Effects of Dietary Steroid Saponins on Growth Performance, Serum and Liver Glucose, Lipid Metabolism and Immune Molecules of Hybrid Groupers (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂Epinephelus lanceolatu) Fed High-Lipid Diets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Diets
2.2. Fish and Feeding Trial
2.3. Sample Collection and Chemical Analysis
2.4. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis of Gene Expression
2.5. Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Whole-Body Proximate Chemical Analysis
3.3. Serum Biochemical Indexes
3.4. Serum Antioxidative Index
3.5. Liver Histochemistry by PAS Stain
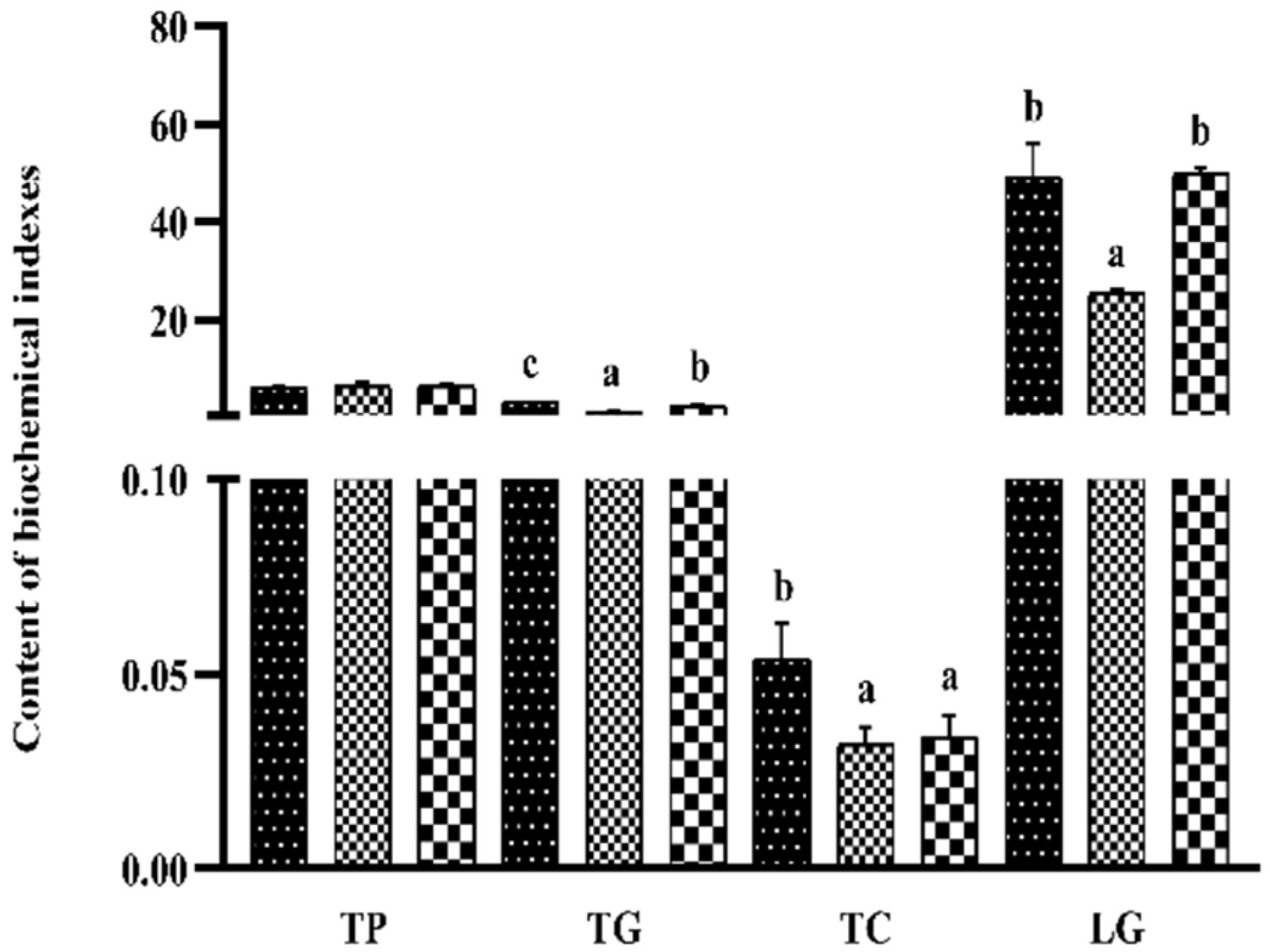
3.6. Liver Biochemical Indexes
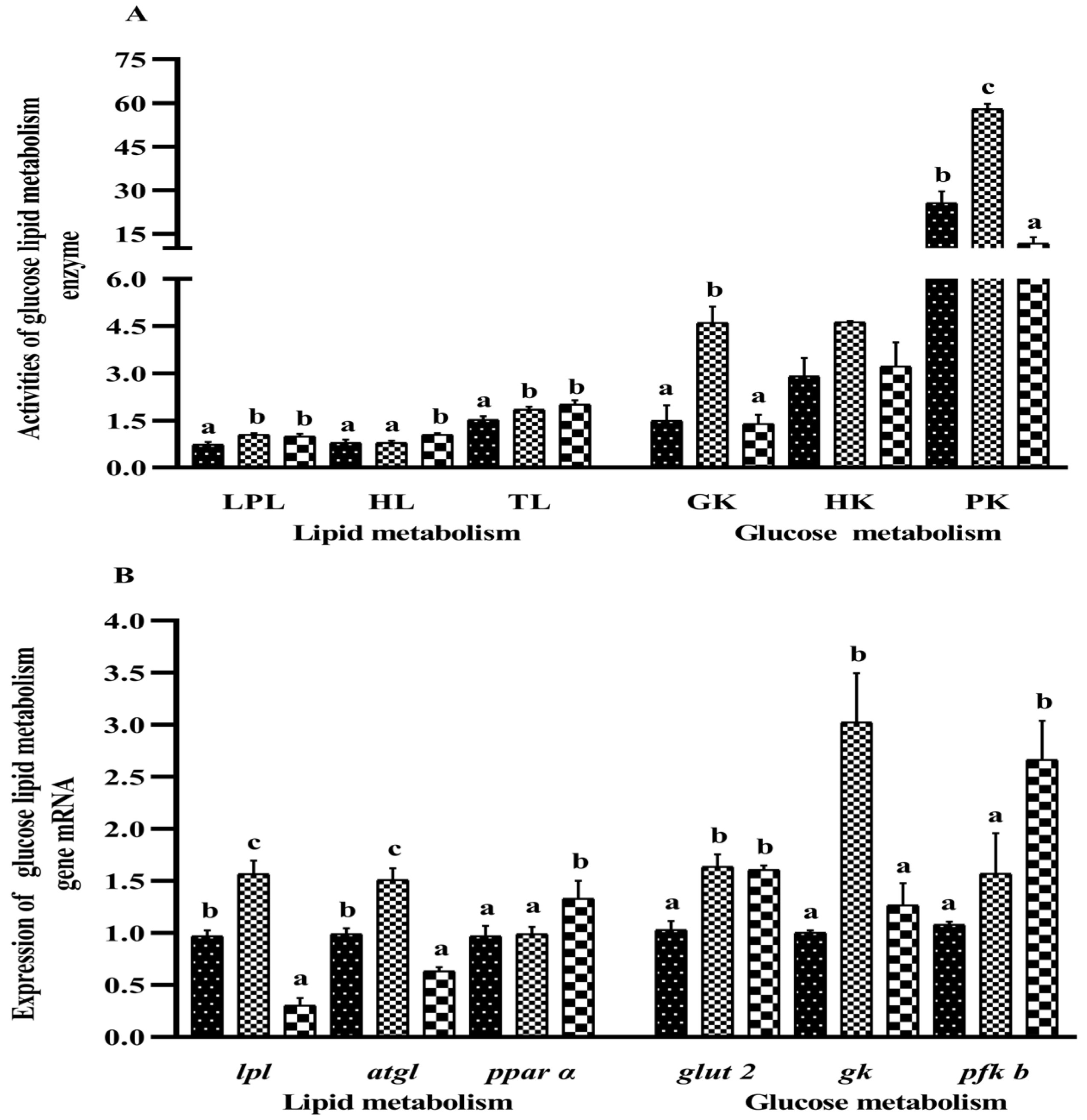
3.7. Liver Immune Molecules
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture: Towards Blue Transition; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gasco, L.; Gai, F.; Maricchiolo, G.; Genovese, L.; Ragonese, S.; Bottari, T.; Caruso, G. Fishmeal Alternative Protein Sources for Aquaculture Feeds. In Feeds for the Aquaculture Sector; Springer Briefs in Molecular Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, G.L.T.; Schneider, M. The politics of flexing soybeans: China, Brazil, and global agro-industrial restructuring. J. Peasant. Stud. 2016, 43, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ye, H.; Zou, C.; Ye, C.; Wang, A.; Lin, H. Effects of dietary ginkgo biloba leaf extract on growth performance, plasma biochemical parameters, fish composition, immune responses, liver histology, and immune and apoptosis-related genes expression of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ × Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀) fed high lipid diets. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 72, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Francis, G.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. Effects of Quillaja saponins on growth, metabolism, egg production and muscle cholesterol in individually reared Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 129, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, M.A.; Gewaily, M.S.; Monier, M.N.; Younis, E.M.; Van Doan, H.; Sewilam, H. The regulatory roles of yucca extract on the growth rate, hepato-renal function, histopathological alterations, and immune-related genes in common carp exposed with acute ammonia stress. Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.J.; Li, J.; Jin, S.X.; Xu, S.Y.; Yan, G.M.; He, Q.J. Hyperlipidemic effect of total steroidal saponins extracted from Allium chinense G. Don in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia rats. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2013, 35, 1615–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.; Yin, L.; Xu, L.; Peng, J. Application of proteomic and bioinformatic techniques for studying the hepatoprotective effect of dioscin against CCl4-induced liver damage in mice. Planta Med. 2010, 77, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, T.; Papadopoulou, K.K.; Osbourn, A. Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.; Jeena, G.S.; Shukla, R.K. Recent advances in steroidal saponins biosynthesis and in vitro production. Planta 2018, 248, 519–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-H.; Xie, G.; He, R.