Risk of Major Cardiovascular Disease after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study on Dialysis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Independent Variables
2.5. Outcome Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Primary Outcome
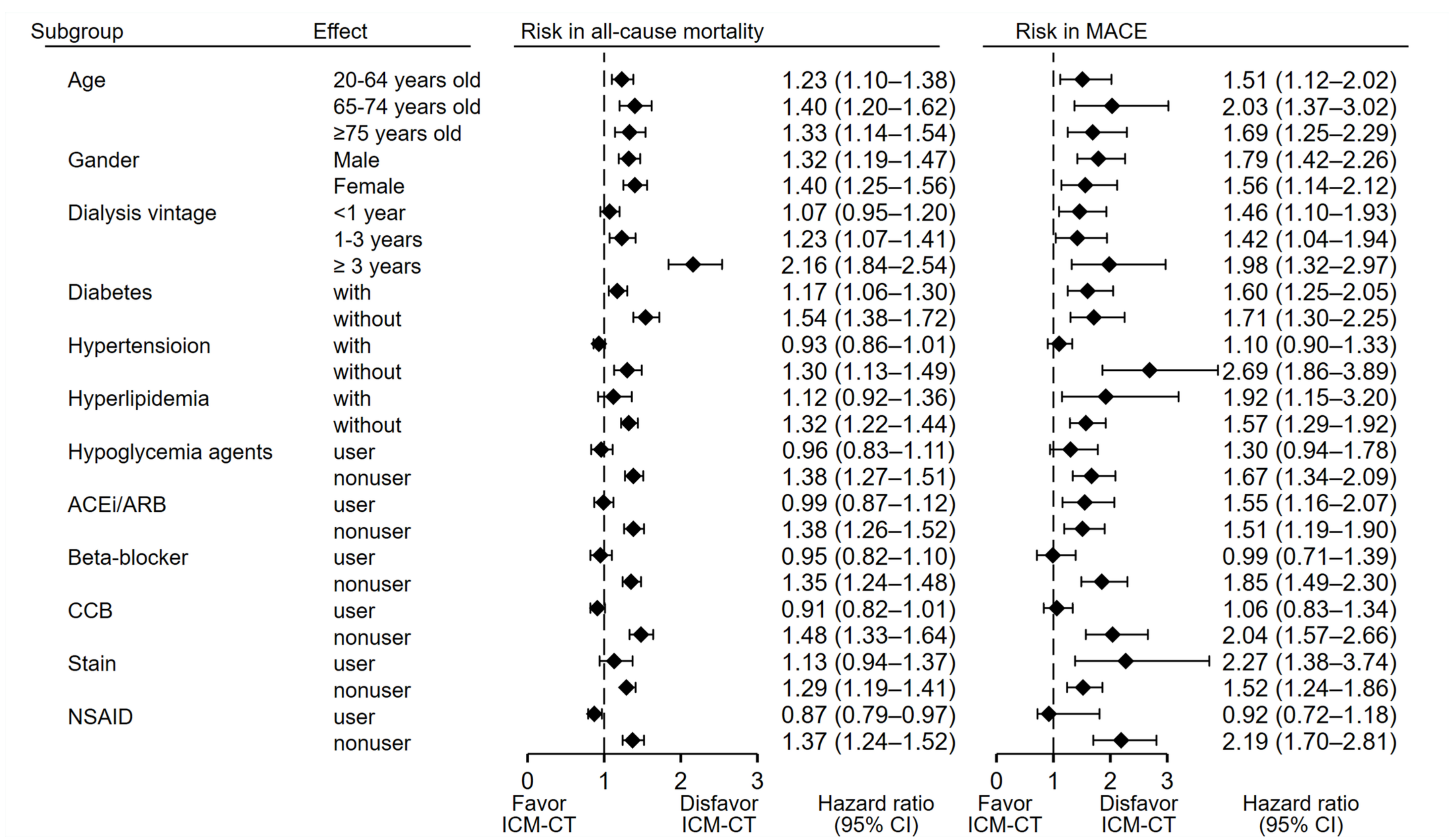
3.3. Sensitivity and Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheung, A.K.; Sarnak, M.J.; Yan, G.; Berkoben, M.; Heyka, R.; Kaufman, A.; Lewis, J.; Rocco, M.; Toto, R.; Windus, D.; et al. Cardiac diseases in maintenance hemodialysis patients: Results of the HEMO Study. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 2380–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, R.N.; Parfrey, P.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32, S112–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.S.; Matsushita, K.; Woodward, M.; Bilo, H.J.; Chalmers, J.; Heerspink, H.J.; Lee, B.J.; Perkins, R.M.; Rossing, P.; Sairenchi, T.; et al. Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without diabetes: A meta-analysis of 1 024 977 individuals. Lancet 2012, 380, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodi, B.K.; Matsushita, K.; Woodward, M.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Cirillo, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Rossing, P.; Sarnak, M.J.; Stengel, B.; Yamagishi, K.; et al. Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without hypertension: A meta-analysis. Lancet 2012, 380, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadmehrabi, S.; Tang, W.H.W. Hemodialysis-induced cardiovascular disease. Semin. Dial. 2018, 31, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, M.; Mangano, M.; Stucchi, A.; Ciceri, P.; Conte, F.; Galassi, A. Cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, iii28–iii34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Golembiewska, E.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. End-Stage Renal Disease, Inflammation and Cardiovascular Outcomes. Contrib. Nephrol. 2017, 191, 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Haugen, E.; Nath, K.A. The involvement of oxidative stress in the progression of renal injury. Blood Purif. 1999, 17, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.S. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and reactive oxygen species: Unwelcome twin visitors to the cardiovascular and kidney disease tables. Hypertension 2012, 59, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.L.; Chonchol, M. Does inflammation affect outcomes in dialysis patients? Semin. Dial. 2018, 31, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.M.; Chuang, Y.W.; Huang, S.T.; Huang, J.A.; Chen, C.H. Risk of Dementia after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbruno, U.; De Caterina, R. Vasomotor effects of iodinated contrast media: Just side effects? Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2003, 1, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, M.; Röhling, D.; Zahorsky, R.; Höfig, M.; Herrmann, G.; Simon, R. Hemodynamic effects of non-ionic iomeprol 350 and ionic diatrizoate 370 during levocardiography and coronary angiography—Double-blind randomized comparison of 2 contrast media. Z. Kardiol. 1994, 83, 626–633. [Google Scholar]
- Aguejouf, O.; Malfatti, E.; Doutremepuich, F.; Doutremepuich, C. Thrombogenic potential of contrast media in an experimental model of laser-induced thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2000, 100, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepenbroek, S.M.; de Jonghe, A.; van Rees, C.; Seebus, E. Heart failure as a serious complication of iodinated contrast-induced hyperthyroidism: Case-report. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Insurance Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan, R.O.C. National Health Insurance Annual Report 2015–2016. Available online: https://www.nhi.gov.tw/Resource/webdata/30285_1_National%20Health%20Insurance%20in%20Taiwan%202015–2016%20(bilingual).pdf (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- National Health Insurance Research Database, Taiwan (2022). Available online: https://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/ (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Quan, H.; Sundararajan, V.; Halfon, P.; Fong, A.; Burnand, B.; Luthi, J.C.; Saunders, L.D.; Beck, C.A.; Feasby, T.E.; Ghali, W.A. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med. Care. 2005, 43, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.L.; Chien, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Lin, S.J.; Yang, Y.H. Validity of in-hospital mortality data among patients with acute myocardial infarction or stroke in National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 201, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Su, C.C.; Shao, S.C.; Sung, S.F.; Lin, S.J.; Kao Yang, Y.H.; Edward Lai, C.C. Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database: Past and future. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.J.; Fine, J. A proportional hazards regression model for the subdistribution with right-censored and left-truncated competing risks data. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 1933–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latouche, A.; Allignol, A.; Beyersmann, J.; Labopin, M.; Fine, J.P. A competing risks analysis should report results on all cause-specific hazards and cumulative incidence functions. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younathan, C.M.; Kaude, J.V.; Cook, M.D.; Shaw, G.S.; Peterson, J.C. Dialysis is not indicated immediately after administration of non-ionic contrast agents in patients with end-stage renal disease treated by maintenance dialysis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 163, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamani, A.; Petitclerc, T.; Jacobs, C.; Deray, G. Is dialysis indicated immediately after administration of iodinated contrast agents in patients on haemodialysis? Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1998, 13, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harazawa, H.; Yamazaki, C.; Mazuki, K. Side effects and pharmacokinetics of non ionic contrast media in hemodialyzed patients. Nippon. Igazku Hoashasen Gakkai Zasshi. 1990, 50, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Telgte, A.; van Leijsen, E.M.C.; Wiegertjes, K.; Klijn, C.J.M.; Tuladhar, A.M.; de Leeuw, F.E. Cerebral small vessel disease: From a focal to a global perspective. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.F.; Safar, M.E. Relationship between aortic stiffening and microvascular disease in brain and kidney: Cause and logic of therapy. Hypertension 2005, 46, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovecchio, P.M.; Thomas, G.D.; Mikulski, Z.; Ehinger, E.; Mueller, K.A.L.; Blatchley, A.; Wu, R.; Miller, Y.I.; Nguyen, A.T.; Taylor, A.M.; et al. Scavenger Receptor CD36 Directs Nonclassical Monocyte Patrolling Along the Endothelium During Early Atherogenesis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C.R.; Stuart, L.M.; Wilkinson, K.; van Gils, J.M.; Deng, J.; Halle, A.; Rayner, K.J.; Boyer, L.; Zhong, R.; Frazier, W.A.; et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a Toll-like receptor 4 and 6 heterodimer. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, J.J.; MacLauchlan, S.; Zuriaga, M.A.; Polackal, M.N.; Ostriker, A.C.; Chakraborty, R.; Wu, C.L.; Sano, S.; Muralidharan, S.; Rius, C.; et al. Clonal hematopoiesis associated with TET2 deficiency accelerates atherosclerosis development in mice. Science 2017, 355, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefond, A.; Skrobek, B.; Lobbens, S.; Eury, E.; Thuillier, D.; Cauchi, S.; Lantieri, O.; Balkau, B.; Riboli, E.; Marre, M.; et al. Association between large detectable clonal mosaicism and type 2 diabetes with vascular complications. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cull, A.H.; Snetsinger, B.; Buckstein, R.; Wells, R.A.; Rauh, M.J. Tet2 restrains inflammatory gene expression in macrophages. Exp. Hematol. 2017, 55, 56–70.