Placental Metabolomics of Fetal Growth Restriction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
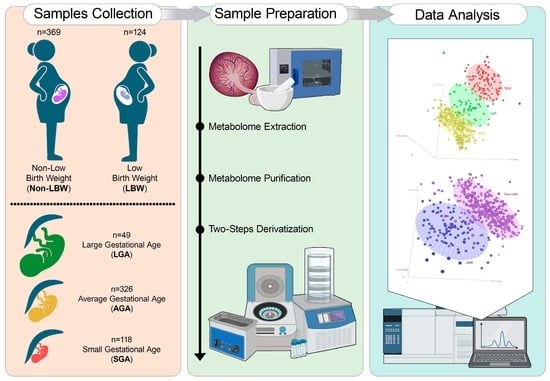
2.1. Tissue Collection
2.2. Birth Weight Centile Calculation
2.3. Metabolite Extraction, Purification and Derivatization
2.4. GC–MS Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Demographics Data Comparison
2.5.2. Metabolomic Data Analysis
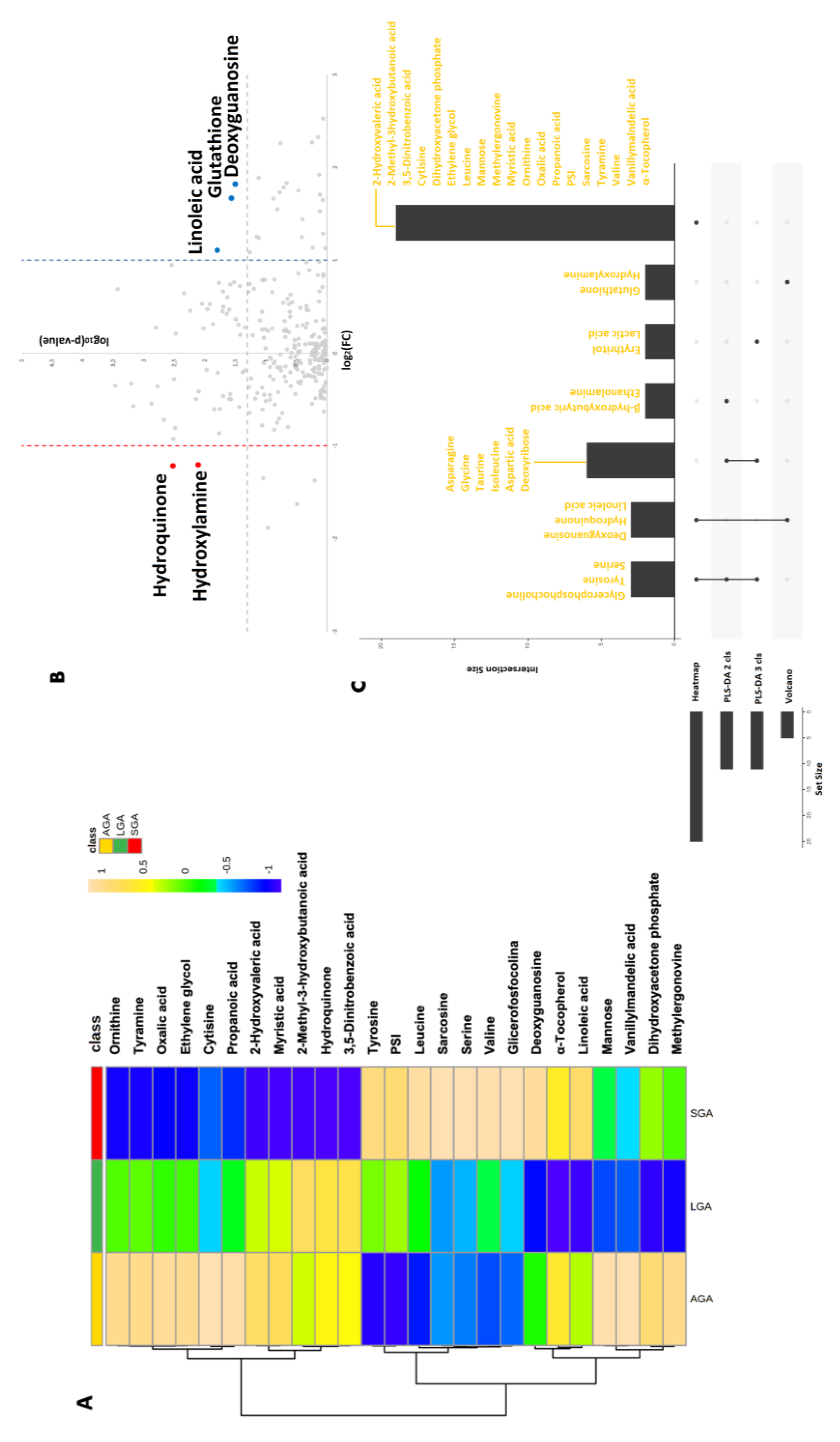
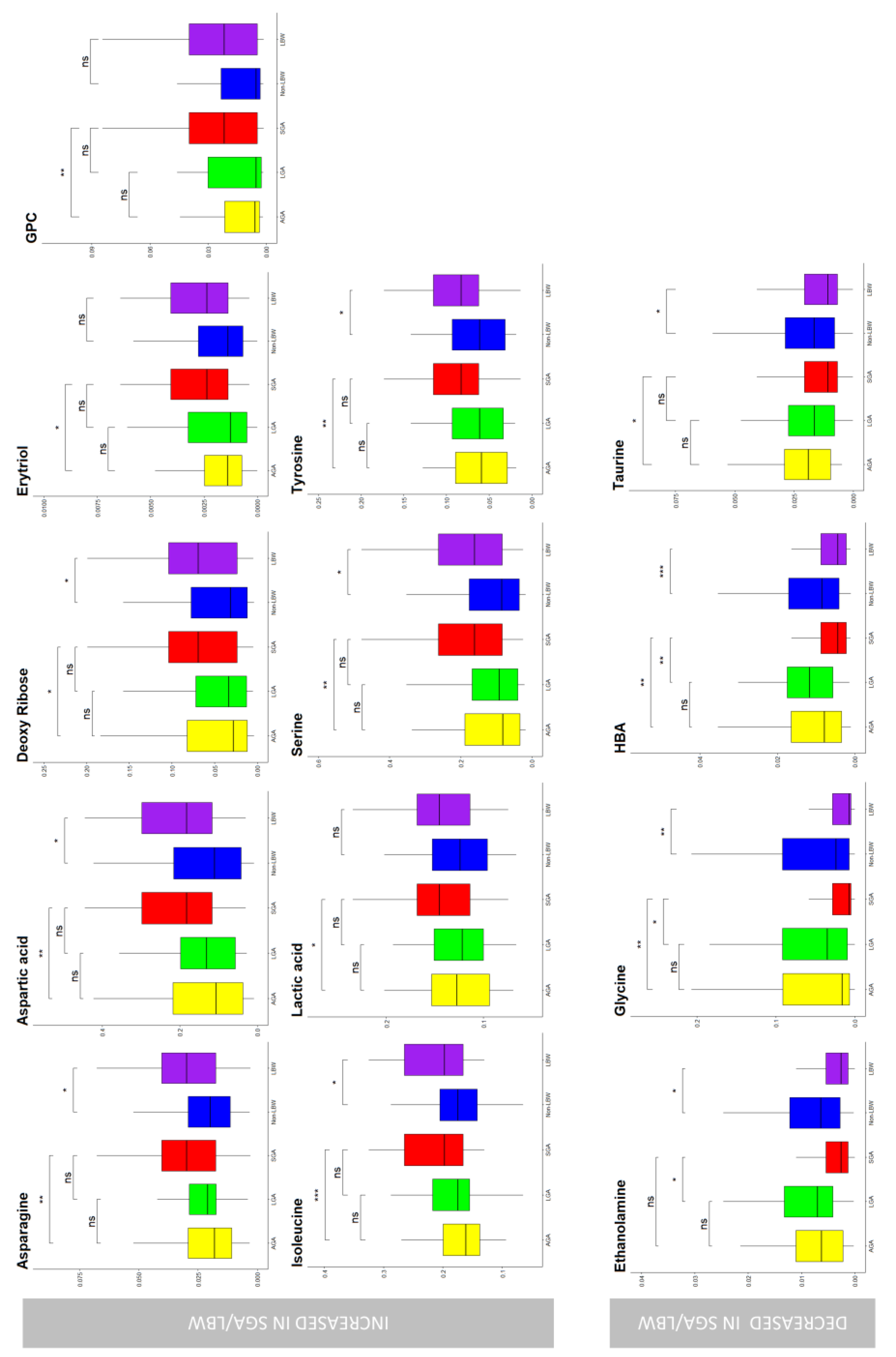
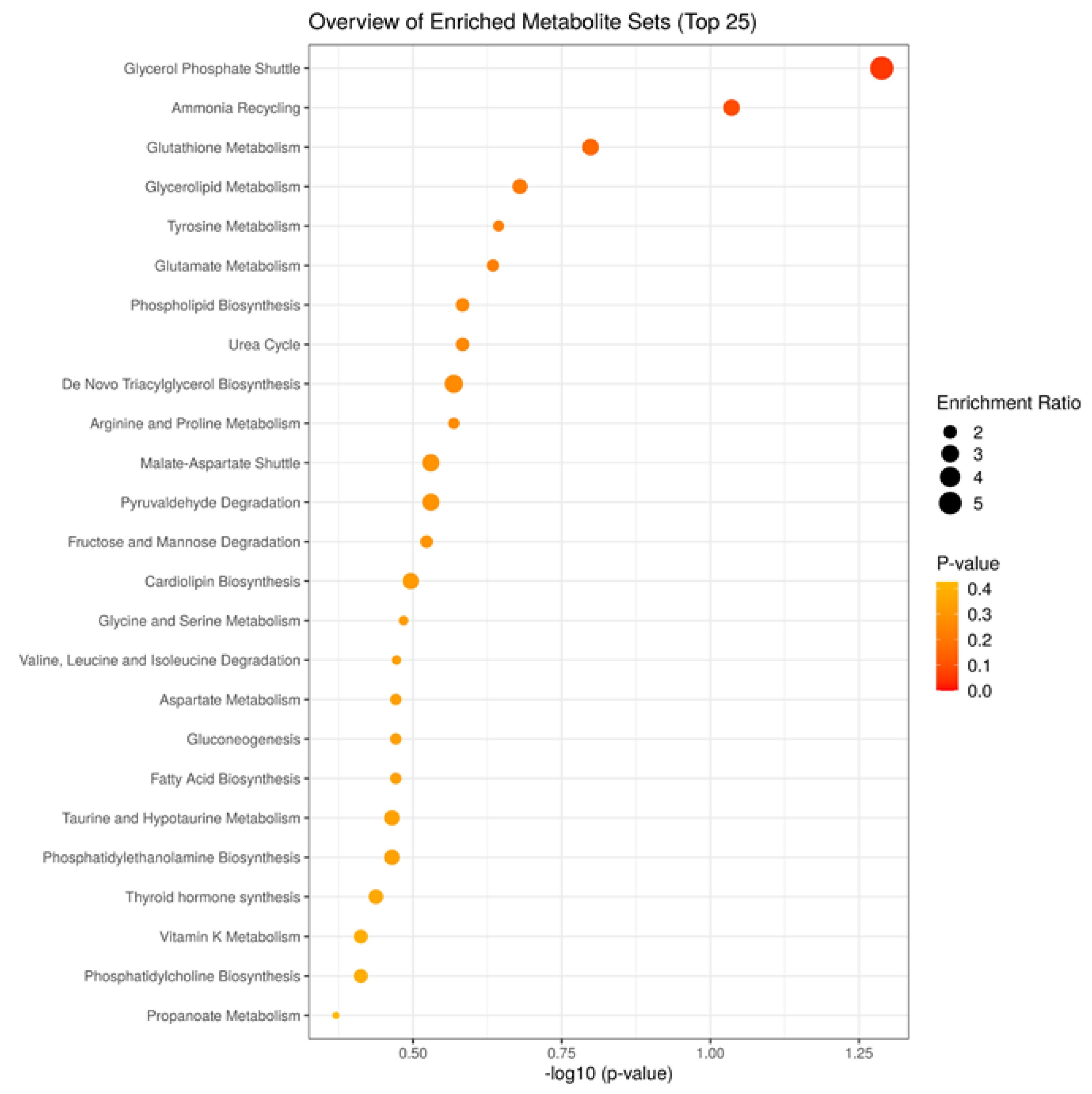
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilcox, A.J.; Skjaerven, R. Birth Weight and Perinatal Mortality: The Effect of Gestational Age. Am. J. Public Health 1992, 82, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.; Winter, P.D.; Osmond, C.; Margetts, B.; Simmonds, S.J. Weight in Infancy and Death from Ischaemic Heart Disease. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1989, 2, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajnik, C.S.; Fall, C.H.; Vaidya, U.; Pandit, A.N.; Bavdekar, A.; Bhat, D.S.; Osmond, C.; Hales, C.N.; Barker, D.J. Fetal Growth and Glucose and Insulin Metabolism in Four-Year-Old Indian Children. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 1995, 12, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurbe, E.; Garcia-Vicent, C.; Torro, M.I.; Aguilar, F.; Redon, J. Associations of Birth Weight and Postnatal Weight Gain with Cardiometabolic Risk Parameters at 5 Years of Age. Hypertens. Dallas Tex 1979 2014, 63, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, J.; Mikelson, C.; Richards, S.; Symes, S.; Adair, D.; Zullo, F.; Guida, M. Placental Concentrations of Bisphenol A and Birth Weight from Births in the Southeastern U.S. Placenta 2014, 35, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikelson, C.; Kovach, M.J.; Troisi, J.; Symes, S.; Adair, D.; Miller, R.K.; Salafia, C.; Johnson, K.; Lin, Z.; Richards, S. Placental 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 2 Expression: Correlations with Birth Weight and Placental Metal Concentrations. Placenta 2015, 36, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.T.; Boaz, V.A. Hamilton Country Community Health Profile; Chattanooga-Hamilton Country Health Department: Chattanooga, TN, USA.