-R.; Zhai, Y.-J.; Li, Y.-F.; Tsoi, B.; Kurihara, H.; Yang, D.-P. Effects of a purified saponin mixture from alfalfa on plasma lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic mice. J. Health Sci. 2011, 57, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ai, Q.H.; Mai, K.M.; Xu, W.; Liufu, Z.G.; Zhang, W.B.; Cai, Y.H. Effects of dietary soybean saponins on feed intake, growth performance, digestibility, and intestinal structure in juvenile Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2011, 318, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, A.; Kortner, T.M.; Penn, M.; Bakke, A.M.; Krogdahl, A.; Oliva-Teles, A. Effects of dietary soy saponins and phytosterols on gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) during the on-growing period. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2014, 198, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.E., Jr. Effects of Quillaja saponins on growth, feed efficiency, digestive enzyme activities and metabolism of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L). Aquac. Nutr. 2013, 19, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. Dietary supplementation with a Quillaja saponin mixture improves growth performance and metabolic efficiency in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquaculture 2002, 203, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisheries Administration of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Areas; National Fisheries Technology Extension Center; China Society of Fisheries. Fishery Statistical Yearbook; Chinese Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Amenyogbe, E.; Chen, G.; Huang, J. Effects of feed fat level on growth performance, body composition and serum biochemical indices of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × Epinephelus polyphekadion). Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yan, X.; Dong, X.; Pan, S.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H. Choline Alleviates Disorders of Lipid Metabolism in Hybrid Grouper (♀ Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂ E. lanceolatus) Caused by High-Lipid. Diet. Aquac. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 998849. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.; Du, L.; Wu, J.; Gan, S.; Li, Q.; Babu, V.S.; Wu, Y.; Lin, L. Saikosaponin d alleviates high-fat-diet induced hepatic steatosis in hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ × Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀) by targeting AMPK/PPARα pathway. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, N.; Xu, X.; Xu, B. Soya-saponins induce intestinal inflammation and barrier dysfunction in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 77, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, S.; Turan, S. Comparison of proximate, fatty acid and amino acid compositions of various types of fish roes. Int. J. Food Prop. 2008, 11, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Determination of crude protein content in grain and oil seeds by dumas combustion method. Sci. Technol. Cereals Oils Foods 2018, 26, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Han, T.