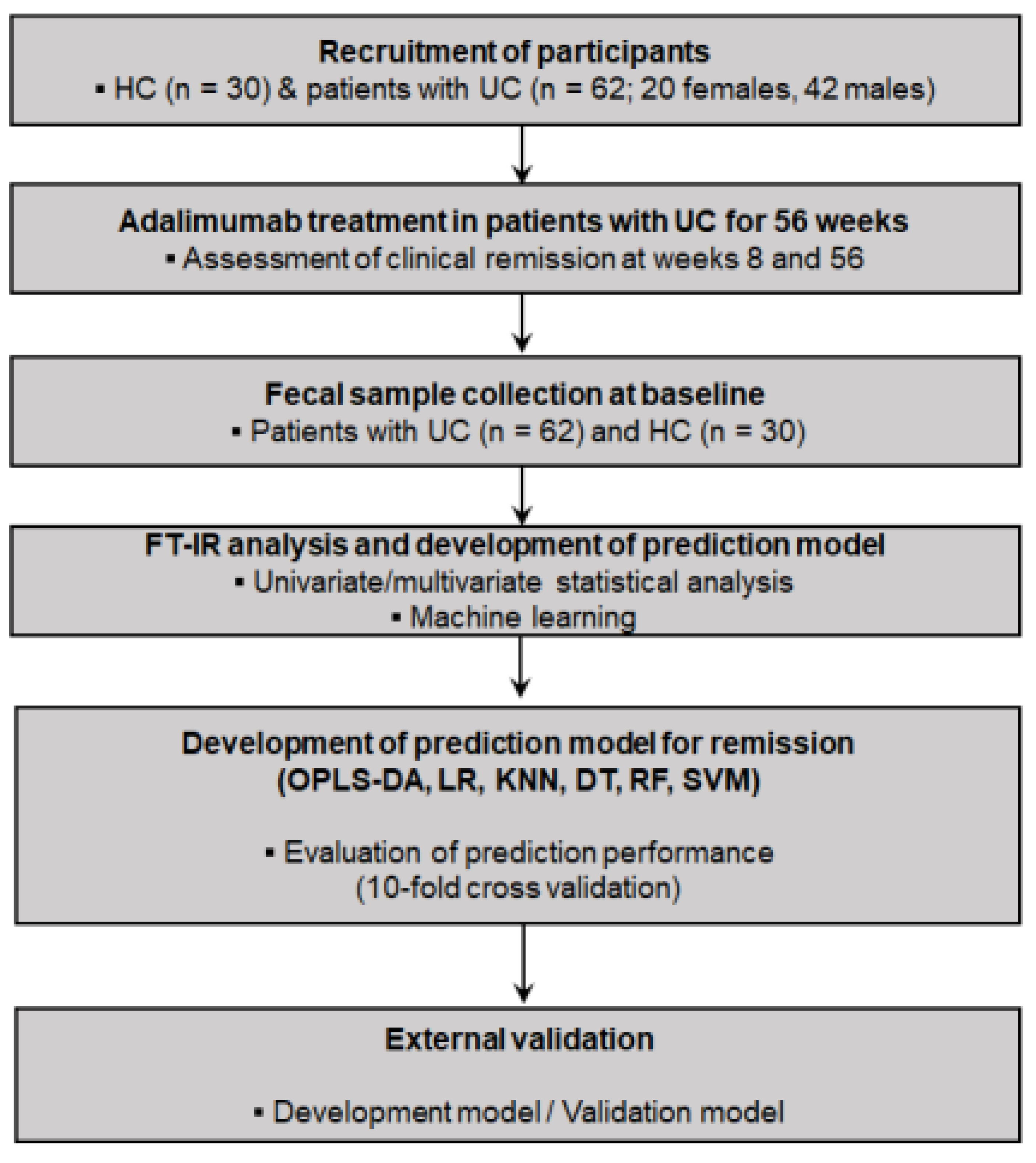
2.1. Participant Recruitment and Study Design
2.2. Patient Assessments
2.3. Fecal Sample Collection and FT–IR Spectroscopy Analysis
2.4. Spectral Data Processing
2.5. Development of Prediction Models by ML Algorithms
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Baseline Characteristics
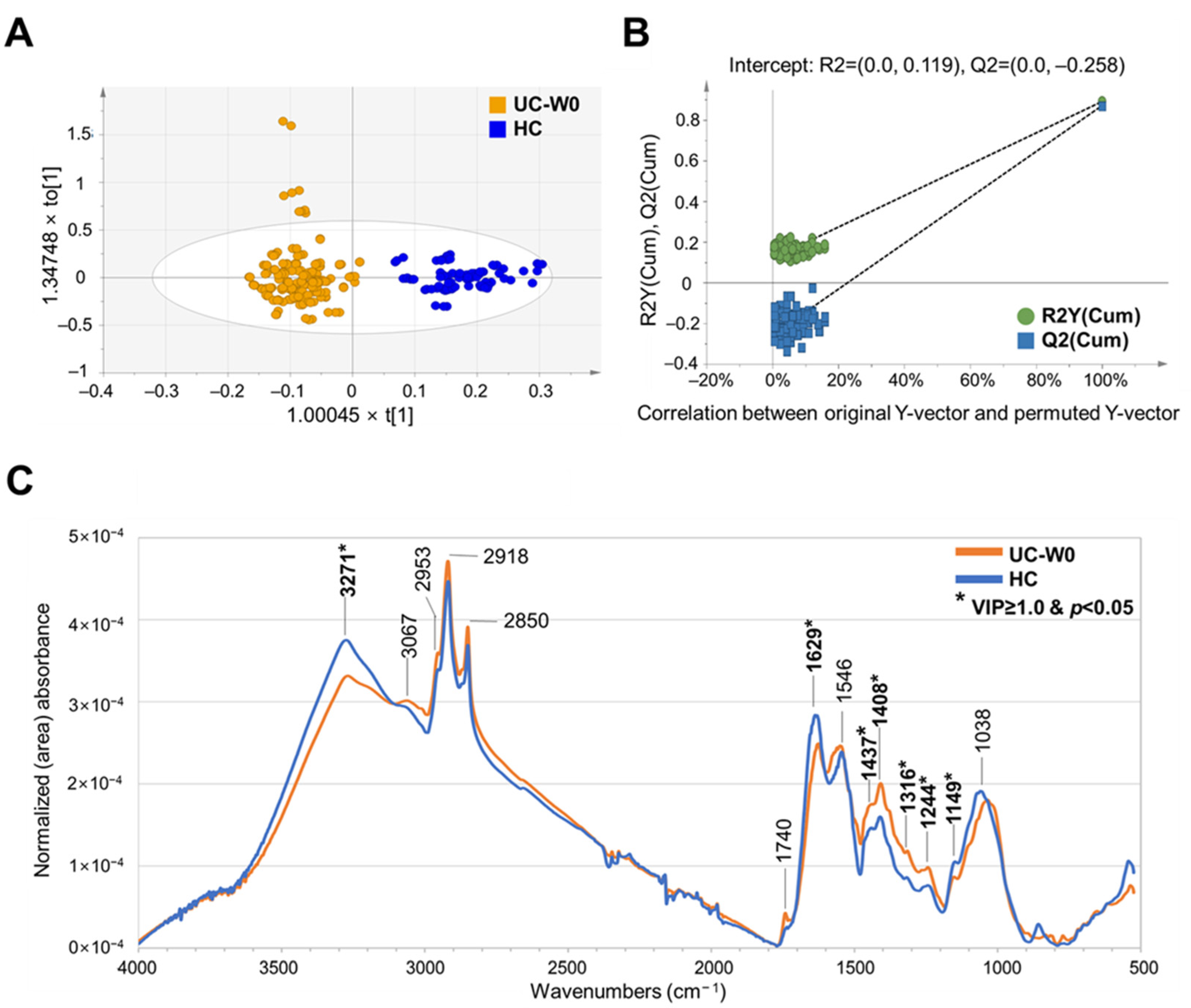
3.2. FT–IR Spectral Assignment of Fecal Samples and Discrimination of HC and Patients with UC
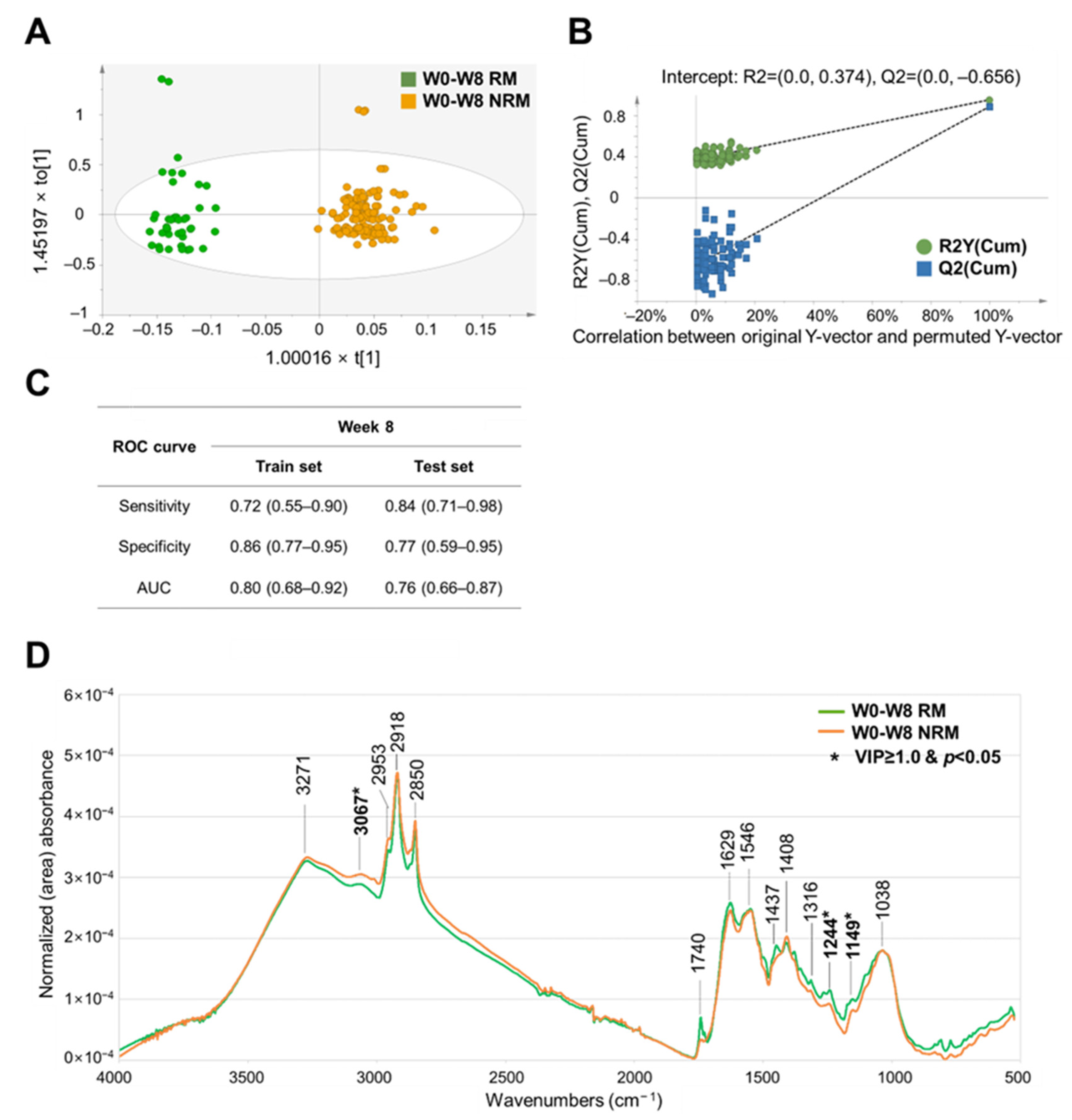
3.3. OPLS–DA-Based Prediction Model for Clinical Remission Associated with Adalimumab Treatment in Patients with UC
3.4. Comparison of the Prediction Performance of Various ML Algorithms
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Silva, B.C.; Lyra, A.C.; Rocha, R.; Santana, G.O. Epidemiology, Demographic Characteristics and Prognostic Predictors of Ulcerative Colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.T.; Meng, S.Y.; Pan, B.R. Drug Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Marín, A.C.; Chaparro, M. Systematic Review: Factors Associated with Relapse of Inflammatory Bowel Disease after Discontinuation of Anti-TNF Therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, C.J.; Hilmi, I.; Banerjee, R.; Chuah, S.W.; Ng, S.C.; Wei, S.C.; Makharia, G.K.; Pisespongsa, P.; Chen, M.H.; Ran, Z.H.; et al. Best Practices on Immunomodulators and Biologic Agents for Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease in Asia. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1296–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papamichael, K.; Gils, A.; Rutgeerts, P.; Levesque, B.G.; Vermeire, S.; Sandborn, W.J.; Vande Casteele, N. Role for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring During Induction Therapy with TNF Antagonists in IBD: Evolution in the Definition and Management of Primary Nonresponse. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, S.; Papamichael, K.; Cheifetz, A.S. Etiology and Management of Lack or Loss of Response to Anti–Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 15, 656. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6935028/ (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Roda, G.; Jharap, B.; Neeraj, N.; Colombel, J.F. Loss of Response to Anti-TNFs: Definition, Epidemiology, and Management. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.S.; Hart, A.; De Cruz, P. Systematic Review: Predicting and Optimising Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn’s Disease—Algorithm for Practical Management. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 30–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vepa, A.; Saleem, A.; Rakhshan, K.; Daneshkhah, A.; Sedighi, T.; Shohaimi, S.; Omar, A.; Salari, N.; Chatrabgoun, O.; Dharmaraj, D.; et al. Using Machine Learning Algorithms to Develop a Clinical Decision-Making Tool for COVID-19 Inpatients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waljee, A.K.; Liu, B.; Sauder, K.; Zhu, J.; Govani, S.M.; Stidham, R.W.; Higgins, P.D.R. Predicting Corticosteroid Free Endoscopic Remission with Vedolizumab in Ulcerative Colitis. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardalaç, F.; Başaranoʇlu, M.; Yüksel, M.; Kutbay, U.; Kaplan, M.; Özin, Y.Ö.; Kiliç, Z.M.Y.; Demirbaʇ, A.E.; Coşkun, O.; Aksoy, A.; et al. The Rate of Mucosal Healing by Azathioprine Therapy and Prediction by Artificial Systems. Turkish J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 26, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, I.V.; Burlacu, A.; Mihai, C. A Machine Learning Model Accurately Predicts Ulcerative Colitis Activity at One Year in Patients Treated with Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor α Agents. Medicina 2020, 56, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, N.; Aden, K.; Blase, J.I.; Baran, N.; Bordoni, D.; Tran, F.; Conrad, C.; Avalos, D.; Jaeckel, C.; Scherer, M.; et al. Longitudinal Multi-Omics Analysis Identifies Early Blood-Based Predictors of Anti-TNF Therapy Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Chaparro, M. Predictors of Primary Response to Biologic Treatment [Anti-TNF, Vedolizumab, and Ustekinumab] in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 694–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.B.; Sun, X.J.; Xu, Y.Z.; Yang, L.M.; Zhang, Y.F.; Weng, S.F.; Shi, J.S.; Wu, J.G. Diagnosis of Gastric Inflammation and Malignancy in Endoscopic Biopsies Based on Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, H.; Ghimire, H.; Hu, X.; Qin, G.; Qin, G.; Perera, A.G.U.; Perera, A.G.U.; Perera, A.G.U. Optimizing Infrared Spectral Discrimination to Enhance Disease Diagnostics: Monitoring the Signatures of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases with Anti-TNFα Therapy. Biomed. Opt. Express. 2020, 11, 4679–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus, J.; Ghimire, H.; Viennois, E.; Merlin, D.; Unil Perera, A.G. Protein Secondary Structure Analysis of Dried Blood Serum Using Infrared Spectroscopy to Identify Markers for Colitis Screening. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acri, G.; Venuti, V.; Costa, S.; Testagrossa, B.; Pellegrino, S.; Crupi, V.; Majolino, D. Raman Spectroscopy as Noninvasive Method of Diagnosis of Pediatric Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallala, J.; Jeynes, C.; Saunders, S.; Smart, N.; Lloyd, G.; Riley, L.; Salmon, D.; Stone, N. Characterization of Colorectal Mucus Using Infrared Spectroscopy: A Potential Target for Bowel Cancer Screening and Diagnosis. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakwaa, F.M.; Chaudhary, K.; Garmire, L.X. Deep Learning Accurately Predicts Estrogen Receptor Status in Breast Cancer Metabolomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, K.M.; Reinke, S.N.; Broadhurst, D.I. A Comparative Evaluation of the Generalised Predictive Ability of Eight Machine Learning Algorithms across Ten Clinical Metabolomics Data Sets for Binary Classification. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Zhang, W.; Ghosh, D.; Kechris, K. Predictive Modeling for Metabolomics Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2104, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, K.M.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Reinke, S.N. The Application of Artificial Neural Networks in Metabolomics: A Historical Perspective. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohtasham Moein, M.; Saradar, A.; Rahmati, K.; Ghasemzadeh Mousavinejad, S.H.; Bristow, J.; Aramali, V.; Karakouzian, M. Predictive Models for Concrete Properties Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches: A Review. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.Y.; Park, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Im, J.P.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, S.A.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.B.; et al. Clinical Outcomes and Predictors of Response for Adalimumab in Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: A KASID Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Intest. Res. 2022, 20, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, K.W.; Tremaine, W.J.; Ilstrup, D.M. Coated Oral 5-Aminosalicylic Acid Therapy for Mildely to Moderately Active Ulcerative Colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, K.V.; Marechal, A.; Rich, P.R. Effects of the Hydration State on the Mid-Infrared Spectra of Urea and Creatinine in Relation to Urine Analyses. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 70, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, R.; Vanga, S.; Ariese, F.; Umapathy, S. Review of Multidimensional Data Processing Approaches for Raman and Infrared Spectroscopy. EPJ Tech. Instrum. 2015, 2, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. Available online: https://www.jmlr.org/papers/volume12/pedregosa11a/pedregosa11a.pdf?ref=https:/ (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Syed-Abdul, S.; Firdani, R.P.; Chung, H.J.; Uddin, M.; Hur, M.