Changes in microRNAs during Storage and Processing of Breast Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
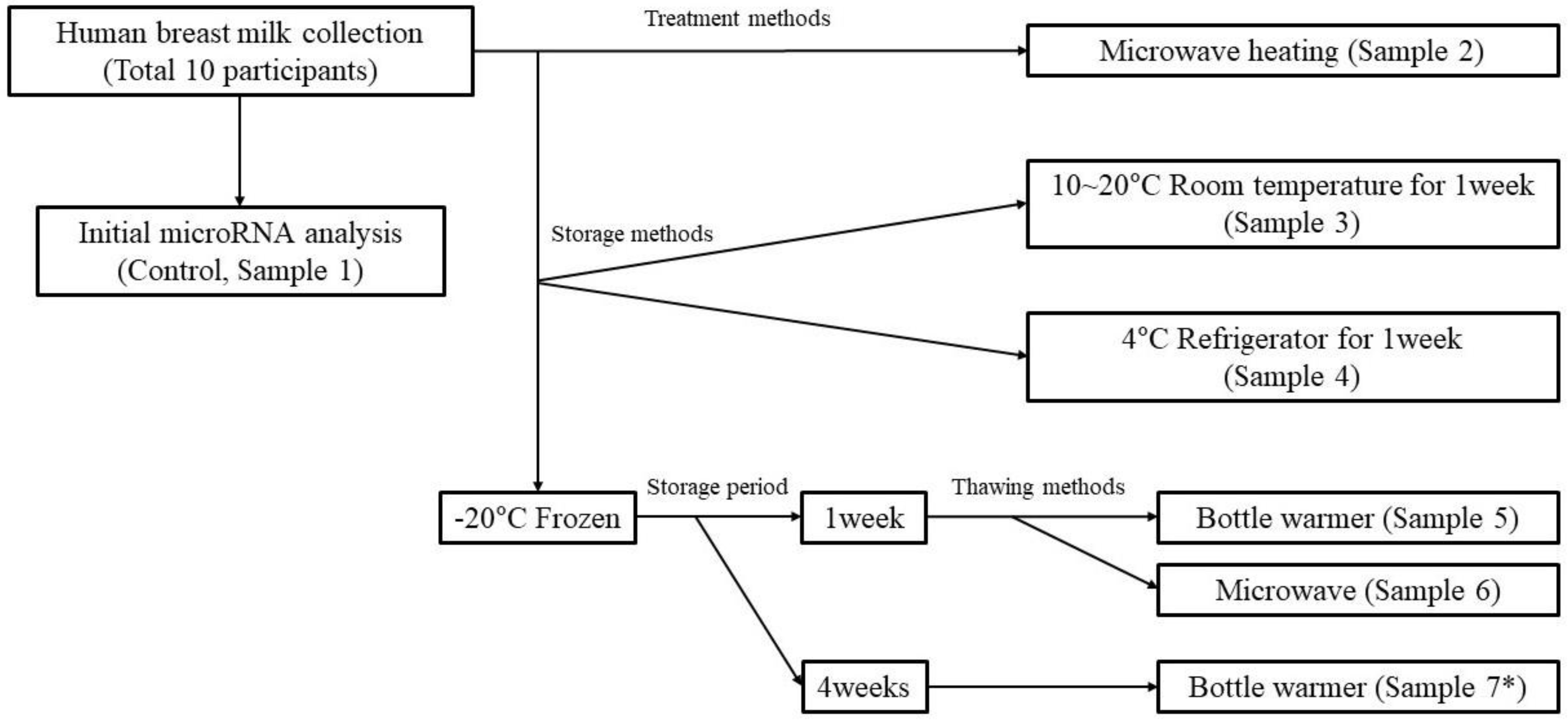
2.1. Collection of Breast Milk and Storage and Processing
2.2. Human Breast Milk Fractionation and miRNA Isolation
2.3. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Information
3.2. Changes in miRNA According to Microwave Treatment of Breast Milk
3.3. Changes in miRNA According to the Storage Conditions of Breast Milk
3.3.1. Changes in miRNA According to One Week of Storage at Room Temperature
3.3.2. Changes in miRNA According to One Week of Refrigerated Storage
3.3.3. Changes in miRNA According to Bottle Warmer Thawing after 1 Week of Frozen Storage
3.4. Changes in miRNA According to the Thawing Method of Breast Milk
3.4.1. Changes in miRNA According to Bottle Warmer Thawing after 1 Week of Frozen Storage
3.4.2. Changes in miRNA According to Microwave Thawing after 1 Week of Frozen Storage
3.5. Changes in miRNA According to the Frozen Period of Breast Milk
3.5.1. Changes in miRNA According to Bottle Warmer Thawing after One Week of Frozen Storage
3.5.2. Changes in miRNA According to Bottle Warmer Thawing after Four Weeks of Frozen Storage
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreas, N.J.; Kampmann, B.; Mehring Le-Doare, K. Human breast milk: A review on its composition and bioactivity. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J. Immunomodulatory Effects of Human Colostrum and Milk. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2021, 24, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, F.; Giannì, M.L. Human milk: Composition and health benefits. Pediatr. Med. Chir. 2017, 39, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauck, F.R.; Thompson, J.M.; Tanabe, K.O.; Moon, R.Y.; Vennemann, M.M. Breastfeeding and reduced risk of sudden infant death syndrome: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Choi, Y.S.; Bae, C.W. Trends of breastfeeding rate in Korea (1994–2012): Comparison with OECD and other countries. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, Y.S. Trends and Determinants in Breastfeeding among Korean Women: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Shim, K.S.; Yi, D.Y.; Lim, I.S.; Chae, S.A.; Yun, S.W.; Lee, N.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S. Macronutrient Analysis of Human Milk according to Storage and Processing in Korean Mother. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.A. Storage of human milk and the influence of procedures on immunological components of human milk. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 1999, 88, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaweed, M.; Lai, C.T.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Kakulas, F. Human milk miRNAs primarily originate from the mammary gland resulting in unique miRNA profiles of fractionated milk. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Lozano, E.; Sebastián-Valles, F.; Knott-Torcal, C. Circulating microRNAs in Breast Milk and Their Potential Impact on the Infant. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, D.; Villén, J.; Shin, C.; Camargo, F.D.; Gygi, S.P.; Bartel, D.P. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008, 455, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaweed, M.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Kakulas, F. MicroRNAs in Breastmilk and the Lactating Breast: Potential Immunoprotectors and Developmental Regulators for the Infant and the Mother. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 13981–14020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, D.L.; Fong, D.Y.; Lok, K.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; Tarrant, M. Practices, predictors and consequences of expressed breast-milk feeding in healthy full-term infants. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, C.W.; Win, N.N.; Zhao, Y.; Scott, J.A. Trends in the expression of breastmilk 1993-2003. Breastfeed Rev. 2006, 14, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Title, A.C.; Denzler, R.; Stoffel, M. Uptake and Function Studies of Maternal Milk-derived MicroRNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 23680–23691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H.; Kosaka, N.; Shimizu, T.; Sekine, K.; Ochiya, T.; Takase, M. Bovine milk contains microRNA and messenger RNA that are stable under degradative conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C.; Stremmel, W.; Weiskirchen, R.; John, S.M.; Schmitz, G. Exosome-Derived MicroRNAs of Human Milk and Their Effects on Infant Health and Development. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yu, S.; Xu, M.; Li, P. Effects of microwave on extracellular vesicles and microRNA in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2932–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikawa, T.; Mizuno, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kohda, C.; Ishii, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Kobayashi, S. Microwave treatment of breast milk for prevention of cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatr. Int. 2019, 61, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slutzah, M.; Codipilly, C.N.; Potak, D.; Clark, R.M.; Schanler, R.J. Refrigerator storage of expressed human milk in the neonatal intensive care unit. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, B.; Lahiri, S.; Kar, K.; Sarkar, N. Changes in biochemical contents of expressed breast milk on refrigerator storage. Indian Pediatr. 2012, 49, 836–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois-Camacho, K.; Diaz-Jimenez, D.; De la Fuente, M.; Quera, R.; Simian, D.; Martínez, M.; Landskron, G.; Olivares-Morales, M.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Xu, X.; et al. Inhibition of miR-378a-3p by Inflammation Enhances IL-33 Levels: A Novel Mechanism of Alarmin Modulation in Ulcerative Colitis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Sheng, X.; Xue, J.; Zhu, D. MicroRNA-365 regulates the occurrence and immune response of sepsis following multiple trauma via interleukin-6. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 3745–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Qu, X.; Shang, D.; Qin, Q.; Xu, T.; Hamid, Q.; Dang, X.; Chang, Y.; et al. MiR-365-3p is a negative regulator in IL-17-mediated asthmatic inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 953714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Lara, N.R.; Escuder-Vieco, D.; García-Algar, O.; De la Cruz, J.; Lora, D.; Pallás-Alonso, C. Effect of freezing time on macronutrients and energy content of breastmilk. Breastfeed Med. 2012, 7, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajkovski, M.; Hausser, J.; Soutschek, J.; Bhat, B.; Akin, A.; Zavolan, M.; Heim, M.H.; Stoffel, M. MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature 2011, 474, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupec, T.; Bleilevens, A.; Iborra, S.; Najjari, L.; Wittenborn, J.; Maurer, J.; Stickeler, E. Stability of circulating microRNAs in serum. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinge, C.; Clauss, S.; Boddum, K.; Jabbari, R.; Jabbari, J.; Risgaard, B.; Tomsits, P.; Hildebrand, B.; Kääb, S.; Wakili, R.; et al. Stability of circulating blood-based microRNAs—Pre-analytic methodological considerations. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0167969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Mu, Z.; Li, Q.; Fu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, G.; Ma, Y.; et al. Detection of dietetically absorbed maize-derived microRNAs in pigs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, T.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Dietary microRNA-A Novel Functional Component of Food. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Petrick, J.S.; Heck, G.; Ivashuta, S.; Marshall, W.S. Lack of detectable oral bioavailability of plant microRNAs after feeding in mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, J.W.; Hale, A.E.; Isaacs, S.K.; Baggish, A.L.; Chan, S.Y. Ineffective delivery of diet-derived microRNAs to recipient animal organisms. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; McAlexander, M.A.; Queen, S.E.; Adams, R.J. Real-time quantitative PCR and droplet digital PCR for plant miRNAs in mammalian blood provide little evidence for general uptake of dietary miRNAs: Limited evidence for general uptake of dietary plant xenomiRs. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Participant Number † | Age of Lactating Mother (Years) | Postpartum Periods (Days) | GA at Birth (Weeks) | Birth Weight (kg) | Sex | Delivery Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 19 | 38 2/7 | 3.92 | F | NSVD |
| 2 | 32 | 70 | 38 3/7 | 3.26 | M | C/S |
| 3 | 39 | 12 | 24 1/7 | 0.609 | F | C/S |
| 4 | 28 | 60 | 40 3/7 | 3.65 | F | NSVD |
| 5 | 29 | 46 | 34 5/7 | 2.87 | M | NSVD |
| 6 | 40 | 146 | 24 1/7 | 0.609 | F | C/S |
| 7 | 36 | 124 | 40 0/7 | 3.31 | F | C/S |
| 8 | 40 | 44 | 32 2/7 | 2.12 | M | NSVD |
| 9 | 31 | 108 | 38 6/7 | 2.3 | M | NSVD |
| 10 | 39 | 217 | 39 3/7 | 3 | F | C/S |
| Average | 34.4 | 84.6 | 35 1/7 | 2.59 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants | |||||||||||
| Sample 2 Microwaved | hsa-miR-24-3p | 0.325 | 0.001 | 2.191 | 0.003 | 3.250 | 0.203 | 0.388 | 0.106 | 3.651 | 52.371 |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 0.344 | 0.007 | 0.063 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.260 | 0.110 | 0.343 | 2.579 | 53.597 | |