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Hu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Harpaz, S. Effects of dietary protein and lipid levels with different protein-to-energy ratios on growth performance, feed utilization and body composition of juvenile, red-spotted grouper (Epinephelus akaara). Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mai, K.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ai, Q. Effects of dietary lipid level on growth, fatty acid composition, digestive enzymes, and expression of some lipid metabolism related genes of orange-spotted grouper larvae (Epinephelus coioides H.). Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Yan, X.; Dong, X.; Li, T.; Suo, X.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. The positive effects of dietary inositol on juvenile hybrid grouper (♀ Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂ E. lanceolatu) fed high-lipid diets: Growth performance, antioxidant capacity and immunity. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 26, 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, S.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Han, D.; Jin, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xie, S. A high-fat diet alters lipid accumulation and oxidative stress and reduces the disease resistance of overwintering hybrid yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco♀ × P. vachelli♂). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Xu, N.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Xiang, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Mai, K.; et al. Effect of dietary bile acid (BA) on the growth performance, body composition, antioxidant responses and expression of lipid metabolism-related genes of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) fed high lipid diets. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Gu, J.N.; Penn, M.; Bakke, A.M.; Lein, I.; Krogdahl, A. Effects of diet supplementation of soya-saponins, isoflavones and phytosterols on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L) fry fed from start -feeding. Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 21, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xue, J.; Chu, W.; Hu, Y. Effects of dietary soy isoflavone and soy saponin on growth performance, intestinal structure, intestinal immunity, and gut microbiota community on rice field eel (Monopterus albus). Aquaculture 2021, 537, 736506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, D.; Li, C.; Cao, D.; Miao, L.; Ge, X.; Wang, L. Preliminarily curative effectiveness of long-term bitter melon Momordica charantia saponins administration for the glucose homeostasis of juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fed a high-starch diet. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Tan, X.; Ye, H.; Zou, C.; Ye, C.; Wang, A. Effects of dietary Panax notoginseng extract on growth performance, fish composition, immune responses, intestinal histology, and immune related genes expression of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂× Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀) fed high lipid diets. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 73, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yuan, X.; Liang, X.-F.