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Gradišek, A.; Dovgan, E. Author Correction: Artificial Intelligence Based Models for Screening of Hematologic Malignancies Using Cell Population Data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The Advantages of the Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) over F1 Score and Accuracy in Binary Classification Evaluation. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.; Khan, A.; Hossain, M.E.; Moni, M.A. Comparing Different Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms for Disease Prediction. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moons, K.G.M.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Macaskill, P.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Collins, G.S. Transparent Reporting of a Multivariable Prediction Model for Individual Prognosis Or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): Explanation and Elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, W1–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, R.; Mazurak, N.; Fantasia, L.; Fusco, S.; Malek, N.P.; Wehkamp, J.; Enck, P.; Klag, T. Quality of Life in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: It Is Not All about the Bowel. Intest. Res. 2021, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuwis, M.A.; Fillet, M.; Geurts, P.; de Seny, D.; Lutteri, L.; Chapelle, J.P.; Bours, V.; Wehenkel, L.; Belaiche, J.; Malaise, M.; et al. Biomarker Discovery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Using Proteomic Serum Profiling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.; Lee, B.H.; Jung, W.M.; Chae, Y.; Lee, H. Herbal Medicine for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Development of Pattern Identification Algorithms by Retrospective Analysis of Case Series Data. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 36, 101114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasson, A.; Simrén, M.; Stotzer, P.O.; Isaksson, S.; Öhman, L.; Strid, H. Fecal Calprotectin Levels Predict the Clinical Course in Patients With New Onset of Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, W.; Bradfield, J.; Li, J.; Cardinale, C.; Frackelton, E.; Kim, C.; Mentch, F.; Van Steen, K.