| Sample 3 Stored at room temperature (10–20 °C) for 1 week | hsa-miR-193b-5p | 0.454 | 15.714 | 5.518 | 34.734 | 0.019 | 0.457 | 2.888 | 1.262 | 1526.7 | 0.349 |
| hsa-miR-365a-3p | 0.361 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 3.971 | 0.008 | 0.057 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| hsa-miR-365b-3p | 0.382 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 3.514 | 0.019 | 0.057 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| hsa-miR-378a-3p | 0.416 | 0.071 | 0.438 | 0.165 | 0.003 | 0.089 | 0.072 | 0.123 | 0.342 | 0.169 | |
| Sample 4 Refrigerated (4 °C) for 1 week | None ** | ||||||||||
| Sample 5 Frozen (−20 °C) for 1 week, then thawed in a bottle warmer | hsa-miR-205-5p | 0.085 | 2.175 | 0.313 | 19.064 | 0.011 | 0.146 | 0.403 | 0.003 | 0.123 | 0.076 |
| hsa-miR-3182 | 0.061 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.069 | 0.028 | 0.159 | 0.007 | 2.651 | 0.316 | 0.091 | |
| Sample 6 Frozen (−20 °C) for 1 week, then thawed by microwave treatment | hsa-miR-10b-5p | 0.065 | 58.722 | 21.386 | 20.856 | 33.252 | 0.153 | 0.047 | 295.56 | 0.002 | 0.442 |
| hsa-miR-205-5p | 0.429 | 0.076 | 0.100 | 51.381 | 0.003 | 0.255 | 2.674 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.414 | |
| hsa-miR-486-5p | 0.207 | 4.039 | 22.914 | 13.471 | 24.941 | 4.238 | 0.115 | 16.666 | 0.006 | 2.099 | |
| hsa-miR-3960 | 9.266 | 5.111 | 32.091 | 0.032 | 15.237 | 4.287 | 3.020 | 5.723 | 5.989 | 2.955 | |
| hsa-miR-24-3p | 0.304 | 0.012 | 0.080 | 3.575 | 0.001 | 0.193 | 0.403 | 0.030 | 0.185 | 0.282 | |
| hsa-miR-378a-3p | 0.324 | 0.006 | 0.262 | 0.200 | 0.005 | 6.643 | 5.442 | 0.094 | 2.549 | 0.171 | |
| Sample 7 Frozen (−20 °C) for 4 weeks, then thawed in a bottle warmer | hsa-miR-103a-3p | 0.163 | 0.011 | 0.032 | 0.012 | *** | 0.251 | 0.225 | 0.297 | 4.490 | 0.015 |
| hsa-miR-193b-5p | 5.107 | 189.26 | 8.350 | 115.6 | *** | 3.341 | 2.711 | 11.067 | 339.79 | 0.370 | |
| hsa-miR-103b | 0.176 | 0.012 | 0.031 | 0.014 | *** | 0.227 | 0.270 | 0.389 | 4.607 | 0.057 | |
| hsa-miR-29a-3p | 0.204 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 2065.6 | *** | 0.390 | 0.442 | 0.054 | 3.260 | 12.458 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.-U.; Min, H.; Lee, E.S.; Lim, I.S.; Song, J.; Kang, I.; Yi, D.Y. Changes in microRNAs during Storage and Processing of Breast Milk. Metabolites 2023, 13, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020139
Kim JH, Kim K-U, Min H, Lee ES, Lim IS, Song J, Kang I, Yi DY. Changes in microRNAs during Storage and Processing of Breast Milk. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jun Hwan, Ki-Uk Kim, Hyeyoung Min, Eun Sun Lee, In Seok Lim, Jeonglyn Song, Insoo Kang, and Dae Yong Yi. 2023. "Changes in microRNAs during Storage and Processing of Breast Milk" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020139
APA StyleKim, J. H., Kim, K.-U., Min, H., Lee, E. S., Lim, I. S., Song, J., Kang, I., & Yi, D. Y. (2023). Changes in microRNAs during Storage and Processing of Breast Milk. Metabolites, 13(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020139