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Fang, J.; Li, J.; He, S.; Xue, M.; et al. Adaptations of lipid metabolism and food intake in response to low and high fat diets in juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Aquaculture 2016, 457, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Hu, Y.; Peng, M.; Chu, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, L. Effects of high-fat diet on growth performance, lipid accumulation and lipid metabolism related MicroRNA/gene expression in the liver of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 234, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.-B.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Hu, C.-T.; Lin, Q.-Y.; Yue, J.-J.; Chen, L.-Q.; Zhang, M.-L.; Du, Z.-Y.; Qiao, F. The individual and combined effects of hypoxia and high-fat diet feeding on nutrient composition and flesh quality in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.H.; Tan, B.P.; Dong, X.H.; Chi, S.Y.; Liu, H.Y. Effects of different levels of Yucca schidigera extract on the growth and nonspecific immunity of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and on culture water quality. Aquaculture 2015, 439, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.; Ai, Q.; Qian, X.; Mai, K. Effects of soya saponins on feed intake, growth performance, and cholesterol metabolism in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L). Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2015, 67, 20734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, P.; Hu, Y.; Ding, S. Erchen decoction mitigates lipid metabolism disorder by the regulation of PPAR γ and LPL gene in a high-fat diet C57BL/6 mice model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fougerat, A.; Schoiswohl, G.; Polizzi, A.; Régnier, M.; Wagner, C.; Smati, S.; Fougeray, T.; Lippi, Y.; Lasserre, F.; Raho, I.; et al. ATGL-dependent white adipose tissue lipolysis controls hepatocyte PPARα activity. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.-X.; Qian, Y.-F.; Zhou, W.-H.; Wang, J.-X.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Luo, Y.; Qiao, F.; Chen, L.-Q.; Zhang, M.-L.; Du, Z.-Y. The Adaptive Characteristics of Cholesterol and Bile Acid Metabolism in Nile Tilapia Fed a High-Fat Diet. Aquac. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, J.N.; Gelman, L.; Michalik, L.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. From molecular action to physiological outputs: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are nuclear receptors at the crossroads of key cellular functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 120–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.K.; Chen, J.C. Effect of saponin immersion on enhancement of the immune response of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and its resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2008, 24, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng’ambi, J.W.; Li, R.; Mu, C.; Song, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, C. Dietary administration of saponin stimulates growth of the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus and enhances its resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 59, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Pan, S.; Li, Q.; Qi, Z.; Deng, W.; Bai, N. Protective effects of glutamine against soy saponins-induced enteritis, tight junction disruption, oxidative damage, and autophagy in the intestine of Scophthalmus maximus L. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 114, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, A.; Kortner, T.M.; Penn, M.; Bakke, A.M.; Krogdahl, Å.; Oliva-Teles, A. Effects of dietary phytosterols and soy saponins on growth, feed utilization efficiency and intestinal integrity of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) juveniles. Aquaculture 2014, 432, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Fan, Z.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Z. Effect of Yucca schidigera extract on the growth performance, intestinal antioxidant status, immune response, and tight junctions of mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 103, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urán, P.A.; Gonçalves, A.A.; Taverne-Thiele, J.J.; Schrama, J.W.; Verreth, J.A.J.; Rombout, J.H.W.M. Soybean meal induces intestinal inflammation in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2008, 25, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.M.; Salnikov, M.; Tessier, T.M.; Mymryk, J.S. Reduced MHC Class I and II Expression in HPV-Negative vs. HPV-Positive Cervical Cancers. Cells 2022, 11, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Pan, S.; Deng, W.; Li, Q.; Qi, Z.; Chen, C.; Bai, N. Effects of glutamine on the IKK/IκB/NF-кB system in the enterocytes of turbot Scophthalmus maximus L. stimulated with soya-saponins. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 119, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.Y.; Zhang, H.; Shuai, Z.F.; Rong, H.; Wang, J.P.; Li, C.H.X. Effects of β-asarone and tenuigenin on expression of SOD, GSH-PX, CAT, MDA and HO-1 in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2017, 29, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar]


| Ingredients | S0 |
|---|---|
| Fish meal | 36.00 |
| Poultry by-product meal | 10.50 |
| Soybean meal | 6.00 |
| Concentrated cottonseed protein | 19.00 |
| Wheat flour | 16.00 |
| Fish oil | 4.25 |
| Soybean oil | 4.25 |
| Choline chloride | 0.50 |
| Ca (H2PO4)2 | 1.50 |
| Vitamin C | 0.05 |
| Vitamin mix 1 | 0.50 |
| Mineral mix 1 | 0.50 |
| Betaine | 0.50 |
| Ethoxyquin | 0.10 |
| Steroid saponins | 0.00 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | 0.35 |
| Total | 100.00 |
| Proximate analysis (%) | |
| Moisture | 11.50 |
| Crude protein | 52.48 |
| Crude lipid | 13.93 |
| Crude ash | 11.74 |
| Gross energy (KJ g−1 DM) | 20.52 |
| Items | Methods | Item Code | Reference/Assay Kits/Section |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition of diets and whole body | |||
| Moisture | Drying at 105 °C to constant weight | Association of Official Analytical Chemists [21] | |
| Crude lipid | Soxhlet extractor method (Petroleum ether) | ||
| Crude ash | Combustion to a constant weight at 550 °C | ||
| Crude protein | Dumas’s combustion method | Jean Baptiste Dumas (2018) [22] | |
| Serum biochemical indexes | |||
| Total cholesterol (TC, mmol/L) | Single reagent GPO-PAP method | A111-1-1 | Assay kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China) |