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Innovation: Metabolomics: The Apogee of the Omics Trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolenska, Z.; Zdrojewski, Z. Metabolomics and Its Potential in Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases. Reumatologia 2015, 53, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, L.; Baker, P. Prediction of a Small-for-Gestational Age (Sga). Infant. Patent Application 13/885, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Heazell, A.E.P.; Bernatavicius, G.; Warrander, L.; Brown, M.C.; Dunn, W.B. A Metabolomic Approach Identifies Differences in Maternal Serum in Third Trimester Pregnancies That End in Poor Perinatal Outcome. Reprod. Sci. Thousand Oaks Calif 2012, 19, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tea, I.; Le Gall, G.; Kuster, A.; Guignard, N.; Alexandre-Gouabau, M.-C.; Darmaun, D.; Robins, R.J. 1H-NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling of Maternal and Umbilical Cord Blood Indicates Altered Materno-Foetal Nutrient Exchange in Preterm Infants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivorra, C.; Garcia-Vicent, C.; Chaves, F.J.; Monleon, D.; Morales, J.M.; Lurbe, E. Metabolomic Profiling in Blood from Umbilical Cords of Low Birth Weight Newborns. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre-Gouabau, M.-C.; Courant, F.; Moyon, T.; Kuster, A.; Le Gall, G.; Tea, I.; Antignac, J.-P.; Darmaun, D. Maternal and Cord Blood LC-HRMS Metabolomics Reveal Alterations in Energy and Polyamine Metabolism, and Oxidative Stress in Very-Low Birth Weight Infants. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2764–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberini, L.; Noto, A.; Fattuoni, C.; Grapov, D.; Casanova, A.; Fenu, G.; Gaviano, M.; Carboni, R.; Ottonello, G.; Crisafulli, M.; et al. Urinary Metabolomics (GC-MS) Reveals That Low and High Birth Weight Infants Share Elevated Inositol Concentrations at Birth. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Perinat. Med. Fed. Asia Ocean. Perinat. Soc. Int. Soc. Perinat. Obstet. 2014, 27 (Suppl. S2), 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassareo, P.P.; Fanos, V.; Mussap, M.; Flore, G.; Noto, A.; Puddu, M.; Saba, L.; Mercuro, G. Urinary NGAL and Hematic ADMA Levels: An Early Sign of Cardio-Renal Syndrome in Young Adults Born Preterm? J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Perinat. Med. Fed. Asia Ocean. Perinat. Soc. Int. Soc. Perinat. Obstet. 2013, 26 (Suppl. S2), 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, R.P.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Dunn, W.B.; Brown, M.; Heazell, A.E.P.; Kell, D.B.; Baker, P.N.; Kenny, L.C. Changes in the Metabolic Footprint of Placental Explant-Conditioned Medium Cultured in Different Oxygen Tensions from Placentas of Small for Gestational Age and Normal Pregnancies. Placenta 2010, 31, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, J.; Cinque, C.; Giugliano, L.; Symes, S.; Richards, S.; Adair, D.; Cavallo, P.; Sarno, L.; Scala, G.; Caiazza, M.; et al. Metabolomic Change Due to Combined Treatment with Myo-Inositol, D-Chiro-Inositol and Glucomannan in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Patients: A Pilot Study. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, J.; Lombardi, M.; Scala, G.; Cavallo, P.; Tayler, R.S.; Symes, S.J.K.; Richards, S.M.; Adair, D.C.; Fasano, A.; McCowan, L.M.; et al. A Screening Test Proposal for Congenital Defects Based on Maternal Serum Metabolomics Profile. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, S0002937822007177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Sarno, L.; Martinelli, P.; Di Carlo, C.; Landolfi, A.; Scala, G.; Rinaldi, M.; D’Alessandro, P.; Ciccone, C.; Guida, M. A Metabolomics-Based Approach for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Chromosomal Anomalies. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Landolfi, A.; Sarno, L.; Richards, S.; Symes, S.; Adair, D.; Ciccone, C.; Scala, G.; Martinelli, P.; Guida, M. A Metabolomics-Based Approach for Non-Invasive Screening of Fetal Central Nervous System Anomalies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Cavallo, P.; Richards, S.; Symes, S.; Colucci, A.; Sarno, L.; Landolfi, A.; Scala, G.; Adair, D.; Ciccone, C. Noninvasive Screening for Congenital Heart Defects Using a Serum Metabolomics Approach. Prenat. Diagn. 2021, 41, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Sarno, L.; Landolfi, A.; Scala, G.; Martinelli, P.; Venturella, R.; Di Cello, A.; Zullo, F.; Guida, M. Metabolomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Raffone, A.; Travaglino, A.; Belli, G.; Belli, C.; Anand, S.; Giugliano, L.; Cavallo, P.; Scala, G.; Symes, S.; et al. Development and Validation of a Serum Metabolomic Signature for Endometrial Cancer Screening in Postmenopausal Women. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2018327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardosi, J.; Chang, A.; Kalyan, B.; Sahota, D.; Symonds, E.M. Customised Antenatal Growth Charts. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1992, 339, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed Minimum Reporting Standards for Chemical Analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metab. Off. J. Metabolomic Soc. 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovats, E.S.Z. Gas-chromatographische Charakterisierung Organischer Verbindungen. Teil 1: Retentionsindices Aliphatischer Halogenide, Alkohole, Aldehyde Und Ketone. Helv. Chim. Acta 1958, 41, 1915–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevik, B.-H.; Wehrens, R. The Pls Package: Principal Component and Partial Least Squares Regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the Caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bijlsma, S.; Bobeldijk, I.; Verheij, E.R.; Ramaker, R.; Kochhar, S.; Macdonald, I.A.; van Ommen, B.; Smilde, A.K. Large-Scale Human Metabolomics Studies: A Strategy for Data (Pre-) Processing and Validation. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. MetPA: A Web-Based Metabolomics Tool for Pathway Analysis and Visualization. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrens, R.; Bloemberg, T.G.; Eilers, P.H.C. Fast Parametric Time Warping of Peak Lists. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3063–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, R.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Smilde, A.K.; van der Werf, M.J. Centering, Scaling, and Transformations: Improving the Biological Information Content of Metabolomics Data. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N.; Strobelt, H.; Vuillemot, R.; Pfister, H. UpSet: Visualization of Intersecting Sets. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2014, 20, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.; Gluckman, P.D.; Godfrey, K.M.; Harding, J.E.; Owens, J.A.; Robinson, J.S. Fetal Nutrition and Cardiovascular Disease in Adult Life. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1993, 341, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdge, G.C.; Lillycrop, K.A. Nutrition, Epigenetics, and Developmental Plasticity: Implications for Understanding Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovi, P.; Andersson, S.; Eriksson, J.G.; Järvenpää, A.-L.; Strang-Karlsson, S.; Mäkitie, O.; Kajantie, E. Glucose Regulation in Young Adults with Very Low Birth Weight. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, M.; Flannery, D.J.; Schluchter, M.; Cartar, L.; Borawski, E.; Klein, N. Outcomes in Young Adulthood for Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Brown, M.; Worton, S.A.; Davies, K.; Jones, R.L.; Kell, D.B.; Heazell, A.E. The Metabolome of Human Placental Tissue: Investigation of First Trimester Tissue and Changes Related to Preeclampsia in Late Pregnancy. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaull, G.; Sturman, J.A.; Räihä, N.C. Development of Mammalian Sulfur Metabolism: Absence of Cystathionase in Human Fetal Tissues. Pediatr. Res. 1972, 6, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, M.; Ditchfield, A.; Hirst, C.R.; Pegorie, C.; Martyn-Smith, K.; Sibley, C.P.; Greenwood, S.L. Reduced Placental Taurine Transporter (TauT) Activity in Pregnancies Complicated by Pre-Eclampsia and Maternal Obesity. In Taurine 8; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Austdal, M.; Thomsen, L.C.V.; Tangeras, L.H.; Skei, B.; Mathew, S.; Bjorge, L.; Austgulen, R.; Bathen, T.F.; Iversen, A.-C. Metabolic Profiles of Placenta in Preeclampsia Using HR-MAS MRS Metabolomics. Placenta 2015, 36, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Jackson, P.; Gunter, C.; Wang, J.; Rock, C.O.; Jackowski, S. Placental Thrombosis and Spontaneous Fetal Death in Mice Deficient in Ethanolamine Kinase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28438–28449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.S.; Bicknell, R. Thymidine Phosphorylase, 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose and Angiogenesis. Biochem. J. 1998, 334, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kletsas, D.; Barbieri, D.; Stathakos, D.; Botti, B.; Bergamini, S.; Tomasi, A.; Monti, D.; Malorni, W.; Franceschi, C. The Highly Reducing Sugar 2-Deoxy-D-Ribose Induces Apoptosis in Human Fibroblasts by Reduced Glutathione Depletion and Cytoskeletal Disruption. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 243, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Deepak, S.M.; Buch, M.H.; McDowell, G.; Spasic, I.; Ellis, D.I.; Brooks, N.; Kell, D.B.; Neyses, L. Serum Metabolomics Reveals Many Novel Metabolic Markers of Heart Failure, Including Pseudouridine and 2-Oxoglutarate. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkwright, P.D.; Rademacher, T.W.; Dwek, R.A.; Redman, C. Pre-Eclampsia Is Associated with an Increase in Trophoblast Glycogen Content and Glycogen Synthase Activity, Similar to That Found in Hydatidiform Moles. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 2744–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, H.H.; Robinette, B.; Shin, Y.Y.; Siew, P.; Shellhaas, C.S.; Tyrey, L. Placental Villous Glucose Metabolism and Hormone Release Respond to Varying Oxygen Tensions. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 1997, 4, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerstaff, E.; Glunde, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Choline Phospholipid Metabolism: A Target in Cancer Cells? J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 90, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikael, L.G.; Pancer, J.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Q.; Caudill, M.; Rozen, R. Low Dietary Folate and Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Deficiency May Lead to Pregnancy Complications through Modulation of A Po AI and IFN-γ in Spleen and Placenta, and through Reduction of Methylation Potential. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, J.M.; Henderson, G.I. Placental Amino Acid Uptake in Normal and Complicated Pregnancies. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1988, 295, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, F.; Regnault, T. Placental Transport and Metabolism of Amino Acids. Placenta 2001, 22, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimasuay, K.G.; Boeuf, P.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Placental Responses to Changes in the Maternal Environment Determine Fetal Growth. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. MTOR Signaling in Growth Control and Disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolini, C.L.; Marconi, A.M.; Ronzoni, S.; Di Noio, M.; Fennessey, P.V.; Pardi, G.; Battaglia, F.C. Placental Transport of Leucine, Phenylalanine, Glycine, and Proline in Intrauterine Growth-Restricted Pregnancies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rising, C.L.; D’Alecy, L.G. Hypoxia-Induced Increases in Hypoxic Tolerance Augmented by Beta-Hydroxybutyrate in Mice. Stroke 1989, 20, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Verpoorte, R. Sample Preparation for Plant Metabolomics. Phytochem. Anal. PCA 2010, 21, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, J.; Symes, S.; Adair, D.; Colucci, A.; Prisco, S.E.; Aquino, C.I.; Vivone, I.; Guida, M.; Richards, S. Placental Tissue Metabolome Analysis by GC-MS: Oven-Drying Is a Viable Sample Preparation Method. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 48, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessner, U.; Wagner, C.; Kopka, J.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Technical Advance: Simultaneous Analysis of Metabolites in Potato Tuber by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 23, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All Patients | LBW | Non-LBW | SGA | AGA | LGA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 493 | 124 (25.2%) | 369 (74.8%) | 118 (23.9%) | 326 (66.1%) | 49 (9.9%) |
| Age (years) | 26.0 ± 5.5 | 25.4 ± 5.6 | 26.2 ± 5.5 | 25.6 ± 5.8 | 25.9 ± 5.4 | 27.8 ± 5.6 |
| Height (cm) | 162.6 ± 10.4 | 162.3 ± 14.5 | 162.7 ± 8.6 | 163.6 ± 7.8 | 162.0 ± 8.9 | 164.8 ± 20.4 |
| Weight before pregnancy (kg) | 71.6 ± 20.7 | 66.2 ± 17.9 * | 73.4 ± 21.3 | 73.3 ± 24.3 | 70.5 ± 19.2 | 74.6 ± 20.5 |
| BMI | 27.7 ± 7.6 | 25.3 ± 6.6 * | 27.7 ± 7.8 | 27.3 ± 8.5 | 26.9 ± 7.2 | 28.0 ± 7.9 |
| Underweight (<19) | 7.5% | 12.9% | 5.7% | 9.3% | 7.1% | 6.1% |
| Normal weight (19–25) | 38.1% | 42.7% | 36.6% | 38.1% | 39.0% | 32.7% |
| Overweight (25–30) | 27.0% | 21.0% | 29.0% | 32.2% | 27.6% | 30.6% |
| Obese (>30) | 27.4% | 23.4% | 28.7% | 20.3% | 26.4% | 30.6% |
| Marital Status | ||||||
| Single | 52.5% | 41.1% | 56.4% | 44.1% | 53.1% | 69.4%¶ |
| Married | 47.5% | 58.9% | 43.6% | 55.9% | 46.9% | 30.6%¶ |
| Race | ||||||
| White | 63.5% | 58.9% | 58.2% | 63.6% | 63.2% | 65.3% |
| Black | 19.9% | 25.8% | 17.9% | 24.6% | 18.7% | 16.3% |
| Hispanic | 16.2% | 15.3% | 23.9% | 11.9% | 17.8% | 16.3% |
| Other | 0.4% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.3% | 2.0% |
| Education | ||||||
| <HS | 32.5% | 32.7% | 32.4% | 27.1% | 36.0% | 21.2% |
| HS/GED | 30.9% | 33.6% | 29.7% | 40.6% | 27.3% | 30.3% |
| College | 36.6% | 33.6% | 37.9% | 32.3% | 36.8% | 48.5% |
| Tobacco use | ||||||
| No | 81.1% | 75.0% | 82.4% | 68.6%¶ | 82.8% | 93.9% |
| Yes | 18.9% | 25.0% | 17.6% | 31.4%¶ | 17.2% | 6.1% |
| Parity | 1.3 ± 1.8 | 1.1 ± 1.4 | 1.4 ± 1.9 | 1.5 ± 3.0 | 1.2 ± 1.2 | 1.5 ± 1.3 |
| Gestational age (day) | 261.9 ± 22.5 | 246.4 ± 24.0 * | 267.2 ± 19.4 | 260.0 ± 26.0 | 263.8 ± 17.8 | 254.1 ± 36.3¶ |
| Infant sex | ||||||
| Male | 52.1% | 54.8% | 47.7% | 52.5% | 50.0% | 65.3%¶ |
| Female | 47.9% | 45.2% | 52.3% | 47.5% | 50.0% | 34.7%¶ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troisi, J.; Symes, S.J.K.; Lombardi, M.; Cavallo, P.; Colucci, A.; Scala, G.; Adair, D.C.; Guida, M.; Richards, S.M. Placental Metabolomics of Fetal Growth Restriction. Metabolites 2023, 13, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020235
Troisi J, Symes SJK, Lombardi M, Cavallo P, Colucci A, Scala G, Adair DC, Guida M, Richards SM. Placental Metabolomics of Fetal Growth Restriction. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020235
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroisi, Jacopo, Steven J. K. Symes, Martina Lombardi, Pierpaolo Cavallo, Angelo Colucci, Giovanni Scala, David C. Adair, Maurizio Guida, and Sean M. Richards. 2023. "Placental Metabolomics of Fetal Growth Restriction" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020235
APA StyleTroisi, J., Symes, S. J. K., Lombardi, M., Cavallo, P., Colucci, A., Scala, G., Adair, D. C., Guida, M., & Richards, S. M. (2023). Placental Metabolomics of Fetal Growth Restriction. Metabolites, 13(2), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020235