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.; Chung, H.; Komada, T. Renal immune surveillance and dipeptidase-1 contribute to contrast-induced acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2894–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, N.; Mou, S.; Zhang, M.; Gu, L.; Shao, X.; Wang, Q.; Qi, C.; Li, S.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome mediates contrast media-induced acute kidney injury by regulating cell apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeoka, A.A.; Mueller, J.L.; Kambo, A. An inflammasome-independent role for epithelial-expressed Nlrp3 in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6277–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilaysane, A.; Chun, J.; Seamone, M.E. The NLRP3 inflammasome promotes renal inflammation and contributes to CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1732–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulay, S.R.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Rupanagudi, K.V. Calcium oxalate crystals induce renal inflammation by NLRP3-mediated IL-1β secretion. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagny, J.Y.; Gaux, J.C. New non-ionic contrast: Effects on the cardiovascular system. Eur. J. Radiol. 1996, 23, S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, S.; Freedman, B.I. Mechanisms of Stroke in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 50, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, R.; Simon, N.; Markus, R.; Muller, D.W.; Kathir, K. Contrast-induced encephalopathy following cardiac catheterization. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 90, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Mori, T.; Tajiri, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; Nakazaki, M. Repeated injection of contrast media inducing dysfunction of the blood-brain barrier: Case report. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2013, 53, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, N.; Izumi, T.; Miyachi, S.; Ota, K.; Wakabayashi, T. Contrast-induced Encephalopathy Following Embolization of Intracranial Aneurysms in Hemodialysis Patients. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2017, 57, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandfort, V.; Persson, M.; Pourmorteza, A.; Noël, P.B.; Fleischmann, D.; Willemink, M.J. Spectral photon-counting CT in cardiovascular imaging. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2021, 15, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
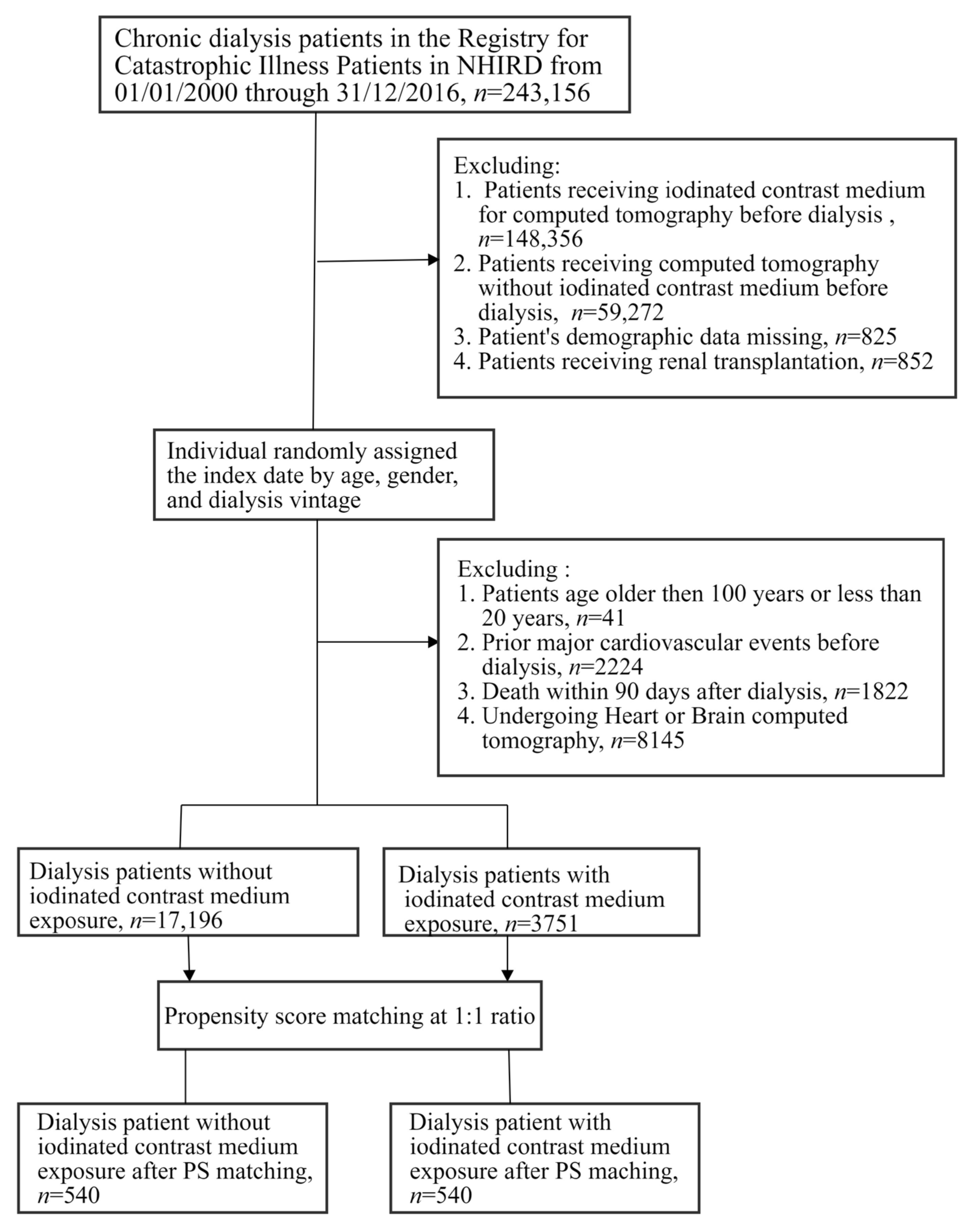

| Before PSM † | After PSM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | ICM-CT Group N = 3751 | Non-ICM Group N = 17,196 | p Value | ICM-CT Group N = 540 | Non-ICM Group N = 540 | p Value |
| Age group | ||||||