| Triglyceride (TG, mmol/L) | Single reagent GPO-PAP method | A110-1-1 | |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C, mmol/L) | Microplate method | A113-1-1 | |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C, mmol/L) | Microplate method | A112-+1-1 | |
| Glucose (GLU, mmol/L) | GOD-PAP method | A154-1-1 | |
| Malondialdehyde (MDA, nmol/mgprot) | TBA method | A003-1 | |
| Superoxide dismutase (SOD, U/mL) | Hydroxylamine method | A001-2-2 | |
| Catalase (CAT, U/mL) | Ammonium molybdate method | A007-1-1 | |
| Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX, U/L) | Colorimetric method | A005-1-2 | |
| Hepatic enzyme activity | |||
| Total protein (TP, mgprot/mL) | Microplate method | A045-4-1 | |
| Liver glycogen (LG, mg/g) | Colorimetric method | A043-1-1 | |
| Total lipase U/mgprot) | Colorimetric method | A067-1 | |
| Hepatic lipase (HL, U/mgprot) | Colorimetric method | A067-1-1 | |
| Lipoprotein lipase (LPL, U/mgprot) | Colorimetric method | A067-1-2 | |
| Glucokinase (GK, ng/mL) | Competition method, ELISA kit | H439-1 | |
| Hexokinase (HK, nmol/min/mgprot) | Spectrophotometric method | A077-3 | |
| Pyruvate kinase (PK, U/mgprot) | Ultraviolet colorimetric method | A076-1-1 | |
| Histochemistry observation | |||
| Liver Section | Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) | Made by Wuhan Service Biotechnology Co, China. | |
| Target Gene | Nucleotide Sequence (5′-3′) | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|
| Lipoprotein lipase (lpl) | F: CCACCTGTTCATCGACTCCC R: TCGGACGGACCTTGTTGAT | EU683732.1 |
| Adipose triglyceride lipase (atgl) | F: GAGGACAATAAAGGCGGTGAG R: AGCTTTGTGCAGGGTGGGT | KY649281.1 |
| Peroxisome alpha (ppar α) | F: TGCTCGCCTCCAGTATGAA R: GTCCAGCTCCAGCGTGTTA | FJ196234.1 |
| Glucose transporter protein 2 (glut 2) | F: TGTTCTGCTTTTCGGCTTC R: CAGTTCCGCATTGTCTATG | KY656467 |
| Glucokinase (gk) | F: TGGGTTTTACCTTCTCCTT R: AGTCCCCTCGTCTCTTGAT | MH213270 |
| Phosphofructokinase type b (pfk b) | F: AAACGCCCATGCAAACTAC R: CAACCTCTCTGACAGCCAC | MH213271 |
| Catalase (cat) | F: GCGTTTGGTTACTTTGAGGTGA R: GAGAAGCGGACAGCAATAGGT | XM_033635388.1 |
| Superoxide dismutase (sod) | F: GGAGACAATACAAACGGGTGC R: CCAGCGTTGCCAGTCTTTA | NM001303360.1 |
| Glutathione reductase (gr) | F: CTTTCACTCCGATGTATCACGC R: GCTTTGGTAGCACCCATTTTG | XM_033633504.1 |
| MHC class II molecule (mhc ii) | F: CAGGTTCAGCAGCAGTTTGG R: AGCAGCCTGGTAGTCAATCCC | JF796053.1 |
| Transforming growth factor-β (tgf-β) | F: CGATGTCACTGACGCCCTGC R: AGCCGCGGTCATCACTTATC | GQ205390.1 |
| Interleukin-10 (il-10) | F: ACACAGCGCTGCTAGACGAG R: GGGCAGCACCGTGTTCAGAT | KJ741852.1 |
| Interferon-gamma (ifn-γ) | F: CCACCAAGATGGAGGCTAAG R: CTGCCACCTCACCATTGCT | JX013936.1 |
| Interleukin-6 (il-6) | F: CCGACAGCCCGACAGG R: CTGCTTTTCGTGGCGTTT | JN806222.1 |
| Tumor necrosis factor-α (tnf-α) | F: CTGGTGATGTGGAGATGGGTC R: CGTCGTGATGTCTGGCTTTC | HQ011925.1 |
| β-actin | F: GGCTACTCCTTCACCACCACA R: TCTGGGCAACGGAACCTCT | AY510710.2 |
| Items | S0 | S0.1 | S0.2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBW/g | 22.73 ± 0.18 | 22.62 ± 0.04 | 22.77 ± 0.10 |
| FBW/g | 102.63 ± 2.20 b | 102.67 ± 2.51 b | 96.52 ± 2.24 a |
| SR/% | 94.67 ± 6.11 | 96.00 ± 0.00 | 89.33 ± 2.31 |
| PWG/% | 351.50 ± 12.75 b | 353.96 ± 11.80 b | 323.72 ± 7.37 a |
| SGR(%/d) | 2.69 ± 0.06 b | 2.70 ± 0.05 b | 2.58 ± 0.03 a |
| PER | 1.77 ± 0.10 b | 1.81 ± 0.06 b | 1.61 ± 0.02 a |