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Large Sample Size, Wide Variant Spectrum, and Advanced Machine-Learning Technique Boost Risk Prediction for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulai, P.S.; Singh, S.; Casteele, N.V.; Meserve, J.; Winters, A.; Chablaney, S.; Aniwan, S.; Shashi, P.; Kochhar, G.; Weiss, A.; et al. Development and Validation of Clinical Scoring Tool to Predict Outcomes of Treatment With Vedolizumab in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.U.; Comerford, R.; Comerford, F.; Ng, N.; Ng, D.; Khan, A.; Lees, C.; Hussain, A. A Comparison of Machine Learning Approaches for Predicting the Progression of Crohn’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), Batu Pahat, Malaysia, 27–29 September 2020; pp. 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayer, T.; Chhatwal, J.; Alagoz, O.; Kahn, C.E.; Woods, R.W.; Burnside, E.S. Comparison of Logistic Regression and Artificial Neural Network Models in Breast Cancer Risk Estimation. Radiographics 2010, 30, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohenford, M.A.; Lim, S.; Brown, C.; Chaudhry, M.A.; Sigdel, S.; Beckelhimer, E.; Rigas, B. FT-IR Microspectroscopy of Mouse Colon Tissues: Insight into the Chemistry of Carcinogenesis and Diagnostic Potential. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podgorelec, V.; Kokol, P.; Stiglic, B.; Rozman, I. Decision Trees: An Overview and Their Use in Medicine. J. Med. Syst. 2002, 26, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Shen, T.C.D.; Chen, E.Z.; Bittinger, K.; Bailey, A.; Roggiani, M.; Sirota-Madi, A.; Friedman, E.S.; Chau, L.; Lin, A.; et al. A Role for Bacterial Urease in Gut Dysbiosis and Crohn’s Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooks, M.G.; Veiga, P.; Wardwell-Scott, L.H.; Tickle, T.; Segata, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Beal, C.; Van Hylckama-Vlieg, J.E.T.; Ballal, S.A.; et al. Gut Microbiome Composition and Function in Experimental Colitis during Active Disease and Treatment-Induced Remission. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.; Chip, S.K.-L. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopic Imaging with Expanded Field of View to Study Formulations and Dissolution. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melucci, D.; Zappi, A.; Poggioli, F.; Morozzi, P.; Giglio, F.; Tositti, L. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy, a New Non-Destructive Approach for the Quantitative Determination of Biogenic Silica in Marine Sediments. Molecules 2019, 24, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, T.W. Scale-Based Normalization of Spectral Data. Cancer Biomark. 2006, 2, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.J.; Trevisan, J.; Bassan, P.; Bhargava, R.; Butler, H.J.; Dorling, K.M.; Fielden, P.R.; Fogarty, S.W.; Fullwood, N.J.; Heys, K.A.; et al. Using Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy to Analyze Biological Materials. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1771–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, H.; Smith, B.; Fritzsch, R.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Palmer, D.; Baker, M. Optimised Spectral Pre-Processing for Discrimination of Biofluids via ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy. Analyst 2018, 143, 6121–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr. Metabolomics 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristic | Patients with UC (n = 62) |
|---|---|
| Female/Male, n | 20/42 |
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 45.6 ± 14.9 |
| Body mass index, mean ± SD, kg/m2 | 23.2 ± 3.9 |
| Mayo score, mean ± SD | 8.5 ± 1.3 |
| Partial Mayo score, mean ± SD | 6.0 ± 1.2 |
| Endoscopic finding, n (%) | |
| Moderate | 33 (53.0) |
| Severe | 29 (47.0) |
| Disease location, n (%) | |
| Proctitis | 13 (21.0) |
| Left-sided colitis | 29 (47.0) |
| Extensive colitis | 20 (32.0) |
| Fecal calprotectin, mg/kg | |
| Mean ± SD | 668.7 ± 509.5 |
| Median | 543.1 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/dL | |
| Mean ± SD | 5.3 ± 14.2 |
| Median | 0.9 |
| IQR | 3 (0.19–3.19) |
| Albumin, g/dL | |
| Mean ± SD | 3.8 ± 0.6 |
| Median | 4.0 |
| Concomitant medication (overlapped), n (%) | |
| 5-Aminosalicylate | 51 (82.3) |
| Methotrexate | 2 (3.2) |
| Azathioprine/6-Mercaptopurine | 30 (48.4) |
| Systemic corticosteroid | 17 (27.4) |
| Prior anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy, n (%) | |
| 1 medication | 12 (19.4) |
| ≥2 medications | 0 (0) |
| Week 8 | Parameters | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1_Score | ROC–AUC | |||||
| Methods | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | |
| LR | C = 1 | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.98–1.01) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 (0.93–1.03) | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.96–1.01) | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) |
| rbf SVM | kernel = ‘rbf’, gamma = 0.0001, C = 100 | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.98–1.01) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 (0.92–1.03) | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.95–1.02) | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.96–1.02) |
| Week 56 | Parameters | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1_score | ROC–AUC | |||||
| Methods | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | |
| rbf SVM | kernel = rbf, gamma = 0.0001, C = 1000 | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.98–1.01) | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.95–1.02) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) |
| Evaluators | Week 8 (LR) | Week 56 (DT) | ||||
| Development Model (n = 51) | Validation Model (n = 11) | Development Model (n = 51) | Validation Model (n = 11) | |||
| Train (95% CI) | Test (95% CI) | Train (95% CI) | Test (95% CI) | |||
| Accuracy | 1.00 | 0.99 (0.98–1.01) | 0.73 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.90 (0.84–0.96) | 0.82 |
| Precision | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.88 (0.77–0.98) | 0.82 |
| Recall | 1.00 | 0.95 (0.84–1.06) | 0.73 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.93 (0.87–0.98) | 0.82 |
| F1_score | 1.00 | 0.97 (0.89–1.04) | 0.72 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.89 (0.82–0.96) | 0.82 |
| ROC–AUC | 1.00 | 0.98 (0.92–1.03) | 0.75 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.91 (0.85–0.96) | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-Y.; Shin, S.Y.; Saeed, M.; Ryu, J.E.; Kim, J.-S.; Ahn, J.; Jung, Y.; Moon, J.M.; Choi, C.H.; Choi, H.-K. Prediction of Clinical Remission with Adalimumab Therapy in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis by Fourier Transform–Infrared Spectroscopy Coupled with Machine Learning Algorithms. Metabolites 2024, 14, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010002
Kim S-Y, Shin SY, Saeed M, Ryu JE, Kim J-S, Ahn J, Jung Y, Moon JM, Choi CH, Choi H-K. Prediction of Clinical Remission with Adalimumab Therapy in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis by Fourier Transform–Infrared Spectroscopy Coupled with Machine Learning Algorithms. Metabolites. 2024; 14(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seok-Young, Seung Yong Shin, Maham Saeed, Ji Eun Ryu, Jung-Seop Kim, Junyoung Ahn, Youngmi Jung, Jung Min Moon, Chang Hwan Choi, and Hyung-Kyoon Choi. 2024. "Prediction of Clinical Remission with Adalimumab Therapy in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis by Fourier Transform–Infrared Spectroscopy Coupled with Machine Learning Algorithms" Metabolites 14, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010002
APA StyleKim, S.-Y., Shin, S. Y., Saeed, M., Ryu, J. E., Kim, J.-S., Ahn, J., Jung, Y., Moon, J. M., Choi, C. H., & Choi, H.-K. (2024). Prediction of Clinical Remission with Adalimumab Therapy in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis by Fourier Transform–Infrared Spectroscopy Coupled with Machine Learning Algorithms. Metabolites, 14(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010002