| Mean(SD) | 57.2 (15.7) | 62.7 (12.8) | <0.001 | 63.1 (16.7) | 55.0 (15.6) | <0.001 |
| Gender | 0.045 | <0.001 | ||||
| Male | 1708 (45.5) | 8140 (47.3) | 241 (44.6) | 309 (57.2) | ||
| Female | 2043 (54.5) | 9056 (52.7) | 299 (55.4) | 231 (42.8) | ||
| Premium level (NT$) | 0.33 | 0.20 | ||||
| <22,000 or low income | 2126 (56.7) | 9956 (57.9) | 285 (52.8) | 283 (52.4) | ||
| 45,000–22,000 | 1397 (37.2) | 6265 (36.4) | 228 (42.2) | 216 (40.0) | ||
| >45,000 | 228 (6.1) | 975 (5.7) | 27 (5) | 41 (7.6) | ||
| Urbanization | <0.001 | 0.74 | ||||
| Highly | 1006 (26.8) | 4844 (28.2) | 141 (26.1) | 154 (28.5) | ||
| Median | 1808 (48.2) | 7635 (44.4) | 261 (48.3) | 259 (48) | ||
| Township | 510 (13.6) | 2570 (14.9) | 72 (13.3) | 70 (13) | ||
| Rural area | 427 (11.4) | 2147 (12.5) | 66 (12.2) | 57 (10.6) | ||
| Comorbidity | ||||||
| Hypertension | 2961 (78.9) | 3743 (21.8) | <0.001 | 363 (67.2) | 416 (77) | <0.001 |
| Diabetic | 1516 (40.4) | 5288 (30.8) | <0.001 | 236 (43.7) | 190 (35.2) | 0.004 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 902 (24) | 1248 (7.3) | <0.001 | 131 (24.3) | 127 (23.5) | 0.78 |
| Dysrhythmia | 336 (9.0) | 281 (1.6) | <0.001 | 27 (5.0) | 24 (4.4) | 0.67 |
| COPD | 816 (21.8) | 722 (4.2) | <0.001 | 68 (12.6) | 69 (12.8) | 0.93 |
| Liver disease | 1008 (26.9) | 938 (5.5) | <0.001 | 89 (16.5) | 79 (14.6) | 0.40 |
| CCI scores | ||||||
| Mean(SD) | 4.3 (1.8) | 3.5 (1.5) | <0.001 | 3.4 (1.2) | 3.5 (1.4) | <0.001 |
| Dialysis vintage, years | 2.8 (3.1) | 3.0 (3.4) | 0.013 | 2.2 (2.8) | 2.6 (3) | <0.001 |
| Concurrent medications | ||||||
| Hypoglycemia agents | 1432 (38.2) | 1556 (9.0) | <0.001 | 95 (17.6) | 73 (13.5) | 0.063 |
| ACEI/ARB | 1240 (33.1) | 1249 (7.3) | <0.001 | 147 (27.2) | 139 (25.7) | 0.58 |
| Beta blocker | 1899 (50.6) | 1887 (11) | <0.001 | 131 (24.3) | 105 (19.4) | 0.06 |
| CCB | 1092 (29.1) | 1022 (5.9) | <0.001 | 203 (37.6) | 159 (29.4) | 0.005 |
| Diuretics | 825 (22) | 878 (5.1) | <0.001 | 114 (21.1) | 76 (14.1) | 0.002 |
| Statins | 1432 (38.2) | 1556 (9) | <0.001 | 77 (14.3) | 95 (17.6) | 0.13 |
| NSAIDs | 1577 (42) | 1453 (8.4) | <0.001 | 143 (26.5) | 131 (24.3) | 0.40 |
| Follow-up time, years | 5.6 (4.6) | 11.3 (5.5) | <0.001 | 3.3 (3.7) | 4.9 (4.7) | <0.001 |
| ICM-CT Cohort N = 3751 | Non-ICM Cohort N = 17,196 | Crude Model | Adjusted Model † | After Propensity Matched Adjusted Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Event | IR | Event | IR | cHR (95% CI) | p Value | aHR (95% Confidence Interval) | p Value | Propensity Score–Matched HRs (95% Confidence Interval) | p Value |
| All-cause mortality | 2042 | 96.49 | 2396 | 12.3 | 5.29 (4.98–5.61) | <0.001 *** | 1.36 (1.26–1.47) | <0.001 *** | 1.66 (1.35–2.04) | <0.001 *** |
| Hospitalization for | ||||||||||