| PDR/% | 31.57 ± 0.41 b | 31.83 ± 1.05 b | 27.9 ± 1.36 a |
| FCR | 1.05 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.02 | 1.03 ± 0.01 |
| FR(%BW/d) | 2.45 ± 0.15 | 2.40 ± 0.04 | 2.58 ± 0.06 |
| CF(g/cm3) | 2.96 ± 0.07 | 3.04 ± 0.11 | 2.82 ± 0.00 |
| HSI/% | 3.40 ± 0.03 a | 4.68 ± 0.08 b | 3.86 ± 0.54 ab |
| VSI/% | 10.31 ± 0.00 a | 13.38 ± 0.38 b | 10.35 ± 0.28 a |
| Items | S0 | S0.1 | S0.2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Moisture | 72.70 ± 0.15 | 72.53 ± 0.02 | 72.59 ± 0.06 |
| Crude protein (% DM) | 61.15 ± 0.99 | 60.74 ± 0.13 | 59.47 ± 0.64 | |
| Crude lipid (% DM) | 21.43 ± 0.20 | 21.44 ± 0.09 | 21.14 ± 0.16 | |
| Final | Moisture | 72.43 ± 0.09 | 73.06 ± 0.43 | 72.74 ± 1.00 |
| Crude protein (% DM) | 62.66 ± 0.61 | 62.79 ± 0.33 | 63.14 ± 0.74 | |
| Crude lipid (% DM) | 21.69 ± 0.61 | 21.56 ± 0.59 | 21.11 ± 0.46 | |
| Indexes | S0 | S0.1 | S0.2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| TG/(mmol/L) | 0.54 ± 0.01 b | 0.43 ± 0.02 a | 0.66 ± 0.02 c |
| TC/(mmol/L) | 2.00 ± 0.14 ab | 1.67 ± 0.14 a | 2.13 ± 0.05 b |
| LDL-C/(mmol/L) | 0.25 ± 0.04 ab | 0.12 ± 0.13 a | 0.36 ± 0.03 b |
| HDL-C/(mmol/L) | 1.11 ± 0.15 a | 2.49 ± 0.50 b | 1.86 ± 0.20 b |
| GLU/(mmol/L) | 6.31 ± 0.13 a | 8.96 ± 0.26 b | 8.45 ± 0.55 b |
| Indexes | S0 | S0.1 | S0.2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MDA/(nmol/mL) | 4.44 ± 0.22 b | 3.24 ± 0.11 a | 4.24 ± 0.21 b |
| SOD/(U/mL) | 309.52 ± 8.19 b | 427.55 ± 18.60 c | 251.81 ± 33.39 a |
| CAT/(U/mL) | 5.42 ± 0.31 a | 7.70 ± 0.56 b | 7.15 ± 0.89 b |
| GSH-PX/(U/L) | 266.52 ± 3.77 a | 285.00 ± 6.46 b | 274.57 ± 6.46 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Dong, X.; Zhang, S.; Liang, W.; Tan, B.; Chi, S. Effects of Dietary Steroid Saponins on Growth Performance, Serum and Liver Glucose, Lipid Metabolism and Immune Molecules of Hybrid Groupers (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂Epinephelus lanceolatu) Fed High-Lipid Diets. Metabolites 2023, 13, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020305
Deng H, Zhang J, Yang Q, Dong X, Zhang S, Liang W, Tan B, Chi S. Effects of Dietary Steroid Saponins on Growth Performance, Serum and Liver Glucose, Lipid Metabolism and Immune Molecules of Hybrid Groupers (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂Epinephelus lanceolatu) Fed High-Lipid Diets. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020305
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Hongjin, Jiacheng Zhang, Qihui Yang, Xiaohui Dong, Shuang Zhang, Weixing Liang, Beiping Tan, and Shuyan Chi. 2023. "Effects of Dietary Steroid Saponins on Growth Performance, Serum and Liver Glucose, Lipid Metabolism and Immune Molecules of Hybrid Groupers (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂Epinephelus lanceolatu) Fed High-Lipid Diets" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020305
APA StyleDeng, H., Zhang, J., Yang, Q., Dong, X., Zhang, S., Liang, W., Tan, B., & Chi, S. (2023). Effects of Dietary Steroid Saponins on Growth Performance, Serum and Liver Glucose, Lipid Metabolism and Immune Molecules of Hybrid Groupers (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂Epinephelus lanceolatu) Fed High-Lipid Diets. Metabolites, 13(2), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020305