| MACE | 347 | 29.65 | 390 | 5.46 | 5.54 (4.76–6.44) | <0.001 *** | 1.67 (1.39–2.01) | <0.001 *** | 3.90 (2.08–7.33) | <0.001 *** |
| ACS | 64 | 5.29 | 45 | 0.63 | 9.98 (6.60–15.1) | <0.001 *** | 2.92 (1.72–4.94) | <0.001 *** | 4.72 (0.48–46.2) | 0.18 |
| AMI | 46 | 3.8 | 26 | 0.36 | 12.1 (7.20–20.3) | <0.001 *** | 3.94 (2.01–7.70) | 0.10 | - | |
| SCA | 31 | 2.56 | 30 | 0.42 | 5.43 (3.28–8.99) | <0.001 *** | 1.69 (0.90–3.18) | <0.001 *** | 6.33 (1.01–39.5) | 0.048 * |
| Heart failure | 153 | 12.81 | 189 | 2.64 | 6.08 (4.82–7.67) | <0.001 *** | 1.71 (1.28–2.27) | <0.001 *** | 3.13 (1.29–7.60) | 0.011 * |
| Stroke | 165 | 13.86 | 161 | 2.24 | 5.20 (4.18–6.47) | <0.001 *** | 1.84 (1.45–2.35) | <0.001 *** | - | |
| Outcome | The Subdistribution Competing Risk Adjusted Hazard Model † | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| aSHR (95% Confidence Interval) | p Value | ||
| Non-ICM Cohort N = 17,196 | ICM-CT Cohort N = 3751 | ||
| Hospitalization for | |||
| MACE | 1 (Reference) | 1.79 (1.46–2.20) | <0.001 *** |
| ACS | 1 (Reference) | 3.14 (1.77–5.56) | <0.001 *** |
| AMI | 1 (Reference) | 3.98 (1.87–8.48) | <0.001 *** |
| Sudden cardiac arrest | 1 (Reference) | 1.39 (0.71–2.71) | 0.33 |
| Heart failure | 1 (Reference) | 1.75 (1.29–2.38) | <0.001 *** |
| Stroke | 1 (Reference) | 2.01 (1.52–2.66) | <0.001 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.-T.; Yu, T.-M.; Chen, C.-H.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chuang, Y.-W.; Cheng, C.-H.; Liu, J.-S.; Hsu, C.-C.; Wu, M.-J. Risk of Major Cardiovascular Disease after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study on Dialysis Patients. Metabolites 2023, 13, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020266
Huang S-T, Yu T-M, Chen C-H, Cheng Y-C, Chuang Y-W, Cheng C-H, Liu J-S, Hsu C-C, Wu M-J. Risk of Major Cardiovascular Disease after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study on Dialysis Patients. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020266
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shih-Ting, Tung-Min Yu, Chia-Hsin Chen, Yun-Chung Cheng, Ya-Wen Chuang, Cheng-Hsu Cheng, Jia-Sin Liu, Chih-Cheng Hsu, and Ming-Ju Wu. 2023. "Risk of Major Cardiovascular Disease after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study on Dialysis Patients" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020266
APA StyleHuang, S.-T., Yu, T.-M., Chen, C.-H., Cheng, Y.-C., Chuang, Y.-W., Cheng, C.-H., Liu, J.-S., Hsu, C.-C., & Wu, M.-J. (2023). Risk of Major Cardiovascular Disease after Exposure to Contrast Media: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study on Dialysis Patients. Metabolites, 13(2), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020266







